Illumina SBS Sequencing and DNBSEQ Perform Similarly for Single-Cell Transcriptomics
Highlights
- DNBSEQ exhibited mildly superior sequence quality compared to Illumina SBS, as evidenced by a higher Phred score and a greater number of genes mapping to the reference genome.
- However, these improvements did not translate into significant differences in the single-cell applications. There was no significant difference in the annotation of cells into different cell types, and both technologies yielded the same top differentially expressed genes between the experimental conditions.
- As we show that the quality between these two technologies is similar, researchers choosing a sequencing technology can give more weight to other external factors such as support, cost, and convenience.
- Competition is gradually driving down scRNA-seq reagent prices. Researchers being aware of different NGS alternatives will increase competition in the sequencing market and also help to reduce sequencing costs.
- This may open the doors to scRNAseq for researchers with limited budgets or allow researchers to add more samples using the same budget, enabling them to answer the same biological questions with a greater statistical power or explore new questions.
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Single-Cell Datasets and Cell Collection
2.2. Sequencing
2.2.1. Illumina SBS Sequencing
2.2.2. DNBSEQ Sequencing
2.3. Bioinformatics
2.4. Statistics
3. Results
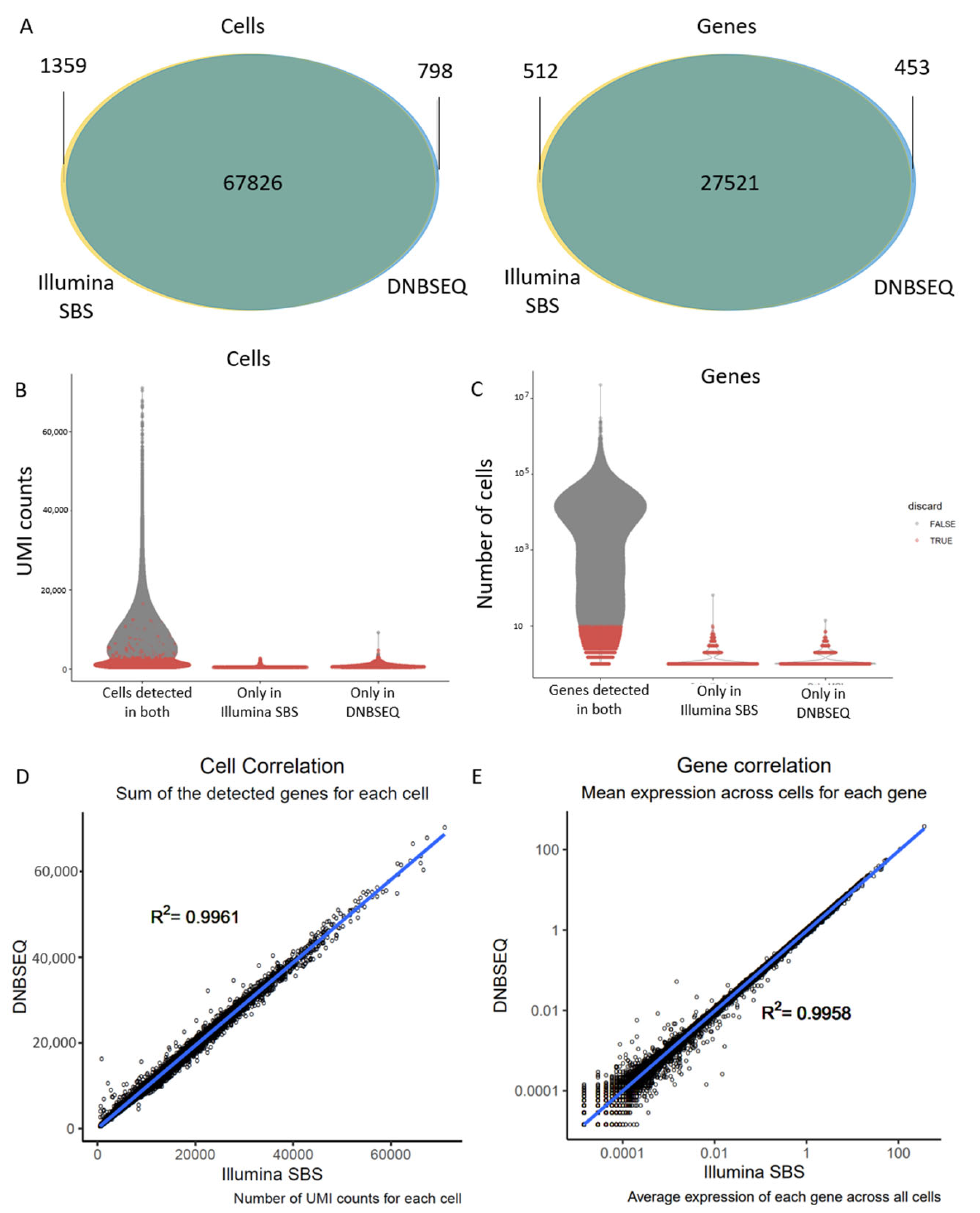
3.1. DNBSEQ Shows Higher Sequencing Quality But No Improvement of Single-Cell RNA-Seq Metrics
3.2. Different Sequencing Technologies Yield Comparable Gene Expression Data
3.3. Similar Cell Populations Were Identified with Both Technologies Using Reference-Based Algorithms as Well as Marker Gene Expression
3.4. The Sequencing Method Used Minimally Affects Meaningful Biological Comparisons
4. Discussion
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Marx, V. ScRNA-Seq: Oh, the Joys. Nat. Methods 2024, 21, 750–753. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jovic, D.; Liang, X.; Zeng, H.; Lin, L.; Xu, F.; Luo, Y. Single-Cell RNA Sequencing Technologies and Applications: A Brief Overview. Clin. Transl. Med. 2022, 12, e694. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Eisenstein, M. Innovative Technologies Crowd the Short-Read Sequencing Market. Nature 2023, 614, 798–800. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Illumina and Gene Sequencing Technology—SBIR Success Story—NCI. Available online: https://sbir.cancer.gov/portfolio/success-stories/illumina (accessed on 4 June 2024).
- Drmanac, R.; Sparks, A.B.; Callow, M.J.; Halpern, A.L.; Burns, N.L.; Kermani, B.G.; Carnevali, P.; Nazarenko, I.; Nilsen, G.B.; Yeung, G.; et al. Human Genome Sequencing Using Unchained Base Reads on Self-Assembling DNA Nanoarrays. Science 2010, 327, 78–81. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jeon, S.A.; Park, J.L.; Kim, J.H.; Kim, J.H.; Kim, Y.S.; Kim, J.C.; Kim, S.Y. Comparison of the MGISEQ-2000 and Illumina HiSeq 4000 Sequencing Platforms for RNA Sequencing. Genom. Inform. 2019, 17, e32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhu, F.Y.; Chen, M.X.; Ye, N.H.; Qiao, W.M.; Gao, B.; Law, W.K.; Tian, Y.; Zhang, D.; Zhang, D.; Liu, T.Y.; et al. Comparative Performance of the BGISEQ-500 and Illumina HiSeq4000 Sequencing Platforms for Transcriptome Analysis in Plants. Plant Methods 2018, 14, 69. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Senabouth, A.; Andersen, S.; Shi, Q.; Shi, L.; Jiang, F.; Zhang, W.; Wing, K.; Daniszewski, M.; Lukowski, S.W.; Hung, S.S.C.; et al. Comparative Performance of the BGI and Illumina Sequencing Technology for Single-Cell RNA-Sequencing. NAR Genom. Bioinform. 2020, 2, lqaa034. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Natarajan, K.N.; Miao, Z.; Jiang, M.; Huang, X.; Zhou, H.; Xie, J.; Wang, C.; Qin, S.; Zhao, Z.; Wu, L.; et al. Comparative Analysis of Sequencing Technologies for Single-Cell Transcriptomics. Genome Biol. 2019, 20, 70. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rojo, R.; Raper, A.; Ozdemir, D.D.; Lefevre, L.; Grabert, K.; Wollscheid-Lengeling, E.; Bradford, B.; Caruso, M.; Gazova, I.; Sánchez, A.; et al. Deletion of a Csf1r Enhancer Selectively Impacts CSF1R Expression and Development of Tissue Macrophage Populations. Nat. Commun. 2019, 10, 14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kenigsbuch, M.; Bost, P.; Halevi, S.; Chang, Y.; Chen, S.; Ma, Q.; Hajbi, R.; Schwikowski, B.; Bodenmiller, B.; Fu, H.; et al. A Shared Disease-Associated Oligodendrocyte Signature among Multiple CNS Pathologies. Nat. Neurosci. 2022, 25, 876–886. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Munro, D.A.D.; Bestard-Cuche, N.; McQuaid, C.; Chagnot, A.; Shabestari, S.K.; Chadarevian, J.P.; Maheshwari, U.; Szymkowiak, S.; Morris, K.; Mohammad, M.; et al. Microglia Protect against Age-Associated Brain Pathologies. Neuron 2024, 112, 2732–2748. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sequencing Requirements for Single Cell 3′—Official 10X Genomics Support. Available online: https://www.10xgenomics.com/support/single-cell-gene-expression/documentation/steps/sequencing/sequencing-requirements-for-single-cell-3 (accessed on 13 July 2024).
- Bolger, A.M.; Lohse, M.; Usadel, B. Trimmomatic: A Flexible Trimmer for Illumina Sequence Data. Bioinformatics 2014, 30, 2114–2120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bushnell, B. BBMap: A Fast, Accurate, Splice-Aware Aligner. In Proceedings of the 9th Annual Genomics of Energy & Environment Meeting, Walnut Creek, CA, USA, 17–20 March 2014. [Google Scholar]
- Babraham Bioinformatics—FastQC A Quality Control Tool for High Throughput Sequence Data. Available online: https://www.bioinformatics.babraham.ac.uk/projects/fastqc/ (accessed on 14 September 2024).
- Ewels, P.; Magnusson, M.; Lundin, S.; Käller, M. MultiQC: Summarize Analysis Results for Multiple Tools and Samples in a Single Report. Bioinformatics 2016, 32, 3047–3048. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- McCarthy, D.J.; Campbell, K.R.; Lun, A.T.L.; Wills, Q.F. Scater: Pre-Processing, Quality Control, Normalization and Visualization of Single-Cell RNA-Seq Data in R. Bioinformatics 2017, 33, 1179–1186. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lun, A.T.L.; Bach, K.; Marioni, J.C. Pooling across Cells to Normalize Single-Cell RNA Sequencing Data with Many Zero Counts. Genome Biol. 2016, 17, 75. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Aran, D.; Looney, A.P.; Liu, L.; Wu, E.; Fong, V.; Hsu, A.; Chak, S.; Naikawadi, R.P.; Wolters, P.J.; Abate, A.R.; et al. Reference-Based Analysis of Lung Single-Cell Sequencing Reveals a Transitional Profibrotic Macrophage. Nat. Immunol. 2019, 20, 163–172. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Finak, G.; McDavid, A.; Yajima, M.; Deng, J.; Gersuk, V.; Shalek, A.K.; Slichter, C.K.; Miller, H.W.; McElrath, M.J.; Prlic, M.; et al. MAST: A Flexible Statistical Framework for Assessing Transcriptional Changes and Characterizing Heterogeneity in Single-Cell RNA Sequencing Data. Genome Biol. 2015, 16, 278. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cock, P.J.A.; Fields, C.J.; Goto, N.; Heuer, M.L.; Rice, P.M. The Sanger FASTQ File Format for Sequences with Quality Scores, and the Solexa/Illumina FASTQ Variants. Nucleic Acids Res. 2010, 38, 1767. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Illumina Quality Scores for Next-Generation Sequencing. 2011. Available online: https://www.illumina.com/documents/products/technotes/technote_Q-Scores.pdf (accessed on 3 May 2024).
- Cell Ranger—Official 10X Genomics Support. Available online: https://www.10xgenomics.com/support/software/cell-ranger/latest (accessed on 4 June 2024).
- Dobin, A.; Gingeras, T.R. Mapping RNA-Seq Reads with STAR. Curr. Protoc. Bioinform. 2015, 51, 11–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McNamara, N.B.; Munro, D.A.D.; Bestard-Cuche, N.; Uyeda, A.; Bogie, J.F.J.; Hoffmann, A.; Holloway, R.K.; Molina-Gonzalez, I.; Askew, K.E.; Mitchell, S.; et al. Microglia Regulate Central Nervous System Myelin Growth and Integrity. Nature 2023, 613, 120–129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Common Considerations for Quality Control Filters for Single Cell RNA-Seq Data—10X Genomics. Available online: https://www.10xgenomics.com/analysis-guides/common-considerations-for-quality-control-filters-for-single-cell-rna-seq-data (accessed on 30 July 2024).
- Póliska, S.; Fareh, C.; Lengyel, A.; Göczi, L.; Tőzsér, J.; Szatmari, I. Comparative Transcriptomic Analysis of Illumina and MGI Next-Generation Sequencing Platforms Using RUNX3- and ZBTB46-Instructed Embryonic Stem Cells. Front. Genet. 2023, 14, 1275383. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jeon, S.A.; Park, J.L.; Park, S.-J.; Kim, H.; Goh, S.-H.; Han, J.-Y.; Kim, S.-Y. Comparison between MGI and Illumina Sequencing Platforms for Whole Genome Sequencing. Genes Genom. 2021, 43, 713–724. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eisenstein, M. Illumina Faces Short-Read Rivals. Nat. Biotechnol. 2023, 41, 3–5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]



Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Bestard-Cuche, N.; Munro, D.A.D.; Beniazza, M.; Priller, J.; Williams, A.; Corsinotti, A. Illumina SBS Sequencing and DNBSEQ Perform Similarly for Single-Cell Transcriptomics. Genes 2024, 15, 1436. https://doi.org/10.3390/genes15111436
Bestard-Cuche N, Munro DAD, Beniazza M, Priller J, Williams A, Corsinotti A. Illumina SBS Sequencing and DNBSEQ Perform Similarly for Single-Cell Transcriptomics. Genes. 2024; 15(11):1436. https://doi.org/10.3390/genes15111436
Chicago/Turabian StyleBestard-Cuche, Nadine, David A. D. Munro, Meryam Beniazza, Josef Priller, Anna Williams, and Andrea Corsinotti. 2024. "Illumina SBS Sequencing and DNBSEQ Perform Similarly for Single-Cell Transcriptomics" Genes 15, no. 11: 1436. https://doi.org/10.3390/genes15111436
APA StyleBestard-Cuche, N., Munro, D. A. D., Beniazza, M., Priller, J., Williams, A., & Corsinotti, A. (2024). Illumina SBS Sequencing and DNBSEQ Perform Similarly for Single-Cell Transcriptomics. Genes, 15(11), 1436. https://doi.org/10.3390/genes15111436





