Identification of Key Genes Involved in Sesquiterpene Synthesis in Nardostachys jatamansi Based on Transcriptome and Component Analysis
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
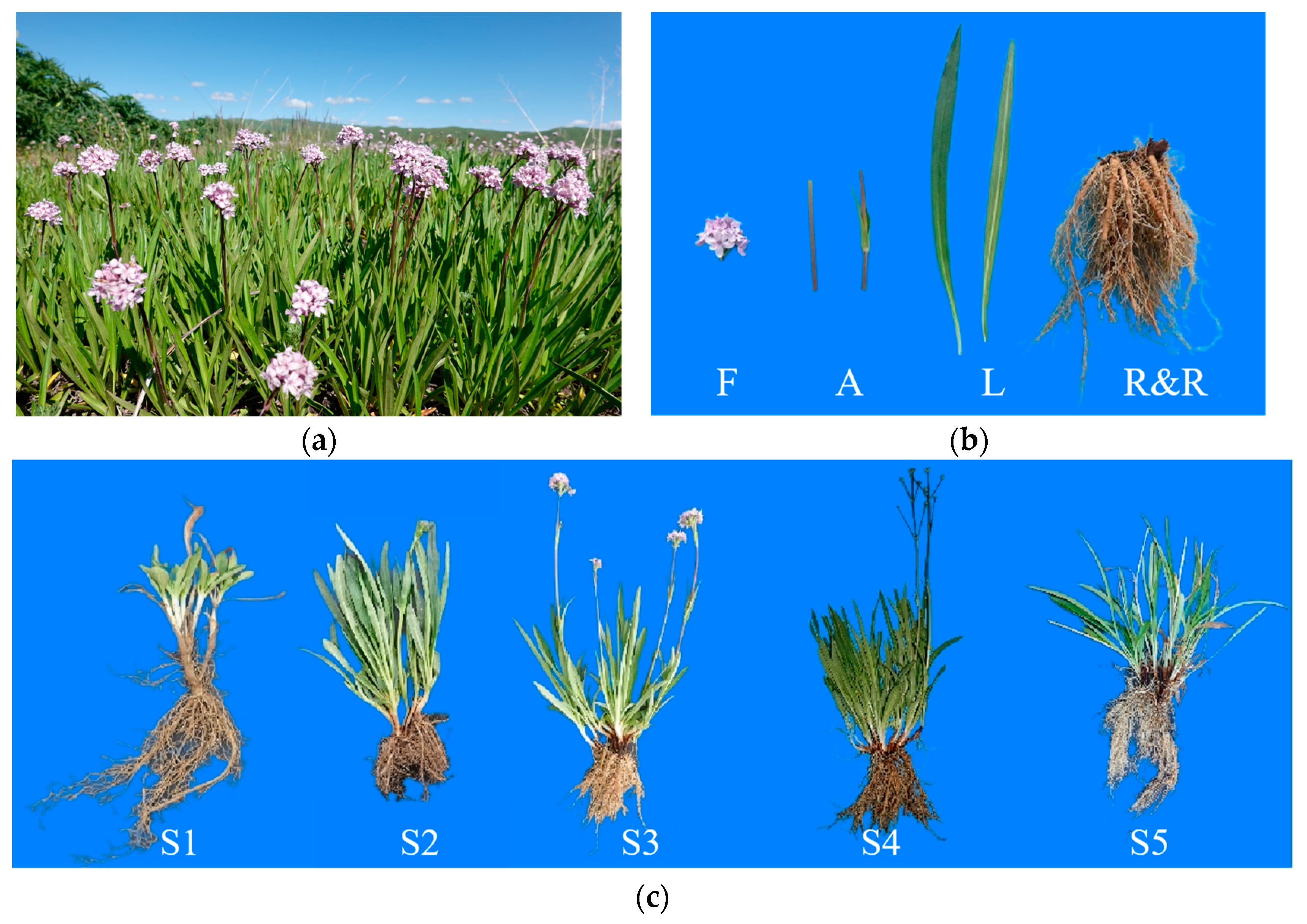
2.1. Plant Materials
2.2. RNA Extraction and Quality Assessment
2.3. RNA-Seq Transcriptome Sequencing
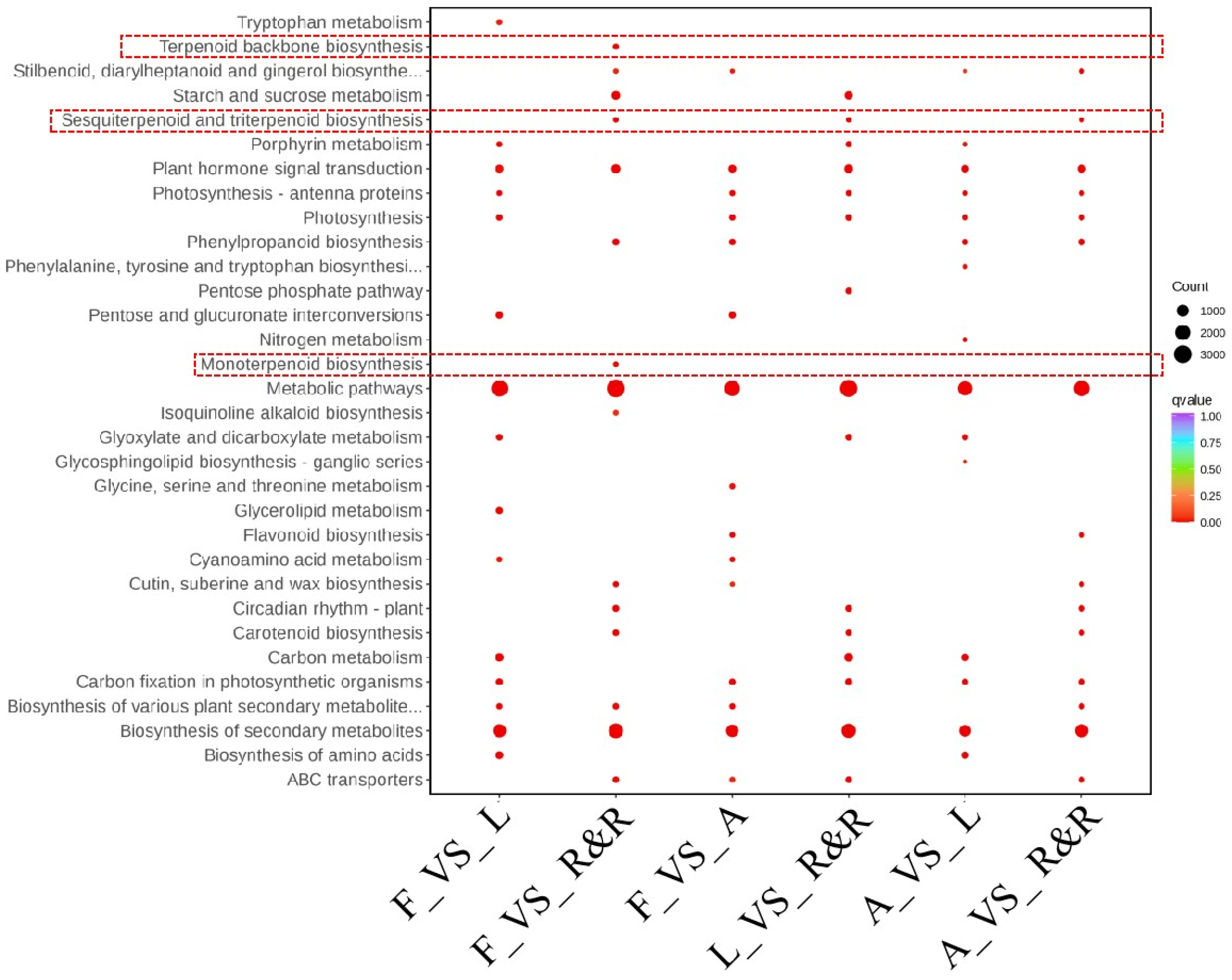
2.4. Gene Functional Annotation and Differential Gene Screening
2.5. Phylogenetic Analysis of Terpenoid Synthesis Genes
2.6. Quantitative Real-Time PCR Verification Analysis
2.7. Expression Analysis of Sesquiterpene Synthase Genes Under MeJA Treatment
2.8. Chemical Component Analysis
3. Results
3.1. Transcriptome Sequencing and Transcript Assembly
3.2. Gene Annotation and Functional Classification
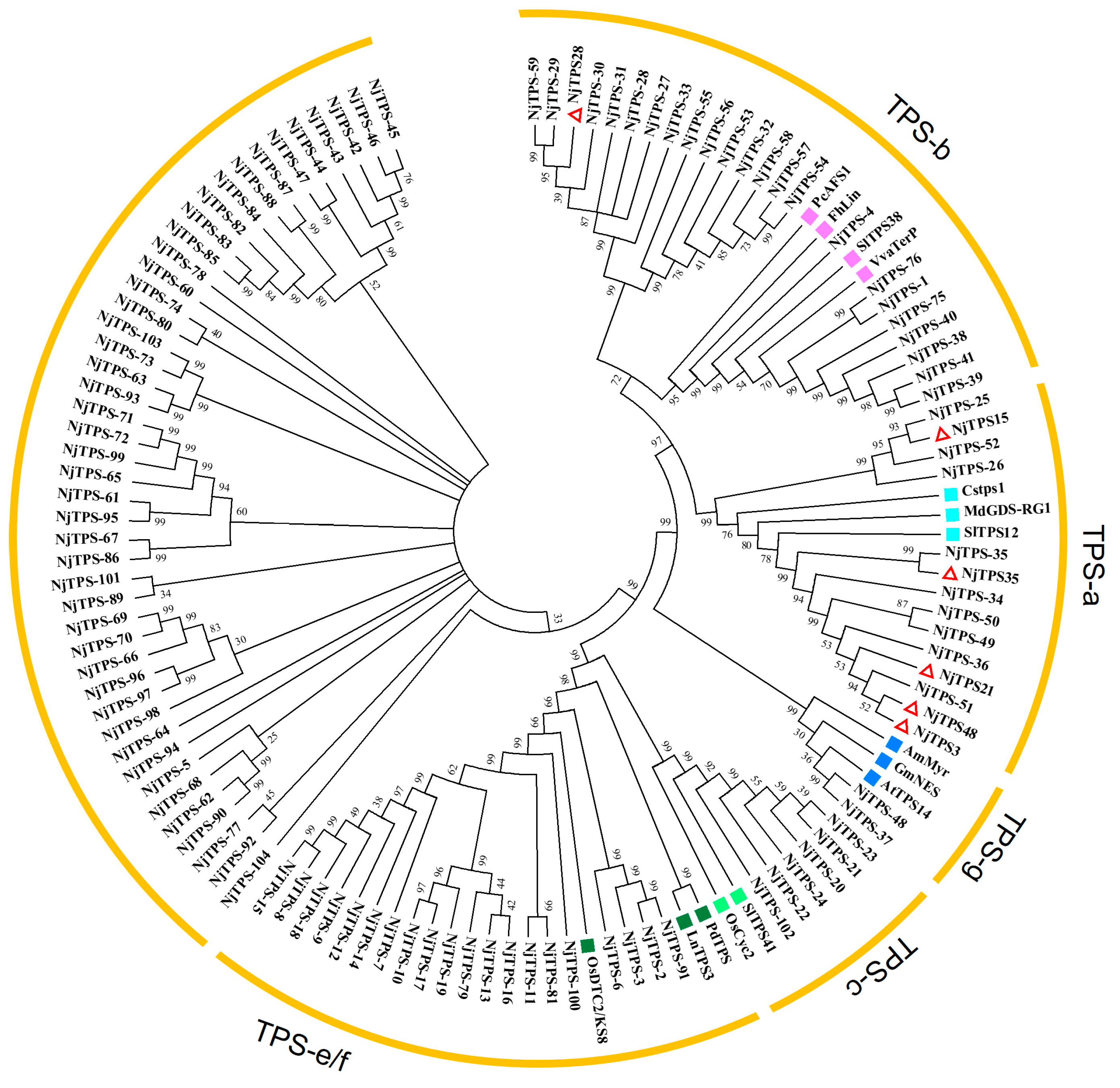
3.3. Phylogenetic Analysis of Terpene Synthase Genes
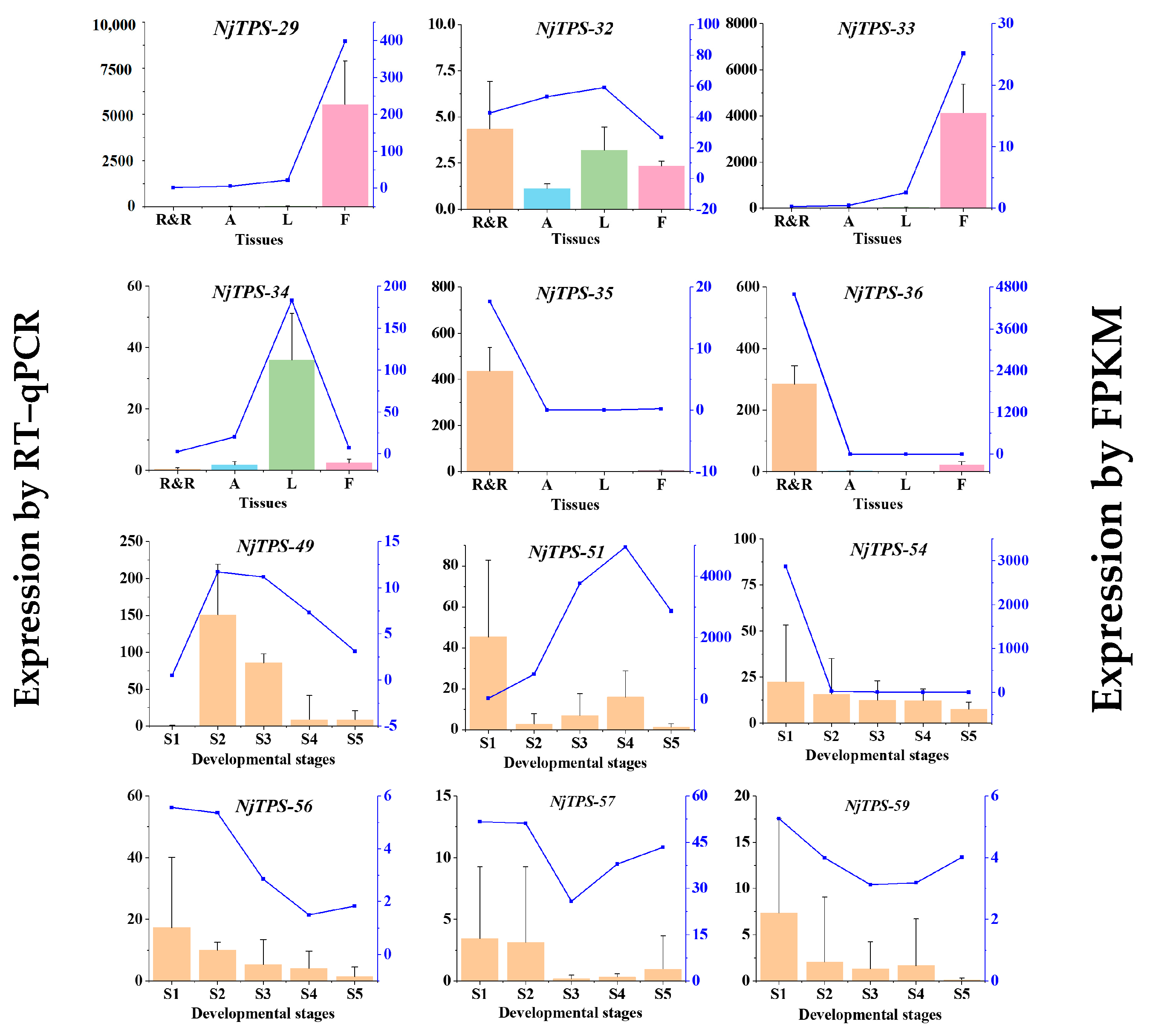
3.4. Gene Expression Pattern Validation and Screening of Sesquiterpene Synthase Genes
3.5. Expression Analysis of Sesquiterpenoid Biosynthesis Genes Under MeJA Treatment
3.6. SSR Identification
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
Glossary
| TPS | terpene synthase |
| SMRT | single-molecule real-time |
| NGS | next-generation sequencing |
| HPLC | High-performance liquid chromatography |
| MEP | 1-deoxy-D-xylulose-5-phosphate/methyl-erythritol-4-phosphate |
| MVA | mevalonate |
| IPP | isopentenyl diphosphate |
| DMAPP | dimethylallyl diphosphate |
| GPPS | geranyl diphosphate synthase |
| GPP | geranyl diphosphate |
| qRT-PCR | quantitative real-time polymerase chain reaction |
| ORF | open reading frames |
| FPKM | fragments per kilobase per million |
| ACCT | acetyl-coenzymeA (CoA)C-acetyltransferase |
| HMGS | 3-hydroxy-3-methylglutaryl-CoA synthase |
| HMGR | 3-hydroxy-3-methylglutaryl-CoA reductase |
| PMK | phosphomevalonate kinase |
| MDC | mevalonate-5-diphosphate |
| DXS | deoxyxyulose-5-phosphate |
| DXR | deoxyxyulose-5-phosphate |
| CMS | 4-diphosphocytidyl-2-C-methyl-D-erythritol synthase |
| CMK | 4-diphosphocytidyl-2-C-methyl-D-erythritol kinase |
| MCS | 4-diphosphocytidyl-2-C-methyl-D-erythritol 2,4-cyclodiphosphate synthase |
| HDS | 1-hydroxy-2-methyl-2(E)-butenyl 4-diphosphate synthase |
| HDR | 1-hydroxy-2-methyl-2(E)-butenyl 4-diphosphate reductase |
| FPPS | farnesyl diphosphate synthase |
| FPP | farnesyl diphosphate |
References
- Wang, M.; Yang, T.-T.; Rao, Y.; Wang, Z.-M.; Dong, X.; Zhang, L.-H.; Han, L.; Zhang, Y.; Wang, T.; Zhu, Y.; et al. A review on traditional uses, phytochemistry, pharmacology, toxicology and the analytical methods of the genus Nardostachys. J. Ethnopharmacol. 2021, 280, 114446. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Maiwulanjiang, M.; Chen, J.; Xin, G.; Gong, A.-G.; Miernisha, A.; Du, C.-Y.; Lau, K.-M.; Lee, P.-S.; Chen, J.; Dong, T.-T.; et al. The volatile oil of Nardostachyos Radix et Rhizoma inhibits the oxidative stress-induced cell injury via reactive oxygen species scavenging and Akt activation in H9c2 cardiomyocyte. J. Ethnopharmacol. 2014, 153, 491–498. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rehman, T.; Ahmad, S. Nardostachys chinensis Batalin: A review of traditional uses, phytochemistry, and pharmacology. Phytother. Res. 2019, 33, 2622–2648. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dhiman, N.; Bhattacharya, A. Nardostachys jatamansi (D.Don) DC.-Challenges and opportunities of harnessing the untapped medicinal plant from the Himalayas. J. Ethnopharmacol. 2020, 246, 112211. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gottumukkala, V.-R.; Annamalai, T.; Mukhopadhyay, T. Phytochemical investigation and hair growth studies on the rhizomes of Nardostachys jatamansi DC. Pharmacogn. Mag. 2011, 7, 146–150. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, R.; Wang, Z.-M.; Wang, Y.; Dong, X.; Zhang, L.-H.; Wang, T.; Zhu, Y.; Gao, X.-M.; Wu, H.-H.; Xu, Y.-T. Antidepressant activities and regulative effects on serotonin transporter of Nardostachys jatamansi DC. J. Ethnopharmacol. 2021, 268, 113601. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bae, G.-S.; Heo, K.-H.; Choi, S.-B.; Jo, I.-J.; Kim, D.-G.; Shin, J.-Y.; Seo, S.-H.; Park, K.-C.; Lee, D.-S.; Oh, H.; et al. Beneficial Effects of Fractions of Nardostachys jatamansi on Lipopolysaccharide-Induced Inflammatory Response. Evid.-Based Complement. Altern. Med. 2014, 2014, 837835. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Heinrich, M.; Jiang, H.; Scotti, F.; Booker, A.; Walt, H.; Weckerle, C.; Maake, C. Medicinal plants from the Himalayan region for potential novel antimicrobial and anti-inflammatory skin treatments. J. Pharm. Pharmacol. 2021, 73, 956–967. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, J.; Yu, J.; Guo, J.; Liu, J.; Wan, G.; Wei, X.; Yang, X.; Shi, J. Nardostachys jatamansi and levodopa combination alleviates Parkinson’s disease symptoms in rats through activation of Nrf2 and inhibition of NLRP3 signaling pathways. Pharm. Biol. 2023, 61, 1175–1185. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wen, J.; Liu, L.; Li, J.; He, Y. A review of nardosinone for pharmacological activities. Eur. J. Pharmacol. 2021, 908, 174343. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiao, Z.-B.; Li, Q.; Niu, Y.-W.; Zhou, X.; Liu, J.-H.; Xu, Y.-B.; Xu, Z.-B. Odor-active compounds of different lavender essential oils and their correlation with sensory attributes. Ind. Crop. Prod. 2017, 108, 748–755. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, Y.-Y.; Ma, B.; Li, Y.-Y.; Han, M.-Z.; Wu, J.; Zhou, X.-F.; Tian, J.; Wang, W.-H.; Leng, P.-S.; Hu, Z.H. Transcriptome analysis identifies key gene LiMYB305 involved in monoterpene biosynthesis in Lilium’Siberia’. Front. Plant Sci. 2022, 13, 1021576. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, L.-C.; Lin, C.-L.; Peng, C.-C.; Huang, T.-L.; Tsai, T.-H.; Kuan, Y.-E.; Chung, Y.-C. Development from Jasminum sambac Flower Extracts of Products with Floral Fragrance and Multiple Physiological Activities. Evid.-Based Complement. Altern. Med. 2021, 2021, 7657628. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sheng, X.; Lin, Y.; Cao, J.; Ning, Y.; Pang, X.; Wu, J.; Kong, F. Comparative Evaluation of Key Aroma-Active Compounds in Sweet Osmanthus (Osmanthus fragrans Lour.) with Different Enzymatic Treatments. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2021, 69, 332–344. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, H.-M.; Liu, W.-B.; Yang, L.-L.; Cao, H.-Q.; Pelosi, P.; Wang, G.-R.; Wang, B. Aromatic Volatiles and Odorant Receptor 25 Mediate Attraction of Eupeodes corollae to Flowers. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2020, 68, 12212–12220. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Keeling, C.-I.; Bohlmann, J. Genes, enzymes and chemicals of terpenoid diversity in the constitutive and induced defence of conifers against insects and pathogens. New Phytol. 2006, 170, 657–675. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.; Zhao, J.; Liu, H.; Zhou, L.; Liu, Z.; Wang, J.; Han, J.; Yu, Z.; Yang, F. Chemical analysis and biological activity of the essential oils of two valerianaceous species from China: Nardostachys chinensis and Valeriana officinalis. Molecules 2010, 15, 6411–6422. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dhiman, N.; Kumar, A.; Kumar, D.; Bhattacharya, A. De novo transcriptome analysis of the critically endangered alpine Himalayan herb Nardostachys jatamansi reveals the biosynthesis pathway genes of tissue-specific secondary metabolites. Sci. Rep. 2020, 10, 17186. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feng, M.; Chen, C.; Qu-Bie, J.; Qu-Bie, A.; Bao, X.; Cui, Q.; Yan, X.; Li, Y.; Liu, Y.; Zhang, S. Metabolome and transcriptome associated analysis of sesquiterpenoid metabolism in Nardostachys jatamansi. Front. Plant Sci. 2022, 13, 1041321. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abdallah, I.-I.; Quax, W.-J. “A Glimpse into the Biosynthesis of Terpenoids.” in NRLS-2016. KnE Life Sci. 2017, 3, 81–98. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, S.; Zhou, Y.; Chen, Y.; Gu, J. fastp: An ultra-fast all-in-one FASTQ preprocessor. Bioinformatics 2018, 34, i884–i890. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Grabherr, M.-G.; Haas, B.-J.; Yassour, M.; Levin, J.-Z.; Thompson, D.-A.; Amit, I.; Adiconis, X.; Fan, L.; Raychowdhury, R.; Zeng, Q.; et al. Full-length transcriptome assembly from RNA-Seq data without a reference genome. Nat. Biotechnol. 2011, 29, 644–652. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Thiel, T.; Michalek, W.; Varshney, R.-K.; Graner, A. Exploiting EST databases for the development and characterization of gene-derived SSR-markers in barley (Hordeum vulgare L.). Theor. Appl. Genet. 2003, 106, 411–422. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Love, M.-I.; Huber, W.; Anders, S. Moderated estimation of fold change and dispersion for RNA-seq data with DESeq2. Genome Biol. 2014, 15, 550. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Varet, H.; Brillet-Guéguen, L.; Coppée, J.-Y.; Dillies, M.-A. SARTools: A DESeq2- and EdgeR-Based R Pipeline for Comprehensive Differential Analysis of RNA-Seq Data. PLoS ONE 2016, 11, e0157022. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, F.; Tholl, D.; Bohlmann, J.; Pichersky, E. The family of terpene synthases in plants: A mid-size family of genes for specialized metabolism that is highly diversified throughout the kingdom. Plant J. 2011, 66, 212–229. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jia, Q.; Brown, R.; Köllner, T.-G.; Fu, J.; Chen, X.; Wong, G.-K.; Gershenzon, J.; Peters, R.-J.; Chen, F. Origin and early evolution of the plant terpene synthase family. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2022, 119, e2100361119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, H.; Kuo, Y.-W.; Chuang, Y.-C.; Yang, Y.-P.; Huang, L.-M.; Jeng, M.-F.; Chen, W.-H.; Chen, H.-H. Terpene Synthase-b and Terpene Synthase-e/f Genes Produce Monoterpenes for Phalaenopsis bellina Floral Scent. Front. Plant Sci. 2021, 12, 700958. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wasternack, C.; Hause, B. Jasmonates: Biosynthesis, perception, signal transduction and action in plant stress response, growth and development. An update to the 2007 review in Annals of Botany. Ann. Bot. 2013, 111, 1021–1058. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, J.; Tang, X.; Ren, C.; Wei, B.; Wu, Y.; Wu, Q.; Pei, J. Full-length transcriptome sequences and the identification of putative genes for flavonoid biosynthesis in safflower. BMC Genom. 2018, 19, 548. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Lu, Y.; Zhang, L.; Zheng, Q.-T.; Xu, L.-Z.; Yang, S.-L. Terpenoids from the roots and rhizomes of Nardostachys chinensis. J. Nat. Prod. 2005, 68, 1131–1133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]



Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Tang, X.; Li, T.; Hao, Z.; Zhao, W.; Han, Y.; Jia, G.; He, Z.; Ren, C.; Rao, K.; Pei, J.; et al. Identification of Key Genes Involved in Sesquiterpene Synthesis in Nardostachys jatamansi Based on Transcriptome and Component Analysis. Genes 2024, 15, 1539. https://doi.org/10.3390/genes15121539
Tang X, Li T, Hao Z, Zhao W, Han Y, Jia G, He Z, Ren C, Rao K, Pei J, et al. Identification of Key Genes Involved in Sesquiterpene Synthesis in Nardostachys jatamansi Based on Transcriptome and Component Analysis. Genes. 2024; 15(12):1539. https://doi.org/10.3390/genes15121539
Chicago/Turabian StyleTang, Xiaohui, Tingju Li, Zhiyu Hao, Wenji Zhao, Yanlong Han, Guofu Jia, Zhengjun He, Chaoxiang Ren, Ke Rao, Jin Pei, and et al. 2024. "Identification of Key Genes Involved in Sesquiterpene Synthesis in Nardostachys jatamansi Based on Transcriptome and Component Analysis" Genes 15, no. 12: 1539. https://doi.org/10.3390/genes15121539
APA StyleTang, X., Li, T., Hao, Z., Zhao, W., Han, Y., Jia, G., He, Z., Ren, C., Rao, K., Pei, J., & Chen, J. (2024). Identification of Key Genes Involved in Sesquiterpene Synthesis in Nardostachys jatamansi Based on Transcriptome and Component Analysis. Genes, 15(12), 1539. https://doi.org/10.3390/genes15121539




