Characterization of the Mitochondrial Genome of Cambaroides schrenckii (Astacidea: Cambaridae) and Its Phylogenetic Implications
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Collection Sample, Extraction of Genomic DNA, and PCR Amplifications
2.2. Mitochondrial Genome Sequencing and Assembly, Gene Annotation, and Sequence Analysis
2.3. Mitochondrial Genome Characteristics and Comparative Analyses
2.4. Phylogenetic Analysis
3. Results
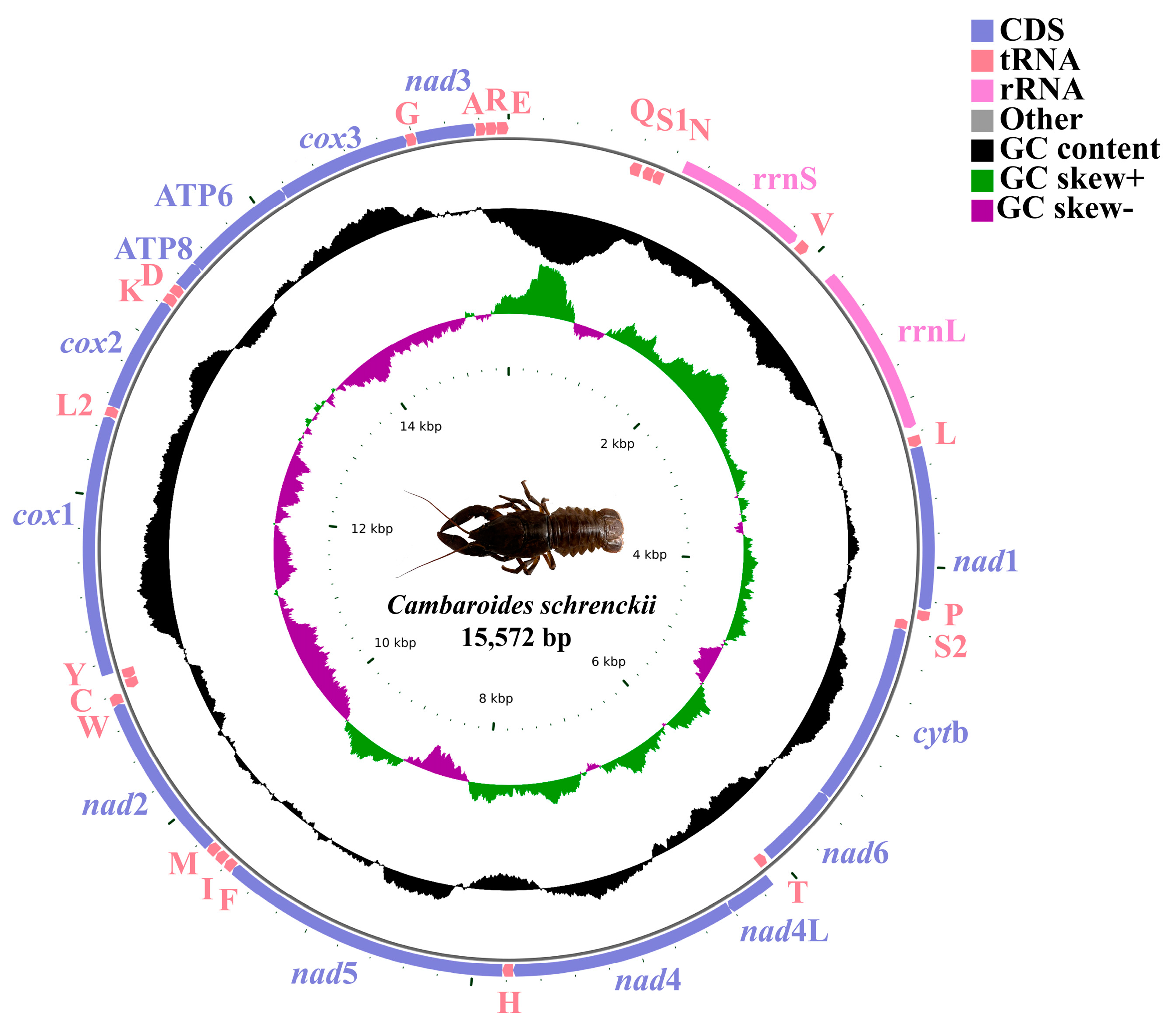
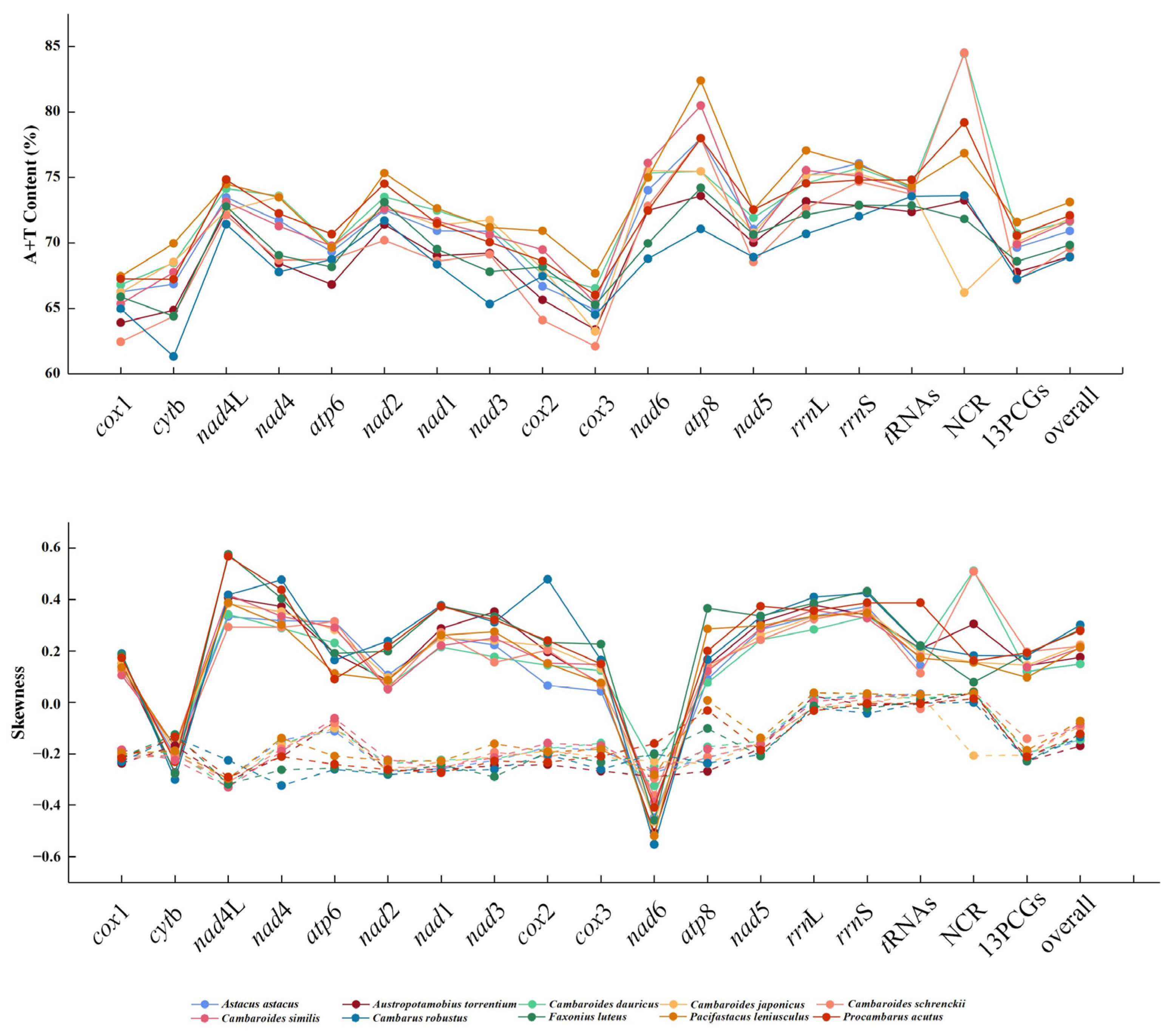
3.1. C. schrenckii Mitochondrial Genome Size and Organisation
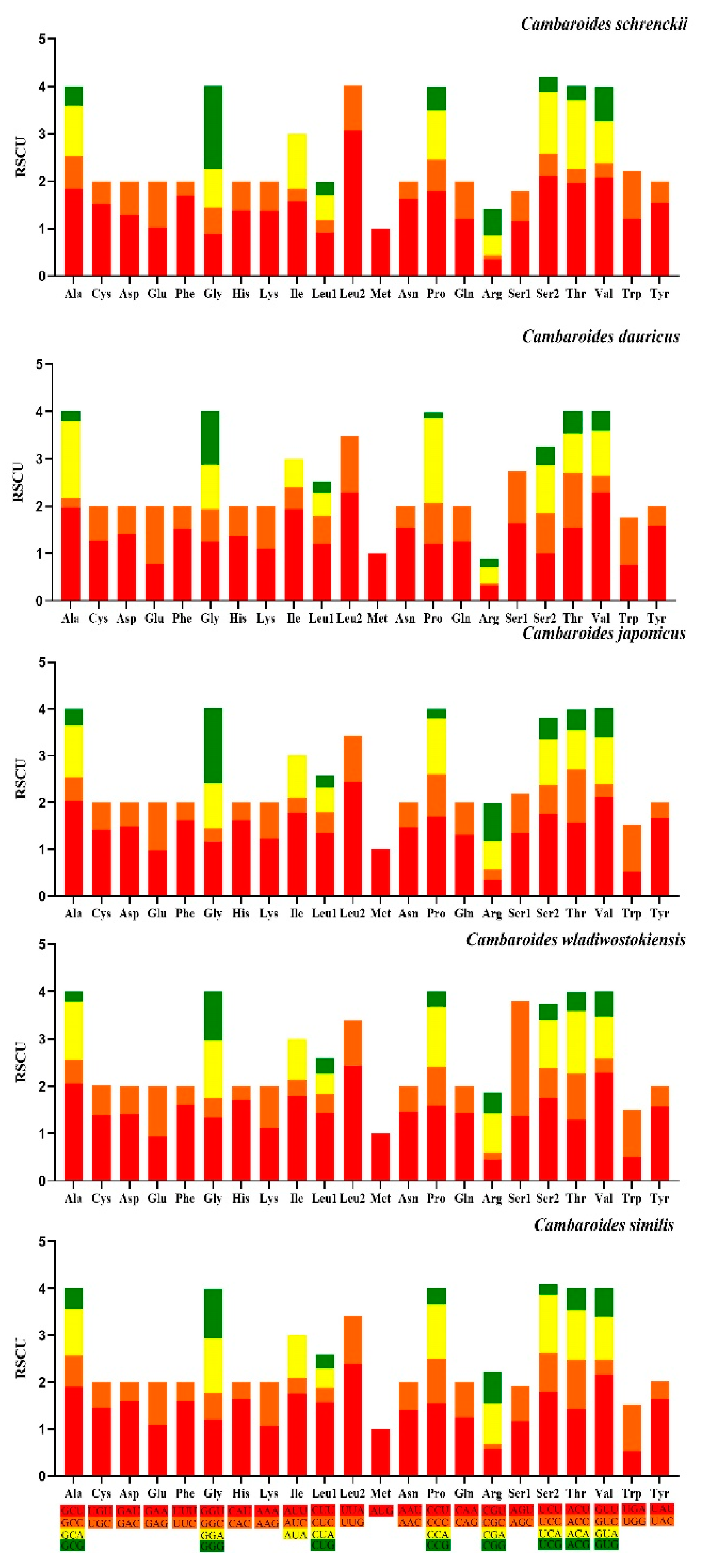
3.2. Protein-Coding Gene
3.3. Transfer RNA and Ribosomal RNA
3.4. Gene Rearrangements
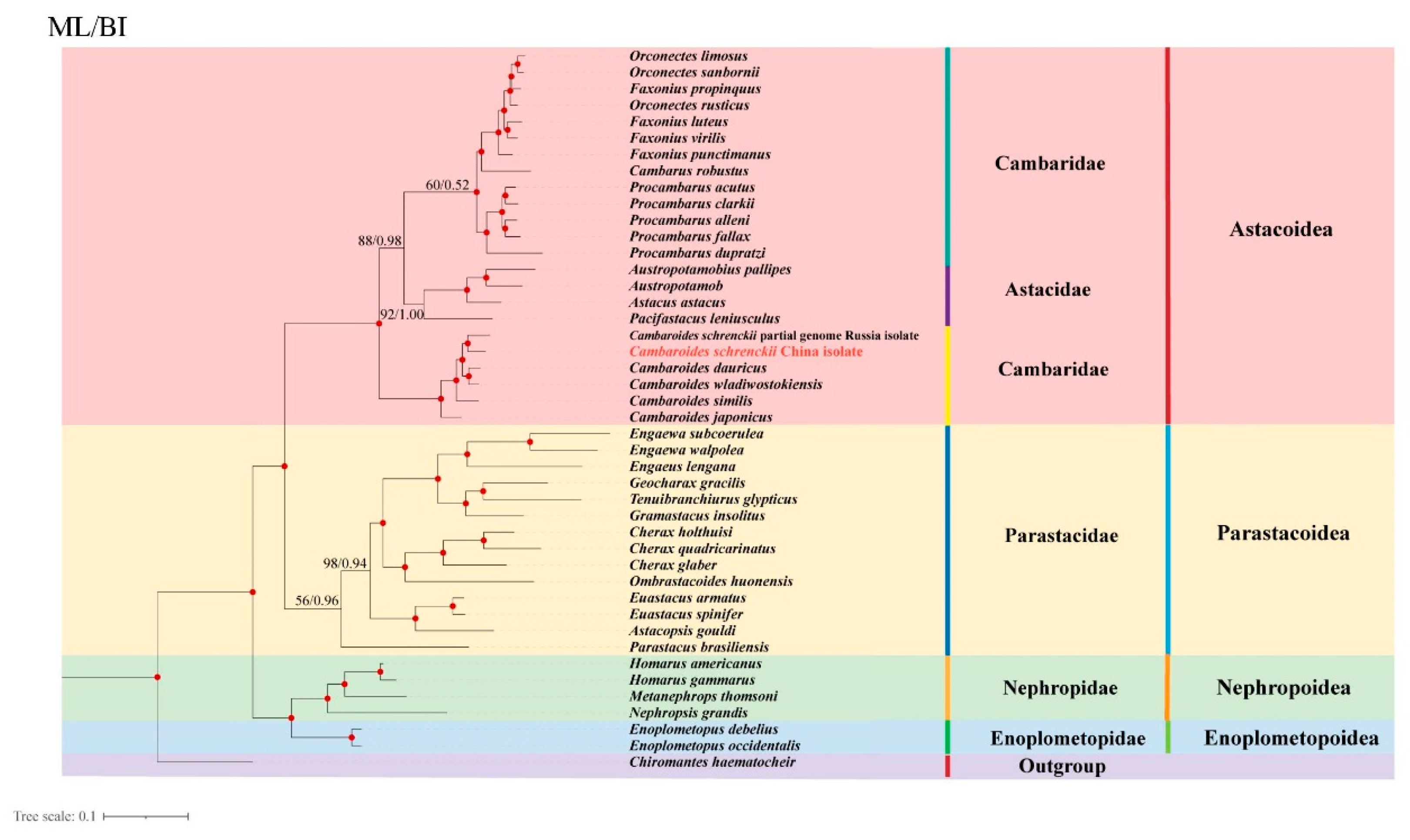
3.5. Phylogenetic Analyses
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Su, C.C.; Tin, Y.C.; Ahyong, S.T. Two New Species of the Rare Lobster Genus Thaumastocheles Wood-Mason, 1874 (Reptantia: Nephropidae) Discovered from Recent Deep-Sea Expeditions in the Indo-West Pacific. J. Crustac. Biol. 2014, 34, 107–122. [Google Scholar]
- Mantelatto, F.L.; Tamburus, A.F.; Carvalho-Batista, A. Checklist of decapod crustaceans from the coast of the So Paulo state (Brazil) supported by integrative molecular and morphological data: V. Dendrobranchiata and Pleocyemata [Achelata, Astacidea, Axiidea, Caridea (Alpheoidea and Processoidea excluded), Gebiidea, Stenopodidea]. Zootaxa 2022, 5121, 1–74. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Richman, N.I.; Böhm, M.; Adams, S.B.; Alvarez, F.; Bergey, E.A.; Bunn, J.J.; Burnham, Q.; Cordeiro, J.; Coughran, J.; Crandall, K.A.; et al. Multiple drivers of decline in the global status of freshwater crayfish (Decapoda: Astacidea). Philos. Trans. R. Soc. Lond. B Biol. Sci. 2015, 370, 20140060. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Luedtke, J.A.; Chanson, J.; Neam, K.; Hobin, L.; Maciel, A.O.; Catenazzi, A.; Borzée, A.; Hamidy, A.; Aowphol, A.; Jean, A.; et al. Ongoing declines for the world’s amphibians in the face of emerging threats. Nature 2023, 622, 308–314. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chai, J.Y.; Jung, B.K. Epidemiology of trematode infections: An update. Adv. Exp. Med. Biol. 2019, 1154, 359–409. [Google Scholar]
- Zhou, X.J.; Yang, Q.; Tan, Q.H.; Zhang, L.Y.; Shi, L.B.; Zou, J.X. Paragonimus and its hosts in China: An update. Acta Trop. 2021, 223, 106094. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Blair, D. Paragonimiasis. Adv. Exp. Med. Biol. 2019, 1154, 105–138. [Google Scholar]
- Blair, D. Lung flukes of the genus Paragonimus: Ancient and re-emerging pathogens. Parasitology 2022, 149, 1286–1295. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gan, H.M.; Tan, M.H.; Gan, H.Y.; Lee, Y.P.; Schultz, M.B.; Austin, C.M. The complete mitogenome of the Australian crayfish Geocharax gracilis Clark 1936 (Crustacea: Decapoda: Parastacidae). Mitochondrial DNA Part A DNA Mapp. Seq. Anal. 2016, 27, 826–827. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, Y.P.; Gan, H.M.; Tan, M.H.; Lys, I.; Page, R.; Dias Wanigasekera, B.; Austin, C.M. The complete mitogenome of the New Zealand freshwater crayfish Paranephrops planifrons White 1842 (Crustacea: Decapoda: Parastacidae). Mitochondrial DNA Part A DNA Mapp. Seq. Anal. 2016, 27, 3333–3334. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Biswal, D.K.; Chatterjee, A.; Bhattacharya, A.; Tandon, V. The mitochondrial genome of Paragonimus westermani (Kerbert, 1878), the Indian isolate of the lung fluke representative of the family Paragonimidae (Trematoda). PeerJ 2014, 2, e484. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, G.; Sun, C.; Hu, H.; Zhang, D.; Li, M. Complete Mitochondrial Genome of the Backswimmer: Notonecta triguttata Motschulsky, 1861 (Hemiptera: Notonectidae): Sequence, Structure, and Phylogenetic Analysis. Diversity 2024, 16, 16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gan, H.M.; Tan, M.H.; Lee, Y.P.; Schultz, M.B.; Horwitz, P.; Burnham, Q.; Austin, C.M. More evolution underground: Accelerated mitochondrial substitution rate in Australian burrowing freshwater crayfishes (Decapoda: Parastacidae). Mol. Phylogenet. Evol. 2018, 118, 88–98. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gan, H.M.; Tan, M.H.; Austin, C.M. The complete mitogenome of the red claw crayfish Cherax quadricarinatus (Von Martens, 1868) (Crustacea: Decapoda: Parastacidae). Mitochondrial DNA Part A DNA Mapp. Seq. Anal. 2016, 27, 385–386. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Trontelj, P.; Machino, Y.; Sket, B. Phylogenetic and phylogeographic relationships in the crayfish genus Austropotamobius inferred from mitochondrial COI gene sequences. Mol. Phylogenet. Evol. 2005, 34, 212–226. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jennifer, E.B.; Keith, A.C. Subterranean phylogeography of freshwater crayfishes shows extensive gene flow and surprisingly large population sizes. Mol. Ecol. 2006, 14, 4259–4273. [Google Scholar]
- Sinclair, E.A.; Fetzner, J.F., Jr.; Buhay, J.E.; Crandall, K.A. Proposal to complete a phylogenetic, taxonomy, and systematic revision for freshwater crayfish (Astacidae). Freshw. Crayfish 2004, 14, 21–29. [Google Scholar]
- Buhay, J.E.; Moni, G.; Mann, N.; Crandall, K.A. Molecular taxonomy in the dark: Evolutionary history, phylogeography, and diversity of cave crayfish in the subgenus Aviticambarus, genus Cambarus. Mol. Phylogenet. Evol. 2007, 42, 435–448. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pedraza-Lara, C.; Gutiérrez-Yurrita, P.J.; Jesus-Bonilla, V.S. A new species of Procambarus (Decapoda, Cambaridae) from the State of Querétaro, Mexico. ZooKeys 2021, 1048, 1–21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fetzner, J.W., Jr. Biochemical systematics and evolution of the crayfish genus Orconectes (Decapoda: Cambaridae). J. Crustac. Biol. 1996, 16, 111–141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schubert, M.; Lindgreen, S.; Orlando, L. AdapterRemoval v2: Rapid adapter trimming, identification, and read merging. BMC Res. Notes 2016, 9, 88. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bankevich, A.; Nurk, S.; Antipov, D.; Gurevich, A.A.; Dvorkin, M.; Kulikov, A.S.; Lesin, V.M.; Nikolenko, S.I.; Pham, S.; Prjibelski, A.D.; et al. SPAdes: A new genome assembly algorithm and its applications to single-cell sequencing. J. Comput. Biol. 2012, 19, 455–477. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jin, J.J.; Yu, W.B.; Yang, J.B.; Song, Y.; dePamphilis, C.W.; Yi, T.S.; Li, D.Z. GetOrganelle: A fast and versatile toolkit for accurate de novo assembly of organelle genomes. Genome Biol. 2020, 21, 241. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lowe, T.M.; Chan, P.P. tRNA scan-SE On-line: Integrating search and context for analysis of transfer RNA genes. Nucleic Acids Res. 2016, 44, 54–57. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bernt, M.; Donath, A.; Jühling, F.; Externbrink, F.; Florentz, C.; Fritzsch, G.; Pütz, J.; Middendorf, M.; Stadler, P.F. MITOS: Improved de novo metazoan mitochondrial genome annotation. Mol. Phylogenet. Evol. 2013, 69, 313–319. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grant, J.R.; Stothard, P. The CGView Server: A comparative genomics tool for circular genomes. Nucleic Acids Res. 2008, 36, 181–184. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumar, S.; Stecher, G.; Li, M.; Knyaz, C.; Tamura, K. MEGA X: Molecular Evolutionary Genetics Analysis across Computing Platforms. Mol. Biol. Evol. 2018, 35, 1547–1549. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Perna, N.T.; Kocher, T.D. Patterns of nucleotide composition at fourfold degenerate sites of animal mitochondrial genomes. J. Mol. Evol. 1995, 41, 353–358. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Librado, P.; Rozas, J. DnaSP v5: A software for comprehensive analysis of DNA polymorphism data. Bioinformatics 2009, 25, 1451–1452. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Katoh, K.; Standley, D.M. MAFFT multiple sequence alignment software version 7: Improvements in performance and usability. Mol. Biol. Evol. 2013, 30, 772–780. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guindon, S.; Gascuel, O. A simple, fast, and accurate algorithm to estimate large phylogenies by maximum likelihood. Syst. Biol. 2003, 52, 696–704. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ronquist, F.; Huelsenbeck, J.P. MrBayes 3: Bayesian phylogenetic inference under mixed models. Bioinformatics 2003, 19, 1572–1574. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kurabayashi, A.; Ueshima, R. Complete sequence of the mitochondrial DNA of the primitive opisthobranch gastropod Pupa strigosa: Systematic implication of the genome organization. Mol. Biol. Evol. 2000, 17, 266–277. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wolstenholme, D.R. Animal mitochondrial DNA: Structure and evolution. Int. Rev. Cytol. 1992, 141, 173–216. [Google Scholar]
- Pereira, S.L. Mitochondrial genome organization and vertebrate phylogenetics. Genet. Mol. Biol. 2000, 23, 745–752. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, Y.; Kurisaki, M.; Hashiguchi, Y.; Kumazawa, Y. Variation and evolution of polyadenylation profiles in sauropsid mitochondrial mRNAs as deduced from the high-throughput RNA sequencing. BMC Genom. 2017, 18, 665. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, L.; Lin, Y.; Xiao, Q.; Lin, Y.; Du, Y.; Lin, C.; Ward-Fear, G.; Hu, C.; Qu, Y.; Li, H. Characterization of the complete mitochondrial genome of the many-lined sun skink (Eutropis multifasciata) and comparison with other Scincomorpha species. Genomics 2021, 113, 2526–2536. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Suleman; Ma, J.; Khan, M.S.; Tkach, V.V.; Muhammad, N.; Zhang, D.; Zhu, X.Q. Characterization of the complete mitochondrial genome of Plagiorchis maculosus (Digenea, Plagiorchiidae), Representative of a taxonomically complex digenean family. Parasitol. Int. 2019, 71, 99–105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, D.; Zou, H.; Wu, S.G.; Li, M.; Jakovlić, I.; Zhang, J.; Chen, R.; Li, W.X.; Wang, G.T. Three new Diplozoidae mitogenomes expose unusual compositional biases within the Monogenea class: Implications for phylogenetic studies. BMC Evol. Biol. 2018, 18, 133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Romero, H.; Zavala, A.; Musto, H. Codon usage in Chlamydia trachomatis is the result of strand-specific mutational biases and a complex pattern of selective forces. Nucleic Acids Res. 2000, 28, 2084–2090. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barbhuiya, R.I.; Uddin, A.; Chakraborty, S. Compositional properties and codon usage pattern of mitochondrial ATP gene in different classes of Arthropoda. Genetica 2019, 147, 231–248. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ananth, P.; Goldsmith, G.; Yathindra, N. An innate twist between Crick’s wobble and Watson-Crick base pairs. RNA 2013, 19, 1038–1053. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, X.; Cao, Y.; Zhang, W.; Simmons, M.P. Adenine·cytosine substitutions are an alternative pathway of compensatory mutation in angiosperm ITS2. RNA 2020, 26, 209–217. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, S.; Park, M.; Jung, J.; Ahn, D.; Sultana, T.; Kim, S.J.; Park, J.; Choi, H.; Min, G. The mitochondrial genomes of Cambaroides similis and Procambarus clarkii (Decapoda: Astacidea: Cambaridae): The phylogenetic implications for Reptantia. Zool. Scr. 2012, 41, 281–292. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiao, W.H.; Zhang, Y.P. Genetics and evolution of mitochondrial dna in fish. Acta Hydrobiologica Sinica. 2000, 24, 384–391. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.B.; Shang, Y.Q.; Wu, X.Y.; Wei, Q.G.; Zhou, S.Y.; Sun, G.L.; Mei, X.S.; Dong, Y.H.; Sha, W.L.; Zhang, H.H. Divergent evolution of mitogenomics in Cetartiodactyla niche adaptation. Org. Divers Evol. 2023, 23, 243–259. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jakovlić, I.; Zou, H.; Zhao, X.M.; Zhang, J.; Wang, G.T.; Zhang, D. Evolutionary history of inversions in directional mutational pressures in crustacean mitochondrial genomes: Implications for evolutionary studies. Mol. Phylogenet. Evol. 2021, 164, 107288. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tao, M.; Chen, J.; Cui, C.; Xu, Y.; Xu, J.; Shi, Z.; Yun, J.; Zhang, J.; Ou, G.Z.; Liu, C.; et al. Identification of a longevity gene through evolutionary rate covariation of insect mito-nuclear genomes. Nat. Aging. 2024, 4, 1076–1088. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shen, H.; Braband, A.; Scholtz, G. Mitogenomic analysis of decapod crustacean phylogeny corroborates traditional views on their relationships. Mol. Phylogenet. Evol. 2013, 66, 776–789. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gan, H.M.; Grandjean, F.; Jenkins, T.L.; Austin, C.M. Absence of evidence is not evidence of absence: Nanopore sequencing and complete assembly of the European lobster (Homarus gammarus) mitogenome uncovers the missing nad2 and a new major gene cluster duplication. BMC Genom. 2019, 20, 335. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Crandall, K.A.; Harris, D.J.; Fetzner, J.W., Jr. The monophyletic origin of freshwater crayfish estimated from nuclear and mitochondrial DNA sequences. Proc. Biol. Sci. 2000, 267, 1679–1686. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hobbs, H.H., Jr. Synopsis of the families and genera of crayfish (Crustacea, Decapoda). Smithson. Contrib. Zool. 1974, 164, 1–32. [Google Scholar]
- Scholtz, G.; Kawai, T. Aspects of embryonic and postembryonic development of the Japanese freshwater crayfish Cambaroides japonicus (Crustacea, Decapoda) including a hypothesis on the evolution of maternal care in the Astacida. Acta Zool. 2002, 83, 203–212. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kawai, T.; Tudge, C.C. Re-examination of the type material of Cambaroides schrenckii (Kessler, 1874) (Decapoda: Cambaridae) with a lectotype designation, re-description, and discussion on its phylogenetic position. Proc. Biol. Soc. Wash. 2008, 121, 158–176. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Braband, A.; Kawai, T.; Scholtz, G. The phylogenetic position of the East Asian freshwater crayfish Cambaroides within the Northern Hemisphere Astacoidea (Crustacea, Decapoda, Astacida) based on molecular data. J. Zool. Syst. Evol. Res. 2008, 44, 17–24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bracken-Grissom, H.D.; Ahyong, S.T.; Wilkinson, R.D.; Feldmann, R.M.; Schweitzer, C.E.; Breinholt, J.W.; Bendall, M.; Palero, F.; Chan, T.Y.; Felder, D.L.; et al. The emergence of lobsters: Phylogenetic relationships, morphological evolution and divergence time comparisons of an ancient group (decapoda: Achelata, astacidea, glypheidea, polychelida). Syst. Biol. 2014, 63, 457–479. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grandjean, F.; Tan, M.H.; Gan, H.M.; Lee, Y.; Kawai, T.; DiStefano, R.J.; Bláha, M.; Roles, A.J.; Austin, C.M. Rapid recovery of nuclear and mitochondrial genes by genome skimming from Northern Hemisphere freshwater crayfish. Zool. Scr. 2017, 46, 718–728. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]


| Gene | Start | Stop | Size (bp) | Direction | Intergenic Nucleotides | Start Codons | Stop Codons | A + T% |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| D-loop | 1 | 763 | 763 | - | - | - | 84.53 | |
| trnQ | 764 | 833 | 70 | - | - | - | - | 71.43 |
| trnS1 | 848 | 914 | 67 | - | 14 | - | - | 67.16 |
| trnN | 915 | 978 | 64 | - | 0 | - | - | 70.31 |
| rrnS | 1071 | 1860 | 790 | + | 92 | - | - | 74.68 |
| trnV | 1885 | 1952 | 68 | + | 24 | - | - | 69.12 |
| rrnL | 2154 | 3170 | 1017 | + | 201 | - | - | 72.66 |
| trnL1 | 3220 | 3284 | 65 | + | 49 | - | - | 72.31 |
| nad1 | 3288 | 4249 | 962 | + | 3 | ATG | TAG | 68.61 |
| trnP | 4257 | 4320 | 64 | + | 7 | - | - | 71.88 |
| trnS2 | 4323 | 4386 | 64 | - | 2 | - | - | 78.12 |
| cytb | 4387 | 5521 | 1135 | - | 0 | ATT | TAA | 64.41 |
| nad6 | 5521 | 6039 | 519 | - | −1 | ATT | TAA | 72.83 |
| trnT | 6060 | 6122 | 63 | - | 20 | - | - | 79.37 |
| nad4L | 6125 | 6418 | 294 | + | 2 | ATG | TAA | 72.11 |
| nad4 | 6418 | 7761 | 1344 | + | −1 | ATG | TAA | 68.68 |
| trnH | 7761 | 7824 | 64 | + | −1 | - | - | 84.38 |
| nad5 | 7825 | 9554 | 1730 | + | 0 | ATG | T | 68.55 |
| trnF | 9555 | 9615 | 61 | + | 0 | - | - | 67.21 |
| trnI | 9621 | 9684 | 64 | + | 5 | - | - | 73.44 |
| trnM | 9688 | 9752 | 65 | + | 3 | - | - | 70.77 |
| nad2 | 9753 | 10,745 | 993 | + | 0 | ATG | TAA | 70.19 |
| trnW | 10,745 | 10,810 | 66 | + | −1 | - | - | 68.18 |
| trnC | 10,810 | 10,872 | 63 | - | −1 | - | - | 77.78 |
| trnY | 10,873 | 10,934 | 62 | - | 0 | - | - | 70.97 |
| cox1 | 10,932 | 12,470 | 1539 | + | −3 | ATC | TAG | 62.44 |
| trnL2 | 12,473 | 12,536 | 64 | + | 2 | - | - | 67.19 |
| cox2 | 12,537 | 13,221 | 685 | + | 0 | ATG | T | 64.09 |
| trnK | 13,222 | 13,285 | 64 | + | 0 | - | - | 71.88 |
| trnD | 13,287 | 13,349 | 63 | + | 1 | - | - | 85.71 |
| atp8 | 13,350 | 13,508 | 159 | + | 0 | ATG | TAA | 77.99 |
| atp6 | 13,505 | 14,176 | 672 | + | −4 | ATA | TAA | 68.75 |
| cox3 | 14,176 | 14,964 | 789 | + | −1 | ATG | TAA | 62.10 |
| trnG | 14,963 | 15,024 | 62 | + | −2 | - | - | 77.42 |
| nad3 | 15,025 | 15,377 | 353 | + | 0 | ATT | TAA | 69.12 |
| trnA | 15,379 | 15,439 | 61 | + | 1 | - | - | 73.77 |
| trnR | 15,440 | 15,504 | 65 | + | 0 | - | - | 73.85 |
| trnE | 15,505 | 15,572 | 68 | + | 0 | - | - | 80.88 |
| A | B | C | D | E | F | G | H | I | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| B | 0.04 | ||||||||
| C | 0.06 | 0.08 | |||||||
| D | 0.07 | 0.06 | 0.07 | ||||||
| E | 0.06 | 0.05 | 0.07 | 0.06 | |||||
| F | 0.05 | 0.05 | 0.05 | 0.06 | 0.05 | ||||
| G | 0.05 | 0.07 | 0.04 | 0.04 | 0.02 | 0.07 | |||
| H | 0.06 | 0.04 | 0.07 | 0.04 | 0.03 | 0.08 | 0.08 | ||
| I | 0.06 | 0.09 | 0.03 | 0.06 | 0.07 | 0.04 | 0.07 | 0.05 | |
| J | 0.06 | 0.04 | 0.07 | 0.05 | 0.06 | 0.05 | 0.05 | 0.05 | 0.07 |
| Genes | Identity of Nucleotides/Amino Acids (%) | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| CSC/CSR | CSC/CD | CSC/CJ | CSC/CS | CSC/CW | |
| cox1 | 100.0/100.0 | 95.8/96.1 | 95.8/96.1 | 95.2/95.1 | 95.8/96.1 |
| cox2 | 99.7/100.0 | 98.7/98.2 | 99.1/99.1 | 96.5/94.3 | 98.8/98.7 |
| atp8 | 100.0/100.0 | 91.7/88.5 | 90.4/88.5 | 91.0/86.5 | 90.4/88.5 |
| atp6 | 99.7/100.0 | 92.5/90.0 | 92.3/90.5 | 91.3/88.7 | 92.4/90.5 |
| cox3 | 100.0/100.0 | 98.2/97.3 | 98.7/98.1 | 98.2/97.7 | 97.8/97.3 |
| nad3 | 100.0/100.0 | 92.6/86.3 | 94.0/88.9 | 93.7/88.9 | 94.6/89.7 |
| nad1 | 100.0/100.0 | 95.5/93.0 | 95.6/93.6 | 95.0/92.0 | 96.1/93.6 |
| cytb | 100.0/100.0 | 96.6/95.0 | 98.1/97.1 | 95.9/94.2 | 97.9/96.8 |
| nad6 | 100.0/100.0 | 93.4/89.5 | 95.0/91.9 | 89.9/85.5 | 93.2/88.4 |
| nad4L | 100.0/100.0 | 96.6/94.8 | 95.2/92.8 | 95.2/91.8 | 95.9/93.8 |
| nad4 | 100.0/100.0 | 94.2/91.5 | 88.6/84.8 | 93.6/90.1 | 94.5/91.9 |
| nad5 | 100.0/100.0 | 95.5/92.5 | 96.6/95.1 | 94.8/91.8 | 96.1/94.1 |
| nad2 | 100.0/100.0 | 93.8/90.3 | 94.5/91.8 | 91.5/87.0 | 93.8/91.2 |
| Total | 99.7/100.0 | 95.3/93.0 | 78.0/89.7 | 80.6/90.2 | 81.4/92.1 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Liu, X.; Li, B.; Yang, Y.; Zhang, J.; Hu, C.; Zhang, Y.; Zhou, J.; Liu, Y.; Qiu, H.; Wang, C.; et al. Characterization of the Mitochondrial Genome of Cambaroides schrenckii (Astacidea: Cambaridae) and Its Phylogenetic Implications. Genes 2024, 15, 1578. https://doi.org/10.3390/genes15121578
Liu X, Li B, Yang Y, Zhang J, Hu C, Zhang Y, Zhou J, Liu Y, Qiu H, Wang C, et al. Characterization of the Mitochondrial Genome of Cambaroides schrenckii (Astacidea: Cambaridae) and Its Phylogenetic Implications. Genes. 2024; 15(12):1578. https://doi.org/10.3390/genes15121578
Chicago/Turabian StyleLiu, Xuewei, Ben Li, Yan Yang, Jun Zhang, Chunbo Hu, Yuxi Zhang, Jiawang Zhou, Yinlong Liu, Hongyu Qiu, Chunren Wang, and et al. 2024. "Characterization of the Mitochondrial Genome of Cambaroides schrenckii (Astacidea: Cambaridae) and Its Phylogenetic Implications" Genes 15, no. 12: 1578. https://doi.org/10.3390/genes15121578
APA StyleLiu, X., Li, B., Yang, Y., Zhang, J., Hu, C., Zhang, Y., Zhou, J., Liu, Y., Qiu, H., Wang, C., & Gao, J. (2024). Characterization of the Mitochondrial Genome of Cambaroides schrenckii (Astacidea: Cambaridae) and Its Phylogenetic Implications. Genes, 15(12), 1578. https://doi.org/10.3390/genes15121578







