X Chromosome-Specific Repeats in Non-Domestic Bovidae
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Chromosome Preparation
2.2. Isolation of X Chromosome Repetitive DNA Sequences
2.3. Fluorescence In Situ Hybridization
2.4. Detection of X Chromosome Repetitive DNA Sequences Using PCR
2.5. Analysis of X Chromosome Repetitive DNA Sequences Using Quantitative Real-Time PCR
2.6. Detection of BTAXr Sequences on Microdissected Chromosomes
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. KDEXr Clone
3.1.1. Sequence Analysis
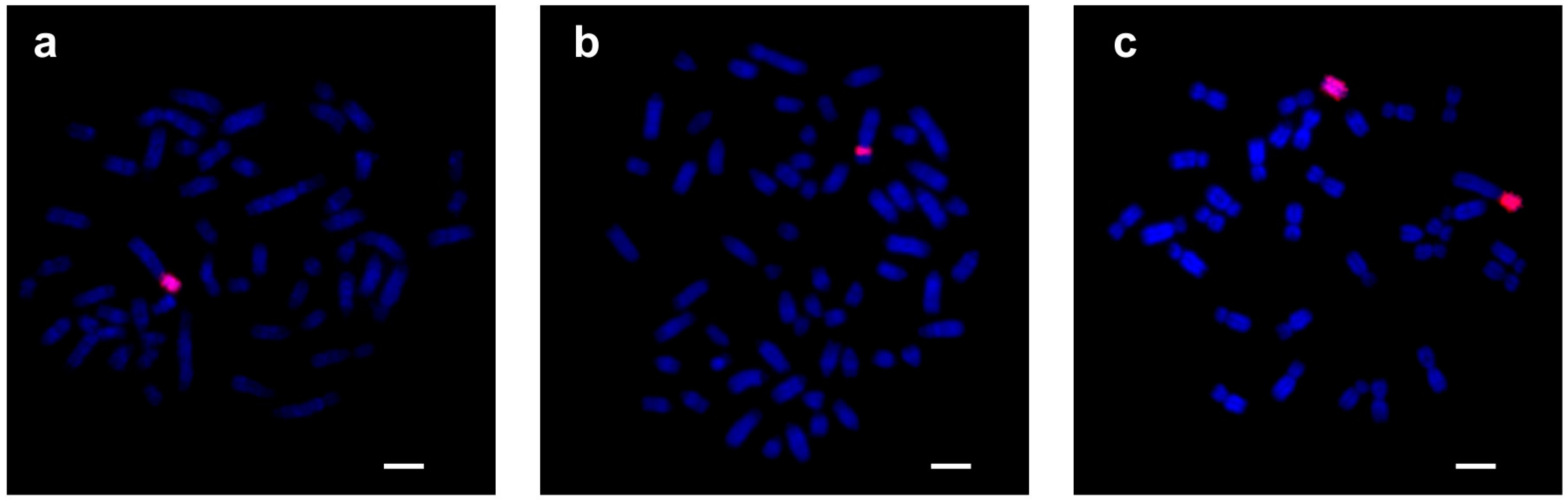
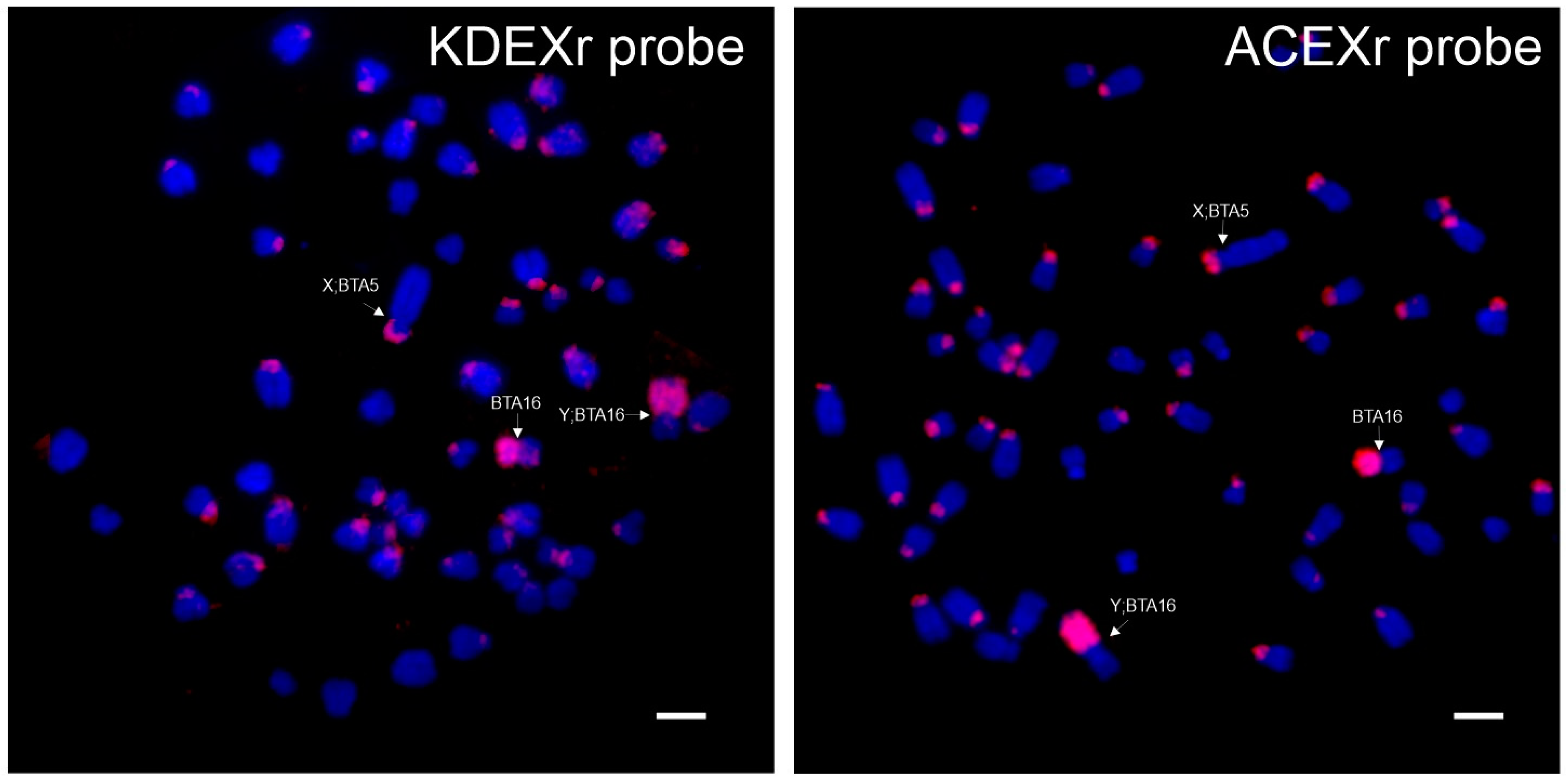
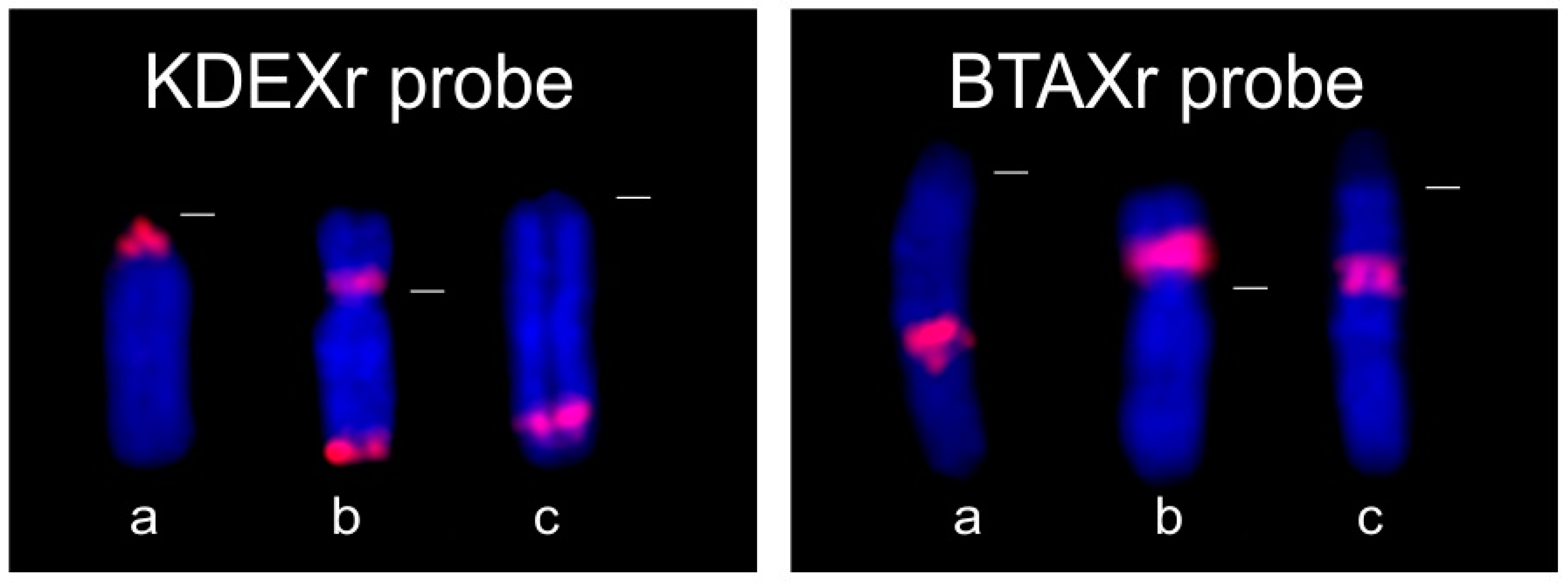
3.1.2. FISH Analysis
3.1.3. Analysis of KDEXr Sequence Using PCR and qPCR
3.2. BTAXr Clone
3.2.1. Sequence Analysis
3.2.2. FISH Analysis
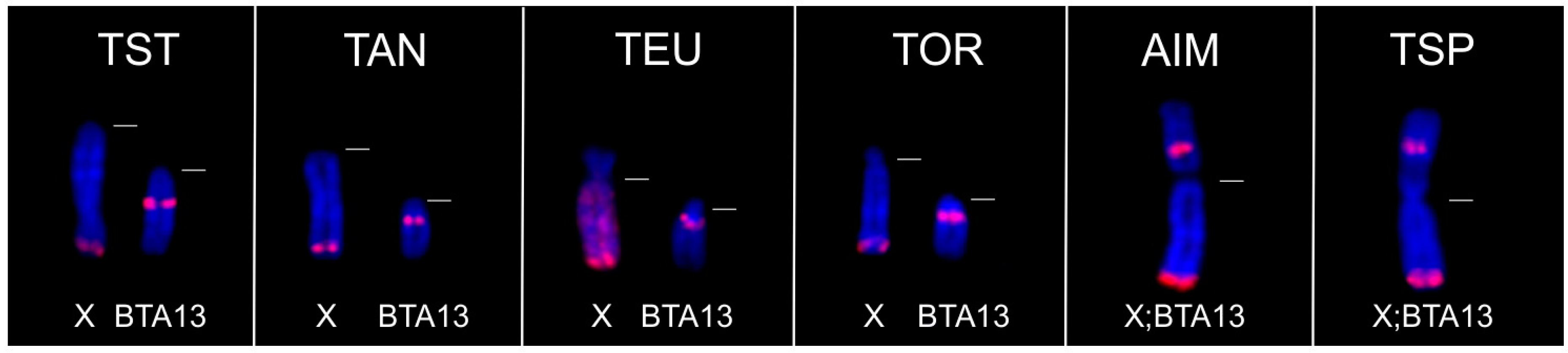
3.2.3. Analysis of BTAXr Sequence Using PCR and qPCR
3.3. ACEXr Clone
3.3.1. Sequence Analysis
3.3.2. FISH Analysis
3.3.3. Analysis of the ACEXr Sequence Using PCR and qPCR
3.4. Co-Localization of KDEXr, BTAXr and ACEXr Sequences in the X Chromosomes of O. aries, C. hircus and B. taurus
4. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Cioffi, M.B.; Bertollo, L.A.C. Chromosomal Distribution and Evolution of Repetitive DNAs in Fish. Genome Dyn. 2012, 7, 197–221. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bierhoff, H.; Postepska-Igielska, A.; Grummt, I. Noisy Silence: Non-Coding RNA and Heterochromatin Formation at Repetitive Elements. Epigenetics 2014, 9, 53–61. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Protasova, M.S.; Andreeva, T.V.; Rogaev, E.I. Factors Regulating the Activity of LINE1 Retrotransposons. Genes 2021, 12, 1562. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ugarković, Đ.; Sermek, A.; Ljubić, S.; Feliciello, I. Satellite DNAs in Health and Disease. Genes 2022, 13, 1154. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chung, T.H.; Zhuravskaya, A.; Makeyev, E.V. Regulation Potential of Transcribed Simple Repeated Sequences in Developing Neurons. Hum. Genet. 2023. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vourc’h, C.; Biamonti, G. Transcription of Satellite DNAs in Mammals. Prog. Mol. Subcell. Biol. 2011, 51, 95–118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hall, L.E.; Mitchell, S.E.; O’Neill, R.J. Pericentric and Centromeric Transcription: A Perfect Balance Required. Chromosome Res. 2012, 20, 535–546. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Biémont, C.; Vieira, C. Genetics: Junk DNA as an Evolutionary Force. Nature 2006, 443, 521–524. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Escudeiro, A.; Adega, F.; Robinson, T.J.; Heslop-Harrison, J.S.; Chaves, R. Conservation, Divergence, and Functions of Centromeric Satellite DNA Families in the Bovidae. Genome Biol. Evol. 2019, 11, 1152–1165. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Raskina, O.; Barber, J.C.; Nevo, E.; Belyayev, A. Repetitive DNA and Chromosomal Rearrangements: Speciation-Related Events in Plant Genomes. Cytogenet. Genome Res. 2008, 120, 351–357. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Żylicz, J.J.; Heard, E. Molecular Mechanisms of Facultative Heterochromatin Formation: An X-Chromosome Perspective. Annu. Rev. Biochem. 2020, 89, 255–282. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mezzasalma, M.; Andreone, F.; Glaw, F.; Guarino, F.M.; Odierna, G.; Petraccioli, A.; Picariello, O. Changes in Heterochromatin Content and Ancient Chromosome Fusion in the Endemic Malagasy Boid Snakes Sanzinia and Acrantophis (Squamata: Serpentes). Salamandra 2019, 55, 140–144. [Google Scholar]
- Thelma, B.K.; Juyal, R.C.; Tewari, R.; Rao, S.R. Does Heterochromatin Variation Potentiate Speciation? A Study in Nesokia. Cytogenet. Cell Genet. 1988, 47, 204–208. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Charlesworth, D.; Charlesworth, B.; Marais, G. Steps in the Evolution of Heteromorphic Sex Chromosomes. Heredity 2005, 95, 118–128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Piumi, F.; Schibler, L.; Vaiman, D.; Oustry, A.; Cribiu, E.P. Comparative Cytogenetic Mapping Reveals Chromosome Rearrangements between the X Chromosomes of Two Closely Related Mammalian Species (Cattle and Goats). Cytogenet. Cell Genet. 1998, 81, 36–41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Robinson, T.J.; Harrison, W.R.; Ponce de León, F.A.; Davis, S.K.; Elder, F.F. A Molecular Cytogenetic Analysis of X Chromosome Repatterning in the Bovidae: Transpositions, Inversions, and Phylogenetic Inference. Cytogenet. Cell Genet. 1998, 80, 179–184. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Robinson, T.J.; Cernohorska, H.; Kubickova, S.; Vozdova, M.; Musilova, P.; Ruiz-Herrera, A. Chromosomal Evolution in Raphicerus Antelope Suggests Divergent X Chromosomes May Drive Speciation through Females, Rather than Males, Contrary to Haldane’s Rule. Sci. Rep. 2021, 11, 3152. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gallagher, D.S.; Davis, S.K.; De Donato, M.; Burzlaff, J.D.; Womack, J.E.; Taylor, J.F.; Kumamoto, A.T. A Molecular Cytogenetic Analysis of the Tribe Bovini (Artiodactyla: Bovidae: Bovinae) with an Emphasis on Sex Chromosome Morphology and NOR Distribution. Chromosome Res. 1999, 7, 481–492. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Iannuzzi, L.; Di Meo, G.P.; Perucatti, A.; Incarnato, D.; Schibler, L.; Cribiu, E.P. Comparative FISH Mapping of Bovid X Chromosomes Reveals Homologies and Divergences between the Subfamilies Bovinae and Caprinae. Cytogenet. Cell Genet. 2000, 89, 171–176. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Iannuzzi, L.; King, W.A.; Di Berardino, D. Chromosome Evolution in Domestic Bovids as Revealed by Chromosome Banding and FISH-Mapping Techniques. Cytogenet. Genome Res. 2009, 126, 49–62. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rubes, J.; Musilova, P.; Kopecna, O.; Kubickova, S.; Cernohorska, H.; Kulemsina, A.I. Comparative Molecular Cytogenetics in Cetartiodactyla. Cytogenet. Genome Res. 2012, 137, 194–207. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Proskuryakova, A.A.; Kulemzina, A.I.; Perelman, P.L.; Makunin, A.I.; Larkin, D.M.; Farré, M.; Kukekova, A.V.; Lynn Johnson, J.; Lemskaya, N.A.; Beklemisheva, V.R.; et al. X Chromosome Evolution in Cetartiodactyla. Genes 2017, 8, 216. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rubes, J.; Kubickova, S.; Pagacova, E.; Cernohorska, H.; Di Berardino, D.; Antoninova, M.; Vahala, J.; Robinson, T.J. Phylogenomic Study of Spiral-Horned Antelope by Cross-Species Chromosome Painting. Chromosome Res. 2008, 16, 935–947. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cernohorska, H.; Kubickova, S.; Vahala, J.; Rubes, J. Molecular Insights into X;BTA5 Chromosome Rearrangements in the Tribe Antilopini (Bovidae). Cytogenet. Genome Res. 2012, 136, 188–198. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cernohorska, H.; Kubickova, S.; Kopecna, O.; Vozdova, M.; Matthee, C.A.; Robinson, T.J.; Rubes, J. Nanger, Eudorcas, Gazella, and Antilope Form a Well-Supported Chromosomal Clade within Antilopini (Bovidae, Cetartiodactyla). Chromosoma 2015, 124, 235–247. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chaves, R.; Guedes-Pinto, H.; Heslop-Harrison, J.S. Phylogenetic Relationships and the Primitive X Chromosome Inferred from Chromosomal and Satellite DNA Analysis in Bovidae. Proc. Biol. Sci. 2005, 272, 2009–2016. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kopecna, O.; Kubickova, S.; Cernohorska, H.; Cabelova, K.; Vahala, J.; Rubes, J. Isolation and Comparison of Tribe-Specific Centromeric Repeats within Bovidae. J. Appl. Genet. 2012, 53, 193–202. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kopecna, O.; Kubickova, S.; Cernohorska, H.; Cabelova, K.; Vahala, J.; Martinkova, N.; Rubes, J. Tribe-specific satellite DNA in non-domestic Bovidae. Chromosome Res. 2014, 22, 277–291. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pauciullo, A.; Kubickova, S.; Cernohorska, H.; Petrova, K.; Di Berardino, D.; Ramunno, L.; Rubes, J. Isolation and Physical Localization of New Chromosome-Specific Centromeric Repeats in Farm Animals. Veterinární Medicína 2006, 51, 224–231. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cabelova, K.; Kubickova, S.; Cernohorska, H.; Rubes, J. Male-Specific Repeats in Wild Bovidae. J. Appl. Genet. 2012, 53, 423–433. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Traut, W.; Vogel, H.; Glöckner, G.; Hartmann, E.; Heckel, D.G. High-Throughput Sequencing of a Single Chromosome: A Moth W Chromosome. Chromosome Res. 2013, 21, 491–505. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rossetti, C.; Genualdo, V.; Incarnato, D.; Mottola, F.; Perucatti, A.; Pauciullo, A. State of the Art on the Physical Mapping of the Y-Chromosome in the Bovidae and Comparison with Other Species—A Review. Anim. Biosci. 2022, 35, 1289–1302. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cernohorska, H.; Kubickova, S.; Vahala, J.; Robinson, T.J.; Rubes, J. Cytotypes of Kirk’s Dik-Dik (Madoqua Kirkii, Bovidae) Show Multiple Tandem Fusions. Cytogenet. Genome Res. 2011, 132, 255–263. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Robinson, T.J.; Cernohorska, H.; Diedericks, G.; Cabelova, K.; Duran, A.; Matthee, C.A. Phylogeny and Vicariant Speciation of the Grey Rhebok, Pelea Capreolus. Heredity 2014, 112, 325–332. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gallagher, D.S., Jr.; Womack, J.E. Chromosome Conservation in the Bovidae. J. Hered. 1992, 83, 287–298. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Groves, C.; Grubb, P. Ungulate Taxonomy, 1st ed.; Johns Hopkins University Press: Baltimore, MD, USA, 2011; ISBN 978-1-4214-0093-8. [Google Scholar]
- Kubickova, S.; Cernohorska, H.; Musilova, P.; Rubes, J. The Use of Laser Microdissection for the Preparation of Chromosome-Specific Painting Probes in Farm Animals. Chromosome Res. 2002, 10, 571–577. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zimin, A.V.; Delcher, A.L.; Florea, L.; Kelley, D.R.; Schatz, M.C.; Puiu, D.; Hanrahan, F.; Pertea, G.; Van Tassell, C.P.; Sonstegard, T.S.; et al. A Whole-Genome Assembly of the Domestic Cow, Bos Taurus. Genome Biol. 2009, 10, R42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Spadafora, C. A Reverse Transcriptase-Dependent Mechanism Plays Central Roles in Fundamental Biological Processes. Syst. Biol. Reprod. Med. 2008, 54, 11–21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chow, J.C.; Ciaudo, C.; Fazzari, M.J.; Mise, N.; Servant, N.; Glass, J.L.; Attreed, M.; Avner, P.; Wutz, A.; Barillot, E.; et al. LINE-1 Activity in Facultative Heterochromatin Formation during X Chromosome Inactivation. Cell 2010, 141, 956–969. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Macia, A.; Muñoz-Lopez, M.; Cortes, J.L.; Hastings, R.K.; Morell, S.; Lucena-Aguilar, G.; Marchal, J.A.; Badge, R.M.; Garcia-Perez, J.L. Epigenetic Control of Retrotransposon Expression in Human Embryonic Stem Cells. Mol. Cell Biol. 2011, 31, 300–316. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Goldammer, T.; Brunner, R.M.; Rebl, A.; Wu, C.H.; Nomura, K.; Hadfield, T.; Maddox, J.F.; Cockett, N.E. Cytogenetic Anchoring of Radiation Hybrid and Virtual Maps of Sheep Chromosome X and Comparison of X Chromosomes in Sheep, Cattle, and Human. Chromosome Res. 2009, 17, 497–506. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Perucatti, A.; Genualdo, V.; Iannuzzi, A.; Rebl, A.; Di Berardino, D.; Goldammer, T.; Iannuzzi, L. Advanced Comparative Cytogenetic Analysis of X Chromosomes in River Buffalo, Cattle, Sheep, and Human. Chromosome Res. 2012, 20, 413–425. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, C.; Griffin, D.K.; O’Brien, P.C.; Yang, F.; Lin, C.C.; Ferguson-Smith, M.A. Defining the Anatomy of the Rangifer Tarandus Sex Chromosomes. Chromosoma 1998, 107, 61–69. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Frohlich, J.; Kubickova, S.; Musilova, P.; Cernohorska, H.; Muskova, H.; Vodicka, R.; Rubes, J. Karyotype Relationships among Selected Deer Species and Cattle Revealed by Bovine FISH Probes. PLoS ONE 2017, 12, e0187559. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, Y.-C.; Cheng, Y.-M.; Hsieh, L.-J.; Ryder, O.A.; Yang, F.; Liao, S.-J.; Hsiao, K.-M.; Tsai, F.-J.; Tsai, C.-H.; Lin, C.C. Karyotypic Evolution of a Novel Cervid Satellite DNA Family Isolated by Microdissection from the Indian Muntjac Y-Chromosome. Chromosoma 2005, 114, 28–38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Steflova, P.; Tokan, V.; Vogel, I.; Lexa, M.; Macas, J.; Novak, P.; Hobza, R.; Vyskot, B.; Kejnovsky, E. Contrasting Patterns of Transposable Element and Satellite Distribution on Sex Chromosomes (XY1Y2) in the Dioecious Plant Rumex Acetosa. Genome Biol. Evol. 2013, 5, 769–782. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fuková, I.; Traut, W.; Vítková, M.; Nguyen, P.; Kubícková, S.; Marec, F. Probing the W Chromosome of the Codling Moth, Cydia Pomonella, with Sequences from Microdissected Sex Chromatin. Chromosoma 2007, 116, 135–145. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dalíková, M.; Zrzavá, M.; Kubíčková, S.; Marec, F. W-Enriched Satellite Sequence in the Indian Meal Moth, Plodia Interpunctella (Lepidoptera, Pyralidae). Chromosome Res. 2017, 25, 241–252. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cioffi, M.B.; Molina, W.F.; Moreira-Filho, O.; Bertollo, L.A.C. Chromosomal Distribution of Repetitive DNA Sequences Highlights the Independent Differentiation of Multiple Sex Chromosomes in Two Closely Related Fish Species. Cytogenet. Genome Res. 2011, 134, 295–302. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Itoh, Y.; Kampf, K.; Arnold, A.P. Molecular Cloning of Zebra Finch W Chromosome Repetitive Sequences: Evolution of the Avian W Chromosome. Chromosoma 2008, 117, 111–121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vozdova, M.; Ruiz-Herrera, A.; Fernandez, J.; Cernohorska, H.; Frohlich, J.; Sebestova, H.; Kubickova, S.; Rubes, J. Meiotic Behaviour of Evolutionary Sex-Autosome Translocations in Bovidae. Chromosome Res. 2016, 24, 325–338. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Milioto, V.; Perelman, P.L.; Paglia, L.L.; Biltueva, L.; Roelke, M.; Dumas, F. Mapping Retrotransposon LINE-1 Sequences into Two Cebidae Species and Homo Sapiens Genomes and a Short Review on Primates. Genes 2022, 13, 1742. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bailey, J.A.; Carrel, L.; Chakravarti, A.; Eichler, E.E. Molecular Evidence for a Relationship between LINE-1 Elements and X Chromosome Inactivation: The Lyon Repeat Hypothesis. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2000, 97, 6634–6639. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Decker, J.E.; Pires, J.C.; Conant, G.C.; McKay, S.D.; Heaton, M.P.; Chen, K.; Cooper, A.; Vilkki, J.; Seabury, C.M.; Caetano, A.R.; et al. Resolving the Evolution of Extant and Extinct Ruminants with High-Throughput Phylogenomics. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2009, 106, 18644–18649. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hassanin, A.; Delsuc, F.; Ropiquet, A.; Hammer, C.; Jansen van Vuuren, B.; Matthee, C.; Ruiz-Garcia, M.; Catzeflis, F.; Areskoug, V.; Nguyen, T.T.; et al. Pattern and Timing of Diversification of Cetartiodactyla (Mammalia, Laurasiatheria), as Revealed by a Comprehensive Analysis of Mitochondrial Genomes. Comptes Rendus Biol. 2012, 335, 32–50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bogenberger, J.M.; Neitzel, H.; Fittler, F. A Highly Repetitive DNA Component Common to All Cervidae: Its Organization and Chromosomal Distribution during Evolution. Chromosoma 1987, 95, 154–161. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- O’Meally, D.; Patel, H.R.; Stiglec, R.; Sarre, S.D.; Georges, A.; Marshall Graves, J.A.; Ezaz, T. Non-Homologous Sex Chromosomes of Birds and Snakes Share Repetitive Sequences. Chromosome Res. 2010, 18, 787–800. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Spencer, T.E.; Palmarini, M. Endogenous Retroviruses of Sheep: A Model System for Understanding Physiological Adaptation to an Evolving Ruminant Genome. J. Reprod. Dev. 2012, 58, 33–37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Garcia-Etxebarria, K.; Jugo, B.M. Evolutionary History of Bovine Endogenous Retroviruses in the Bovidae Family. BMC Evol. Biol. 2013, 13, 256. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lowe, C.B.; Bejerano, G.; Haussler, D. Thousands of Human Mobile Element Fragments Undergo Strong Purifying Selection near Developmental Genes. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2007, 104, 8005–8010. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Plohl, M.; Luchetti, A.; Mestrović, N.; Mantovani, B. Satellite DNAs between Selfishness and Functionality: Structure, Genomics and Evolution of Tandem Repeats in Centromeric (Hetero) Chromatin. Gene 2008, 409, 72–82. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hassanin, A.; Douzery, E.J.P. Molecular and Morphological Phylogenies of Ruminantia and the Alternative Position of the Moschidae. Syst. Biol. 2003, 52, 206–228. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
| Class | Order | Suborder | Infraorder | Family | Species |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Mammalia | Carnivora | Ursidae | Ailuropoda melanoleuca | ||
| Perissodactyla | Rhinocerotidae | Ceratotherium simum simum | |||
| Artiodactyla | Tylopoda | Camelidae | Vicugna pacos | ||
| Suina | Suidae | Sus scrofa | |||
| Ruminantia | Pecora | Giraffidae | Giraffa camelopardalis | ||
| Antilocapridae | Antilocapra americana | ||||
| Cervidae | Cervus elaphus | ||||
| Bovidae | see Table 2 |
| Subfamily | Tribe | Species (Sex-Autosomal Fusion) | KDEXr Probe | BTAXr Probe | ACEXr Probe | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| X | Y | A | X | Y | A | X | Y | A | |||
| Antilopinae | Caprini | Ovis aries | + | 0 | 0 | + | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 |
| Capra hircus | + | 0 | 0 | + | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | |||
| Ammotragus lervia | + | 0 | 0 | + | 0 | 0 | |||||
| Ovibos moschatus | + | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | |||||
| Alcelaphini | Connochaetes taurinus | + | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | ||
| Connochaetes gnou | + | 0 | 0 | ||||||||
| Connochaetes albojubatus | + | 0 | 0 | ||||||||
| Damaliscus phillipsi | + | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | |||||
| Hippotragini | Oryx dammah | + | 0 | 0 | |||||||
| Oryx leucoryx | + | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | ||
| Oryx gazella | + | 0 | 0 | ||||||||
| Hippotragus equinus | + | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | |||||
| Hippotragus niger | + | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | ||
| Addax nasomaculatus | + | 0 | 0 | ||||||||
| Reduncini | Kobus defassa | + | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | |
| Kobus ellipsiprymnus | + | 0 | 0 | ||||||||
| Kobus leche | + | 0 | 0 | ||||||||
| Kobus megaceros | + | 0 | 0 | ||||||||
| Redunca fulvorufula | + | + | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | ||||
| Aepycerotini | Aepyceros melampus | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | |||
| Antilopini | Nanger dama (X;BTA5) (Y;BTA16) | + | + | + | 0 | + | + | ||||
| Antilope cervicapra (X;BTA5) | + | + | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | + | + | 0 | ||
| Antidorcas marsupialis | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | |||||
| Gazella leptoceros (X;BTA5) | + | 0 | + | + | 0 | ||||||
| Raphicerus sharpei | + | 0 | 0 | 0 | + | 0 | |||||
| Madoqua kirkii | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | |||
| Eudorcas thomsonii (X;BTA5) (Y;BTA16) | + | + | + | 0 | 0 | 0 | + | + | + | ||
| Oreotragini | Oreotragus oreotragus | + | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | ||||
| Bovinae | Bovini | Bos taurus | + | 0 | 0 | + | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 |
| Bubalus depressicornis | + | 0 | 0 | + | + | 0 | |||||
| Bubalus bubalis | + | 0 | 0 | + | 0 | 0 | 0 | ||||
| Bison bonasus | + | 0 | 0 | ||||||||
| Syncerus cafer | + | + | 0 | + | + | 0 | |||||
| Syncerus cafer nanus | + | 0 | 0 | + | + | 0 | 0 | 0 | |||
| Boselaphini | Boselaphus tragocamelus(X;BTA14) (Y;BTA14) | + | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | |
| Tragelaphini | Tragelaphus strepsiceros (Y;BTA13) | + | 0 | + | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | |
| Ammelaphus imberbis (X;BTA13) (Y;BTA13) | + | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | |||||
| Tragelaphus angasii (Y;BTA13) | + | 0 | + | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | ||
| Tragelaphus spekii (X;BTA13) (Y;BTA13) | + | 0 | 0 | ||||||||
| Tragelaphus eurycerus (Y;BTA13) | + | 0 | + | ||||||||
| Taurotragus oryx (Y;BTA13) | + | 0 | + | 0 | 0 | 0 | |||||
| Subfamily | Tribe | Species | FISH Results | ||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| KDEXr Probe | BTAXr Probe | ACEXr Probe | |||||||||
| X | Y | A | X | Y | A | X | Y | A | |||
| Cervidae | Cervini | C. elaphus | + | + | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 |
| Giraffidae | G. camelopardalis | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | ||||
| Antilocapridae | A. americana | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | ||||
| Family, Tribe, Species Analyzed | Sex | KDEXr | BTAXr | ACEXr | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Bovidae | Caprini | O. aries | ♂ | 166 | 12 | |
| O. moschatus | ♂ | 14 | ||||
| Alcelaphini | C. taurinus | ♀ | 18 | 6 | ||
| Hippotragini | H. equinus | ♂ | 4 | 2 | ||
| Reduncini | K. defassa | ♂ | 5052 | 10 | 8 | |
| Aepycerotini | A. melampus | ♂ | 2 | 4 | 2 | |
| Antilopini | N. dama | ♀ | 24 | 40 | ||
| N. dama | ♂ | 164 | 328 | |||
| A. cervicapra | ♀ | 172 | 2882 | |||
| A. marsupialis | ♂ | 16 | 6 | 12 | ||
| G. leptoceros | ♂ | 1846 | ||||
| M. kirkii | ♂ | 16 | 4 | 12 | ||
| Oreotragini | O. oreotragus | ♀ | 2 | 30 | ||
| Bovini | B. taurus | ♀ | 530 | 508 | 10 | |
| S. cafer | ♀ | 50 | ||||
| Boselaphini | B. tragocamelus | ♂ | 8 | 26 | ||
| Tragelaphini | A. imberbis | ♀ | 6 | 12 | ||
| Cervidae | Cervini | C. elaphus | ♂ | 700 | 6 | 2 |
| Giraffidae | G. camelopardalis | ♂ | 6 | |||
| Antilocapridae | A. americana | ♀ | 2 | 114 | 0 | |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Kubickova, S.; Kopecna, O.; Cernohorska, H.; Rubes, J.; Vozdova, M. X Chromosome-Specific Repeats in Non-Domestic Bovidae. Genes 2024, 15, 159. https://doi.org/10.3390/genes15020159
Kubickova S, Kopecna O, Cernohorska H, Rubes J, Vozdova M. X Chromosome-Specific Repeats in Non-Domestic Bovidae. Genes. 2024; 15(2):159. https://doi.org/10.3390/genes15020159
Chicago/Turabian StyleKubickova, Svatava, Olga Kopecna, Halina Cernohorska, Jiri Rubes, and Miluse Vozdova. 2024. "X Chromosome-Specific Repeats in Non-Domestic Bovidae" Genes 15, no. 2: 159. https://doi.org/10.3390/genes15020159
APA StyleKubickova, S., Kopecna, O., Cernohorska, H., Rubes, J., & Vozdova, M. (2024). X Chromosome-Specific Repeats in Non-Domestic Bovidae. Genes, 15(2), 159. https://doi.org/10.3390/genes15020159






