Olfactory Receptor OR2K2 Expression in Human Choroid Plexus as a Potential Marker in Early Sporadic Alzheimer’s Disease
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
3. Results
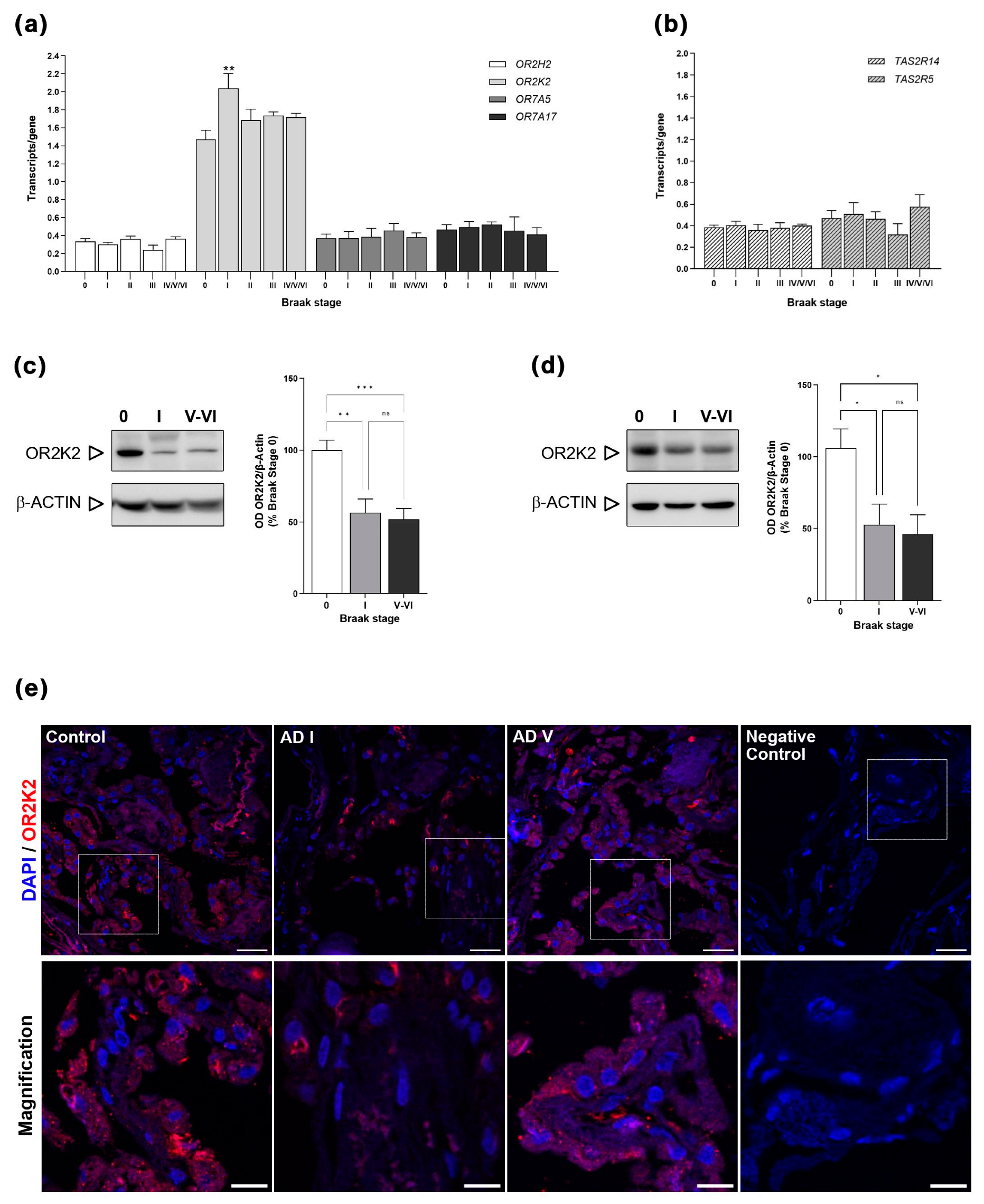
3.1. OR and TAS2R Gene Expression in CP of Control and AD
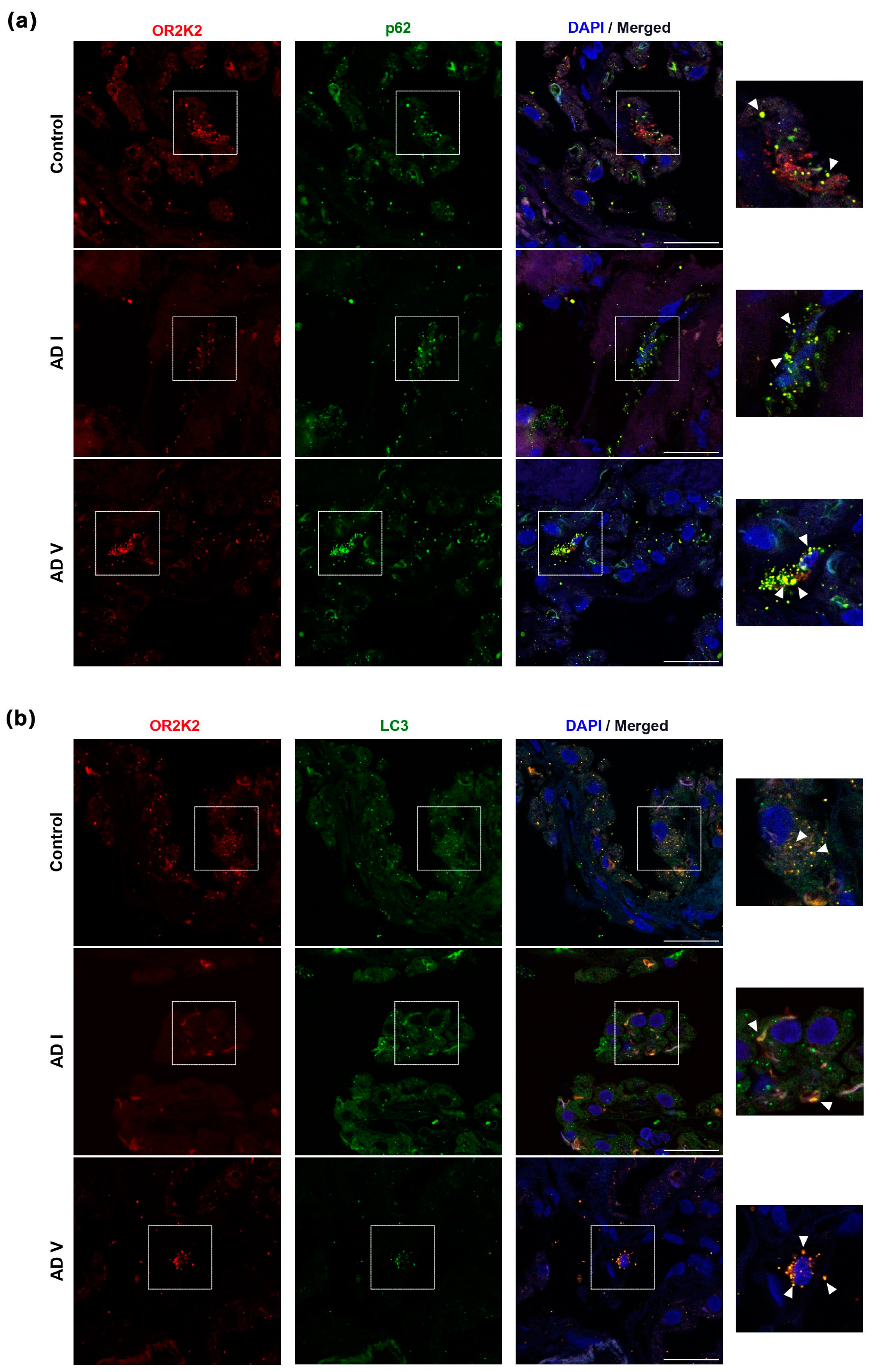
3.2. OR2K2 Protein Is Reduced in the Choroid Plexus at Early Stages of AD
4. Discussion
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Lun, M.P.; Monuki, E.S.; Lehtinen, M.K. Development and functions of the choroid plexus–cerebrospinal fluid system. Nat. Rev. Neurosci. 2015, 16, 445–457. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kaiser, K.; Bryja, V. Choroid Plexus: The Orchestrator of Long-Range Signalling Within the CNS. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2020, 21, 4760. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Santos, C.R.A.; Duarte, A.C.; Costa, A.R.; Tomás, J.; Quintela, T.; Gonçalves, I. The senses of the choroid plexus. Prog. Neurobiol. 2019, 182, 101680. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ferrer, I.; Garcia-Esparcia, P.; Carmona, M.; Carro, E.; Aronica, E.; Kovacs, G.G.; Grison, A.; Gustincich, S. Olfactory Receptors in Non-Chemosensory Organs: The Nervous System in Health and Disease. Front. Aging Neurosci. 2016, 8, 163. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Garcia-Esparcia, P.; Schlüter, A.; Carmona, M.; Moreno, J.; Ansoleaga, B.; Torrejón-Escribano, B.; Gustincich, S.; Pujol, A.; Ferrer, I. Functional Genomics Reveals Dysregulation of Cortical Olfactory Receptors in Parkinson Disease: Novel Putative Chemoreceptors in the Human Brain. J. Neuropathol. Exp. Neurol. 2013, 72, 524–539. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alves, V.C.; Figueiro-Silva, J.; Ferrer, I.; Carro, E. Epigenetic silencing of OR and TAS2R genes expression in human orbitofrontal cortex at early stages of sporadic Alzheimer’s disease. Cell. Mol. Life Sci. 2023, 80, 196. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ansoleaga, B.; Garcia-Esparcia, P.; Llorens, F.; Moreno, J.; Aso, E.; Ferrer, I. Dysregulation of brain olfactory and taste receptors in AD, PSP and CJD, and AD-related model. Neuroscience 2013, 248, 369–382. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nakashima, A.; Nakashima, N.; Nakashima, K.; Takano, M. Olfactory receptor 78 is expressed in hypothalamic vasopressin/oxytocin neurons, parenchymal microglia and choroidal macrophages in mice. Mol. Brain 2022, 15, 29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gonçalves, I.; Hubbard, P.C.; Tomás, J.; Quintela, T.; Tavares, G.; Caria, S.; Barreiros, D.; Santos, C.R. ‘Smelling’ the cerebrospinal fluid: Olfactory signaling molecules are expressed in and mediate chemosensory signaling from the choroid plexus. FEBS J. 2016, 283, 1748–1766. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- DeTure, M.A.; Dickson, D.W. The neuropathological diagnosis of Alzheimer’s disease. Mol. Neurodegener. 2019, 14, 32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Balusu, S.; Brkic, M.; Libert, C.; Vandenbroucke, R. The choroid plexus-cerebrospinal fluid interface in Alzheimer′s disease: More than just a barrier. Neural Regen. Res. 2016, 11, 534. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Čarna, M.; Onyango, I.G.; Katina, S.; Holub, D.; Novotny, J.S.; Nezvedova, M.; Jha, D.; Nedelska, Z.; Lacovich, V.; Vyvere, T.V.; et al. Pathogenesis of Alzheimer’s disease: Involvement of the choroid plexus. Alzheimer’s Dement. 2023, 19, 3537–3554. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gião, T.; Teixeira, T.; Almeida, M.R.; Cardoso, I. Choroid Plexus in Alzheimer’s Disease—The Current State of Knowledge. Biomedicines 2022, 10, 224. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Montine, T.J.; Phelps, C.H.; Beach, T.G.; Bigio, E.H.; Cairns, N.J.; Dickson, D.W.; Duyckaerts, C.; Frosch, M.P.; Masliah, E.; Mirra, S.S.; et al. National Institute on Aging–Alzheimer’s Association guidelines for the neuropathologic assessment of Alzheimer’s disease: A practical approach. Acta Neuropathol. 2012, 123, 1–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Podlesniy, P.; Trullas, R. Absolute measurement of gene transcripts with Selfie-digital PCR. Sci. Rep. 2017, 7, 8328. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bossers, K.; Wirz, K.T.; Meerhoff, G.F.; Essing, A.H.; van Dongen, J.W.; Houba, P.; Kruse, C.G.; Verhaagen, J.; Swaab, D.F. Concerted changes in transcripts in the prefrontal cortex precede neuropathology in Alzheimer’s disease. Brain 2010, 133, 3699–3723. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bustin, S.A.; Benes, V.; Garson, J.A.; Hellemans, J.; Huggett, J.; Kubista, M.; Mueller, R.; Nolan, T.; Pfaffl, M.W.; Shipley, G.L.; et al. The MIQE Guidelines: Minimum Information for Publication of Quantitative Real-Time PCR Experiments. Clin. Chem. 2009, 55, 611–622. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Park, P.S.-H.; Filipek, S.; Wells, J.W.; Palczewski, K. Oligomerization of G Protein-Coupled Receptors: Past, Present, and Future. Biochemistry 2004, 43, 15643–15656. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pfleger, K.D.G.; Eidne, K.A. Monitoring the formation of dynamic G-protein-coupled receptor–protein complexes in living cells. Biochem. J. 2005, 385, 625–637. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wade, F.; Espagne, A.; Persuy, M.-A.; Vidic, J.; Monnerie, R.; Merola, F.; Pajot-Augy, E.; Sanz, G. Relationship between Homo-oligomerization of a Mammalian Olfactory Receptor and Its Activation State Demonstrated by Bioluminescence Resonance Energy Transfer. J. Biol. Chem. 2011, 286, 15252–15259. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lu, M.; Echeverri, F.; Moyer, B.D. Endoplasmic Reticulum Retention, Degradation, and Aggregation of Olfactory G-Protein Coupled Receptors. Traffic 2003, 4, 416–433. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Janssen, S.F.; van der Spek, S.J.F.; Brink, J.B.T.; Essing, A.H.W.; Gorgels, T.G.M.F.; van der Spek, P.J.; Jansonius, N.M.; Bergen, A.A.B. Gene Expression and Functional Annotation of the Human and Mouse Choroid Plexus Epithelium. PLoS ONE 2013, 8, e83345. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bergen, A.A.; Kaing, S.; Brink, J.B.T.; Gorgels, T.G.; Janssen, S.F. Gene expression and functional annotation of human choroid plexus epithelium failure in Alzheimer’s disease. BMC Genom. 2015, 16, 956. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Stopa, E.G.; Tanis, K.Q.; Miller, M.C.; Nikonova, E.V.; Podtelezhnikov, A.A.; Finney, E.M.; Stone, D.J.; Camargo, L.M.; Parker, L.; Verma, A.; et al. Comparative transcriptomics of choroid plexus in Alzheimer’s disease, frontotemporal dementia and Huntington’s disease: Implications for CSF homeostasis. Fluids Barriers CNS 2018, 15, 18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, Z.; Yang, X.; Song, Y.-Q.; Tu, J. Autophagy in Alzheimer’s disease pathogenesis: Therapeutic potential and future perspectives. Ageing Res. Rev. 2021, 72, 101464. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bordi, M.; Berg, M.J.; Mohan, P.S.; Peterhoff, C.M.; Alldred, M.J.; Che, S.; Ginsberg, S.D.; Nixon, R.A. Autophagy flux in CA1 neurons of Alzheimer hippocampus: Increased induction overburdens failing lysosomes to propel neuritic dystrophy. Autophagy 2016, 12, 2467–2483. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chung, K.M.; Hernández, N.; Sproul, A.A.; Yu, W.H. Alzheimer’s disease and the autophagic-lysosomal system. Neurosci. Lett. 2019, 697, 49–58. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jaeger, P.A.; Pickford, F.; Sun, C.-H.; Lucin, K.M.; Masliah, E.; Wyss-Coray, T. Regulation of Amyloid Precursor Protein Processing by the Beclin 1 Complex. PLoS ONE 2010, 5, e11102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, W.H.; Cuervo, A.M.; Kumar, A.; Peterhoff, C.M.; Schmidt, S.D.; Lee, J.-H.; Mohan, P.S.; Mercken, M.; Farmery, M.R.; Tjernberg, L.O.; et al. Macroautophagy—A novel β-amyloid peptide-generating pathway activated in Alzheimer’s disease. J. Cell Biol. 2005, 171, 87–98. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sohn, H.-Y.; Kim, S.-I.; Park, J.-Y.; Park, S.-H.; Koh, Y.H.; Kim, J.; Jo, C. ApoE4 attenuates autophagy via FoxO3a repression in the brain. Sci. Rep. 2021, 11, 17604. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vaillant-Beuchot, L.; Mary, A.; Pardossi-Piquard, R.; Bourgeois, A.; Lauritzen, I.; Eysert, F.; Kinoshita, P.F.; Cazareth, J.; Badot, C.; Fragaki, K.; et al. Accumulation of amyloid precursor protein C-terminal fragments triggers mitochondrial structure, function, and mitophagy defects in Alzheimer’s disease models and human brains. Acta Neuropathol. 2021, 141, 39–65. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bartolome, F.; Krzyzanowska, A.; de la Cueva, M.; Pascual, C.; Antequera, D.; Spuch, C.; Villarejo-Galende, A.; Rabano, A.; Fortea, J.; Alcolea, D.; et al. Annexin A5 prevents amyloid-β-induced toxicity in choroid plexus: Implication for Alzheimer’s disease. Sci. Rep. 2020, 10, 9391. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cong, X.; Ren, W.; Pacalon, J.; Xu, R.; Xu, L.; Li, X.; de March, C.A.; Matsunami, H.; Yu, H.; Yu, Y.; et al. Large-Scale G Protein-Coupled Olfactory Receptor–Ligand Pairing. ACS Cent. Sci. 2022, 8, 379–387. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Maßberg, D.; Hatt, H. Human Olfactory Receptors: Novel Cellular Functions Outside of the Nose. Physiol. Rev. 2018, 98, 1739–1763. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Weidinger, D.; Jacobsen, J.; Jameel, K.J.; Alisch, D.; Uebner, H.; Kronsbein, J.; Peters, M.; Reuter, S.; Hatt, H.; Knobloch, J. Olfactory receptors affect inflammatory processes of lung epithelial cells. Pneumologie 2023, 77, S63. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, W.; Ho, L.; Varghese, M.; Yemul, S.; Dams-O’Connor, K.; Gordon, W.; Knable, L.; Freire, D.; Haroutunian, V.; Pasinetti, G.M. Decreased Level of Olfactory Receptors in Blood Cells Following Traumatic Brain Injury and Potential Association with Tauopathy. J. Alzheimer’s Dis. 2013, 34, 417–429. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
| Variable | Braak 0 | Braak I | Braak II | Braak III | Braak IV–VI | p-Value |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Number of samples | 11 | 7 | 7 | 3 | 9 | |
| Sex male/female, n | 6/5 | 4/3 | 3/4 | 3/0 | 4/5 | |
| Age at death, mean years (range) | 77.36 (70–85) | 75.86 (70–82) | 76.43 (72–80) | 80.00 (77–82) | 78.67 (73–83) | ns |
| PMI, mean hours ± SEM | 7.18 ± 0.81 | 8.91 ± 2.20 | 7.00 ± 1.23 | 8.56 ± 2.04 | 5.35 ± 0.64 | ns |
| APOE4 carriers, n (%) | 3 (27.3%) | 0 (0%) | 1 (7.1%) | 1 (25%) | 6 (75%) |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Alves, V.C.; Figueiro-Silva, J.; Trullas, R.; Ferrer, I.; Carro, E. Olfactory Receptor OR2K2 Expression in Human Choroid Plexus as a Potential Marker in Early Sporadic Alzheimer’s Disease. Genes 2024, 15, 385. https://doi.org/10.3390/genes15030385
Alves VC, Figueiro-Silva J, Trullas R, Ferrer I, Carro E. Olfactory Receptor OR2K2 Expression in Human Choroid Plexus as a Potential Marker in Early Sporadic Alzheimer’s Disease. Genes. 2024; 15(3):385. https://doi.org/10.3390/genes15030385
Chicago/Turabian StyleAlves, Victoria Cunha, Joana Figueiro-Silva, Ramon Trullas, Isidre Ferrer, and Eva Carro. 2024. "Olfactory Receptor OR2K2 Expression in Human Choroid Plexus as a Potential Marker in Early Sporadic Alzheimer’s Disease" Genes 15, no. 3: 385. https://doi.org/10.3390/genes15030385
APA StyleAlves, V. C., Figueiro-Silva, J., Trullas, R., Ferrer, I., & Carro, E. (2024). Olfactory Receptor OR2K2 Expression in Human Choroid Plexus as a Potential Marker in Early Sporadic Alzheimer’s Disease. Genes, 15(3), 385. https://doi.org/10.3390/genes15030385








