Abstract
The MAF gene encodes a transcription factor in which pathogenic variants have been associated with both isolated and syndromic congenital cataracts. We aim to review the MAF variants in the C-terminal DNA-binding domain associated with non-syndromic congenital cataracts and describe a patient with a novel, disease-causing de novo missense variant. Published reports of C-terminal MAF variants and their associated congenital cataracts and ophthalmic findings were reviewed. The patient we present and his biological parents had genetic testing via a targeted gene panel followed by trio-based whole exome sequencing. A 4-year-old patient with a history of bilateral nuclear and cortical cataracts was found to have a novel, likely pathogenic de novo variant in MAF, NM_005360.5:c.922A>G (p.Lys308Glu). No syndromic findings or anterior segment abnormalities were identified. We report the novel missense variant, c.922A>G (p.Lys308Glu), in the C-terminal DNA-binding domain of MAF classified as likely pathogenic and associated with non-syndromic bilateral congenital cataracts.
1. Introduction
Congenital cataract is a crystalline lens opacification noted within the first year of life and may be an isolated finding or a part of a syndrome. Its etiologies include genetic causes, prenatal infections, and intrauterine exposures [1]. The most commonly identified genetic causes include pathogenic variants in lens crystallins (45%), gap junction connexins (16%), and developmental transcription factors such as MAF (MIM #177075) and PITX3 (MIM #602669) (12%) [2]. Further, there is an interplay with environmental factors as evidenced by phenotypic variation among individuals with identical pathogenic variants [3].
We review cases of C-terminal domain variants in MAF that have been reported in the literature and summarize the association with non-syndromic congenital cataract. We also describe a 4-year-old patient with bilateral congenital cataracts identified at 6 weeks of age who was found to have a novel variant in the MAF gene [4].
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Patient Information and History
Our patient was referred to the Division of Ophthalmology at the Ann & Robert H. Lurie Children’s Hospital of Chicago at 6 weeks old for bilateral visually significant nuclear and cortical congenital cataracts. The pregnancy was complicated by gestational diabetes and maternal hypothyroidism, and delivery was performed at full term without complications. There was no family history of childhood eye disease or strabismus including no family member (including parents) with congenital cataracts. Family history is only significant for his mother who had glaucoma. Written informed consent for a prospective research protocol was obtained from the parents under an IRB-approved study (IRB 2021-4730), and the study abided the tenets of the Declaration of Helsinki and was conducted in accordance with the Health Insurance Portability and Accountability Act.
The patient underwent sequential lensectomy and anterior vitrectomy of the right eye at 7 and left eye at 8 weeks of age and was subsequently fitted with aphakic contact lenses. His right eye underwent two additional capsulectomy surgeries for capsular phimosis and developed glaucoma following cataract surgery controlled with topical anti-hypertensives at 9 months of age. At that time, axial length was 20.61 mm in the right eye (normal range) and 17.86 mm in the left eye (hyperopic). As a result, his right eye developed anisometropic amblyopia requiring part-time occlusion therapy, and he also became esotropic. He underwent bilateral medial rectus recessions at 4 years of age. At final follow-up at 5 years of age, the patient’s best corrected visual acuity was 20/125 in the right eye and 20/40 in the left eye. The patient remained otherwise healthy and met all developmental milestones. No other anterior segment abnormalities were noted on examination.
2.2. Genetic Testing
The proband underwent pediatric assessments and genetic testing beginning with a comprehensive early-onset cataract gene panel by next-generation sequencing. The laboratory utilized their proprietary bioinformatic analysis pipeline to filter and analyze the 153 targeted genes with NGS reads aligned to genome build GRCh37/hg19; they cited a greater than 99% coverage at a minimum depth of 50×, with copy number variant (CNV) resolution at a single exon for nearly all targeted exons. This testing, initially considered nondiagnostic, was followed by trio-based whole exome sequencing (WES) at a second commercial laboratory to assess for another molecular etiology. Their proprietary analysis pipeline was utilized with reads also aligned to genome build GRCh37/hg19, citing that 98.9% of targeted regions were covered at a minimum depth of 10×, an overall average depth of 143×, and CNV resolution at a level of approximately three or more exons. Finally, the trio WES dataset was re-analyzed by the Lurie Children’s Molecular Diagnostics Laboratory on a research basis, using the Illumina DRAGEN Bio-IT Platform 3.9 with alignment of the data to genome build GRCh38/hg38.
3. Results
3.1. Exome Sequencing
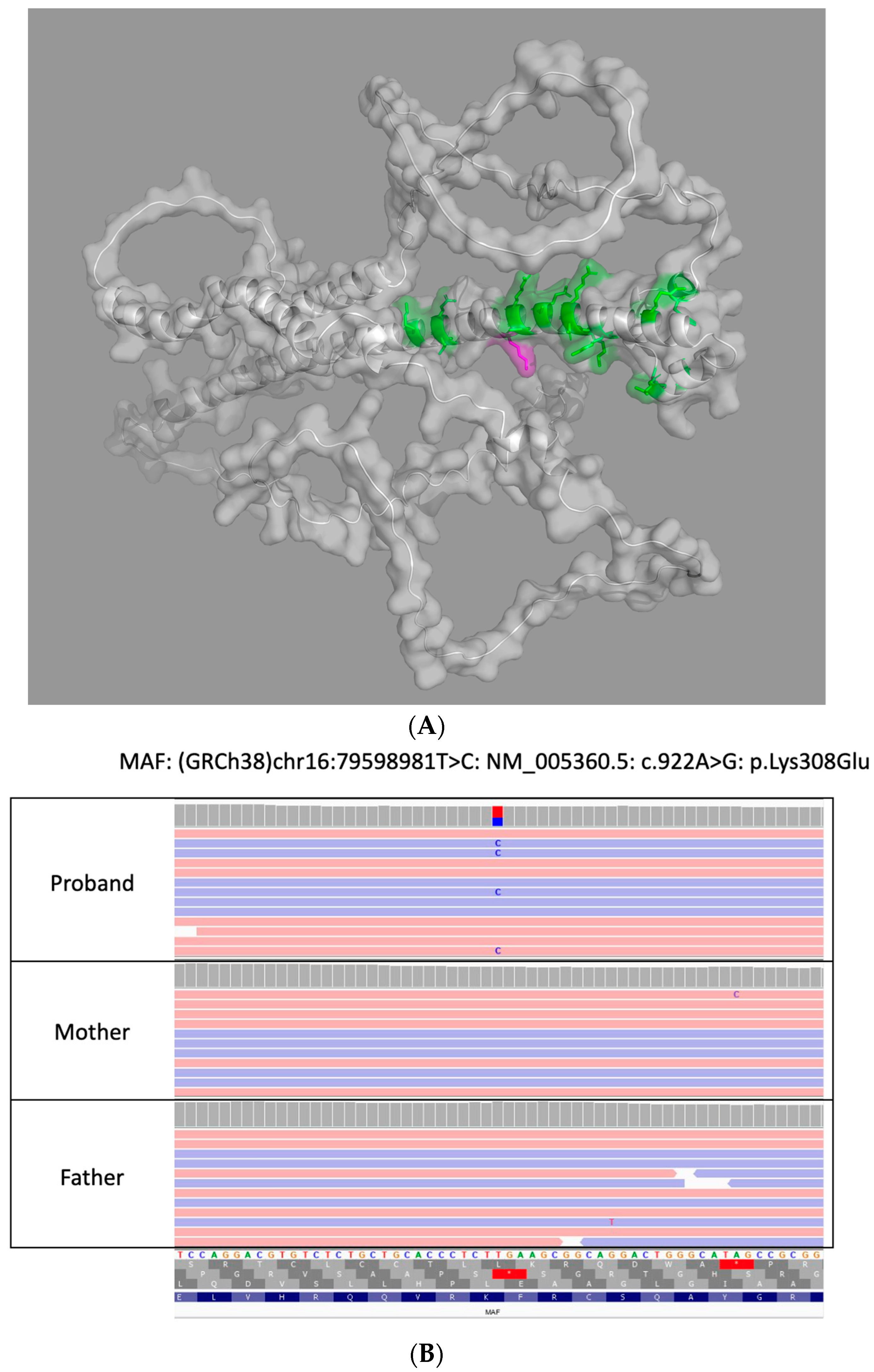
The initial commercial genetic testing via an early-onset cataract next-generation sequencing gene panel identified a heterozygous variant in MAF, NM_005360.5 c.922A>G (p.Lys308Glu), that was classified as a variant of uncertain significance (VUS). Subsequent testing by trio-based WES at a second CLIA-certified laboratory revealed that the aforementioned heterozygous MAF variant was not present in either parent and was thus de novo in our patient; the variant was classified and reported as likely pathogenic (LP). Though the variant did not undergo orthogonal confirmation by either laboratory due to satisfaction of their internal quality metrics, its identification by both laboratories utilizing different target enrichment/hybrid capture kits and bioinformation pipelines functions as the orthogonal confirmation of this variant’s presence in our patient. A 3D reconstruction of the protein with the variant is included in Figure 1A (AlphaFold, Google DeepMind) along with MAF genetic testing results in our patient and biologic parents in Integrative Genomics Viewer (IGV) in Figure 1B.
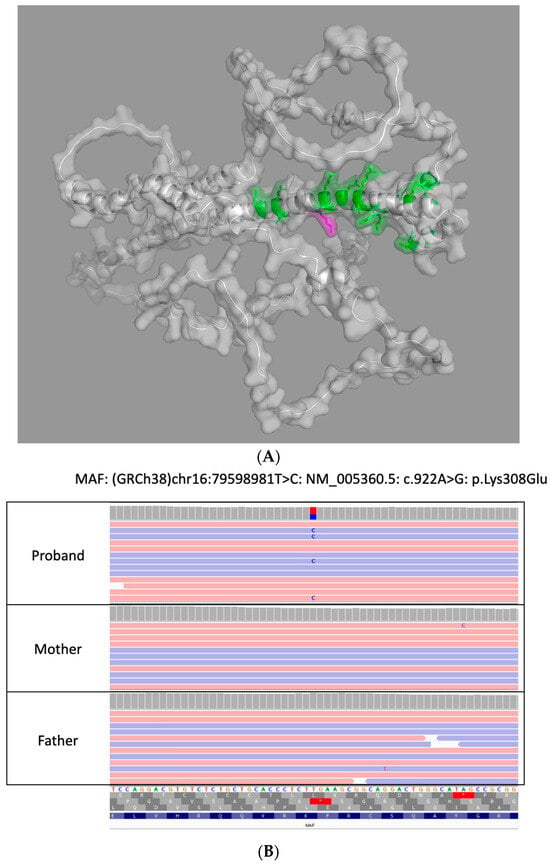
Figure 1.
(A) 3D Reconstruction of MAF protein in our patient. This is a 3D reconstruction of the altered MAF protein due to our variant (MAF, c.922A>G (p.Lys308Glu)) flanking the leucine-zipper region utilizing AlphaFold. (B) Genetic testing results of patient and biologic parents. Genetic testing results of patient and biologic parents in Integrative Genomics Viewer (IGV) that highlights the de novo variant in MAF identified in our patient with congenital cataracts.
Re-analysis of the trio WES data by the Lurie Children’s Molecular Diagnostics Laboratory did not reveal any additional potentially clinically relevant variants and supported the disease-causing nature of this variant. In addition to this finding being consistent with our patient’s phenotype including congenital cataracts, myopia, and secondary glaucoma, this previously unreported variant is absent from gnomAD [5], is strongly predicted in silico (REVEL score = 0.934) to be damaging to the encoded MAF transcription factor’s structure and/or function [6], and is located within a functionally important domain with little benign variation [7,8]. ACMG-AMP criteria applied are as follows: PS2, PM1, PM2, and PP3 [9].
3.2. Literature Review
A literature review of pathogenic and likely pathogenic variants in the C-terminal region of MAF was conducted by HGMD database extraction to evaluate for any genotype–phenotype associations (Table 1) [7,10,11,12,13,14,15,16,17,18,19,20,21,22,23]. Seventeen variants have been described in the literature associated with isolated, non-syndromic congenital cataracts (Table 1, Figure 2), similar to our patient. All variants were missense, as in our patient, and either inherited in an autosomal dominant fashion or de novo (similar to our patient) [7,8,10,11,12,13,14,15,16,17,18,19,20,21,22,23]. Additional ocular findings included microcornea, which was noted in association with one variant in the extended homology region, with four variants in the basic motif, and with one variant in the bZIP domain [7,11,14,16,18,23]. Iris coloboma was also noted in some cases with microcornea but was not present in isolation in any case [7,14,18]. Secondary glaucoma was noted in two patients as seen in our patient. Additionally, intra-familial variable expressivity of different anterior segment manifestations has been observed with pathogenic variants [7,14]. Table 2 is included as a brief summary of experiments using MAF mutations in cellular and animal models and their main findings that establish the relationship between the MAF domain and the congenital cataract phenotype.

Table 1.
Reported functional variants in the C-terminal of the MAF gene associated with non-syndromic congenital cataracts [7,10,11,12,13,14,15,16,17,18,19,20,21,22,23].
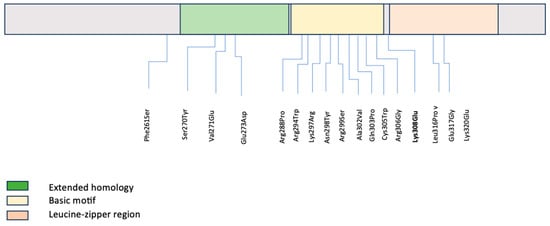
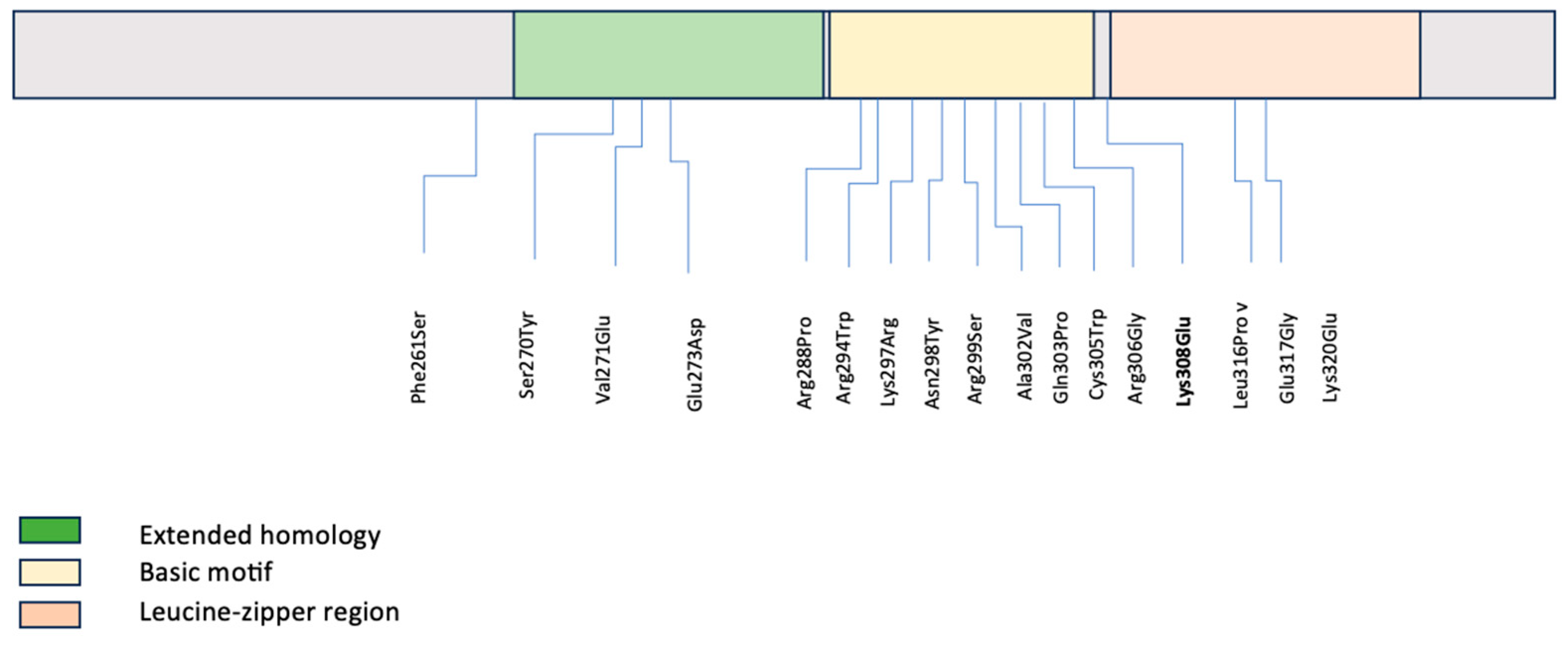
Figure 2.
Summary diagram of MAF functional domains in the C-terminal including both our novel variant and previously reported variants.

Table 2.
A brief summary of reports of animal and cellular models that demonstrate the relationship between the MAF domain and the congenital cataract phenotype [12,14,24,25,26,27,28].
This figure demonstrates that MAF variants described in the literature along the C-terminal domain are located in different domains. The variant identified in our patient is flanking the leucine-zipper region.
4. Discussion
MAF, v-maf musculoaponeurotic fibrosarcoma oncogene homolog, encodes a transcription factor that uses the basic region domain to bind target genes before dimerizing using the leucine zipper domain [29]. Its interactions are stabilized by the extended homology region and result in a conformational change [30]. MAF is expressed in the lens placode, vesicle, and fiber proteins and is key to ocular development by regulating lens fiber cell development and chondrocyte terminal differentiation and by increasing the apoptosis susceptibility of T-cells [14,31].
Known pathogenic variants in MAF are linked to congenital cataracts and anterior segment abnormalities, including microcornea and iris coloboma. The MAF protein has two functional domains, with the associated phenotypes dependent on the domain in which the variant is located; Aymé-Gripp syndrome is associated with N-terminal transactivation domain variants, while non-syndromic ocular abnormalities are associated with variants in the C-terminal DNA-binding domain [7,8,12,18,32,33,34]. Aymé-Gripp syndrome is characterized by sensorineural hearing loss, seizures, distinct craniofacial features, short stature, and developmental delay in addition to congenital cataracts [33,34]. In contrast, MAF pathogenic variants in the C-terminal domain are associated with a non-syndromic ocular phenotype of childhood cataracts and iris coloboma and/or microcornea [7,10,11,12,13,14,15,16,17,18,19,20,21,22,23].
The basic region of the C-terminal is the most frequently impacted region among the known MAF variants [7,10,11,12,13,14,15,16,17,18,19,20,21,22,23]. The putative mechanism causing congenital cataracts is the impaired activation of β-crystallin genes and the many non-crystallin genes involved in lens development [35]. Our patient’s variant is in the basic leucine zipper (bZIP) domain within the C-terminal, near other variants associated with congenital cataracts with and without anterior segment abnormalities (UniProt) [36]. While our patient did not have microcornea or coloboma, he did have secondary glaucoma, which has been previously reported in association with two other C-terminal variants, c.809C>A (p.Ser270Tyr) and c.915C>T p.(Cys305Trp) [11,13].
Identification of this previously unreported MAF variant, c.922A>G (p.Lys308Glu), supports the body of evidence that the C-terminal domain is necessary for appropriate lens development as abnormalities have a causative association with non-syndromic, congenital, and juvenile-onset cataracts with and without anterior segment abnormalities. Importantly, it expands the library of MAF variants affecting the C-terminal with variable ocular manifestations. The identification and detailed phenotyping of additional individuals and families with MAF C-terminal domain variant will help facilitate the further assessment of genotype–phenotype correlations for this gene–disease relationship.
5. Conclusions
The phenotypic variation seen in MAF variants leading to congenital cataracts emphasizes the need for further study of the protein’s role in development and how variants in the C-terminal domain of the gene result in ophthalmologic abnormalities. This understanding could help identify future targeted treatments in individuals with pathogenic MAF variants.
In conclusion, our case and review of the pre-existing literature reinforces the association between missense variation in the C-terminal DNA-binding domain of MAF and non-syndromic ocular abnormalities, specifically bilateral congenital cataracts. This report serves to foster improved interpretation and classification for MAF variants and to strengthen the association between C-terminal MAF missense variants and isolated congenital cataracts with additional ocular features.
Author Contributions
Conceptualization, J.L.R. and S.H.Z.; methodology, J.L.R. and S.H.Z.; investigation, S.H.Z. and J.L.R.; resources, A.D., A.I., P.M., V.A., A.G. and S.P.K.; writing—original draft preparation, S.H.Z. and J.L.R.; writing—review and editing, A.D., A.I., A.S., B.L.B., H.R.R., J.L.R., K.L.Y., S.P.K. and S.H.Z.; visualization, S.H.Z.; supervision, J.L.R. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This research received no external funding.
Institutional Review Board Statement
The study was conducted in accordance with the Declaration of Helsinki. The study was approved by Ann & Robert H. Lurie Children’s Hospital of Chicago Institutional Review Board (IRB# 2021-4730).
Informed Consent Statement
Informed consent was obtained from all subjects involved in the study.
Data Availability Statement
The results of the genetic testing were included in the manuscript of this paper.
Acknowledgments
We thank the patient and family members for their contribution.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
References
- Shiels, A.; Hejtmancik, J.F. Mutations and mechanisms in congenital and age-related cataracts. Exp. Eye Res. 2017, 156, 95–102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Shiels, A.; Bennett, T.M.; Hejtmancik, J.F. Cat-Map: Putting cataract on the map. Mol. Vis. 2010, 16, 2007–2015. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Rossen, J.L.; Bohnsack, B.L.; Zhang, K.X.; Ing, A.; Drackley, A.; Castelluccio, V.; Ralay-Ranaivo, H. Evaluation of Genetic Testing in a Cohort of Diverse Pediatric Patients in the United States with Congenital Cataracts. Genes 2023, 14, 608. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Franklin by Genoox: The Future of Genomic Medicine. 2023. Available online: https://franklin.genoox.com (accessed on 1 July 2023).
- Lek, M.; Karczewski, K.J.; Minikel, E.V.; Samocha, K.E.; Banks, E.; Fennell, T.; O’Donnell-Luria, A.H.; Ware, J.S.; Hill, A.J.; Cummings, B.B.; et al. Analysis of protein-coding genetic variation in 60,706 humans. Nature 2016, 536, 285–291. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ioannidis, N.M.; Rothstein, J.H.; Pejaver, V.; Middha, S.; McDonnell, S.K.; Baheti, S.; Musolf, A.; Li, Q.; Holzinger, E.; Karyadi, D.; et al. REVEL: An Ensemble Method for Predicting the Pathogenicity of Rare Missense Variants. Am. J. Hum. Genet. 2016, 99, 877–885. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Narumi, Y.; Nishina, S.; Tokimitsu, M.; Aoki, Y.; Kosaki, R.; Wakui, K.; Azuma, N.; Murata, T.; Takada, F.; Fukushima, Y.; et al. Identification of a novel missense mutation of MAF in a Japanese family with congenital cataract by whole exome sequencing: A clinical report and review of literature. Am. J. Med. Genet. A 2014, 164A, 1272–1276. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jamieson, R.V.; Munier, F.; Balmer, A.; Farrar, N.; Perveen, R.; Black, G.C. Pulverulent cataract with variably associated microcornea and iris coloboma in a MAF mutation family. Br. J. Ophthalmol. 2003, 87, 411–412. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Richards, S.; Aziz, N.; Bale, S.; Bick, D.; Das, S.; Gastier-Foster, J.; Grody, W.W.; Hegde, M.; Lyon, E.; Spector, E.; et al. Standards and guidelines for the interpretation of sequence variants: A joint consensus recommendation of the American College of Medical Genetics and Genomics and the Association for Molecular Pathology. Genet. Med. 2015, 17, 405–424. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jackson, D.; Malka, S.; Harding, P.; Palma, J.; Dunbar, H.; Moosajee, M. Molecular diagnostic challenges for non-retinal developmental eye disorders in the United Kingdom. Am. J. Med. Genet. C Semin Med. Genet. 2020, 184, 578–589. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Dudakova, L.; Stranecky, V.; Ulmanova, O.; Hlavova, E.; Trková, M.; Vincent, A.L.; Liskova, P. Segregation of a novel p.(Ser270Tyr) MAF mutation and p.(Tyr56∗) CRYGD variant in a family with dominantly inherited congenital cataracts. Mol. Biol. Rep. 2017, 44, 435–440, Erratum in Mol. Biol. Rep. 2017, 44, 441. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Si, N.; Song, Z.; Meng, X.; Li, X.; Xiao, W.; Zhang, X. A novel MAF missense mutation leads to congenital nuclear cataract by impacting the transactivation of crystallin and noncrystallin genes. Gene 2019, 692, 113–118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ma, A.S.; Grigg, J.R.; Ho, G.; Prokudin, I.; Farnsworth, E.; Holman, K.; Cheng, A.; Billson, F.A.; Martin, F.; Fraser, C.; et al. Sporadic and Familial Congenital Cataracts: Mutational Spectrum and New Diagnoses Using Next-Generation Sequencing. Hum. Mutat. 2016, 37, 371–384. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Jamieson, R.V.; Perveen, R.; Kerr, B.; Carette, M.; Yardley, J.; Heon, E.; Wirth, M.G.; van Heyningen, V.; Donnai, D.; Munier, F.; et al. Domain disruption and mutation of the bZIP transcription factor, MAF, associated with cataract, ocular anterior segment dysgenesis and coloboma. Hum. Mol. Genet. 2002, 11, 33–42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sun, W.; Xiao, X.; Li, S.; Guo, X.; Zhang, Q. Exome Sequencing of 18 Chinese Families with Congenital Cataracts: A New Sight of the NHS Gene. PLoS ONE 2014, 9, e100455. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vanita, V.; Singh, D.; Robinson, P.N.; Sperling, K.; Singh, J.R. A novel mutation in the DNA-binding domain of MAF at 16q23.1 associated with autosomal dominant “cerulean cataract” in an Indian family. Am. J. Med. Genet. A 2006, 140, 558–566. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Patel, A.; Hayward, J.D.; Tailor, V.; Nyanhete, R.; Ahlfors, H.; Gabriel, C.; Jannini, T.B.; Abbou-Rayyah, Y.; Henderson, R.; Nischal, K.K.; et al. The Oculome Panel Test: Next-Generation Sequencing to Diagnose a Diverse Range of Genetic Developmental Eye Disorders. Ophthalmology 2019, 126, 888–907. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hansen, L.; Eiberg, H.; Rosenberg, T. Novel MAF mutation in a family with congenital cataract-microcornea syndrome. Mol. Vis. 2007, 13, 2019–2022. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Rechsteiner, D.; Issler, L.; Koller, S.; Lang, E.; Bähr, L.; Feil, S.; Rüegger, C.M.; Kottke, R.; Toelle, S.P.; Zweifel, N.; et al. Genetic Analysis in a Swiss Cohort of Bilateral Congenital Cataract. JAMA Ophthalmol. 2021, 139, 691–700. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Ma, A.; Grigg, J.R.; Flaherty, M.; Smith, J.; Minoche, A.E.; Cowley, M.J.; Nash, B.M.; Ho, G.; Gayagay, T.; Lai, T.; et al. Genome sequencing in congenital cataracts improves diagnostic yield. Hum. Mutat. 2021, 42, 1173–1183. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, Q.; Qin, T.; Tan, H.; Ding, X.; Lin, X.; Li, J.; Lin, Z.; Sun, L.; Lin, H.; Chen, W. Broadening the genotypic and phenotypic spectrum of MAF in three Chinese Han congenital cataracts families. Am. J. Med. Genet. A 2022, 188, 2888–2898. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, J.; Leng, Y.; Han, S.; Yan, L.; Lu, C.; Luo, Y.; Zhang, X.; Cao, L. Clinical and genetic characteristics of Chinese patients with familial or sporadic pediatric cataract. Orphanet. J. Rare Dis. 2018, 13, 94. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hansen, L.; Mikkelsen, A.; Nürnberg, P.; Nürnberg, G.; Anjum, I.; Eiberg, H.; Rosenberg, T. Comprehensive Mutational Screening in a Cohort of Danish Families with Hereditary Congenital Cataract. Investig. Ophthalmol. Vis. Sci. 2009, 50, 3291–3303. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kawauchi, S.; Takahashi, S.; Nakajima, O.; Ogino, H.; Morita, M.; Nishizawa, M.; Yasuda, K.; Yamamoto, M. Regulation of lens fiber cell differentiation by transcription factor c-Maf. J. Biol. Chem. 1999, 274, 19254–19260. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sakai, M.; Serria, M.S.; Ikeda, H.; Yoshida, K.; Imaki, J.; Nishi, S. Regulation of c-Maf gene expression by Pax6 in cultured cells. Nucleic Acids Res. 2001, 29, 1228–1237. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Chen, Q.; Dowhan, D.H.; Liang, D.; Moore, D.D.; Overbeek, P.A. CREB-binding protein/p300 co-activation of crystallin gene expression. J. Biol. Chem. 2002, 277, 24081–24089. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lyon, M.F.; Jamieson, R.V.; Perveen, R.; Glenister, P.H.; Griffiths, R.; Boyd, Y.; Glimcher, L.H.; Favor, J.; Munier, F.L.; Black, G.C.M. A dominant mutation within the DNA-binding domain of the bZIP transcription factor Maf causes murine cataract and results in selective alteration in DNA binding. Hum. Mol. Genet. 2003, 12, 585–594. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Perveen, R.; Favor, J.; Jamieson, R.V.; Ray, D.W.; Black, G.C. A heterozygous c-Maf transactivation domain mutation causes congenital cataract and enhances target gene activation. Hum. Mol. Genet. 2007, 16, 1030–1038. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pellegrino, S.; Ronda, L.; Annoni, C.; Contini, A.; Erba, E.; Gelmi, M.L.; Piano, R.; Paredi, G.; Mozzarelli, A.; Bettati, S. Molecular insights into dimerization inhibition of c-Maf transcription factor. Biochim. Biophys. Acta 2014, 1844, 2108–2115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lu, X.; Guanga, G.; Wan, C.; Rose, R. A Novel DNA Binding Mechanism for Maf Basic Region-Leucine Zipper Factors Inferred from a MafA–DNA Complex Structure and Binding Specificities. Biochemistry 2012, 51, 9706–9717. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yi, J.; Yun, J.; Li, Z.K.; Xu, C.T.; Pan, B.R. Epidemiology and molecular genetics of congenital cataracts. Int. J. Ophthalmol. 2011, 4, 422–432. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Javadiyan, S.; Craig, J.E.; Sharma, S.; Lower, K.M.; Casey, T.; Haan, E.; Souzeau, E.; Burdon, K.P. Novel missense mutation in the bZIP transcription factor, MAF, associated with congenital cataract, developmental delay, seizures and hearing loss (Aymé-Gripp syndrome). BMC Med. Genet. 2017, 18, 52. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Aymé, S.; Philip, N. Fine-Lubinsky syndrome: A fourth patient with brachycephaly, deafness, cataract, microstomia and mental retardation. Clin. Dysmorphol. 1996, 5, 55–60. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gripp, K.W.; Nicholson, L.; Scott, C.I., Jr. Apparently new syndrome of congenital cataracts, sensorineural deafness, Down syndrome-like facial appearance, short stature, and mental retardation. Am. J. Med. Genet. 1996, 61, 382–386. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ring, B.Z.; Cordes, S.P.; Overbeek, P.A.; Barsh, G.S. Regulation of mouse lens fiber cell development and differentiation by the Maf gene. Development 2000, 127, 307–317. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- The UniProt Consortium. UniProt: The Universal Protein Knowledgebase in 2023. Nucleic Acids Res. 2023, 51, D523–D531. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).