Genetic Analysis of the Plasmid-Based Temperature-Lethal Mutant pa1792|lpxH(Ts) in Pseudomonas aeruginosa
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. DNA, Plasmids, and Bacterial Cultures
2.2. Plasmid Construction
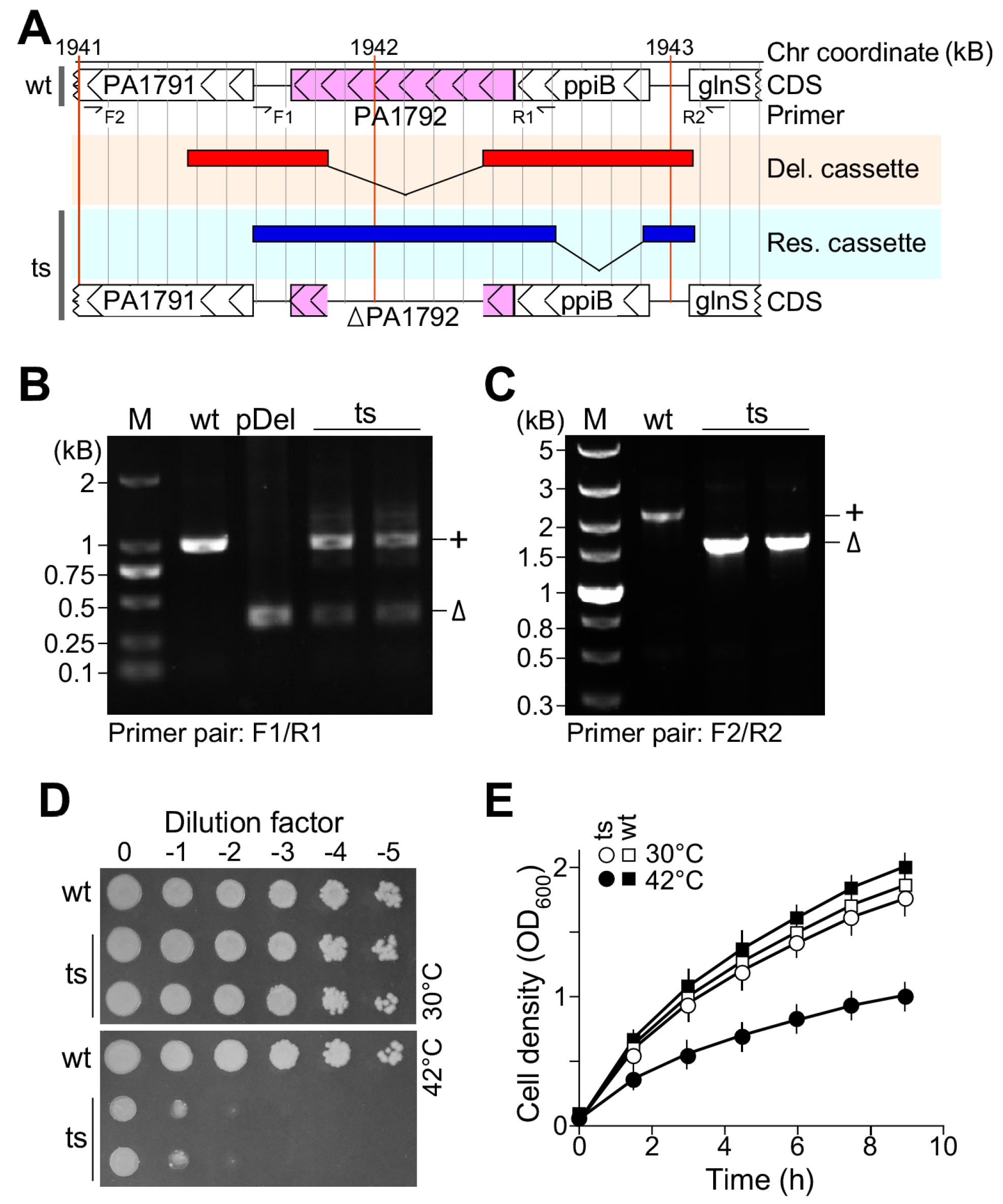
2.3. Plasmid-Based ts-Mutant Strain Construction
2.4. Spot-Plating Assay
2.5. Fluorescence Microscopic Analysis
2.6. LPS Preparation
2.7. SDS-PAGE and Silver Staining
2.8. Western Blotting Analysis
2.9. Spontaneous Mutagenesis Screening
3. Results
3.1. Plasmid-Based Temperature-Sensitive Mutant lpxH(Ts) Is Lethal at the Restrictive Temperature in P. aeruginosa
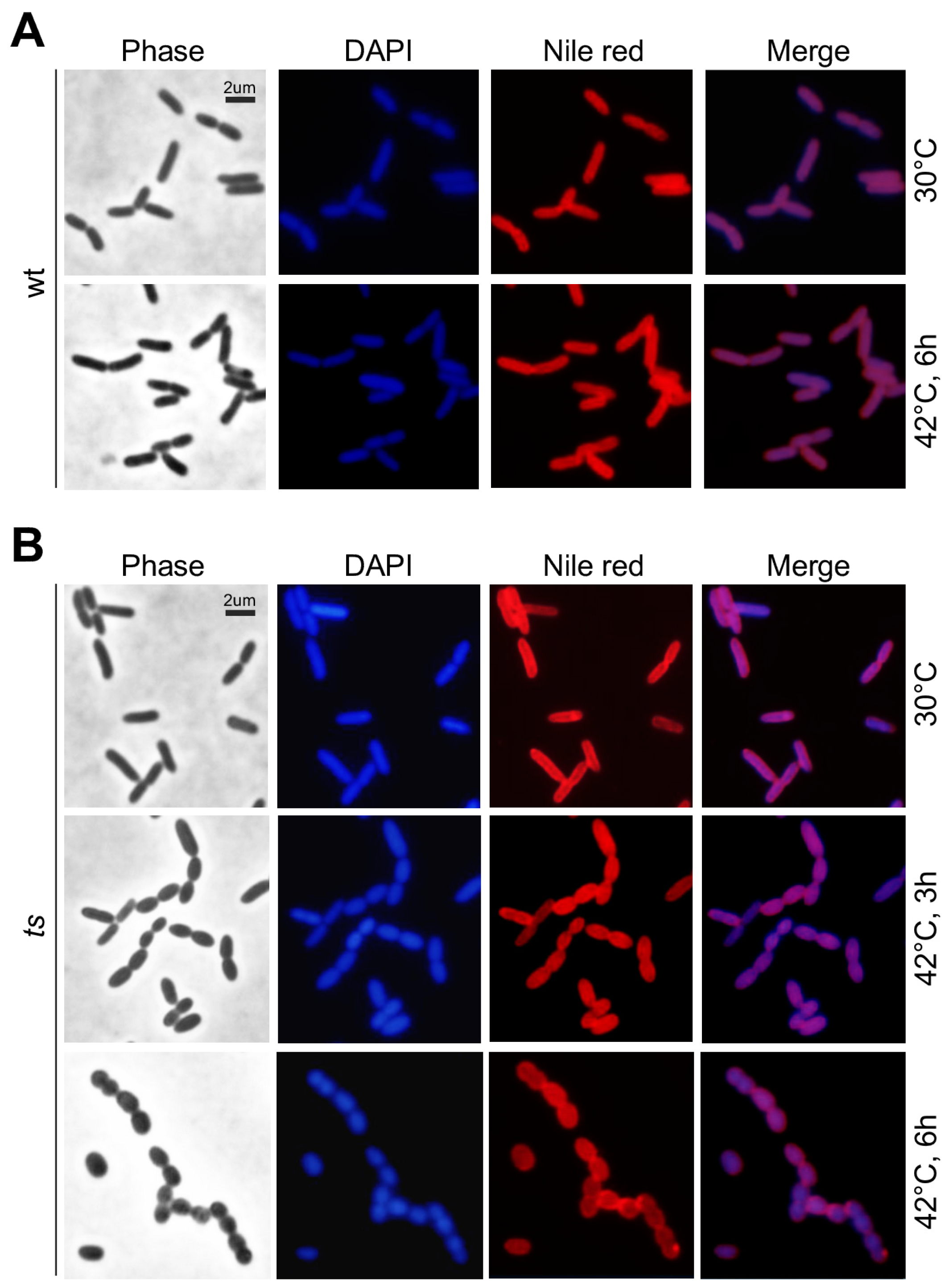
3.2. lpxH(Ts) Exhibits an Oval-Shaped Morphology at the Restrictive Temperature
3.3. Growth Defect of lpxH(Ts) at the Restrictive Temperature Is Rescued by the araC-PBAD Promoter-Controlled E. coli lpxH or ec.lpxH at the Leaky Expression Level
3.4. Lipid A Is Missing in lpxH(Ts) at the Restrictive Temperature in P. aeruginosa
3.5. Expression of the Non-Homolog UDP-2,3-Diacylglucosamine Hydrolyses Cc.LpxI and Ct.LpxG Compensate for the Loss of LpxH in P. aeruginosa
3.6. Lethality of lpxH(Ts) at the Restrictive Temperature Is Suppressed by a Sup Mutant Identified from Spontaneous Mutagenesis
4. Discussion
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Bassetti, M.; Vena, A.; Croxatto, A.; Righi, E.; Guery, B. How to manage Pseudomonas aeruginosa infections. Drugs Context 2018, 7, 212527. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- WHO. WHO Bacterial Priority Pathogens List, 2024: Bacterial Pathogens of Public Health Importance to Guide Research, Development and Strategies to Prevent and Control Antimicrobial Resistance; World Health Organization: Geneva, Switzerland, 2024; Available online: https://iris.who.int/bitstream/handle/10665/376776/9789240093461-eng.pdf?sequence=1 (accessed on 22 May 2024).
- Raetz, C.R.; Reynolds, C.M.; Trent, M.S.; Bishop, R.E. Lipid A modification systems in gram-negative bacteria. Annu. Rev. Biochem. 2007, 76, 295–329. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Whitfield, C.; Valvano, M.A. Biosynthesis and expression of cell-surface polysaccharides in gram-negative bacteria. Adv. Microb. Physiol. 1993, 35, 135–246. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lam, J.S.; Taylor, V.L.; Islam, S.T.; Hao, Y.; Kocíncová, D. Genetic and functional diversity of Pseudomonas aeruginosa lipopolysaccharide. Front. Microbiol. 2011, 2, 118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Simpson, B.W.; Trent, M.S. Pushing the envelop: LPS modifications and their consequences. Nat. Rev. Microbiol. 2019, 17, 403–416. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dowhan, W. The Raetz Pathway for Lipid A Biosynthesis: Christian Rudolf Hubert Raetz, MD PhD, 1946–2011. J. Lipid. Res. 2011, 52, 1857–1860. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Klein, G.; Brabetz, W.; Brade, H.; Raina, S. Escherichia coli K-12 Suppressor-free Mutants Lacking Early Glycosyltransferases and Late Acyltransferases. J. Biol. Chem. 2009, 284, 15369–15389. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jenkins, R.J.; Dotson, G.D. Dual targeting antibacterial peptide inhibitor of early lipid A biosynthesis. ACS Chem. Biol. 2012, 7, 1170–1177. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jenkins, R.J.; Heslip, K.A.; Meagher, J.L.; Stuckey, J.A.; Dotson, G.D. Structural basis for the recognition of peptide RJPXD33 by acyltransferases in lipid A biosynthesis. J. Biol. Chem. 2014, 289, 15527–15535. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Metzger, L.E.; Raetz, C.R. An Alternative Route for UDP-Diacylglucosamine Hydrolysis in Bacterial Lipid A Biosynthesis. Biochem. 2010, 49, 715–726. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Young, H.E.; Zhao, J.; Barker, J.R.; Guan, Z.; Valdivia, R.H.; Zhou, P. Discovery of the elusive UDP-diacylglucosamine hydrolase in the lipid A biosynthetic pathway in Chlamydia trachomatis. mBio 2016, 7, e00090-16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tian, L.; Yang, Z.; Wang, J.; Liu, J. Analysis of the plasmid-based ts-mutant ΔfabA/pTS-fabA reveals its lethality under aerobic growth conditions that is suppressed by mild overexpression of desA at a restrictive temperature in Pseudomonas aeruginosa. Microbiol. Spectr. 2023, 11, e0133823. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, Z.; Zhang, Z.; Zhu, J.; Ma, Y.; Wang, J.; Liu, J. Analysis of the plasmid-based ts-allele of PA0006 reveals its function in regulation of cell morphology and biosynthesis of core LPS in Pseudomonas aeruginosa. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 2022, 88, e0048022. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kovach, M.E.; Elzer, P.H.; Hill, D.S.; Robertson, G.T.; Farris, M.A.; Roop, R.M.; Peterson, K.M. Four new derivatives of the broad-host-range cloning vector pBBR1MCS, carrying different antibiotic-resistance cassettes. Gene 1995, 166, 175–176. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hung, C.-W.; Martínez-Márquez, J.Y.; Fatima, T.; Javed, F.T.; Duncan, M.C. A simple and inexpensive quantitative technique for determining chemical sensitivity in Saccharomyces cerevisiae. Sci. Rep. 2018, 8, 11919. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hitchcock, P.J.; Brown, T.M. Morphological heterogeneity among Salmonella lipopolysaccharide chemotypes in silver-stained polyacrylamide gels. J. Bacteriol. 1983, 154, 269–277. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fomsgaard, A.; Freudenberg, M.A.; Galanos, C. Modification of the silver staining technique to detect lipopolysaccharide in polyacrylamide gels. J. Clin. Microbiol. 1990, 28, 2627–2631. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, X.; Wang, Y.; Guo, J.; Yu, Y.; Li, J.; Guo, Y.; Liu, C. Comparing two functions for optical density and cell numbers in bacterial exponential growth phase. J. Pure Appl. Microbiol. 2015, 9, 299–305. [Google Scholar]
- van Leeuwen, J.; Pons, C.; Boone, C.; Brenda, J.A. Mechanisms of suppression: The wiring of genetic resilience. BioEssays 2017, 39, 1700042. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, S.A.; Gallagher, L.A.; Thongdee, M.; Staudinger, B.J.; Lippman, S.; Singh, P.K.; Manoil, C. General and condition-specific essential functions of Pseudomonas aeruginosa. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2015, 112, 5189–5194. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Babinski, K.J.; Ribeiro, A.A.; Raetz, C.R. The Escherichia coli gene encoding the UDP-2,3-diacylglucosamine pyrophosphatase of lipid A biosynthesis. J. Biol. Chem. 2002, 277, 25937–25946. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- King, J.D.; Kocíncová, D.; Westman, E.L.; Lam, J.S. Lipopolysaccharide biosynthesis in Pseudomonas aeruginosa. Innate. Immun. 2009, 15, 261–312. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Guzman, L.-M.; Belin, D.; Carson, M.J.; Beckwith, J. Tight Regulation, Modulation, and High-Level Expression by Vectors Containing the Arabinose PBAD Promoter. J. Bacteriol. 1995, 177, 4121–4130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chandler, C.E.; Horspool, A.M.; Hill, P.J.; Wozniak, D.J.; Schertzer, J.W.; Rasko, D.A.; Ernst, R.K. Genomic and phenotypic diversity among ten laboratory isolates of pseudomonas aeruginosa PAO1. J. Bacteriol. 2019, 201, e00595-18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mohan, S.; Kelly, T.M.; Eveland, S.S.; Raetz, C.R.; Anderson, M.S. An Escherichia coli gene (fabZ) encoding (3R)-hydroxymyristoyl acyl carrier protein dehydrase. J. Biol. Chem. 1994, 269, 32896–32903. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]




| (A) Oligonucleotides | ||
| Name | Sequence (5′-3′) | Usage |
| F1 | TGATCACGATCATTCCTTGATGC | Assay lpxH alleles in chr and TS-plasmid |
| R1 | TGGACGTGGTCAACAAGATCAAG | Ditto |
| F2 | TTCCTTGCGCTTGATCAGGTAC | Assay lpxH alleles in chr but not TS-plasmid |
| R2 | CCGATGTGCAGGTAACCGTTG | Ditto |
| (B) Plasmids | ||
| Name | Relevant Genotype | Reference |
| pDEL | pUC-Gmr-sacB | [13,14] |
| pRES or pTS | pUC-Tcr-orits | [13,14] |
| pOE | pBBRMCS-5-araC-PBAD-Gmr | [13,14] |
| pDEL-lpxH | lpxH deletion cassette in pDEL | This study |
| pRES-lpxH | lpxH rescue cassette in pTS | This study |
| pOE-pa.lpxH | araC-PBAD-pa.lpxH in pOE | This study |
| pOE-ec.lpxH | araC-PBAD-ec.lpxH in pOE | This study |
| pOE-cc.lpxI | araC-PBAD-cc.lpxI in pOE | This study |
| pOE-ct.lpxG | araC-PBAD-ct.lpxG in pOE | This study |
| (C) Strains | ||
| Name | Relevant Genotype/Usage | Reference |
| PAO1 | Wild type | [13,14] |
| ΔlpxH/pTS-lpxH | lpxH(Ts) ts-allele | This study |
| ΔlpxH/pTS-lpxH/pOE-lpxH | lpxH-OE in ts | This study |
| ΔlpxH/pTS-lpxH/pOE-ec.lpxH | ec.lpxH-OE in ts | This study |
| ΔlpxH/pTS-lpxH/pOE-cc.lpxI | cc.lpxI-OE in ts | This study |
| ΔlpxH/pTS-lpxH/pOE-ct.lpxG | ct.lpxH-OE in ts | This study |
| wt/pOE-lpxH | lpxH-OE in wt | This study |
| wt/pOE-ec.lpxH | ec.lpxH-OE in wt | This study |
| wt/pOE-cc.lpxI | cc.lpxI-OE in wt | This study |
| wt/pOE-ct.lpxG | ct.lpxH-OE in wt | This study |
| sup | sup ΔlpxH | This study |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Zhang, H.; Yang, Z.; Liu, J. Genetic Analysis of the Plasmid-Based Temperature-Lethal Mutant pa1792|lpxH(Ts) in Pseudomonas aeruginosa. Genes 2024, 15, 784. https://doi.org/10.3390/genes15060784
Zhang H, Yang Z, Liu J. Genetic Analysis of the Plasmid-Based Temperature-Lethal Mutant pa1792|lpxH(Ts) in Pseudomonas aeruginosa. Genes. 2024; 15(6):784. https://doi.org/10.3390/genes15060784
Chicago/Turabian StyleZhang, Haoyang, Zhili Yang, and Jianhua Liu. 2024. "Genetic Analysis of the Plasmid-Based Temperature-Lethal Mutant pa1792|lpxH(Ts) in Pseudomonas aeruginosa" Genes 15, no. 6: 784. https://doi.org/10.3390/genes15060784
APA StyleZhang, H., Yang, Z., & Liu, J. (2024). Genetic Analysis of the Plasmid-Based Temperature-Lethal Mutant pa1792|lpxH(Ts) in Pseudomonas aeruginosa. Genes, 15(6), 784. https://doi.org/10.3390/genes15060784






