A Comprehensive Systematic Review Coupled with an Interacting Network Analysis Identified Candidate Genes and Biological Pathways Related to Bovine Temperament
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Systematic Review
2.2. Development of Interaction Network and Gene Enrichment
3. Results
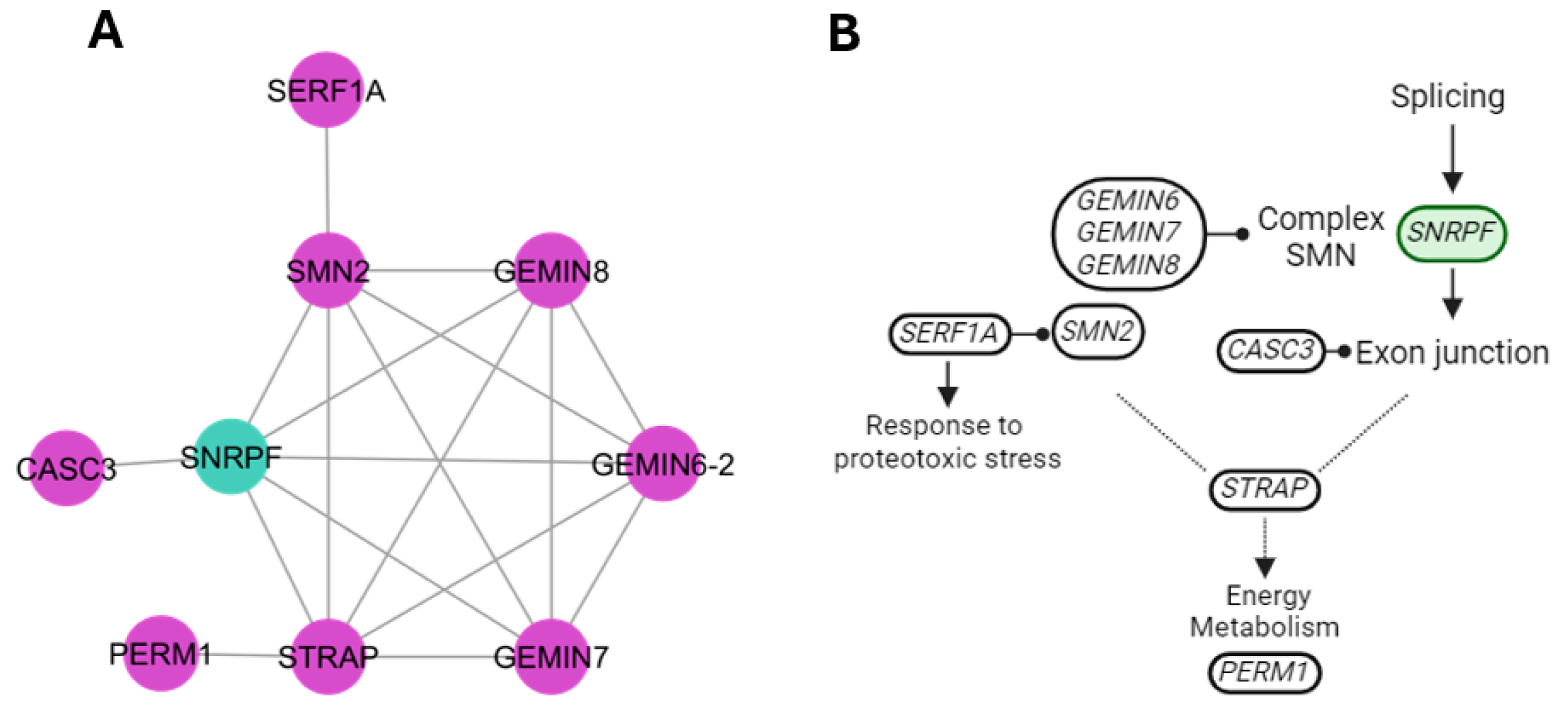
3.1. Establishing the Gene Interaction Network
3.2. Gene Clusters and Pathways
4. Discussion
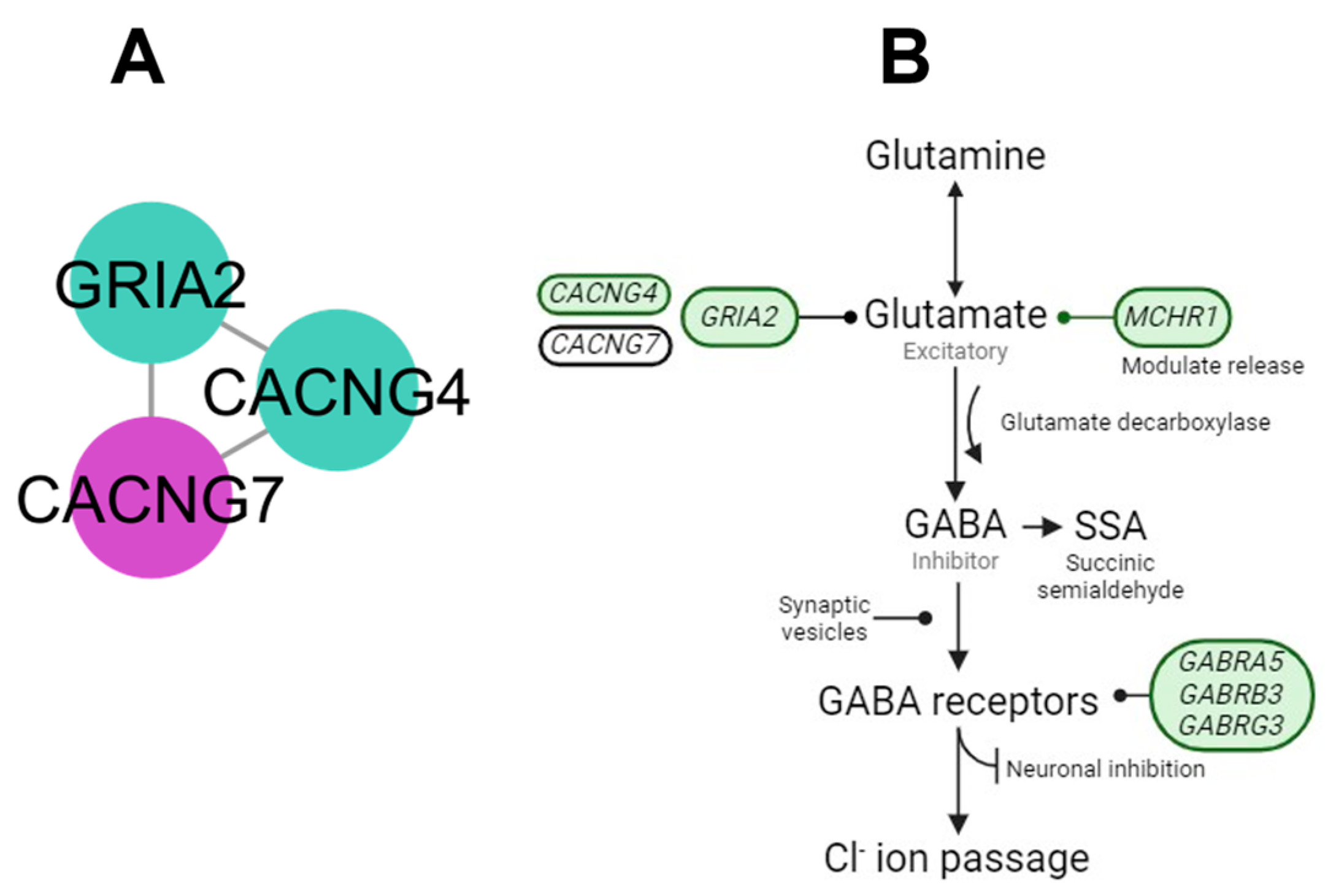
4.1. AMPA Cluster
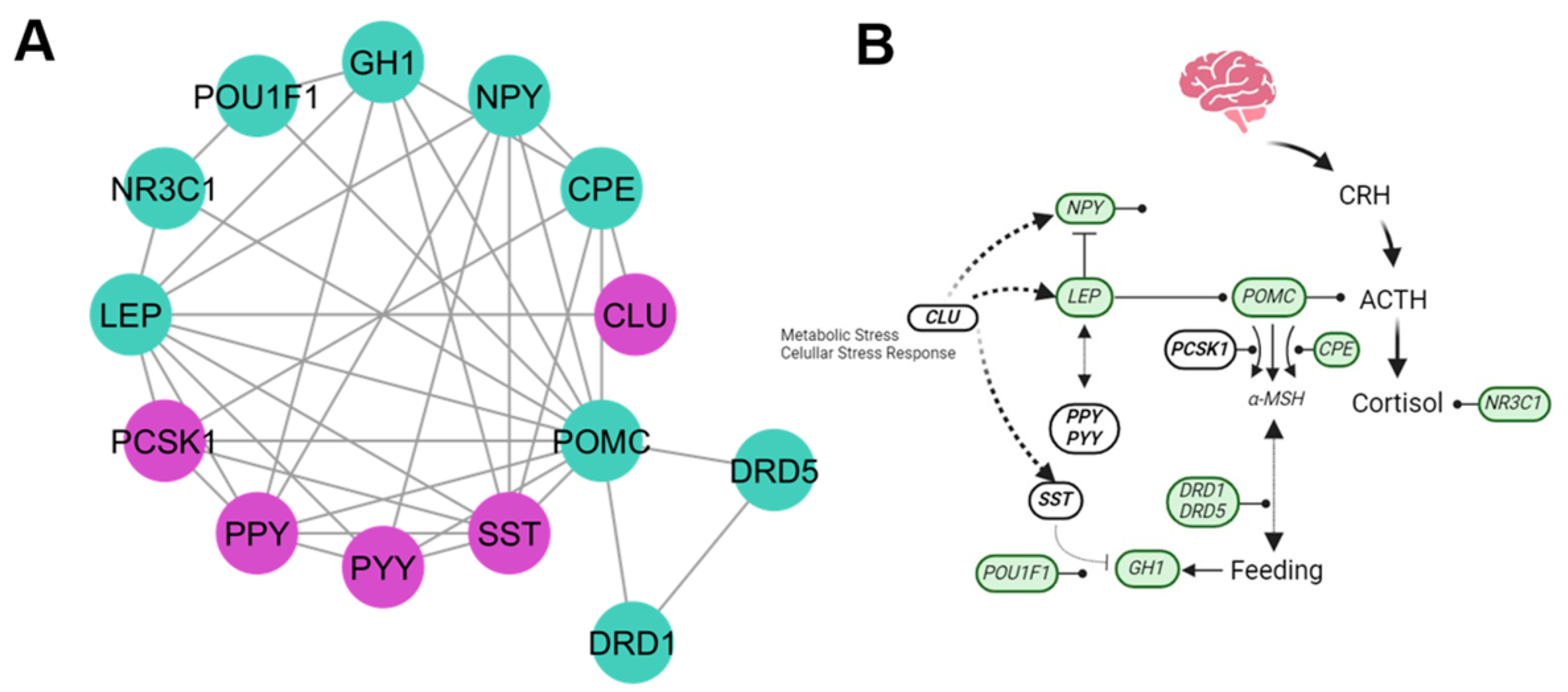
4.2. Hormones Cluster
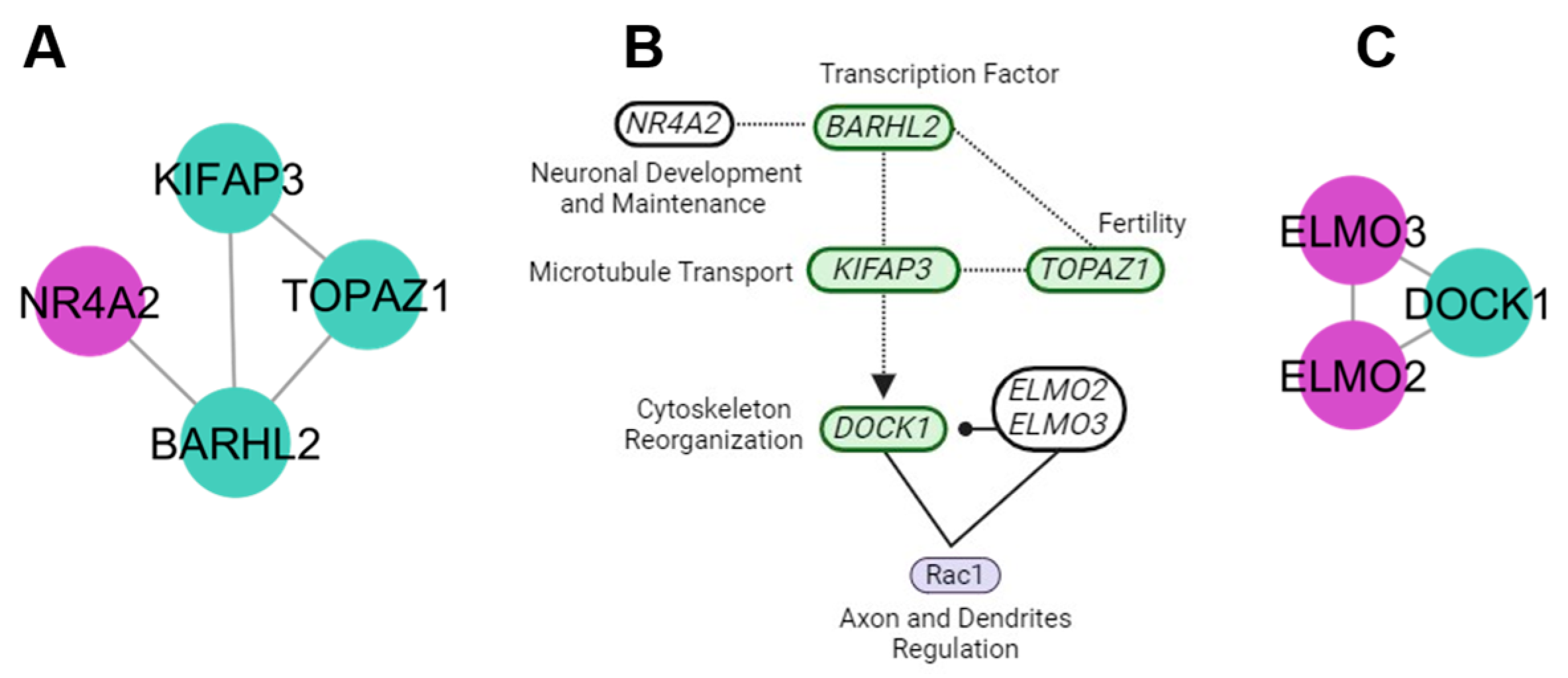
4.3. Neuronal Maintenance Cluster
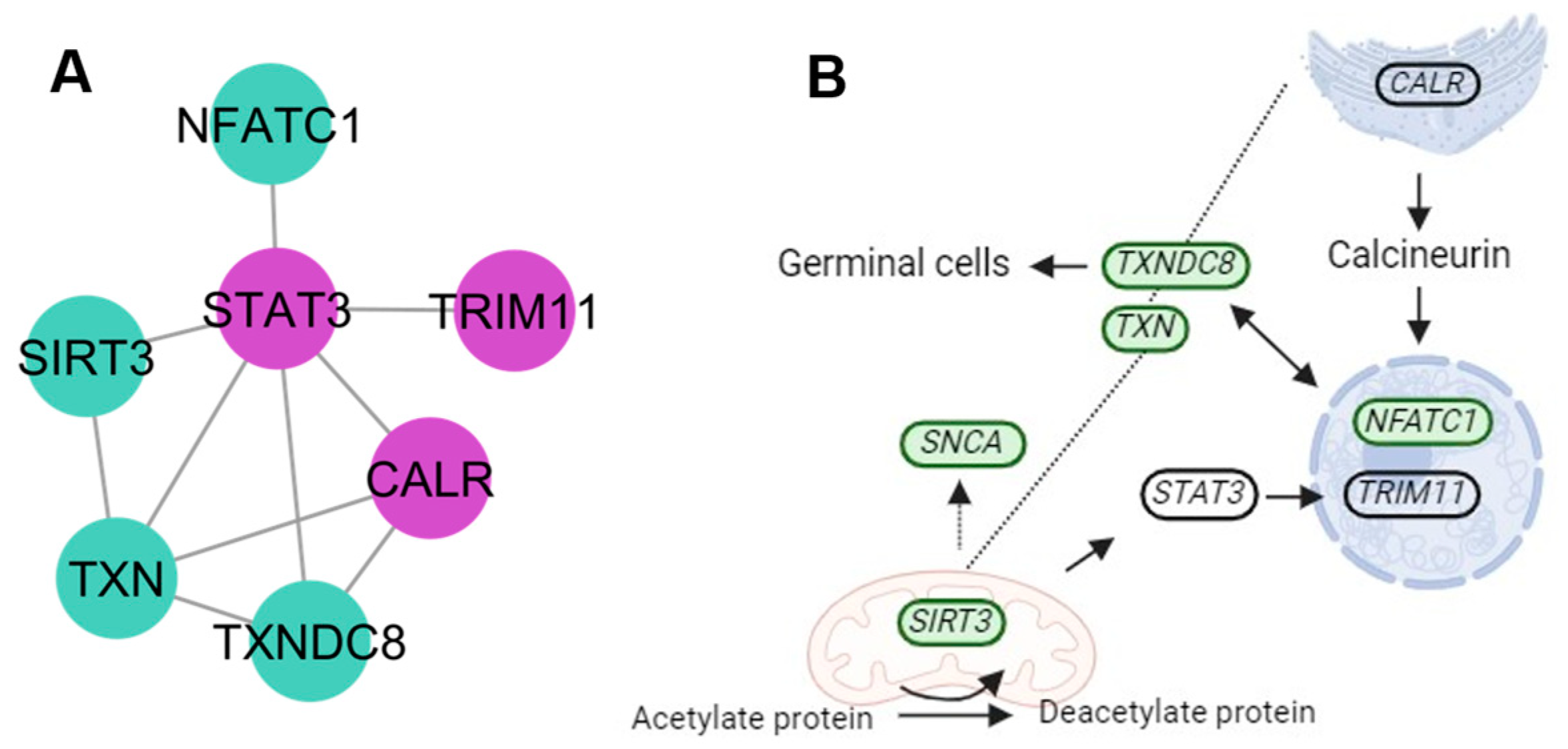
4.4. Protein Signalization and Ubiquitination Clusters
4.5. Regulation Neuron Cluster
4.6. Serotonin Synthesis Cluster
4.7. Splicing Cluster
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Hernandez, A.; Galina, C.S.; Geffroy, M.; Jung, J.; Westin, R.; Berg, C. Cattle welfare aspects of production systems in the tropics. Anim. Prod. Sci. 2022, 62, 1203–1218. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Titterington, F.M.; Knox, R.; Morrison, S.J.; Shirali, M. Behavioural traits in Bos taurus cattle, their heritability, potential genetic markers, and associations with production traits. Animals 2022, 12, 2602. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Haskell, M.J.; Simm, G.; Turner, S.P. Genetic selection for temperament traits in dairy and beef cattle. Front. Genet. 2014, 5, 368. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Takeda, K.; Uchida, H.; Inoue, K. Genetic relationships between temperament of calves at auction and carcass traits in Japanese Black cattle. Anim. Sci. J. 2017, 88, 1475–1481. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Friedrich, J.; Brand, B.; Schwerin, M. Genetics of cattle temperament and its impact on livestock production and breeding—A review. Arch. Anim. Breed. 2015, 58, 13–21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kilgour, R. The open-field test as an assessment of the temperament of dairy cows. Anim. Behav. 1975, 23, 615–624. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Benhajali, H.; Boivin, X.; Sapa, J.; Pellegrini, P.; Boulesteix, P.; Lajudie, P.; Phocas, F. Assessment of different on-farm measures of beef cattle temperament for use in genetic evaluation. J. Anim. Sci. 2010, 88, 3529–3537. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Burdick, N.C.; Agado, B.; White, J.C.; Matheney, K.J.; Neuendorff, D.A.; Riley, D.G.; Vann, R.C.; Welsh, T.H., Jr.; Randel, R.D. Evolution of exit velocity in suckling Brahman calves. J. Anim. Sci. 2011, 89, 233–236. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Curley, K.O., Jr.; Paschal, J.C.; Welsh, T.H., Jr.; Randel, R.D. Exit velocity as a measure of cattle temperament is repeatable and associated with serum concentration of cortisol in Brahman bulls. J. Anim. Sci. 2006, 84, 3100–3103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gutiérrez-Gil, B.; Ball, N.; Burton, D.; Haskell, M.; Williams, J.L.; Wiener, P. Identification of quantitative trait loci affecting cattle temperament. J. Hered. 2008, 99, 629–638. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Garza-Brenner, E.; Sifuentes-Rincón, A.M.; Rodríguez-Almeida, F.A.; Randel, R.D.; Parra-Bracamonte, G.M.; Arellano-Vera, W. Influence of genetic markers on the feeding behavior of yearling bulls. Rev. Colomb. Cienc. Pec. 2019, 32, 14–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Paredes-Sánchez, F.A.; Sifuentes-Rincón, A.M.; Casas, E.; Arellano-Vera, W.; Parra-Bracamonte, G.M.; Riley, D.G.; Welsh, T.H., Jr.; Randel, R.D. Novel genes involved in the genetic architecture of temperament in Brahman cattle. PLoS ONE 2020, 15, e0237825. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, S.Y.; Oliveira, H.R.; Schenkel, F.S.; Pedrosa, V.B.; Melka, M.G.; Brito, L.F. Using imputed whole-genome sequence variants to uncover candidate mutations and genes affecting milking speed and temperament in Holstein cattle. J. Dairy Sci. 2020, 103, 10383–10398. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lindholm-Perry, A.K.; Kuehn, L.A.; Freetly, H.C.; Snelling, W.M. Genetic markers that influence feed efficiency phenotypes also affect cattle temperament as measured by flight speed. Anim. Genet. 2014, 46, 60–64. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Aierqing, S.; Nakagawa, A.; Bungo, T. Association between temperament and polymorphisms of CRH and leptin in Japanese Black Cattle. J. Adv. Vet. Anim. Res. 2020, 7, 1–5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Graceli, J.B.; Dettogni, R.S.; Merlo, E.; Nino, O.; da Costa, C.S.; Zanol, J.F.; Ríos, M.E.A.; Miranda-Alves, L.; Denicol, A.C. The impact of endocrine-disrupting chemical exposure in the mammalian hypothalamic-pituitary axis. Mol. Cell. Endocrinol. 2020, 518, 110997. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Burdick, N.C.; Randel, R.D.; Carroll, J.A.; Welsh, T.H., Jr. Interactions between temperament, stress, and immune function in cattle. Int. J. Zool. 2011, 2011, 373197. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sarkis-Onofre, R.; Catalá-López, F.; Aromataris, E.; Lockwood, C. How to properly use the PRISMA Statement. Syst. Rev. 2021, 10, 117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Moher, D.; Liberati, A.; Tetzlaff, J.; Altman, D.G. Preferred reporting items for systematic reviews and meta-analyses: The PRISMA statement. PLoS Med. 2009, 6, e1000097. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bettany-Saltikov, J. Learning how to undertake a systematic review: Part 2. Nurs. Stand. 2010, 24, 47. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alvarenga, A.B.; Oliveira, H.R.; Chen, S.Y.; Miller, S.P.; Marchant-Forde, J.N.; Grigoletto, L.; Brito, L.F. A systematic review of genomic regions and candidate genes underlying behavioral traits in farmed mammals and their link with human disorders. Animals 2021, 11, 715. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Szklarczyk, D.; Gable, A.L.; Lyon, D.; Junge, A.; Wyder, S.; Huerta-Cepas, J.; Simonovic, M.; Doncheva, N.T.; Morris, J.H.; Bork, P.; et al. STRING v11: Protein–protein association networks with increased coverage, supporting functional discovery in genome-wide experimental datasets. Nucleic Acids Res. 2019, 47, D607–D613. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Srikanth, K.; Lee, S.H.; Chung, K.Y.; Park, J.E.; Jang, G.W.; Park, M.R.; Kim, N.Y.; Kim, T.H.; Chai, H.H.; Park, W.C.; et al. A gene-set enrichment and protein–protein interaction network-based GWAS with regulatory SNPs identifies candidate genes and pathways associated with carcass traits in Hanwoo Cattle. Genes 2020, 11, 316. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, J.; Yuan, Y.; Wu, X.; Liu, A.; Wang, J.; Yang, S.; Liu, B.; Kong, Y.; Wang, L.; Zhang, K.; et al. Excitatory SST neurons in the medial paralemniscal nucleus control repetitive self-grooming and encode reward. Neuron 2022, 110, 3356–3373. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fino, E.; Vandecasteele, M.; Perez, S.; Saudou, F.; Venance, L. Region-specific and state-dependent action of striatal GABAergic interneurons. Nat. Commun. 2018, 9, 3339. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fee, C.; Prevot, T.D.; Misquitta, K.; Knutson, D.E.; Li, G.; Mondal, P.; Cook, J.M.; Banasr, M.; Sibille, E. Behavioral deficits induced by somatostatin-positive GABA neuron silencing are rescued by alpha 5 GABA-A receptor potentiation. Int. J. Neuropsychopharmacol. 2021, 24, 505–518. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pech-Pool, S.; Berumen, L.C.; Martínez-Moreno, C.G.; García-Alcocer, G.; Carranza, M.; Luna, M.; Arámburo, C. Thyrotropin-releasing hormone (TRH) and somatostatin (SST), but not growth hormone-releasing hormone (GHRH) nor ghrelin (GHRL), regulate expression and release of immune growth hormone (GH) from chicken bursal B-lymphocyte cultures. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2020, 21, 1436. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hu, H.T.; Huang, T.N.; Hsueh, Y.P. KLHL17/Actinfilin, a brain-specific gene associated with infantile spasms and autism, regulates dendritic spine enlargement. J. Biomed. Sci. 2020, 27, 103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhai, F.; Li, J.; Jin, X. The functions and effects of CUL3-E3 ligases mediated non-degradative ubiquitination. Gene 2022, 832, 146562. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Perissinotti, P.P.; Martínez-Hernández, E.; He, Y.; Koob, M.D.; Piedras-Rentería, E.S. Genetic deletion of KLHL1 leads to hyperexcitability in hypothalamic POMC neurons and lack of electrical responses to leptin. Front. Neurosci. 2021, 15, 718464. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tomita, S.; Nicoll, R.A.; Bredt, D.S. PDZ protein interactions regulating glutamate receptor function and plasticity. J. Cell Biol. 2001, 153, F19–F24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kious, B.M.; Baker, C.V.H.; Bronner-Fraser, M.; Knecht, A.K. Identification and characterization of a calcium channel γ subunit expressed in differentiating neurons and myoblasts. Dev. Biol. 2002, 243, 249–259. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ruiz-De-La-Cruz, G.; Sifuentes-Rincón, A.M.; Casas, E.; Paredes-Sánchez, F.A.; Parra-Bracamonte, G.M.; Riley, D.G.; Perry, G.A.; Welsh, T.H., Jr.; Randel, R.D. Genetic variants and their putative effects on microRNA-seed sites: Characterization of the 3′ untranslated region of genes associated with temperament. Genes 2023, 14, 1004. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ruiz-De-La-Cruz, G.; Sifuentes-Rincón, A.M.; Paredes-Sánchez, F.A.; Parra-Bracamonte, G.M.; Casas, E.; Welsh, T.H., Jr.; Riley, D.G.; Perry, G.A.; Randel, R.D. Characterization of intronic SNP located in candidate genes influencing cattle temperament. Rev. Bras. Zootec. 2023, 52, e20220057. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Giaretta, E.; Mongillo, P.; Dalt, L.D.; Gianesella, M.; Bortoletti, M.; Degano, L.; Vicario, D.; Gabai, G. Temperature and humidity index (THI) affects salivary cortisol (HC) and dehydroepiandrosterone (DHEA) concentrations in growing bulls following stress generated by performance test procedures. Front. Vet. Sci. 2023, 10, 1237634. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Garza-Brenner, E.; Sifuentes-Rincón, A.M.; Randel, R.D.; Paredes-Sánchez, F.A.; Parra-Bracamonte, G.M.; Arellano-Vera, W.; Rodríguez-Almeida, F.A.; Segura-Cabrera, A. Association of SNPs in dopamine and serotonin pathway genes and their interacting genes with temperament traits in Charolais cows. J. Appl. Genet. 2017, 58, 363–371. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Belous, A.A.; Sermyagin, A.A.; Zinovieva, N.A. Genetic assessment of projected residual feed consumption and expression of significant candidate genes in Duroc pigs and second-generation commercial blends. Russ. J. Genet. 2023, 59, 1158–1172. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Southey, B.R.; Rodriguez-Zas, S.L. Changes in neuropeptide prohormone genes among Cetartiodactyla livestock and wild species associated with evolution and domestication. Vet. Sci. 2022, 9, 247. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Viitala, S.; Szyda, J.; Blott, S.; Schulman, N.; Lidauer, M.; Mäki-Tanila, A.; Vilkki, J. The role of the bovine growth hormone receptor and prolactin receptor genes in milk, fat and protein production in Finnish Ayrshire dairy cattle. Genetics 2006, 173, 2151–2164. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huang, W.; Maltecca, C.; Khatib, H. A proline-to-histidine mutation in POU1F1 is associated with production traits in dairy cattle. Anim. Genet. 2008, 39, 554–557. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Broberg, M.; Helaakoski, V.; Kiiskinen, T.; Paunio, T.; Jones, S.E.; Mars, N.; Lane, J.M.; Gen, F.; Saxena, R.; Ollila, H.M. Genetics of sleep medication purchases suggests causality from sleep problems to psychiatric traits. Sleep 2024, 47, zsad279. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hou, Y.; Ding, M.; Wang, C.; Yang, X.; Ye, T.; Yu, H. TRIM11 promotes lymphomas by activating the β-catenin signaling and Axin1 ubiquitination degradation. Exp. Cell Res. 2020, 387, 111750. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ba, C.; Ni, X.; Yu, J.; Zou, G.; Zhu, H. Ubiquitin conjugating enzyme E2 M promotes apoptosis in osteoarthritis chondrocytes via Wnt/β-catenin signaling. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 2020, 529, 970–976. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhou, W.; Xu, J.; Tan, M.; Li, H.; Li, H.; Wei, W.; Sun, Y. UBE2M is a stress-inducible dual E2 for neddylation and ubiquitylation that promotes targeted degradation of UBE2F. Mol. Cell 2018, 70, 1008–1024. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Z.Y.; Harischandra, D.S.; Wang, R.; Ghaisas, S.; Zhao, J.Y.; McMonagle, T.P.; Zhu, G.; Lacuarta, K.D.; Song, J.; Trojanowski, J.Q.; et al. TRIM11 protects against tauopathies and is down-regulated in Alzheimer’s disease. Science 2023, 381, eadd6696. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ahsan, N.; Shariq, M.; Surolia, A.; Raj, R.; Khan, M.F.; Kumar, P. Multipronged regulation of autophagy and apoptosis: Emerging role of TRIM proteins. Cell. Mol. Biol. Lett. 2024, 29, 13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Choo, Y.Y.; Hagen, T. Mechanism of cullin3 E3 ubiquitin ligase dimerization. PLoS ONE 2012, 7, e41350. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, Z.; Xiang, Y.; Sun, G. The KCTD family of proteins: Structure, function, disease relevance. Cell Biosci. 2013, 3, 45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Teng, X.; Aouacheria, A.; Lionnard, L.; Metz, K.A.; Soane, L.; Kamiya, A.; Hardwick, J.M. KCTD: A new gene family involved in neurodevelopmental and neuropsychiatric disorders. CNS Neurosci. Ther. 2019, 25, 887–902. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, W.; Wang, W.; Kong, Y.; Zheng, S. Structural basis for the ubiquitination of G protein βγ subunits by KCTD5/Cullin3 E3 ligase. Sci. Adv. 2023, 9, eadg8369. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barger, J.L.; Anderson, R.M.; Newton, M.A.; da Silva, C.; Vann, J.A.; Pugh, T.D.; Someya, S.; Prolla, T.A.; Weindruchet, R. A conserved transcriptional signature of delayed aging and reduced disease vulnerability is partially mediated by SIRT3. PLoS ONE 2015, 10, e0120738. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nguyen, D.T.; Le, T.M.; Hattori, T.; Takarada-Iemata, M.; Ishii, H.; Roboon, J.; Tamatani, T.; Kannon, T.; Hosomichi, K.; Tajima, A.; et al. The ATF6β-calreticulin axis promotes neuronal survival under endoplasmic reticulum stress and excitotoxicity. Sci. Rep. 2021, 11, 13086. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nakka, V.P.; Gusain, A.; Raghubir, R. Endoplasmic reticulum stress plays critical role in brain damage after cerebral ischemia/reperfusion in rats. Neurotox. Res. 2010, 17, 189–202. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, H.; Dai, S.; Yang, Y.; Wei, J.; Li, X.; Luo, P.; Jiang, X. Role of sirtuin 3 in degenerative diseases of the central nervous system. Biomolecules 2023, 13, 735. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pinkas, D.M.; Sanvitale, C.E.; Bufton, J.C.; Sorrell, F.J.; Solcan, N.; Chalk, R.; Doutch, J.; Bullock, A.N. Structural complexity in the KCTD family of Cullin3-dependent E3 ubiquitin ligases. Biochem. J. 2017, 474, 3747–3761. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chang, L.; Yang, J.; Jo, C.H.; Boland, A.; Zhang, Z.; McLaughlin, S.H.; Abu-Thuraia, A.; Killoran, R.C.; Smith, M.J.; Côté, J.F.; et al. Structure of the DOCK2−ELMO1 complex provides insights into regulation of the auto-inhibited state. Nat. Commun. 2020, 11, 3464. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Badawy, A.A.; Guillemin, G.J. Species differences in tryptophan metabolism and disposition. Int. J. Tryptophan Res. 2022, 15, 11786469221122511. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, Y.; Gao, S.; Xia, S.; Yang, H.; Bao, X.; Zhang, Q.; Xu, Y. Linarin ameliorates ischemia-reperfusion injury by the inhibition of endoplasmic reticulum stress targeting AKR1B1. Brain Res. Bull. 2024, 207, 110868. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vernau, K.M.; Struys, E.; Letko, A.; Woolard, K.D.; Aguilar, M.; Brown, E.A.; Cissell, D.D.; Dickinson, P.J.; Shelton, G.D.; Broome, M.R.; et al. A missense variant in ALDH5A1 associated with canine succinic semialdehyde dehydrogenase deficiency (SSADHD) in the Saluki dog. Genes 2020, 11, 1033. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Littlejohn, B.P.; Price, D.M.; Neuendorff, D.A.; Carroll, J.A.; Vann, R.C.; Riggs, P.K.; Riley, D.G.; Long, C.R.; Welsh, T.H., Jr.; Randel, R.D. Prenatal transportation stress alters genome-wide DNA methylation in suckling Brahman bull calves. J. Anim. Sci. 2018, 96, 12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yurdakul, E.; Barlas, Y.; Ulgen, K.O. Circadian clock crosstalks with autism. Brain. Behav. 2023, 13, e3273. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mertsch, S.; Schlicht, K.; Melkonyan, H.; Schlatt, S.; Thanos, S. snRPN controls the ability of neurons to regenerate axons. Restor. Neurol. Neurosci. 2018, 36, 31–43. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schlautmann, L.P.; Gehring, N.H. A day in the life of the exon junction complex. Biomolecules 2020, 10, 866. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gruss, O.J.; Meduri, R.; Schilling, M.; Fischer, U. UsnRNP biogenesis: Mechanisms and regulation. Chromosoma 2017, 126, 577–593. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pánek, J.; Roithová, A.; Radivojević, N.; Sýkora, M.; Prusty, A.B.; Huston, N.; Wan, H.; Pyle, A.M.; Fischer, U.; Staněk, D. The SMN complex drives structural changes in human snRNAs to enable snRNP assembly. Nat. Commun. 2023, 14, 6580. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cho, Y.; Hazen, B.C.; Gandra, P.G.; Ward, S.R.; Schenk, S.; Russell, A.P.; Kralli, A. Perm1 enhances mitochondrial biogenesis, oxidative capacity, and fatigue resistance in adult skeletal muscle. FASEB J. 2016, 30, 674. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ubaida-Mohien, C.; Spendiff, S.; Lyashkov, A.; Moaddel, R.; MacMillan, N.J.; Filion, M.E.; Morais, J.A.; Taivassalo, T.; Ferrucci, L.; Hepple, R.T. Unbiased proteomics, histochemistry, and mitochondrial DNA copy number reveal better mitochondrial health in muscle of high-functioning octogenarians. eLife 2022, 11, e74335. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, X.; Chen, Q.; Ouyang, Q.; Rong, P.; Feng, W.; Quan, C.; Li, M.; Jiang, Q.; Liang, H.; Zhao, T.J.; et al. Tissue-specific splicing and dietary interaction of a mutant As160 allele determine muscle metabolic fitness in rodents. Diabetes 2021, 70, 1826–1842. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jin, L.; Chen, Y.; Crossman, D.K.; Datta, A.; Vu, T.; Mobley, J.A.; Basu, M.K.; Scarduzio, M.; Wang, H.; Chang, C.; et al. STRAP regulates alternative splicing fidelity during lineage commitment of mouse embryonic stem cells. Nat. Commun. 2020, 11, 5941. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bagnicka, E.; Kawecka-Grochocka, E.; Pawlina-Tyszko, K.; Zalewska, M.; Kapusta, A.; Kościuczuk, E.; Marczak, S.; Ząbek, T. MicroRNA expression profile in bovine mammary gland parenchyma infected by coagulase-positive or coagulase-negative staphylococci. Vet. Res. 2021, 52, 41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Butchbach, M.E.R. Genomic variability in the survival motor neuron genes (SMN1 and SMN2): Implications for spinal muscular atrophy phenotype and therapeutics development. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2021, 22, 7896. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lejman, J.; Zieliński, G.; Gawda, P.; Lejman, M. Alternative splicing role in new therapies of spinal muscular atrophy. Genes 2021, 12, 1346. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]



| Group | Gene | Name | Biological Function |
|---|---|---|---|
| Enzyme | AKR1B1 ID:317748 | aldo-keto reductase family 1, member B1 (aldose reductase) | Carbohydrate metabolism. Catalyzes the reduction of glucose to sorbitol during hyperglycemia. Pentose and glucuronate interconversions, fructose and mannose metabolism. Reduces steroids and their derivatives and prostaglandins and participates in folate biosynthesis. |
| PCSK1 ID:281967 | proprotein convertase subtilisin/kexin type 1 | Involved in hormone and protein processing. Substrates include proopiomelanocortin (POMC), renin, enkephalin, dynorphin, somatostatin, insulin, and agouti-related protein (AGRP). | |
| UBE2M ID:613343 | ubiquitin-conjugating enzyme E2 M | Ubiquitin-mediated protein degradation, cell cycle regulation. | |
| Protein | CACNG7 ID:539969 | calcium voltage-gated channel auxiliary subunit γ 7 | Regulation of voltage-gated calcium channel activity. |
| CALR ID:281036 | calreticulin | Protein processing and folding in the endoplasmic reticulum, endoplasmic reticulum stress response, regulation of calcium homeostasis. | |
| CASC3 ID:531673 | CASC3 exon junction complex subunit | Regulation of messenger RNA splicing, exon junction complex (EJC). | |
| CLU ID:280750 | clusterin | Apoptosis, cellular stress response, lipid transport and metabolism. | |
| ELMO2 ID:508361 | engulfment and cell motility 2 | Phagocytosis of apoptotic cells, Rho GTPase signaling. | |
| ELMO3 ID:525427 | engulfment and cell motility 3 | Phagocytosis of apoptotic cells, cell migration, and cytoskeletal remodeling. | |
| GEMIN6 ID:525263 | gem nuclear-organelle-associated protein 6 | Assembly of the small nuclear RNA (snRNP) complex, RNA biogenesis. | |
| GEMIN7 ID:618024 | gem nuclear-organelle-associated protein 7 | Assembly of the small nuclear RNA (snRNP) complex, RNA biogenesis. | |
| GEMIN8 ID:515968 | gem nuclear-organelle-associated protein 8 | Assembly of the small nuclear RNA (snRNP) complex, RNA biogenesis. | |
| KLHL12 ID:768068 | kelch-like family member 12 | Ubiquitin-mediated protein degradation, vesicle formation. | |
| KLHL13 ID:528138 | kelch-like family member 13 | Ubiquitin-mediated protein degradation, vesicular trafficking. | |
| KLHL20 ID:511387 | kelch-like family member 20 | Ubiquitin-mediated protein degradation, response to hypoxia. | |
| KLHL21 ID:506632 | kelch-like family member 21 | Ubiquitin-mediated protein degradation, cell cycle. | |
| KLHL3 ID:533364 | kelch-like family member 3 | Potassium homeostasis, ion transport. | |
| KLHL9 ID:767834 | kelch-like family member 9 | Ubiquitin-mediated protein degradation, cell cycle regulation. | |
| PPY ID:280900 | pancreatic polypeptide | Regulation of appetite, energy metabolism. | |
| PYY ID:615800 | peptide YY | Regulation of appetite, gastrointestinal motility. | |
| KCTD13 ID:507911 | potassium channel tetramerization domain containing 13 | Regulation of ubiquitin-mediated protein degradation, GABA signaling. | |
| KCTD5 ID:100125308 | potassium channel tetramerization domain containing 5 | Regulation of ubiquitin-mediated protein degradation, GABA signaling. | |
| PERM1 ID:520080 | PPARGC1- and ESRR-induced regulator, muscle 1 | Regulation of mitochondrial metabolism, mitochondrial biogenesis. | |
| STRAP ID:510201 | serine/threonine kinase receptor-associated protein | TGF-β signaling, regulation of cell growth. | |
| SERF1A ID:526395 | small EDRK-rich factor 1A (telomeric) | Specifically unknown, but it may be involved in cellular stress processes. | |
| STT ID:280932 | Somatostatin | Inhibition of hormone release, regulation of cell growth. | |
| SPOP ID:530618 | speckle-type BTB/POZ protein | Ubiquitin-mediated protein degradation, signaling cell growth pathways. | |
| SMN2 ID:281492 | survival of motor neuron 2 | RNA splicing, snRNP biogenesis. | |
| TRIM11 ID:514580 | tripartite motif-containing 11 | Ubiquitin-mediated protein degradation, antiviral response. | |
| NR4A2 ID:540245 | nuclear receptor subfamily 4 group A member 2 | Transcription of genes involved in neurogenesis, inflammatory response. | |
| STAT3 ID:508541 | signal transducer and activator of transcription 3 | Cytokine signaling, cell proliferation and survival. |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Ruiz-De-La-Cruz, G.; Welsh, T.H., Jr.; Randel, R.D.; Sifuentes-Rincón, A.M. A Comprehensive Systematic Review Coupled with an Interacting Network Analysis Identified Candidate Genes and Biological Pathways Related to Bovine Temperament. Genes 2024, 15, 981. https://doi.org/10.3390/genes15080981
Ruiz-De-La-Cruz G, Welsh TH Jr., Randel RD, Sifuentes-Rincón AM. A Comprehensive Systematic Review Coupled with an Interacting Network Analysis Identified Candidate Genes and Biological Pathways Related to Bovine Temperament. Genes. 2024; 15(8):981. https://doi.org/10.3390/genes15080981
Chicago/Turabian StyleRuiz-De-La-Cruz, Gilberto, Thomas H. Welsh, Jr., Ronald D. Randel, and Ana María Sifuentes-Rincón. 2024. "A Comprehensive Systematic Review Coupled with an Interacting Network Analysis Identified Candidate Genes and Biological Pathways Related to Bovine Temperament" Genes 15, no. 8: 981. https://doi.org/10.3390/genes15080981
APA StyleRuiz-De-La-Cruz, G., Welsh, T. H., Jr., Randel, R. D., & Sifuentes-Rincón, A. M. (2024). A Comprehensive Systematic Review Coupled with an Interacting Network Analysis Identified Candidate Genes and Biological Pathways Related to Bovine Temperament. Genes, 15(8), 981. https://doi.org/10.3390/genes15080981





