Cell-Free DNA Hydroxymethylation in Cancer: Current and Emerging Detection Methods and Clinical Applications
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Biological Functions and Mechanisms of DNA Hydroxymethylation
2.1. DNA Hydroxymethylation in the Demethylation Pathway
2.2. Biological Functions and Distribution of DNA Hydroxymethylation
2.3. Cell-Free DNA and the Hydroxymethylome
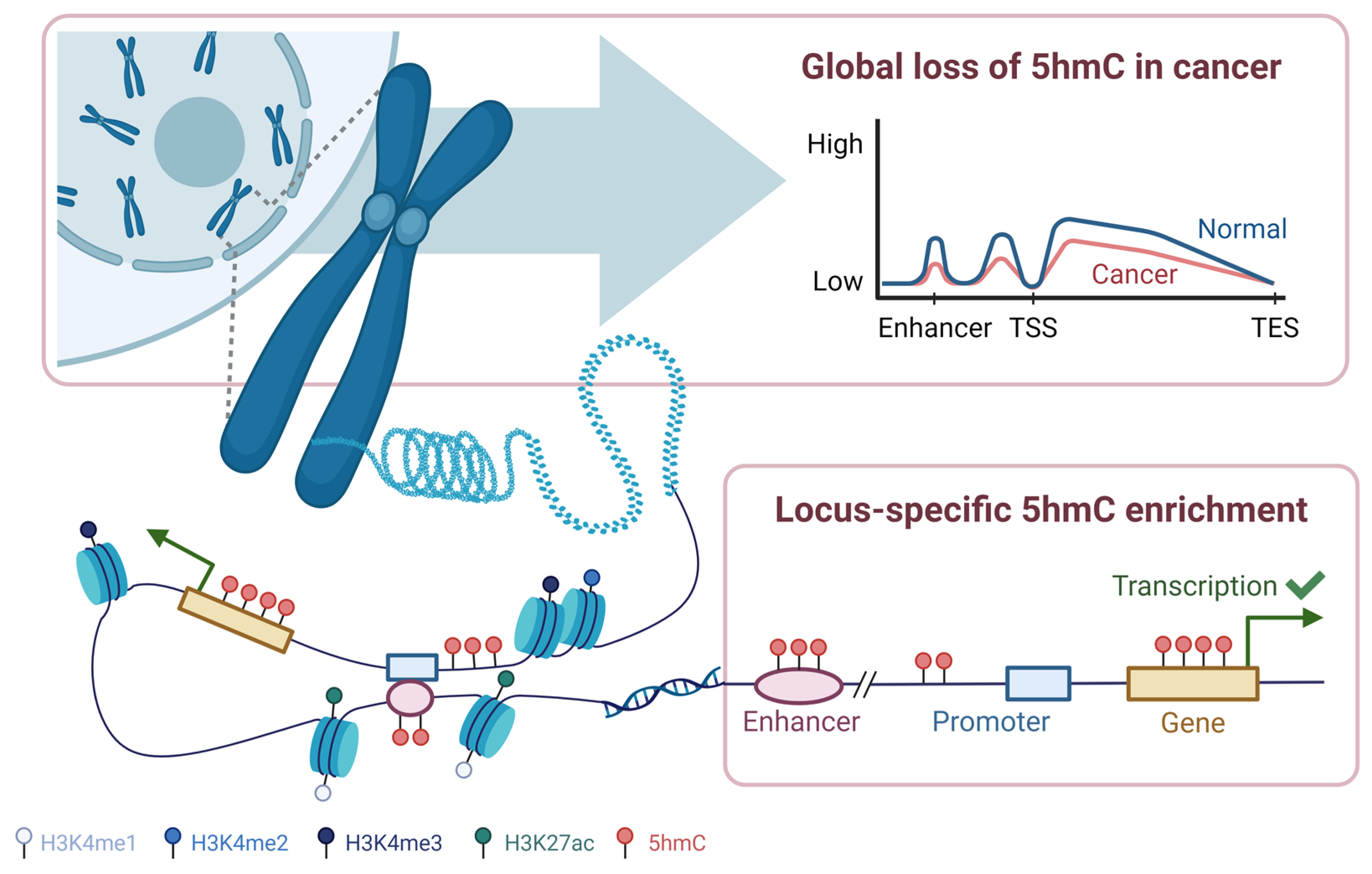
2.4. DNA Hydroxymethylation Patterns in Cancer
3. Evolution of Hydroxymethylation Detection Methods
3.1. Bisulfite Sequencing Approaches
3.2. Enzymatic and Affinity-Based Approaches
3.2.1. Chemical Capture and Glucosylation-Based Techniques
3.2.2. DNA Deamination Methods
3.2.3. Oxidation-Based Strategies
3.2.4. Antibody-Based Methods
3.3. Emerging Hydroxymethylation Profiling Methods
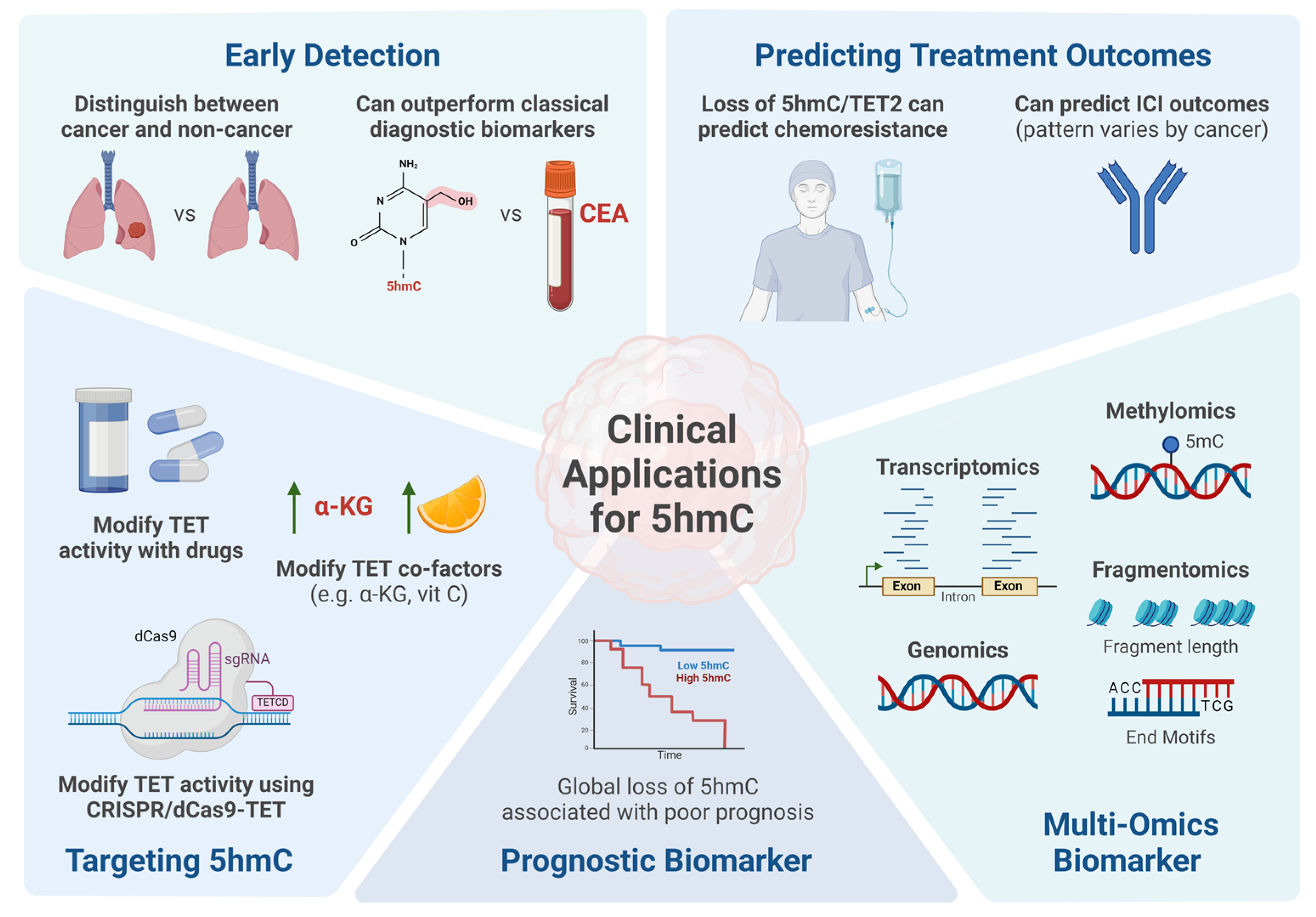
4. DNA Hydroxymethylation and Clinical Applications
4.1. DNA Hydroxymethylation as a Biomarker for Cancer Detection
4.2. Prognostic Value of DNA Hydroxymethylation in Cancer
4.3. Predicting Chemotherapy and Immunotherapy Response with 5hmC
4.4. Integrating DNA Hydroxymethylation in Multi-Omics Analysis
4.5. Targeting DNA Hydroxymethylation as a Potential Therapeutic for Cancer
5. Challenges and Future Directions
5.1. Choosing the Right 5hmC Detection Method
5.2. Multi-Omics Analyses Using Cell-Free DNA Hydroxymethylation
6. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Thomson, J.P.; Meehan, R.R. The Application of Genome-Wide 5-Hydroxymethylcytosine Studies in Cancer Research. Epigenomics 2017, 9, 77–91. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pfeifer, G.P.; Kadam, S.; Jin, S.-G. 5-Hydroxymethylcytosine and Its Potential Roles in Development and Cancer. Epigenet. Chromatin 2013, 6, 10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kudo, Y.; Tateishi, K.; Yamamoto, K.; Yamamoto, S.; Asaoka, Y.; Ijichi, H.; Nagae, G.; Yoshida, H.; Aburatani, H.; Koike, K. Loss of 5-hydroxymethylcytosine Is Accompanied with Malignant Cellular Transformation. Cancer Sci. 2012, 103, 670–676. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- García-Pardo, M.; Makarem, M.; Li, J.J.N.; Kelly, D.; Leighl, N.B. Integrating Circulating-Free DNA (cfDNA) Analysis into Clinical Practice: Opportunities and Challenges. Br. J. Cancer 2022, 127, 592–602. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cescon, D.W.; Bratman, S.V.; Chan, S.M.; Siu, L.L. Circulating Tumor DNA and Liquid Biopsy in Oncology. Nat. Cancer 2020, 1, 276–290. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, T.; Gao, H. Hydroxymethylation and Tumors: Can 5-Hydroxymethylation Be Used as a Marker for Tumor Diagnosis and Treatment? Hum. Genom. 2020, 14, 15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xu, L.; Zhou, Y.; Chen, L.; Bissessur, A.S.; Chen, J.; Mao, M.; Ju, S.; Chen, L.; Chen, C.; Li, Z.; et al. Deoxyribonucleic Acid 5-Hydroxymethylation in Cell-Free Deoxyribonucleic Acid, a Novel Cancer Biomarker in the Era of Precision Medicine. Front. Cell Dev. Biol. 2021, 9, 744990. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Besaratinia, A.; Caceres, A.; Tommasi, S. DNA Hydroxymethylation in Smoking-Associated Cancers. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2022, 23, 2657. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Smith, Z.D.; Meissner, A. DNA Methylation: Roles in Mammalian Development. Nat. Rev. Genet. 2013, 14, 204–220. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ooi, S.K.T.; O’Donnell, A.H.; Bestor, T.H. Mammalian Cytosine Methylation at a Glance. J. Cell Sci. 2009, 122, 2787–2791. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tahiliani, M.; Koh, K.P.; Shen, Y.; Pastor, W.A.; Bandukwala, H.; Brudno, Y.; Agarwal, S.; Iyer, L.M.; Liu, D.R.; Aravind, L.; et al. Conversion of 5-Methylcytosine to 5-Hydroxymethylcytosine in Mammalian DNA by MLL Partner TET1. Science 2009, 324, 930–935. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ito, S.; Shen, L.; Dai, Q.; Wu, S.C.; Collins, L.B.; Swenberg, J.A.; He, C.; Zhang, Y. Tet Proteins Can Convert 5-Methylcytosine to 5-Formylcytosine and 5-Carboxylcytosine. Science 2011, 333, 1300–1303. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wu, X.; Zhang, Y. TET-Mediated Active DNA Demethylation: Mechanism, Function and Beyond. Nat. Rev. Genet. 2017, 18, 517–534. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Globisch, D.; Münzel, M.; Müller, M.; Michalakis, S.; Wagner, M.; Koch, S.; Brückl, T.; Biel, M.; Carell, T. Tissue Distribution of 5-Hydroxymethylcytosine and Search for Active Demethylation Intermediates. PLoS ONE 2010, 5, e15367. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, L.; Lu, J.; Cheng, J.; Rao, Q.; Li, Z.; Hou, H.; Lou, Z.; Zhang, L.; Li, W.; Gong, W.; et al. Structural Insight into Substrate Preference for TET-Mediated Oxidation. Nature 2015, 527, 118–122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hashimoto, H.; Hong, S.; Bhagwat, A.S.; Zhang, X.; Cheng, X. Excision of 5-Hydroxymethyluracil and 5-Carboxylcytosine by the Thymine DNA Glycosylase Domain: Its Structural Basis and Implications for Active DNA Demethylation. Nucleic Acids Res. 2012, 40, 10203–10214. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nabel, C.S.; Jia, H.; Ye, Y.; Shen, L.; Goldschmidt, H.L.; Stivers, J.T.; Zhang, Y.; Kohli, R.M. AID/APOBEC Deaminases Disfavor Modified Cytosines Implicated in DNA Demethylation. Nat. Chem. Biol. 2012, 8, 751–758. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kohli, R.M.; Zhang, Y. TET Enzymes, TDG and the Dynamics of DNA Demethylation. Nature 2013, 502, 472–479. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- He, Y.-F.; Li, B.-Z.; Li, Z.; Liu, P.; Wang, Y.; Tang, Q.; Ding, J.; Jia, Y.; Chen, Z.; Li, L.; et al. Tet-Mediated Formation of 5-Carboxylcytosine and Its Excision by TDG in Mammalian DNA. Science 2011, 333, 1303–1307. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maiti, A.; Drohat, A.C. Thymine DNA Glycosylase Can Rapidly Excise 5-Formylcytosine and 5-Carboxylcytosine: Potential Implications for Active Demethylation of CpG Sites. J. Biol. Chem. 2011, 286, 35334–35338. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bachman, M.; Uribe-Lewis, S.; Yang, X.; Williams, M.; Murrell, A.; Balasubramanian, S. 5-Hydroxymethylcytosine Is a Predominantly Stable DNA Modification. Nat. Chem. 2014, 6, 1049–1055. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ito, S.; D’Alessio, A.C.; Taranova, O.V.; Hong, K.; Sowers, L.C.; Zhang, Y. Role of Tet Proteins in 5mC to 5hmC Conversion, ES-Cell Self-Renewal and Inner Cell Mass Specification. Nature 2010, 466, 1129–1133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ficz, G.; Branco, M.R.; Seisenberger, S.; Santos, F.; Krueger, F.; Hore, T.A.; Marques, C.J.; Andrews, S.; Reik, W. Dynamic Regulation of 5-Hydroxymethylcytosine in Mouse ES Cells and during Differentiation. Nature 2011, 473, 398–402. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guibert, S.; Weber, M. Functions of DNA Methylation and Hydroxymethylation in Mammalian Development. Curr. Top. Dev. Biol. 2013, 104, 47–83. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dawlaty, M.M.; Breiling, A.; Le, T.; Barrasa, M.I.; Raddatz, G.; Gao, Q.; Powell, B.E.; Cheng, A.W.; Faull, K.F.; Lyko, F.; et al. Loss of Tet Enzymes Compromises Proper Differentiation of Embryonic Stem Cells. Dev. Cell 2014, 29, 102–111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vasconcelos, S.; Caniçais, C.; Chuva de Sousa Lopes, S.M.; Marques, C.J.; Dória, S. The Role of DNA Hydroxymethylation and TET Enzymes in Placental Development and Pregnancy Outcome. Clin. Epigenet. 2023, 15, 66. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gao, Y.; Chen, J.; Li, K.; Wu, T.; Huang, B.; Liu, W.; Kou, X.; Zhang, Y.; Huang, H.; Jiang, Y.; et al. Replacement of Oct4 by Tet1 during iPSC Induction Reveals an Important Role of DNA Methylation and Hydroxymethylation in Reprogramming. Cell Stem Cell 2013, 12, 453–469. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Neri, F.; Incarnato, D.; Krepelova, A.; Dettori, D.; Rapelli, S.; Maldotti, M.; Parlato, C.; Anselmi, F.; Galvagni, F.; Oliviero, S. TET1 Is Controlled by Pluripotency-Associated Factors in ESCs and Downmodulated by PRC2 in Differentiated Cells and Tissues. Nucleic Acids Res. 2015, 43, 6814–6826. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, X.; Li, G.; Xie, R. Decoding the Role of TET Family Dioxygenases in Lineage Specification. Epigenet. Chromatin 2018, 11, 58. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Senner, C.E.; Chrysanthou, S.; Burge, S.; Lin, H.-Y.; Branco, M.R.; Hemberger, M. TET1 and 5-Hydroxymethylation Preserve the Stem Cell State of Mouse Trophoblast. Stem Cell Rep. 2020, 15, 1301–1316. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cheng, Y.; Xie, N.; Jin, P.; Wang, T. DNA Methylation and Hydroxymethylation in Stem Cells. Cell Biochem. Funct. 2015, 33, 161–173. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tsagaratou, A.; Äijö, T.; Lio, C.-W.J.; Yue, X.; Huang, Y.; Jacobsen, S.E.; Lähdesmäki, H.; Rao, A. Dissecting the Dynamic Changes of 5-Hydroxymethylcytosine in T-Cell Development and Differentiation. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2014, 111, E3306–E3315. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tsiouplis, N.J.; Bailey, D.W.; Chiou, L.F.; Wissink, F.J.; Tsagaratou, A. TET-Mediated Epigenetic Regulation in Immune Cell Development and Disease. Front. Cell Dev. Biol. 2020, 8, 623948. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xiao, Q.; Nobre, A.; Piñeiro, P.; Berciano-Guerrero, M.-Á.; Alba, E.; Cobo, M.; Lauschke, V.M.; Barragán, I. Genetic and Epigenetic Biomarkers of Immune Checkpoint Blockade Response. J. Clin. Med. 2020, 9, 286. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- McPherson, R.C.; Konkel, J.E.; Prendergast, C.T.; Thomson, J.P.; Ottaviano, R.; Leech, M.D.; Kay, O.; Zandee, S.E.J.; Sweenie, C.H.; Wraith, D.C.; et al. Epigenetic Modification of the PD-1 (Pdcd1) Promoter in Effector CD4(+) T Cells Tolerized by Peptide Immunotherapy. eLife 2014, 3, e03416. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khoodoruth, M.A.S.; Khoodoruth, W.N.C.; Alwani, R.A. Exploring the Epigenetic Landscape: The Role of 5-Hydroxymethylcytosine in Neurodevelopmental Disorders. Camb. Prisms Precis. Med. 2024, 2, e5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cui, X.-L.; Nie, J.; Ku, J.; Dougherty, U.; West-Szymanski, D.C.; Collin, F.; Ellison, C.K.; Sieh, L.; Ning, Y.; Deng, Z.; et al. A Human Tissue Map of 5-Hydroxymethylcytosines Exhibits Tissue Specificity through Gene and Enhancer Modulation. Nat. Commun. 2020, 11, 6161. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stroud, H.; Feng, S.; Morey Kinney, S.; Pradhan, S.; Jacobsen, S.E. 5-Hydroxymethylcytosine Is Associated with Enhancers and Gene Bodies in Human Embryonic Stem Cells. Genome Biol. 2011, 12, R54. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Szulwach, K.E.; Li, X.; Li, Y.; Song, C.-X.; Han, J.W.; Kim, S.; Namburi, S.; Hermetz, K.; Kim, J.J.; Rudd, M.K.; et al. Integrating 5-Hydroxymethylcytosine into the Epigenomic Landscape of Human Embryonic Stem Cells. PLoS Genet. 2011, 7, e1002154. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pastor, W.A.; Pape, U.J.; Huang, Y.; Henderson, H.R.; Lister, R.; Ko, M.; McLoughlin, E.M.; Brudno, Y.; Mahapatra, S.; Kapranov, P.; et al. Genome-Wide Mapping of 5-Hydroxymethylcytosine in Embryonic Stem Cells. Nature 2011, 473, 394–397. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kranzhöfer, D.K.; Gilsbach, R.; Grüning, B.A.; Backofen, R.; Nührenberg, T.G.; Hein, L. 5′-Hydroxymethylcytosine Precedes Loss of CpG Methylation in Enhancers and Genes Undergoing Activation in Cardiomyocyte Maturation. PLoS ONE 2016, 11, e0166575. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Uribe-Lewis, S.; Stark, R.; Carroll, T.; Dunning, M.J.; Bachman, M.; Ito, Y.; Stojic, L.; Halim, S.; Vowler, S.L.; Lynch, A.G.; et al. 5-Hydroxymethylcytosine Marks Promoters in Colon That Resist DNA Hypermethylation in Cancer. Genome Biol. 2015, 16, 69. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, J.; Lee, D.; Kim, H.-P.; Kim, T.-Y.; Bang, D. EBS-Seq: Enrichment-Based Method for Accurate Analysis of 5-Hydroxymethylcytosine at Single-Base Resolution. Clin. Epigenet. 2023, 15, 34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, D.; Lu, X.; Shih, A.H.; Nie, J.; You, Q.; Xu, M.M.; Melnick, A.M.; Levine, R.L.; He, C. A Highly Sensitive and Robust Method for Genome-Wide 5hmC Profiling of Rare Cell Populations. Mol. Cell 2016, 63, 711–719. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Branco, M.R.; Ficz, G.; Reik, W. Uncovering the Role of 5-Hydroxymethylcytosine in the Epigenome. Nat. Rev. Genet. 2011, 13, 7–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, H.; D’Alessio, A.C.; Ito, S.; Wang, Z.; Cui, K.; Zhao, K.; Sun, Y.E.; Zhang, Y. Genome-Wide Analysis of 5-Hydroxymethylcytosine Distribution Reveals Its Dual Function in Transcriptional Regulation in Mouse Embryonic Stem Cells. Genes Dev. 2011, 25, 679–684. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, M.K.; Azizgolshani, N.; Zhang, Z.; Perreard, L.; Kolling, F.W.; Nguyen, L.N.; Zanazzi, G.J.; Salas, L.A.; Christensen, B.C. Associations in Cell Type-Specific Hydroxymethylation and Transcriptional Alterations of Pediatric Central Nervous System Tumors. Nat. Commun. 2024, 15, 3635. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Valinluck, V.; Tsai, H.-H.; Rogstad, D.K.; Burdzy, A.; Bird, A.; Sowers, L.C. Oxidative Damage to Methyl-CpG Sequences Inhibits the Binding of the Methyl-CpG Binding Domain (MBD) of Methyl-CpG Binding Protein 2 (MeCP2). Nucleic Acids Res. 2004, 32, 4100–4108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mellén, M.; Ayata, P.; Dewell, S.; Kriaucionis, S.; Heintz, N. MeCP2 Binds to 5hmC Enriched within Active Genes and Accessible Chromatin in the Nervous System. Cell 2012, 151, 1417–1430. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, D.-Q.; Ali, I.; Tang, J.; Yang, W.-C. New Insights into 5hmC DNA Modification: Generation, Distribution and Function. Front. Genet. 2017, 8, 100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, B.; Zhang, C.; Zhang, X.; Fan, Y.; Zeng, H.; Liu, J.; Meng, H.; Bai, D.; Peng, J.; Zhang, Q.; et al. Tissue-Specific 5-Hydroxymethylcytosine Landscape of the Human Genome. Nat. Commun. 2021, 12, 4249. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nestor, C.E.; Ottaviano, R.; Reddington, J.; Sproul, D.; Reinhardt, D.; Dunican, D.; Katz, E.; Dixon, J.M.; Harrison, D.J.; Meehan, R.R. Tissue Type Is a Major Modifier of the 5-Hydroxymethylcytosine Content of Human Genes. Genome Res. 2012, 22, 467–477. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, W.; Liu, M. Distribution of 5-Hydroxymethylcytosine in Different Human Tissues. J. Nucleic Acids 2011, 2011, 870726. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, C.-X.; Szulwach, K.E.; Fu, Y.; Dai, Q.; Yi, C.; Li, X.; Li, Y.; Chen, C.-H.; Zhang, W.; Jian, X.; et al. Selective Chemical Labeling Reveals the Genome-Wide Distribution of 5-Hydroxymethylcytosine. Nat. Biotechnol. 2011, 29, 68–72. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Haffner, M.C.; Chaux, A.; Meeker, A.K.; Esopi, D.M.; Gerber, J.; Pellakuru, L.G.; Toubaji, A.; Argani, P.; Iacobuzio-Donahue, C.; Nelson, W.G.; et al. Global 5-Hydroxymethylcytosine Content Is Significantly Reduced in Tissue Stem/Progenitor Cell Compartments and in Human Cancers. Oncotarget 2011, 2, 627–637. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Munari, E.; Chaux, A.; Vaghasia, A.M.; Taheri, D.; Karram, S.; Bezerra, S.M.; Gonzalez Roibon, N.; Nelson, W.G.; Yegnasubramanian, S.; Netto, G.J.; et al. Global 5-Hydroxymethylcytosine Levels Are Profoundly Reduced in Multiple Genitourinary Malignancies. PLoS ONE 2016, 11, e0146302. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gambichler, T.; Sand, M.; Skrygan, M. Loss of 5-Hydroxymethylcytosine and Ten-Eleven Translocation 2 Protein Expression in Malignant Melanoma. Melanoma Res. 2013, 23, 218–220. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, C.-X.; Yin, S.; Ma, L.; Wheeler, A.; Chen, Y.; Zhang, Y.; Liu, B.; Xiong, J.; Zhang, W.; Hu, J.; et al. 5-Hydroxymethylcytosine Signatures in Cell-Free DNA Provide Information about Tumor Types and Stages. Cell Res. 2017, 27, 1231–1242. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, W.; Zhang, X.; Lu, X.; You, L.; Song, Y.; Luo, Z.; Zhang, J.; Nie, J.; Zheng, W.; Xu, D.; et al. 5-Hydroxymethylcytosine Signatures in Circulating Cell-Free DNA as Diagnostic Biomarkers for Human Cancers. Cell Res. 2017, 27, 1243–1257. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, J.; Han, X.; Gao, C.; Xing, Y.; Qi, Z.; Liu, R.; Wang, Y.; Zhang, X.; Yang, Y.-G.; Li, X.; et al. 5-Hydroxymethylome in Circulating Cell-Free DNA as A Potential Biomarker for Non-Small-Cell Lung Cancer. Genom. Proteom. Bioinform. 2018, 16, 187–199. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cai, J.; Chen, L.; Zhang, Z.; Zhang, X.; Lu, X.; Liu, W.; Shi, G.; Ge, Y.; Gao, P.; Yang, Y.; et al. Genome-Wide Mapping of 5-Hydroxymethylcytosines in Circulating Cell-Free DNA as a Non-Invasive Approach for Early Detection of Hepatocellular Carcinoma. Gut 2019, 68, 2195–2205. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Guler, G.D.; Ning, Y.; Ku, C.-J.; Phillips, T.; McCarthy, E.; Ellison, C.K.; Bergamaschi, A.; Collin, F.; Lloyd, P.; Scott, A.; et al. Detection of Early Stage Pancreatic Cancer Using 5-Hydroxymethylcytosine Signatures in Circulating Cell Free DNA. Nat. Commun. 2020, 11, 5270. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chiu, B.C.-H.; Zhang, Z.; You, Q.; Zeng, C.; Stepniak, E.; Bracci, P.M.; Yu, K.; Venkataraman, G.; Smith, S.M.; He, C.; et al. Prognostic Implications of 5-Hydroxymethylcytosines from Circulating Cell-Free DNA in Diffuse Large B-Cell Lymphoma. Blood Adv. 2019, 3, 2790–2799. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cai, Z.; Zhang, J.; He, Y.; Xia, L.; Dong, X.; Chen, G.; Zhou, Y.; Hu, X.; Zhong, S.; Wang, Y.; et al. Liquid Biopsy by Combining 5-Hydroxymethylcytosine Signatures of Plasma Cell-Free DNA and Protein Biomarkers for Diagnosis and Prognosis of Hepatocellular Carcinoma. ESMO Open 2021, 6, 100021. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shao, J.; Shah, S.; Ganguly, S.; Zu, Y.; He, C.; Li, Z. Classification of Acute Myeloid Leukemia by Cell-Free DNA 5-Hydroxymethylcytosine. Genes 2023, 14, 1180. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shao, J.; Xu, Y.; Olsen, R.J.; Kasparian, S.; Sun, K.; Mathur, S.; Zhang, J.; He, C.; Chen, S.-H.; Bernicker, E.H.; et al. 5-Hydroxymethylcytosine in Cell-Free DNA Predicts Immunotherapy Response in Lung Cancer. Cells 2024, 13, 715. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, P.; Lin, S.; Cai, M.; Zhu, Y.; Song, Y.; Sui, Y.; Lin, J.; Liu, J.; Lu, X.; Zhong, Y.; et al. 5-Hydroxymethylcytosine Profiling from Genomic and Cell-Free DNA for Colorectal Cancers Patients. J. Cell. Mol. Med. 2019, 23, 3530–3537. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Peng, D.; Ge, G.; Gong, Y.; Zhan, Y.; He, S.; Guan, B.; Li, Y.; Xu, Z.; Hao, H.; He, Z.; et al. Vitamin C Increases 5-Hydroxymethylcytosine Level and Inhibits the Growth of Bladder Cancer. Clin. Epigenet. 2018, 10, 94. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Applebaum, M.A.; Barr, E.K.; Karpus, J.; Nie, J.; Zhang, Z.; Armstrong, A.E.; Uppal, S.; Sukhanova, M.; Zhang, W.; Chlenski, A.; et al. 5-Hydroxymethylcytosine Profiles Are Prognostic of Outcome in Neuroblastoma and Reveal Transcriptional Networks That Correlate with Tumor Phenotype. JCO Precis. Oncol. 2019, 3, 1–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ramasamy, D.; Rao, A.K.D.M.; Balaiah, M.; Vittal Rangan, A.; Sundersingh, S.; Veluswami, S.; Thangarajan, R.; Mani, S. Locus-Specific Enrichment Analysis of 5-Hydroxymethylcytosine Reveals Novel Genes Associated with Breast Carcinogenesis. Cells 2022, 11, 2939. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Z.; Shi, X.; Guo, L.; Li, Y.; Luo, M.; He, J. Decreased 5-Hydroxymethylcytosine Levels Correlate with Cancer Progression and Poor Survival: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. Oncotarget 2016, 8, 1944–1952. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dong, Z.-R.; Zhang, C.; Cai, J.-B.; Zhang, P.-F.; Shi, G.-M.; Gao, D.-M.; Sun, H.-C.; Qiu, S.-J.; Zhou, J.; Ke, A.-W.; et al. Role of 5-Hydroxymethylcytosine Level in Diagnosis and Prognosis Prediction of Intrahepatic Cholangiocarcinoma. Tumour Biol. J. Int. Soc. Oncodev. Biol. Med. 2015, 36, 2763–2771. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liao, Y.; Gu, J.; Wu, Y.; Long, X.; Ge, D.I.; Xu, J.; Ding, J. Low Level of 5-Hydroxymethylcytosine Predicts Poor Prognosis in Non-Small Cell Lung Cancer. Oncol. Lett. 2016, 11, 3753–3760. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, Y.; Wu, K.; Shao, Y.; Sui, F.; Yang, Q.; Shi, B.; Hou, P.; Ji, M. Decreased 5-Hydroxymethylcytosine (5-hmC) Predicts Poor Prognosis in Early-Stage Laryngeal Squamous Cell Carcinoma. Am. J. Cancer Res. 2016, 6, 1089–1098. [Google Scholar]
- Qiu, L.; Liu, F.; Yi, S.; Li, X.; Liu, X.; Xiao, C.; Lian, C.G.; Tu, P.; Wang, Y. Loss of 5-Hydroxymethylcytosine Is an Epigenetic Biomarker in Cutaneous T-Cell Lymphoma. J. Investig. Dermatol. 2018, 138, 2388–2397. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ren, Y.; Zhang, Z.; She, Y.; He, Y.; Li, D.; Shi, Y.; He, C.; Yang, Y.; Zhang, W.; Chen, C. A Highly Sensitive and Specific Non-Invasive Test through Genome-Wide 5-Hydroxymethylation Mapping for Early Detection of Lung Cancer. Small Methods 2023, 8, e2300747. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bhattacharyya, S.; Pradhan, K.; Campbell, N.; Mazdo, J.; Vasantkumar, A.; Maqbool, S.; Bhagat, T.D.; Gupta, S.; Suzuki, M.; Yu, Y.; et al. Altered Hydroxymethylation Is Seen at Regulatory Regions in Pancreatic Cancer and Regulates Oncogenic Pathways. Genome Res. 2017, 27, 1830–1842. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shao, J.; Bernicker, E.H.; He, C.; Li, Z. Cell-Free DNA 5-Hydroxymethylcytosine as a Marker for Common Cancer Detection. Clin. Transl. Discov. 2022, 2, e136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sjöström, M.; Zhao, S.G.; Levy, S.; Zhang, M.; Ning, Y.; Shrestha, R.; Lundberg, A.; Herberts, C.; Foye, A.; Aggarwal, R.; et al. The 5-Hydroxymethylcytosine Landscape of Prostate Cancer. Cancer Res. 2022, 82, 3888–3902. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fu, Y.; Jiang, J.; Wu, Y.; Cao, D.; Jia, Z.; Zhang, Y.; Li, D.; Cui, Y.; Zhang, Y.; Cao, X. Genome-Wide 5-Hydroxymethylcytosines in Circulating Cell-Free DNA as Noninvasive Diagnostic Markers for Gastric Cancer. Gastric Cancer Off. J. Int. Gastric Cancer Assoc. Jpn. Gastric Cancer Assoc. 2024, 27, 735–746. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wagner, M.; Steinbacher, J.; Kraus, T.F.J.; Michalakis, S.; Hackner, B.; Pfaffeneder, T.; Perera, A.; Müller, M.; Giese, A.; Kretzschmar, H.A.; et al. Age-Dependent Levels of 5-Methyl-, 5-Hydroxymethyl-, and 5-Formylcytosine in Human and Mouse Brain Tissues. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2015, 54, 12511–12514. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kriaucionis, S.; Heintz, N. The Nuclear DNA Base 5-Hydroxymethylcytosine Is Present in Purkinje Neurons and the Brain. Science 2009, 324, 929–930. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kroeze, L.I.; Aslanyan, M.G.; van Rooij, A.; Koorenhof-Scheele, T.N.; Massop, M.; Carell, T.; Boezeman, J.B.; Marie, J.-P.; Halkes, C.J.M.; de Witte, T.; et al. Characterization of Acute Myeloid Leukemia Based on Levels of Global Hydroxymethylation. Blood 2014, 124, 1110–1118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shahal, T.; Green, O.; Hananel, U.; Michaeli, Y.; Shabat, D.; Ebenstein, Y. Simple and Cost-Effective Fluorescent Labeling of 5-Hydroxymethylcytosine. Methods Appl. Fluoresc. 2016, 4, 044003. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Berney, M.; McGouran, J.F. Methods for Detection of Cytosine and Thymine Modifications in DNA. Nat. Rev. Chem. 2018, 2, 332–348. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zeng, C.; Stroup, E.K.; Zhang, Z.; Chiu, B.C.-H.; Zhang, W. Towards Precision Medicine: Advances in 5-Hydroxymethylcytosine Cancer Biomarker Discovery in Liquid Biopsy. Cancer Commun. 2019, 39, 12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, T.; Loo, C.E.; Kohli, R.M. Enzymatic Approaches for Profiling Cytosine Methylation and Hydroxymethylation. Mol. Metab. 2022, 57, 101314. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- He, B.; Yao, H.; Yi, C. Advances in the Joint Profiling Technologies of 5mC and 5hmC. RSC Chem. Biol. 2024, 5, 500–507. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Frommer, M.; McDonald, L.E.; Millar, D.S.; Collis, C.M.; Watt, F.; Grigg, G.W.; Molloy, P.L.; Paul, C.L. A Genomic Sequencing Protocol That Yields a Positive Display of 5-Methylcytosine Residues in Individual DNA Strands. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 1992, 89, 1827–1831. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Booth, M.J.; Branco, M.R.; Ficz, G.; Oxley, D.; Krueger, F.; Reik, W.; Balasubramanian, S. Quantitative Sequencing of 5-Methylcytosine and 5-Hydroxymethylcytosine at Single-Base Resolution. Science 2012, 336, 934–937. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stewart, S.K.; Morris, T.J.; Guilhamon, P.; Bulstrode, H.; Bachman, M.; Balasubramanian, S.; Beck, S. oxBS-450K: A Method for Analysing Hydroxymethylation Using 450K BeadChips. Methods 2015, 72, 9–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Matsushita, T.; Moriyama, Y.; Nagae, G.; Aburatani, H.; Okamoto, A. DNA-Friendly Cu(Ii)/TEMPO-Catalyzed 5-Hydroxymethylcytosine-Specific Oxidation. Chem. Commun. 2017, 53, 5756–5759. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fukuzawa, S.; Takahashi, S.; Tachibana, K.; Tajima, S.; Suetake, I. Simple and Accurate Single Base Resolution Analysis of 5-Hydroxymethylcytosine by Catalytic Oxidative Bisulfite Sequencing Using Micelle Incarcerated Oxidants. Bioorg. Med. Chem. 2016, 24, 4254–4262. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Skvortsova, K.; Zotenko, E.; Luu, P.-L.; Gould, C.M.; Nair, S.S.; Clark, S.J.; Stirzaker, C. Comprehensive Evaluation of Genome-Wide 5-Hydroxymethylcytosine Profiling Approaches in Human DNA. Epigenet. Chromatin 2017, 10, 16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, M.; Hon, G.C.; Szulwach, K.E.; Song, C.-X.; Zhang, L.; Kim, A.; Li, X.; Dai, Q.; Shen, Y.; Park, B.; et al. Base-Resolution Analysis of 5-Hydroxymethylcytosine in the Mammalian Genome. Cell 2012, 149, 1368–1380. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Moran, S.; Arribas, C.; Esteller, M. Validation of a DNA Methylation Microarray for 850,000 CpG Sites of the Human Genome Enriched in Enhancer Sequences. Epigenomics 2016, 8, 389–399. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hahn, M.A.; Li, A.X.; Wu, X.; Pfeifer, G.P. Single Base Resolution Analysis of 5-Methylcytosine and 5-Hydroxymethylcytosine by RRBS and TAB-RRBS. Methods Mol. Biol. 2015, 1238, 273–287. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pastor, W.A.; Huang, Y.; Henderson, H.R.; Agarwal, S.; Rao, A. The GLIB Technique for Genome-Wide Mapping of 5-Hydroxymethylcytosine. Nat. Protoc. 2012, 7, 1909–1917. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Robertson, A.B.; Dahl, J.A.; Ougland, R.; Klungland, A. Pull-down of 5-Hydroxymethylcytosine DNA Using JBP1-Coated Magnetic Beads. Nat. Protoc. 2012, 7, 340–350. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cui, L.; Chung, T.H.; Tan, D.; Sun, X.; Jia, X.-Y. JBP1-Seq: A Fast and Efficient Method for Genome-Wide Profiling of 5hmC. Genomics 2014, 104, 368–375. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nestor, C.E.; Meehan, R.R. Hydroxymethylated DNA Immunoprecipitation (hmeDIP). Methods Mol. Biol. 2014, 1094, 259–267. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, Y.; Pastor, W.A.; Zepeda-Martínez, J.A.; Rao, A. The Anti-CMS Technique for Genome-Wide Mapping of 5-Hydroxymethylcytosine. Nat. Protoc. 2012, 7, 1897–1908. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schutsky, E.K.; DeNizio, J.E.; Hu, P.; Liu, M.Y.; Nabel, C.S.; Fabyanic, E.B.; Hwang, Y.; Bushman, F.D.; Wu, H.; Kohli, R.M. Nondestructive, Base-Resolution Sequencing of 5-Hydroxymethylcytosine Using a DNA Deaminase. Nat. Biotechnol. 2018, 36, 1083–1090. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Skvortsova, K.; Bogdanovic, O. TAB-Seq and ACE-Seq Data Processing for Genome-Wide DNA Hydroxymethylation Profiling. Methods Mol. Biol. 2021, 2272, 163–178. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vaisvila, R.; Ponnaluri, V.K.C.; Sun, Z.; Langhorst, B.W.; Saleh, L.; Guan, S.; Dai, N.; Campbell, M.A.; Sexton, B.S.; Marks, K.; et al. Enzymatic Methyl Sequencing Detects DNA Methylation at Single-Base Resolution from Picograms of DNA. Genome Res. 2021, 31, 1280–1289. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zeng, H.; He, B.; Xia, B.; Bai, D.; Lu, X.; Cai, J.; Chen, L.; Zhou, A.; Zhu, C.; Meng, H.; et al. Bisulfite-Free, Nanoscale Analysis of 5-Hydroxymethylcytosine at Single Base Resolution. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2018, 140, 13190–13194. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.; Siejka-Zielińska, P.; Velikova, G.; Bi, Y.; Yuan, F.; Tomkova, M.; Bai, C.; Chen, L.; Schuster-Böckler, B.; Song, C.-X. Bisulfite-Free Direct Detection of 5-Methylcytosine and 5-Hydroxymethylcytosine at Base Resolution. Nat. Biotechnol. 2019, 37, 424–429. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, L.; Liu, Y.; Han, S.; Yang, L.; Cui, X.; Gao, Y.; Dai, Q.; Lu, X.; Kou, X.; Zhao, Y.; et al. Jump-Seq: Genome-Wide Capture and Amplification of 5-Hydroxymethylcytosine Sites. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2019, 141, 8694–8697. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gibas, P.; Narmontė, M.; Staševskij, Z.; Gordevičius, J.; Klimašauskas, S.; Kriukienė, E. Precise Genomic Mapping of 5-Hydroxymethylcytosine via Covalent Tether-Directed Sequencing. PLoS Biol. 2020, 18, e3000684. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, X.; Shi, X.; Gong, Y.; Guo, W.; Liu, Y.; Peng, C.; Xu, Y. Selective Chemical Labeling and Sequencing of 5-Hydroxymethylcytosine in DNA at Single-Base Resolution. Front. Genet. 2021, 12, 749211. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xie, N.-B.; Wang, M.; Chen, W.; Ji, T.-T.; Guo, X.; Gang, F.-Y.; Wang, Y.-F.; Feng, Y.-Q.; Liang, Y.; Ci, W.; et al. Whole-Genome Sequencing of 5-Hydroxymethylcytosine at Base Resolution by Bisulfite-Free Single-Step Deamination with Engineered Cytosine Deaminase. ACS Cent. Sci. 2023, 9, 2315–2325. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Flusberg, B.A.; Webster, D.R.; Lee, J.H.; Travers, K.J.; Olivares, E.C.; Clark, T.A.; Korlach, J.; Turner, S.W. Direct Detection of DNA Methylation during Single-Molecule, Real-Time Sequencing. Nat. Methods 2010, 7, 461–465. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, C.-X.; Clark, T.A.; Lu, X.-Y.; Kislyuk, A.; Dai, Q.; Turner, S.W.; He, C.; Korlach, J. Sensitive and Specific Single-Molecule Sequencing of 5-Hydroxymethylcytosine. Nat. Methods 2011, 9, 75–77. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Füllgrabe, J.; Gosal, W.S.; Creed, P.; Liu, S.; Lumby, C.K.; Morley, D.J.; Ost, T.W.B.; Vilella, A.J.; Yu, S.; Bignell, H.; et al. Simultaneous Sequencing of Genetic and Epigenetic Bases in DNA. Nat. Biotechnol. 2023, 41, 1457–1464. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Viswanathan, R.; Cheruba, E.; Wong, P.-M.; Yi, Y.; Ngang, S.; Chong, D.Q.; Loh, Y.-H.; Tan, I.B.; Cheow, L.F. DARESOME Enables Concurrent Profiling of Multiple DNA Modifications with Restriction Enzymes in Single Cells and Cell-Free DNA. Sci. Adv. 2023, 9, eadi0197. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bai, D.; Zhang, X.; Xiang, H.; Guo, Z.; Zhu, C.; Yi, C. Simultaneous Single-Cell Analysis of 5mC and 5hmC with SIMPLE-Seq. Nat. Biotechnol. 2024. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fabyanic, E.B.; Hu, P.; Qiu, Q.; Berríos, K.N.; Connolly, D.R.; Wang, T.; Flournoy, J.; Zhou, Z.; Kohli, R.M.; Wu, H. Joint Single-Cell Profiling Resolves 5mC and 5hmC and Reveals Their Distinct Gene Regulatory Effects. Nat. Biotechnol. 2024, 42, 960–974. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chialastri, A.; Sarkar, S.; Schauer, E.E.; Lamba, S.; Dey, S.S. Combinatorial Quantification of 5mC and 5hmC at Individual CpG Dyads and the Transcriptome in Single Cells Reveals Modulators of DNA Methylation Maintenance Fidelity. Nat. Struct. Mol. Biol. 2024, 31, 1296–1308. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, Y.; Pastor, W.A.; Shen, Y.; Tahiliani, M.; Liu, D.R.; Rao, A. The Behaviour of 5-Hydroxymethylcytosine in Bisulfite Sequencing. PLoS ONE 2010, 5, e8888. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, X.; Liu, Y.; Salz, T.; Hansen, K.D.; Feinberg, A. Whole-Genome Analysis of the Methylome and Hydroxymethylome in Normal and Malignant Lung and Liver. Genome Res. 2016, 26, 1730–1741. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Booth, M.J.; Ost, T.W.B.; Beraldi, D.; Bell, N.M.; Branco, M.R.; Reik, W.; Balasubramanian, S. Oxidative Bisulfite Sequencing of 5-Methylcytosine and 5-Hydroxymethylcytosine. Nat. Protoc. 2013, 8, 1841–1851. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Janku, F.; Huang, H.J.; Pereira, D.Y.; Kobayashi, M.; Chiu, C.H.; Call, S.G.; Woodbury, K.T.; Chao, F.; Marshak, D.R.; Chiu, R.Y.T. A Novel Method for Liquid-Phase Extraction of Cell-Free DNA for Detection of Circulating Tumor DNA. Sci. Rep. 2021, 11, 19653. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tanaka, K.; Okamoto, A. Degradation of DNA by Bisulfite Treatment. Bioorg. Med. Chem. Lett. 2007, 17, 1912–1915. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Szwagierczak, A.; Bultmann, S.; Schmidt, C.S.; Spada, F.; Leonhardt, H. Sensitive Enzymatic Quantification of 5-Hydroxymethylcytosine in Genomic DNA. Nucleic Acids Res. 2010, 38, e181. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shahal, T.; Koren, O.; Shefer, G.; Stern, N.; Ebenstein, Y. Hypersensitive Quantification of Global 5-Hydroxymethylcytosine by Chemoenzymatic Tagging. Anal. Chim. Acta 2018, 1038, 87–96. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, X.; Luo, K.; Shi, H.; Yan, X.; Huang, R.; Zhao, B.; Zhang, J.; Xie, D.; Zhang, W. Integrated 5-Hydroxymethylcytosine and Fragmentation Signatures as Enhanced Biomarkers in Lung Cancer. Clin. Epigenet. 2022, 14, 15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thomson, J.P.; Hunter, J.M.; Nestor, C.E.; Dunican, D.S.; Terranova, R.; Moggs, J.G.; Meehan, R.R. Comparative Analysis of Affinity-Based 5-Hydroxymethylation Enrichment Techniques. Nucleic Acids Res. 2013, 41, e206. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gordevičius, J.; Narmontė, M.; Gibas, P.; Kvederavičiūtė, K.; Tomkutė, V.; Paluoja, P.; Krjutškov, K.; Salumets, A.; Kriukienė, E. Identification of Fetal Unmodified and 5-Hydroxymethylated CG Sites in Maternal Cell-Free DNA for Non-Invasive Prenatal Testing. Clin. Epigenet. 2020, 12, 153. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Siriwardena, S.; Chen, K.; Bhagwat, A.S. The Functions and Malfunctions of AID/APOBEC Family Deaminases: The Known Knowns and the Known Unknowns. Chem. Rev. 2016, 116, 12688–12710. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Siejka-Zielińska, P.; Cheng, J.; Jackson, F.; Liu, Y.; Soonawalla, Z.; Reddy, S.; Silva, M.; Puta, L.; McCain, M.V.; Culver, E.L.; et al. Cell-Free DNA TAPS Provides Multimodal Information for Early Cancer Detection. Sci. Adv. 2021, 7, eabh0534. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, H.-Q.; Chen, D.-J.; Li, Y.; Yuan, W.-B.; Fan, J.; Zhang, Z.; Han, F.; Jiang, X.; Chen, J.-P.; Wang, D.-D.; et al. Epigenetic Silencing of TET1 Mediated Hydroxymethylation of Base Excision Repair Pathway during Lung Carcinogenesis. Environ. Pollut. 2021, 268, 115860. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gabrieli, T.; Sharim, H.; Nifker, G.; Jeffet, J.; Shahal, T.; Arielly, R.; Levi-Sakin, M.; Hoch, L.; Arbib, N.; Michaeli, Y.; et al. Epigenetic Optical Mapping of 5-Hydroxymethylcytosine in Nanochannel Arrays. ACS Nano 2018, 12, 7148–7158. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Laszlo, A.H.; Derrington, I.M.; Brinkerhoff, H.; Langford, K.W.; Nova, I.C.; Samson, J.M.; Bartlett, J.J.; Pavlenok, M.; Gundlach, J.H. Detection and Mapping of 5-Methylcytosine and 5-Hydroxymethylcytosine with Nanopore MspA. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2013, 110, 18904–18909. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Du, Y.; Wang, Y.; Hu, X.; Liu, J.; Diao, J. Single-Molecule Quantification of 5-Methylcytosine and 5-Hydroxymethylcytosine in Cancer Genome. View 2020, 1, e9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Scarano, C.; Veneruso, I.; De Simone, R.R.; Di Bonito, G.; Secondino, A.; D’Argenio, V. The Third-Generation Sequencing Challenge: Novel Insights for the Omic Sciences. Biomolecules 2024, 14, 568. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cao, Y.; Bai, Y.; Yuan, T.; Song, L.; Fan, Y.; Ren, L.; Song, W.; Peng, J.; An, R.; Gu, Q.; et al. Single-Cell Bisulfite-Free 5mC and 5hmC Sequencing with High Sensitivity and Scalability. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2023, 120, e2310367120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chang, W.; Zhang, Z.; Jia, B.; Ding, K.-F.; Pan, Z.; Su, G.; Zhang, W.; Liu, T.; Zhong, Y.; He, G.; et al. A 5-Hydroxymethylcytosine-Based Non-Invasive Model for Early Detection of Colorectal Carcinomas and Advanced Adenomas: The METHOD-2 Study. Clin. Cancer Res. Off. J. Am. Assoc. Cancer Res. 2024, 30, 3337–3348. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fu, Y.-L.; Wu, Y.-H.; Cao, D.-H.; Jia, Z.-F.; Shen, A.; Jiang, J.; Cao, X.-Y. Increased 5-Hydroxymethylcytosine Is a Favorable Prognostic Factor of Helicobacter Pylori-Negative Gastric Cancer Patients. World J. Gastrointest. Oncol. 2022, 14, 1295–1306. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kuang, L.; Zhang, J.; Li, Y.; Wang, Q.; Liu, J.; Zhang, B. Association of Tet Methylcytosine Dioxygenase 2 and 5-Hydroxymethylcytosine in Endometrioid Adenocarcinoma and Its Clinical Significance. BMC Women’s Health 2024, 24, 188. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shao, J.; Olsen, R.J.; Kasparian, S.; He, C.; Bernicker, E.H.; Li, Z. Cell-Free DNA 5-Hydroxymethylcytosine Signatures for Lung Cancer Prognosis. Cells 2024, 13, 298. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, X.-J.; Huang, X.-Y.; Yang, X.; Lu, J.-C.; Wei, C.-Y.; Gao, C.; Pei, Y.-Z.; Chen, Y.; Sun, Q.-M.; Cai, J.-B.; et al. Loss of 5-Hydroxymethylcytosine Induces Chemotherapy Resistance in Hepatocellular Carcinoma via the 5-hmC/PCAF/AKT Axis. Cell Death Dis. 2023, 14, 79. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, H.-Y.; Zhang, W.-L.; Zhang, L.; Yang, P.; Li, F.; Yang, Z.-R.; Wang, J.; Pang, M.; Hong, Y.; Yan, C.; et al. 5-Hydroxymethylcytosine Profiles of cfDNA Are Highly Predictive of R-CHOP Treatment Response in Diffuse Large B Cell Lymphoma Patients. Clin. Epigenet. 2021, 13, 33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guler, G.D.; Ning, Y.; Coruh, C.; Mognol, G.P.; Phillips, T.; Nabiyouni, M.; Hazen, K.; Scott, A.; Volkmuth, W.; Levy, S. Plasma Cell-Free DNA Hydroxymethylation Profiling Reveals Anti-PD-1 Treatment Response and Resistance Biology in Non-Small Cell Lung Cancer. J. Immunother. Cancer 2024, 12, e008028. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, Z.; Pi, X.; Gao, C.; Zhang, J.; Xia, L.; Yan, X.; Hu, X.; Yan, Z.; Zhang, S.; Wei, A.; et al. Integrated Fragmentomic Profile and 5-Hydroxymethylcytosine of Capture-Based Low-Pass Sequencing Data Enables Pan-Cancer Detection via cfDNA. Transl. Oncol. 2023, 34, 101694. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, Z.-D.; Han, X.-X.; Song, Z.-J.; Dong, Y.; Pang, K.; Wang, X.-L.; Liu, X.-Y.; Lu, H.; Xu, G.-Z.; Hao, L.; et al. Integrative Multi-Omics Analysis Depicts the Methylome and Hydroxymethylome in Recurrent Bladder Cancers and Identifies Biomarkers for Predicting PD-L1 Expression. Biomark. Res. 2023, 11, 47. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kilgour, E.; Rothwell, D.G.; Brady, G.; Dive, C. Liquid Biopsy-Based Biomarkers of Treatment Response and Resistance. Cancer Cell 2020, 37, 485–495. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, S.; Zhang, J.; Hu, X.; Yin, S.; Yuan, Y.; Xia, L.; Cao, F.; Yan, X.; Yan, Z.; Mao, Q.; et al. Noninvasive Detection of Brain Gliomas Using Plasma Cell-Free DNA 5-Hydroxymethylcytosine Sequencing. Int. J. Cancer 2023, 152, 1707–1718. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Storebjerg, T.M.; Strand, S.H.; Høyer, S.; Lynnerup, A.-S.; Borre, M.; Ørntoft, T.F.; Sørensen, K.D. Dysregulation and Prognostic Potential of 5-Methylcytosine (5mC), 5-Hydroxymethylcytosine (5hmC), 5-Formylcytosine (5fC), and 5-Carboxylcytosine (5caC) Levels in Prostate Cancer. Clin. Epigenet. 2018, 10, 105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Azizgolshani, N.; Petersen, C.L.; Chen, Y.; Levy, J.J.; Salas, L.A.; Perreard, L.; Nguyen, L.N.; Christensen, B.C. DNA 5-Hydroxymethylcytosine in Pediatric Central Nervous System Tumors May Impact Tumor Classification and Is a Positive Prognostic Marker. Clin. Epigenet. 2021, 13, 176. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shen, Y.; Wang, L.; Ou, J.; Wang, B.; Cen, X. Loss of 5-Hydroxymethylcytosine as a Poor Prognostic Factor for Primary Testicular Diffuse Large B-Cell Lymphoma. Int. J. Med. Sci. 2022, 19, 225–232. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sharma, A.E.; Olivas, A.; Parilla, M.; Yassan, L.; Wang, H.; Zhang, S.S.; Weber, C.; Keutgen, X.M.; Hart, J.; Krausz, T.; et al. Epigenetic Dysregulation of 5-Hydroxymethylcytosine in Well-Differentiated Pancreatic Neuroendocrine Tumors. Appl. Immunohistochem. Mol. Morphol. AIMM 2022, 30, e11–e15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wu, H.-X.; Chen, Y.-X.; Wang, Z.-X.; Zhao, Q.; He, M.-M.; Wang, Y.-N.; Wang, F.; Xu, R.-H. Alteration in TET1 as Potential Biomarker for Immune Checkpoint Blockade in Multiple Cancers. J. Immunother. Cancer 2019, 7, 264. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Peng, D.; He, A.; He, S.; Ge, G.; Wang, S.; Ci, W.; Li, X.; Xia, D.; Zhou, L. Ascorbic Acid Induced TET2 Enzyme Activation Enhances Cancer Immunotherapy Efficacy in Renal Cell Carcinoma. Int. J. Biol. Sci. 2022, 18, 995–1007. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, N.; Zhang, J.; Yan, M.; Chen, L.; Wu, J.; Tao, Q.; Yan, B.; Chen, X.; Peng, C. Supplementation with α-Ketoglutarate Improved the Efficacy of Anti-PD1 Melanoma Treatment through Epigenetic Modulation of PD-L1. Cell Death Dis. 2023, 14, 170. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Doroshow, D.B.; Sanmamed, M.F.; Hastings, K.; Politi, K.; Rimm, D.L.; Chen, L.; Melero, I.; Schalper, K.A.; Herbst, R.S. Immunotherapy in Non-Small Cell Lung Cancer: Facts and Hopes. Clin. Cancer Res. Off. J. Am. Assoc. Cancer Res. 2019, 25, 4592–4602. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chakraborty, S.; Sharma, G.; Karmakar, S.; Banerjee, S. Multi-OMICS Approaches in Cancer Biology: New Era in Cancer Therapy. Biochim. Biophys. Acta Mol. Basis Dis. 2024, 1870, 167120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Penny, L.; Main, S.C.; De Michino, S.D.; Bratman, S.V. Chromatin- and Nucleosome-Associated Features in Liquid Biopsy: Implications for Cancer Biomarker Discovery. Biochem. Cell Biol. 2024, 102, 291–298. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hudecova, I.; Smith, C.G.; Hänsel-Hertsch, R.; Chilamakuri, C.S.; Morris, J.A.; Vijayaraghavan, A.; Heider, K.; Chandrananda, D.; Cooper, W.N.; Gale, D.; et al. Characteristics, Origin, and Potential for Cancer Diagnostics of Ultrashort Plasma Cell-Free DNA. Genome Res. 2022, 32, 215–227. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, L.; Abou-Alfa, G.K.; Zheng, B.; Liu, J.-F.; Bai, J.; Du, L.-T.; Qian, Y.-S.; Fan, R.; Liu, X.-L.; Wu, L.; et al. Genome-Scale Profiling of Circulating Cell-Free DNA Signatures for Early Detection of Hepatocellular Carcinoma in Cirrhotic Patients. Cell Res. 2021, 31, 589–592. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Walker, N.J.; Rashid, M.; Yu, S.; Bignell, H.; Lumby, C.K.; Livi, C.M.; Howell, K.; Morley, D.J.; Morganella, S.; Barrell, D.; et al. Hydroxymethylation Profile of Cell-Free DNA Is a Biomarker for Early Colorectal Cancer. Sci. Rep. 2022, 12, 16566. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kamdar, S.N.; Ho, L.T.; Kron, K.J.; Isserlin, R.; van der Kwast, T.; Zlotta, A.R.; Fleshner, N.E.; Bader, G.; Bapat, B. Dynamic Interplay between Locus-Specific DNA Methylation and Hydroxymethylation Regulates Distinct Biological Pathways in Prostate Carcinogenesis. Clin. Epigenet. 2016, 8, 32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dang, Y.; Xu, R.; Pan, J.; Xiao, X.; Zhang, S.; Zhou, W.; Xu, Y.; Ji, G. Dynamic Changes in DNA Methylation and Hydroxymethylation Revealed the Transformation of Advanced Adenoma into Colorectal Carcinoma. Clin. Transl. Med. 2023, 13, e1202. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Delhommeau, F.; Dupont, S.; Della Valle, V.; James, C.; Trannoy, S.; Massé, A.; Kosmider, O.; Le Couedic, J.-P.; Robert, F.; Alberdi, A.; et al. Mutation in TET2 in Myeloid Cancers. N. Engl. J. Med. 2009, 360, 2289–2301. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abdel-Wahab, O.; Mullally, A.; Hedvat, C.; Garcia-Manero, G.; Patel, J.; Wadleigh, M.; Malinge, S.; Yao, J.; Kilpivaara, O.; Bhat, R.; et al. Genetic Characterization of TET1, TET2, and TET3 Alterations in Myeloid Malignancies. Blood 2009, 114, 144–147. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ko, M.; Huang, Y.; Jankowska, A.M.; Pape, U.J.; Tahiliani, M.; Bandukwala, H.S.; An, J.; Lamperti, E.D.; Koh, K.P.; Ganetzky, R.; et al. Impaired Hydroxylation of 5-Methylcytosine in Myeloid Cancers with Mutant TET2. Nature 2010, 468, 839–843. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lian, C.G.; Xu, Y.; Ceol, C.; Wu, F.; Larson, A.; Dresser, K.; Xu, W.; Tan, L.; Hu, Y.; Zhan, Q.; et al. Loss of 5-Hydroxymethylcytosine Is an Epigenetic Hallmark of Melanoma. Cell 2012, 150, 1135–1146. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boudra, R.; Woappi, Y.; Wang, D.; Xu, S.; Wells, M.; Schmults, C.D.; Lian, C.G.; Ramsey, M.R. Regulation of 5-Hydroxymethylcytosine by TET2 Contributes to Squamous Cell Carcinoma Tumorigenesis. J. Investig. Dermatol. 2022, 142, 1270–1279.e2. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alrehaili, A.A.; Gharib, A.F.; Alghamdi, S.A.; Alhazmi, A.; Al-Shehri, S.S.; Hagag, H.M.; Alsaeedi, F.A.; Alhuthali, H.M.; Raafat, N.; Etewa, R.L.; et al. Evaluation of TET Family Gene Expression and 5-Hydroxymethylcytosine as Potential Epigenetic Markers in Non-Small Cell Lung Cancer. In Vivo 2023, 37, 445–453. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheng, G.; Wu, J.; Ji, M.; Hu, W.; Wu, C.; Jiang, J. TET2 Inhibits the Proliferation and Metastasis of Lung Adenocarcinoma Cells via Activation of the cGAS-STING Signalling Pathway. BMC Cancer 2023, 23, 825. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pavlovic, V.; Ciric, M.; Petkovic, M.; Golubovic, M. Vitamin C and Epigenetics: A Short Physiological Overview. Open Med. 2023, 18, 20230688. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, X.; Hu, C.; Ferchen, K.; Nie, J.; Cui, X.; Chen, C.-H.; Cheng, L.; Zuo, Z.; Seibel, W.; He, C.; et al. Targeted Inhibition of STAT/TET1 Axis as a Therapeutic Strategy for Acute Myeloid Leukemia. Nat. Commun. 2017, 8, 2099. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Choudhury, S.R.; Cui, Y.; Lubecka, K.; Stefanska, B.; Irudayaraj, J. CRISPR-dCas9 Mediated TET1 Targeting for Selective DNA Demethylation at BRCA1 Promoter. Oncotarget 2016, 7, 46545–46556. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Morita, S.; Noguchi, H.; Horii, T.; Nakabayashi, K.; Kimura, M.; Okamura, K.; Sakai, A.; Nakashima, H.; Hata, K.; Nakashima, K.; et al. Targeted DNA Demethylation in Vivo Using dCas9-Peptide Repeat and scFv-TET1 Catalytic Domain Fusions. Nat. Biotechnol. 2016, 34, 1060–1065. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, X.; Tan, X.; Tampe, B.; Wilhelmi, T.; Hulshoff, M.S.; Saito, S.; Moser, T.; Kalluri, R.; Hasenfuss, G.; Zeisberg, E.M.; et al. High-Fidelity CRISPR/Cas9- Based Gene-Specific Hydroxymethylation Rescues Gene Expression and Attenuates Renal Fibrosis. Nat. Commun. 2018, 9, 3509. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nguyen, T.V.; Lister, R. Genomic Targeting of TET Activity for Targeted Demethylation Using CRISPR/Cas9. Methods Mol. Biol. 2021, 2272, 181–194. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bayliak, M.M.; Lushchak, V.I. Pleiotropic Effects of α-Ketoglutarate as a Potential Anti-Ageing Agent. Ageing Res. Rev. 2021, 66, 101237. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, W.; Yang, H.; Liu, Y.; Yang, Y.; Wang, P.; Kim, S.-H.; Ito, S.; Yang, C.; Wang, P.; Xiao, M.-T.; et al. Oncometabolite 2-Hydroxyglutarate Is a Competitive Inhibitor of α-Ketoglutarate-Dependent Dioxygenases. Cancer Cell 2011, 19, 17–30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, S.; Liu, Y.; Cai, S.J.; Qian, M.; Ding, J.; Larion, M.; Gilbert, M.R.; Yang, C. IDH Mutation in Glioma: Molecular Mechanisms and Potential Therapeutic Targets. Br. J. Cancer 2020, 122, 1580–1589. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jin, S.-G.; Jiang, Y.; Qiu, R.; Rauch, T.A.; Wang, Y.; Schackert, G.; Krex, D.; Lu, Q.; Pfeifer, G.P. 5-Hydroxymethylcytosine Is Strongly Depleted in Human Cancers but Its Levels Do Not Correlate with IDH1 Mutations. Cancer Res. 2011, 71, 7360–7365. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Minor, E.A.; Court, B.L.; Young, J.I.; Wang, G. Ascorbate Induces Ten-Eleven Translocation (Tet) Methylcytosine Dioxygenase-Mediated Generation of 5-Hydroxymethylcytosine. J. Biol. Chem. 2013, 288, 13669–13674. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yin, R.; Mao, S.-Q.; Zhao, B.; Chong, Z.; Yang, Y.; Zhao, C.; Zhang, D.; Huang, H.; Gao, J.; Li, Z.; et al. Ascorbic Acid Enhances Tet-Mediated 5-Methylcytosine Oxidation and Promotes DNA Demethylation in Mammals. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2013, 135, 10396–10403. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Agathocleous, M.; Meacham, C.E.; Burgess, R.J.; Piskounova, E.; Zhao, Z.; Crane, G.M.; Cowin, B.L.; Bruner, E.; Murphy, M.M.; Chen, W.; et al. Ascorbate Regulates Haematopoietic Stem Cell Function and Leukaemogenesis. Nature 2017, 549, 476–481. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gustafson, C.B.; Yang, C.; Dickson, K.M.; Shao, H.; Van Booven, D.; Harbour, J.W.; Liu, Z.-J.; Wang, G. Epigenetic Reprogramming of Melanoma Cells by Vitamin C Treatment. Clin. Epigenet. 2015, 7, 51. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, H.; Park, K.U. Clinical Circulating Tumor DNA Testing for Precision Oncology. Cancer Res. Treat. Off. J. Korean Cancer Assoc. 2023, 55, 351–366. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fiala, C.; Diamandis, E.P. Utility of Circulating Tumor DNA in Cancer Diagnostics with Emphasis on Early Detection. BMC Med. 2018, 16, 166. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kustanovich, A.; Schwartz, R.; Peretz, T.; Grinshpun, A. Life and Death of Circulating Cell-Free DNA. Cancer Biol. Ther. 2019, 20, 1057–1067. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- van der Pol, Y.; Mouliere, F. Toward the Early Detection of Cancer by Decoding the Epigenetic and Environmental Fingerprints of Cell-Free DNA. Cancer Cell 2019, 36, 350–368. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Webster, J.; Dang, H.X.; Chauhan, P.S.; Feng, W.; Shiang, A.; Harris, P.K.; Pachynski, R.K.; Chaudhuri, A.A.; Maher, C.A. PACT: A Pipeline for Analysis of Circulating Tumor DNA. Bioinformatics 2023, 39, btad489. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ul Haq, S.; Schmid, S.; Aparnathi, M.K.; Hueniken, K.; Zhan, L.J.; Sacdalan, D.; Li, J.J.N.; Meti, N.; Patel, D.; Cheng, D.; et al. Cell-Free DNA Methylation-Defined Prognostic Subgroups in Small Cell Lung Cancer Identified by Leukocyte Methylation Subtraction. iScience 2022, 25, 105487. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

| Method | Year | Description | Advantages | Disadvantages |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Enzymatic/bisulfite (BS) sequencing methods | ||||
| BS-seq [89] (Bisulfite sequencing) | 1992 |
|
|
|
| OxBS-seq [90] (Oxidative BS-seq) | 2012 |
|
|
|
| TAB-seq [95] (TET-assisted BS-seq) | 2012 |
|
|
|
| Enzymatic or affinity-based methods | ||||
| GLIB [40,98] (Glucosylation, periodate oxidation, biotinylation) | 2011 |
|
|
|
| HMe-SEAL [54,58] (5hmC-selective chemical labeling assay) | 2011 |
|
|
|
| JBP1-seq [99,100] (J-binding protein 1 sequencing) | 2012 |
|
|
|
| hMeDIP-seq [101] (5hmC DNA immunoprecipitation) | 2014 |
|
|
|
| ACE-seq [103,104] (APOBEC-coupled epigenetic sequencing) | 2018 |
|
|
|
| hmC-CATCH [106] (Chemical-assisted C-to-T conversion of 5hmC sequencing) | 2018 |
|
|
|
| TAPS-seq [107] (TET-assisted pyridine borane sequencing) | 2019 |
|
|
|
| Jump-seq [108] | 2019 |
|
|
|
| hmTOP-seq [109] (5hmC-specific tethered oligonucleotide-primed sequencing) | 2020 |
|
|
|
| DIP-CAB-Seq [110] (DNA immunoprecipitation-coupled chemical modification-assisted bisulfite sequencing) | 2021 |
|
|
|
| SSD-seq [111] (Single-step deamination sequencing) | 2023 |
|
|
|
| EBS-seq [43] (Enrichment-based sequencing) | 2023 |
|
|
|
| Simultaneous epigenetic and genetic sequencing | ||||
| SMRT [112,113] (Single molecule, real-time sequencing) | 2010 |
|
|
|
| 6-letter seq [114] | 2023 |
|
|
|
| DARESOME [115] (DNA analysis by restriction enzyme for simultaneous detection of multiple epigenomic states) | 2023 |
|
|
|
| SIMPLE-seq [116] (Single-cell intracellular metabolite profiling and labeling experiment sequencing) | 2024 |
|
|
|
| Joint-snhmC-seq [117] | 2024 |
|
|
|
| Dyad-seq [118] | 2024 |
|
|
|
| Study | Cancer (n) | Profiling Method | Sample Type | Key Findings |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Diagnostic biomarker | ||||
| Shao et al., 2022 [78] | Pan cancer (Bladder [n = 41], breast [n = 62], colorectal [n = 45], kidney [n = 54], lung [n = 57], prostate [n = 125)) | Nano-hmC-Seal | cfDNA |
|
| Chang et al., 2024 [137] | Colorectal cancer (n = 2576) | HMe-SEAL | cfDNA |
|
| Prognostic biomarker | ||||
| Dong et al., 2015 [72] | Intrahepatic cholangiocarcinoma (n = 16) | IHC, dot blot, tissue microarray | Tissue |
|
| Fu et al., 2022 [138] | Gastric cancer (n = 144) | ELISA | Tissue |
|
| Kuang et al., 2024 [139] | Endometrial cancer (n = 264) | IHC | Tissue |
|
| Chiu et al., 2019 [63] | Diffuse large B-cell lymphoma (n = 48) | HMe-SEAL | cfDNA |
|
| Cai et al., 2021 [64] | Hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC, n = 135) | HMe-SEAL | cfDNA |
|
| Shao et al., 2023 [65] | Acute myeloid leukemia (AML, n = 54) | HMe-SEAL | cfDNA |
|
| Shao et al., 2024 [140] | Lung cancer (n = 97) | Nano-hmC-Seal | cfDNA |
|
| Predictive biomarker | ||||
| Guo et al., 2023 [141] | Hepatocellular carcinoma (n = 101) | IHC, tissue microarray | Tissue |
|
| Chen et al., 2021 [142] | Diffuse large B-cell lymphoma (DLBCL, n = 86) | HMe-SEAL | cfDNA |
|
| Shao et al., 2024 [66] | Lung cancer (n = 83) | Nano-hmC-Seal | cfDNA |
|
| Guler et al., 2024 [143] | Lung cancer (n = 31 with plasma, n = 18 with tissue) | Chemical capture with biotin and streptavidin beads | cfDNA |
|
| Multi-omics biomarker | ||||
| Hu et al., 2022 [126] | Lung cancer (n = 157) | HMe-SEAL | cfDNA |
|
| Zhang et al., 2023 [144] | Pan cancer (Liver [n = 132], pancreas [n = 74], lung [n = 33], glioblastoma [n = 33]) | HMe-SEAL | cfDNA |
|
| Shi et al., 2023 [145] | Bladder cancer (n = 44) | RRBS, oxRRBS | cfDNA |
|
| Lee et al., 2024 [47] | Pediatric central nervous system tumours (n = 32) | Infinium Human-Methylation EPIC BeadChips OxBS-seq | cfDNA |
|
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Li, J.J.N.; Liu, G.; Lok, B.H. Cell-Free DNA Hydroxymethylation in Cancer: Current and Emerging Detection Methods and Clinical Applications. Genes 2024, 15, 1160. https://doi.org/10.3390/genes15091160
Li JJN, Liu G, Lok BH. Cell-Free DNA Hydroxymethylation in Cancer: Current and Emerging Detection Methods and Clinical Applications. Genes. 2024; 15(9):1160. https://doi.org/10.3390/genes15091160
Chicago/Turabian StyleLi, Janice J. N., Geoffrey Liu, and Benjamin H. Lok. 2024. "Cell-Free DNA Hydroxymethylation in Cancer: Current and Emerging Detection Methods and Clinical Applications" Genes 15, no. 9: 1160. https://doi.org/10.3390/genes15091160
APA StyleLi, J. J. N., Liu, G., & Lok, B. H. (2024). Cell-Free DNA Hydroxymethylation in Cancer: Current and Emerging Detection Methods and Clinical Applications. Genes, 15(9), 1160. https://doi.org/10.3390/genes15091160






