Construction of Promoter Elements for Strong, Moderate, and Weak Gene Expression in Drosophila melanogaster
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
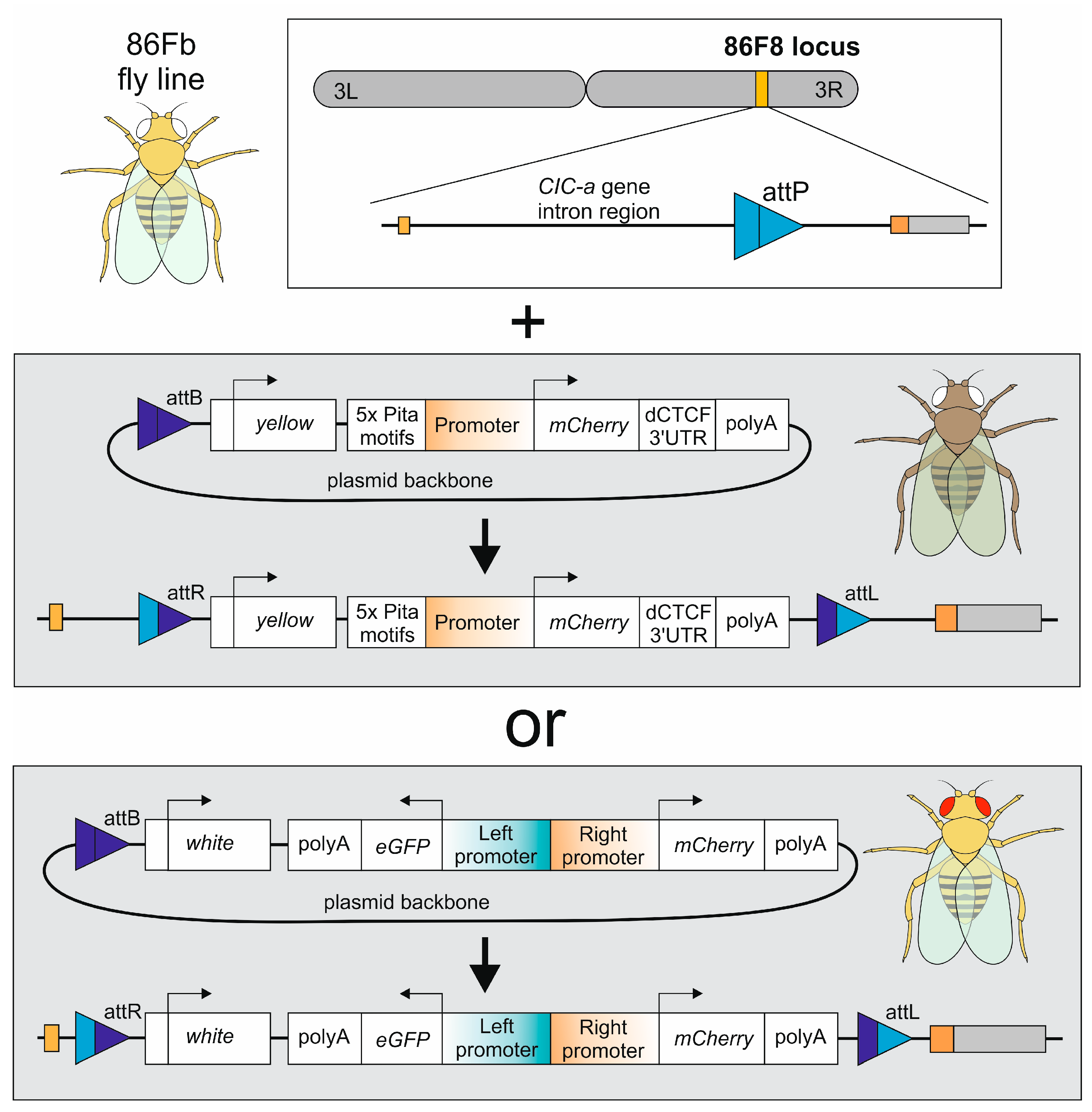
2.1. Transgenic Fly Generation
2.2. S2 Cell Line Transfection
2.3. Plasmid Construction
2.4. Fluorescence and Confocal Microscopy
2.5. Flow Cytometry
2.6. Image Processing and Data Analysis
3. Results
3.1. Promoter Design Rationale
3.2. Analysis of the Strength of Single Promoters in the Model Systems in S2 Cells and Transgenic Drosophila
3.3. Strength of Bidirectional Promoters in the Model Systems in S2 Cells and Transgenic Drosophila
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Thummel, C.S.; Boulet, A.M.; Lipshitz, H.D. Vectors for Drosophila P-Element-Mediated Transformation and Tissue Culture Transfection. Gene 1988, 74, 445–456. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Klemenz, R.; Weber, U.; Gehring, W.J. The White Gene as a Marker in a New P-Element Vector for Gene Transfer in Drosophila. Nucleic Acids Res. 1987, 15, 3947–3959. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ackermann, R.; Brack, C. A Strong Ubiquitous Promoter-Enhancer for Development and Aging of Drosophila melanogaster. Nucleic Acids Res. 1996, 24, 2452–2453. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed][Green Version]
- Bond, B.J.; Davidson, N. The Drosophila melanogaster Actin 5C Gene Uses Two Transcription Initiation Sites and Three Polyadenylation Sites to Express Multiple mRNA Species. Mol. Cell. Biol. 1986, 6, 2080–2088. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Halder, G.; Callaerts, P.; Gehring, W.J. Induction of Ectopic Eyes by Targeted Expression of the Eyeless Gene in Drosophila. Science 1995, 267, 1788–1792. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yuka, A.; Merriam, J.R. Genes with Ectopic Expression Phenotypes Are Common, Not Rare. Drosoph. Inf. Serv. 2001, 84, 30–132. [Google Scholar]
- Hemphälä, J.; Uv, A.; Cantera, R.; Bray, S.; Samakovlis, C. Grainy Head Controls Apical Membrane Growth and Tube Elongation in Response to Branchless/FGF Signalling. Dev. Camb. Engl. 2003, 130, 249–258. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Myllymäki, H.; Rämet, M. Transcription Factor Zfh1 Downregulates Drosophila Imd Pathway. Dev. Comp. Immunol. 2013, 39, 188–197. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Baek, S.-E.; Kwon, Y.; Yoon, J.-W.; Kim, H.-S.; Yang, J.-Y.; Lee, D.-S.; Yeom, E. The Overexpression of DSP1 in Neurons Induces Neuronal Dysfunction and Neurodegeneration Phenotypes in Drosophila. Mol. Brain 2024, 17, 43. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kozak, M. Point Mutations Close to the AUG Initiator Codon Affect the Efficiency of Translation of Rat Preproinsulin in Vivo. Nature 1984, 308, 241–246. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Acevedo, J.M.; Hoermann, B.; Schlimbach, T.; Teleman, A.A. Changes in Global Translation Elongation or Initiation Rates Shape the Proteome via the Kozak Sequence. Sci. Rep. 2018, 8, 4018. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nemsick, S.; Hansen, A.S. Molecular Models of Bidirectional Promoter Regulation. Curr. Opin. Struct. Biol. 2024, 87, 102865. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Trinklein, N.D.; Aldred, S.F.; Hartman, S.J.; Schroeder, D.I.; Otillar, R.P.; Myers, R.M. An Abundance of Bidirectional Promoters in the Human Genome. Genome Res. 2004, 14, 62–66. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Behura, S.K.; Severson, D.W. Bidirectional Promoters of Insects: Genome-Wide Comparison, Evolutionary Implication and Influence on Gene Expression. J. Mol. Biol. 2015, 427, 521–536. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, L.; Yu, J. A Comparative Analysis of Divergently-Paired Genes (DPGs) among Drosophila and Vertebrate Genomes. BMC Evol. Biol. 2009, 9, 55. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cohen, N.; Salzberg, A.; Lev, Z. A Bidirectional Promoter Is Regulating the Drosophila Ras2 Gene. Oncogene 1988, 3, 137–142. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Lightfoot, K.; Maltby, L.; Duarte, R.; Veale, R.; Segev, O. Conserved Cis-Elements Bind a Protein Complex That Regulates Drosophila ras2/rop Bidirectional Expression. Br. J. Cancer 1994, 69, 264–273. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Bischof, J.; Maeda, R.K.; Hediger, M.; Karch, F.; Basler, K. An Optimized Transgenesis System for Drosophila Using Germ-Line-Specific phiC31 Integrases. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2007, 104, 3312–3317. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shaul, O. How Introns Enhance Gene Expression. Int. J. Biochem. Cell Biol. 2017, 91, 145–155. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sabirov, M.; Kyrchanova, O.; Pokholkova, G.V.; Bonchuk, A.; Klimenko, N.; Belova, E.; Zhimulev, I.F.; Maksimenko, O.; Georgiev, P. Mechanism and Functional Role of the Interaction between CP190 and the Architectural Protein Pita in Drosophila melanogaster. Epigenetics Chromatin 2021, 14, 16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baumann, D.G.; Gilmour, D.S. A sequence-specific core promoter-binding transcription factor recruits TRF2 to coordinately transcribe ribosomal protein genes. Nucleic Acids Res. 2017, 45, 10481–10491. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zolotarev, N.; Maksimenko, O.; Kyrchanova, O.; Sokolinskaya, E.; Osadchiy, I.; Girardot, C.; Bonchuk, A.; Ciglar, L.; Furlong, E.E.M.; Georgiev, P. Opbp is a new architectural/insulator protein required for ribosomal gene expression. Nucleic Acids Res. 2017, 45, 12285–12300. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ciabrelli, F.; Atinbayeva, N.; Pane, A.; Iovino, N. Epigenetic Inheritance and Gene Expression Regulation in Early Drosophila Embryos. EMBO Rep. 2024, 25, 4131–4152. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Powers, E.N.; Chan, C.; Doron-Mandel, E.; Llacsahuanga Allcca, L.; Kim Kim, J.; Jovanovic, M.; Brar, G.A. Bidirectional Promoter Activity from Expression Cassettes Can Drive Off-Target Repression of Neighboring Gene Translation. eLife 2022, 11, e81086. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]


| Name | D. melanogaster Gene | Modification | Size (bp) |
|---|---|---|---|
| Single promoters | |||
| pUbi | ubiquitin-63E | - | 2001 |
| pUbi-K | ubiquitin-63E | CAAAatgC Kozak seq. is mutated to GTGAatgC | 2001 |
| pCG10321 | CG10321 | - | 1191 |
| pCP190 | centrosomal protein 190kD | - | 1065 |
| pPzg | putzig | - | 844 |
| pZipic | ZIPIC | - | 266 |
| Bidirectional promoters | |||
| pTecr—pUbi | Trans-2,3-enoyl-CoA reductase/ubiquitin-63E | - | 1805 |
| mini-pRpl—pUbi | ribosomal protein L27a/ubiquitin-63E | - | 1949 |
| mini-pRpl—pRpl* | ribosomal protein L27a/ribosomal protein L27a* | *: M1BP (cggtcacactg) and Opbp (caaccgcagccaactt) motifs of mini-pRpl27a were replaced with sequence tatcgata-tttt-tatcgata | 386 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Kudryashova, K.S.; Deriglazova, I.O.; Osadchiy, I.S.; Georgiev, P.; Maksimenko, O. Construction of Promoter Elements for Strong, Moderate, and Weak Gene Expression in Drosophila melanogaster. Genes 2025, 16, 3. https://doi.org/10.3390/genes16010003
Kudryashova KS, Deriglazova IO, Osadchiy IS, Georgiev P, Maksimenko O. Construction of Promoter Elements for Strong, Moderate, and Weak Gene Expression in Drosophila melanogaster. Genes. 2025; 16(1):3. https://doi.org/10.3390/genes16010003
Chicago/Turabian StyleKudryashova, Ksenia S., Irina O. Deriglazova, Igor S. Osadchiy, Pavel Georgiev, and Oksana Maksimenko. 2025. "Construction of Promoter Elements for Strong, Moderate, and Weak Gene Expression in Drosophila melanogaster" Genes 16, no. 1: 3. https://doi.org/10.3390/genes16010003
APA StyleKudryashova, K. S., Deriglazova, I. O., Osadchiy, I. S., Georgiev, P., & Maksimenko, O. (2025). Construction of Promoter Elements for Strong, Moderate, and Weak Gene Expression in Drosophila melanogaster. Genes, 16(1), 3. https://doi.org/10.3390/genes16010003






