Genome-Wide Identification of the PAL Gene Family in Camellia nitidissima and Functional Characterization of CnPAL1 Gene by In Vitro Expression
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Materials
2.2. Identification and Physicochemical Characterization of the CnPAL Genes in C. nitidissima
2.3. The Analysis of Evolutionary and Structural Characterization of the CnPAL Genes
2.4. Chromosomal Location, Gene Duplication, and Collinearity Analysis of the CnPAL Genes
2.5. Analysis of Cis-Acting Elements in the CnPAL Genes Promoter
2.6. Analysis of Expression Levels of the CnPAL Genes
2.7. qRT-PCR Validation of the CnPALs
2.8. Construction of Expression Vectors for the CnPAL1 Gene
2.9. Prokaryotic Expression and Purification of CnPAL1 Protein
2.10. Assessment of Recombinant Enzyme Activity
2.11. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
3.1. Genome-Wide Analysis of the PAL Gene Family in C. nitidissima and Physicochemical Characterization of PAL Proteins
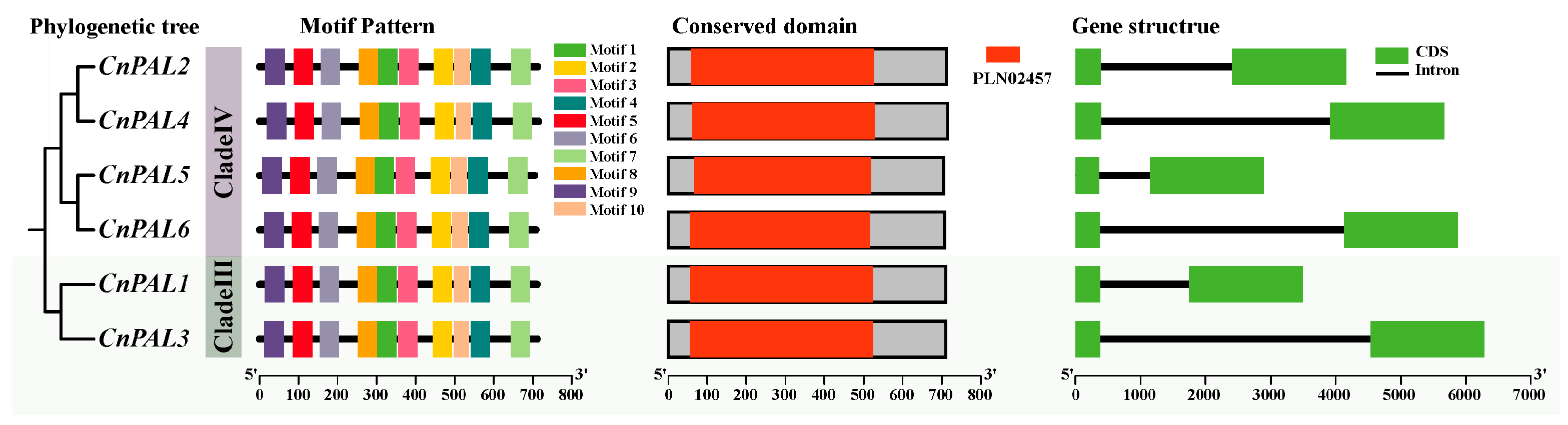
3.2. Gene Structure and Conserved Motif Analysis of the CnPAL Gene Family
3.3. Phylogenetic Analysis of the CnPAL Gene Family
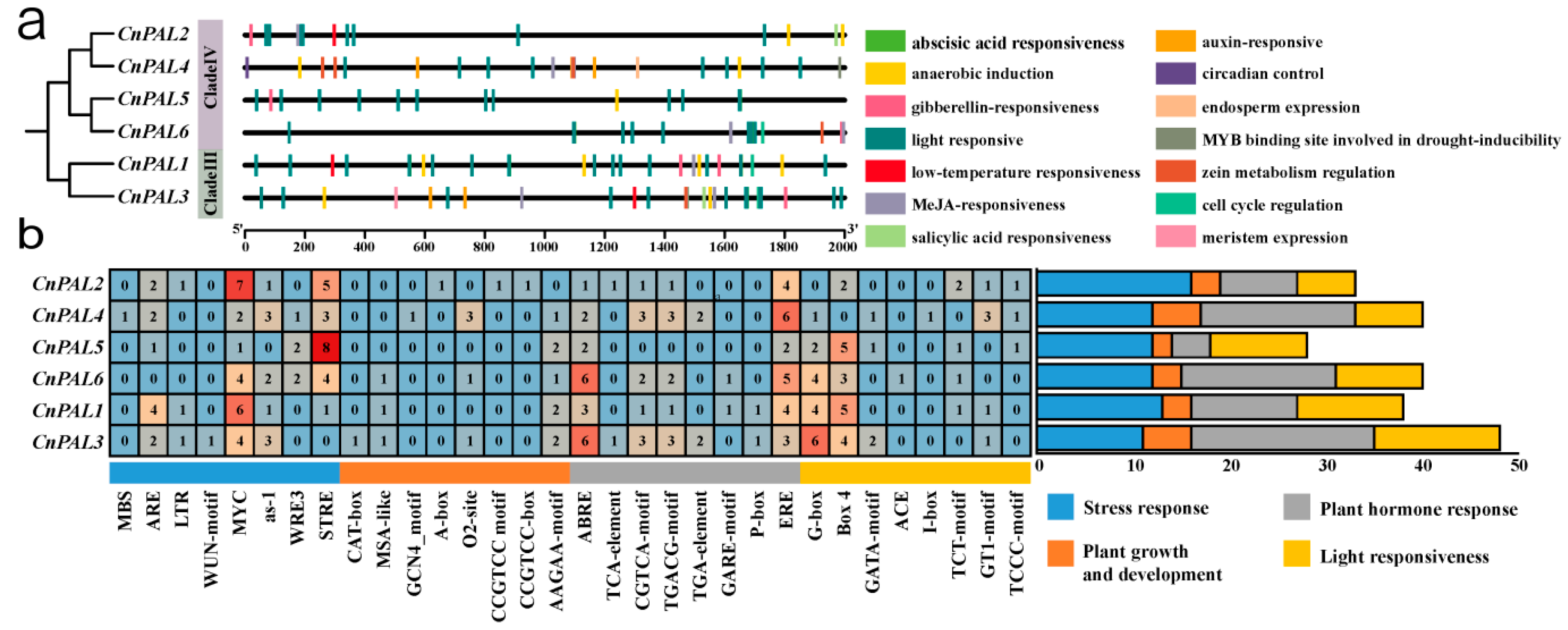
3.4. Analysis of Promoter Cis-Acting Elements of the CnPAL Gene Family
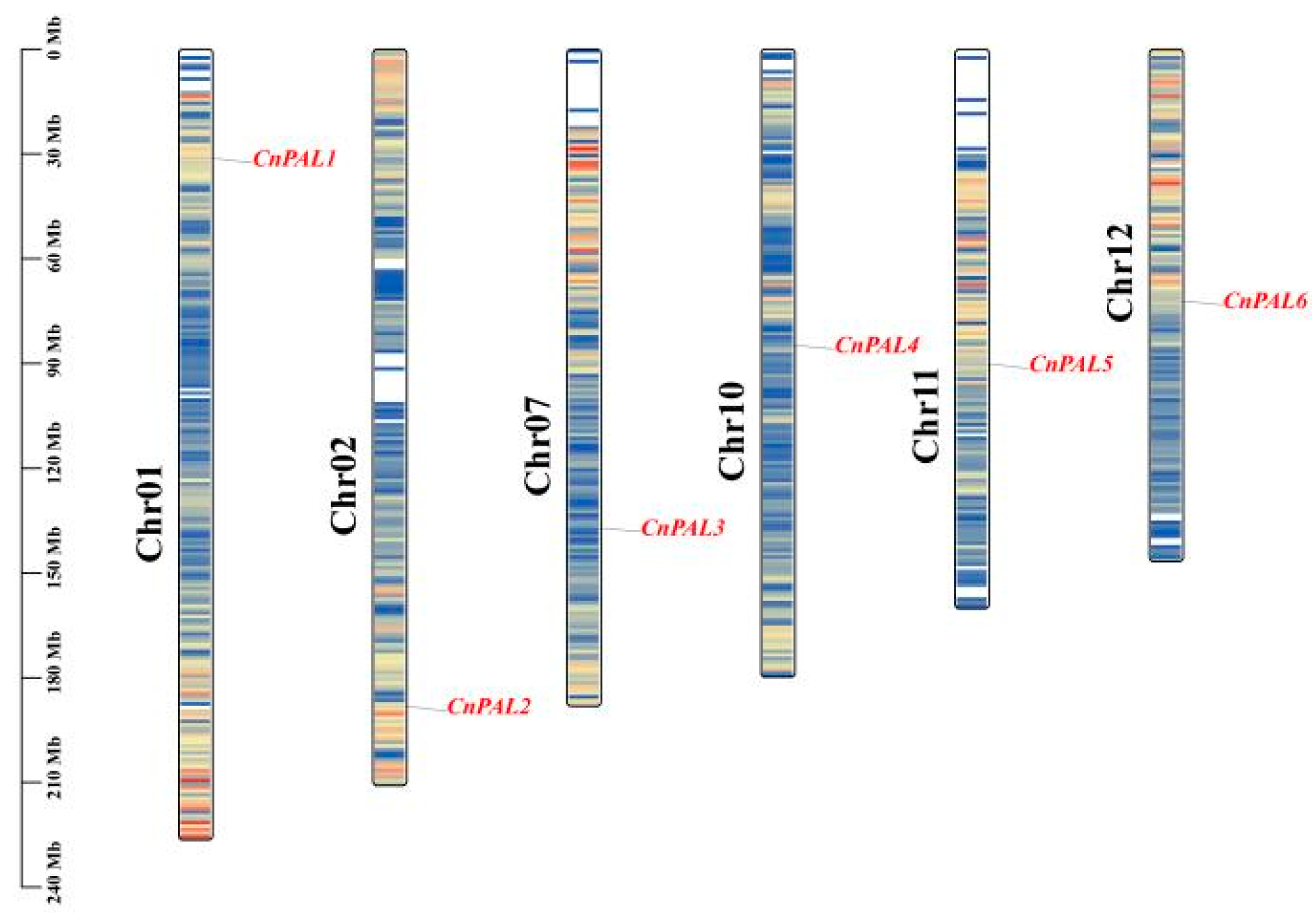
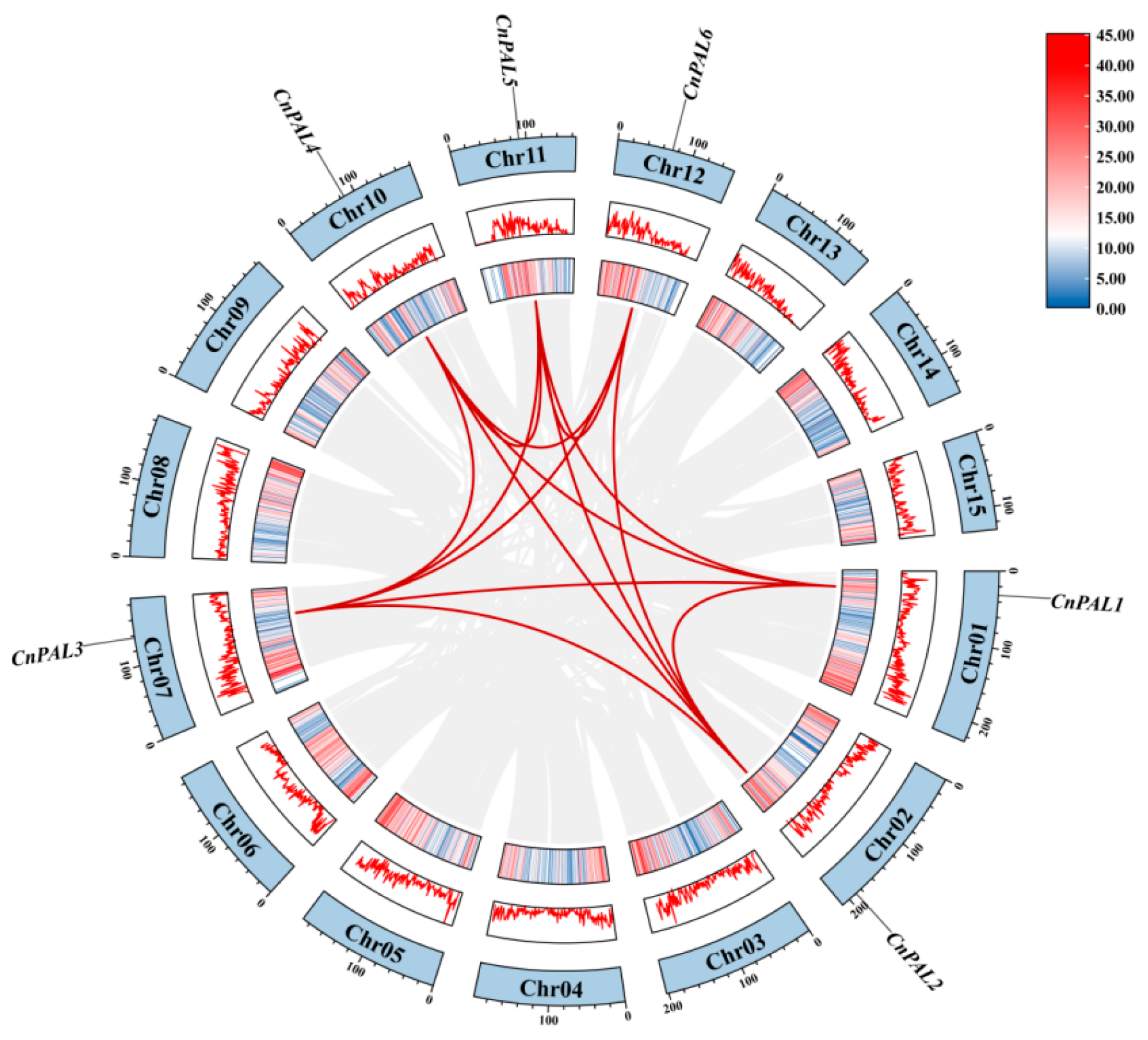
3.5. Chromosomal Location and Collinear Analysis of the CnPAL Gene Family
3.6. Expression Analysis of the CnPAL Gene Family
3.7. Cloning, Prokaryotic Expression, and Enzyme Activity Analysis of CnPAL1 Gene
4. Discussion
4.1. Characteristics of the CnPAL Gene Family in C. nitidissima
4.2. Analysis of the Expression Characteristics of the CnPAL Genes and Functional Validation of the CnPAL1 Gene
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| bHLH | Basic-Helix-Loop-Helix |
| cDNA | DNA complementary to RNA |
| L-Phe | L-phenylalanine |
| PAL | phenylalanine ammonia-lyase |
| qRT-PCR | Real-time Quantitative PCR |
| IPTG | Isopropyl-beta-D-thiogalactopyranoside |
| PMSF | Phenylmethanesulfonyl fluoride |
References
- Chai, S.F.; Wei, X.; Jiang, Y.S.; Wei, J.Q.; Jiang, S.Y.; Wang, M.L. The flowering phenology and characteristics of reproductive modules of endangered plant Camellia nitidissima. J. Trop. Subtrop. Bot. 2009, 17, 5–11. [Google Scholar]
- Hattori, M.; Huang, X.L.; Che, Q.M.; Kawata, Y.; Tezuka, Y.; Kikuchi, T.; Namba, T. 6-Hydroxykaempferol and its glycosides from Carthamus tinctorius petals. Phytochemistry 1992, 31, 4001–4004. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hou, X.; Du, H.; Yang, R.; Qi, J.; Huang, Y.; Feng, S.; Wu, Y.; Lin, S.; Liu, Z.; Jia, A.Q. The antitumor activity screening of chemical constituents from Camellia nitidissima Chi. Int. J. Mol. Med. 2018, 41, 2793–2801. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, W.; Liu, H.; Wang, Z.; Qi, J.; Yuan, S.; Zhang, W.; Chen, H.; Finley, J.W.; Gu, L.; Jia, A.Q. Phytochemicals from Camellia nitidissima Chi inhibited the formation of advanced glycation end-products by scavenging methylglyoxal. Food Chem. 2016, 205, 204–211. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, L.X.; Wang, X.S.; Zheng, X.Q.; Huang, D. Polyphenolic antioxidant profiles of yellow camellia. Food Chem. 2011, 129, 351–357. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, D.; Li, X.; Sai, X.; Wang, L.; Li, S.; Xu, Y. Camellia nitidissima C.W. Chi: A review of botany, chemistry, and pharmacology. Phytochem. Rev. 2018, 17, 327–349. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, X.L.; Wang, J.T.; Sun, Z.Y.; Wang, J.; Yin, H.F.; Fan, Z.Q.; Li, J.Y. UPLC-QTOF-MS Analysis of Flowers and Leaves of Camellia nitidissima. For. Res. 2018, 31, 83–88. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, X.W.; Fan, Z.Q.; Chen, Y.; Zhu, Y.L.; Li, J.Y.; Yin, H.F. Functional analyses of a flavonol synthase-like gene from Camellia nitidissima reveal its roles in flavonoid metabolism during floral pigmentation. J. Biosci. 2013, 38, 593–604. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lin, J.N.; Lin, H.Y.; Yang, N.S.; Li, Y.H.; Lee, M.R.; Chuang, C.H.; Ho, C.T.; Kuo, S.C.; Way, T.D. Chemical constituents and anticancer activity of yellow camellias against MDA-MB-231 human breast cancer cells. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2013, 61, 9638–9644. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jiang, L.N.; Han, L.Q.; Zhang, W.X.; Gao, Y.F.; Xu, X.Y.; Chen, J.; Feng, S.; Fan, Z.Q.; Li, J.Y.; Li, X.L.; et al. Elucidation of the key flavonol biosynthetic pathway in golden Camellia and its application in genetic modification of tomato fruit metabolism. Hortic. Res. 2024, 12, uhae308. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Peng, X.; Yu, D.Y.; Feng, B.M.; Wang, Y.Q.; Shi, L.Y. A new acylated flavonoid glycoside from the flowers of Camellia nitidissima and its effect on the induction of apoptosis in human lymphoma U937 cells. J. Asian Nat. Prod. Res. 2012, 14, 799–804. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Winkel-Shirley, B. Flavonoid biosynthesis. A colorful model for genetics, biochemistry, cell biology, and biotechnology. Plant Physiol. 2001, 126, 485–493. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, B.W.; Gong, C.C.; Song, H.F.; Cui, Y.Y. Effects of anthocyanins on the prevention and treatment of cancer. Br. J. Pharmacol. 2017, 174, 1226–1243. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kimble, R.; Keane, K.M.; Lodge, J.K.; Howatson, G. Dietary intake of anthocyanins and risk of cardiovascular disease: A systematic review and meta-analysis of prospective cohort studies. Crit. Rev. Food Sci. Nutr. 2019, 59, 3032–3043. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, S.; Wang, X.J.; Cheng, Y.; Gao, H.S.; Chen, X.H. A review of classification, biosynthesis, biological activities and potential applications of flavonoids. Molecules 2023, 28, 4982. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deng, Y.X.; Lu, S.F. Biosynthesis and Regulation of Phenylpropanoids in Plants. Crit. Rev. Plant Sci. 2017, 36, 257–290. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barros, J.; Dixon, R.A. Plant phenylalanine/tyrosine ammonia-lyases. Trends Plant Sci. 2020, 5, 66–79. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Olsen, K.M.; Lea, U.S.; Slimestad, R.; Verheul, M.; Lillo, C. Differential expression of four Arabidopsis PAL genes; PAL1 and PAL2 have functional specialization in abiotic environmental-triggered flavonoid synthesis. J. Plant Physiol. 2008, 165, 1491–1499. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, A.L.; Zhu, Y.; Wang, Y.H.; Wang, T.Y.; Zhao, S.P.; Feng, K.; Li, L.J.; Wu, P. Molecular identification of phenylalanine ammonia lyase-encoding genes EfPALs and EfPAL2-interacting transcription factors in Euryale ferox. Front. Plant Sci. 2023, 14, 1114345. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cochrane, F.C.; Davin, L.B.; Lewis, N.G. The Arabidopsis phenylalanine ammonia lyase gene family: Kinetic characterization of the four PAL isoforms. Phytochemistry 2004, 65, 1557–1564. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, X.G.; Hu, Y.P.; Xu, Z.B.; Peng, D.Q.; Guo, Q.R. Expression profiling of the phenylalanine ammonia-lyase (PAL) gene family in Ginkgo biloba L. Plant Signal. Behav. 2023, 18, 2271807. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reichert, A.I.; He, X.Z.; Dixon, R.A. Phenylalanine ammonia-lyase (PAL) from tobacco (Nicotiana tabacum): Characterization of the four tobacco PAL genes and active heterotetrameric enzymes. Biochem. J. 2009, 424, 233–242. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mo, F.Y.; Li, L.; Zhang, C.; Yang, C.H.; Chen, G.; Niu, Y.; Si, J.X.; Liu, T.; Sun, X.X.; Wang, S.L.; et al. Genome-wide analysis and expression profiling of the phenylalanine ammonia-lyase gene family in Solanum tuberosum. Int. J. Mech. Sci. 2022, 23, 6833. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhao, T.; Li, R.M.; Yao, W.; Wang, Y.J.; Zhang, C.H.; Li, Y. Genome-wide identification and characterisation of phenylalanine ammonia-lyase gene family in grapevine. J. Hortic. Sci. Biotechnol. 2021, 96, 456–468. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, J.L.; Gu, M.; Lai, Z.B.; Fan, B.F.; Shi, K.; Zhou, Y.H.; Yu, J.Q.; Chen, Z.X. Functional analysis of the Arabidopsis PAL gene family in plant growth, development, and response to environmental stress. Plant Physiol. 2010, 153, 1526–1538. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, H.Y.; Zhang, X.H.; Zhao, H.X.; Hu, J.; Wang, Z.Y.; Yang, G.S.; Zhou, X.M.; Wan, H.P. Genome-wide identification and expression analysis of phenylalanine ammonia-lyase (PAL) family in rapeseed (Brassica napus L.). BMC Plant Biol. 2023, 23, 481. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, F.L.; Wang, J.; Li, X.G.; Zhang, J.; Liu, Y.X.; Chen, Y.J.; Yu, Q.H.; Li, N. Genome-wide identification and expression analyses of phenylalanine ammonia-lyase gene family members from tomato (Solanum lycopersicum) reveal their role in root-knot nematode infection. Front. Plant Sci. 2023, 14, 1204990. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wanner, L.A.; Li, G.; Ware, D.; Somssich, I.E.; Davis, K.R. The phenylalanine ammonia-lyase gene family in Arabidopsis thaliana. Plant Mol. Biol. 1995, 27, 327–338. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, H.X.; Liu, Q.; Chen, Y.L.; Zhu, Y.L.; Zhou, X.W.; Li, B. Full-length transcriptome sequencing provides insights into flavonoid biosynthesis in Camellia nitidissima Petals. Gene 2023, 850, 146924. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.F.; Liu, T.J.; Feng, T.; Huang, H.R.; Zou, P.; Wei, X.; Wu, X.; Chai, S.F.; Yan, H.F. A telomere-to-telomere genome assembly of Camellia nitidissima. Sci. Data 2025, 12, 815. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- El-Gebali, S.; Mistry, J.; Bateman, A.; Eddy, S.R.; Luciani, A.; Potter, S.C.; Qureshi, M.; Richardson, L.J.; Salazar, G.A.; Smart, A.; et al. The Pfam protein families database in 2019. Nucleic Acids Res. 2019, 47, D427–D432. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wilkins, M.R.; Gasteiger, E.; Bairoch, A.; Sanchez, J.C.; Williams, K.L.; Appel, R.D.; Hochstrasser, D.F. Protein identification and analysis tools in the ExPASy server. Methods Mol. Biol. 1999, 112, 531–552. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tamura, K.; Stecher, G.; Kumar, S. MEGA11: Molecular Evolutionary Genetics Analysis Version 11. Mol. Biol. Evol. 2021, 38, 3022–3027. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bailey, T.L.; Johnson, J.; Grant, C.E.; Noble, W.S. The MEME Suite. Nucleic Acids Res. 2015, 43, W39–W49. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, C.J.; Chen, H.; Zhang, Y.; Thomas, H.R.; Frank, M.H.; He, Y.H.; Xia, R. TBtools: An Integrative Toolkit Developed for Interactive Analyses of Big Biological Data. Mol. Plant 2020, 13, 1194–1202. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.P.; Tang, H.B.; Debarry, J.D.; Tan, X.; Li, J.P.; Wang, X.Y.; Lee, T.H.; Jin, H.Z.; Marler, B.; Guo, H.; et al. MCScanX: A toolkit for detection and evolutionary analysis of gene synteny and collinearity. Nucleic Acids Res. 2012, 40, e49. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lescot, M.; Déhais, P.; Thijs, G.; Marchal, K.; Moreau, Y.; Van de Peer, Y.; Rouzé, P.; Rombauts, S. PlantCARE, a database of plant cis-acting regulatory elements and a portal to tools for In Silico analysis of promoter sequences. Nucleic Acids Res. 2002, 30, 325–327. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, S.F.; Zhou, Y.Q.; Chen, Y.R.; Gu, J. fastp: An ultra-fast all-in-one FASTQ preprocessor. Bioinformatics 2018, 34, 884–890. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, D.; Langmead, B.; Salzberg, S.L. HISAT: A fast spliced aligner with low memory requirements. Nat. Methods 2015, 12, 357–360. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pertea, M.; Pertea, G.M.; Antonescu, C.M.; Chang, T.C.; Mendell, J.T.; Salzberg, S.L. StringTie enables improved reconstruction of a transcriptome from RNA-seq reads. Nat. Biotechnol. 2015, 33, 290–295. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, B.; Dewey, C.N. RSEM: Accurate transcript quantification from RNA-Seq data with or without a reference genome. BMC Bioinform. 2011, 12, 323. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Livak, K.J.; Schmittgen, T.D. Analysis of relative gene expression data using real-time quantitative PCR and the 2−ΔΔCT Method. Methods 2001, 25, 402–408. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Q.Q.; Luo, L.; Zheng, L.Q. Lignins: Biosynthesis and Biological Functions in Plants. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2018, 19, 335. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baldi, P.; Moser, M.; Brilli, M.; Vrhovsek, U.; Pindo, M.; Si-Ammour, A. Fine-tuning of the flavonoid and monolignol pathways during apple early fruit development. Planta 2017, 245, 1021–1035. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, X.J.; Wang, P.J.; Gu, M.Y.; Hou, B.H.; Zhang, C.R.; Zheng, Y.C.; Sun, Y.; Jin, S.; Ye, N.X. Identification of PAL genes related to anthocyanin synthesis in tea plants and its correlation with anthocyanin content. Hortic. Plant J. 2022, 8, 381–394. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, C.Q.; Fan, X.L.; Shen, G.A.; Guo, B.L. Genome-wide identification of the phenylalanine ammonia-lyase gene from Epimedium pubescens Maxim. (Berberidaceae): Novel insight into the evolution of the PAL gene family. BMC Plant Biol. 2024, 24, 831. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yin, T.; Xu, R.; Zhu, L.; Yang, X.Y.; Zhang, M.J.; Li, X.L.; Zi, Y.Q.; Wen, K.; Zhao, K.; Cai, H.B.; et al. Comparative analysis of the PAL gene family in nine citruses provides new insights into the stress resistance mechanism of Citrus species. BMC Genom. 2024, 25, 1020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Amjad, M.; Wang, Y.X.; Han, S.M.; Haider, M.Z.; Sami, A.; Batool, A.; Shafiq, M.; Ali, Q.; Dong, J.H.; Sabir, I.A.; et al. Genome wide identification of phenylalanine ammonia-lyase (PAL) gene family in Cucumis sativus (cucumber) against abiotic stress. BMC Genom. Data 2024, 25, 76. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chai, P.P.; Cui, M.J.; Zhao, Q.; Chen, L.J.; Guo, T.D.; Guo, J.K.; Wu, C.D.; Du, P.; Liu, H.; Xu, J.; et al. Genome-Wide Characterization of the Phenylalanine Ammonia-Lyase Gene Family and Their Potential Roles in Response to Aspergillus flavus L. Infection in Cultivated Peanut (Arachis hypogaea L.). Genes 2024, 15, 265. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Karamat, U.; Guo, J.X.; Jiang, S.Z.; Khan, I.; Lu, M.T.; Fu, M.; Li, G.H. Comprehensive, Genome-Wide Identification and Expression Analyses of Phenylalanine Ammonia-Lyase Family under Abiotic Stresses in Brassica oleracea. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2024, 25, 10276. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, L.L.; Yang, J.; Wang, R.J. Identification and Expressions of PAL, C4H, and 4CL Families in Tea Plant. Acta Tea Sin. 2024, 65, 34–46. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Fu, X.Q.; Hao, X.L.; Zhang, L.D.; Wang, L.Y.; Qian, H.M.; Zhao, J.Y. Molecular cloning and promoter analysis of the specific salicylic acid biosynthetic pathway gene phenylalanine ammonia-lyase (AaPAL1) from Artemisia annua. Biotechnol. Appl. Biochem. 2016, 63, 514–524. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bhat, W.W.; Razdan, S.; Rana, S.; Dhar, N.; Wani, T.A.; Qazi, P.; Vishwakarma, R.; Lattoo, S.K. A phenylalanine ammonia-lyase ortholog (PkPAL1) from Picrorhiza kurrooa Royle ex. Benth: Molecular cloning, promoter analysis and response to biotic and abiotic elicitors. Gene 2014, 547, 245–256. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xu, F.; Deng, G.; Cheng, S.Y.; Zhang, W.W.; Huang, X.H.; Li, L.L.; Cheng, H.; Rong, X.F.; Li, J.B. Molecular cloning, characterization and expression of the phenylalanine ammonia-lyase gene from Juglans regia. Molecules 2012, 17, 7810–7823. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Feng, Y.; Li, J.Y.; Yin, H.F.; Shen, J.; Liu, W.X. Multi-omics analysis revealed the mechanism underlying flavonol biosynthesis during petal color formation in Camellia nitidissima. BMC Plant Biol. 2024, 24, 847. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tohge, T.; Nishiyama, Y.; Hirai, M.Y.; Yano, M.; Nakajima, J.; Awazuhara, M.; Inoue, E.; Takahashi, H.; Goodenowe, D.B.; Kitayama, M.; et al. Functional genomics by integrated analysis of metabolome and transcriptome of Arabidopsis plants over-expressing an MYB transcription factor. Plant J. 2005, 42, 218–235. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Czemmel, S.; Heppel, S.C.; Bogs, J. R2R3 MYB transcription factors: Key regulators of the flavonoid biosynthetic pathway in grapevine. Protoplasma 2012, 249, 109–118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cui, Y.; Cao, Q.; Li, Y.P.; He, M.Q.; Liu, X.G. Advances in cis-element- and natural variation-mediated transcriptional regulation and applications in gene editing of major crops. J. Exp. Bot. 2023, 74, 5441–5457. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Braidot, E.; Zancani, M.; Petrussa, E.; Peresson, C.; Bertolini, A.; Patui, S.; Macrì, F.; Vianello, A. Transport and accumulation of flavonoids in grapevine (Vitis vinifera L.). Plant Signal. Behav. 2008, 3, 626–632. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]



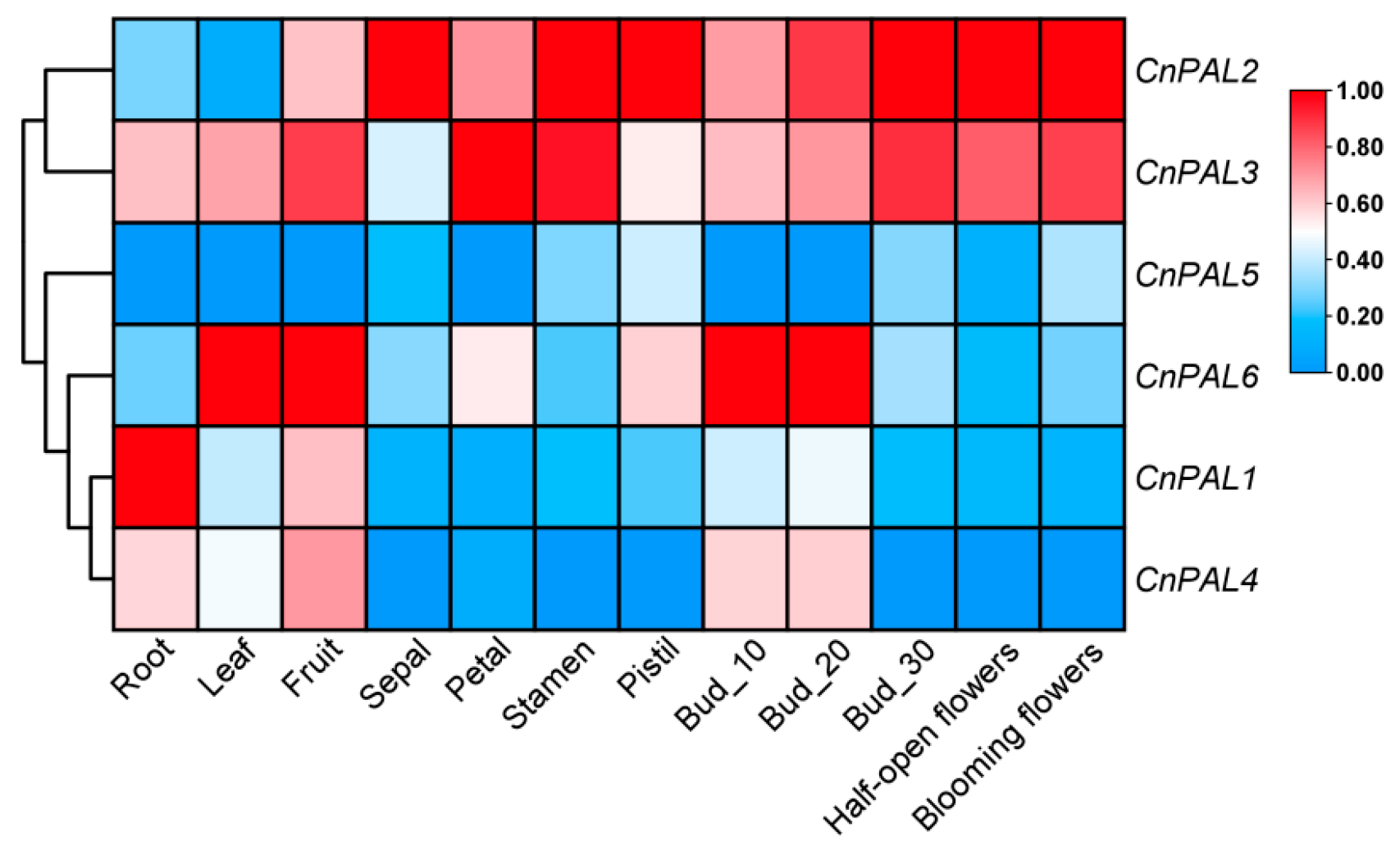
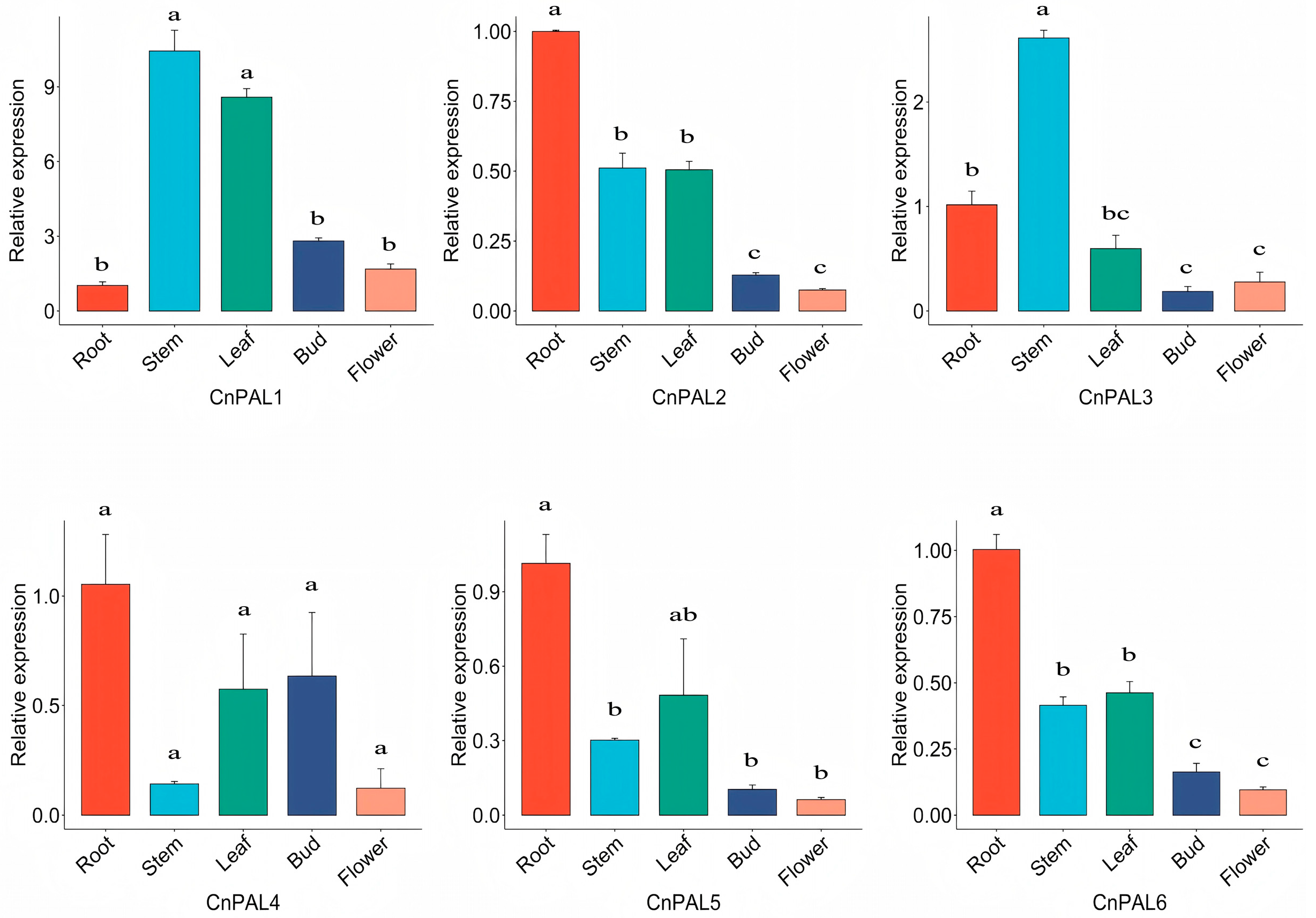
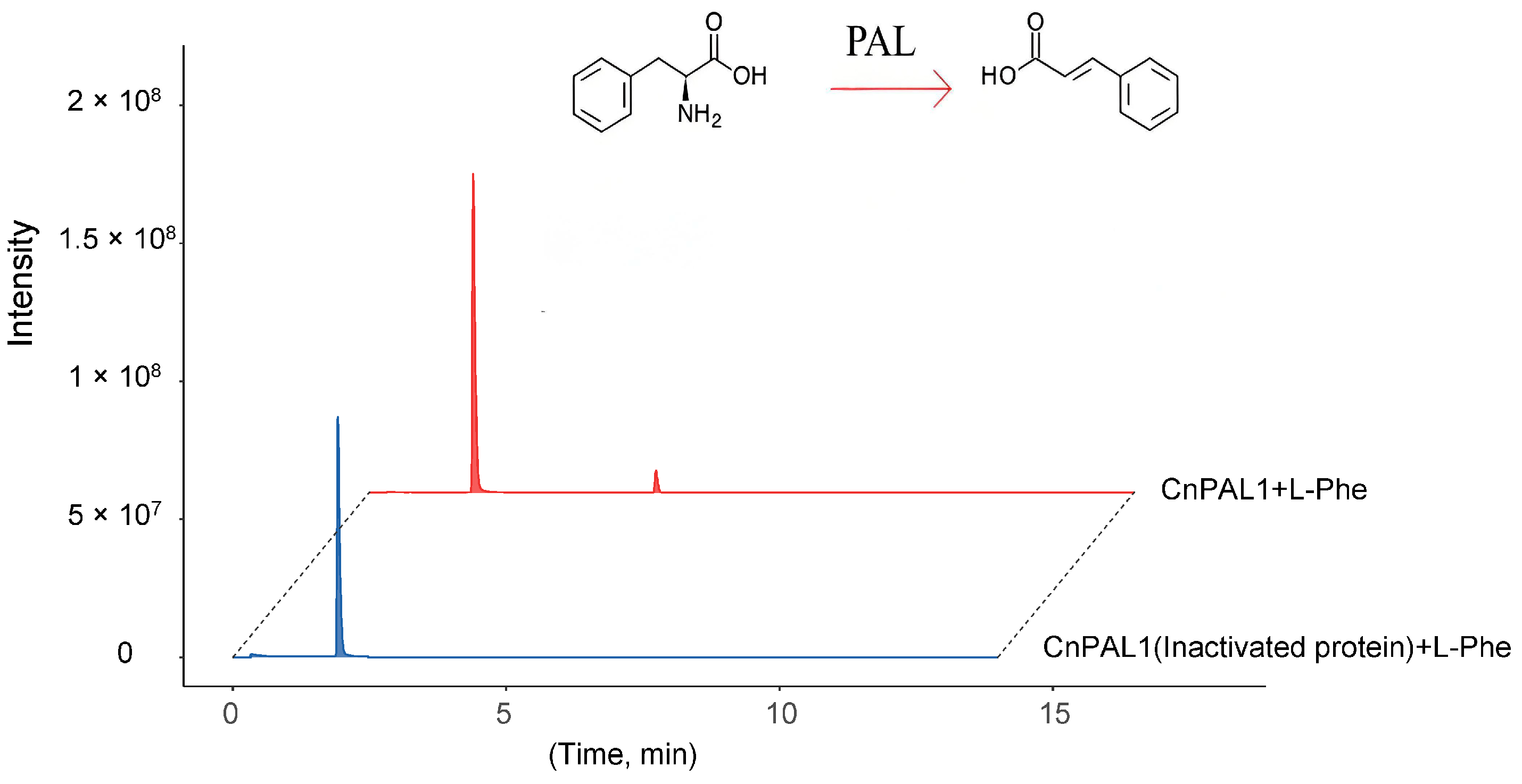
| Gene Name | Gene ID | Number of Amino Acids | Molecular Weight | Theoretical pI | Instability Index | Aliphatic Index | Grand Average of Hydropathicity | Subcellular Localization Prediction |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| CnPAL1 | Cpet01g03790.t1 | 709 | 77,358.56 | 5.90 | 32.88 | 95.74 | −0.11 | Chloroplast |
| CnPAL2 | Cpet02g23820.t1 | 711 | 77,454.46 | 6.29 | 33.96 | 90.55 | −0.19 | Chloroplast |
| CnPAL3 | Cpet07g18270.t1 | 709 | 77,304.45 | 6.29 | 34.81 | 92.19 | −0.15 | Chloroplast |
| CnPAL4 | Cpet10g09570.t1 | 714 | 77,760.93 | 5.97 | 36.73 | 90.29 | −0.15 | Chloroplast |
| CnPAL5 | Cpet11g11740.t1 | 703 | 76,646.69 | 5.84 | 35.26 | 93.93 | −0.13 | Cytoplasmic |
| CnPAL6 | Cpet12g14570.t1 | 706 | 77,084.20 | 6.16 | 33.81 | 91.74 | −0.15 | Cytoplasmic |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Liu, H.; Li, B. Genome-Wide Identification of the PAL Gene Family in Camellia nitidissima and Functional Characterization of CnPAL1 Gene by In Vitro Expression. Genes 2025, 16, 1251. https://doi.org/10.3390/genes16111251
Liu H, Li B. Genome-Wide Identification of the PAL Gene Family in Camellia nitidissima and Functional Characterization of CnPAL1 Gene by In Vitro Expression. Genes. 2025; 16(11):1251. https://doi.org/10.3390/genes16111251
Chicago/Turabian StyleLiu, Hexia, and Bo Li. 2025. "Genome-Wide Identification of the PAL Gene Family in Camellia nitidissima and Functional Characterization of CnPAL1 Gene by In Vitro Expression" Genes 16, no. 11: 1251. https://doi.org/10.3390/genes16111251
APA StyleLiu, H., & Li, B. (2025). Genome-Wide Identification of the PAL Gene Family in Camellia nitidissima and Functional Characterization of CnPAL1 Gene by In Vitro Expression. Genes, 16(11), 1251. https://doi.org/10.3390/genes16111251





