Analysis of the Codon Usage Bias Pattern in the Chloroplast Genomes of Chloranthus Species (Chloranthaceae)
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Sampling, DNA Extraction, Sequencing, Chloroplast Genome Assembly, and Annotation
2.2. Phylogenetic Analysis
2.3. Calculation of Parameters Related to Codon Usage Bias
2.4. Neutrality Plot Analysis
2.5. ENC-Plot Analysis
2.6. Parity Rule 2 (PR2) Bias Plot Analysis
2.7. Identification of Optimal Codons
3. Results
3.1. Chloroplast Genome Characters of C. angustifolius
3.2. Phylogenetic Analysis
3.3. Calculation of Parameters Related to Codon Usage Bias
3.4. Neutrality Plot Analysis
3.5. ENC-Plot Analysis
3.6. Parity-Rule 2 (PR2) Bias Plot Analysis
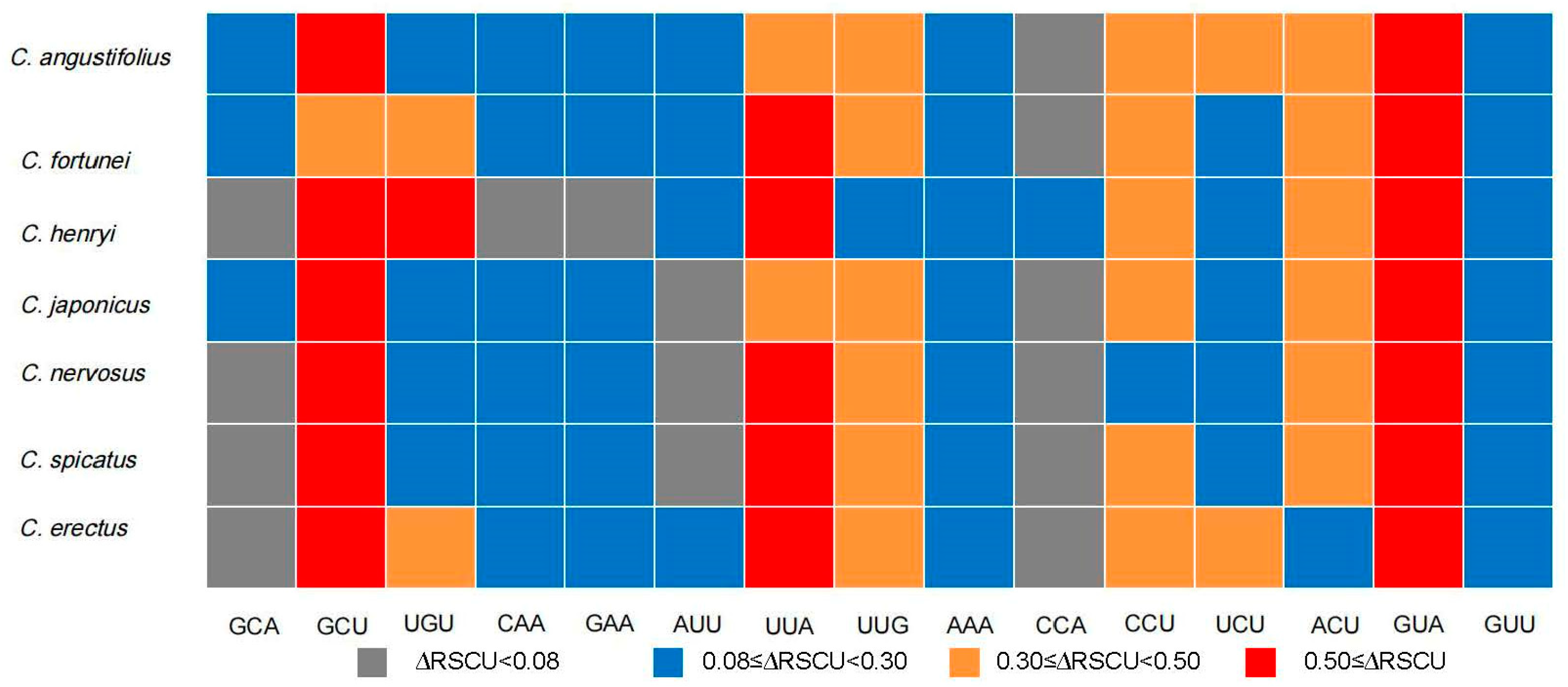
3.7. Identification of Optimal Codons
4. Discussion
4.1. The Chloroplast Characters and Phylogenetic Relationships Among Chloranthus
4.2. Natural Selection Plays a Key Role in the Codons Usage of Chloranthus
4.3. Optimal Codons Offers New Insights for Chloroplast Genetic Engineering in Chloranthus
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Li, N.; Li, Y.; Zheng, C.; Huang, J.; Zhang, S. Genome-wide comparative analysis of the codon usage patterns in plants. Genes Genom. 2016, 38, 723–731. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Iriarte, A.; Lamolle, G.; Musto, H. Codon usage bias: An endless tale. J. Mol. Evol. 2021, 89, 589–593. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chakraborty, S.; Yengkhom, S.; Uddin, D.A. Analysis of codon usage bias of chloroplast genes in Oryza species. Planta 2020, 252, 67. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tyagi, S.; Kabade, P.G.; Gnanapragasam, N.; Singh, U.M.; Singh Gurjar, A.K.; Rai, A.; Sinha, P.; Kumar, A.; Singh, V.K. Codon usage provide insights into the adaptation of rice genes under stress condition. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2023, 24, 1098. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fages-Lartaud, M.; Hundvin, K.; Hohmann-Marriott, M.F. Mechanisms governing codon usage bias and the implications for protein expression in the chloroplast of Chlamydomonas reinhardtii. Plant J. 2022, 112, 919–945. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Romero, H.; Zavala, A.; Musto, H. Codon usage in Chlamydia trachomatis is the result of strand-specific mutational biases and a complex pattern of selective forces. Nucl. Acid. Res. 2000, 28, 2084–2090. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Duret, L. tRNA gene number and codon usage in the C. elegans genome are co-adapted for optimal translation of highly expressed genes. Trends Genet. 2000, 16, 287–289. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xu, C.; Cai, X.-N.; Chen, Q.-Z.; Zhou, H.-X.; Cai, Y.; Ben, A.-L. Factors affecting synonymous codon usage bias in chloroplast genome of Oncidium Gower Ramsey. Evol. Bioinform. 2011, 7, 271–278. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dobrogojski, J.; Adamiec, M.; Luciński, R. The chloroplast genome: A review. Acta Physiol. Plant. 2020, 42, 98. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Green, B.R. Chloroplast genomes of photosynthetic eukaryotes. Plant J. 2011, 66, 34–44. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Daniell, H.; Lin, C.-S.; Yu, M.; Chang, W.-J. Chloroplast genomes: Diversity, evolution, and applications in genetic engineering. Genome Biol. 2016, 17, 134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Daniell, H.; Jin, S.; Zhu, X.-G.; Gitzendanner, M.A.; Soltis, D.E.; Soltis, P.S. Green giant-a tiny chloroplast genome with mighty power to produce high-value proteins: History and phylogeny. Plant Biotechnol. J. 2021, 19, 430–447. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, Y.-T.; Dong, Y.; Liu, Y.-C.; Yu, X.-Y.; Yang, M.-S.; Huang, Y.-R. Comparative analyses of Euonymus chloroplast genomes: Genetic structure, screening for loci with suitable polymorphism, positive selection genes, and phylogenetic relationships within Celastrineae. Front. Plant Sci. 2021, 11, 593984. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hao, J.; Liang, Y.; Ping, J.; Li, J.; Shi, W.; Su, Y.; Wang, T. Chloroplast gene expression level is negatively correlated with evolutionary rates and selective pressure while positively with codon usage bias in Ophioglossum vulgatum L. BMC Plant Biol. 2022, 22, 580. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Quax, T.E.F.; Claassens, N.J.; Söll, D.; van der Oost, J. Codon Bias as a Means to Fine-Tune Gene Expression. Mol. Cell. 2015, 59, 149–161. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bhattacharyya, D.; Uddin, A.; Das, S.; Chakraborty, S. Mutation pressure and natural selection on codon usage in chloroplast genes of two species in Pisum L. (Fabaceae: Faboideae). Mitochondrial DNA Part A. 2019, 30, 664–673. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, S.-X.; Xu, L.-L.; Huang, R.; Wang, Q.-X. Improved biohydrogen production with an expression of codon-optimized hemH and lba genes in the chloroplast of Chlamydomonas reinhardtii. Bioresour. Technol. 2011, 102, 2610–2616. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kwon, K.-C.; Chan, H.-T.; León, I.R.; Williams-Carrier, R.; Barkan, A.; Daniell, H. Codon Optimization to Enhance Expression Yields Insights into Chloroplast Translation. Plant Physiol. 2016, 172, 62–77. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xia, N.; Jérémie, J. Chloranthaceae Blume. In Flora of China; Wu, Z.-Y., Raven, P.H., Hong, D.-Y., Eds.; Science Press: Beijing, China, 1999; Volume 4, pp. 132–138. [Google Scholar]
- Kong, H.-Z.; Chen, Z.-D.; Lu, A.-M. Phylogeny of Chloranthus (Chloranthaceae) based on nuclear ribosomal ITS and plastid trnL-F sequence data. Am. J. Bot. 2002, 89, 940–946. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Eklund, H.; Doyle, J.A.; Herendeen, P.S. Morphological phylogenetic analysis of living and fossil Chloranthaceae. Int. J. Plant Sci. 2004, 165, 107–151. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hansen, D.R.; Dastidar, S.G.; Cai, Z.-Q.; Penaflor, C.; Kuehl, J.V.; Boore, J.L.; Jansen, R.K. Phylogenetic and evolutionary implications of complete chloroplast genome sequences of four early-diverging angiosperms: Buxus (Buxaceae), Chloranthus (Chloranthaceae), Dioscorea (Dioscoreaceae), and Illicium (Schisandraceae). Mol. Phylogenet. Evol. 2007, 45, 547–563. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Zhang, Q.; Feild, T.S.; Antonelli, A. Assessing the impact of phylogenetic incongruence on taxonomy, floral evolution, biogeographical history, and phylogenetic diversity. Am. J. Bot. 2015, 102, 566–580. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, Y.-B.; Jiang, Y.-L.; Qin, X.-M.; Zhang, Q. Morphological diversity and geographical distribution of Chloranthus in China. Guihaia 2020, 40, 31–43. [Google Scholar]
- Chen, F.-Y.; Bian, Y.-T.; Huang, W.-M.; Chen, Z.-C.; Shuang, P.-C.; Feng, Z.-G.; Luo, Y.-M. Research progress on chemical constituents from Chloranthus plants and their biological activities. China J. Chin. Mater. Med. 2021, 46, 3789–3796. [Google Scholar]
- Heo, J.-E.; Jin, J.-L.; Lee, Y.-Y.; Yunchoi, H.-S. Chemical Constituents of the Aerial Parts of Chloranthus japonicus Sieb. Nat. Prod. Sci. 2005, 11, 41–44. [Google Scholar]
- Li, C.-J.; Zhang, D.-M.; Luo, Y.-M. Studies on the chemical constituents from the roots of Chloranthus henryi. Acta Pharm. Sin. B 2005, 40, 525–528. [Google Scholar]
- Cao, C.-M.; Peng, Y.; Shi, Q.-W.; Xiao, P.-G. Chemical constituents and bioactivities of plants of Chloranthaceae. Chem. Biodivers. 2008, 5, 219–238. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yao, S.-T.; Lu, Y.-B.; Zhang, Z.-J.; Li, C.; Wang, P.-F.; Qin, X.-M. The complete chloroplast genome of Chloranthus nervosus Collrtt ex Hemsl. 1890 (Chloranthaceae). Mitochondrial DNA B 2023, 8, 1224–1228. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Doyle, J.J.; Doyle, J.L. A rapid DNA isolation procedure for small amounts of fresh leaf tissue. Phytochem. Bull. 1987, 19, 11–15. [Google Scholar]
- Brown, J.; Pirrung, M.; McCue, L.A. FQC Dashboard: Integrates FastQC results into a web-based, interactive, and extensible FASTQ quality control tool. Bioinformatics 2017, 33, 3137–3139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bolger, A.M.; Lohse, M.; Usadel, B. Trimmomatic: A flexible trimmer for Illumina sequence data. Bioinformatics 2014, 30, 2114–2120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jin, J.-J.; Yu, W.-B.; Yang, J.-B.; Song, Y.; dePamphilis, C.W.; Yi, T.-S.; Li, D.-Z. GetOrganelle: A fast and versatile toolkit for accurate de novo assembly of organelle genomes. Genome Biol. 2020, 21, 241. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wick, R.R.; Schultz, M.B.; Zobel, J.; Holt, K.E. Bandage: Interactive visualization of de novo genome assemblies. Bioinformatics 2015, 31, 3350–3352. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tillich, M.; Lehwark, P.; Pellizzer, T.; Ulbricht-Jones, E.S.; Fischer, A.; Bock, R.; Greiner, S. GeSeq-versatile and accurate annotation of organelle genomes. Nucleic Acids Res. 2017, 45, 6–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Angiosperm Phylogeny Group; Chase, M.W.; Christenhusz, M.J.M.; Fay, M.F.; Byng, J.W.; Judd, W.S.; Soltis, D.E.; Mabberley, D.J.; Sennikov, A.N.; Soltis, P.S.; et al. An update of the Angiosperm Phylogeny Group classification for the orders and families of flowering plants: APG IV. Bot. J. Linn. Soc. 2016, 181, 1–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Katoh, K.; Toh, H. Parallelization of the MAFFT multiple sequence alignment program. Bioinformatics 2010, 26, 1899–1900. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stamatakis, A. RAxML version 8: A tool for phylogenetic analysis and post-analysis of large phylogenies. Bioinformatics 2014, 30, 1312–1313. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Swofford, D.L. PAUP*: Phylogenetic Analysis Using Parsimony (*and Other Methods); Version 4.0b10.; Sinauer: Sunderland, Massachusetts, 2003. [Google Scholar]
- Lee, S.; Weon, S.; Lee, S.; Kang, C. Relative codon adaptation index, a sensitive measure of codon usage bias. Evol. Bioinform. 2010, 6, 47–55. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wright, F. The ‘effective number of codons’ used in a gene. Gene 1990, 87, 23–29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nasrullah, I.; Butt, A.M.; Tahir, S.; Idrees, M.; Tong, Y. Genomic analysis of codon usage shows influence of mutation pressure, natural selection, and host features on Marburg virus evolution. BMC Evol. Biol. 2015, 15, 174. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vicario, S.; Moriyama, E.N.; Powell, J.R. Codon usage in twelve species of Drosophila. BMC Evol. Biol. 2007, 7, 226. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tao, P.; Dai, L.; Luo, M.; Tang, F.; Tien, P.; Pan, Z. Analysis of synonymous codon usage in classical swine fever virus. Virus Genes 2009, 38, 104–112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sueoka, N. Intrastrand parity rules of DNA base composition and usage biases of synonymous codons. J. Mol. Evol. 1995, 40, 318–325. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sueoka, N. Translation-coupled violation of Parity Rule 2 in human genes is not the cause of heterogeneity of the DNA G+C content of third codon position. Gene 1999, 238, 53–58. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sueoka, N. Near homogeneity of PR2-bias fingerprints in the human genome and their implications in phylogenetic analyses. J. Mol. Evol. 2001, 53, 469–476. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bu, Y.; Wu, X.; Sun, N.; Man, Y.; Jing, Y. Codon usage bias predicts the functional MYB10 gene in Populus. J. Plant Physiol. 2021, 265, 153491. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, Y.-F.; Wen, F.; Hong, X.; Li, Z.L.; Mi, Y.L.; Zhao, B. Comparative chloroplast genome analyses of Paraboea (Gesneriaceae): Insights into adaptive evolution and phylogenetic analysis. Front. Plant Sci. 2022, 13, 1019831. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, J.-L.; Wang, F.; Zhao, Z.; Li, M.-H.; Liu, Z.-J.; Peng, D.-H. Complete chloroplast genomes and comparative analyses of three Paraphalaenopsis (Aeridinae, Orchidaceae) species. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2023, 24, 11167. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Comeron, J.M.; Aguadé, M. An evalution of measures of synonymous codon usage bias. J. Mol. Evol. 1998, 47, 268–274. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sablok, G.; Nayak, K.C.; Vazquez, F.; Tatarinova, T.V. Synonymous codon usage, GC(3), and evolutionary patterns across plastomes of three pooid model species: Emerging grass genome models for monocots. Mol. Biotechnol. 2011, 49, 116–128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ling, L.; Zhang, S.; Yang, T. Analysis of codon usage bias in chloroplast genomes of Dryas octopetala var. asiatica (Rosaceae). Genes 2024, 15, 899. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ikemura, T. Correlation between the abundance of Escherichia coli transfer RNAs and the occurrence of the respective codons in its protein genes. J. Mol. Biol. 1981, 146, 1–21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hershberg, R.; Petrov, D.A. Selection on codon bias. Annu. Rev. Genet. 2008, 42, 287–299. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Palidwor, G.A.; Perkins, T.J.; Xia, X. A general model of codon bias due to GC mutational bias. PLoS ONE 2010, 5, e13431. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Duan, H.; Zhang, Q.; Wang, C.; Li, F.; Tian, F.; Lu, Y.; Hu, Y.; Yang, H.; Cui, G. Analysis of codon usage patterns of the chloroplast genome in Delphinium grandiflorum L. reveals a preference for AT-ending codons as a result of major selection constraints. Peer J. 2021, 9, e10787. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, C.-Q.; Chen, F.-D.; Teng, N.-J.; Xu, Y.-C.; Dai, Z.-L. Comparative analysis of the complete chloroplast genome of seven Nymphaea species. Aquat. Bot. 2021, 170, 103353. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Z.-J.; Cai, Q.-W.; Wang, Y.; Li, M.-H.; Wang, C.-C.; Wang, Z.-X.; Jiao, C.-Y.; Xu, C.-C.; Wang, H.-Y.; Zhang, Z.-L. Comparative analysis of codon bias in the chloroplast genomes of Theaceae species. Front. Genet. 2022, 13, 824610. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, Y.-H.; Wei, Q.-Y.; Xue, T.-Y.; He, S.-X.; Fang, J.; Zeng, C.-L. Comparative and phylogenetic analysis of the complete chloroplast genomes of 10 Artemisia selengensis resources based on high-throughput sequencing. BMC Genomics. 2024, 25, 561. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sebastin, R.; Kim, J.; Jo, I.-H.; Yu, J.-K.; Jang, W.; Han, S.; Park, H.S.; AlGarawi, A.M.; Hatamleh, A.A.; So, Y.-S.; et al. Comparative chloroplast genome analyses of cultivated and wild Capsicum species shed light on evolution and phylogeny. BMC Plant Biol. 2024, 24, 797. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kong, W.-Q.; Yang, J.-H. The complete chloroplast genome sequence of Morus cathayana and Morus multicaulis, and comparative analysis within genus Morus L. PeerJ. 2017, 8, e3037. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, Z.-J.; Xu, B.-B.; Li, B.; Zhou, Q.-Q.; Wang, G.-Y.; Jiang, X.-Z.; Wang, C.-C.; Xu, Z.-D. Comparative analysis of codon usage patterns in chloroplast genomes of six Euphorbiaceae species. PeerJ. 2020, 8, e8251. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, L.-J.; Roossinck, M.J. Comparative analysis of expressed sequences reveals a conserved pattern of optimal codon usage in plants. Plant Mol. Biol. 2006, 61, 699–710. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ji, K.-K.; Song, X.-Q.; Chen, C.-G.; Li, G.; Xie, S.-Q. Codon usage profiling of chloroplast genome in Magnoliaceae. J. Agric. Sci. Technol. 2022, 22, 52–62. [Google Scholar]
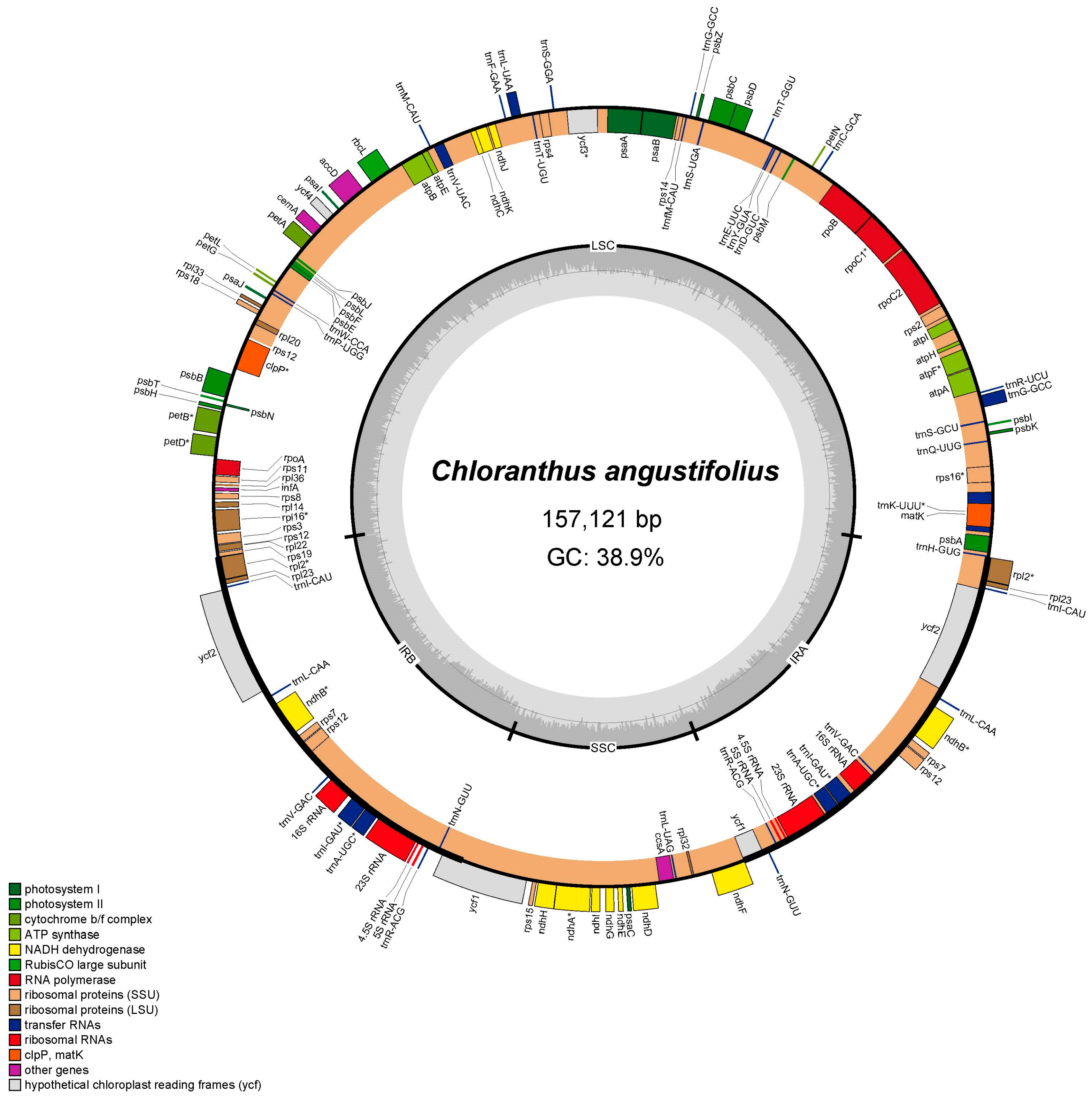

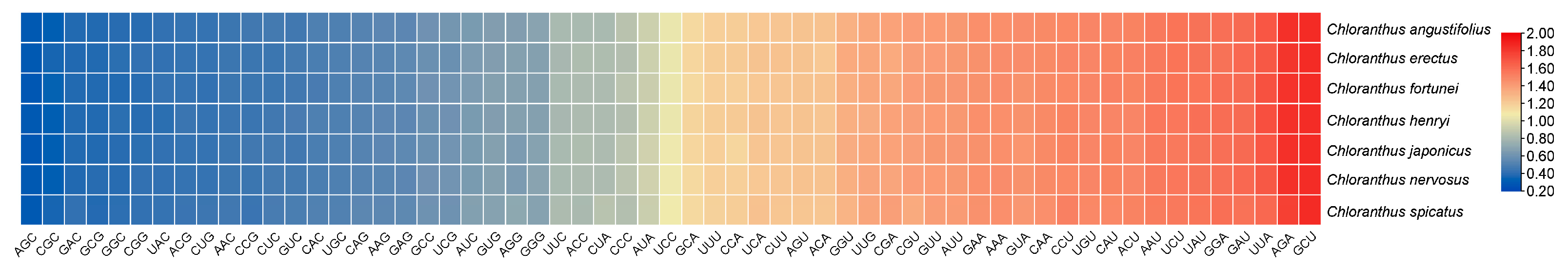
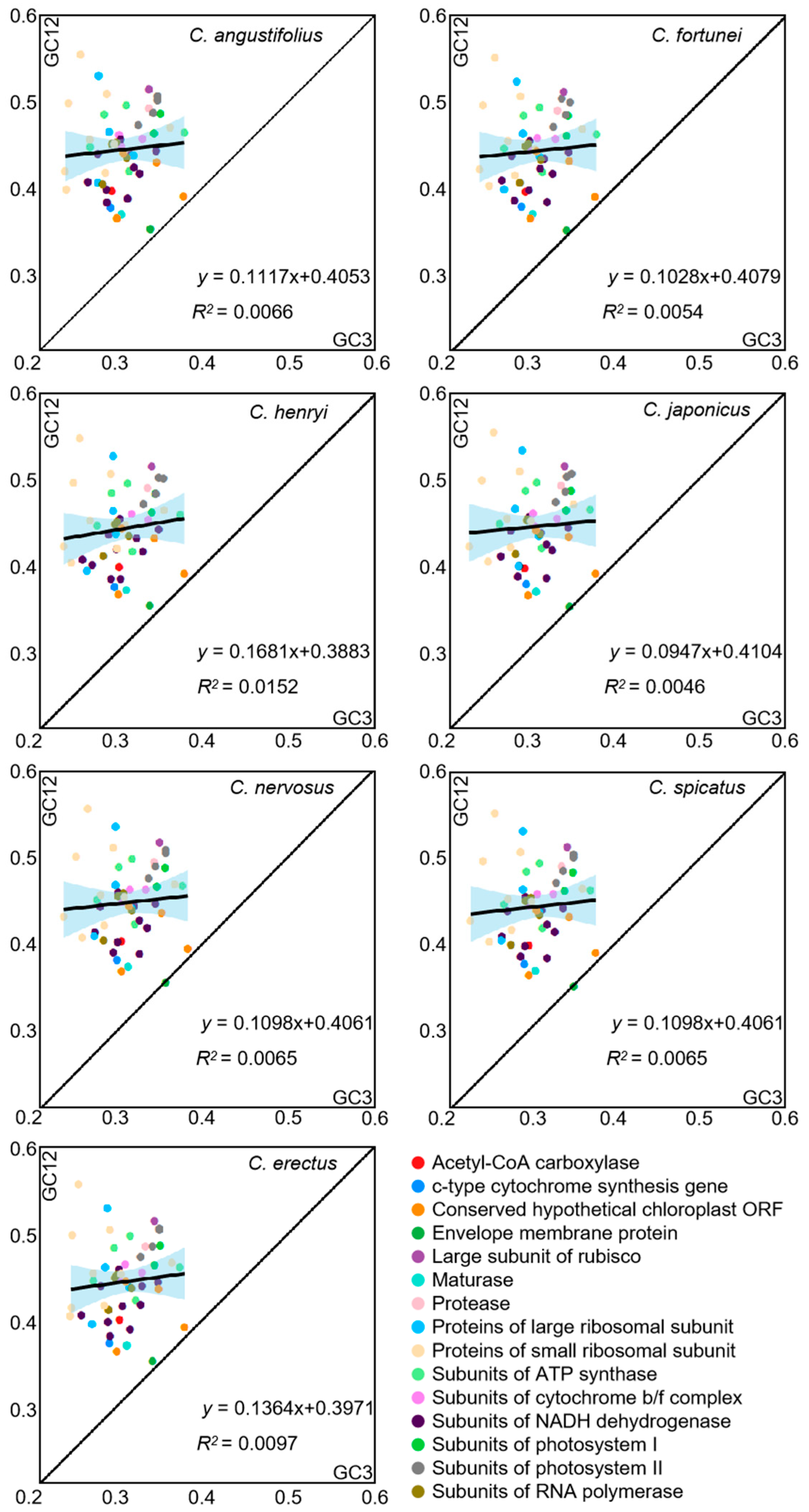
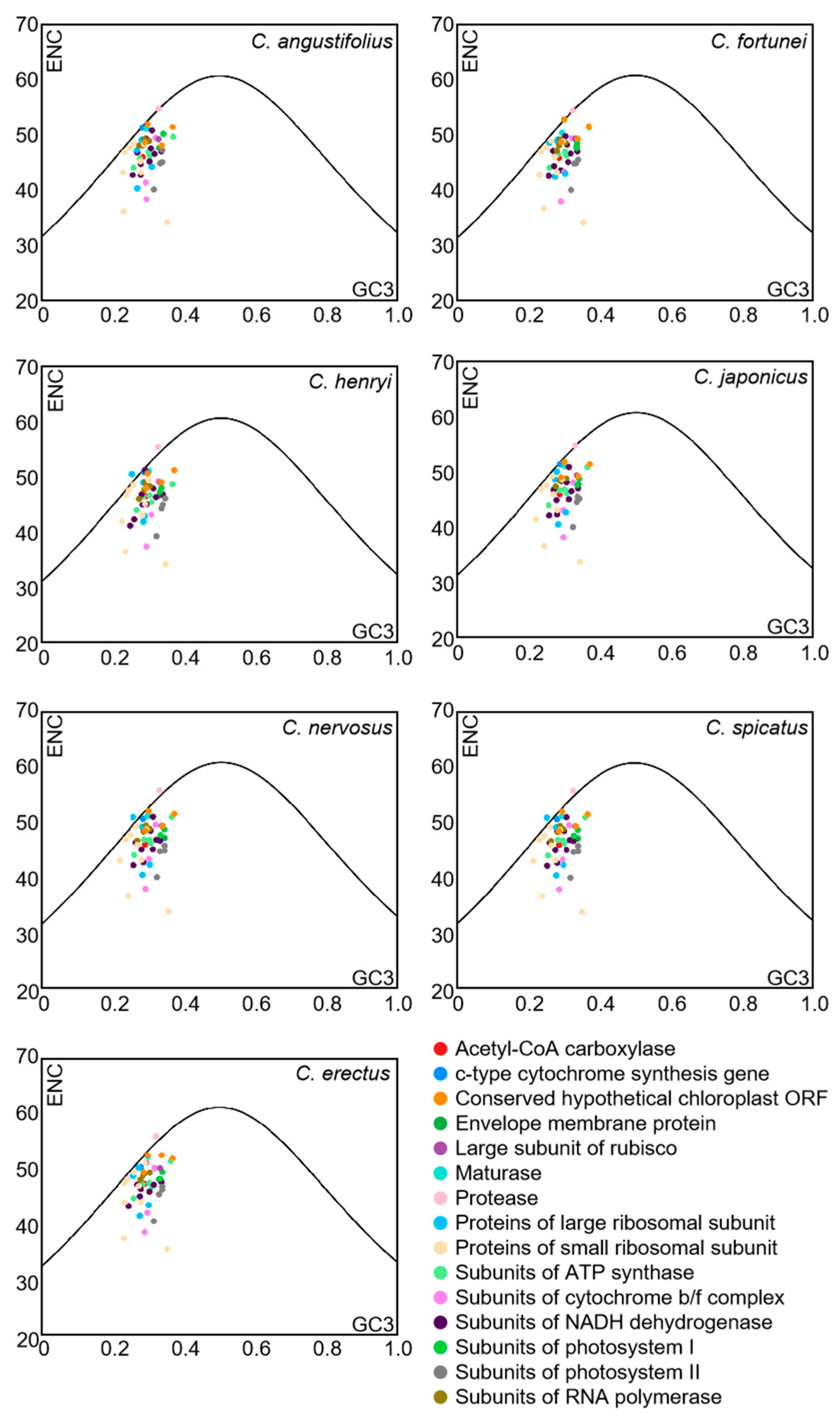


| Species | Genbank No. | N. | GC1 | GC2 | GC3 | GCall | ENC | GC3s |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| C. angustifolius | MW581013 | 20 728 | 0.475 | 0.403 | 0.301 | 0.393 | 46.26 | 0.302 |
| C. nervosus | NC_082096 | 20 728 | 0.475 | 0.403 | 0.301 | 0.393 | 46.32 | 0.302 |
| C. spicatus | NC_009598 | 20 728 | 0.475 | 0.403 | 0.301 | 0.393 | 46.32 | 0.302 |
| C. japonicus | NC_026565 | 20 758 | 0.475 | 0.403 | 0.302 | 0.393 | 46.27 | 0.302 |
| C. erectus | NC_039627 | 20 719 | 0.473 | 0.403 | 0.300 | 0.392 | 46.47 | 0.301 |
| C. henryi | MK922064 | 20 718 | 0.473 | 0.403 | 0.299 | 0.392 | 46.23 | 0.299 |
| C. fortunei | NC_065306 | 20 721 | 0.474 | 0.403 | 0.301 | 0.393 | 46.29 | 0.302 |
| Species | Variation | Codon Parameters | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| GC1 | GC2 | GC3 | GCall | ENC | ||
| C. angustifolius | GC2 | 0.245 | ||||
| GC3 | 0.179 | −0.065 | ||||
| GCall | 0.808 ** | 0.675 ** | 0.408 ** | |||
| ENC | 0.218 | −0.371 ** | 0.249 | 0.014 | ||
| Codon No. | −0.103 | −0.274 | 0.274 | −0.122 | 0.313 * | |
| C. nervosus | GC2 | 0.241 | ||||
| GC3 | 0.161 | −0.046 | ||||
| GCall | 0.801 ** | 0.677 ** | 0.410 ** | |||
| ENC | 0.224 | −0.380 ** | 0.184 | −0.007 | ||
| Codon No. | −0.102 | −0.274 | 0.272 | −0.121 | 0.280 * | |
| C. spicatus | GC2 | 0.241 | ||||
| GC3 | 0.161 | −0.046 | ||||
| GCall | 0.801 ** | 0.677 ** | 0.410 ** | |||
| ENC | 0.224 | −0.380 ** | 0.184 | −0.007 | ||
| Codon No. | −0.102 | −0.274 | 0.272 | −0.121 | 0.280 * | |
| C. japonicus | GC2 | 0.242 | ||||
| GC3 | 0.160 | −0.067 | ||||
| GCall | 0.806 ** | 0.676 ** | 0.393 ** | |||
| ENC | 0.19 | −0.389 ** | 0.239 | −0.016 | ||
| Codon No. | −0.098 | −0.274 | 0.277 * | −0.119 | 0.300 * | |
| C. erectus | GC2 | 0.259 | ||||
| GC3 | 0.179 | −0.036 | ||||
| GCall | 0.807 ** | 0.687 ** | 0.419 ** | |||
| ENC | 0.192 | −0.371 ** | 0.233 | −0.008 | ||
| Codon No. | −0.088 | −0.277 * | 0.290 * | −0.108 | 0.276 * | |
| C. henryi | GC2 | 0.214 | ||||
| GC3 | 0.218 | −0.036 | ||||
| GCall | 0.802 ** | 0.687 ** | 0.419 ** | |||
| ENC | 0.212 | −0.371 ** | 0.233 | −0.008 | ||
| Codon No. | −0.082 | −0.277 * | 0.290 * | −0.108 | 0.276 * | |
| C. fortunei | GC2 | 0.231 | ||||
| GC3 | 0.163 | −0.060 | ||||
| GCall | 0.802 ** | 0.675 ** | 0.397 ** | |||
| ENC | 0.243 | −0.360 ** | 0.214 | 0.023 | ||
| Codon No. | −0.095 | −0.277 * | 0.268 | −0.123 | 0.289 * | |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Zhang, J.; Feng, M. Analysis of the Codon Usage Bias Pattern in the Chloroplast Genomes of Chloranthus Species (Chloranthaceae). Genes 2025, 16, 186. https://doi.org/10.3390/genes16020186
Zhang J, Feng M. Analysis of the Codon Usage Bias Pattern in the Chloroplast Genomes of Chloranthus Species (Chloranthaceae). Genes. 2025; 16(2):186. https://doi.org/10.3390/genes16020186
Chicago/Turabian StyleZhang, Jisi, and Miao Feng. 2025. "Analysis of the Codon Usage Bias Pattern in the Chloroplast Genomes of Chloranthus Species (Chloranthaceae)" Genes 16, no. 2: 186. https://doi.org/10.3390/genes16020186
APA StyleZhang, J., & Feng, M. (2025). Analysis of the Codon Usage Bias Pattern in the Chloroplast Genomes of Chloranthus Species (Chloranthaceae). Genes, 16(2), 186. https://doi.org/10.3390/genes16020186






