Identification of Novel Mosaic Variants in Focal Epilepsy-Associated Patients’ Brain Lesions
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Recruitment and Cohort Profile
2.2. Whole-Exome Sequencing and Data Analysis
2.3. Somatic Variants Identification and Mosaic Fraction Calculation Methodology
2.4. Bioinformatics In Silico Analysis
2.5. Data Analysis and Visualization
3. Results
3.1. Clinical Characteristics of FCDIII Patients in This Study
3.2. WES Analyses Identified Ten Novel Potential Pathogenic Candidate Variants in Eight FCDIII Patients
3.3. The Novel Identified Pathogenic Mosaic Variants That Showed Phenotypic Consistency and Severe Protein Structural Damage
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| FCD | Focal cortical dysplasia |
| MAF | Mutant allele fraction |
| NGS | Next-generation sequencing |
| WES | Whole-exome sequencing |
| VCF | Variant call format |
| OMIM | Online Mendelian Inheritance in Man |
References
- Guerrini, R.; Barba, C. Focal cortical dysplasia: An update on diagnosis and treatment. Expert Rev. Neurother. 2021, 21, 1213–1224. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chung, C.; Yang, X.; Bae, T.; Vong, K.I.; Mittal, S.; Donkels, C.; Westley Phillips, H.; Li, Z.; Marsh, A.P.; Breuss, M.W.; et al. Comprehensive multi-omic profiling of somatic mutations in malformations of cortical development. Nat. Genet. 2023, 55, 209–220. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Blümcke, I.; Thom, M.; Aronica, E.; Armstrong, D.D.; Vinters, H.V.; Palmini, A.; Jacques, T.S.; Avanzini, G.; Barkovich, A.J.; Battaglia, G. The clinicopathologic spectrum of focal cortical dysplasias: A consensus classification proposed by an ad hoc task force of the ILAE Diagnostic Methods Commission 1. Comp. Study 2011, 52, 158–174. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Barkovich, A.J.; Guerrini, R.; Kuzniecky, R.I.; Jackson, G.D.; Dobyns, W.B. A developmental and genetic classification for malformations of cortical development: Update 2012. Brain 2012, 135, 1348–1369. [Google Scholar]
- Blumcke, I.; Spreafico, R.; Haaker, G.; Coras, R.; Kobow, K.; Bien, C.G.; Pfäfflin, M.; Elger, C.; Widman, G.; Schramm, J. Histopathological findings in brain tissue obtained during epilepsy surgery. N. Engl. J. Med. 2017, 377, 1648–1656. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Pinheiro, J.; Honavar, M. Focal cortical dysplasia: Updates. Indian J. Pathol. Microbiol. 2022, 65, S189–S197. [Google Scholar]
- Krsek, P.; Pieper, T.; Karlmeier, A.; Hildebrandt, M.; Kolodziejczyk, D.; Winkler, P.; Pauli, E.; Blümcke, I.; Holthausen, H. Different presurgical characteristics and seizure outcomes in children with focal cortical dysplasia type I or II. Epilepsia 2009, 50 (Suppl. S1), 125–137. [Google Scholar]
- Specchio, N.; Wirrell, E.; Scheffer, I.; Nabbout, R.; Riney, K.; Samia, P. ILAE classification and definition of epilepsy syndromes with onset in childhood: Position paper by the ILAE task force on nosology and definitions. Epilepsia 2022, 63, 1398–1442. [Google Scholar]
- Wan, H.J.; Hu, W.H.; Wang, X.; Zhang, C.; Wang, S.S.; Zheng, Z.; Zhou, F.; Sang, L.; Zhang, K.; Zhang, J.G. Interictal pattern on scalp electroencephalogram predicts excellent surgical outcome of epilepsy caused by focal cortical dysplasia. Epilepsia Open 2022, 7, 350–360. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lara, C.; JC, S.A. Focal cortical dysplasia and refractory epilepsy. Surgical treatment. Rev. De Neurol. 2001, 32, 738–742. [Google Scholar]
- Najm, I.; Lal, D.; Alonso Vanegas, M.; Cendes, F.; Lopes-Cendes, I.; Palmini, A.; Paglioli, E.; Sarnat, H.B.; Walsh, C.A.; Wiebe, S. The ILAE consensus classification of focal cortical dysplasia: An update proposed by an ad hoc task force of the ILAE diagnostic methods commission. Epilepsia 2022, 63, 1899–1919. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Shroff, S. Pediatric Epilepsy: A “Histo”-Pathologic Perspective. J. Pediatr. Epilepsy 2016, 5, 153–158. [Google Scholar]
- Wasilewska, K.; Gambin, T.; Rydzanicz, M.; Szczałuba, K.; Płoski, R. Postzygotic mutations and where to find them–recent advances and future implications in the field of non-neoplastic somatic mosaicism. Mutat. Res. Rev. Mutat. Res. 2022, 790, 108426. [Google Scholar]
- Krochmalnek, E.; Accogli, A.; St-Onge, J.; Addour-Boudrahem, N.; Prakash, G.; Kim, S.-H.; Brunette-Clement, T.; Alhajaj, G.; Mougharbel, L.; Bruneau, E. mTOR pathway somatic pathogenic variants in focal malformations of cortical development: Novel variants, topographic mapping, and clinical outcomes. Neurol. Genet. 2023, 9, e200103. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Ye, Z.; McQuillan, L.; Poduri, A.; Green, T.E.; Matsumoto, N.; Mefford, H.C.; Scheffer, I.E.; Berkovic, S.F.; Hildebrand, M.S. Somatic mutation: The hidden genetics of brain malformations and focal epilepsies. Epilepsy Res. 2019, 155, 106161. [Google Scholar]
- D’Gama, A.M.; Poduri, A. Precision therapy for epilepsy related to brain malformations. Neurotherapeutics 2021, 18, 1548–1563. [Google Scholar]
- Yang, X.; Xu, X.; Breuss, M.W.; Antaki, D.; Ball, L.L.; Chung, C.; Shen, J.; Li, C.; George, R.D.; Wang, Y. Control-independent mosaic single nucleotide variant detection with DeepMosaic. Nat. Biotechnol. 2023, 41, 870–877. [Google Scholar]
- Ma, Q.; Chen, G.; Li, Y.; Guo, Z.; Zhang, X. The molecular genetics of PI3K/PTEN/AKT/mTOR pathway in the malformations of cortical development. Genes Dis. 2024, 11, 101021. [Google Scholar]
- Benegas, G.; Albors, C.; Aw, A.J.; Ye, C.; Song, Y.S. A DNA language model based on multispecies alignment predicts the effects of genome-wide variants. Nat. Biotechnol. 2025, 1–6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Andrews, S. FastQC: A Quality Control Tool for High Throughput Sequence Data. Available online: https://www.bioinformatics.babraham.ac.uk/projects/fastqc/ (accessed on 1 March 2010).
- Ewels, P.; Magnusson, M.; Lundin, S.; Käller, M. MultiQC: Summarize analysis results for multiple tools and samples in a single report. Bioinformatics 2016, 32, 3047–3048. [Google Scholar]
- Li, H.; Durbin, R. Fast and accurate short read alignment with Burrows–Wheeler transform. Bioinformatics 2009, 25, 1754–1760. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- McKenna, A.; Hanna, M.; Banks, E.; Sivachenko, A.; Cibulskis, K.; Kernytsky, A.; Garimella, K.; Altshuler, D.; Gabriel, S.; Daly, M. The Genome Analysis Toolkit: A MapReduce framework for analyzing next-generation DNA sequencing data. Genome Res. 2010, 20, 1297–1303. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cingolani, P.; Platts, A.; Wang, L.L.; Coon, M.; Nguyen, T.; Wang, L.; Land, S.J.; Lu, X.; Ruden, D.M. A program for annotating and predicting the effects of single nucleotide polymorphisms, SnpEff: SNPs in the genome of Drosophila melanogaster strain w1118; iso-2; iso-3. Fly 2012, 6, 80–92. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Béroud, C.; Collod-Béroud, G.; Boileau, C.; Soussi, T.; Junien, C. UMD (Universal mutation database): A generic software to build and analyze locus-specific databases. Hum. Mutat. 2000, 15, 86–94. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, Y.; Zhou, B.; Pache, L.; Chang, M.; Khodabakhshi, A.H.; Tanaseichuk, O.; Benner, C.; Chanda, S.K. Metascape provides a biologist-oriented resource for the analysis of systems-level datasets. Nat. Commun. 2019, 10, 1523. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jumper, J.; Evans, R.; Pritzel, A.; Green, T.; Figurnov, M.; Ronneberger, O.; Tunyasuvunakool, K.; Bates, R.; Žídek, A.; Potapenko, A. Highly accurate protein structure prediction with AlphaFold. Nature 2021, 596, 583–589. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhou, Y.; Pan, Q.; Pires, D.E.; Rodrigues, C.H.; Ascher, D.B. DDMut: Predicting effects of mutations on protein stability using deep learning. Nucleic Acids Res. 2023, 51, W122–W128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ferri, L.; Menghi, V.; Licchetta, L.; Dimartino, P.; Minardi, R.; Davì, C.; Di Vito, L.; Cifaldi, E.; Zenesini, C.; Gozzo, F. Detection of somatic and germline pathogenic variants in adult cohort of drug-resistant focal epilepsies. Epilepsy Behav. 2024, 153, 109716. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Urbach, H.; Kellner, E.; Kremers, N.; Blümcke, I.; Demerath, T. MRI of focal cortical dysplasia. Neuroradiology 2022, 64, 443–452. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, W.S.; Baldassari, S.; Stephenson, S.E.; Lockhart, P.J.; Baulac, S.; Leventer, R.J. Cortical dysplasia and the mTOR pathway: How the study of human brain tissue has led to insights into epileptogenesis. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2022, 23, 1344. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baldassari, S.; Ribierre, T.; Marsan, E.; Adle-Biassette, H.; Ferrand-Sorbets, S.; Bulteau, C.; Dorison, N.; Fohlen, M.; Polivka, M.; Weckhuysen, S. Dissecting the genetic basis of focal cortical dysplasia: A large cohort study. Acta Neuropathol. 2019, 138, 885–900. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schwarz, J.M.; Becker, L.-L.; Wahle, M.; Faßbender, J.; Thomale, U.-W.; Tietze, A.; Morales-Gonzalez, S.; Knierim, E.; Schuelke, M.; Kaindl, A.M. Somatic DNA Variants in Epilepsy Surgery Brain Samples from Patients with Lesional Epilepsy. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2025, 26, 815. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jamuar, S.S.; Walsh, C.A. Genomic variants and variations in malformations of cortical development. Pediatr. Clin. 2015, 62, 571–585. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Van Horebeek, L.; Goris, A.; Dubois, B. Somatic Mosaicism in Multiple Sclerosis: Detection and Insights into Disease. Ph.D. Thesis, University of Leuven, Leuven, Belgium, 2022. [Google Scholar]
- Auvin, S. Finally, a controversy about neonatal seizure treatment. Epilepsia 2022, 63, 1880–1882. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- D’Gama, A.M.; Walsh, C.A. Somatic mosaicism and neurodevelopmental disease. Nat. Neurosci. 2018, 21, 1504–1514. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rimmerman, N.; Verdiger, H.; Goldenberg, H.; Naggan, L.; Robinson, E.; Kozela, E.; Gelb, S.; Reshef, R.; Ryan, K.M.; Ayoun, L. Microglia and their LAG3 checkpoint underlie the antidepressant and neurogenesis-enhancing effects of electroconvulsive stimulation. Mol. Psychiatry 2022, 27, 1120–1135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cui, J.; Wang, L.; Ren, X.; Zhang, Y.; Zhang, H. LRPPRC: A multifunctional protein involved in energy metabolism and human disease. Front. Physiol. 2019, 10, 595. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jecan-Toader, D.; Trifa, A.; Lucian, B.; Pop, T.L.; Cainap, S.S. Alström syndrome—Wide clinical variability within the same variant: A case report and literature review. Front. Pediatr. 2024, 12, 1463903. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Parcerisas, A.; Rubio, S.E.; Muhaisen, A.; Gomez-Ramos, A.; Pujadas, L.; Puiggros, M.; Rossi, D.; Urena, J.; Burgaya, F.; Pascual, M. Somatic signature of brain-specific single nucleotide variations in sporadic Alzheimer’s disease. J. Alzheimer’s Dis. 2014, 42, 1357–1382. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sajan, S.A.; Gradisch, R.; Vogel, F.D.; Coffey, A.J.; Salyakina, D.; Soler, D.; Jayakar, P.; Jayakar, A.; Bianconi, S.E.; Cooper, A.H. De novo variants in GABRA4 are associated with a neurological phenotype including developmental delay, behavioral abnormalities and epilepsy. Eur. J. Hum. Genet. 2024, 32, 912–919. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bujko, M.; Machnicki, M.M.; Grecka, E.; Rusetska, N.; Matyja, E.; Kober, P.; Mandat, T.; Rydzanicz, M.; Płoski, R.; Krajewski, R. Mutational analysis of recurrent meningioma progressing from atypical to Rhabdoid subtype. World Neurosurg. 2017, 97, 754.e1–754.e6. [Google Scholar]

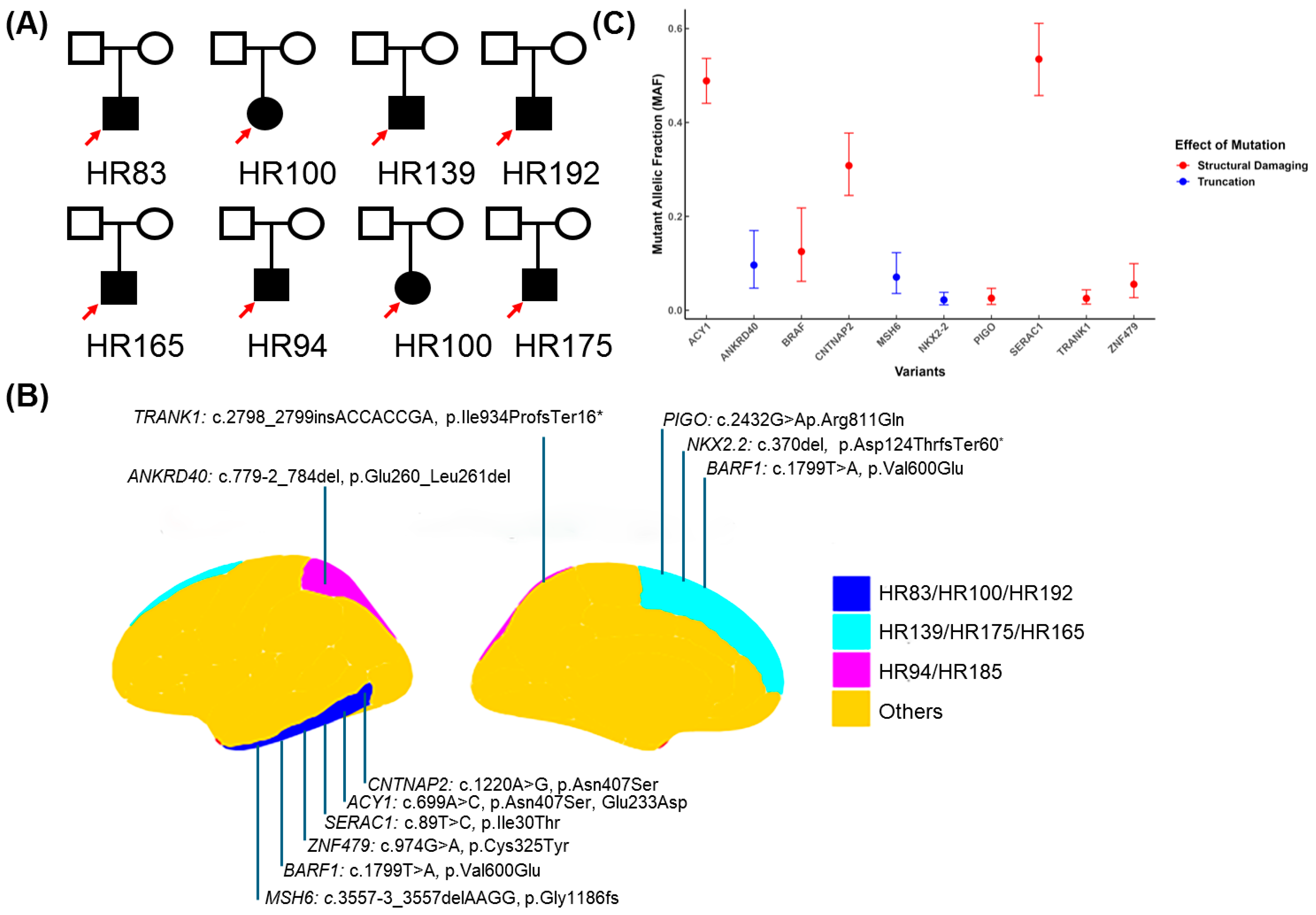
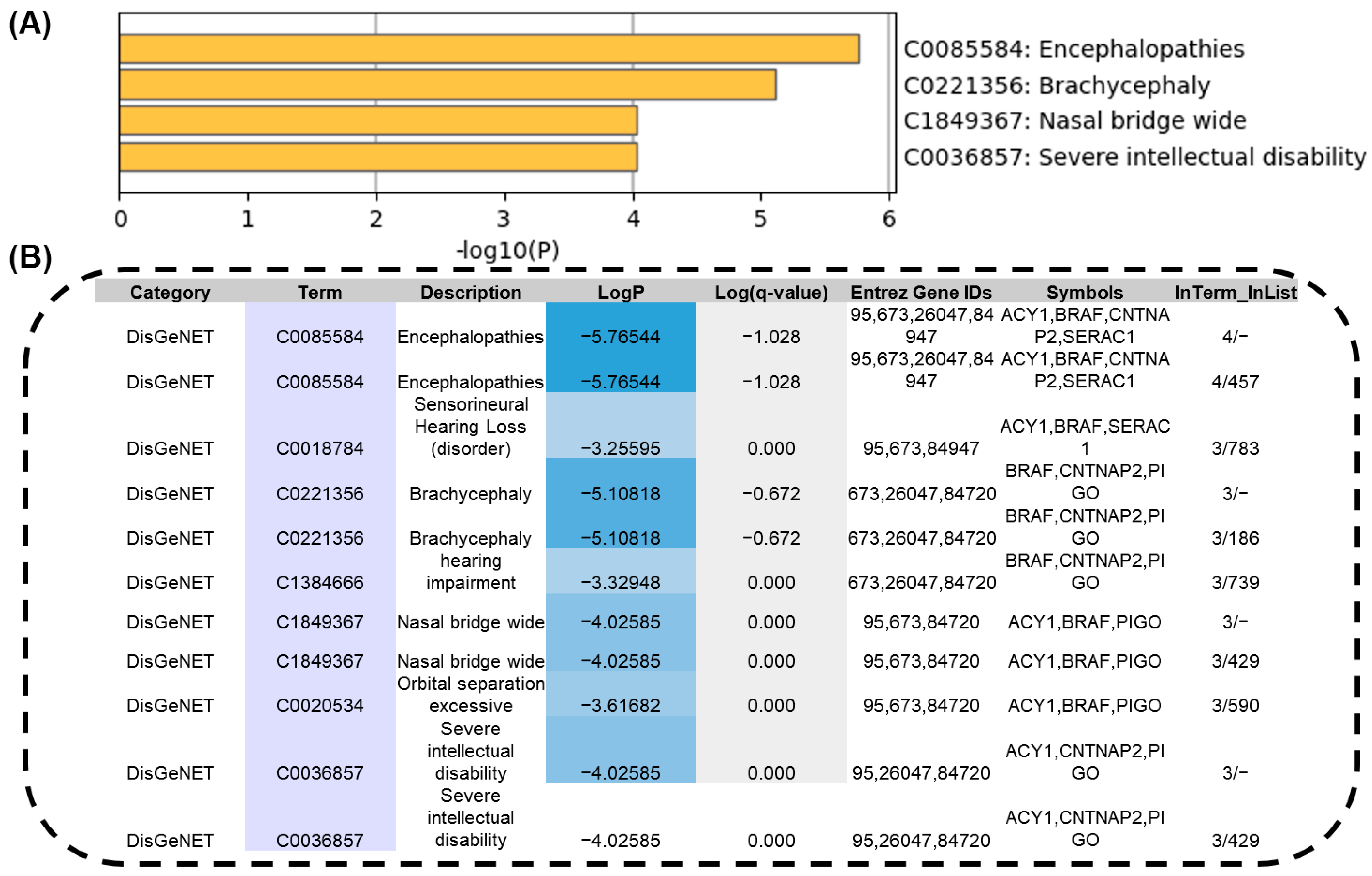
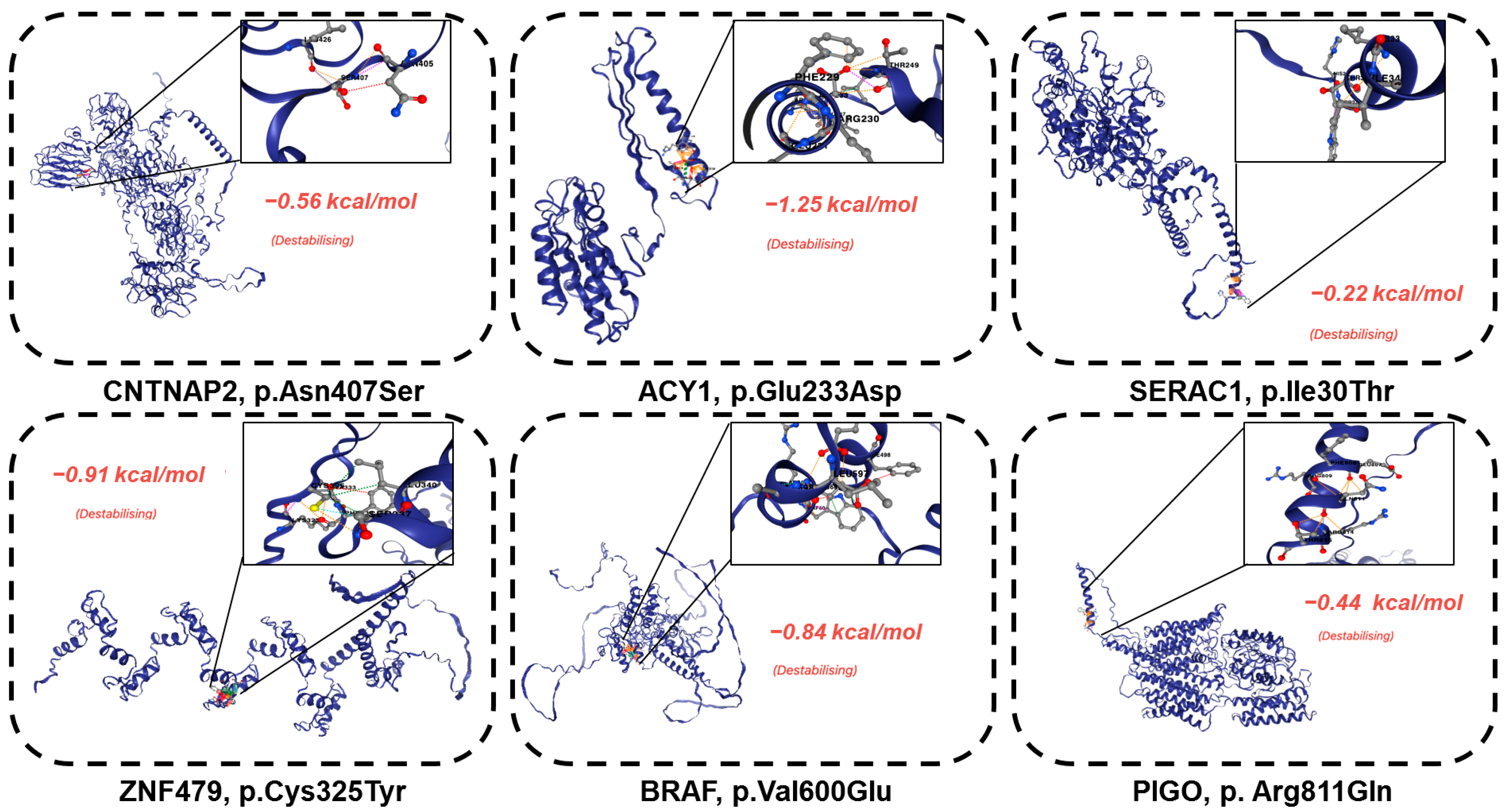
| ID | HR83 | HR100 | HR139 | HR175 | HR185 | HR192 | HR165 | HR94 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| HOSPITAL ID | 1207695H | 0769405C | 1184599D | 1073501B | 0905454I | 1524999G | 1432293H | 1286326H |
| LOBE | RIGHT TEMPORAL | RIGHT/TEMPORAL | RIGHT/FRONTAL | LEFT/FRONTAL | RIGHT/TEMPORAL/PARIETAL | RIGHT/TEMPORAL | LEFT/FRONTAL | RIGHT/MULTILOBAR |
| WES | BLOOD/FROZEN TISSUE | BLOOD/FROZEN TISSUE | BLOOD/FROZEN TISSUE | BLOOD/FROZEN TISSUE | BLOOD/FROZEN TISSUE | BLOOD/FROZEN TISSUE | BLOOD/FROZEN TISSUE | BLOOD/FROZEN TISSUE |
| Sex | Male | Female | Male | Male | Male | Male | Female | Male |
| Date of Birth | 12/19/1997 | 2005/8/3 | 03/29/2007 | 03/26/2013 | 09/14/2005 | 12/21/2006 | 09/13/2010 | 01/14/2012 |
| Date of Surgery | 2010/4/7 | 03/24/2014 | 11/16/2015 | 09/28/2015 | 2017/2/8 | 09/18/2017 | 11/30/2017 | 2013/4/10 |
| Onset of Epilepsy | 5 years | 7 months | 4 years | 4 months | 7 months | 8 years | 2 years | 2 months |
| Monthly Seizure Frequency/Pre-operative | 90 | 900 | 2.5 | 450 | 60 | 540 | 2000 | 90 |
| Type of Seizure | Focal | Generalized tonic–clonic | Structural focal | Generalized | Generalized | Symptomatic focal | Structural focal | Focal |
| ADNPM | N | N | N | Y | Y | N | N | Y |
| Neuropsychomotor Impairment | N | Y | Y | Y | Y | Y | Y | Y |
| Hemiparesis | N | N | N | N | N | N | Y | N |
| Ocular Deviation Nystagmus | N | N | N | N | N | N | Y | Y |
| Macrocephaly | N | N | N | N | N | N | N | N |
| Number of Medications | 2 | 3 | 2 | 3 | 3 | 1 | 4 | 2 |
| Treatment Reoperation | N | Y | N | N | N | N | N | N |
| Engel 1 Year | 1 | 4 | 1 | 3 | 1 | 3 | 1 | NO DATA |
| Engel 5 Years | 1 | 4 | 1 | 0 | NO DATA | NO DATA | NO DATA | NO DATA |
| Mosaic Missense Pathogenic Variants | |||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| ID | Gene | FCDIII Type | Location | Mutation | Mosaic Fractions | HGVSc | HGVSp | SIFT | PolyPhen | CADD PHRAD | GPN-MSA_SCORES | gnomADe_AF | Transcript_ID | Reference_Genome | Gene_ENST |
| HR83 | CNTNAP2 | FCDIIIb | 7:147132381-147132381 | missense variant | 62% | ENST00000361727.3:c.1220A>G | ENSP00000354778.3:p.Asn407Ser | tolerated (0.73) | benign (0.01) | 8.396 | −12.63 | 0.0006432 | ENST00000361727 | GRCh38 | CNTNAP2-201 |
| HR83 | ACY1 | FCDIIIb | 3:51987188-51987188 | missense variant | 97.72% | ENST00000404366.2:c.699A>C | ENSP00000384296.2:p.Glu233Asp | deleterious (0.01) | probably_damaging (0.95) | 22.6 | −5.98 | 0.00004446 | ENST00000404366 | GRCh38 | ACY1-201 |
| HR83 | SERAC1 | FCDIIIb | 6:158158275-158158275 | missense variant | 100%(CNV) | ENST00000647468.2:c.89T>C | ENSP00000496731.1:p.Ile30Thr | deleterious (0.01) | benign (0.05) | 17.95 | −1.63 | 0.0009691 | ENST00000647468 | GRCh38 | SERAC1-217 |
| HR100 | ZNF479 | FCDIIIb | 7:57120441-57120441 | missense variant | 11% | ENST00000319636.10:c.974G>A | ENSP00000324518.6:p.Cys325Tyr | tolerated_low_confidence (1) | benign (0) | 0.02 | −4.3 | 0.0001944 | ENST00000319636 | GRCh38 | ZNF479-201 |
| HR139 | BRAF | FCDIIId | 7:140753336-140753336 | missense variant | 18% | ENST00000646891.2:c.1799T>A | ENSP00000493543.1:p.Val600Glu | deleterious (0) | probably_damaging (0.963) | 29.8 | −12.63 | 3.161 × 10−12 | ENST00000646891 | GRCh38 | BRAF-220 |
| HR192 | BRAF | FCDIIId | 7:140753336-140753336 | missense variant | 54% | ENST00000646891.2:c.1799T>A | ENSP00000493543.1:p.Val600Glu | deleterious_low_confidence (0) | probably_damaging (0.935) | 29.8 | −12.63 | 6.905 × 10−7 | ENST00000646891 | GRCh38 | BRAF-220 |
| HR165 | PIGO | FCDIIId | 9:35091455-35091455 | Missense variant | 5% | ENST00000378617.4:c.2432G>A | ENSP00000367880.3:p.Arg811Gln | tolerated (0.2) | benign (0.007) | 18.7 | −7.39 | 0.000591 | ENST00000378617 | GRCh38 | PIGO-203 |
| Mosaic Loss of Function Pathogenic Variants | |||||||||||||||
| ID | Gene | FCDIII Type | Location | Mutation | Mosaic Fractions | HGVSc | HGVSp | SIFT | PolyPhen | CADD PHRAD | GPN-MSA_SCORES | gnomADe_AF | Transcript_ID | Reference_Genome | Gene_ENST |
| HR94 | TRANK1 | FCDIIIa | 3:36856923-36856924 | frameshift_variant | 5% | ENST00000645898.2:c.2798_2799insACCACCGA | ENSP00000494480.1:p.Ile934ProfsTer16 | - | - | 19.45 | 3.72 | 0.00000275 | ENST00000645898 | GRCh38 | TRANK1-205 |
| HR100 | MSH6 | FCDIIIb | 2:47805615-47805618 | splice_acceptor_variant,coding_sequence_variant,intron_variant | 14% | ENST00000234420.11:c.3557-3_3557del | - | - | - | 39 | 3.18 | 0.00000138 | ENST00000234420 | GRCh38 | MSH6-201 |
| HR185 | ANKRD40 | FCDIIId | 17:50697116-50697123 | splice_acceptor_variant,coding_sequence_variant | 19% | ENST00000285243.7:c.779-2_784del | - | - | - | 35 | - | 0.00000206 | ENST00000285243 | GRCh38 | ANKRD40-201 |
| HR175 | NKX2-2 | FCDIIId | 20:21512375-21512381 | frameshift_variant | 4% | ENST00000377142.4:c.370del | ENSP00000366347.4:p.Asp124ThrfsTer60 | - | - | 35 | - | 0.0000062 | ENST00000377142 | GRCh38 | NKX2-2-201 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Garcia, C.A.B.; Zubair, M.; Santos, M.V.; Lee, S.H.; Graham, I.A.; Stanley, V.; George, R.D.; Gleeson, J.G.; Machado, H.R.; Yang, X. Identification of Novel Mosaic Variants in Focal Epilepsy-Associated Patients’ Brain Lesions. Genes 2025, 16, 421. https://doi.org/10.3390/genes16040421
Garcia CAB, Zubair M, Santos MV, Lee SH, Graham IA, Stanley V, George RD, Gleeson JG, Machado HR, Yang X. Identification of Novel Mosaic Variants in Focal Epilepsy-Associated Patients’ Brain Lesions. Genes. 2025; 16(4):421. https://doi.org/10.3390/genes16040421
Chicago/Turabian StyleGarcia, Camila Araújo Bernardino, Muhammad Zubair, Marcelo Volpon Santos, Sang Hyun Lee, Ian Alfred Graham, Valentina Stanley, Renee D. George, Joseph G. Gleeson, Hélio Rubens Machado, and Xiaoxu Yang. 2025. "Identification of Novel Mosaic Variants in Focal Epilepsy-Associated Patients’ Brain Lesions" Genes 16, no. 4: 421. https://doi.org/10.3390/genes16040421
APA StyleGarcia, C. A. B., Zubair, M., Santos, M. V., Lee, S. H., Graham, I. A., Stanley, V., George, R. D., Gleeson, J. G., Machado, H. R., & Yang, X. (2025). Identification of Novel Mosaic Variants in Focal Epilepsy-Associated Patients’ Brain Lesions. Genes, 16(4), 421. https://doi.org/10.3390/genes16040421







