Cryptic Diversity Hidden within the Leafminer Genus Liriomyza (Diptera: Agromyzidae)
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Sampling Collection, DNA Extraction and Sequencing
2.2. Assembling the Data Sets
2.3. Genetic Variability
2.4. Phylogenetic Analyses
2.5. Species Delimitation Analyses
3. Results
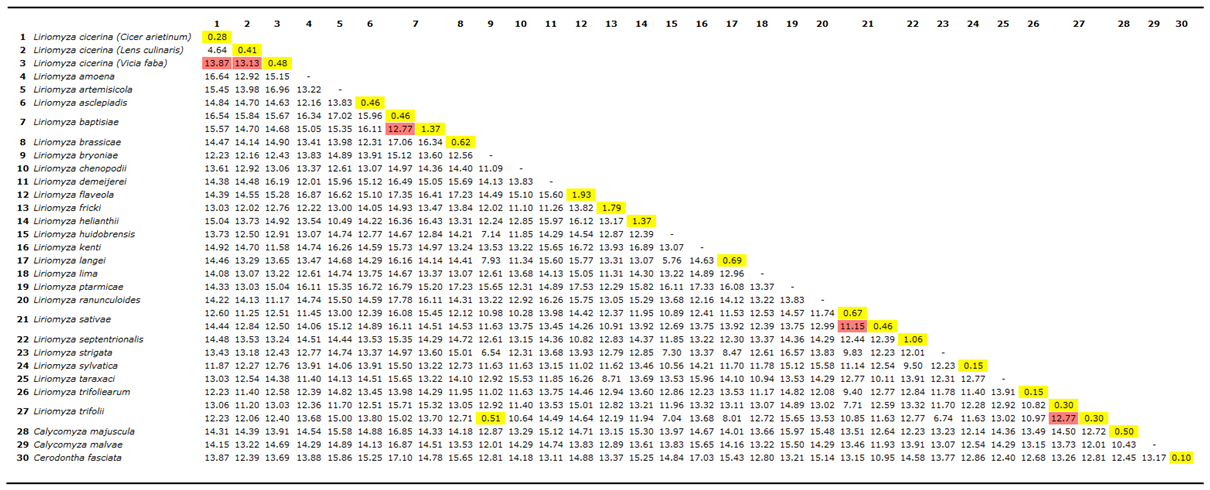
3.1. Haplotypes and Population Genetics Analyses
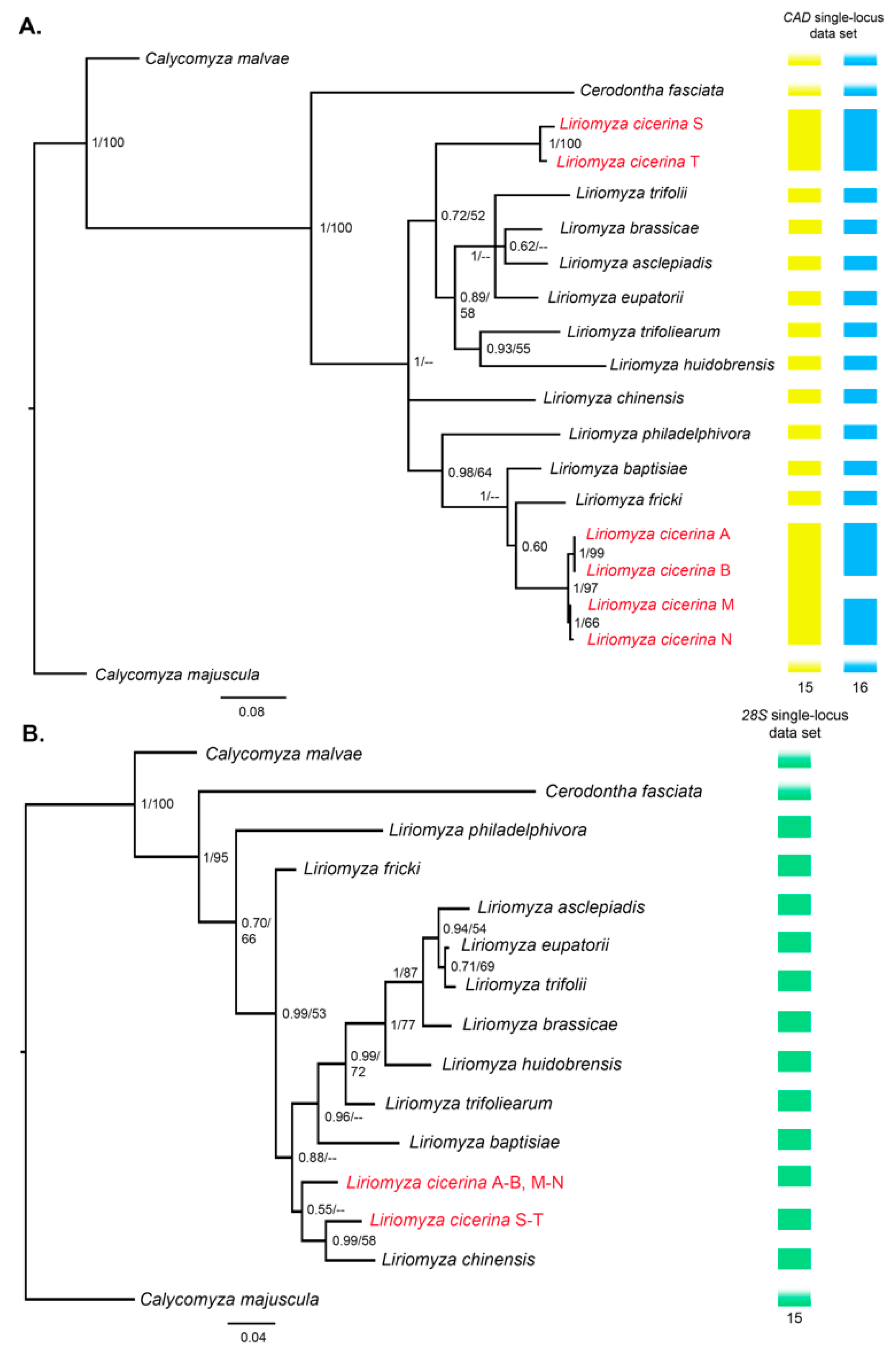
3.2. Phylogeny of the Genus Liriomyza
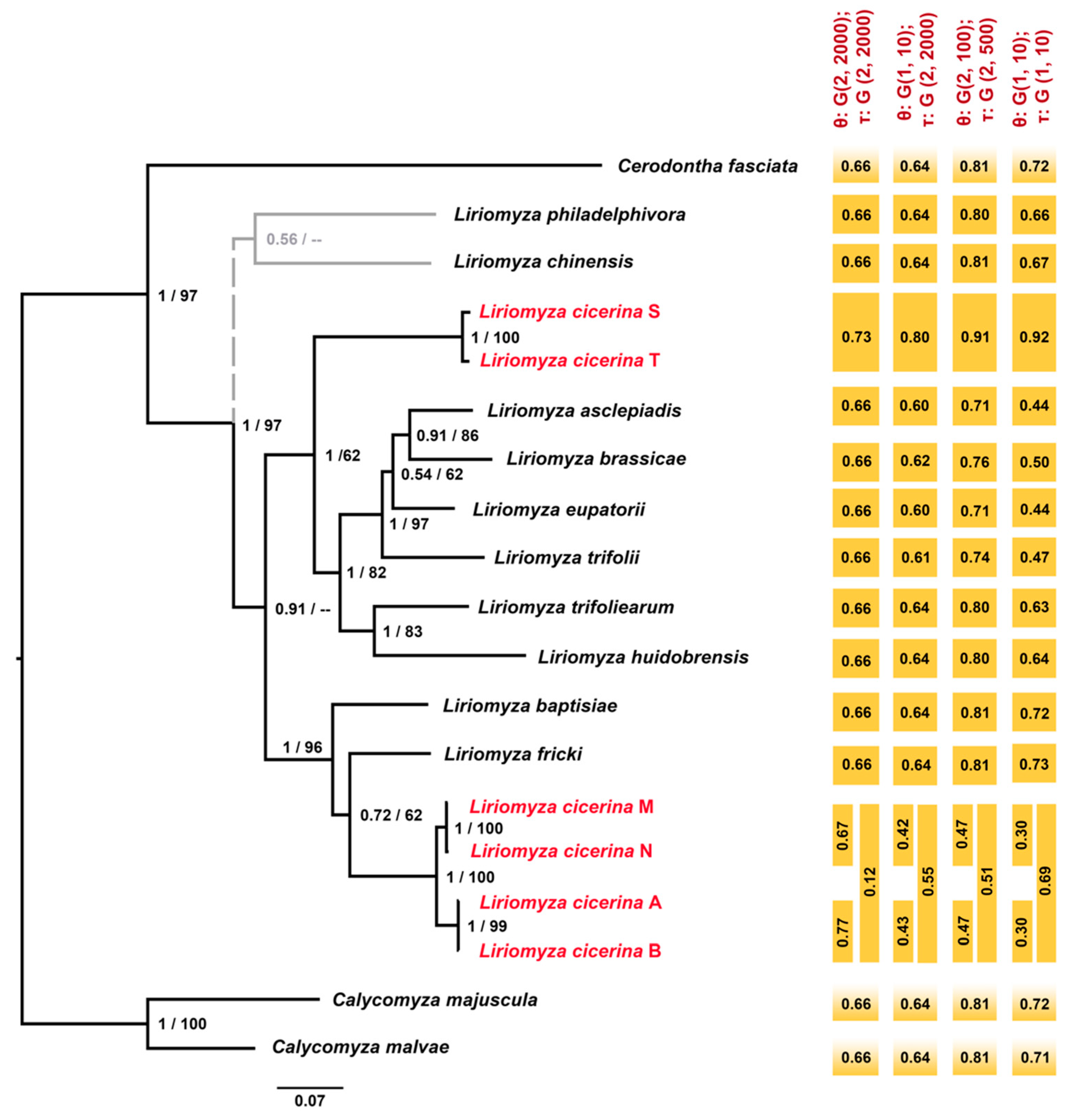
3.3. Molecular Species Delimitation
4. Discussion
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Scheffer, S.J.; Winkler, I.S.; Wiegmann, B.M. Phylogenetic relationships within the leaf-mining flies (Diptera: Agromyzidae) inferred from sequence data from multiple genes. Mol. Phylogenet. Evol. 2007, 42, 756–775. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Spencer, K.A. Agromyzidae (Diptera) of Economic Importance; Series Entomologica 9; Dr. W. Junk B.V.: The Hague, The Netherlands, 1973; pp. 1–418. [Google Scholar]
- EPPO A2 List of Pests Recommended for Regulation as Quarantine Pests—Version 2017-09. Available online: https://www.eppo.int/ACTIVITIES/plant_quarantine/A2_list (accessed on 28 August 2018).
- Reitz, S.R.; Trumble, J.T. Interspecific and intraspecific differences in two Liriomyza leafminer species in California. Entomol. Exp. Appl. 2002, 102, 101–113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shiao, S.F. Morphological diagnosis of six Liriomyza species (Diptera: Agromyzidae) of quarantine importance in Taiwan. Appl. Entomol. Zool. 2004, 39, 27–39. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Weintraub, P.G.; Scheffer, S.J.; Visser, D.; Valladares, G.; Correa, A.S.; Shepard, B.M.; Rauf, A.; Murphy, S.T.; Mujica, N.; MacVean, C.; et al. The invasive Liriomyza huidobrensis (Diptera: Agromyzidae): understanding its pest status and management globally. J. Insect Sci. 2017, 17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, S.Y.; Lei, Z.R.; Wang, H.H.; Dong, B.X.; Ren, B.Z. The complete mitochondrial genome of the leafminer Liriomyza trifolii (Diptera: Agromyzidae). Mol. Biol. Rep. 2011, 38, 687–692. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, F.; Du, Y.Z.; Wang, L.P.; Cao, J.M.; Yu, W.W. The complete mitochondrial genome of the leafminer Liriomyza sativae (Diptera: Agromyzidae): Great difference in the A+T-rich region compared to Liriomyza trifolii. Gene 2011, 485, 7–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, F.; Du, Y.Z.; Cao, J.M.; Huang, F.N. Analysis of three leafminers’ complete mitochondrial genomes. Gene 2013, 529, 1–6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Scheffer, S.J.; Lewis, M.L.; Gaimari, S.D.; Reitz, S.R. Molecular survey for the invasive leafminer pest Liriomyza huidobrensis (Diptera: Agromyzidae) in California uncovers only the native pest Liriomyza langei. J. Econ. Entomol. 2014, 107, 1959–1964. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Scheffer, S.J.; Wijesekara, A.; Visser, D.; Hallett, R.H. Polymerase chain reaction-restriction fragment-length polymorphism method to distinguish Liriomyza huidobrensis from L. langei (Diptera: Agromyzidae) applied to three recent leafminer invasions. J. Econ. Entomol. 2001, 94, 1177–1182. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kox, L.F.F.; Van Den Beld, H.E.; Lindhout, B.I.; De Goffau, L.J.W. Identification of economically important Liriomyza species by PCR-RFLP analysis. EPPO Bull. 2005, 35, 79–85. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nakamura, S.; Masuda, T.; Mochizuki, A.; Konishi, K.; Tokumaru, S.; Ueno, K.; Yamaguchi, T. Primer design for identifying economically important Liriomyza species (Diptera: Agromyzidae) by multiplex PCR. Mol. Ecol. Resour. 2013, 13, 96–102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sooda, A.; Gunawardana, D.; Li, D.M.; Kumarasinghe, L. Multiplex real-time PCR assay for the detection of three invasive leafminer species: Liriomyza huidobrensis, L. sativae and L. trifolii (Diptera: Agromyzidae). Austral Entomol. 2017, 56, 153–159. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- El-Serwy, S.A. Studies on the leafminer; Liriomyza cicerina (Rondani) and Liriomyza bryoniae (Kaltenbach) (Diptera: Agromyzidae) and their parasitoids in faba bean in Egypt. Egypt J. Agric. Res. 2003, 81, 1581–1593. [Google Scholar]
- Sukumaran, J.; Knowles, L.L. Multispecies coalescent delimits structure, not species. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2017, 114, 1607–1612. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- De Queiroz, K. Species concepts and species delimitation. Syst. Biol. 2007, 56, 879–886. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shutterstock. Available online: https://www.shutterstock.com/it/ (accessed on 25 July 2018).
- Folmer, O.; Black, M.; Hoeh, W.; Lutz, R.; Vrijenhoek, R. DNA primers for amplification of mitochondrial cytochrome c oxidase subunit I from diverse metazoan invertebrates. Mol. Mar. Biol. Biotechnol. 1994, 3, 294–299. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Mesquite 3.51. Available online: https://github.com/MesquiteProject/MesquiteCore (accessed on 28 June 2018).
- Castresana, J. Selection of conserved blocks from multiple alignments for their use in phylogenetic analysis. Mol. Biol. Evol. 2000, 17, 540–552. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Clement, M.; Posada, D.; Crandall, K.A. TCS: A computer program to estimate gene genealogies. Mol. Ecol. 2000, 9, 1657–1659. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Villesen, P. FaBox: An online toolbox for FASTA sequences. Mol. Ecol. Notes 2007, 7, 965–968. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Paradis, E.; Claude, J.; Strimmer, K. APE: Analyses of phylogenetics and evolution in R language. Bioinformatics 2004, 20, 289–290. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lanfear, R.; Frandsen, P.B.; Wright, A.M.; Senfeld, T.; Calcott, B. PartitionFinder 2: New methods for selecting partitioned models of evolution for molecular and morphological phylogenetic analyses. Mol. Biol. Evol. 2017, 34, 772–773. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Stamatakis, A. RAxML version 8: A tool for phylogenetic analysis and post-analysis of large phylogenies. Bioinformatics 2014, 30, 1312–1313. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ronquist, F.; Teslenko, M.; van der Mark, P.; Ayres, D.L.; Darling, A.; Hohna, S.; Larget, B.; Liu, L.; Suchard, M.A.; Huelsenbeck, J.P. MrBayes 3.2: Efficient Bayesian phylogenetic inference and model choice across a large model space. Syst. Biol. 2012, 61, 539–542. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Miller, M.A.; Schwartz, T.; Pickett, B.E.; He, S.; Klem, E.B.; Scheuermann, R.H.; Passarotti, M.; Kaufman, S.; O’Leary, M.A. A RESTful API for access to phylogenetic pools via the CIPRES Science Gateway. Evol. Bioinform. Online 2015, 11, 43–48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Puillandre, N.; Lambert, A.; Brouillet, S.; Achaz, G. ABGD, Automatic Barcode Gap Discovery for primary species delimitation. Mol. Ecol. 2012, 21, 1864–1877. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Species Identifier. Available online: https://github.com/gaurav/taxondna/releases/tag/1.8 (accessed on 23 June 2018).
- Zhang, J.J.; Kapli, P.; Pavlidis, P.; Stamatakis, A. A general species delimitation method with applications to phylogenetic placements. Bioinformatics 2013, 29, 2869–2876. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bouckaert, R.; Heled, J.; Kuhnert, D.; Vaughan, T.; Wu, C.H.; Xie, D.; Suchard, M.A.; Rambaut, A.; Drummond, A.J. BEAST 2: A software platform for Bayesian evolutionary analysis. PLoS Comput. Biol. 2014, 10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Brower, A.V.Z. Rapid morphological radiation and convergence among races of the butterfly Heliconius erato inferred from patterns of mitochondrial-DNA evolution. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 1994, 91, 6491–6495. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rambaut, A.; Drummond, A.J.; Xie, D.; Baele, G.; Suchard, M.A. Posterior summarization in Bayesian phylogenetics using Tracer 1.7. Syst. Biol. 2018, 67, 901–904. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- FigTree v1.4.3. Available online: http://tree.bio.ed.ac.uk/software/figtree/ (accessed on 28 August 2018).
- Fujisawa, T.; Barraclough, T.G. Delimiting species using single-locus data and the Generalized Mixed Yule Coalescent approach: A revised method and evaluation on simulated data sets. Syst. Biol. 2013, 62, 707–724. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- R Core Team. R: A Language and Environment for Statistical Computing; R Foundation for Statistical Computing: Vienna, Austria, 2014. Available online: http://www.R-project.org/ (accessed on 2 July 2018).
- Ezard, T.; Fujisawa, T.; Barraclough, T. Splits: Species’ Limits by Threshold Statistics. R Package Version 1.0–19. 2014. Available online: http://R-Forge.R-project.org/projects/splits/ (accessed on 23 May 2018).
- Yang, Z.; Rannala, B. Unguided species delimitation using DNA sequence data from multiple loci. Mol. Biol. Evol. 2014, 31, 3125–3135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Scheffer, S.J.; Lewis, M.L. Mitochondrial phylogeography of vegetable pest Liriomyza sativae (Diptera: Agromyzidae): Divergent clades and invasive Populations. Ann. Entomol. Soc. Am. 2005, 98, 181–186. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Scheffer, S.J. Molecular evidence of cryptic species within the Liriomyza huidobrensis (Diptera: Agromyzidae). J. Econ. Entomol. 2000, 93, 1146–1151. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- International Plant Protection Convention (ISPM 27—Annex 16). DP 16: Genus Liriomyza. Available online: https://www.ippc.int/static/media/files/publication/en/2017/01/DP_16_2016_En_2017-01-30.pdf (accessed on 28 August 2018).
- Maharjan, R.; Oh, H.W.; Jung, C. Morphological and genetic characteristics of Liriomyza huidobrensis (Blanchard) (Diptera: Agromyzidae) infesting potato crops in Korea. J. Asia-Pac. Entomol. 2014, 17, 281–286. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]


| Collection site | Label | Coordinates | Host Plant | n | cox1 Haplotypes |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Béja | BEJ | 36°43′ N; 9°10′ E | Cicer arietinum | 10 | A(9), B(1) |
| Lens culinaris | 5 | A(1), L(1), M(1), N(1), O(1) | |||
| Vicia faba | 8 | P(1), Q(1), R(1), S(3), T(1), U(1) | |||
| Amdoun | AMD | 36°46′ N; 9°05′ E | Cicer arietinum | 13 | A(12), F(1) |
| Hamrounia | HAM | 36°72′ N; 9°11′ E | Cicer arietinum | 10 | A(10) |
| Hamem Sayela | HSA | 36°39′ N; 9°8′ E | Cicer arietinum | 10 | A(8), G(1), H(1) |
| Le Kef | KEF | 36°11′ N; 8°42′ E | Cicer arietinum | 12 | A(8), C(1) |
| Mornag | MOR | 36°41′ N; 10°1′ E | Cicer arietinum | 10 | A(8), D(1), E(1) |
| Oued Meliz | JEN | 36°28′ N; 8°33′ E | Cicer arietinum | 10 | A(9), C(1) |
| Mateur | MAT | 37°02′ N; 9°39′ E | Cicer arietinum | 10 | A(10) |
| Bizerte | BIZ | 37°16′ N; 9°52′ E | Cicer arietinum | 10 | A(10) |
| Menzel Bourguiba | MBO | 37°9′ N; 9°47′ E | Cicer arietinum | 10 | A(7), I(1), J(1), K(1) |
© 2018 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Carapelli, A.; Soltani, A.; Leo, C.; Vitale, M.; Amri, M.; Mediouni-Ben Jemâa, J. Cryptic Diversity Hidden within the Leafminer Genus Liriomyza (Diptera: Agromyzidae). Genes 2018, 9, 554. https://doi.org/10.3390/genes9110554
Carapelli A, Soltani A, Leo C, Vitale M, Amri M, Mediouni-Ben Jemâa J. Cryptic Diversity Hidden within the Leafminer Genus Liriomyza (Diptera: Agromyzidae). Genes. 2018; 9(11):554. https://doi.org/10.3390/genes9110554
Chicago/Turabian StyleCarapelli, Antonio, Abir Soltani, Chiara Leo, Matteo Vitale, Moez Amri, and Jouda Mediouni-Ben Jemâa. 2018. "Cryptic Diversity Hidden within the Leafminer Genus Liriomyza (Diptera: Agromyzidae)" Genes 9, no. 11: 554. https://doi.org/10.3390/genes9110554
APA StyleCarapelli, A., Soltani, A., Leo, C., Vitale, M., Amri, M., & Mediouni-Ben Jemâa, J. (2018). Cryptic Diversity Hidden within the Leafminer Genus Liriomyza (Diptera: Agromyzidae). Genes, 9(11), 554. https://doi.org/10.3390/genes9110554






