Cellular Genomic Sites of Hepatitis B Virus DNA Integration
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Hepatitis B Virus DNA Integration
3. Possible Functions of Hepatitis B Virus DNA Integration
4. Detection of Hepatitis B Virus Integration
5. Site Specificity of Hepatitis B Virus Integrations
5.1. Recurrent Genes
5.2. Recurrent Structures
5.2.1. Telomeres
5.2.2. CpG Islands
5.2.3. Repetitive Regions (LINEs and SINEs)
5.2.4. Transcriptionally Active Sites
5.3. Recurrent Motifs
5.3.1. Homology between Hepatitis B Virus and Cellular Sequences
5.3.2. GC-Rich Regions
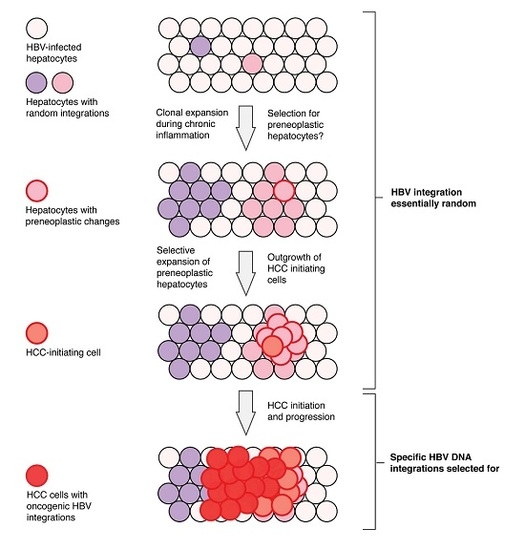
6. Current Model of Hepatitis B Virus DNA Integration during Disease Progression
7. Open Questions Regarding Hepatitis B Virus Integration
7.1. What Proportion of Integrations Alter Cell Phenotype or Are Truly Pro-Carcinogenic? How and When during Disease Progression Do They Act?
7.2. What Controls the Frequency of Integration? Why Doesn’t Hepatitis B Virus Integration Occur More or Less Often?
7.3. How Does Hepatitis B Virus Integration Occur Multiple Times in the Same Cellular Clone?
- The lack of nuclear import of the de novo-generated mature nucleocapsids or superinfection exclusion is not absolute, but instead occurs at a slow rate in a chronically-infected hepatocyte. This allows multiple integrations to eventually accumulate within infected cells. This also predicts that the number of cccDNA per cell should also increase over long periods of time, which has not yet been observed. While only weeks-long in vitro models are available, no change in cccDNA levels has been observed after the initial formation [89]. Moreover, we have found that HBV mutants incapable of expressing HBcAg show no difference in cccDNA levels compared to wild-type after six weeks of infection cell [90], showing that nuclear import of nucleocapsids in infected cells is low in these models.
- Not all cells are equally likely to contain integrations. In the liver cell population, there may be hepatocytes that have a susceptibility to HBV DNA integrations (e.g., cells with increased double-stranded breaks) in which multiple integrations could occur at the time of initial infection. Such an explanation could be explored using integration detection methods in single cells shortly after HBV infection.
- Not all integrations express L-protein (e.g., due to epigenetic silencing, HBV truncations, mutations or lack of downstream poly-A in the integrated form), allowing re-infection of a cellular clone if cccDNA is cleared (e.g., through cell mitosis [91]. This mechanism would predict that only a single integration in a cellular clone (the most recent) would express the L-protein.
7.4. How Does the Structure of Integrated Hepatitis B Virus DNA Affect Viral Dynamics and Pathogenesis?
8. Summary
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Collaborators, T.P.O. Global Prevalence, Treatment, and Prevention of Hepatitis B Virus Infection in 2016: A Modelling Study. Lancet Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 2018, 3, 383–403. [Google Scholar]
- Ferlay, J.; Soerjomataram, I.; Dikshit, R.; Eser, S.; Mathers, C.; Rebelo, M.; Parkin, D.M.; Forman, D.; Bray, F. Cancer Incidence and Mortality Worldwide: Sources, Methods and Major Patterns in Globocan 2012. Int. J. Cancer 2015, 136, E359–E386. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- El-Serag, H.B. Epidemiology of Viral Hepatitis and Hepatocellular Carcinoma. Gastroenterology 2012, 142, 1264–1273.e1261. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- WHO. Global Health Estimates 2015: Estimated Deaths by Cause, 2000 and 2015. Available online: http://www.who.int/entity/healthinfo/global_burden_disease/GHE2015_Deaths_Global_2000_2015.xls (accessed on 10 April 2017).
- Singal, A.K.; Salameh, H.; Kuo, Y.F.; Fontana, R.J. Meta-Analysis: The Impact of Oral Anti-Viral Agents on the Incidence of Hepatocellular Carcinoma in Chronic Hepatitis B. Aliment. Pharmacol. Ther. 2013, 38, 98–106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wong, G.L.; Tse, Y.K.; Yip, T.C.; Chan, H.L.; Tsoi, K.K.; Wong, V.W. Long-Term Use of Oral Nucleos(T)Ide Analogues for Chronic Hepatitis B Does Not Increase Cancer Risk—A Cohort Study of 44 494 Subjects. Aliment. Pharmacol. Ther. 2017, 45, 1213–1224. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Papatheodoridis, G.V.; Idilman, R.; Dalekos, G.N.; Buti, M.; Chi, H.; van Boemmel, F.; Calleja, J.L.; Sypsa, V.; Goulis, J.; Manolakopoulos, S.; et al. The Risk of Hepatocellular Carcinoma Decreases after the First 5 Years of Entecavir or Tenofovir in Caucasians with Chronic Hepatitis B. Hepatology 2017, 66, 1444–1453. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tu, T.; Buhler, S.; Bartenschlager, R. Chronic Viral Hepatitis and Its Association with Liver Cancer. Biol. Chem. 2017, 398, 817–837. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tu, T.; Budzinska, M.A.; Shackel, N.A.; Jilbert, A.R. Conceptual Models for the Initiation of Hepatitis B Virus-Associated Hepatocellular Carcinoma. Liver Int. 2015, 35, 1786–1800. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yip, T.C.; Chan, H.L.; Wong, V.W.; Tse, Y.K.; Lam, K.L.; Wong, G.L. Impact of Age and Gender on Risk of Hepatocellular Carcinoma after Hepatitis B Surface Antigen Seroclearance. J. Hepatol. 2017, 67, 902–908. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhao, X.L.; Yang, J.R.; Lin, S.Z.; Ma, H.; Guo, F.; Yang, R.F.; Zhang, H.H.; Han, J.C.; Wei, L.; Pan, X.B. Serum Viral Duplex-Linear DNA Proportion Increases with the Progression of Liver Disease in Patients Infected with HBV. Gut 2016, 65, 502–511. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ni, Y.; Lempp, F.A.; Mehrle, S.; Nkongolo, S.; Kaufman, C.; Falth, M.; Stindt, J.; Koniger, C.; Nassal, M.; Kubitz, R.; et al. Hepatitis B and D Viruses Exploit Sodium Taurocholate Co-Transporting Polypeptide for Species-Specific Entry into Hepatocytes. Gastroenterology 2014, 146, 1070–1083. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yan, H.; Zhong, G.; Xu, G.; He, W.; Jing, Z.; Gao, Z.; Huang, Y.; Qi, Y.; Peng, B.; Wang, H.; et al. Sodium Taurocholate Cotransporting Polypeptide Is a Functional Receptor for Human Hepatitis B and D Virus. eLife 2012, 1, e00049. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Blondot, M.L.; Bruss, V.; Kann, M. Intracellular Transport and Egress of Hepatitis B Virus. J. Hepatol. 2016, 64, S49–S59. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nassal, M. HBV cccdna: Viral Persistence Reservoir and Key Obstacle for a Cure of Chronic Hepatitis B. Gut 2015, 64, 1972–1984. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tu, T.; Budzinska, M.A.; Vondran, F.W.R.; Shackel, N.A.; Urban, S. Hepatitis B Virus DNA Integration Occurs Early in the Viral Life Cycle in an in vitro Infection Model Via NTCP-Dependent Uptake of Enveloped Virus Particles. J. Virol. 2018. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bill, C.A.; Summers, J. Genomic DNA Double-Strand Breaks Are Targets for Hepadnaviral DNA Integration. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2004, 101, 11135–11140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sung, W.K.; Zheng, H.; Li, S.; Chen, R.; Liu, X.; Li, Y.; Lee, N.P.; Lee, W.H.; Ariyaratne, P.N.; Tennakoon, C.; et al. Genome-Wide Survey of Recurrent HBV Integration in Hepatocellular Carcinoma. Nat. Genet. 2012, 44, 765–769. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jhunjhunwala, S.; Jiang, Z.; Stawiski, E.W.; Gnad, F.; Liu, J.; Mayba, O.; Du, P.; Diao, J.; Johnson, S.; Wong, K.F.; et al. Diverse Modes of Genomic Alteration in Hepatocellular Carcinoma. Genome Biol. 2014, 15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, L.H.; Liu, X.; Yan, H.X.; Li, W.Y.; Zeng, X.; Yang, Y.; Zhao, J.; Liu, S.P.; Zhuang, X.H.; Lin, C.; et al. Genomic and Oncogenic Preference of HBV Integration in Hepatocellular Carcinoma. Nat. Commun. 2016, 7, 12992. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jiang, Z.; Jhunjhunwala, S.; Liu, J.; Haverty, P.M.; Kennemer, M.I.; Guan, Y.; Lee, W.; Carnevali, P.; Stinson, J.; Johnson, S.; et al. The Effects of Hepatitis B Virus Integration into the Genomes of Hepatocellular Carcinoma Patients. Genome Res. 2012, 22, 593–601. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fujimoto, A.; Furuta, M.; Totoki, Y.; Tsunoda, T.; Kato, M.; Shiraishi, Y.; Tanaka, H.; Taniguchi, H.; Kawakami, Y.; Ueno, M.; et al. Whole-Genome Mutational Landscape and Characterization of Noncoding and Structural Mutations in Liver Cancer. Nat. Genet. 2016, 48, 500–509. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fujimoto, A.; Totoki, Y.; Abe, T.; Boroevich, K.A.; Hosoda, F.; Nguyen, H.H.; Aoki, M.; Hosono, N.; Kubo, M.; Miya, F.; et al. Whole-Genome Sequencing of Liver Cancers Identifies Etiological Influences on Mutation Patterns and Recurrent Mutations in Chromatin Regulators. Nat. Genet. 2012, 44, 760–764. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tu, T.; Urban, S. Virus Entry and Its Inhibition to Prevent and Treat Hepatitis B and Hepatitis D Virus Infections. Curr. Opin. Virol. 2018, 30, 68–79. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Freitas, N.; Cunha, C.; Menne, S.; Gudima, S.O. Envelope Proteins Derived from Naturally Integrated Hepatitis B Virus DNA Support Assembly and Release of Infectious Hepatitis Delta Virus Particles. J. Virol. 2014, 88, 5742–5754. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mason, W.S.; Jilbert, A.R.; Summers, J. Clonal Expansion of Hepatocytes During Chronic Woodchuck Hepatitis Virus Infection. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2005, 102, 1139–1144. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Summers, J.; Mason, W.S. Residual Integrated Viral DNA after Hepadnavirus Clearance by Nucleoside Analog Therapy. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2004, 101, 638–640. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, W.; Summers, J. Integration of Hepadnavirus DNA in Infected Liver: Evidence for a Linear Precursor. J. Virol. 1999, 73, 9710–9717. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Mason, W.S.; Low, H.C.; Xu, C.; Aldrich, C.E.; Scougall, C.A.; Grosse, A.; Clouston, A.; Chavez, D.; Litwin, S.; Peri, S.; et al. Detection of Clonally Expanded Hepatocytes in Chimpanzees with Chronic Hepatitis B Virus Infection. J. Virol. 2009, 83, 8396–8408. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wooddell, C.I.; Yuen, M.-F.; Chan, H.L.-Y.; Gish, R.G.; Locarnini, S.A.; Chavez, D.; Ferrari, C.; Given, B.D.; Hamilton, J.; Kanner, S.B.; et al. RNAi-Based Treatment of Chronically Infected Patients and Chimpanzees Reveals That Integrated Hepatitis B Virus DNA Is a Source of HBsAg. Sci. Transl. Med. 2017, 9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mason, W.S.; Liu, C.; Aldrich, C.E.; Litwin, S.; Yeh, M.M. Clonal Expansion of Normal-Appearing Human Hepatocytes During Chronic Hepatitis B Virus Infection. J. Virol. 2010, 84, 8308–8315. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tu, T.; Mason, W.S.; Clouston, A.D.; Shackel, N.A.; McCaughan, G.W.; Yeh, M.M.; Schiff, E.R.; Ruszkiewicz, A.R.; Chen, J.W.; Harley, H.A.; et al. Clonal Expansion of Hepatocytes with a Selective Advantage Occurs During All Stages of Chronic Hepatitis B Virus Infection. J. Viral Hepat. 2015, 22, 737–753. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mason, W.S.; Gill, U.S.; Litwin, S.; Zhou, Y.; Peri, S.; Pop, O.; Hong, M.L.; Naik, S.; Quaglia, A.; Bertoletti, A.; et al. HBV DNA Integration and Clonal Hepatocyte Expansion in Chronic Hepatitis B Patients Considered Immune Tolerant. Gastroenterology 2016, 151, 986–998.e984. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Brechot, C.; Gozuacik, D.; Murakami, Y.; Paterlini-Brechot, P. Molecular Bases for the Development of Hepatitis B Virus (HBV)-Related Hepatocellular Carcinoma (HCC). Semin. Cancer Biol. 2000, 10, 211–231. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schluter, V.; Meyer, M.; Hofschneider, P.H.; Koshy, R.; Caselmann, W.H. Integrated Hepatitis B Virus X and 3′ Truncated Pres/S Sequences Derived from Human Hepatomas Encode Functionally Active Transactivators. Oncogene 1994, 9, 3335–3344. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Tu, T.; Budzinska, M.A.; Shackel, N.A.; Urban, S. HBV DNA Integration: Molecular Mechanisms and Clinical Implications. Viruses 2017, 9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pfefferkorn, M.; Bohm, S.; Schott, T.; Deichsel, D.; Bremer, C.M.; Schroder, K.; Gerlich, W.H.; Glebe, D.; Berg, T.; van Bommel, F. Quantification of Large and Middle Proteins of Hepatitis B Virus Surface Antigen (HBsAg) as a Novel Tool for the Identification of Inactive HBV Carriers. Gut 2017. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hu, B.; Wang, R.; Fu, J.; Su, M.; Du, M.; Liu, Y.; Li, H.; Wang, H.; Lu, F.; Jiang, J. Integration of Hepatitis B Virus S Gene Impacts on Hepatitis B Surface Antigen Levels in Patients with Antiviral Therapy. J. Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 2018, 33, 1389–1396. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fowler, M.J.; Greenfield, C.; Chu, C.M.; Karayiannis, P.; Dunk, A.; Lok, A.S.; Lai, C.L.; Yeoh, E.K.; Monjardino, J.P.; Wankya, B.M.; et al. Integration of HBV-DNA May Not Be a Prerequisite for the Maintenance of the State of Malignant Transformation. An Analysis of 110 Liver Biopsies. J. Hepatol. 1986, 2, 218–229. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shafritz, D.A.; Shouval, D.; Sherman, H.I.; Hadziyannis, S.J.; Kew, M.C. Integration of Hepatitis B Virus DNA into the Genome of Liver Cells in Chronic Liver Disease and Hepatocellular Carcinoma. Studies in Percutaneous Liver Biopsies and Post-Mortem Tissue Specimens. N. Engl. J. Med. 1981, 305, 1067–1073. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hino, O.; Kitagawa, T.; Koike, K.; Kobayashi, M.; Hara, M.; Mori, W.; Nakashima, T.; Hattori, N.; Sugano, H. Detection of Hepatitis B Virus DNA in Hepatocellular Carcinomas in Japan. Hepatology 1984, 4, 90–95. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, J.Y.; Harrison, T.J.; Lee, C.S.; Chen, D.S.; Zuckerman, A.J. Detection of Hepatitis B Virus DNA in Hepatocellular Carcinoma: Analysis by Hybridization with Subgenomic DNA Fragments. Hepatology 1988, 8, 518–523. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Esumi, M.; Tanaka, Y.; Tozuka, S.; Shikata, T. Clonal State of Human Hepatocellular Carcinoma and Non-Tumorous Hepatocytes. Cancer Chemother. Pharmacol. 1989, 23 (Suppl. 1), S1–S3. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Koch, S.; von Loringhoven, A.F.; Kahmann, R.; Hofschneider, P.H.; Koshy, R. The Genetic Organization of Integrated Hepatitis B Virus DNA in the Human Hepatoma Cell Line PLC/PRF/5. Nucl. Acids Res. 1984, 12, 6871–6886. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Takada, S.; Gotoh, Y.; Hayashi, S.; Yoshida, M.; Koike, K. Structural Rearrangement of Integrated Hepatitis B Virus DNA as Well as Cellular Flanking DNA Is Present in Chronically Infected Hepatic Tissues. J. Virol. 1990, 64, 822–828. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Hino, O.; Kitagawa, T.; Hirama, T.; Yokoyama, S. Hepatitis B Virus DNA Integration in Hepatoblastoma. Lancet 1984, 1, 462–463. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Choo, K.B.; Liu, M.S.; Chang, P.C.; Wu, S.M.; Su, M.W.; Pan, C.C.; Han, S.H. Analysis of Six Distinct Integrated Hepatitis B Virus Sequences Cloned from the Cellular DNA of a Human Hepatocellular Carcinoma. Virology 1986, 154, 405–408. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Murakami, Y.; Saigo, K.; Takashima, H.; Minami, M.; Okanoue, T.; Brechot, C.; Paterlini-Brechot, P. Large Scaled Analysis of Hepatitis B Virus (HBV) DNA Integration in HBV Related Hepatocellular Carcinomas. Gut 2005, 54, 1162–1168. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Saitta, C.; Tripodi, G.; Barbera, A.; Bertuccio, A.; Smedile, A.; Ciancio, A.; Raffa, G.; Sangiovanni, A.; Navarra, G.; Raimondo, G.; et al. Hepatitis B Virus (HBV) DNA Integration in Patients with Occult HBV Infection and Hepatocellular Carcinoma. Liver Int. 2015, 35, 2311–2317. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rendon, J.C.; Cortes-Mancera, F.; Restrepo-Gutierrez, J.C.; Hoyos, S.; Navas, M.C. Molecular Characterization of Occult Hepatitis B Virus Infection in Patients with End-Stage Liver Disease in Colombia. PLoS ONE 2017, 12, e0180447. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, A.; Wu, L.; Lin, J.; Han, L.; Bian, J.; Wu, Y.; Robson, S.C.; Xue, L.; Ge, Y.; Sang, X.; et al. Whole-Exome Sequencing Reveals the Origin and Evolution of Hepato-Cholangiocarcinoma. Nat. Commun. 2018, 9, 894. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gao, Q.; Wang, Z.C.; Duan, M.; Lin, Y.H.; Zhou, X.Y.; Worthley, D.L.; Wang, X.Y.; Niu, G.; Xia, Y.; Deng, M.; et al. Cell Culture System for Analysis of Genetic Heterogeneity within Hepatocellular Carcinomas and Response to Pharmacologic Agents. Gastroenterology 2017, 152, 232–242.e234. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dong, H.; Zhang, L.; Qian, Z.; Zhu, X.; Zhu, G.; Chen, Y.; Xie, X.; Ye, Q.; Zang, J.; Ren, Z.; et al. Identification of HBV-MLL4 Integration and Its Molecular Basis in Chinese Hepatocellular Carcinoma. PLoS ONE 2015, 10, e0123175. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lau, C.C.; Sun, T.; Ching, A.K.; He, M.; Li, J.W.; Wong, A.M.; Co, N.N.; Chan, A.W.; Li, P.S.; Lung, R.W.; et al. Viral-Human Chimeric Transcript Predisposes Risk to Liver Cancer Development and Progression. Cancer Cell 2014, 25, 335–349. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yoo, S.; Wang, W.; Wang, Q.; Fiel, M.I.; Lee, E.; Hiotis, S.P.; Zhu, J. A Pilot Systematic Genomic Comparison of Recurrence Risks of Hepatitis B Virus-Associated Hepatocellular Carcinoma with Low- and High-Degree Liver Fibrosis. BMC Med. 2017, 15, 214. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Batzer, M.A.; Deininger, P.L. Alu Repeats and Human Genomic Diversity. Nat. Rev. Genet. 2002, 3, 370–379. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tu, T. Clonal Proliferation of Hepatocytes During Chronic Hepatitis B Virus Infection. Ph.D. Thesis, The University of Adelaide, Adelaide, Australia, 2012. [Google Scholar]
- Tu, T.; Jilbert, A.R. Detection of Hepatocyte Clones Containing Integrated Hepatitis B Virus DNA Using Inverse Nested Pcr. Methods Mol. Biol. 2017, 1540, 97–118. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Budzinska, M.A.; Shackel, N.A.; Urban, S.; Tu, T. Sequence Analysis of Integrated Hepatitis B Virus DNA During HBeAg-Seroconversion. Emerg. Microbes Infect. in press.
- Jiang, S. Re-Evaluation of the Carcinogenic Significance of Hepatitis B Virus Integration in Hepatocarcinogenesis. PLoS ONE 2012, 7, e40363. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ding, D.; Lou, X.; Hua, D.; Yu, W.; Li, L.; Wang, J.; Gao, F.; Zhao, N.; Ren, G.; Li, L.; et al. Recurrent Targeted Genes of Hepatitis B Virus in the Liver Cancer Genomes Identified by a Next-Generation Sequencing-Based Approach. PLoS Genet. 2012, 8, e1003065. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, X.; Wu, L.; Lin, J.; Wang, A.; Wan, X.; Wu, Y.; Robson, S.C.; Sang, X.; Zhao, H. Distinct Hepatitis B Virus Integration Patterns in Hepatocellular Carcinoma and Adjacent Normal Liver Tissue. Int. J. Cancer 2017, 140, 1324–1330. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kawai-Kitahata, F.; Asahina, Y.; Tanaka, S.; Kakinuma, S.; Murakawa, M.; Nitta, S.; Watanabe, T.; Otani, S.; Taniguchi, M.; Goto, F.; et al. Comprehensive Analyses of Mutations and Hepatitis B Virus Integration in Hepatocellular Carcinoma with Clinicopathological Features. J. Gastroenterol. 2016, 51, 473–486. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Totoki, Y.; Tatsuno, K.; Covington, K.R.; Ueda, H.; Creighton, C.J.; Kato, M.; Tsuji, S.; Donehower, L.A.; Slagle, B.L.; Nakamura, H.; et al. Trans-Ancestry Mutational Landscape of Hepatocellular Carcinoma Genomes. Nat. Genet. 2014, 46, 1267–1273. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Toh, S.T.; Jin, Y.; Liu, L.; Wang, J.; Babrzadeh, F.; Gharizadeh, B.; Ronaghi, M.; Toh, H.C.; Chow, P.K.; Chung, A.Y.; et al. Deep Sequencing of the Hepatitis B Virus in Hepatocellular Carcinoma Patients Reveals Enriched Integration Events, Structural Alterations and Sequence Variations. Carcinogenesis 2013, 34, 787–798. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yan, H.; Yang, Y.; Zhang, L.; Tang, G.; Wang, Y.; Xue, G.; Zhou, W.; Sun, S. Characterization of the Genotype and Integration Patterns of Hepatitis B Virus in Early- and Late-Onset Hepatocellular Carcinoma. Hepatology 2015, 61, 1821–1831. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cao, S.; Wendl, M.C.; Wyczalkowski, M.A.; Wylie, K.; Ye, K.; Jayasinghe, R.; Xie, M.; Wu, S.; Niu, B.; Grubb, R., III; et al. Divergent Viral Presentation among Human Tumors and Adjacent Normal Tissues. Sci. Rep. 2016, 6, 28294. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chami, M.; Gozuacik, D.; Saigo, K.; Capiod, T.; Falson, P.; Lecoeur, H.; Urashima, T.; Beckmann, J.; Gougeon, M.L.; Claret, M.; et al. Hepatitis B Virus-Related Insertional Mutagenesis Implicates SERCA1 Gene in the Control of Apoptosis. Oncogene 2000, 19, 2877–2886. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Saigo, K.; Yoshida, K.; Ikeda, R.; Sakamoto, Y.; Murakami, Y.; Urashima, T.; Asano, T.; Kenmochi, T.; Inoue, I. Integration of Hepatitis B Virus DNA into the Myeloid/Lymphoid or Mixed-Lineage Leukemia (MLL4) Gene and Rearrangements of MLL4 in Human Hepatocellular Carcinoma. Hum. Mutat. 2008, 29, 703–708. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shiraishi, Y.; Fujimoto, A.; Furuta, M.; Tanaka, H.; Chiba, K.; Boroevich, K.A.; Abe, T.; Kawakami, Y.; Ueno, M.; Gotoh, K.; et al. Integrated Analysis of Whole Genome and Transcriptome Sequencing Reveals Diverse Transcriptomic Aberrations Driven by Somatic Genomic Changes in Liver Cancers. PLoS ONE 2014, 9, e114263. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- O’Donnell, K.A.; Keng, V.W.; York, B.; Reineke, E.L.; Seo, D.; Fan, D.; Silverstein, K.A.; Schrum, C.T.; Xie, W.R.; Mularoni, L.; et al. A Sleeping Beauty Mutagenesis Screen Reveals a Tumor Suppressor Role for Ncoa2/Src-2 in Liver Cancer. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2012, 109, E1377–E1386. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tschida, B.R.; Temiz, N.A.; Kuka, T.P.; Lee, L.A.; Riordan, J.D.; Tierrablanca, C.A.; Hullsiek, R.; Wagner, S.; Hudson, W.A.; Linden, M.A.; et al. Sleeping Beauty Insertional Mutagenesis in Mice Identifies Drivers of Steatosis-Associated Hepatic Tumors. Cancer Res. 2017, 77, 6576–6588. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bard-Chapeau, E.A.; Nguyen, A.T.; Rust, A.G.; Sayadi, A.; Lee, P.; Chua, B.Q.; New, L.S.; de Jong, J.; Ward, J.M.; Chin, C.K.; et al. Transposon Mutagenesis Identifies Genes Driving Hepatocellular Carcinoma in a Chronic Hepatitis B Mouse Model. Nat. Genet. 2014, 46, 24–32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Oh, B.K.; Jo Chae, K.; Park, C.; Kim, K.; Jung Lee, W.; Han, K.H.; Nyun Park, Y. Telomere Shortening and Telomerase Reactivation in Dysplastic Nodules of Human Hepatocarcinogenesis. J. Hepatol. 2003, 39, 786–792. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oh, B.K.; Kim, Y.J.; Park, C.; Park, Y.N. Up-Regulation of Telomere-Binding Proteins, TRF1, TRF2, and TIN2 Is Related to Telomere Shortening During Human Multistep Hepatocarcinogenesis. Am. J. Pathol. 2005, 166, 73–80. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, Y.H.; Oh, B.K.; Yoo, J.E.; Yoon, S.M.; Choi, J.; Kim, K.S.; Park, Y.N. Chromosomal Instability, Telomere Shortening, and Inactivation of p21WAF1/CIP1 in Dysplastic Nodules of Hepatitis B Virus-Associated Multistep Hepatocarcinogenesis. Mod. Pathol. 2009, 22, 1121–1131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liang, H.W.; Wang, N.; Wang, Y.; Wang, F.; Fu, Z.; Yan, X.; Zhu, H.; Diao, W.; Ding, Y.; Chen, X.; et al. Hepatitis B Virus-Human Chimeric Transcript HBx-LINE1 Promotes Hepatic Injury Via Sequestering Cellular microRNA-122. J. Hepatol. 2016, 64, 278–291. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cao, Q.; Imbeaud, S.; Datta, S.; Zucman-Rossi, J. Authors’ Response: Virus-Host Interactions in HBV-Related Hepatocellular Carcinoma: More to Be Revealed? Gut 2015, 64, 853–854. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, X.; Zhang, J.; Yang, Z.; Kang, J.; Jiang, S.; Zhang, T.; Chen, T.; Li, M.; Lv, Q.; Chen, X.; et al. The Function of Targeted Host Genes Determines the Oncogenicity of HBV Integration in Hepatocellular Carcinoma. J. Hepatol. 2014, 60, 975–984. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zerial, M.; Salinas, J.; Filipski, J.; Bernardi, G. Genomic Localization of Hepatitis B Virus in a Human Hepatoma Cell Line. Nucl. Acids Res. 1986, 14, 8373–8386. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lander, E.S.; Linton, L.M.; Birren, B.; Nusbaum, C.; Zody, M.C.; Baldwin, J.; Devon, K.; Dewar, K.; Doyle, M.; FitzHugh, W.; et al. Initial Sequencing and Analysis of the Human Genome. Nature 2001, 409, 860–921. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Arhondakis, S.; Clay, O.; Bernardi, G. GC Level and Expression of Human Coding Sequences. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 2008, 367, 542–545. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Paeschke, K.; McDonald, K.R.; Zakian, V.A. Telomeres: Structures in Need of Unwinding. FEBS Lett. 2010, 584, 3760–3772. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Summers, J.; Jilbert, A.R.; Yang, W.; Aldrich, C.E.; Saputelli, J.; Litwin, S.; Toll, E.; Mason, W.S. Hepatocyte Turnover During Resolution of a Transient Hepadnaviral Infection. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2003, 100, 11652–11659. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Budzinska, M.A.; Tu, T.; d’Avigdor, W.M.; McCaughan, G.W.; Luciani, F.; Shackel, N.A. Accumulation of Deleterious Passenger Mutations Is Associated with the Progression of Hepatocellular Carcinoma. PLoS ONE 2016, 11, e0162586. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bowcock, A.M.; Pinto, M.R.; Bey, E.; Kuyl, J.M.; Dusheiko, G.M.; Bernstein, R. The PLC/PRF/5 Human Hepatoma Cell Line. II. Chromosomal Assignment of Hepatitis B Virus Integration Sites. Cancer Genet. Cytogenet. 1985, 18, 19–26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tay, N.; Chan, S.H.; Ren, E.C. Detection of Integrated Hepatitis B Virus DNA in Hepatocellular Carcinoma Cell Lines by Nonradioactive in situ Hybridization. J. Med. Virol. 1990, 30, 266–271. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Walters, K.A.; Joyce, M.A.; Addison, W.R.; Fischer, K.P.; Tyrrell, D.L. Superinfection Exclusion in Duck Hepatitis B Virus Infection Is Mediated by the Large Surface Antigen. J. Virol. 2004, 78, 7925–7937. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Winer, B.Y.; Huang, T.S.; Pludwinski, E.; Heller, B.; Wojcik, F.; Lipkowitz, G.E.; Parekh, A.; Cho, C.; Shrirao, A.; Muir, T.W.; et al. Long-Term Hepatitis B Infection in a Scalable Hepatic Co-Culture System. Nat. Commun. 2017, 8, 125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zehnder, B.; Estrada Girona, G.; Lemke, E.A.; Urban, S. Amber suppression mediated genetic code expansion as a novel tool for labelling and live-cell imaging of HBV core protein. Presented at International Meeting on the Molecular Biology of Hepatitis B Viruses, Washington, DC, USA, 3 September 2017. Oral-80. [Google Scholar]
- Allweiss, L.; Volz, T.; Giersch, K.; Kah, J.; Raffa, G.; Petersen, J.; Lohse, A.W.; Beninati, C.; Pollicino, T.; Urban, S.; et al. Proliferation of Primary Human Hepatocytes and Prevention of Hepatitis B Virus Reinfection Efficiently Deplete Nuclear Cccdna in vivo. Gut 2018, 67, 542–552. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yaginuma, K.; Kobayashi, M.; Yoshida, E.; Koike, K. Hepatitis B Virus Integration in Hepatocellular Carcinoma DNA: Duplication of Cellular Flanking Sequences at the Integration Site. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 1985, 82, 4458–4462. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lan, P.; Zhang, C.; Han, Q.; Zhang, J.; Tian, Z. Therapeutic Recovery of Hepatitis B Virus (HBV)-Induced Hepatocyte-Intrinsic Immune Defect Reverses Systemic Adaptive Immune Tolerance. Hepatology 2013, 58, 73–85. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Michler, T.; Grosse, S.; Mockenhaupt, S.; Roder, N.; Stuckler, F.; Knapp, B.; Ko, C.; Heikenwalder, M.; Protzer, U.; Grimm, D. Blocking Sense-Strand Activity Improves Potency, Safety and Specificity of Anti-Hepatitis B Virus Short Hairpin RNA. EMBO Mol. Med. 2016, 8, 1082–1098. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, B.; Sun, S.; Li, M.; Cheng, X.; Li, H.; Kang, F.; Kang, J.; Dornbrack, K.; Nassal, M.; Sun, D. Suppression of Hepatitis B Virus Antigen Production and Replication by Wild-Type HBV Dependently Replicating HBV Shrna Vectors in vitro and in vivo. Antivir. Res. 2016, 134, 117–129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Slagle, B.L.; Andrisani, O.M.; Bouchard, M.J.; Lee, C.G.; Ou, J.H.; Siddiqui, A. Technical Standards for Hepatitis B Virus X Protein (HBX) Research. Hepatology 2015, 61, 1416–1424. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]


| Technique | Biases | Drawbacks | Advantages | Suitable Uses | Ref. |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Southern blot |
|
|
| Detecting presence of integrated HBV DNA in highly clonal samples | [39,40,42,43,44,45,46] |
| Direct cloning and Sanger sequencing |
|
|
| Determining structure of integrated HBV genome in highly clonal samples | [45,47] |
| Alu PCR |
|
|
| Detecting and sequencing integrated HBV DNA in clonal samples | [48,49,50] |
| invPCR |
|
|
| Detecting and quantifying rare HBV DNA integrations | [16,26,28,29,31,32,33] |
| WGS |
|
|
| Integration site detection in highly clonal samples | [18,19,20,21,22,23] |
| WES |
|
|
| Integration site detection in coding regions | [51,52] |
| RNA-Seq |
|
|
| Virus-fusion transcripts | [19,22,53,54,55] |
| Feature in Which Integration Occurs | Enrichment in HCC | Enrichment in Non-Tumour Tissue |
|---|---|---|
| Specific HCC driver genes | Yes, but minority of HCCs (TERT, MLL4) | FN1 |
| Telomeres | Yes | No |
| CpG islands | Yes | Slight (~2-fold greater than expected) |
| Repetitive regions (e.g., LINEs and SINEs) | No, except one report [54] | No |
| Transcriptionally-active sites | Yes | No |
| Exons and Introns | Yes | Slight |
| Fragile sites | Yes | No |
| Promoter regions | Yes | Slight |
© 2018 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Budzinska, M.A.; Shackel, N.A.; Urban, S.; Tu, T. Cellular Genomic Sites of Hepatitis B Virus DNA Integration. Genes 2018, 9, 365. https://doi.org/10.3390/genes9070365
Budzinska MA, Shackel NA, Urban S, Tu T. Cellular Genomic Sites of Hepatitis B Virus DNA Integration. Genes. 2018; 9(7):365. https://doi.org/10.3390/genes9070365
Chicago/Turabian StyleBudzinska, Magdalena A., Nicholas A. Shackel, Stephan Urban, and Thomas Tu. 2018. "Cellular Genomic Sites of Hepatitis B Virus DNA Integration" Genes 9, no. 7: 365. https://doi.org/10.3390/genes9070365
APA StyleBudzinska, M. A., Shackel, N. A., Urban, S., & Tu, T. (2018). Cellular Genomic Sites of Hepatitis B Virus DNA Integration. Genes, 9(7), 365. https://doi.org/10.3390/genes9070365