Abstract
Peroxisomes are central to eukaryotic metabolism, including the oxidation of fatty acids—which subsequently provide an important source of metabolic energy—and in the biosynthesis of cholesterol and plasmalogens. However, the presence and nature of peroxisomes in the parasitic apicomplexan protozoa remains controversial. A survey of the available genomes revealed that genes encoding peroxisome biogenesis factors, so-called peroxins (Pex), are only present in a subset of these parasites, the coccidia. The basic principle of peroxisomal protein import is evolutionarily conserved, proteins harbouring a peroxisomal-targeting signal 1 (PTS1) interact in the cytosol with the shuttling receptor Pex5 and are then imported into the peroxisome via the membrane-bound protein complex formed by Pex13 and Pex14. Surprisingly, whilst Pex5 is clearly identifiable, Pex13 and, perhaps, Pex14 are apparently absent from the coccidian genomes. To investigate the functionality of the PTS1 import mechanism in these parasites, expression of Pex5 from the model coccidian Toxoplasma gondii was shown to rescue the import defect of Pex5-deleted Saccharomyces cerevisiae. In support of these data, green fluorescent protein (GFP) bearing the enhanced (e)PTS1 known to efficiently localise to peroxisomes in yeast, localised to peroxisome-like bodies when expressed in Toxoplasma. Furthermore, the PTS1-binding domain of Pex5 and a PTS1 ligand from the putatively peroxisome-localised Toxoplasma sterol carrier protein (SCP2) were shown to interact in vitro. Taken together, these data demonstrate that the Pex5–PTS1 interaction is functional in the coccidia and indicate that a nonconventional peroxisomal import mechanism may operate in the absence of Pex13 and Pex14.
1. Introduction
Peroxisomes were first biochemically characterised and named by Christian de Duve and colleagues following purification from rat liver tissue, and later the protozoa [1,2]. Within the isolated, membrane-bound microbodies, they identified several oxidases that oxidize substrates whilst reducing oxygen to hydrogen peroxide (H2O2), as well as two enzyme classes able to reduce this damaging H2O2: peroxidases and catalases [2]. The following decades saw peroxisomes identified as apparently ubiquitous, functionally diverse, eukaryotic organelles involved in many catabolic functions including lipid, amino acid and purine metabolism [3,4]. This biogenesis and functionality of peroxisomes is dependent on a group of proteins known as peroxins (Pex). Furthermore, the topogenic import signals for the import of matrix proteins is conserved across evolution [5]. For most imported proteins this motif comprises a short tripeptide sequence at the extreme C-terminus. Prototypically, this motif, serine–lysine–leucine (-SKL) or neutral variants, is known as peroxisomal-targeting signal 1 (PTS1) [6]. The PTS1 receptor is the peroxin Pex5, a shuttling receptor, which translocates the PTS1-bearing ligand from the cytosol to the peroxisome matrix via interaction with a membrane docking complex of Pex13 and Pex14 (and Pex17 in yeast) [7,8].
Illustrative of the essential function of peroxisomes in many eukaryotes is the association of mutations in the Pex5–PTS1 import system with human diseases such as Zellweger syndrome [9]. However, despite the crucial roles these organelles can play, eukaryotic microbes such as the intestinal parasite Entamoeba histolytica have been reported to lack peroxisomes, presumably due to their existence in low-oxygen environments and the consequent lack of H2O2 [10]. Other intracellular parasites such as the fungal Microsporidia and the protozoan Apicomplexa (including the malaria parasite Plasmodium spp.), as well as intestinal parasitic helminths, have also been reported to lack peroxisomes and encoded Pex proteins [4,11]. However, as the genome databases have developed it has become clear that some apicomplexan parasites, the coccidia which include Eimeria spp. (coccidiosis in poultry) and Toxoplasma gondii (toxoplasmosis), encode many of the Pex proteins synonymous with the presence of these organelles [5].
Obligate intracellular organisms rely on the host cell for many of their nutritional requirements. For example, Toxoplasma is auxotrophic for cholesterol and is reliant on that scavenged from the host via endocytosis of low-density lipoprotein (LDL) [12,13], a process that has been proposed as a possible drug target [14]. This salvage of LDL requires molecular mechanisms for coordinated delivery to the desired organelles, and a sterol carrier protein (SCP2) has been characterised as playing a key role in this process [15]. In the Eukaryota, SCP2 is specifically targeted to peroxisomes via a PTS1, a process important for the β-oxidation of fatty acids [16]. Similarly, the Toxoplasma SCP2, which harbours a putative PTS1 (SRL), is localised to peroxisomes in mammalian cells, and to the lumen of well-defined vesicles in the parasite [15]. However, the identity of these vesicles as peroxisomes is controversial, with the predicted PTS1 signal of Toxoplasma catalase failing to direct green fluorescent protein (GFP) to membrane-bound microbodies in one study [17]. However, a parallel study showed the parasite catalase localising to vesicles in Toxoplasma and to mammalian peroxisomes, with the putative PTS1 signal responsible [18].
Clearly, the nature and/or presence of peroxisomes in the Apicomplexa requires further analyses. However, bioinformatic studies have very recently provided evidence, by virtue of the presence of encoded Pex and PTS-bearing proteins, that Toxoplasma and related coccidia harbour peroxisomes [5,19,20]. Here, we have taken a functional biology approach to define the Toxoplasma Pex5 as a functional orthologue of the yeast, but not human, protein. In addition, we have shown that the enhanced (e)PTS1 identified from Saccharomyces cerevisiae [21] efficiently localises GFP to peroxisome-like bodies when expressed in Toxoplasma. Finally, we have biochemically demonstrated that the PTS1 ligand domain of the parasite SCP2 interacts with the PTS1-binding domain from Toxoplasma Pex5 in vitro. Taken together with previous studies, these data strongly suggest the presence of peroxisomes in this group of parasites.
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Toxoplasma Pex5 Complementation of Yeast and Human Mutant Lines
The complete coding region of the Toxoplasma protein, TgPex5 (TGGT1_231870), was synthesised by GenScript (Piscataway, NJ, USA). Using the Infusion system (Takara, Kusatsu, Japan) according to manufacturer’s instructions, this sequence was amplified and cloned into:
(i) the mammalian bicistronic expression vector pIRES2-enhanced(e)GFP-SKL [22] using the primer pair:
F:5′CTCAAGCTTCGAATTCTGATGGCTTTCCGTGCG3′
R:5′GAGGGAGAGGGGCGGATCCGGTTAGACGTTCTTGATC3′
(ii) the yeast expression vector pRS416 (containing the ScPEX5 promoter) [23] using the primer pair:
F:5′CAATATATCATAACACGTCGACTGATGGCTTTCCGTGCG3′
R:5′CTTAGCGGCCGCACTAGTAGATCTTTAGACGTTCTTGATCATCCC3′
The plasmid resulting from (i), pIRES2-TgPex5-eGFP-SKL, and pIRES2-HsPEX5-eGFP-SKL as a positive control, were transfected into human skin fibroblast cell line GM5756 T (wild-type and Zellweger patient-derived PEX5-deficient) [24]. Wild-type and mutant cells were maintained in Dulbecco Modified Eagle Media (DMEM; Sigma Aldrich, St. Louis, MO, USA) supplemented with 10% Fetal Bovine Serum (FBS; ThermoFisher Scientific, Waltham, MA, USA), 4 mM L-glutamine (Sigma Aldrich), 1% penicillin/streptomycin (Sigma Aldrich) at 37 °C, 5% CO2. Transfection was carried out using the X-tremeGENE 9 DNA transfection kit (Roche, Basel, Switzerland) according to the manufacturer’s protocol and the cells incubated for 72 h.
The plasmid resulting from (ii), pRS416-TgPex5, and pRS416-ScPex5 as a positive control (both containing ScPEX5 promoter), were transformed into Saccharomyces cerevisiae UTL-7A (wild-type and pex5 deletion strains) for growth assay, or co-transformed with pRS415-based plasmid encoding GFP-SKL as a PTS1 peroxisomal marker for microscopy [23]. For transformation, yeast were grown to exponential phase and transformed as previously described [25,26,27,28,29,30]. Single or double transformants were selected on −Ura or −Ura−Leu plates, respectively, and later cultured in selective liquid media containing 0.3% (w/v) glucose or 0.1% (w/v) oleic acid as previously described [31].
After incubation, human cells were washed with Dulbecco Phosphate-Buffered Saline (DPBS; Sigma Aldrich) and fixed in 4% v/v paraformaldehyde (Roth, Karsruhe, Germany) in DPBS for 20 min at room temperature. Cells fixed on cover-slips were then mounted on glass slides under the anti-fade reagent Mowiol (Sigma Aldrich) containing 4′,6-ciamidino-2-phenylindole (DAPI; ThermoFisher Scientific). Yeast cells were directly visualized under microscopy. For imaging, wide-field fluorescence microscopy was performed using an Axioplan 2 microscope with an AxioCam MR digital camera and Axiovision software version 4.6.3 (Zeiss, Oberkochen, Germany). Green fluorescent protein signal was visualized using 450–490 nm band pass excitation filter, a 510 nm dichromatic mirror and a 515–565 nm band pass emission filter.
2.2. Growth Analyses of Toxoplasma Pex5 Complementation of Yeast Mutant Line
Serial 10-fold dilutions of exponentially growing UTL-7A Pex5 deleted yeast, transformed with TgPex5, ScPex5 or empty vector, were spotted onto −Ura glucose or oleate plates and incubated at 30 °C for 3 to 4 days before image capture as previously described [31,32].
2.3. Localisation of Enhanced PTS1-Tagged GFP in Toxoplasma
The GFP-enhanced(e)PTS1 cassette was amplified from the vector pFA6a-GFP-eSKL [21] using the primer pair:
F:5′GAAAACTACTCGTTGGCATTTTTTCTTGAATTCCATGAGTAAAGGAGAAGAACTTTTCACTGG3′
R:5′GAGAAGTGAGCACAACGGTGATTAATTAACTACAATTTGGATCTTCTACCTCTTCCCAATG3′
Using the restriction-free methodology [33], following purification, the PCR product was cloned into pTUB8-myc-GFP to form pTUB8-GFP-ePTS1.
Toxoplasma RH strain were transfected with pTUB8-GFP-ePTS1 and used to infect human foreskin fibroblasts cultured on glass coverslips as previously described [29]. After 24 h, cells were fixed with 4% paraformaldehyde (20 min, room temperature) and washed in PBS, before permeabilization and blocking in PBS/0.02% Triton-X-100/2% Bovine Serum Albumin (BSA; 20 min, room temperature). Cells were then incubated for 60 min at room temperature with the primary antibodies (anti-IMC1 [34] and anti-GFP, Roche) diluted 1:1000, washed three times, and incubated with Alexa488 goat anti-mouse and Alexa594 goat anti-rabbit (ThermoFisher Scientific; 45 min, room temperature), all in PBS/0.02% Triton-X-100/2% BSA.
Images were obtained using a DeltaVision Core microscope (GE Heathcare, Chicago, IL, USA) and processed using Softworx (GE Heathcare) and FIJI software [35]. Parasites with heavily distorted cell shape and fragmented mitochondria were excluded from the analysis.
2.4. Analyses of the Interaction of Toxoplasma Pex5 and SCP2
Regions encoding domains for the predicted PTS1 of TgSCP2 (TgSCP2PTS1: TgSCP2 499-625) and the PTS1-binding region of receptor TgPex5 (TgPex5C: TgPex5 581-899) were synthesized with an Escherichia coli codon bias and cloned into the bacterial expression vector pETM-30 by GenScript. The resulting pETM-30-TgSCP2PTS1 and pETM-30-TgPex5C were transformed into E. coli BL21 (DE3) (ThermoFisher Scientific), and grown in pH 7.5 buffered Luria-Bertani (LB) medium, supplemented with 1% (w/v) glucose and 50 mg/mL kanamycin (Sigma-Aldrich) at 37 °C. When exponential growth was reached, the temperature was reduced to 20 °C for 1 h, before induction with 0.5 mM IsoPropyl β-D-1-ThioGalactopyranoside (IPTG; Sigma Aldrich) and overnight incubation at 30 °C. Cell pellets were flash frozen before resuspension in Buffer A: 100 mM KH2PO4 pH 7.4, 5 mM 2-mercaptoethanol, EDTA-free complete protease inhibitor cocktail, 1 mg/mL lysozyme, 1 mg/mL DNase I and 1 mg/mL RNAse A (Sigma-Aldrich). The bacteria were then sonicated (Electronic UW2200; Bandelin, Berlin, Germany) and, following centrifugation, the supernatant collected through a 0.45 µm filter (Sigma Aldrich). This supernatant was then applied to a 1 mL Glutathione Sepharose 4B resin column (GSTrap) (GE Healthcare), which was pre- equilibrated with Buffer A. Following a Buffer A wash, the protein was eluted with Buffer A containing 20 mM reduced glutathione. The TgPex5C HIS-GST-tag was cleaved using TEV protease (Sigma Aldrich) in accordance with manufacturer’s instructions, before dialysis into Buffer A and application to a 1 mL Ni-NTA (ThermoFisher Scientific) column equilibrated in Buffer A and eluted with Buffer A supplemented with 250 mM imidazole, pH 7.4. To analyse the interaction, TgSCP2 PTS1 containing His6(HIS)-GST-tag was bound to a GSTrap column and isolated TgPex5C applied in Buffer A. Following a Buffer A wash, the proteins were eluted with Buffer A containing 20 mM reduced glutathione before analyses by SDS–PAGE.
3. Results
3.1. Functional Complementation Analyses of TgPex5 in Yeast and Human Cell Lines
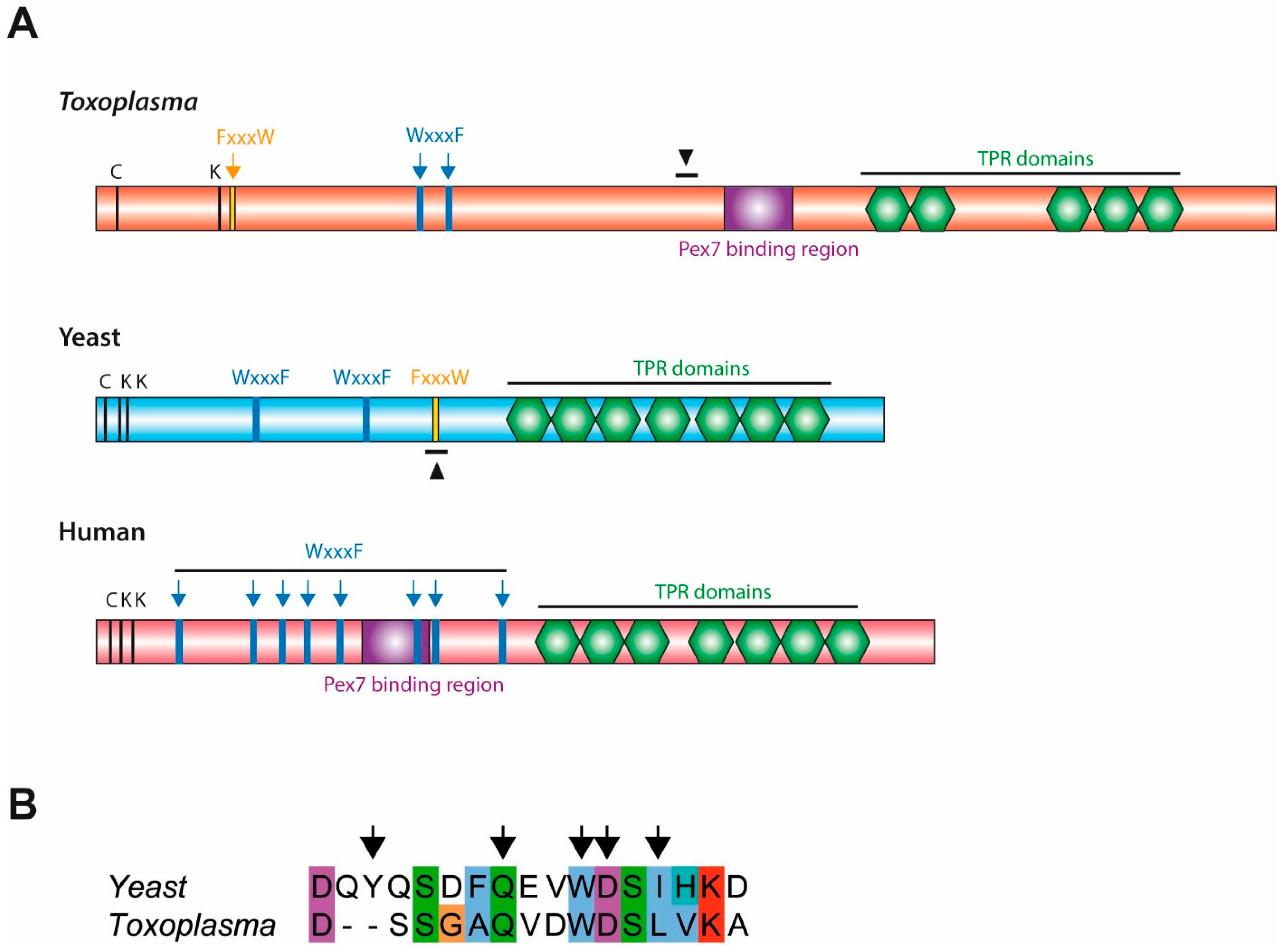
Bioinformatic analyses of Toxoplasma, yeast and human Pex5 protein sequences indicated that parasite Pex5 contains structural features characteristic of Pex5 proteins. These include (i) C-terminal TetratricoPeptide Repeat (TPR) motifs forming the PTS1-binding site; (ii) within the probably unstructured N-terminal domain, three so-called WxxxF motifs required for receptor docking; and (iii) a single cysteine at a conserved position, which becomes ubiquitinated to initiate recycling of the receptor into the cytosol (Figure 1A). Toxoplasma Pex5 was heterologously expressed in human or yeast cells for functional complementation analysis. In contrast to the positive control, human HsPex5L [24], expression of Toxoplasma TgPex5 in Pex5-deficient human fibroblasts was unable to restore the PTS1-mediated trafficking of eGFP to peroxisomal compartments (Figure 2). However, parallel analyses in S. cerevisiae demonstrated that TgPex5 could clearly restore GFP-PTS1 targeting to peroxisomes in a cellular context (Figure 3). The results of this localisation assay were augmented by the observation that TgPex5, like ScPex5 [23], was able to restore peroxisomal function and β-oxidation as characterised by increased growth and the utilisation of fatty acid oleate, which results in halo formation around the colonies on oleate plates (Figure 4) [31,32]. Growth complementation indicates that the heterologous TgPex5 targets not only the artificial cargo GFP-PTS1, but also the endogenous yeast enzymes, into peroxisomes. It is remarkable that TgPex5 restored translocation into the organellar lumen of not only the β-oxidation enzymes with typical PTS1, but also of the non-PTS acyl-CoA oxidase Fox1, the initial enzyme required for the fatty acid catabolic pathway. The Fox1 binding regions have been assigned to the N-terminal half of ScPex5 [36]. Sequence alignments between yeast and Toxoplasma Pex5 suggest that the key residues required for Fox1 interaction are largely conserved (Figure 1B). Taken together, these data indicate that Toxoplasma TgPex5 is a functional orthologue of the yeast Pex5, and heterologous expression of this protein can functionally replace its yeast but not its human counterpart.
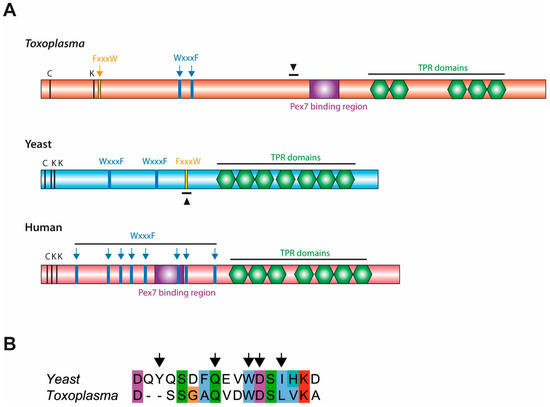
Figure 1.
(A) Toxoplasma Peroxin 5 (Pex5) contains structural characteristics conserved in yeast and human Pex5. Bioinformatic comparison of the Toxoplasma Pex5 protein sequence with yeast and human counterparts indicated the presence of critical cysteine and lysine residues (C, K), pentapeptide motifs (WxxxF/FxxxW) and structural domains (Pex7-binding region and TetratricoPeptide Repeat [TPR] domains which bind peroxisomal-targeting signal 1 [PTS1] ligands) characteristic of Pex5. Additionally, a region homologous to the Fox1 binding site in yeast Pex5 is also found in Toxoplasma Pex5; indicated by black arrowheads. (B) Sequence alignment of the Fox1 binding site in yeast Pex5 (ScPex5251-267) with Toxoplasma Pex5 (TgPex5442-456), arrows indicate positions in ScPex5 critical for Fox1 binding [36].
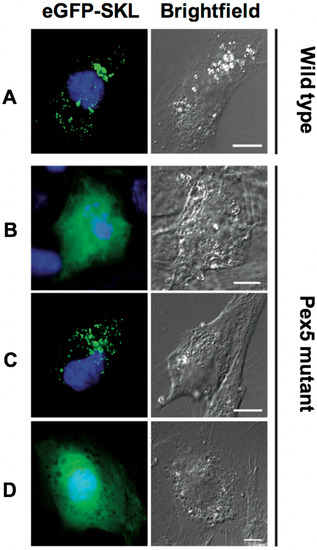
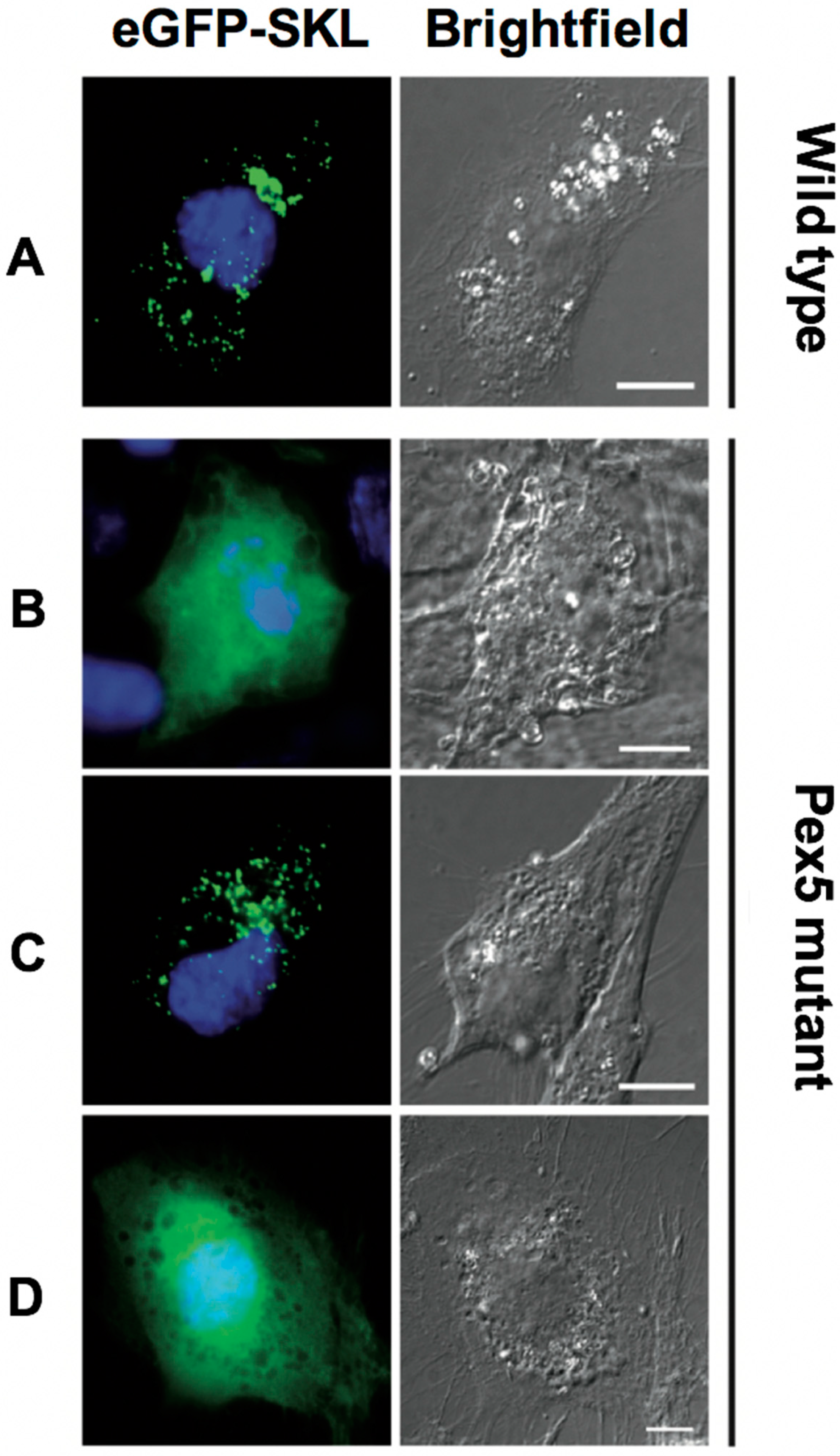
Figure 2.
TgPex5 does not functionally replace Pex5 function in human fibroblast cells. In wild-type cells (A), peroxisomal reporter enhanced (e) GFP-SKL is imported into peroxisomes, resulting in a characteristic punctuate pattern. In Pex5 mutant cells (B, negative control), eGFP-SKL is mislocalised to the cytosol, resulting in the diffuse cytosolic pattern of GFP. Co-expression of human Pex5 (HsPex5L, C, positive control) restored the localisation of eGFP-SKL to peroxisomes. In contrast, co-expression of TgPex5 (D) did not localise eGFP-SKL to peroxisomes. Scale bar is 10 µm.
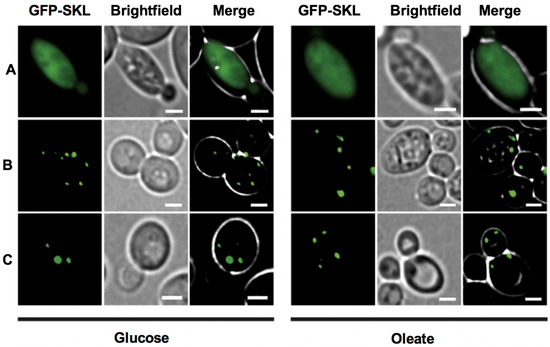
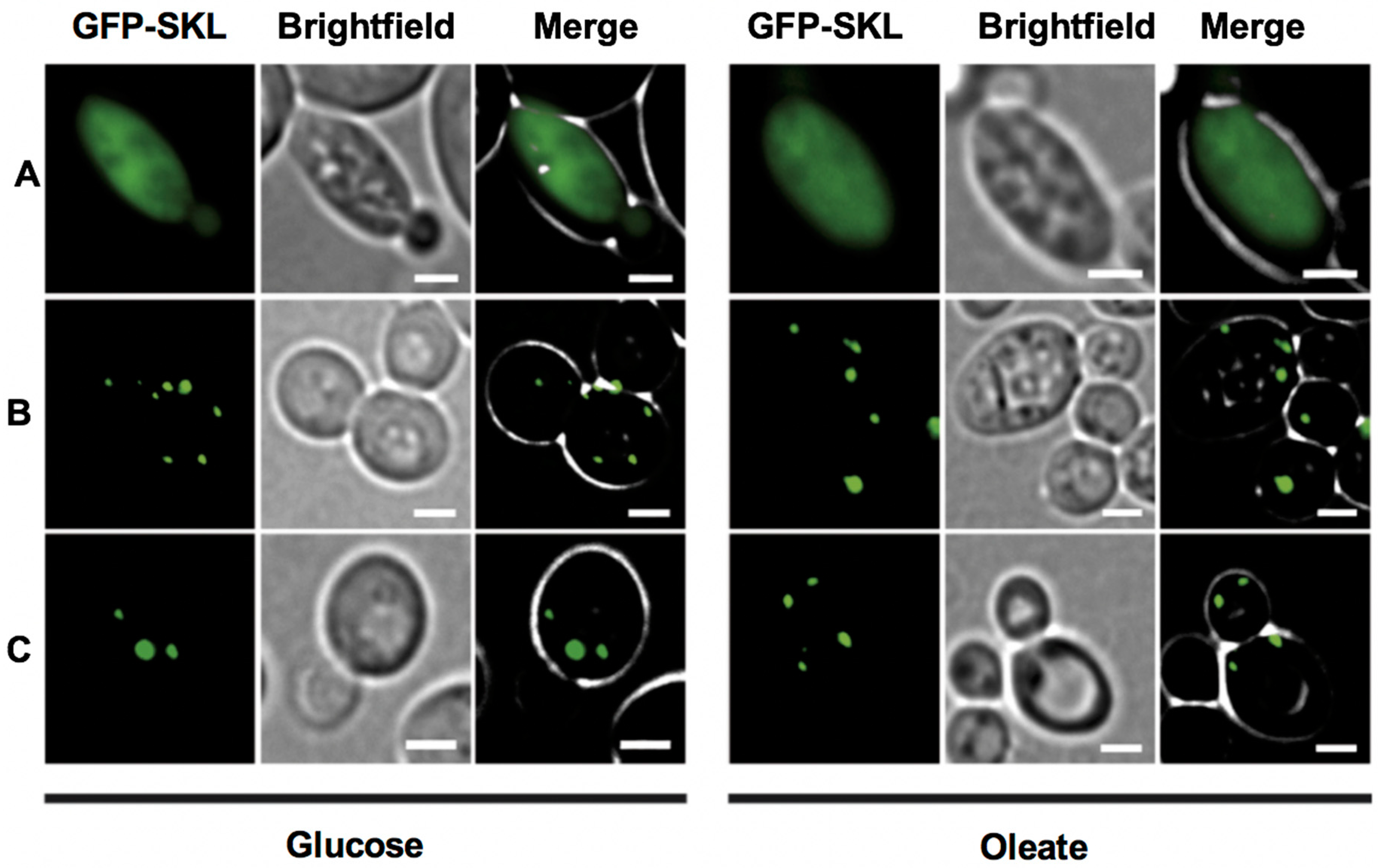
Figure 3.
TgPex5 complements for the loss of Pex5 in Δpex5 mutant yeast when grown on medium containing either glucose or oleate as the sole carbon source. No complementation is indicated by a mislocalization of the heterologously expressed GFP-SKL to the cytosol as seen for the empty vector control (A). Functional complementation restored peroxisomal import of the GFP-SKL and led to the appearance of a punctate pattern, as seen upon expression of the gene coding for yeast Pex5 (B), and the gene encodingTgPex5 (C). These results indicated that TgPex5 can functionally replace the yeast Pex5p in PTS1-protein import into peroxisomes. Scale bar is 5 µm.
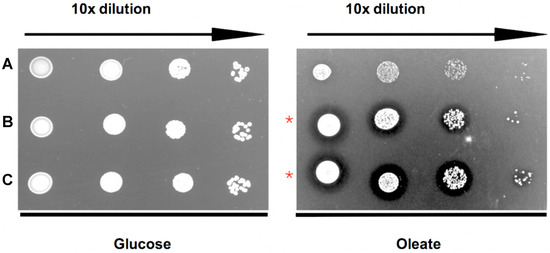
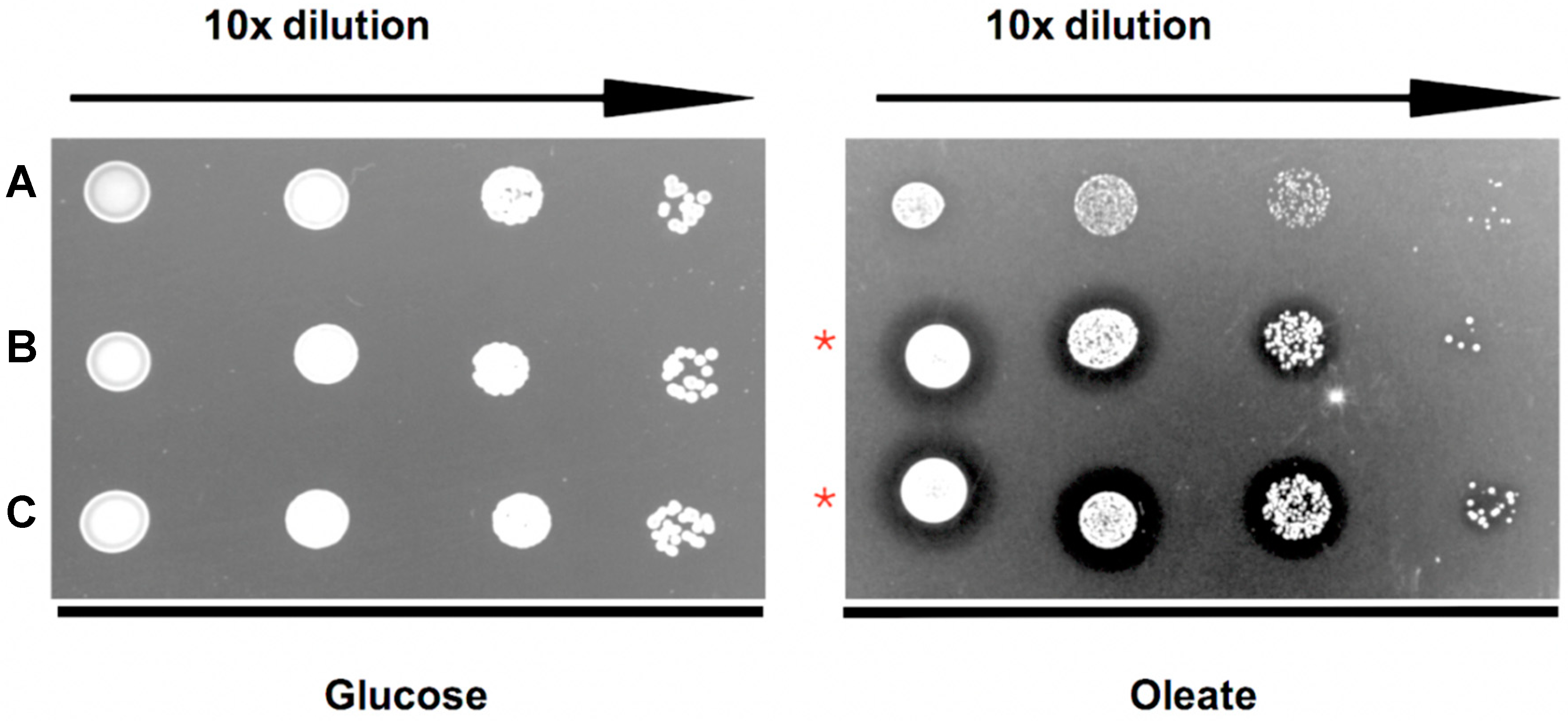
Figure 4.
TgPex5 expression complements the growth defect of yeast Δpex5 mutant cells on oleic acid media. (A) Empty vector negative control; (B) ScPex5 positive control; and (C) TgPex5. 10-fold dilutions (from the left) spotted onto either glucose and oleate plates. As expected, all strains grow well in the presence of glucose. On oleate medium, the growth of the Δpex5 mutant transformed with the empty vector control is affected. In contrast, Δpex5 mutant cells transformed with plasmids coding for either ScPex5 (B) or TgPex5 (C) showed enhanced growth and a halo that is characteristic of efficient oleate utilisation and peroxisomal oxidation (red stars).
3.2. Localization of GFP Tagged with Enhanced PTS1 (GFP-ePTS1) in Toxoplasma
Enhanced (e)PTS1 was identified by screening a randomised library for linker sequences (directly upstream of PTS1) for the ability to more efficiently localise fluorescent protein to peroxisomes in S. cerevisiae [21]. When GFP-ePTS1 was expressed in Toxoplasma, it localised to punctate structures with diameters ranging from 129–311 nm (Figure 5), this concurs with the diameter of peroxisomes (100–200 nm) and previous observations in this parasite [15,18]. This observation supports (i) the interaction of PTS1 (from yeast, as well as Toxoplasma) with Pex5 in the parasite; (ii) the existence of peroxisomes with the canonical translocation machinery in the coccidia.
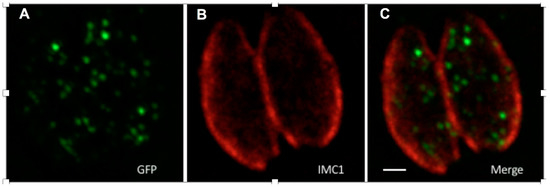
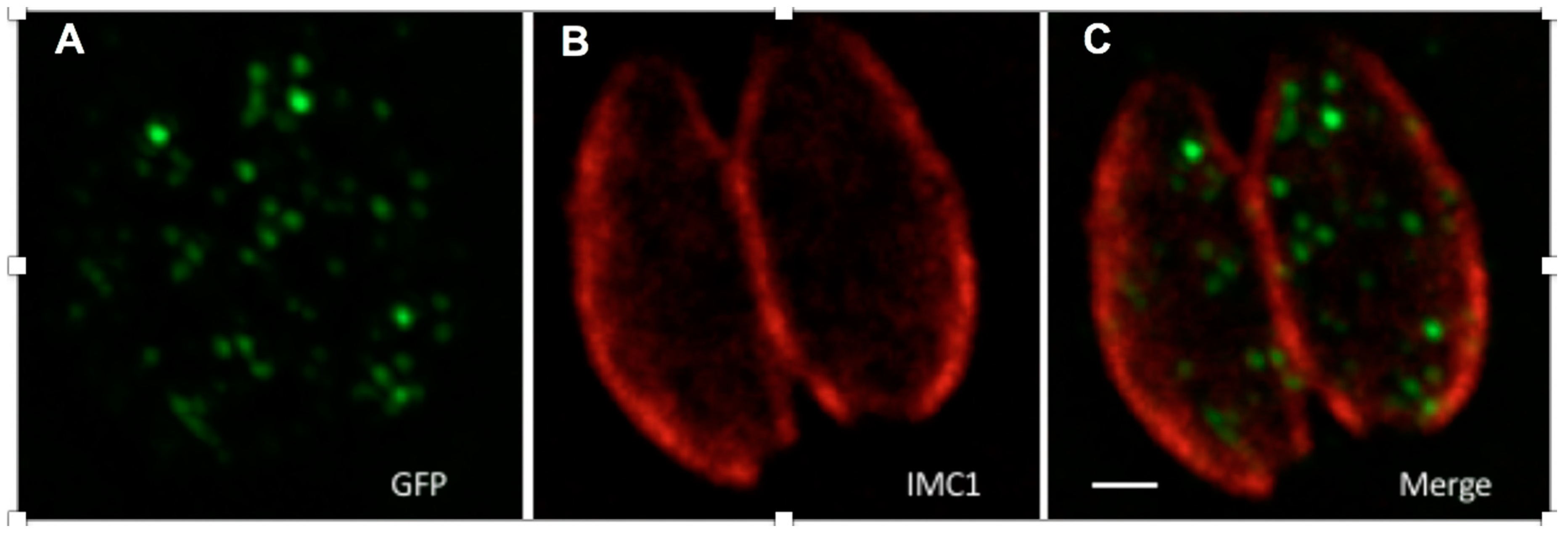
Figure 5.
GFP tagged with ePTS1 localised in peroxisome-like bodies when transiently expressed in Toxoplasma. The image shows two parasites within a human fibroblast vacuole, GFP-ePTS1 stained with anti-GFP antibody (A, green), the parasite pellicle stained with anti-IMC1 antibody (B, red), and a merge of A and B (C). The scale bar is 1 µM.
3.3. In Vitro Analyses of the Interaction of TgPex5 and TgSCP2
Regions encoding the following domains were expressed in E. coli: (i) predicted TgSCP2 PTS1 (TgSCP2PTS1: TgSCP2 499–625) containing the PTS1-targeting signal; and (ii) TgPex5 PTS1 receptor (TgPex5C: TgPex5 581–899), harbouring the predicted PTS1-binding domain. The recombinant proteins were isolated and subjected to in vitro binding studies. Using HIS-GST-tagged TgSCP2 PTS1 (43.4 kDa) bound to a GSTrap column as bait, the binding of TgPex5C (34.5 kDa) was analysed. Following stringent washes, the elution of bound material demonstrated interaction with TgSCP2PTS1, showing that the Toxoplasma Pex5 can bind to the parasite PTS1 (Figure 6).
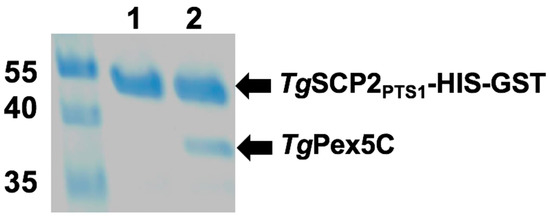
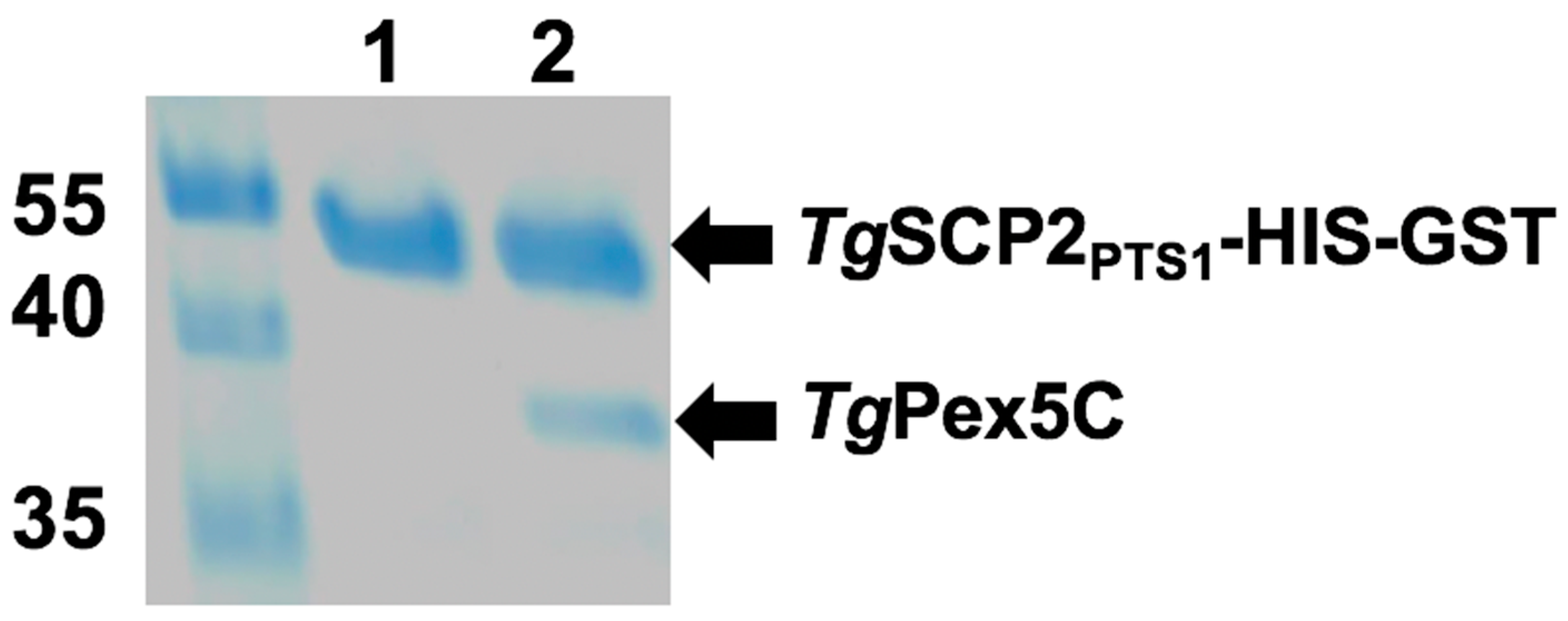
Figure 6.
Interaction of TgSCP2 PTS1 and TgPEX5C in vitro. Pull-down assay was performed using the bait TgSCP2 PTS1 with a HIS-GST tag. Eluates of the pull-down without prey protein (Lane 1, negative control) and TgPEX5C (Lane 2) are shown. Molecular weight markers are in kilodaltons.
4. Discussion
With recent bioinformatic analyses demonstrating the presence of a suite of Pex proteins in the coccidian apicomplexans, but not in other subclasses [5,19,20], functional analyses are demanded. However, previous studies in Toxoplasma have proven to be controvertible. The Toxoplasma catalase was localised to peroxisome-like vesicles in one study [18], however, in the same year it was reported that the putative catalase PTS1 failed to direct GFP to these membrane-bound microbodies [17]. The sterol carrier protein SCP2 has also been shown to localise to peroxisome-like bodies in Toxoplasma [15].
To improve the molecular understanding of the putative peroxisomal bodies in Toxoplasma and the related coccidians, here we report a series of cellular and biochemical studies of the parasite Pex5 orthologue. Like human, plant and nematode [37], the Toxoplasma protein clearly rescues the targeting of GFP bearing a canonical PTS1 sequence (SKL) in yeast, indicating that TgPex5 is a functional peroxin involved in the trafficking of PTS1-bearing proteins to the peroxisomes. In addition, yeast-derived ePTS1 was sufficient to localise GFP to peroxisome-like bodies in Toxoplasma [15,18], and TgSCPPTS1 (-SRL) clearly binds to the parasite TgPex5 PTS1-binding domain in vitro. Furthermore, heterologous expression of TgPex5 restored the utilisation of oleate in Pex5-deficient yeast, clearly demonstrating that a complete set of endogenous fatty acid-degrading enzymes with, and without, typical PTS1 sequences are recognized and targeted to peroxisomes by the parasite peroxin. This common cargo selectivity of the yeast and Toxoplasma receptor will include Fox1, which is recognized by a PTS1-independent binding domain N-terminal of the yeast Pex5 PTS1-binding region. Importantly, unlike the mammalian orthologue, TgPex5 maintains a Fox1-binding region. In contrast to yeast, TgPex5 was unable to direct eGFP-SKL to human fibroblast peroxisomes and thus rescue the import defect of an equivalent mammalian Pex5-deficient cell line. Taken together, these data indicate that TgPex5 is a functional orthologue of the yeast but not the human peroxin. A difference that may be exploited by consideration of the TgPex5-PTS1 interaction as a drug target, as has been described in the protozoan pathogen Trypansoma brucei [38].
Therefore, in summary we have demonstrated that the Toxoplasma Pex5 is functional in the context of a ∆pex5 yeast strain and interacts with the protozoan PTS1 in vitro. Coupled with the localization of ePTS1-tagged GFP to peroxisome-like bodies in Toxoplasma, this strongly suggests that the coccidia harbour peroxisomes. The relative lack of structural evidence may be due to lifecycle-dependent expression, with the peroxins characterised by upregulation during the extracellular stages of the lifecycle, oocysts and sporozoites. Future studies should be directed here, rather than at the more tractable, intracellular, tachyzoite forms [20]. In addition, in all eukaryotic systems studied to date, a membrane-bound docking complex of Pex13 and Pex14 is required for peroxisomal protein import [7,8]. However, an obvious Pex13 is missing in the genome of Toxoplasma and related coccidian parasites [19,20]. Furthermore, the identity and presence of Pex14 in Toxoplasma is disputed [5,19,20]. Therefore, the exact mode of Pex5-mediated protein import into peroxisomes in the coccidia is unclear and further bioinformatic and functional analyses are warranted.
Author Contributions
Conceptualization, P.W.D., E.P., E.Z., L.S. and W.A.S.; Methodology, R.E., W.A.S., W.S., L.S. and V.C.K.; Validation, P.W.D., L.S., W.S. and R.E.; Formal analysis, P.W.D., E.P., W.A.S., R.E., W.S., L.S. and V.C.K.; Investigation, A.J.M., W.A.S., V.C.K. and N.D.; Resources, P.W.D., L.S., W.S. and R.E.; Data curation, P.W.D., L.S., W.S. and R.E.; Writing-Original Draft Preparation, P.W.D., V.C.K. and A.J.M.; Writing-Review & Editing, P.W.D., V.C.K., W.S. and R.E.; Visualization, A.J.M., W.A.S., V.C.K. and N.D.; Supervision, P.W.D., E.P., W.S., R.E. and E.Z.; Project administration, P.W.D.; Funding acquisition, P.W.D., E.P., W.S. and R.E.
Funding
This work was supported by the Biotechnology and Biological Research Council (BB/M024156/1 to P.W.D. and E.P.), FoRUM Grants of the Ruhr-University Bochum (F883-2016 and F913-2017 to V.C.K., W.S. and R.E.) and a Durham Biophysical Sciences Pump Priming award (to P.W.D.). A.J.M. benefited from a British Society for Parasitology International Training and Fieldwork Award which part supported her research secondment at Ruhr University Bochum. L.S. is a Royal Society of Edinburgh Fellow.
Acknowledgments
We thank Yoav Peleg for constructing the pTUB8-GFP-ePTS1 plasmid.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest. The funders had no role in the design of the study; in the collection, analyses, or interpretation of data; in the writing of the manuscript, and in the decision to publish the results.
References
- Opperdoes, F.R.; Borst, P. Localization of nine glycolytic enzymes in a microbody-like organelle in Trypanosoma brucei: The glycosome. FEBS Lett. 1977, 80, 360–364. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Duve, C. Evolution of the peroxisome. Ann. N. Y. Acad. Sci. 1969, 168, 369–381. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schrader, M.; Fahimi, H.D. The peroxisome: Still a mysterious organelle. Histochem. Cell Biol. 2008, 129, 421–440. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zarsky, V.; Tachezy, J. Evolutionary loss of peroxisomes—not limited to parasites. Biol. Direct 2015, 10, 74. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gabaldon, T.; Ginger, M.L.; Michels, P.A. Peroxisomes in parasitic protists. Mol. Biochem. Parasit. 2016, 209, 35–45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Brocard, C.; Hartig, A. Peroxisome targeting signal 1: Is it really a simple tripeptide? Biochim. Biophys. Acta 2006, 1763, 1565–1573. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Emmanouilidis, L.; Gopalswamy, M.; Passon, D.M.; Wilmanns, M.; Sattler, M. Structural biology of the import pathways of peroxisomal matrix proteins. Biochim. Biophys. Acta 2016, 1863, 804–813. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rucktaschel, R.; Girzalsky, W.; Erdmann, R. Protein import machineries of peroxisomes. Biochim. Biophys. Acta 2011, 1808, 892–900. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fujiki, Y. Peroxisome biogenesis and human peroxisome-deficiency disorders. Proc. Jpn. Acad. Ser. B Phys. Biol. Sci. 2016, 92, 463–477. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vanacova, S.; Liston, D.R.; Tachezy, J.; Johnson, P.J. Molecular biology of the amitochondriate parasites, Giardia intestinalis, Entamoeba histolytica and Trichomonas vaginalis. Int. J. Parasitol. 2003, 33, 235–255. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gabaldon, T. Peroxisome diversity and evolution. Philos. Trans. R. Soc. Lond. B Biol. Sci. 2010, 365, 765–773. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Coppens, I.; Sinai, A.P.; Joiner, K.A. Toxoplasma gondii exploits host low-density lipoprotein receptor-mediated endocytosis for cholesterol acquisition. J. Cell Biol. 2000, 149, 167–180. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nishikawa, Y.; Quittnat, F.; Stedman, T.T.; Voelker, D.R.; Choi, J.Y.; Zahn, M.; Yang, M.; Pypaert, M.; Joiner, K.A.; Coppens, I. Host cell lipids control cholesteryl ester synthesis and storage in intracellular Toxoplasma. Cell Microbiol. 2005, 7, 849–867. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Coppens, I. Targeting lipid biosynthesis and salvage in apicomplexan parasites for improved chemotherapies. Nat. Rev. Microbiol. 2013, 11, 823–835. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lige, B.; Jayabalasingham, B.; Zhang, H.; Pypaert, M.; Coppens, I. Role of an ancestral d-bifunctional protein containing two sterol-carrier protein-2 domains in lipid uptake and trafficking in Toxoplasma. Mol. Biol. Cell 2009, 20, 658–672. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Seedorf, U.; Ellinghaus, P.; Roch Nofer, J. Sterol carrier protein-2. Biochim. Biophys. Acta 2000, 1486, 45–54. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ding, M.; Clayton, C.; Soldati, D. Toxoplasma gondii catalase: Are there peroxisomes in toxoplasma? J. Cell Sci. 2000, 113 Pt 13, 2409–2419. [Google Scholar]
- Kaasch, A.J.; Joiner, K.A. Targeting and subcellular localization of Toxoplasma gondii catalase. Identification of peroxisomes in an apicomplexan parasite. J. Biol. Chem. 2000, 275, 1112–1118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ludewig-Klingner, A.K.; Michael, V.; Jarek, M.; Brinkmann, H.; Petersen, J. Distribution and evolution of peroxisomes in Alveolates (apicomplexa, dinoflagellates, ciliates). Genome Biol. Evol. 2018, 10, 1–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Moog, D.; Przyborski, J.M.; Maier, U.G. Genomic and proteomic evidence for the presence of a peroxisome in the apicomplexan parasite Toxoplasma gondii and other Coccidia. Genome Biol. Evol. 2017, 9, 3108–3121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- DeLoache, W.C.; Russ, Z.N.; Dueber, J.E. Towards repurposing the yeast peroxisome for compartmentalizing heterologous metabolic pathways. Nat. Commun. 2016, 7, 11152. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Emmanouilidis, L.; Schutz, U.; Tripsianes, K.; Madl, T.; Radke, J.; Rucktaschel, R.; Wilmanns, M.; Schliebs, W.; Erdmann, R.; Sattler, M. Allosteric modulation of peroxisomal membrane protein recognition by farnesylation of the peroxisomal import receptor PEX19. Nat. Commun. 2017, 8, 14635. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schafer, A.; Kerssen, D.; Veenhuis, M.; Kunau, W.H.; Schliebs, W. Functional similarity between the peroxisomal PTS2 receptor binding protein Pex18p and the N-terminal half of the PTS1 receptor Pex5p. Mol. Cell Biol. 2004, 24, 8895–8906. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dodt, G.; Braverman, N.; Wong, C.; Moser, A.; Moser, H.W.; Watkins, P.; Valle, D.; Gould, S.J. Mutations in the PTS1 receptor gene, PXR1, define complementation group 2 of the peroxisome biogenesis disorders. Nat. Genet. 1995, 9, 115–125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Alqaisi, A.Q.I.; Mbekeani, A.J.; Llorens, M.B.; Elhammer, A.P.; Denny, P.W. The antifungal Aureobasidin A and an analogue are active against the protozoan parasite Toxoplasma gondii but do not inhibit sphingolipid biosynthesis. Parasitology 2018, 145, 148–155. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Denny, P.W.; Shams-Eldin, H.; Price, H.P.; Smith, D.F.; Schwarz, R.T. The protozoan inositol phosphorylceramide synthase: A novel drug target that defines a new class of sphingolipid synthase. J. Biol. Chem. 2006, 281, 28200–28209. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mina, J.G.; Okada, Y.; Wansadhipathi-Kannangara, N.K.; Pratt, S.; Shams-Eldin, H.; Schwarz, R.T.; Steel, P.G.; Fawcett, T.; Denny, P.W. Functional analyses of differentially expressed isoforms of the Arabidopsis inositol phosphorylceramide synthase. Plant Mol. Biol. 2010, 73, 399–407. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mina, J.G.; Pan, S.Y.; Wansadhipathi, N.K.; Bruce, C.R.; Shams-Eldin, H.; Schwarz, R.T.; Steel, P.G.; Denny, P.W. The Trypanosoma brucei sphingolipid synthase, an essential enzyme and drug target. Mol. Biochem. Parasit. 2009, 168, 16–23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mina, J.G.; Thye, J.K.; Alqaisi, A.Q.I.; Bird, L.E.; Dods, R.H.; Groftehauge, M.K.; Mosely, J.A.; Pratt, S.; Shams-Eldin, H.; Schwarz, R.T.; et al. Functional and phylogenetic evidence of a bacterial origin for the first enzyme in sphingolipid biosynthesis in a phylum of eukaryotic protozoan parasites. J. Biol. Chem. 2017, 292, 12208–12219. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Norcliffe, J.L.; Mina, J.G.; Alvarez, E.; Cantizani, J.; de Dios-Anton, F.; Colmenarejo, G.; Valle, S.G.; Marco, M.; Fiandor, J.M.; Martin, J.J.; et al. Identifying inhibitors of the Leishmania inositol phosphorylceramide synthase with antiprotozoal activity using a yeast-based assay and ultra-high throughput screening platform. Sci. Rep. 2018, 8, 3938. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schwartzkopff, B.; Platta, H.W.; Hasan, S.; Girzalsky, W.; Erdmann, R. Cysteine-specific ubiquitination protects the peroxisomal import receptor Pex5p against proteasomal degradation. Biosci. Rep. 2015, 35, e00215. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Huber, A.; Koch, J.; Kragler, F.; Brocard, C.; Hartig, A. A subtle interplay between three Pex11 proteins shapes de novo formation and fission of peroxisomes. Traffic 2012, 13, 157–167. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Unger, T.; Jacobovitch, Y.; Dantes, A.; Bernheim, R.; Peleg, Y. Applications of the restriction free (RF) cloning procedure for molecular manipulations and protein expression. J. Struct. Biol. 2010, 172, 34–44. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wichroski, M.J.; Melton, J.A.; Donahue, C.G.; Tweten, R.K.; Ward, G.E. Clostridium septicum alpha-toxin is active against the parasitic protozoan Toxoplasma gondii and targets members of the SAG family of glycosylphosphatidylinositol-anchored surface proteins. Infect. Immun. 2002, 70, 4353–4361. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schindelin, J.; Arganda-Carreras, I.; Frise, E.; Kaynig, V.; Longair, M.; Pietzsch, S.; Rueden, C.; Saalfeld, S.; Tinevez, J.Y.; White, D.J.; et al. Fiji: An open-source platform for biological-image analysis. Nat. Methods 2012, 9, 676–682. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Klein, A.T.; van den Berg, M.; Bottger, G.; Tabak, H.F.; Distel, B. Saccharomyces cerevisiae acyl-CoA oxidase follows a novel, non-PTS1, import pathway into peroxisomes that is dependent on Pex5p. J. Biol. Chem. 2002, 277, 25011–25019. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gurvitz, A.; Wabnegger, L.; Langer, S.; Hamilton, B.; Ruis, H.; Hartig, A. The tetratricopeptide repeat domains of human, tobacco, and nematode PEX5 proteins are functionally interchangeable with the analogous native domain for peroxisomal import of PTS1-terminated proteins in yeast. Mol. Genet. Genom. 2001, 265, 276–286. [Google Scholar]
- Sampathkumar, P.; Roach, C.; Michels, P.A.; Hol, W.G. Structural insights into the recognition of peroxisomal targeting signal 1 by Trypanosoma brucei peroxin 5. J. Mol. Biol. 2008, 381, 867–880. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
© 2018 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).