Synthesis of Zn-Saponite Using a Microwave Circulating Reflux Method under Atmospheric Pressure
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Experimental Methods
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Crystalinity and Phase Purity
3.2. Cation Exchange Capacity
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Bergaya, F.; Lagaly, G. General introduction: Clays, clay minerals, and clay science. In Developments in Clay Science; Faïza, B., Benny, K.G.T., Gerhard, L., Eds.; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2006; pp. 1–18. [Google Scholar]
- Vaccari, A. Clays and catalysis: A promising future. Appl. Clay Sci. 1999, 14, 161–198. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thomas, J.M.; Theocharis, C.R. Perspectives in Catalysis; Blackwell Scientific: London, UK, 1992; 431p. [Google Scholar]
- Lambert, J.-F.; Chevelier, S.; Frank, R.; Barthomeuf, D. Al-Pillared saponites. Part 2.-NMR studies. J. Chem. Soc. Faraday Trans. 1994, 90, 675–682. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Golubeva, O.Y.; Gusarov, V.V. Layered silicates with a montmorillonite structure: Preparation and prospects for the use in polymer nanocomposites. Glass Phys. Chem. 2007, 33, 237–241. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Whitney, G. Hydrothermal reactivity of saponite. Clays Clay Miner. 1983, 31, 1–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bisio, C.; Gatti, G.; Boccaleri, E.; Marchese, L.; Superti, G.B.; Pastore, H.O.; Thommes, M. Understanding physico-chemical properties of saponite synthetic clays. Microporous Mesoporous Mater. 2008, 107, 90–101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Costenaro, D.; Gatti, G.; Carniato, F.; Paul, G.; Bisio, C.; Marchese, L. The effect of synthesis gel dilution on the physico-chemical properties of acid saponite clays. Microporous Mesoporous Mater. 2012, 162, 159–167. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vicente, I.; Salagre, P.; Cesteros, Y. Preparation of pure hectorite using microwaves. Phys. Procedia. 2010, 8, 88–93. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Trujillano, R.; Rico, E.; Vicente, M.A.; Rives, V.; Sobrados, I.; Sanz, J. Saponites containing divalent transition metal cations in octahedral positions—Exploration of synthesis possibilities using microwave radiation and NMR characterization. Appl. Clay Sci. 2015, 115, 24–29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baron, F.; SC Pushparaj, S.; Fontaine, C.; V Sivaiah, M.; Decarreau, A.; Petit, S. Microwave-assisted hydrothermal synthesis of Ni–Mg layered silicate clays. Curr. Miccowave Chem. 2016, 3, 85–89. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Trujillano, R.; Rico, E.; Vicente, M.A.; Rives, V.; Bergaoui, L.; Ben Chaabene, S.; Ghorbel, A. Microwave-Assisted Synthesis of Fe3+ Saponites. Characterization by X-Ray Diffraction and FT-IR Spectroscopy. Rev. Soc. Esp. Miner. 2009, 11, 189–190. [Google Scholar]
- Trujillano, R.; Rico, E.; Vicente, M.A.; Herrero, M.; Rives, V. Microwave radiation and mechanical grinding as new ways for preparation of saponite-like materials. Appl. Clay Sci. 2010, 48, 32–38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Trujillano, R.; Rico, E.; Vicente, M.A.; Rives, V.; Ciuffi, K.J.; Cestari, A.; Gil, A.; Korili, S.A. Rapid microwave-assisted synthesis of saponites and their use as oxidation catalysts. Appl. Clay Sci. 2011, 53, 326–330. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vicente, I.; Salagre, P.; Cesteros, Y.; Guirado, F.; Medina, F.; Sueiras, J.E. Fast microwave synthesis of hectorite. Appl. Clay Sci. 2009, 43, 103–107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vicente, I.; Salagre, P.; Cesteros, Y.; Medina, F.; Sueiras, J.E. Microwave-assisted synthesis of saponite. Appl. Clay Sci. 2010, 48, 26–31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vogels, R.J.M.J.; Kerkhoffs, M.J.H.V.; Geus, J.W. Non-hydrothermal synthesis, characterisation and catalytic properties of saponite clays. Stud. Surf. Sci. Catal. 1995, 91, 1153–1161. [Google Scholar]
- Kloprogge, J.T.; Komarneni, S.; Amonette, J.E. Synthesis of smectite clay minerals: A critical review. Clays Clay Miner. 1999, 47, 529–544. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Prikhod’ko, R.V.; Sychev, M.V.; Astrelin, I.M.; Erdmann, K.; Hensen, E.J.M.; Van Santen, R.A. Nonhydrothermal synthesis and properties of saponite-like materials. Russ. J. Appl. Chem. 2003, 76, 700–705. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vogels, R.J.M.J.; Kloprogge, J.T.; Geus, J.W. Synthesis and characterization of saponite clays. Am. Miner. 2005, 90, 931–944. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, C.; He, H.; Tao, Q.; Ji, S.; Li, S.; Ma, L.; Zhu, J. Metal occupancy and its influence on thermal stability of synthetic saponites. Appl. Clay Sci. 2017, 135, 282–288. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Petit, S.; Righi, D.; Decarreau, A. Transformation of synthetic Zn-stevensite to Zn-talc induced by the Hofmann-Klemen effect. Clays Clay Miner. 2008, 56, 645–654. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, B.S.; Liu, Y.Y. Improvement in phase purity and yield of hydrothermally synthesized smectite using Taguchi method. Appl. Clay Sci. 2018, 161, 103–109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bergmann, J.; Friedel, P.; Kleeberg, R. BGMN—A new fundamental parameter based Rietveld program for laboratory X-ray sources, its use in quantitative analysis and structure investigations. CPD Newsl. 1998, 20, 5–8. [Google Scholar]
- Bergaya, F.; Vayer, M. CEC of clays: Measurement by adsorption of a copper ethylenediamine complex. Appl. Clay Sci. 1997, 12, 275–280. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grauby, O.; Petit, S.; Decarreau, A.; Baronnet, A. The beidellite–saponite series: An experimental approach. Eur. J. Miner. 1993, 5, 623–635. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pascua, C.S.; Ohnuma, M.; Matsushita, Y.; Tamura, K.; Yamada, H.; Cuadros, J.; Ye, J. Synthesis of monodisperse Zn-smectite. Appl. Clay Sci. 2010, 48, 55–59. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Girnus, I.; Jancke, K.; Vetter, R.; Richter-Mendau, J.; Caro, J. Large AlPO4-5 crystals by microwave heating. Zeolites 1995, 15, 33–39. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, J.Y.; Zhang, J.X.; Zhou, H.F.; Qin, W.Q.; Chai, L.Y.; Hu, Y.H. Microwave-assisted synthesis and characterization of ZnO-nanorod arrays. Trans. Nonferrous Met. Soc. China 2009, 19, 1578–1582. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Zhong, S.; Zhang, M.; Lin, Y. Antibacterial activity of silver-loaded zeolite A prepared by a fast microwave-loading method. J. Mater. Sci. 2009, 44, 457–462. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fan, D.; Wang, L.; Chen, W.; Ma, S.; Ma, W.; Liu, X.; Zhao, J.; Zhang, H. Effect of microwave on lamellar parameters of rice starch through small-angle X-ray scattering. Food Hydrocoll. 2014, 35, 620–626. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Murray, H.H.; Lyons, S.C. Further correlations of kaolinite crystallinity with chemical and physical properties. Clays Clay Miner. 1960, 8, 11–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ormsby, W.C.; Shartsis, J.M.; Woodside, K.H. Exchange behavior of kaolins of varying degrees of crystallinity. J. Am. Ceram. Soc. 1962, 45, 361–366. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peigneur, P.; Maes, A.; Cremers, A. Heterogeneity of charge density distribution in montmorillonite as inferred from cobalt adsorption. Clays Clay Miner. 1975, 23, 71–75. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Siantar, D.P.; Millman, W.S. Structural defects and cation exchange capacity in dealuminated Y zeolites. Zeolites 1995, 15, 556–560. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

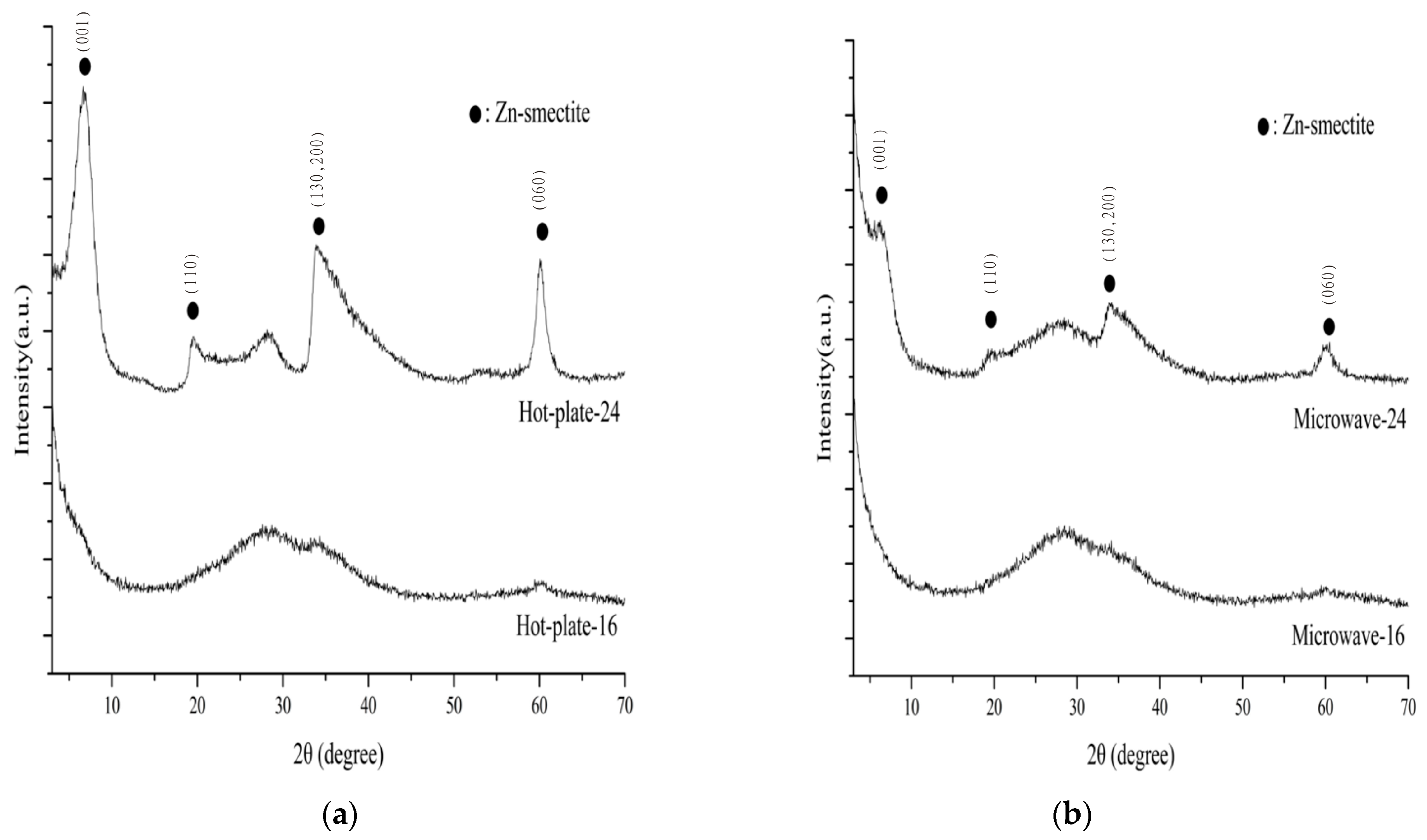
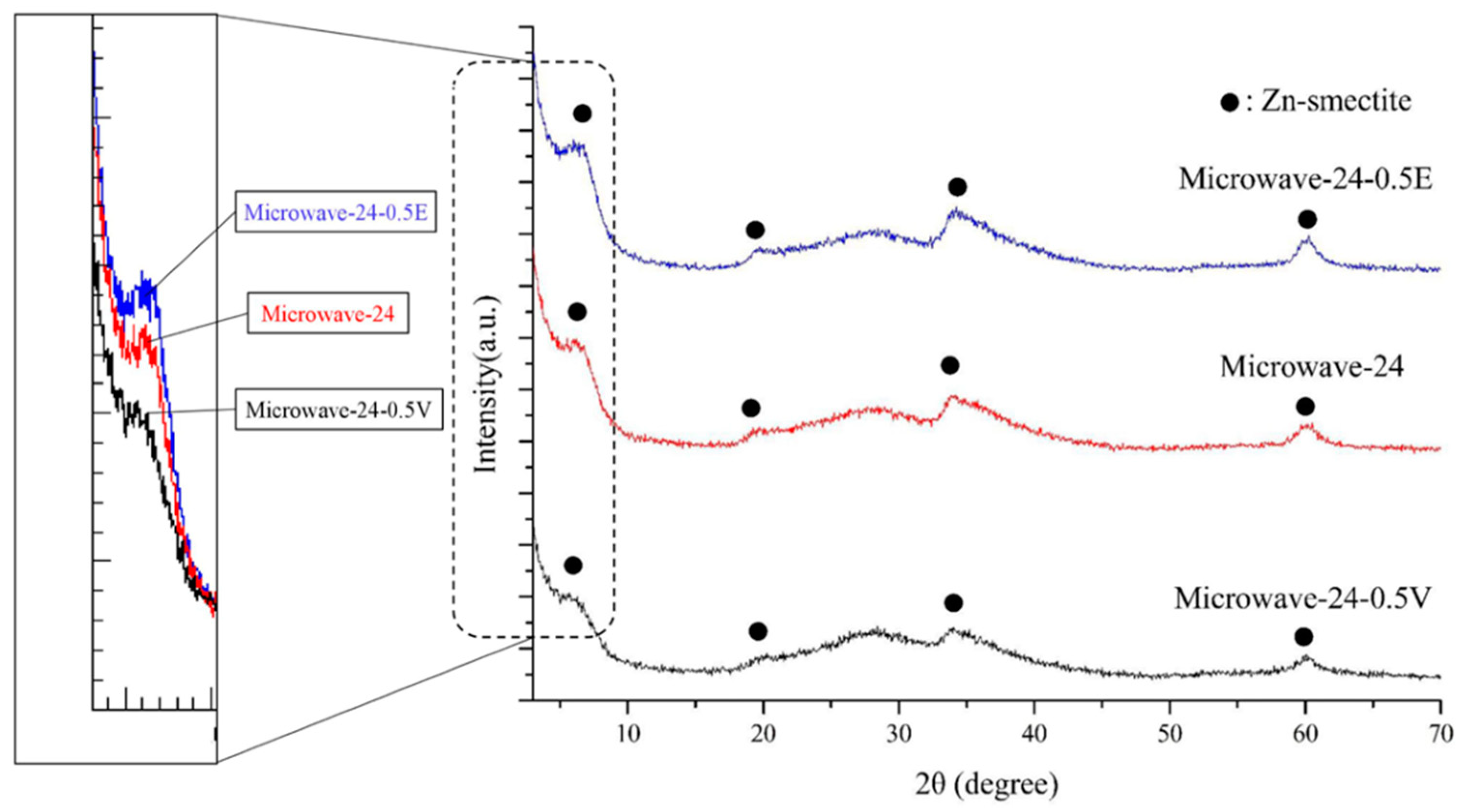
| Sample Number | Phase Purity (%) | Basal Spacing (nm) | d060 (nm) |
|---|---|---|---|
| Hot-plate-24 | 97.3 | 1.298 ± 0.003 | 0.1539 ± 0.0004 |
| Microwave-24 | 45.0 | 1.325 ± 0.003 | 0.1539 ± 0.0004 |
| Microwave-24-0.5E | 50.2 | 1.303 ± 0.003 | 0.1538 ± 0.0004 |
| Microwave-24-0.5V | 43.9 | 1.383 ± 0.003 | 0.1539 ± 0.0004 |
| Sample Number | Reaction Time (h) | CEC (cmol(+)/kg) |
|---|---|---|
| Hot-plate-16 | 16 | 84 |
| Hot-plate-24 | 24 | 91 |
| Microwave-16 | 16 | 96 |
| Microwave-24 | 24 | 105 |
| Microwave-24-0.5E | 24 | 112 |
| Microwave-24-0.5V | 24 | 120 |
© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Yu, B.-S.; Hung, W.-H.; Fang, J.-N.; Yu, Y.-T. Synthesis of Zn-Saponite Using a Microwave Circulating Reflux Method under Atmospheric Pressure. Minerals 2020, 10, 45. https://doi.org/10.3390/min10010045
Yu B-S, Hung W-H, Fang J-N, Yu Y-T. Synthesis of Zn-Saponite Using a Microwave Circulating Reflux Method under Atmospheric Pressure. Minerals. 2020; 10(1):45. https://doi.org/10.3390/min10010045
Chicago/Turabian StyleYu, Bing-Sheng, Wei-Hsiang Hung, Jiann-Neng Fang, and Yu-Ting Yu. 2020. "Synthesis of Zn-Saponite Using a Microwave Circulating Reflux Method under Atmospheric Pressure" Minerals 10, no. 1: 45. https://doi.org/10.3390/min10010045
APA StyleYu, B.-S., Hung, W.-H., Fang, J.-N., & Yu, Y.-T. (2020). Synthesis of Zn-Saponite Using a Microwave Circulating Reflux Method under Atmospheric Pressure. Minerals, 10(1), 45. https://doi.org/10.3390/min10010045




