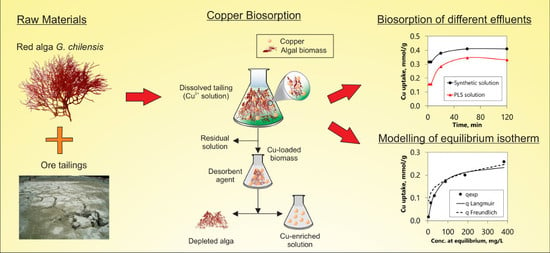
Recovery of Copper from Leached Tailing Solutions by Biosorption
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Tailings and Biomass
2.2. Mineral Leaching
2.3. Batch Biosorption Procedure
2.4. Desorption
3. Results and Discussions
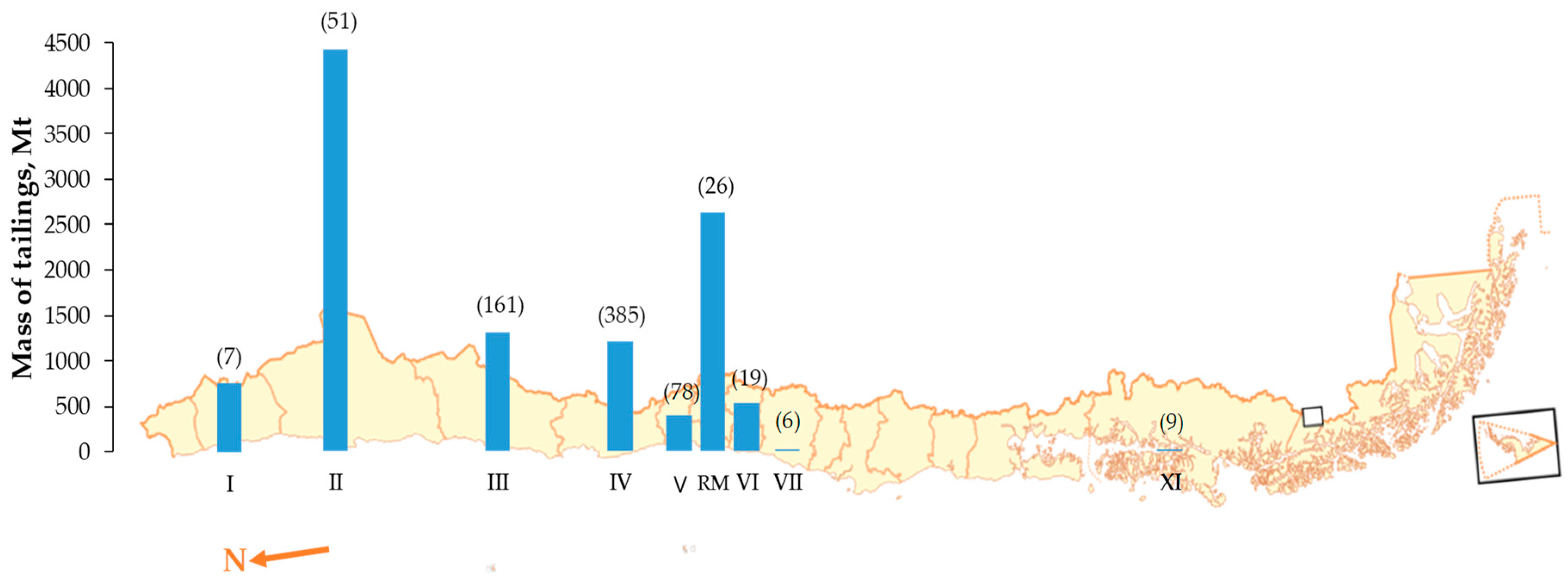
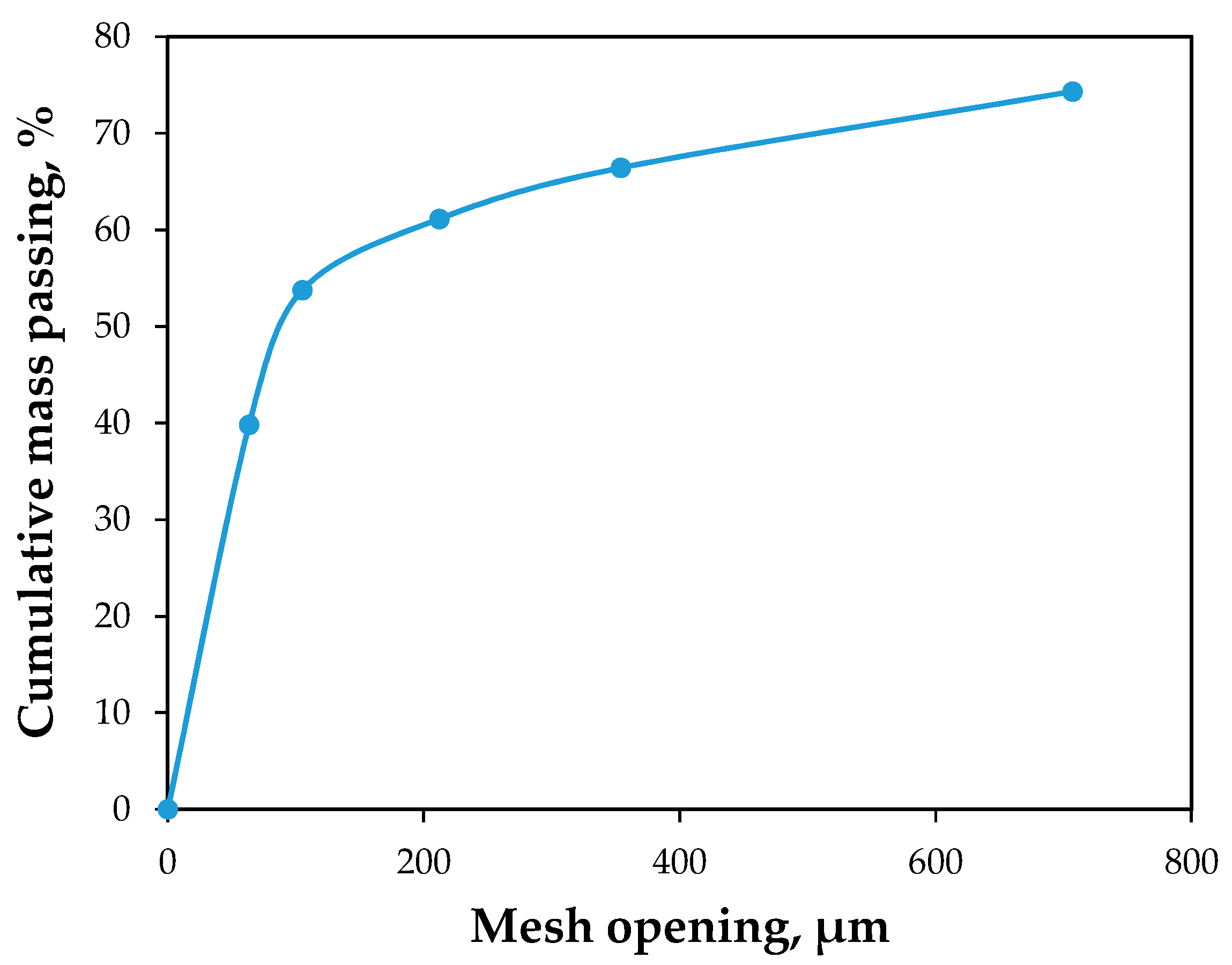
3.1. Characteristic of Tailing Sample
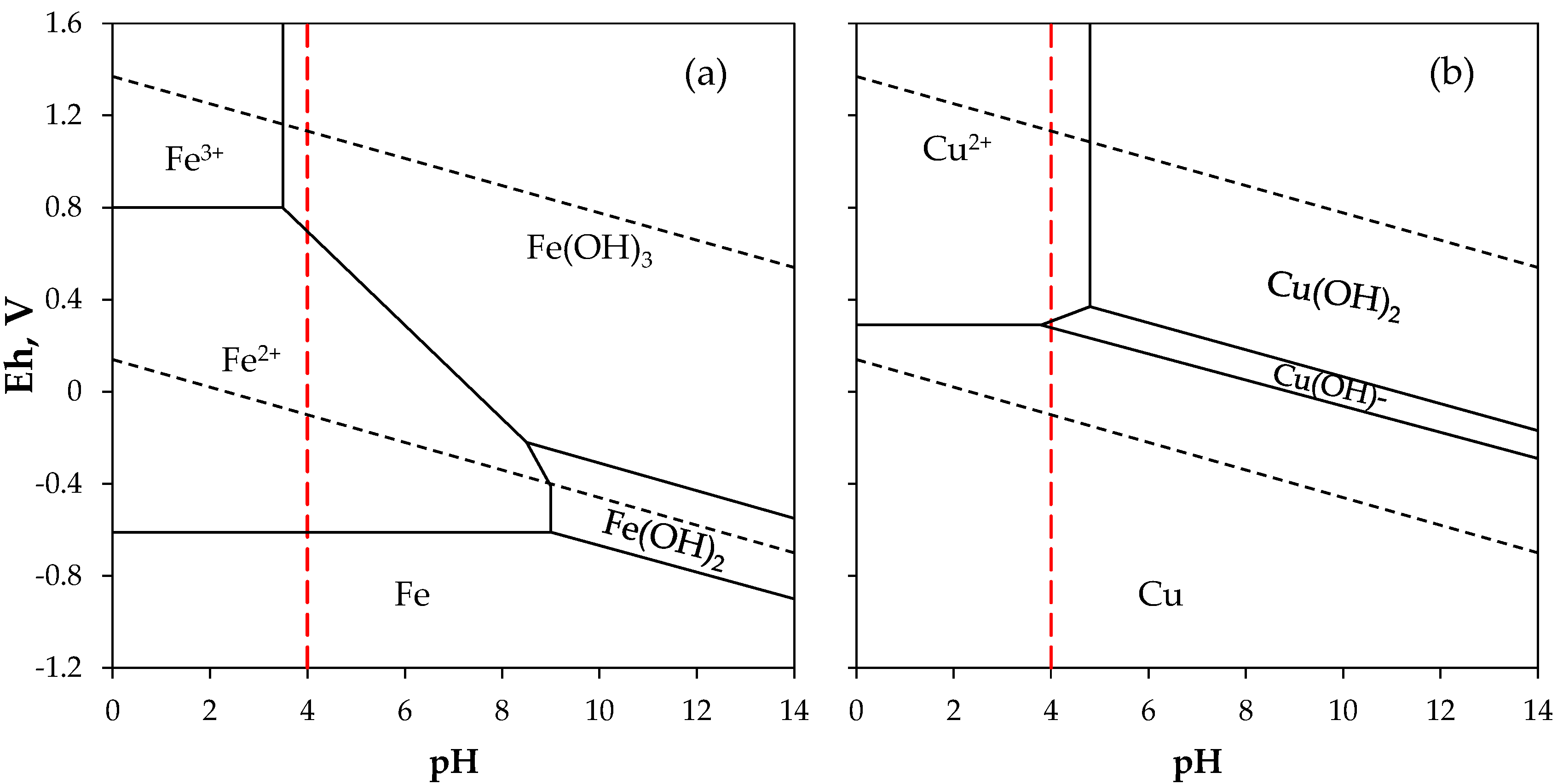
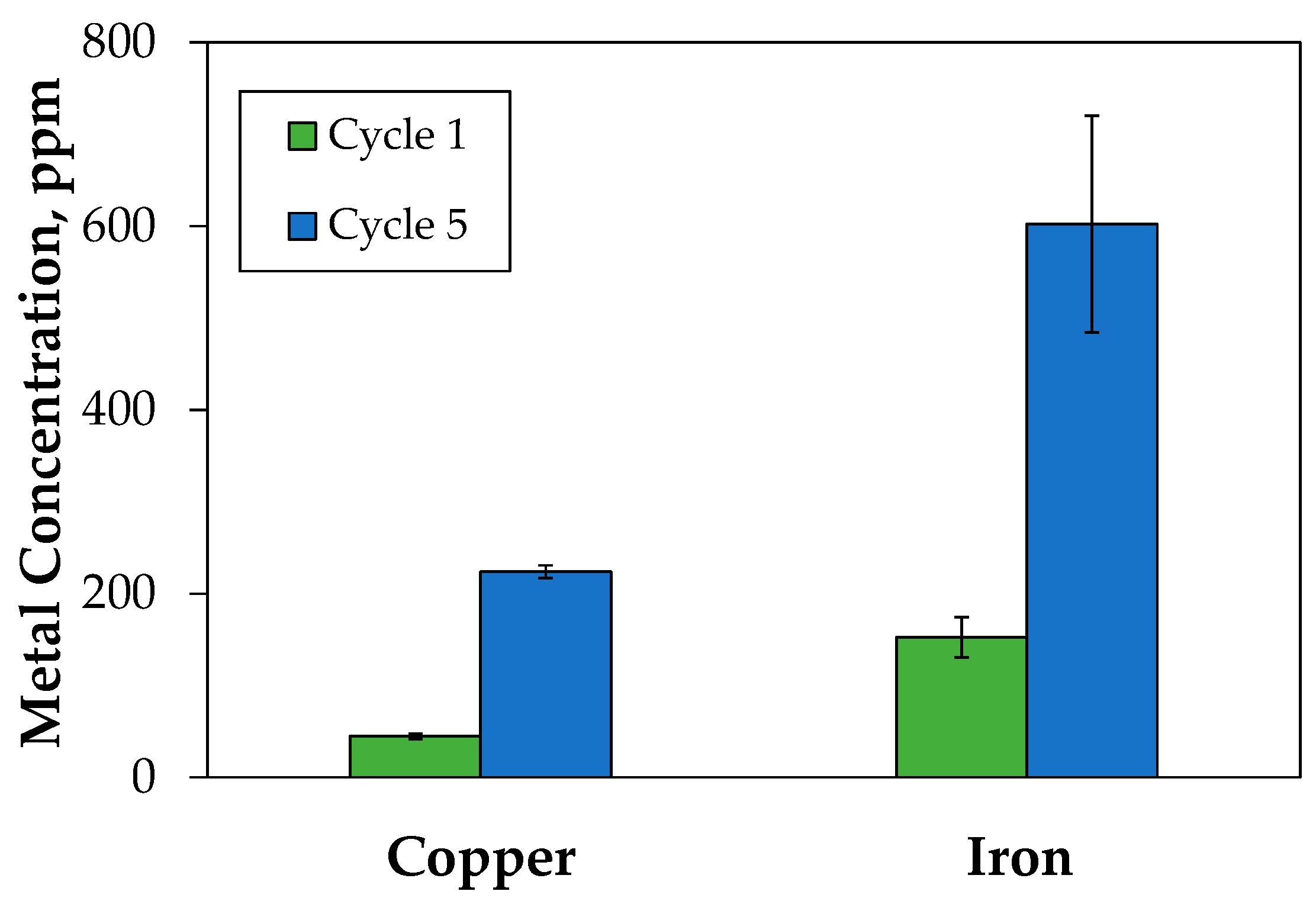
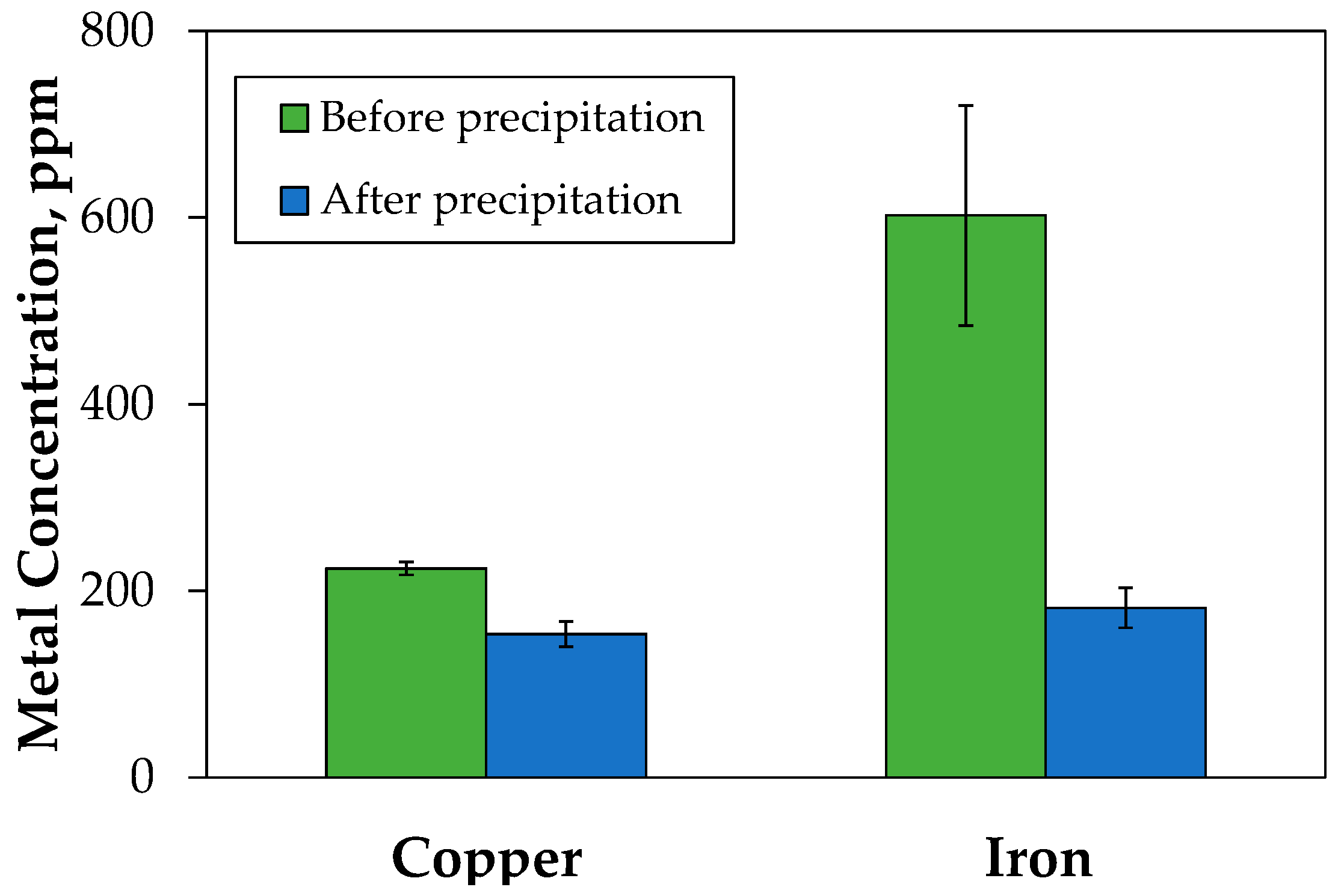
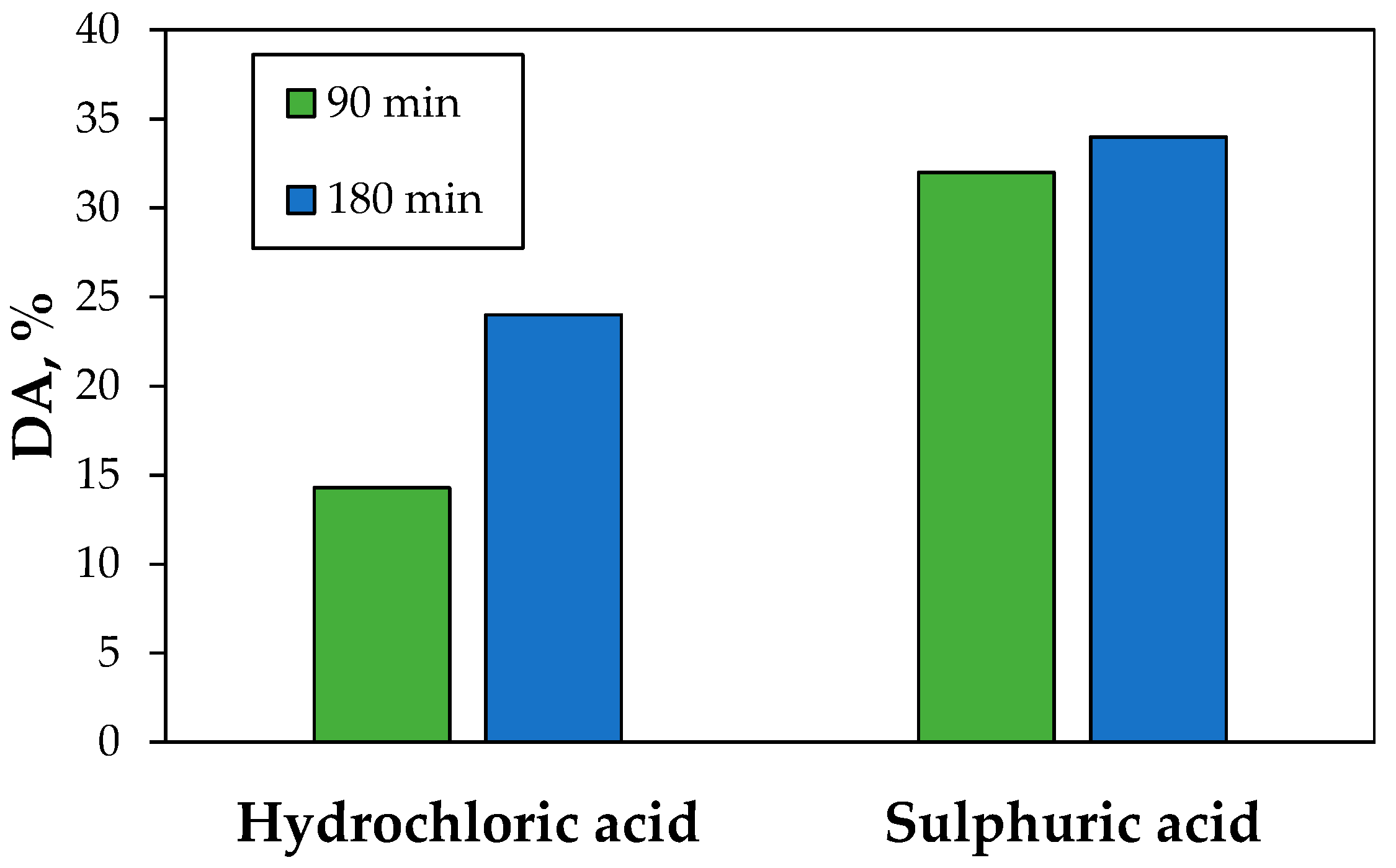
3.2. Leaching and Treatment of Tailings
3.3. Biosorption from Synthetic and Leached Tailing Solutions
3.3.1. FTIR
3.3.2. Biosorption Kinetics and Desorption
3.3.3. Equilibrium Isotherms
4. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- COCHILCO. Copper and Other Minerals Statistics; COCHILCO: Santiago, Chile, 2017. [Google Scholar]
- US Geological Survey (USGS). Mineral Commodities Summaries. Available online: https://pubs.er.usgs.gov/publication/70140094 (accessed on 10 February 2020).
- SERNAGEOMIN. Catastro de Depósitos de Relaves en Chile; SERNAGEOMIN: Santiago, Chile, 2018. [Google Scholar]
- CORFO. Identificar Elementos de Valor en Residuos Mineros (Relaves) Y Evaluar Su Recuperación Como Productos Comerciales 13BPC3-19021; CORFO: Santiago, Chile, 2013. [Google Scholar]
- Rojas, S. Estudio de la existencia de tierras raras en tranques de relaves y ripios de las plantas de ENAMI. Undergraduate Thesis, Universidad de Atacama, Copiapó, Chile, 2003. [Google Scholar]
- Gómez-Ordóñez, E.; Jiménez-Escrig, A.; Rupérez, P. Dietary fibre and physicochemical properties of several edible seaweeds from the northwestern Spanish coast. Food Res. Int. 2010, 43, 2289–2294. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bixler, H.J.; Porse, H. A decade of change in the seaweed hydrocolloids industry. J. Appl. Phycol. 2011, 23, 321–335. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vásquez, J.A.; Piaget, N.; Vega, J.M.A. The Lessonia nigrescens fishery in northern Chile: How you harvest is more important than how much you harvest. J. Appl. Phycol. 2012, 24, 417–426. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rebours, C.; Marinho-Soriano, E.; Zertuche-González, J.A.; Hayashi, L.; Vásquez, J.A.; Kradolfer, P.; Soriano, G.; Ugarte, R.; Abreu, M.H.; Bay-Larsen, I.; et al. Seaweeds: An opportunity for wealth and sustainable livelihood for coastal communities. J. Appl. Phycol. 2014, 26, 1939–1951. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Buschmann, A.H.; Prescott, S.; Potin, P.; Faugeron, S.; Vásquez, J.A.; Camus, C.; Infante, J.; Hernández-González, M.C.; Gutierrez, A.; Varela, D.A. The status of kelp exploitation and marine agronomy, with emphasis on Macrocystis pyrifera, in Chile. Adv. Bot. Res. 2004, 71, 161–188. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- FAO. World Aquaculture 2010; FAO: Rome, Italy, 2011. [Google Scholar]
- SERNAPESCA. Informe de Estadísticas Oficiales, Enero-Noviembre 2016; SERNAPESCA: Valparaíso, Chile, 2016. [Google Scholar]
- Cui, J.; Zhang, L. Metallurgical recovery of metals from electronic waste: A review. J. Hazard. Mater. 2008, 158, 228–256. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Michalak, I.; Chojnacka, K.; Witek-Krowiak, A. State of the art for the biosorption process—A review. Appl. Biochem. Biotechnol. 2013, 170, 1389–1416. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Vijayaraghavan, K.; Yun, Y.-S. Bacterial biosorbents and biosorption. Biotechnol. Adv. 2008, 26, 266–291. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baysal, Z.; Çinar, E.; Bulut, Y.; Alkan, H.; Dogru, M. Equilibrium and thermodynamic studies on biosorption of Pb(II) onto Candida albicans biomass. J. Hazard. Mater. 2009, 161, 62–67. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sathishkumar, M.; Mahadevan, A.; Vijayaraghavan, K.; Pavagadhi, S.; Balasubramanian, R. Green recovery of gold through biosorption, biocrystallization, and pyro-crystallization. Ind. Eng. Chem. Res. 2010, 49, 7129–7135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Selatnia, A.; Madani, A.; Bakhti, M.Z.; Kertous, L.; Mansouri, Y.; Yous, R. Biosorption of Ni2+ from aqueous solution by a NaOH-treated bacterial dead Streptomyces rimosus biomass. Miner. Eng. 2004, 17, 903–911. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Davis, T.A.; Volesky, B.; Mucci, A. A review of the biochemistry of heavy metal biosorption by brown algae. Water Res. 2003, 37, 4311–4330. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kuyucak, N. Feasibility of Biosorbents Application. In Biosorption of Heavy Metals; Volesky, B., Ed.; CRC Press: Boca Raton, FL, USA, 1990. [Google Scholar]
- Figueira, M.M.; Volesky, B.; Mathieu, H.J. Instrumental analysis study of iron species biosorption by Sargassum biomass. Environ. Sci. Technol. 1999, 33, 1840–1846. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fourest, E.; Canal, C.; Roux, J.-C. Improvement of heavy metal biosorption by mycelial dead biomasses (Rhizopus arrhizus, Mucor miehei and Penicillium chrysogenum): PH control and cationic activation. FEMS Microbiol. Rev. 1994, 14, 325–332. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Khoo, K.-M.; Ting, Y.-P. Biosorption of gold by immobilized fungal biomass. Biochem. Eng. J. 2001, 8, 51–59. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Raize, O.; Argaman, Y.; Yannai, S. Mechanisms of biosorption of different heavy metals by brown marine macroalgae. Biotechnol. Bioeng. 2004, 87, 451–458. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Mata, Y.N.; Torres, E.; Blázquez, M.L.; Ballester, A.; González, F.; Muñoz, J.A. Gold(III) biosorption and bioreduction with the brown alga Fucus vesiculosus. J. Hazard. Mater. 2009, 166, 612–618. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Romera, E.; González, F.; Ballester, A.; Blázquez, M.L.; Muñoz, J.A. Comparative study of biosorption of heavy metals using different types of algae. Bioresour. Technol. 2007, 98, 3344–3353. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Plaza Cazón, J.; Benítez, L.; Donati, E.; Viera, M. Biosorption of chromium(III) by two brown algae Macrocystis pyrifera and Undaria pinnatifida: Equilibrium and kinetic study. Eng. Life Sci. 2012, 12, 95–103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luna, A.S.; Costa, A.L.H.; da Costa, A.C.A.; Henriques, C.A. Competitive biosorption of cadmium(II) and zinc(II) ions from binary systems by Sargassum filipendula. Bioresour. Technol. 2010, 101, 5104–5111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mata, Y.N.; Blázquez, M.L.; Ballester, A.; González, F.; Muñoz, J.A. Characterization of the biosorption of cadmium, lead and copper with the brown alga Fucus vesiculosus. J. Hazard. Mater. 2008, 158, 316–323. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Plaza Cazón, J.; Bernardelli, C.; Viera, M.; Donati, E.; Guibal, E. Zinc and cadmium biosorption by untreated and calcium-treated Macrocystis pyrifera in a batch system. Bioresour. Technol. 2012, 116, 195–203. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Plaza Cazón, J.; Viera, M.; Donati, E.; Guibal, E. Biosorption of mercury by Macrocystis pyrifera and Undaria pinnatifida: Influence of zinc, cadmium and nickel. J. Environ. Sci. 2011, 23, 1778–1786. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Crist, R.H.; Martin, J.R.; Crist, D.R. Interaction of Metal Ions with Acid Sites of Biosorbents Peat Moss and Vaucheria and Model Substances Alginic and Humic Acids. Environ. Sci. Technol. 1999, 33, 2252–2256. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Volesky, B. Biosorption of Heavy Metals; Nova Science Publishers: Boca Raton, FL, USA, 1990. [Google Scholar]
- Esposito, A.; Pagnanelli, F.; Vegliò, F. PH-related equilibria models for biosorption in single metal systems. Chem. Eng. Sci. 2002, 57, 307–313. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gavrilescu, M. Removal of Heavy Metals from the Environment by Biosorption. Eng. Life Sci. 2004, 4, 219–232. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, J.; Volesky, B. Modeling Uranium-Proton Ion Exchange in Biosorption. Environ. Sci. Technol. 1999, 33, 4079–4085. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Goyal, N.; Jain, S.; Banerjee, U. Comparative studies on the microbial adsorption of heavy metals. Adv. Environ. Res. 2003, 7, 7–311. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gamez, G.; Dokken, K.; Herrera, I.; Parsons, J.G.; Tiemann, K.J.; Gardea-Torresdey, J.L. Chemical processes involved in Au (III) binding and bioreduction by alfalfa biomass. In Proceedings of the 2000 Conference on Hazardous Waste Research, Denver, CO, USA, 23–25 May 2000. [Google Scholar]
- Gericke, M.; Pinches, A. Biological synthesis of metal nanoparticles. Hydrometallurgy 2006, 83, 132–140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Torres, E.; Mata, Y.N.; Blázquez, M.L.; Muñoz, J.A.; González, F.; Ballester, A. Gold and Silver Uptake and Nanoprecipitation on Calcium Alginate Beads. Langmuir 2005, 21, 7951–7958. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Castro, L.; Blázquez, M.L.; Muñoz, J.A.; González, F.; Ballester, A. Biological synthesis of metallic nanoparticles using algae. IET Nanobiotechnol. 2013, 7, 109–116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mack, C.; Wilhelmi, B.; Duncan, J.R.; Burgess, J.E. Biosorption of precious metals. Biotechnol. Adv. 2007, 25, 264–271. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mandal, S.; Phadtare, S.; Sastry, M. Interfacing biology with nanoparticles. Curr. Appl. Phys. 2005, 5, 118–127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wong-Pinto, L.; Menzies, A.; Ordóñez, J.I. Bionanomining: Biotechnological synthesis of metal nanoparticles from mining waste—opportunity for sustainable management of mining environmental liabilities. Appl. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 2020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- He, J.; Chen, J.P. A comprehensive review on biosorption of heavy metals by algal biomass: Materials, performances, chemistry, and modeling simulation tools. Bioresour. Technol. 2014, 160, 67–78. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Falagán, C.; Grail, B.M.; Johnson, D.B. New approaches for extracting and recovering metals from mine tailings. Miner. Eng. 2017, 106, 71–78. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lesmana, S.O.; Febriana, N.; Soetaredjo, F.E.; Sunarso, J.; Ismadji, S. Studies on potential applications of biomass for the separation of heavy metals from water and wastewater. Biochem. Eng. J. 2009, 44, 19–41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.; Chen, C. Biosorbents for heavy metals removal and their future. Biotechnol. Adv. 2009, 27, 195–226. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Reddy, K.R. Green synthesis, morphological and optical studies of CuO nanoparticles. J. Mol. Struct. 2017, 1150, 553–557. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Usman, M.; El Zowalaty, M.; Shameli, K.; Norhazlin, Z.; Salama, M.; Ibrahim, N.A. Synthesis, characterization, and antimicrobial properties of copper nanoparticles. Int. J. Nanomed. 2013, 8, 4467–4479. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Lavania-Baloo, I.N.; Salihi, I.U.; Zainoddin, J. The use of macroalgae (Gracilaria changii) as bio-adsorbent for Copper (II) removal. IOP Conf. Ser. Mater. Sci. Eng. 2017, 012031. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Teimouri, A.; Eslamian, S.; Shabankare, A. Removal of heavy metals from aqueous solution by red alga Gracilaria corticata as a new biosorbent. Trends Life Sci. 2016, 5, 236–243. [Google Scholar]
- Higuera, O.; Escalante, H.; Laverde, D. Reducción de cromo contenido en efluentes líquidos de la industria del cuero mediante un proceso de adsorción-desorción con algas marinas. Sci. Tech. 2005, 29, 115–120. [Google Scholar]
- Pagnanelli, F. Equilibrium, Kinetic and Dynamic Modelling of Biosorption Processes. In Microbial Biosorption of Metals; Kotrba, P., Mackova, M., Macek, T., Eds.; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2011. [Google Scholar]
- Romera, E.; Ballester, A. Biosorption with Algae: A Statistical Review. Crit. Rev. Biotechnol. 2006, 223–235. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gadd, G.M. Biosorption: Critical review of scientific rationale, environmental importance and significance for pollution treatment. J. Chem. Technol. Biotechnol. 2009, 84, 13–28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cuizano, N.; Navarro, A.E. Biosorción de metales pesados por algas marinas: Posible solución a la contaminación a bajas concentraciones. Química y Medio Ambient. 2008, 104, 120–125. [Google Scholar]
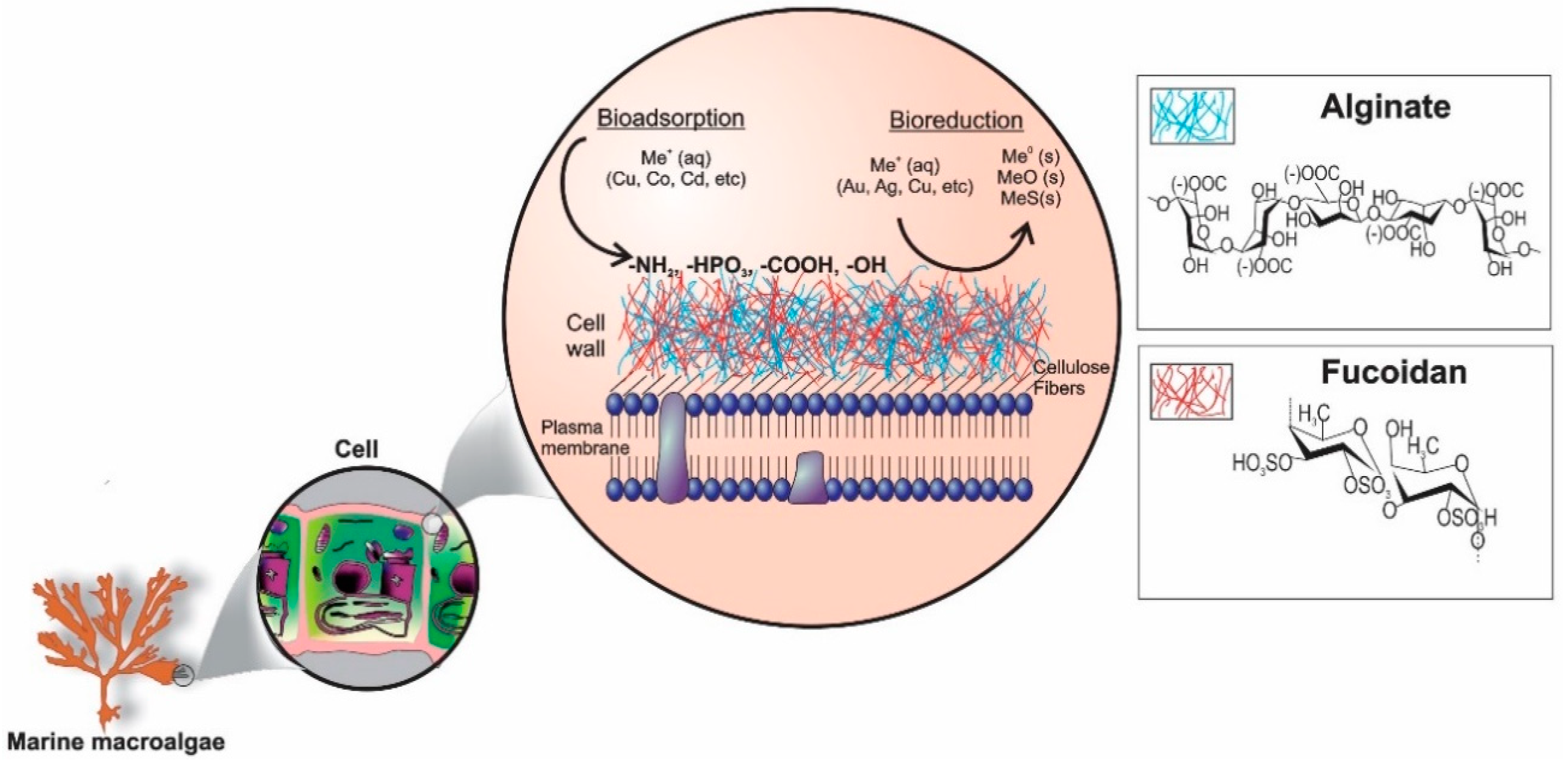
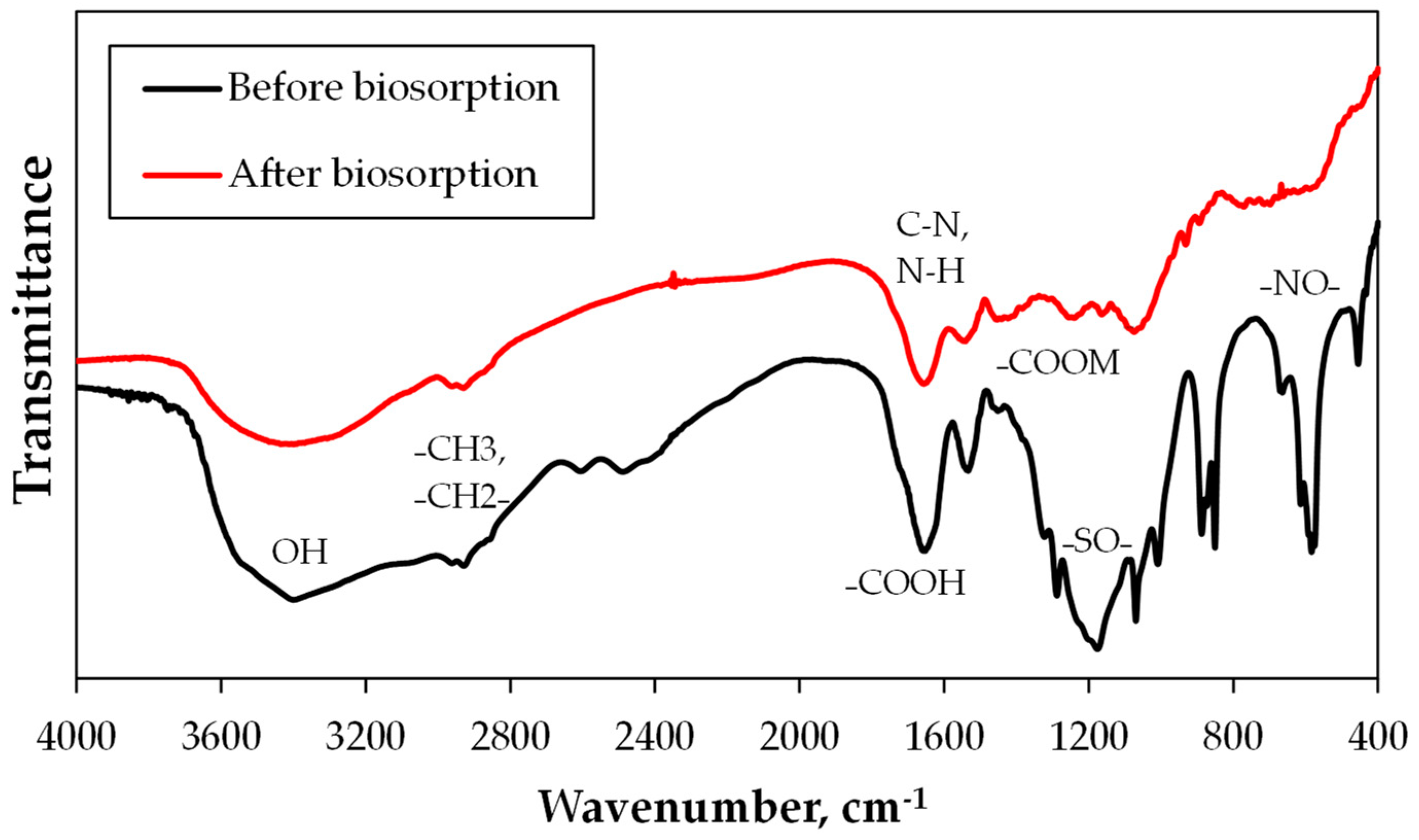



| Functional Groups | Formula | Wavenumber (cm−1) |
|---|---|---|
| Hydroxyl | –OH | 3200–3600 |
| Carboxyl | –COOH | 1670–1760 (C=O); 1000–1300 (C–O) |
| Carboxylate | –COOM | 1400–1650 |
| Amine | –NH2, –R2NH | 3200–3500 (–NH); 1500–1650 (C–N and N–H) |
| Sulphur | –SO– | 1000–1400; 1000–1300 (–SO3) |
| Phosphorous | –PO– | 1000–1400 |
| Carbonyl | –HC=O, R2C=O | 1680–1750 (C=O) |
| Alcoholic | –R3C–OH | 1000–1200 (C–O) |
| Nitro | –NO– | 400–700 |
| Methyl, methylene | –CH3, –CH2– | 2800–3000 |
| Major Metals (%) | Minor Metals (mg/kg) | ||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Al | Fe | K | Ca | Mg | Na | Ti | Cu | P | Mn | Ba | Zn | Ce | Sr |
| 8.3 | 7.2 | 4.1 | 2.9 | 2.3 | 1.5 | 0.4 | 1527 | 1384 | 1379 | 690 | 221 | 234 | 219 |
| Mineral (Crystalline Phase) | Formula | % |
|---|---|---|
| Orthoclase | KAlSi3O8 | 22.2 |
| Chlorite (1MIIb) | (Mg5Al)(Si,Al)4O10(OH)8 | 20.2 |
| Albite | NaAlSi3O8 | 17.7 |
| Quartz | SiO2 | 14.0 |
| Muscovite (1 M) | KAl2(Si3Al)O10(OH)2 | 5.7 |
| Phlogopite | KMg3(Si3AlO10)(OH)2 | 5.4 |
| Halite | NaCl | 4.5 |
| Calcite | CaCO3 | 2.5 |
| Chalcoalumite | CuAl4SO4(OH)12·3H2O | 2.0 |
| Magnetite | Fe3O4 | 2.0 |
| Gypsum | CaSO4·2H2O | 2.0 |
| Others | - | <2.0 |
| Parameter | Langmuir Model | Freundlich Model |
|---|---|---|
| (mmol/g) | 0.311 | 0.247 |
| (L/mmol) | 9.149 | - |
| (L/g) | - | 0.069 |
| - | 4.667 | |
| R2 | 0.972 | 0.771 |
| Alga | Type | ||
|---|---|---|---|
| Codium vermilara | Green | 8.920 | 0.266 |
| Spirogyra insignis | Green | 5.510 | 0.304 |
| Asparagopsis armata | Red | 8.370 | 0.335 |
| Chondrus crispus | Red | 2.470 | 0.637 |
| Gracilaria chilensis * | Red | 9.149 | 0.311 |
| Ascophyllum nodosum | Brown | 10.870 | 0.925 |
| Fucus spiralis | Brown | 10.390 | 1.116 |
© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Cortés, S.; Soto, E.E.; Ordóñez, J.I. Recovery of Copper from Leached Tailing Solutions by Biosorption. Minerals 2020, 10, 158. https://doi.org/10.3390/min10020158
Cortés S, Soto EE, Ordóñez JI. Recovery of Copper from Leached Tailing Solutions by Biosorption. Minerals. 2020; 10(2):158. https://doi.org/10.3390/min10020158
Chicago/Turabian StyleCortés, Sonia, Elizabeth E. Soto, and Javier I. Ordóñez. 2020. "Recovery of Copper from Leached Tailing Solutions by Biosorption" Minerals 10, no. 2: 158. https://doi.org/10.3390/min10020158
APA StyleCortés, S., Soto, E. E., & Ordóñez, J. I. (2020). Recovery of Copper from Leached Tailing Solutions by Biosorption. Minerals, 10(2), 158. https://doi.org/10.3390/min10020158