The Effect of Pulsed Laser Heating on the Stability of Ferropericlase at High Pressures
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Sample Preparation
2.2. Experiment 1
2.3. Experiment 2
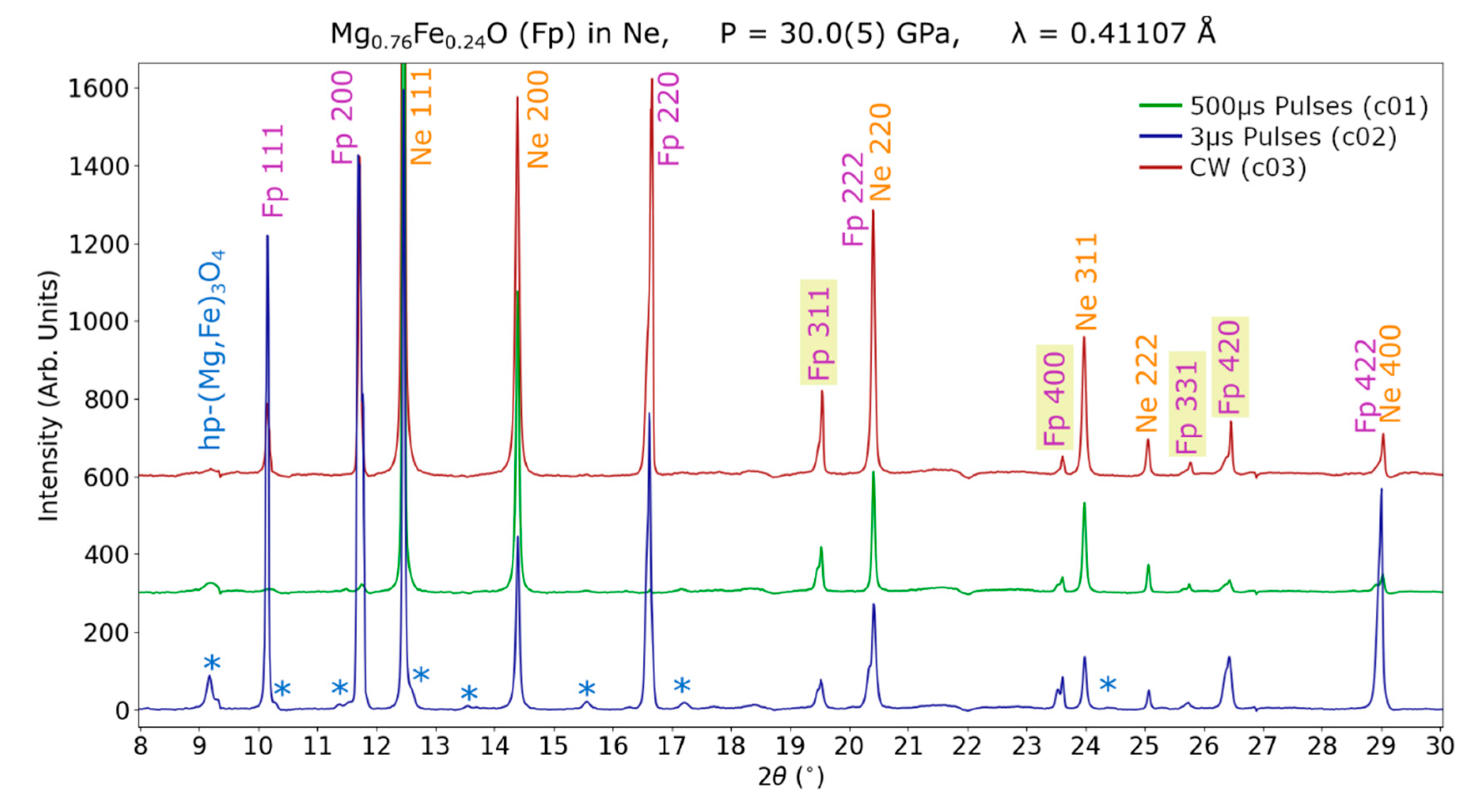
3. Results
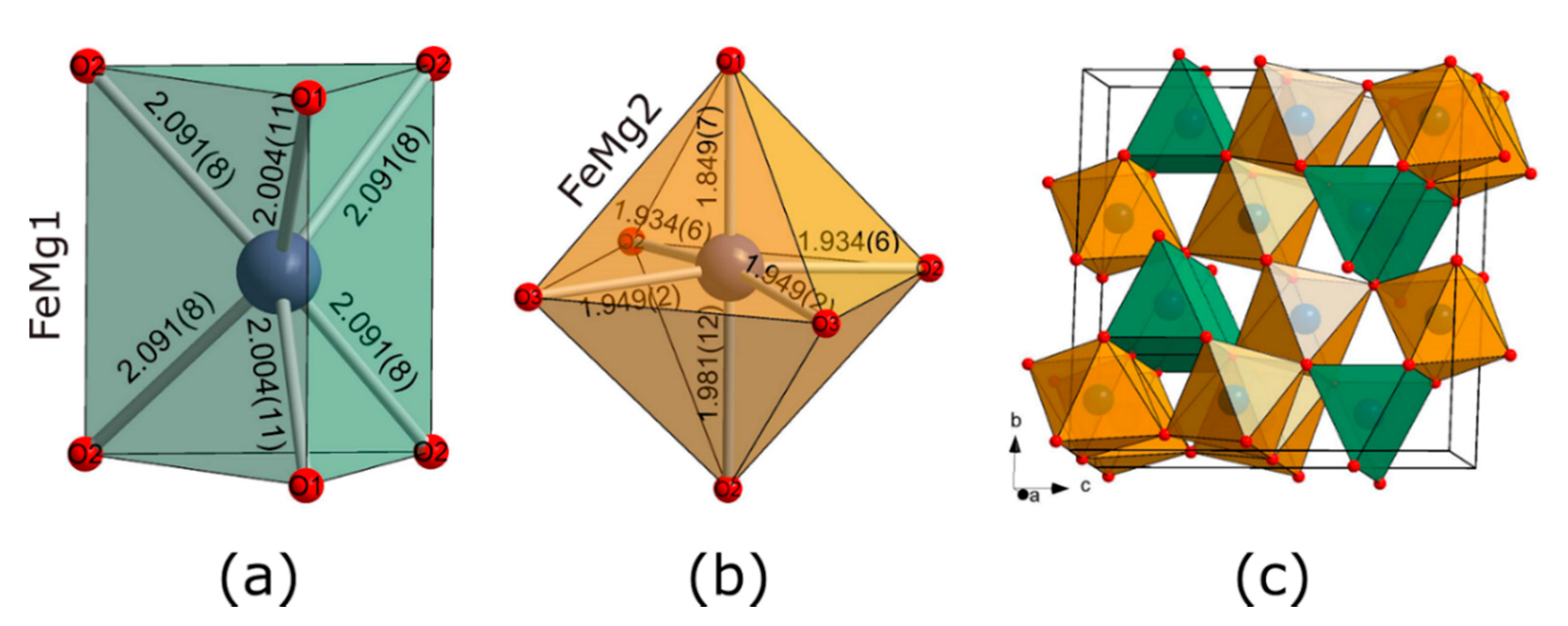
3.1. Formation of CaTi2O4-Structured hp-(Mg,Fe)3O4 Phase
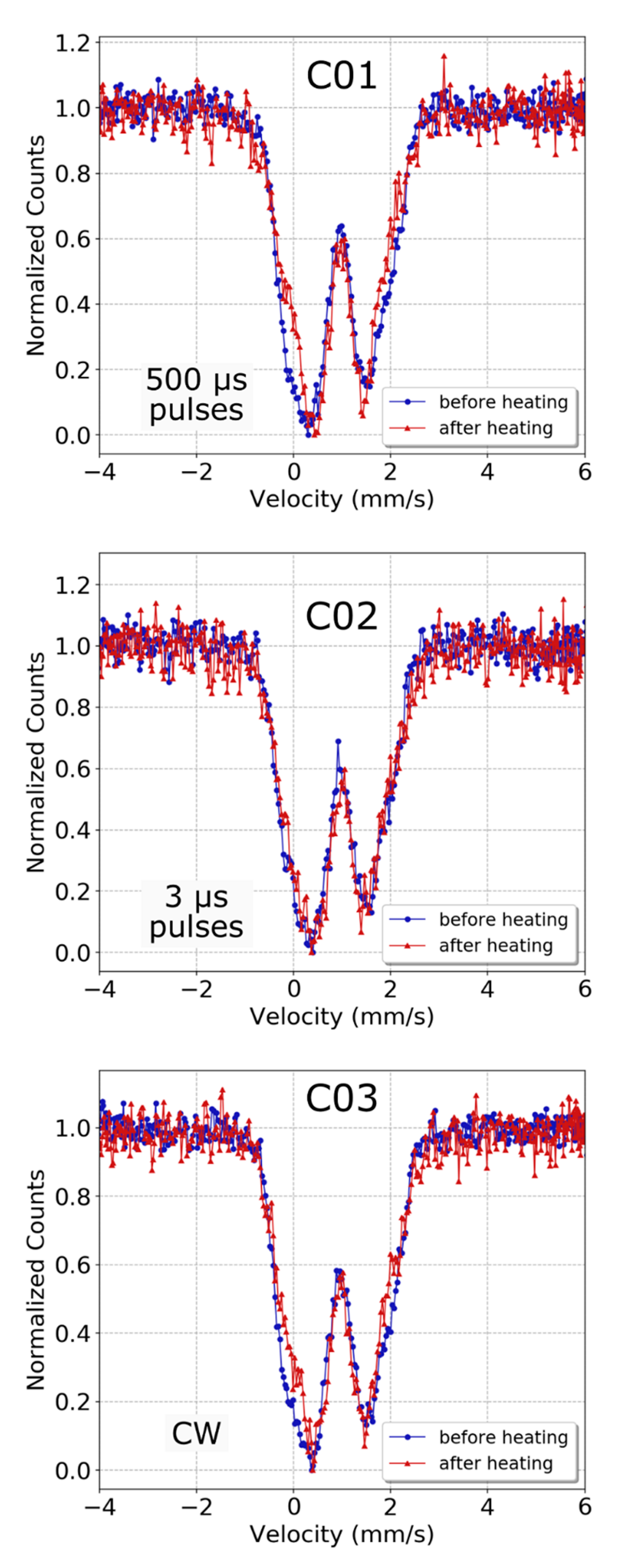
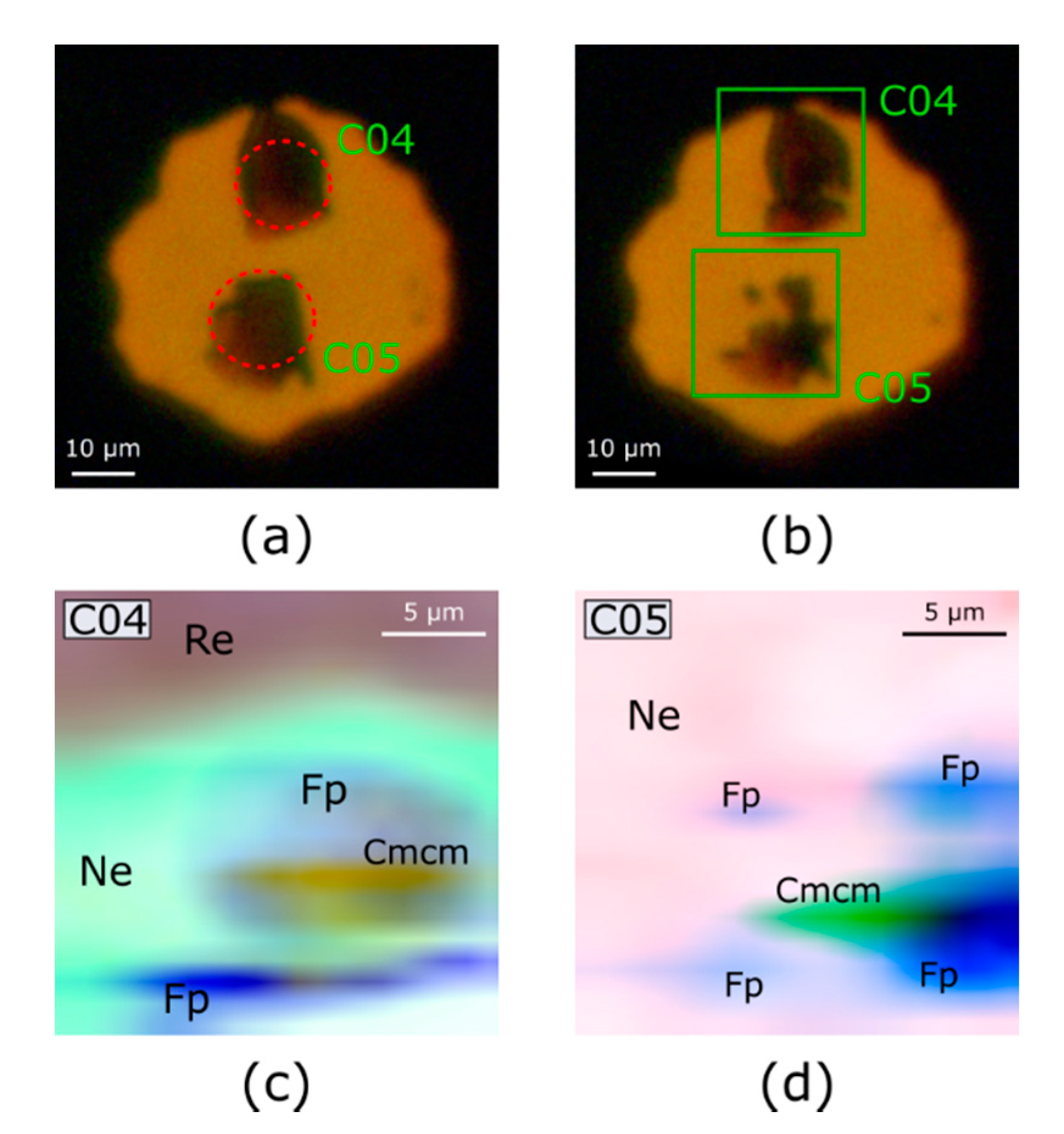
3.2. Dissociation of (Mg,Fe)O
4. Discussion
4.1. Formation of hp-(Mg,Fe)3O4 by Laser Heating of Ferropericlase
4.2. Dissociation of (Mg,Fe)O into Fe-Rich and Fe-Poor Components
4.3. Effect of Pulsed Laser Heating
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Kaminsky, F.V. The Earth’s Lower Mantle; Springer Geology; Springer International Publishing: Cham, Switzerland, 2017; ISBN 978-3-319-55683-3. [Google Scholar]
- Lee, K.K.M.; O’Neill, B.; Panero, W.R.; Shim, S.-H.; Benedetti, L.R.; Jeanloz, R. Equations of state of the high-pressure phases of a natural peridotite and implications for the Earth’s lower mantle. Earth Planet. Sci. Lett. 2004, 223, 381–393. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tschauner, O.; Ma, C.; Beckett, J.R.; Prescher, C.; Prakapenka, V.B.; Rossman, G.R. Discovery of bridgmanite, the most abundant mineral in Earth, in a shocked meteorite. Science 2014, 346, 1100–1102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xu, W.; Lithgow-Bertelloni, C.; Stixrude, L.; Ritsema, J. The effect of bulk composition and temperature on mantle seismic structure. Earth Planet. Sci. Lett. 2008, 275, 70–79. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Irifune, T. Absence of an aluminous phase in the upper part of the Earth’s lower mantle. Nature 1994, 370, 131–133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wood, B.J. Phase transformations and partitioning relations in peridotite under lower mantle conditions. Earth Planet. Sci. Lett. 2000, 174, 341–354. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mao, H.; Guoyin, S.; Hemley, R.J. Multivariable Dependence of Fe-Mg Partitioning in the Lower Mantle. Science 1997, 278, 2098–2100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Katsura, T.; Ito, E. Determination of Fe-Mg partitioning between perovskite and magnesiowüstite. Geophys. Res. Lett. 1996, 23, 2005–2008. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, J.-F.; Heinz, D.L.; Mao, H.-K.; Hemley, R.J.; Devine, J.M.; Li, J.; Shen, G. Stability of magnesiowüstite in Earth’s lower mantle. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2003, 100, 4405–4408. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Murakami, M.; Hirose, K.; Kawamura, K.; Sata, N.; Ohishi, Y. Post-Perovskite Phase Transition in MgSiO3. Science 2004, 304, 855–858. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Badro, J.; Fiquet, G.; Guyot, F.; Rueff, J.-P.; Struzhkin, V.V.; Vankó, G.; Monaco, G. Iron Partitioning in Earth’s Mantle: Toward a Deep Lower Mantle Discontinuity. Science 2003, 300, 789–791. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dubrovinsky, L.S. Stability of Ferropericlase in the Lower Mantle. Science 2000, 289, 430–432. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dubrovinsky, L.; Dubrovinskaia, N.; Annersten, H.; Hålenius, E.; Harryson, H. Stability of (Mg0.5Fe0.5)O and (Mg0.8Fe0.2)O magnesiowustites in the lower mantle. Eur. J. Mineral. 2001, 13, 857–861. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kondo, T.; Ohtani, E.; Hirao, N.; Yagi, T.; Kikegawa, T. Phase transitions of (Mg,Fe)O at megabar pressures. Phys. Earth Planet. Inter. 2004, 143–144, 201–213. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, J.-F.; Weir, S.T.; Jackson, D.D.; Evans, W.J.; Vohra, Y.K.; Qiu, W.; Yoo, C.-S. Electrical conductivity of the lower-mantle ferropericlase across the electronic spin transition. Geophys. Res. Lett. 2007, 34, 2–5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fei, Y.; Zhang, L.; Corgne, A.; Watson, H.; Ricolleau, A.; Meng, Y.; Prakapenka, V. Spin transition and equations of state of (Mg, Fe)O solid solutions. Geophys. Res. Lett. 2007, 34, L17307. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kaminsky, F. Mineralogy of the lower mantle: A review of ‘super-deep’ mineral inclusions in diamond. Earth Sci. Rev. 2012, 110, 127–147. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deng, J.; Lee, K.K.M. Viscosity jump in the lower mantle inferred from melting curves of ferropericlase. Nat. Commun. 2017, 8, 1997. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Karlov, N.V.; Kirichenko, N.A.; Luk’yanchuk, B.S. Laser Thermochemistry: Fundamentals and Applications; Cambridge International Science Pub.: Cambridge, UK, 2000; ISBN 9781898326090. [Google Scholar]
- Goncharov, A.F.; Montoya, J.A.; Subramanian, N.; Struzhkin, V.V.; Kolesnikov, A.; Somayazulu, M.; Hemley, R.J. Laser heating in diamond anvil cells: Developments in pulsed and continuous techniques. J. Synchrotron Radiat. 2009, 16, 769–772. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Goncharov, A.F.; Prakapenka, V.B.; Struzhkin, V.V.; Kantor, I.; Rivers, M.L.; Dalton, D.A. X-ray diffraction in the pulsed laser heated diamond anvil cell. Rev. Sci. Instrum. 2010, 81, 113902. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aprilis, G.; Kantor, I.; Kupenko, I.; Cerantola, V.; Pakhomova, A.; Collings, I.E.; Torchio, R.; Fedotenko, T.; Chariton, S.; Bykov, M.; et al. Comparative study of the influence of pulsed and continuous wave laser heating on the mobilization of carbon and its chemical reaction with iron in a diamond anvil cell. J. Appl. Phys. 2019, 125, 095901. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Katsura, T.; Yoneda, A.; Yamazaki, D.; Yoshino, T.; Ito, E. Adiabatic temperature profile in the mantle. Phys. Earth Planet. Inter. 2010, 183, 212–218. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Trubitsyn, V.P.; Trubitsyna, A.P. Effects of compressibility in the mantle convection Equations. Izv. Phys. Solid Earth 2015, 51, 801–813. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Longo, M.; McCammon, C.A.; Jacobsen, S.D. Microanalysis of the iron oxidation state in (Mg,Fe)O and application to the study of microscale processes. Contrib. Mineral. Petrol. 2011, 162, 1249–1257. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Prescher, C.; McCammon, C.; Dubrovinsky, L. MossA: A program for analyzing energy-domain Mössbauer spectra from conventional and synchrotron sources. J. Appl. Crystallogr. 2012, 45, 329–331. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kantor, I.; Prakapenka, V.; Kantor, A.; Dera, P.; Kurnosov, A.; Sinogeikin, S.; Dubrovinskaia, N.; Dubrovinsky, L. BX90: A new diamond anvil cell design for X-ray diffraction and optical measurements. Rev. Sci. Instrum. 2012, 83, 125102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boehler, R.; De Hantsetters, K. New anvil designs in diamond-cells. High Press. Res. 2004, 24, 391–396. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kurnosov, A.; Kantor, I.; Boffa-Ballaran, T.; Lindhardt, S.; Dubrovinsky, L.; Kuznetsov, A.; Zehnder, B.H. A novel gas-loading system for mechanically closing of various types of diamond anvil cells. Rev. Sci. Instrum. 2008, 79, 045110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Akahama, Y.; Kawamura, H. Pressure calibration of diamond anvil Raman gauge to 310GPa. J. Appl. Phys. 2006, 100, 043516. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dewaele, A.; Datchi, F.; Loubeyre, P.; Mezouar, M. High pressure–high temperature equations of state of neon and diamond. Phys. Rev. B 2008, 77, 094106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kupenko, I.; Dubrovinsky, L.; Dubrovinskaia, N.; McCammon, C.; Glazyrin, K.; Bykova, E.; Ballaran, T.B.; Sinmyo, R.; Chumakov, A.I.; Potapkin, V.; et al. Portable double-sided laser-heating system for Mössbauer spectroscopy and X-ray diffraction experiments at synchrotron facilities with diamond anvil cells. Rev. Sci. Instrum. 2012, 83, 124501. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aprilis, G.; Strohm, C.; Kupenko, I.; Linhardt, S.; Laskin, A.; Vasiukov, D.M.; Cerantola, V.; Koemets, E.G.; McCammon, C.; Kurnosov, A.; et al. Portable double-sided pulsed laser heating system for time-resolved geoscience and materials science applications. Rev. Sci. Instrum. 2017, 88, 084501. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Potapkin, V.; Chumakov, A.I.; Smirnov, G.V.; Celse, J.-P.; Rüffer, R.; McCammon, C.; Dubrovinsky, L. The 57Fe Synchrotron Mössbauer Source at the ESRF. J. Synchrotron Radiat. 2012, 19, 559–569. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rüffer, R.; Chumakov, A.I. Nuclear Resonance Beamline at ESRF. Hyperfine Interact. 1996, 97–98, 589–604. [Google Scholar]
- Merlini, M.; Hanfland, M. Single-crystal diffraction at megabar conditions by synchrotron radiation. High Press. Res. 2013, 33, 511–522. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Prescher, C.; Prakapenka, V.B. DIOPTAS: A program for reduction of two-dimensional X-ray diffraction data and data exploration. High Press. Res. 2015, 35, 223–230. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- CrysAlisPro Software System. Version 1.171.38.43; Rigaku Oxford Diffraction; Rigaku: Tokyo, Japan, 2015.
- Petříček, V.; Dušek, M.; Palatinus, L. Crystallographic Computing System JANA2006: General features. Z. Krist. Cryst. Mater. 2014, 229, 345–352. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liermann, H.P.; Konôpková, Z.; Morgenroth, W.; Glazyrin, K.; Bednarčik, J.; McBride, E.E.; Petitgirard, S.; Delitz, J.T.; Wendt, M.; Bican, Y.; et al. The Extreme Conditions Beamline P02.2 and the Extreme Conditions Science Infrastructure at PETRA III. J. Synchrotron Radiat. 2015, 22, 908–924. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hrubiak, R.; Smith, J.S.; Shen, G. Multimode scanning X-ray diffraction microscopy for diamond anvil cell experiments. Rev. Sci. Instrum. 2019, 90, 025109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dubrovinsky, L.S.; Dubrovinskaia, N.A.; McCammon, C.; Rozenberg, G.K.; Ahuja, R.; Osorio-Guillen, J.M.; Dmitriev, V.; Weber, H.-P.; Bihan, T.L.; Johansson, B. The structure of the metallic high-pressure Fe3O4 polymorph: Experimental and theoretical study. J. Phys. Condens. Matter 2003, 15, 7697–7706. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Haavik, C.; Stølen, S.; Fjellvåg, H.; Hanfland, M.; Häusermann, D. Equation of state of magnetite and its high-pressure modification: Thermodynamics of the Fe-O system at high pressure. Am. Mineral. 2000, 85, 514–523. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Uenver-Thiele, L.; Woodland, A.B.; Ballaran, T.B.; Miyajima, N.; Frost, D.J. Phase relations of MgFe2O4 at conditions of the deep upper mantle and transition zone. Am. Mineral. 2017, 102, 632–642. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Uenver-Thiele, L.; Woodland, A.B.; Ballaran, T.B.; Miyajima, N.; Frost, D.J. Phase relations of Fe-Mg spinels including new high-pressure post-spinel phases and implications for natural samples. Am. Mineral. 2017, 102, 2054–2064. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Greenberg, E.; Xu, W.M.; Nikolaevsky, M.; Bykova, E.; Garbarino, G.; Glazyrin, K.; Merkel, D.G.; Dubrovinsky, L.; Pasternak, M.P.; Rozenberg, G.K. High-pressure magnetic, electronic, and structural properties of MFe2O4 (M = Mg,Zn,Fe) ferric spinels. Phys. Rev. B 2017, 95, 195150. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wirth, R.; Dobrzhinetskaya, L.; Harte, B.; Schreiber, A.; Green, H.W. High-Fe (Mg, Fe)O inclusion in diamond apparently from the lowermost mantle. Earth Planet. Sci. Lett. 2014, 404, 365–375. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kaminsky, F.V.; Lin, J.-F. Iron partitioning in natural lower-mantle minerals: Toward a chemically heterogeneous lower mantle. Am. Mineral. 2017, 102, 824–832. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Anzolini, C.; Nestola, F.; Mazzucchelli, M.L.; Alvaro, M.; Nimis, P.; Gianese, A.; Morganti, S.; Marone, F.; Campione, M.; Hutchison, M.T.; et al. Depth of diamond formation obtained from single periclase inclusions. Geology 2019, 47, 219–222. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boffa Ballaran, T.; Uenver-Thiele, L.; Woodland, A.B. Complete substitution of Fe2+ by Mg in Fe4O5: The crystal structure of the Mg2Fe2O5 end-member. Am. Mineral. 2015, 100, 628–632. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ishii, T.; Uenver-Thiele, L.; Woodland, A.B.; Alig, E.; Ballaran, T.B. Synthesis and crystal structure of Mg-bearing Fe9O11: New insight in the complexity of Fe-Mg oxides at conditions of the deep upper mantle. Am. Mineral. 2018, 103, 1873–1876. [Google Scholar]
- Kantor, I.; Dubrovinsky, L.; McCammon, C.; Kantor, A.; Pascarelli, S.; Aquilanti, G.; Crichton, W.; Mattesini, M.; Ahuja, R.; Almeida, J.; et al. Pressure-induced phase transition in Mg0.8Fe0.2O ferropericlase. Phys. Chem. Miner. 2006, 33, 35–44. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dubrovinsky, L.; Dubrovinskaia, N.; Kantor, I.; McCammon, C.; Crichton, W.; Urusov, V. Decomposition of ferropericlase (Mg0.80Fe0.20)O at high pressures and temperatures. J. Alloys Compd. 2005, 390, 41–45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sinmyo, R.; Hirose, K. The Soret diffusion in laser-heated diamond-anvil cell. Phys. Earth Planet. Inter. 2010, 180, 172–178. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fu, S.; Yang, J.; Zhang, Y.; Liu, J.; Greenberg, E.; Prakapenka, V.B.; Okuchi, T.; Lin, J.-F. Melting behavior of the lower-mantle ferropericlase across the spin crossover: Implication for the ultra-low velocity zones at the lowermost mantle. Earth Planet. Sci. Lett. 2018, 503, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, J.-F.; Vanko, G.; Jacobsen, S.D.; Iota, V.; Struzhkin, V.V.; Prakapenka, V.B.; Kuznetsov, A.; Yoo, C.-S. Spin Transition Zone in Earth’s Lower Mantle. Science 2007, 317, 1740–1743. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, R.Y.; Liou, J.G. Exsolution Lamellae in Minerals from Ultrahigh-Pressure Rocks. Int. Geol. Rev. 1999, 41, 981–993. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pakhomova, A.S.; Danisi, R.M.; Armbruster, T.; Lazic, B.; Gfeller, F.; Krivovichev, S.V.; Yakovenchuk, V.N. High-temperature induced dehydration, phase transition and exsolution in amicite: A single-crystal X-ray study. Microporous Mesoporous Mater. 2013, 182, 207–219. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martirosyan, N.S.; Litasov, K.D.; Lobanov, S.S.; Goncharov, A.F.; Shatskiy, A.; Ohfuji, H.; Prakapenka, V. The Mg-carbonate–Fe interaction: Implication for the fate of subducted carbonates and formation of diamond in the lower mantle. Geosci. Front. 2019, 10, 1449–1458. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kaminsky, F.V.; Wirth, R.; Schreiber, A. A microinclusion of lower-mantle rock and other minerals and nitrogen lower-mantle inclusions in a diamond. Can. Mineral. 2015, 53, 83–104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]



| Fe2+ (Dark Green) | Fe2+ (Cyan) | Fe3+ (Light Green) | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| CS (mm/s) | QS (mm/s) | CS (mm/s) | QS (mm/s) | CS (mm/s) | QS (mm/s) | ||
| Starting material | 0.94(1) | 1.27(49) | 0.94(1) | 2.48(12) | 0.01(29) | - | |
| After CW heating | 0.92(2) | 1.06(9) | 1.00(6) | 2.26(14) | 0.17(15) | 0.98(18) | |
| Crystal | Heating Method | Heating Time | Temperature (Upstream) | Temperature (Downstream) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| C01 | Pulsed, 1 kHz/500 μs | 25 min | 1800–2100 K | 1550–1650 K |
| C02 | Pulsed, 25 kHz/3 μs | 12 min | 1800–2100 K | 1650–1950 K |
| C03 | Continuous wave | 11 min | 1900–2300 K | 1700–1800 K |
| Crystal | Heating Method | Heating Time | Maximum Temperature (Side A) | Maximum Temperature (Side B) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| C04 | Pulsed, 2 kHz/250 μs | 30 s | 2800 K | 3100 K |
| C05 | Pulsed, 25 kHz/11 μs | 30 s | 3100 K | 3400 K |
| Crystal Data | |
| Composition | Mg4.71Fe7.29O16 |
| Space Group | Cmcm |
| a, Å | 2.742(1) |
| b, Å | 9.170(4) |
| c, Å | 9.313(3) |
| Volume, Å3 | 234.2(2) |
| Z | 1 |
| Data Collection | |
| Wavelength, Å | 0.41107 |
| Max. θ° | 20.68 |
| Index Ranges | −3 ≤ h ≤ 3 −12 ≤ k ≤ 9 −12 ≤ l ≤ 12 |
| No. Meas. Refl. | 247 |
| No. Unique Refl. | 135 |
| No. Obs. Refl. (I > 3σ(I)) | 107 |
| No. of Variables | 14 |
| Rint | 0.0575 |
| Rσ | 0.0709 |
| R1, I > 3σ(I) | 0.0766 |
| R1, all data | 0.0915 |
| wR2, I > 3σ(I) | 0.2018 |
| wR2, all data | 0.2279 |
| GooF | 1.134 |
| FeMg1O6 Trigonal Prism | FeMg2O6 Octahedra | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| FeMg1-O1 | 2.004(11) Å x2 | FeMg2-O1 | 1.849(7) Å | FeMg1-FeMg1 | 2.7419(10) Å |
| FeMg1-O2 | 2.091(9) Å x4 | FeMg2-O2 | 1.933(7) Å x2 | FeMg1-FeMg2 | 2.822(5) Å |
| FeMg2-O3 | 1.9496(17) Å x2 | FeMg2-FeMg2 | 2.7419(10) Å | ||
| FeMg2-O2 | 1.981(12) Å | FeMg2-FeMg2 | 2.772(5) Å | ||
| FeMg2-FeMg2 | 2.901(4) Å | ||||
| <FeMg1-O> | 2.06(1) Å | <FeMg2-O> | 1.932(6) Å | ||
| Volume | 8.2718 Å3 | Volume | 9.5666 Å3 | ||
© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Aprilis, G.; Pakhomova, A.; Chariton, S.; Khandarkhaeva, S.; Melai, C.; Bykova, E.; Bykov, M.; Fedotenko, T.; Koemets, E.; McCammon, C.; et al. The Effect of Pulsed Laser Heating on the Stability of Ferropericlase at High Pressures. Minerals 2020, 10, 542. https://doi.org/10.3390/min10060542
Aprilis G, Pakhomova A, Chariton S, Khandarkhaeva S, Melai C, Bykova E, Bykov M, Fedotenko T, Koemets E, McCammon C, et al. The Effect of Pulsed Laser Heating on the Stability of Ferropericlase at High Pressures. Minerals. 2020; 10(6):542. https://doi.org/10.3390/min10060542
Chicago/Turabian StyleAprilis, Georgios, Anna Pakhomova, Stella Chariton, Saiana Khandarkhaeva, Caterina Melai, Elena Bykova, Maxim Bykov, Timofey Fedotenko, Egor Koemets, Catherine McCammon, and et al. 2020. "The Effect of Pulsed Laser Heating on the Stability of Ferropericlase at High Pressures" Minerals 10, no. 6: 542. https://doi.org/10.3390/min10060542
APA StyleAprilis, G., Pakhomova, A., Chariton, S., Khandarkhaeva, S., Melai, C., Bykova, E., Bykov, M., Fedotenko, T., Koemets, E., McCammon, C., Chumakov, A. I., Hanfland, M., Dubrovinskaia, N., & Dubrovinsky, L. (2020). The Effect of Pulsed Laser Heating on the Stability of Ferropericlase at High Pressures. Minerals, 10(6), 542. https://doi.org/10.3390/min10060542







