Abstract
This study investigates the removal of aluminum and iron from rare earth element (REE) containing solutions by solvent extraction with saponified naphthenic acid and by hydrolysis-precipitation. The results emphasize both, the preferential application as well as limitations of every method. We find that emulsification occurring during the solvent extraction of aluminum is caused by its slow extraction rate in comparison to the neutralization reaction and by the proximity of the pH value required for aluminum extraction and the pH value at which hydrolysis of aluminum occurs. However, by choosing a long shaking time of at least 4 h, the emulsion recedes. The formation of emulsion can be avoided by strict control of pH value during the extraction. Moreover, the loading capacity of the organic phase with aluminum is limited due to the strong increase in viscosity of the organic phase with increasing aluminum concentration and due to the gel formation. Regarding the extraction of iron, the amount of extracted ions is limited due to the overlap of the pH range required for the extraction with pH range in which sparingly soluble iron oxides/hydroxides are formed. In summary, aluminum and iron can be simultaneously removed from REE-sulfate solution by solvent extraction with saponified naphthenic acid in one extraction stage only from diluted solutions. However, in comparison to the hydrolysis-precipitation method, a higher purity of the solution is achieved. A complete removal of aluminum and iron from concentrated solutions can be achieved in two stages. First, the content of aluminum and iron should be reduced by hydrolysis-precipitation. After that, a high-purity solution can be obtained by subsequent solvent extraction by saponified naphthenic acid.
1. Introduction
Due to their unique properties, rare earth elements (REEs) find a broad application in different areas such as catalysts, alloys, glass polishing, ceramics and permanent magnets [1]. However, the common occurrence and the low concentration in ores [2] means the extraction of REEs as pure elements is costly and it requires more complex flowsheets than used for other metals such as gold [3]. The whole extraction process comprises not only the REE extraction from raw materials but also a subsequent separation of individual REEs. Furthermore, the Chinese export restrictions, very few effective substitutes for certain REEs, low recycling rates, growing demand and negative effects of REE extraction on the environment impede the secure supply, especially of countries without their own natural reserves [4]. Consequently, alternative REE supply sources must be found [5], recycling rate has to be improved [6] as well as economic and efficient extraction processes have to be developed for the new raw materials.
The extraction process depends strongly on the REE mineralogy and on the ore/concentrate grade resulting in two routes. On the one hand, the REEs are extracted from high-grade ore concentrates obtained by beneficiation. For example, it is possible to produce a bastnäsite concentrate containing 70 wt% of REO by physical beneficiation and subsequent HCl leaching [7]. The leach liquors obtained by this route contain high amounts of REEs and a low concentration of impurities. The subsequent separation of individual REEs can be carried out directly or after impurity removal, e.g., by hydrolysis-precipitation. On the other hand, REEs are extracted from low grade raw materials without the beneficiation step (e.g., ion-adsorption deposits [8], umbers [9], ferromanganese nodules [10]) or from ore concentrates with low enrichment (e.g., eudialyte [11], apatite [12]). The REE solutions obtained by leaching of the low grade raw materials are more contaminated by elements that dissolve together with the REEs and usually contain only several grams of REO per liter [11,13] or even less [9]. In this case the separation of individual REEs can only be carried out after REE enrichment and REE separation from impurities. For the impurity separation there are mainly three different ways:
- modification of the chemical state of the impurities before leaching (e.g., selective roasting [14], carbothermic reduction of iron [15], magnetizing roasting of iron [16], reduction of Fe to Fe and subsequent solvent extraction with primary amines [17]),
- REE removal from the leach liquor (e.g., sulfate/double sulfate precipitation [7,18,19], oxalate precipitation [7,9], ammonium bicarbonate precipitation [20], solvent extraction [21]),
- impurity removal from the leach liquor (hydrolysis-precipitation [22], solvent extraction [23,24]).
Impurities can be divided into two groups according to their value: low-value compounds (e.g., aluminum, iron, calcium) and high-value compounds (e.g., zirconium, manganese, niobium). Aluminum and iron represent typical low-value compounds which are very often associated with REEs in primary (e.g., ion-adsorption deposits [25], umbers [9], ferromanganese nodules [10]) as well as in secondary raw materials (e.g., red mud [26], Bayan Obo tailings [16], FCC catalyst waste slag [22], NdFeB magnets [21]). In research papers found the separation of aluminum and iron from REEs is performed (apart from the modification of chemical state of iron [14,15,16,17] and aluminum [14]) generally after leaching in subsequent operations (Table 1). The applied techniques include REE oxalate precipitation [9], solvent extraction of Nd with D2EHPA [21], hydrolysis-precipitation of Al [22], solvent extraction of Al with saponified naphthenic acid [23] and other less common methods. Due to the complexity of the whole extraction process, the REE separation from impurities should be uncomplicated and inexpensive. According to that, the impurity removal by solvent extraction with naphthenic acid and by hydrolysis-precipitation are particularly suitable as the price of naphthenic acid (NA) is low, compared to phosphate and amine based extractants, and the hydrolysis-precipitation requires less chemicals than oxalate or double sulfate precipitation. However, it is not obvious in which cases which method should be applied preferentially. The main purpose of this study is to clarify this question.

Table 1.
Methods for separation of aluminum and iron from rare earth element (REE) containing solutions.
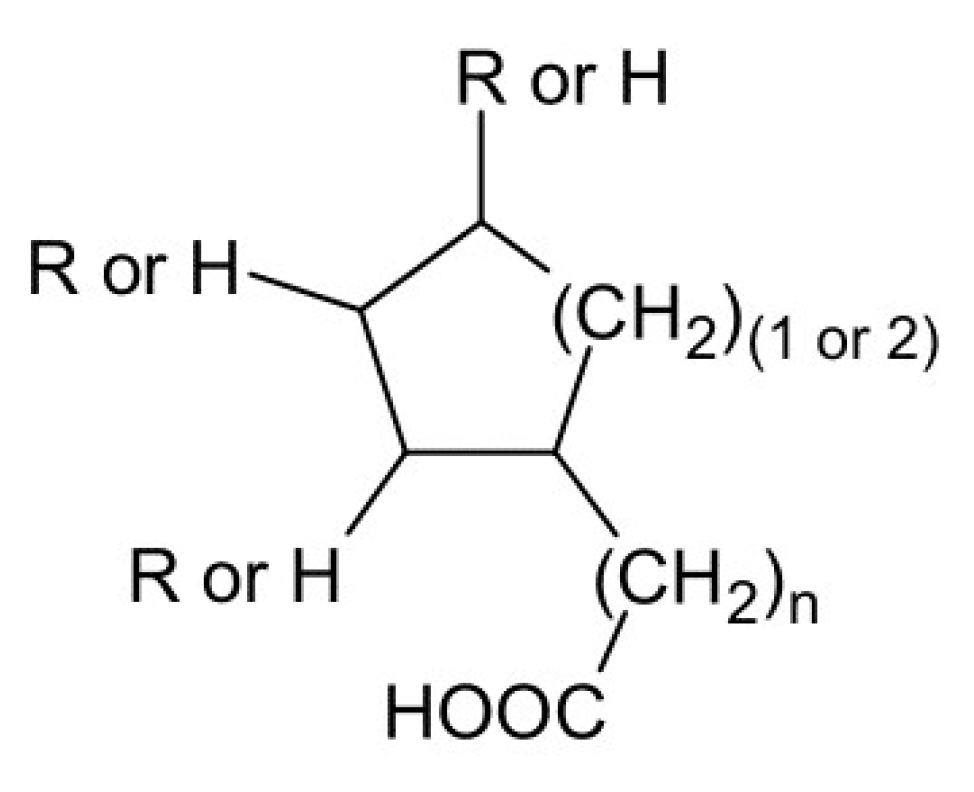
Naphthenic acid (NA), or more precisely, naphthenic acids are produced from petroleum or crude oil and are mainly composed of cyclic aliphatic monocarboxylic acids with varying composition (Figure 1). The major advantages of NA are low cost, high loading capacity in regard to REEs and easy stripping [31].
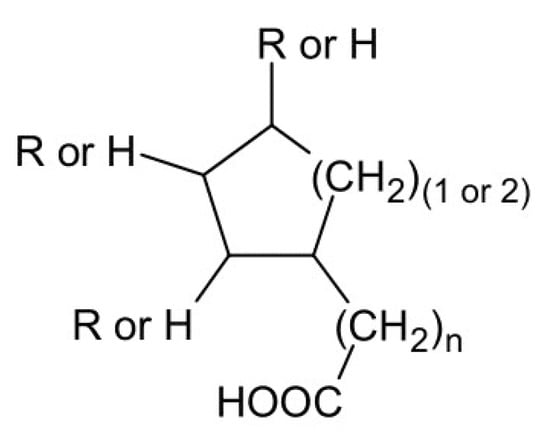
Figure 1.
Chemical structure of naphthenic acids.
The application of NA is severely limited by the acid number range of NA. For example, it is scientifically proven that only NA with the acid number higher than 170 mg KOH/g can extract yttrium effectively from REEs [32].
The impurity removal with NA has been already patented [33,34] and the process has been employed in industry [30]. In addition to the mentioned application, NA has been used for REE extraction since the 1960s. It is beside di(2-ethylhexyl)phosphoric acid and 2-ethylhexyl phosphoric acid mono-2-ethylhexyl ester a main extractant in the REE separation industry [17]. Other applications of naphthenic acid are REE enrichment from diluted solutions and anion exchange. Usually both processes are carried out if REEs are leached with sulfuric acid or ammonium sulfate from low grade raw materials such as ion adsorption clays. The REE enrichment and the anion exchange should be performed because the separation of individual REEs is done preferable from chloridic or nitric solutions with high REE content [7]. Furthermore, the REE solubility in sulfate solution is in comparison to hydrochloric or nitric solutions lower, especially whether the solution is contaminated with alkali metal ions (formation of double sulfates).
As mentioned above, the present paper deals with the removal of aluminum and iron from REEs represented by lanthanum by solvent extraction with saponified NA in the system M(SO) [M = La, Al, Fe]-HSO-HO/SAP-NA-2-oct.-kerosene and by hydrolysis-precipitation. Both methods are chosen due to their economic manner (low costs of NA in comparison to phosphate and amine based extractants; low chemical consumption by hydrolysis-precipitation) and industrial significance. The study compares both methods and shows in which cases which method should be applied preferentially. Moreover, limitations of both methods are discussed and explained. Finally, a process for the production of high-purity REE solution is proposed.
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Determination of the Acid Number of Naphthenic Acid
NA has been provided by Acros Organics (practical grade). Its acid number (AN) defined by Equation (1) was determined dissolving 0.5 g of NA in 50 mL ethanol and titrating the solution with 0.1 mol/L standardized potassium hydroxide solution in ethanol.
The determined acid number of naphthenic acid of 235 mg KOH/g is higher than the recommended minimum face value of 170 mg KOH/g [32]. It can be therefore concluded that the contamination of used naphthenic acid with other organic compounds is low. Considering the measured density of naphthenic acid of 0.92 g/mL, the concentration of naphthenic acid amounts to 3.86 mol/L.
2.2. Extraction Experiments
The extraction experiments were conducted with saponified organic phase consisting of 20 vol% NA (Sigma-Aldrich, St. Louis, MO, USA, technical grade) and 20 vol% 2-octanol dissolved in kerosene. The saponification was done by mixing a certain amount of NHOH solution (c = 8.6–8.9 mol/L) with organic phase at room temperature a day before carrying out extraction experiments. After saponification a transparent liquid was obtained as water-in-oil microemulsion [35]. The saponification value (SAP) was calculated with Equation (2).
2.2.1. Stability of Microemulsion
For the investigation of the stability of the microemulsion (experiment (1), Table 2) a certain amount of saponified organic phase was mixed with 5 mL HNO solution (c = 0.2 mol/L) and the mixture was shaken in an overhead shaker at different phase ratios (PR, Equation (3)) at room temperature for 30 min.

Table 2.
Experimental conditions for extraction experiments: (1) stability of microemulsion; (2) extraction equilibrium experiments from single-component solutions; (3) kinetics of Al extraction; (4) extraction equilibrium experiments from double-component solutions; (5) removal of aluminum and iron from ternary-component solutions.
After phase separation, the pH value of the aqueous phase was measured. All other experimental parameters are listed in Table 2.
2.2.2. Experiments from Single- and Double-Component Solutions
The subsequent equilibrium extraction experiments were conducted from single- and double-component solutions varying phase ratios and concentrations of metal ions in the starting solutions (experiments (2) and (5), Table 2). The rise in phase ratio (PR) causes not only an increase in the excess of extractant but also in the amount of OH ions present in the extraction system causing an increase in the pH value of aqueous phase and thus, higher extraction yields of metal ions. The metal ion solutions were produced by dissolving corresponding metal sulfates (Al(SO)18HO, extra pure, Carl Roth; Fe(SO)xHO, reagent grade, VWR; La(SO)xHO, Alfa Aesar) in diluted sulfuric acid. The concentration of metal ions in the starting solutions and all other extraction parameters are listed in Table 2.
Additionally, the kinetics of aluminum extraction was investigated in order to explain the formation of emulsion (experiment (3), Table 2).
2.3. Aluminum and Iron Removal from Ternary-Component Solutions
Finally, the removal of aluminum and iron from ternary-component solutions by solvent extraction (experiment (5), Table 2) and by hydrolysis-precipitation was investigated. The composition of the aqueous phase is given in Table 2. The procedure for the solvent extraction experiments is the same as described above. In precipitation experiments to 50 mL of metal ion solution a certain amount of NHOH solution (c = 0.92 mol/L) was added until a certain pH value was reached. After 24 h stirring at room temperature the liquid phase was separated by vacuum filtration.
2.4. Analytics
The chemical composition of all liquid samples (starting solutions, raffinates and solutions obtained by hydrolysis-precipitation) was determined by ICP-OES (Thermo Scientific IRIS Intrepid II XDL). Additionally, kinematic viscosity and density of loaded organic phase with aluminum were measured (Anton Paar SVM 2001).
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Stability of Microemulsion
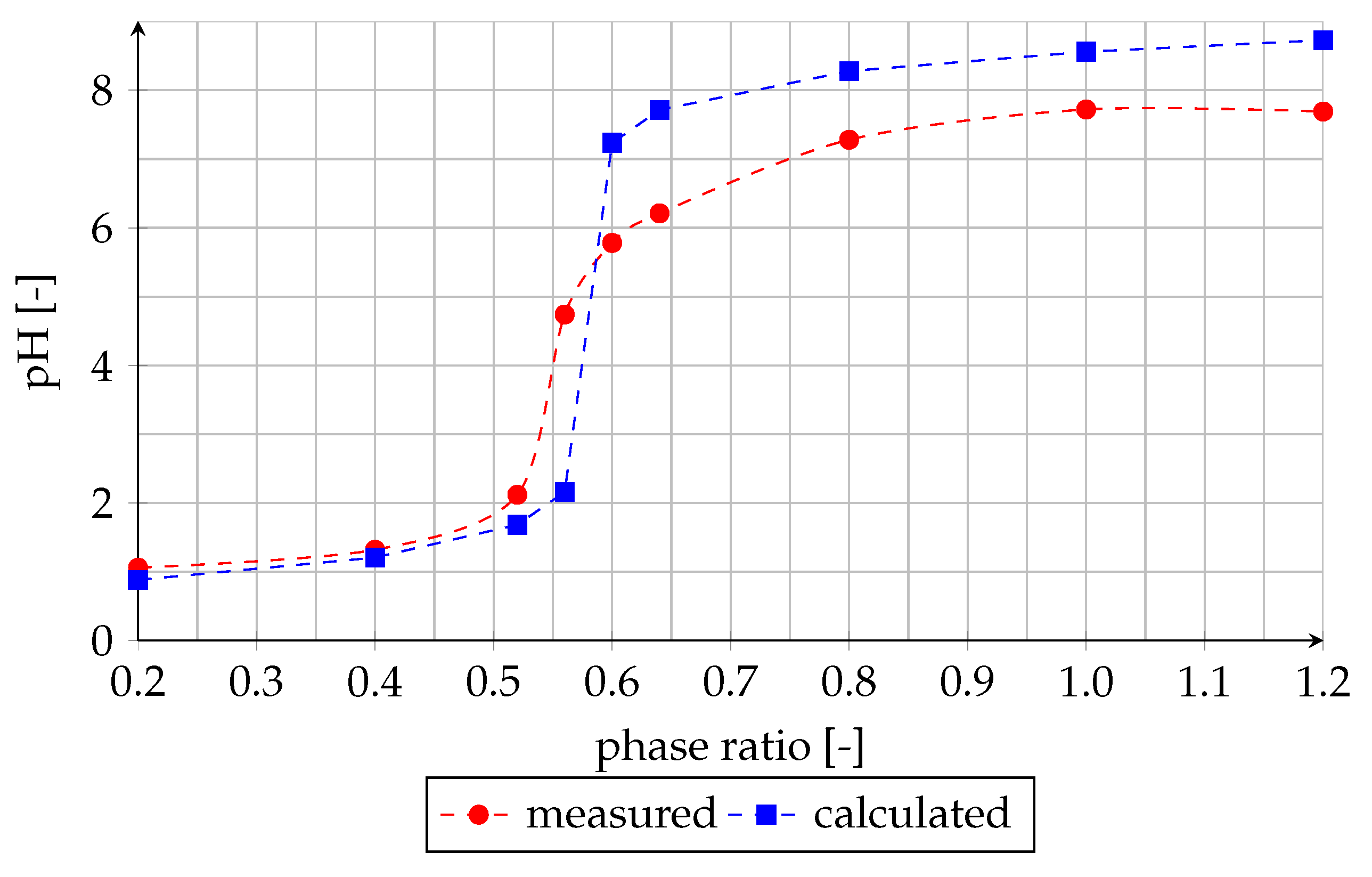
First, the stability of saponified organic phase after mixing with acidic water was investigated. The measured pH value of the aqueous phase depending on the phase ratio is shown in Figure 2. Additionally, in the diagram a theoretical curve is plotted which would result after a complete neutralization of all OH ions present in the organic phase.
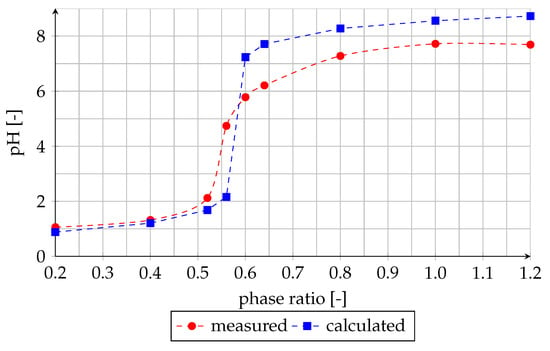
Figure 2.
Effect of phase ratio on pH value of the aqueous phase after mixing of saponified organic phase with acidic water (experiment (1)).
After mixing the saponified organic phase with acidic water the pH value of the aqueous phase increases (Figure 2); the neutralization reaction takes place (Equation (4)).
This implies that the microemulsion decomposes. When comparing the measured values with the theoretical curve it becomes obvious that a complete neutralization and thus a complete decomposition occurs only when the equilibrium pH value of the aqueous phase after the extraction is below 5.5. At higher pH values, a part of OH ions remains in the organic phase.
Additionally, the kinematic viscosity and the density of the organic phase were measured before (OP), after (SAP-OP) saponification and after mixing with acidic water (E-OP) at a phase ratio of 0.6. The results are shown in Table 3.

Table 3.
Kinematicviscosity and density of organic phase before (OP), after (SAP-OP) saponification and after mixing with acidic water (E-OP) at phase ratio of 0.6.
The results in Table 3 indicate that the kinematic viscosity and the density of the organic phase increase after saponification. Nevertheless, after mixing with acidic water the values are comparable with those of unsaponified organic phase. It confirms the decomposition of the microemulsion.
3.2. Equilibrium Extraction Experiments from Single-Component Solutions
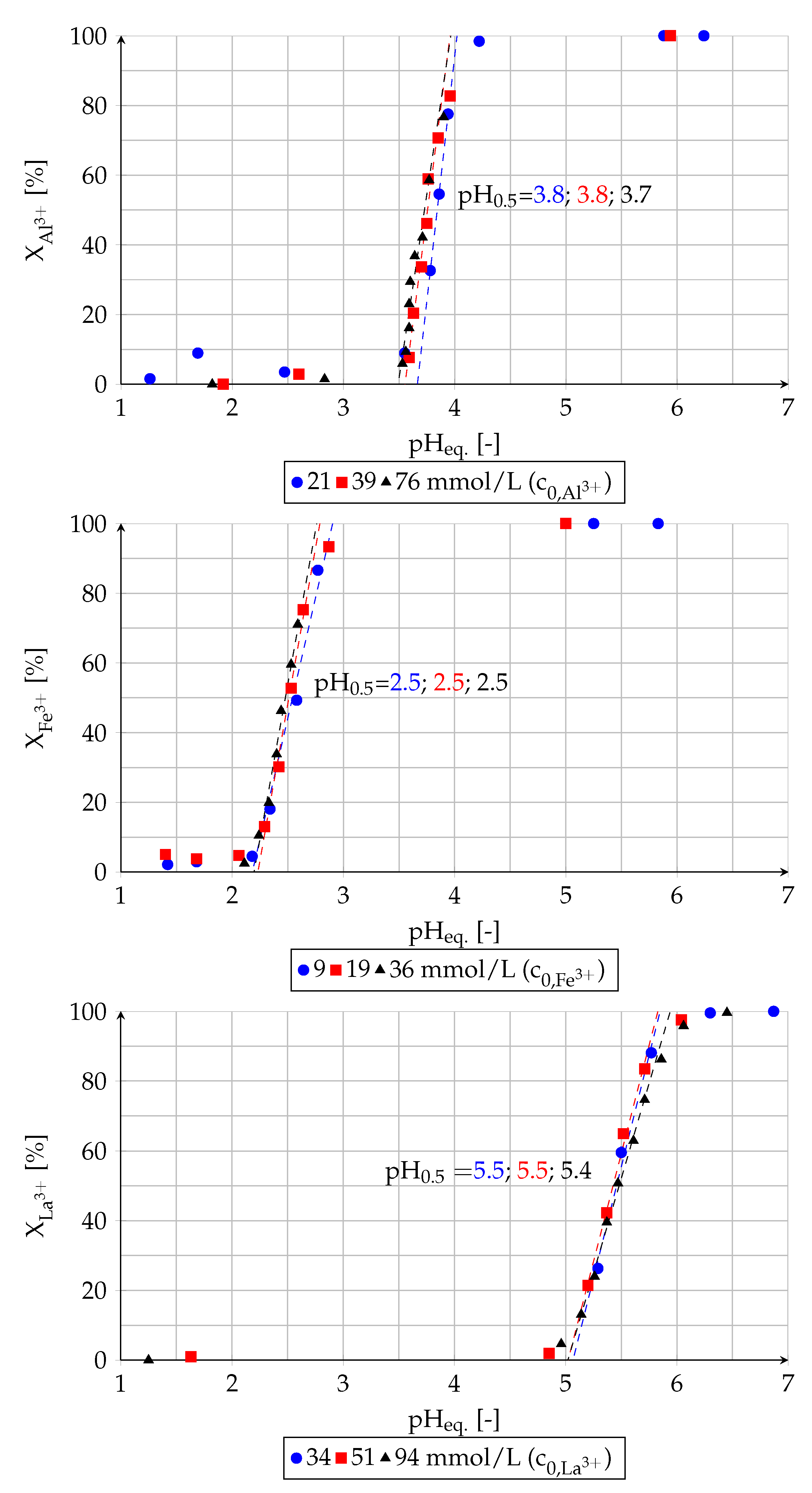
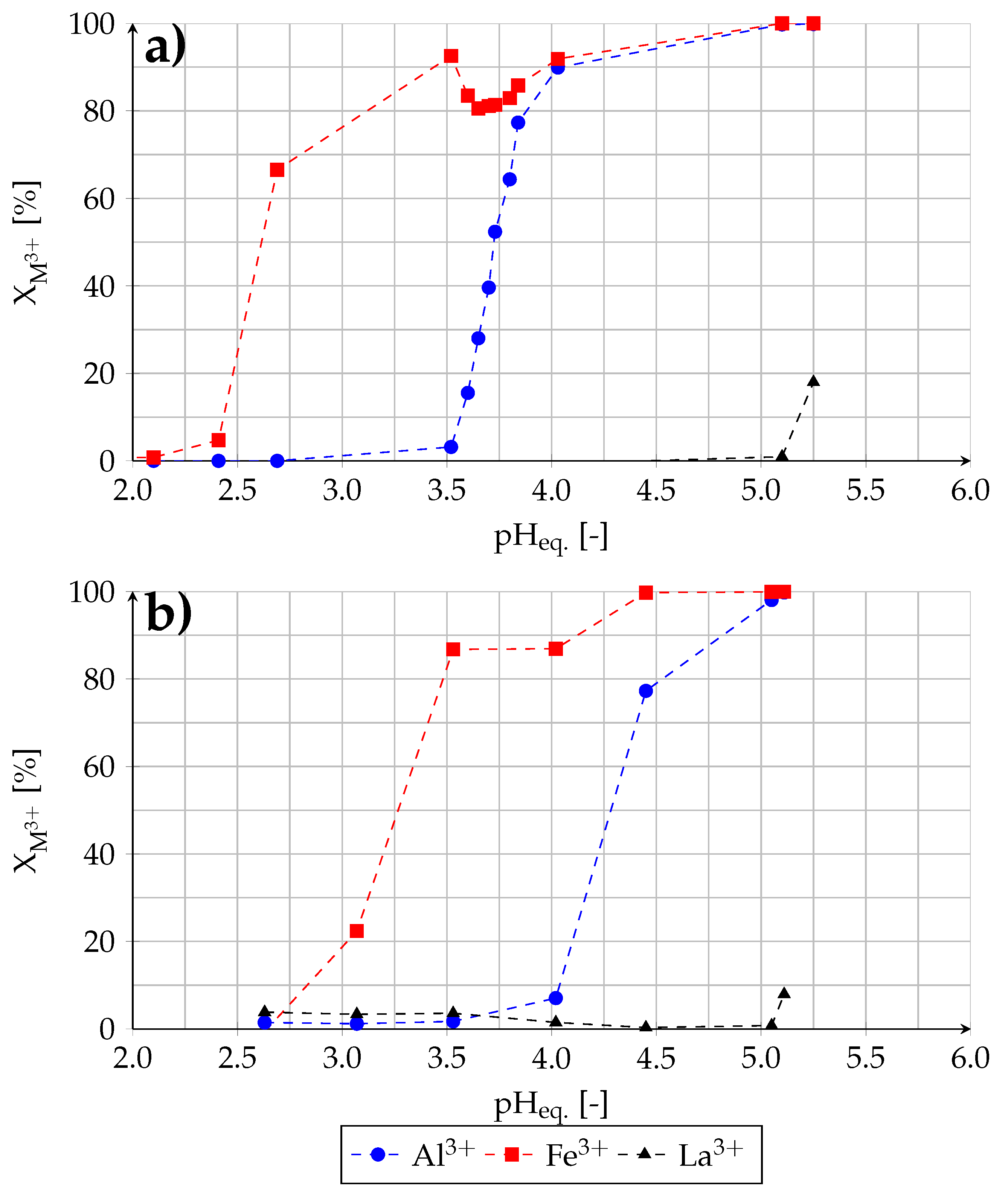
The influence of the equilibrium pH value on the extraction of Al, Fe and La from single-component solutions was investigated for different initial concentrations of the elements. The obtained extraction yields (X) are shown in Figure 3.
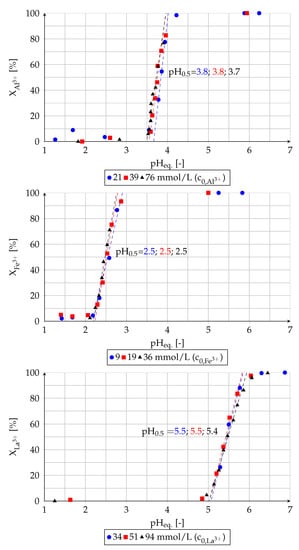
Figure 3.
Effect of equilibrium pH value of raffinate on extraction yield from single-component solutions (experiment (2)).
As it can be seen, the extraction takes place after the raffinate reaches a certain pH value. After that, the extraction yields between 15% and 85% increase in all cases nearly linearly. The corresponding pH values can be determined from a regression line which are listed in Table 4.

Table 4.
Determined and literature [36] pH values for the extraction of aluminum, iron and lanthanum.
According to the determined pH values, the extractability increases in the following order: Fe>Al>La, which is consistent with the sequence determined by Preston (1985) [36]. However, each determined pH value is higher. The discrepancy can be attributed to the different composition of organic and aqueous phase. Preston (1985) [36] conducted extraction experiments without addition of a modifier and naphthenic acid was dissolved in xylene. Furthermore, the aqueous phase contained metal nitrates and sodium nitrate.
To explain the difference between the pH values in more detail, certain preliminary experiments were conducted which are discussed shortly. The exchange of sulfate by chloride ions causes a lowering of the pH from 5.5 to 5.0 during the lanthanum extraction. Moreover, it was observed that during the aluminum extraction from sulfate solution without addition of 2-octanol emulsion is formed which does not recede even after long shaking time. Furthermore, the pH value is almost the same as with the addition of modifier. In summary, apparently the composition of aqueous phase mainly affects the pH value. However, more detailed studies on the effect of the composition of organic and aqueous phase on the shift of pH value required for the extraction of each metal ion should be carried out.
3.3. Limitations by Extraction of Aluminum and Iron
In the previous section, it has been shown that saponified naphthenic acid is able to extract aluminum, iron and lanthanum from sulfuric acid solutions. However, the extraction process of aluminum and iron has some limitations which are discussed in this section.
It is well known that during the aluminum extraction with saponified naphthenic acid emulsion is formed under certain conditions [23,24]. According to Yang and Qiu (2017) [23], the emulsification is caused by extraction of macromolecular aluminum hydroxides. This study reveals additional information about the formation of emulsions. It was found that the emulsification occurs mainly due to the slow rate of aluminum extraction and due to the high pH value required for the extraction. This has been investigated in the experiment (3). The detailed explanation is provided below.
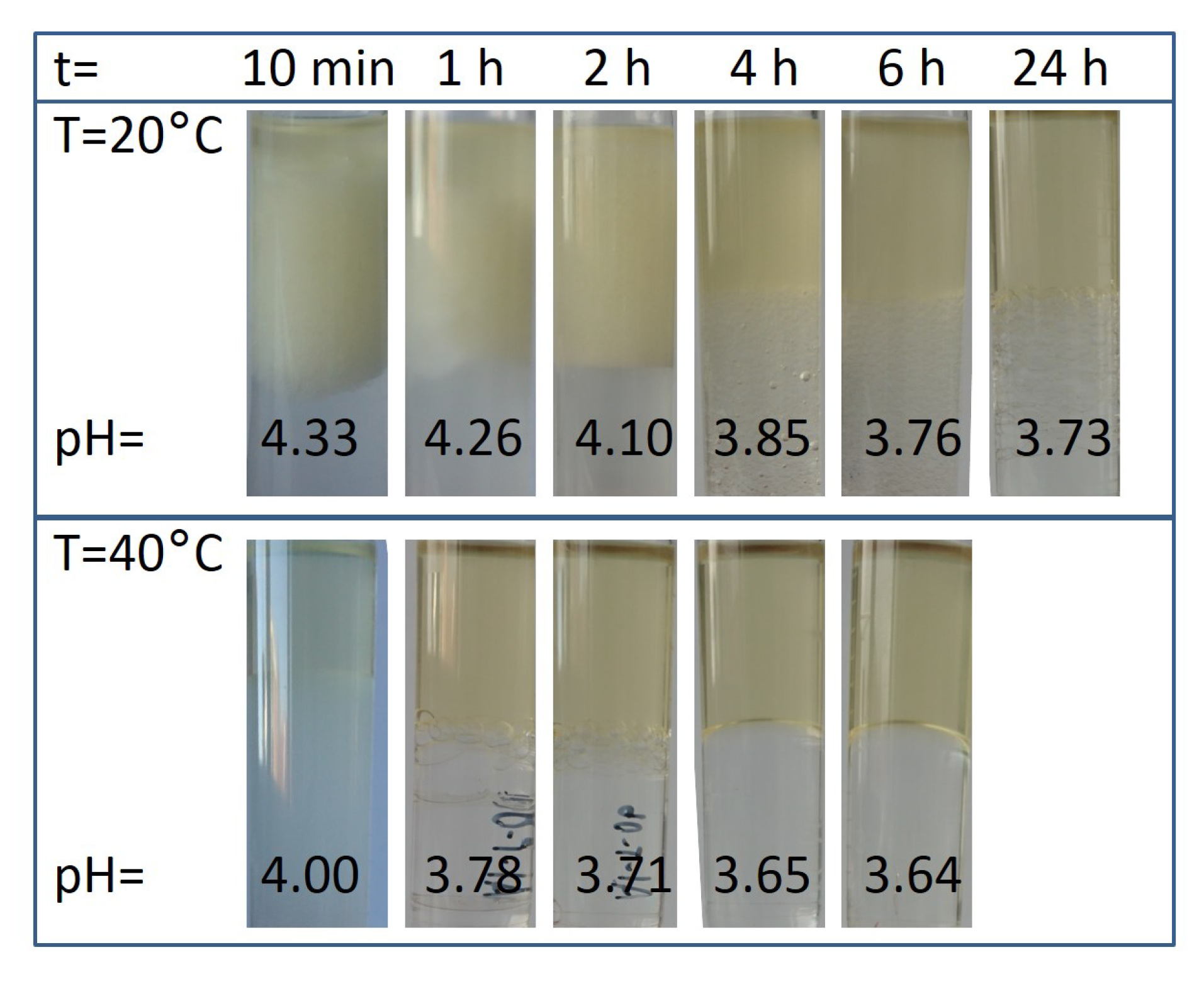
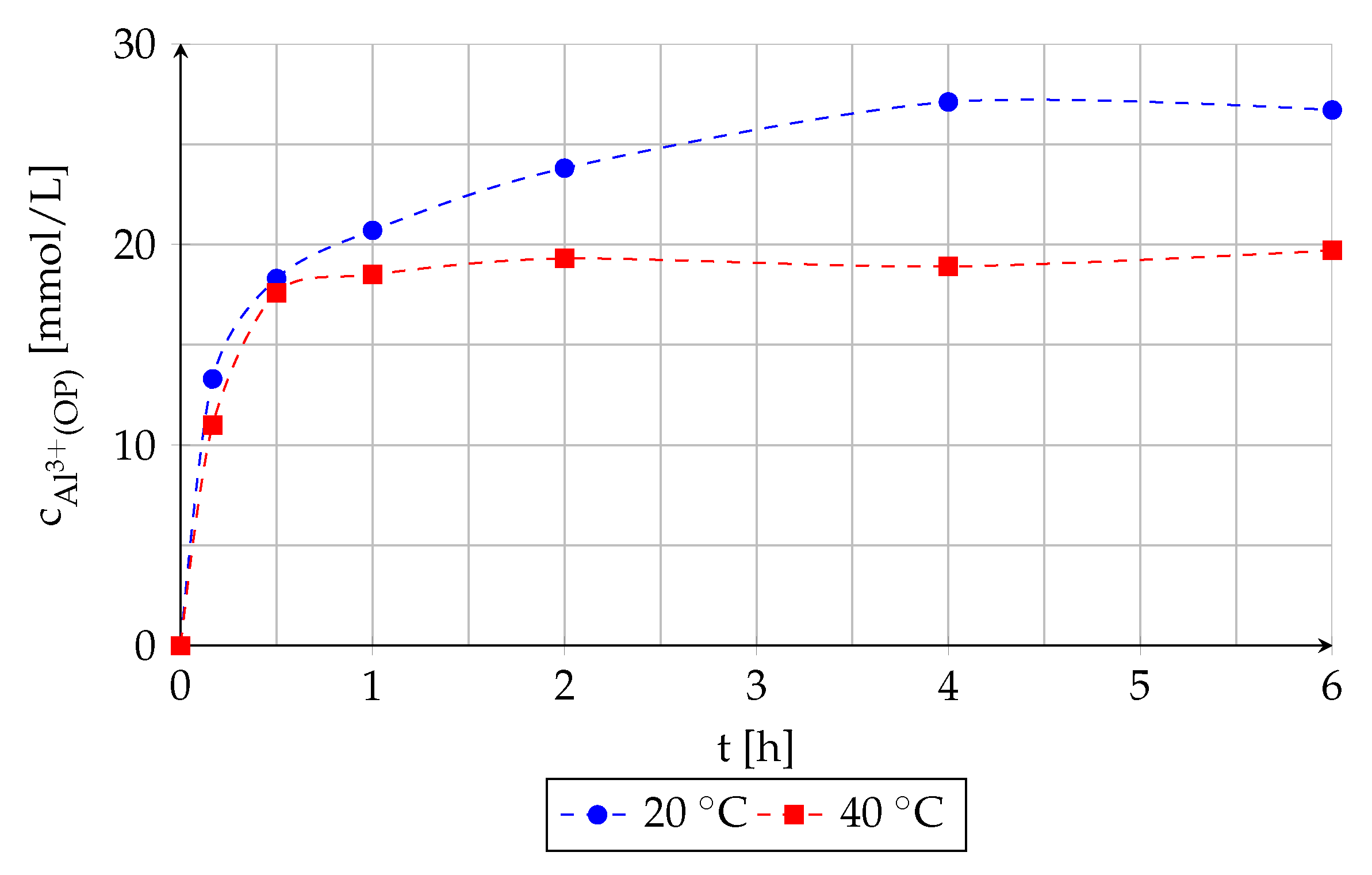
Figure 4 shows the mixture of organic and water phase and corresponding pH values of the raffinate during aluminum extraction as a function of shaking time and extraction temperature.
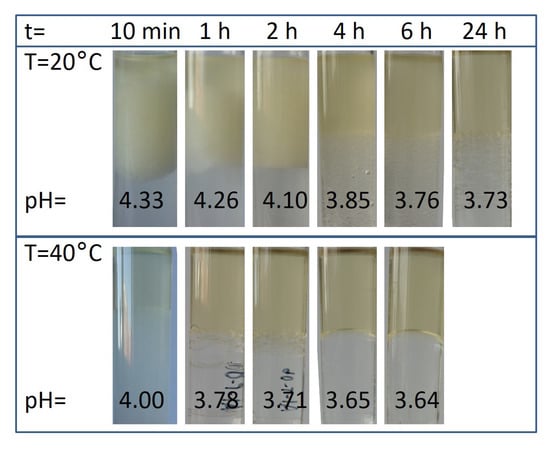
Figure 4.
Effect of shaking time and extraction temperature on the equilibrium pH of the aqueous phase and phase separation.
The observations during these investigations indicate that at the beginning of the extraction at room temperature the pH value of the aqueous phase increases strongly from approx. 1.00 to 4.33 and an emulsification occurs. Moreover, both phases become turbid and the rate of phase separation is slow. An extension of shaking time leads to the decrease in pH value of raffinate, to the receding of the emulsion and to the improvement in phase separation. Conducting the extraction at higher temperatures accelerate the processes.
The strong increase in pH value at the beginning of the extraction indicates that the rate of decomposition of the microemulsion occurs much faster than the rate of aluminum extraction. This statement confirms the measured aluminum concentration in organic phase in dependence of extraction time outlined in Figure 5. The complete aluminum extraction at room temperature takes approximately 4 h. The increase in extraction temperature accelerates the receding of the emulsion, however, lower amounts of aluminum ions are extracted probably because of the evaporation of ammonia.

Figure 5.
Kinetics of Al extraction (experiment (3)).
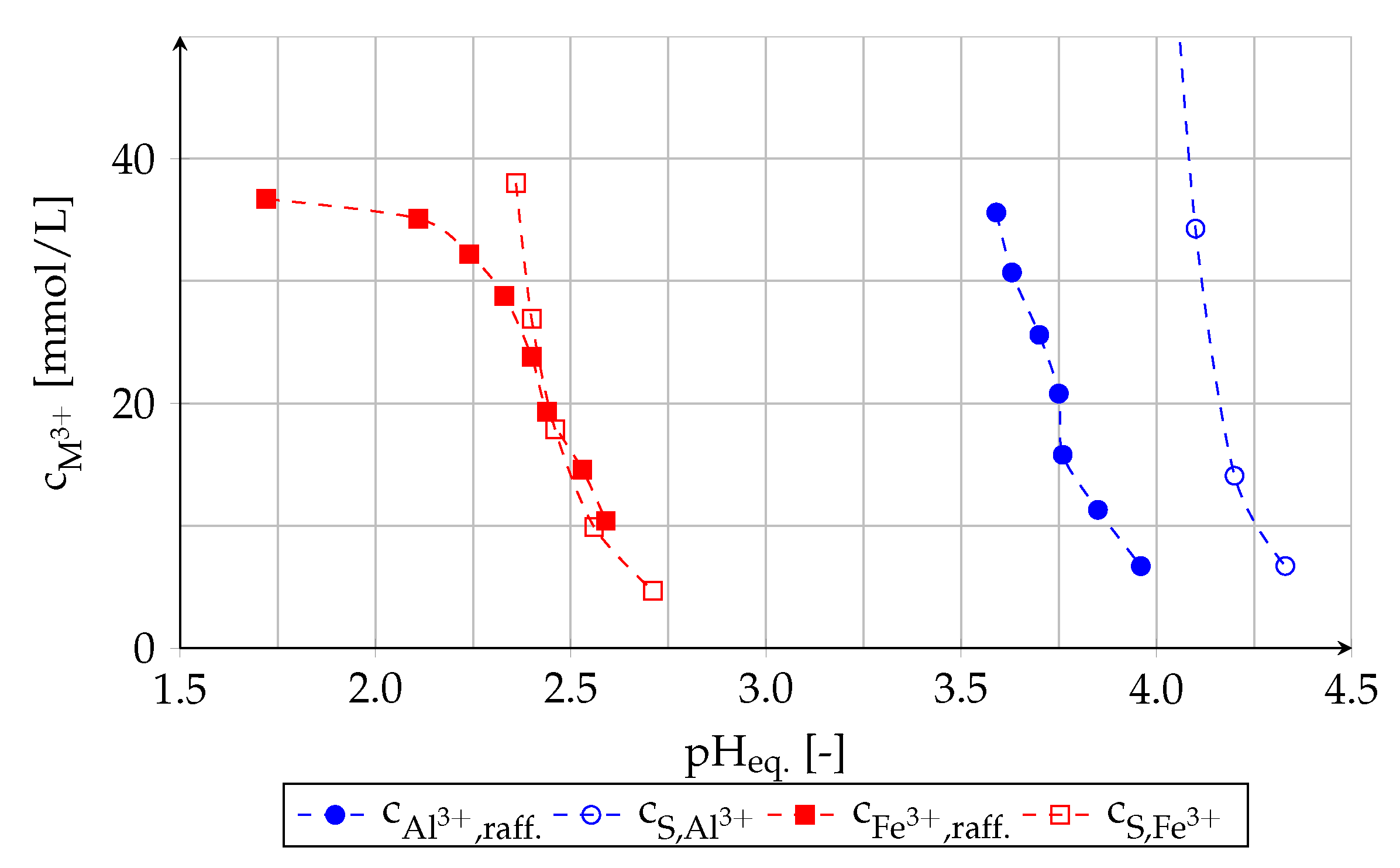
Due to the slow rate of aluminum extraction the pH value of the raffinate becomes higher than 4 at the beginning of the process. In this pH range the hydrolysis of aluminum ions takes place (Equation (5) [37]); soluble as well as insoluble hydroxides are formed. The solubility (c) of aluminum ions, which was determined in preliminary experiments, decreases strongly above a pH value of 4 (Figure 6).
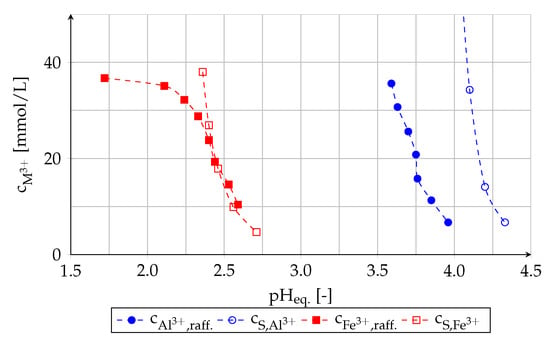
Figure 6.
Concentration of aluminum and iron in the raffinate at the equilibrium (c = 39 mmol/L; c = 36 mmol/L) and solubility of metal ions determined in preliminary experiments.
The emulsification can be therefore explained by the strong increase in the pH value at the beginning of the extraction and by the resulting hydrolysis of aluminum ions. The key conclusion is that the emulsification can be avoided by strict controlling of the pH value during the extraction (e.g., by slowly adding the organic phase) or by lowering of the pH value (e.g., by modification of the composition of organic and aqueous phase).
Another important point which has to be considered during the aluminum extraction is the viscosity of the loaded organic phase. Table 5 provides determined values for the kinematic viscosity and for the density of the loaded organic phase depending on the aluminum concentration.

Table 5.
Effect of concentration of aluminum ions on kinematic viscosity and density of organic phase.
The kinematic viscosity of the loaded organic phase increases strongly with aluminum concentration. At a concentration of about 60 mmol/L the viscosity of the organic phase becomes approximately 20 times higher than that of the unloaded organic phase. Moreover, the organic phase becomes gelatinous. Hence the maximum loading capacity of organic phase is limited by the strong increase in its viscosity and by gelling. According to Wang et al. (2018) [24], the maximum loading capacity of saponified naphthenic acid with aluminum is 1.82 g/L (67 mmol/L) without mentioning of gelation of the organic phase. The exact composition of the organic phase is not given in the publication. Future work should therefore include investigations of the effect of the composition of the organic phase on its viscosity.
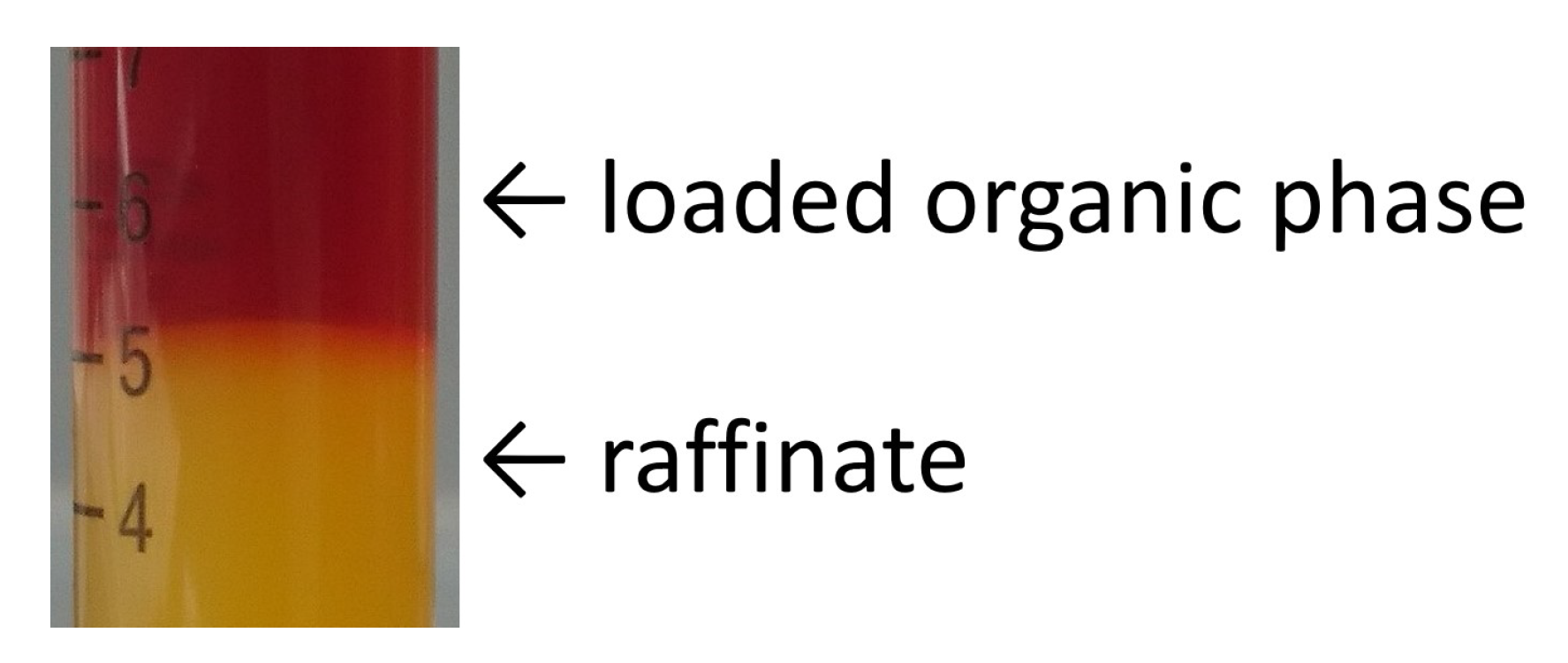
Regarding the iron extraction, a formation of emulsion and a slow rate of phase separation do not occur. However, the pH value of the raffinate overlaps with the pH range at which hydrolysis of iron ions occurs (see Figure 6). The iron solubility curve and the concentration of iron in raffinate are very close to each other. At too high amount of iron remaining in the raffinate sparingly soluble oxides/hydroxides are formed and iron precipitates (Figure 7).
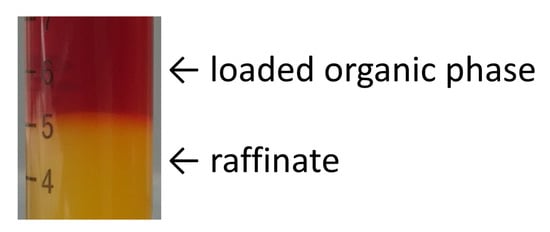
Figure 7.
Precipitation of iron oxides/hydroxides from the raffinate at pH = 2.88 (c = 36 mmol/L).
This implies that a complete iron removal from concentrated solutions cannot be achieved in one extraction stage due to the iron precipitation.
3.4. Removal of Aluminum and Iron from Binary-Component Solutions
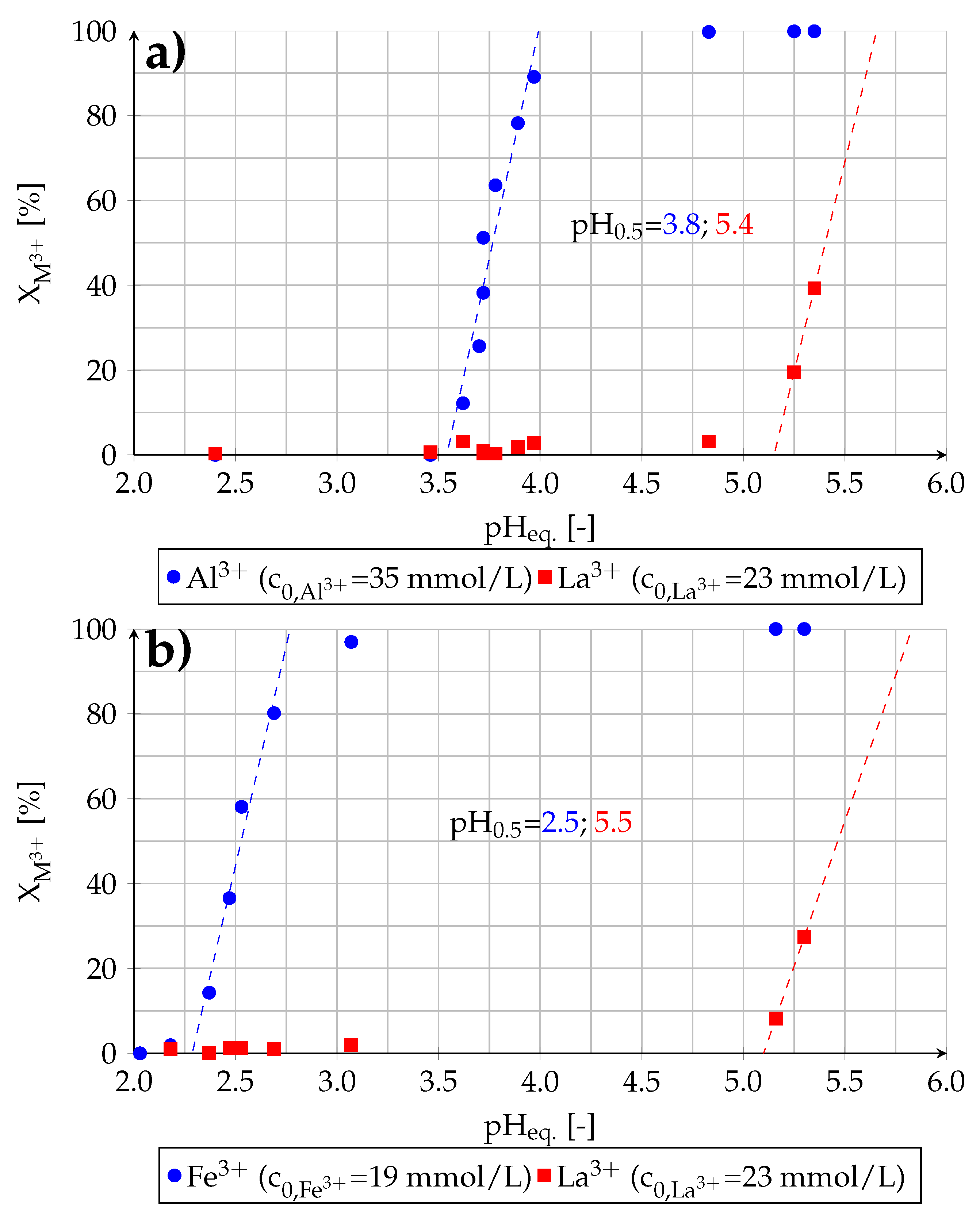
In this section the effect of the presence of lanthanum on the extractability of aluminum and iron in binary-component solutions is examined. The determined extraction yields in dependence of the equilibrium pH value are shown in Figure 8.
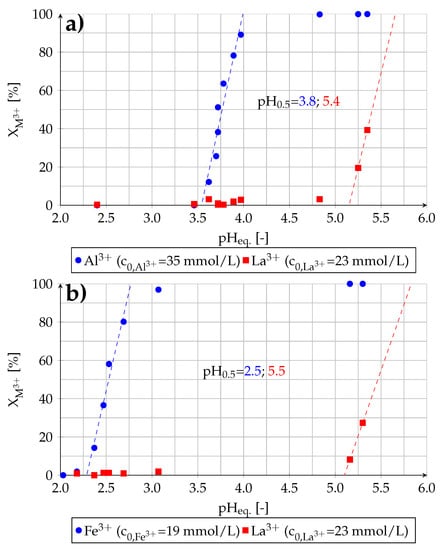
Figure 8.
Removal of (a) aluminum and (b) iron from binary-component solutions by solvent extraction (experiment (4)).
The presence of lanthanum in the solution does not affect the extractability of impurities. The determined pH values for the extraction of aluminum (pH = 3.8), iron (pH = 2.5) and lanthanum (pH = 5.4; 5.5) are comparable with the values obtained in experiments with single-component solutions (see Section 3.2).
3.5. Removal of Aluminum and Iron from Ternary-Component Solutions
In this section the removal of aluminum and iron from ternary-component solutions by solvent extraction and by hydrolysis-precipitation is investigated. The results are shown in Figure 9.
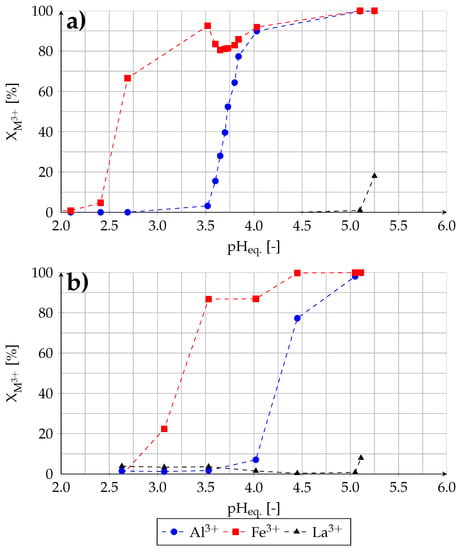
Figure 9.
Removal of aluminum and iron from ternary-component solutions (a) by solvent extraction (experiment (5)) and (b) by hydrolysis-precipitation.
As demonstrated in Figure 9a, the iron extraction is affected by the aluminum extraction. The extraction yields of iron drop after an increase to about 80% and then rise gradually with aluminum extraction up to an aluminum extraction yield of approx. 90%. The incomplete iron extraction can lead to iron oxides/hydroxides precipitation when the iron concentration in the raffinate is higher than its solubility at corresponding pH value. Up to a pH value of about 4.0 aluminum is extracted without noteworthy co-extraction of lanthanum. However, at an equilibrium pH value of about 3.7 the emulsion is formed which does not recede even after long shaking time. It can be therefore concluded that the loading capacity of organic phase is lower by the simultaneous extraction of iron and aluminum.
In comparison to the solvent extraction method, iron and aluminum are removed by the hydrolysis-precipitation at higher pH values (Figure 9b). First, above a pH value of 2.6 iron oxides/hydroxides and above 4.0 aluminum hydroxides precipitate. At a pH value of 5.05 high amounts of aluminum and iron can be removed from the solution without noteworthy losses of lanthanum; further increase in pH value causes co-precipitation of lanthanum. The concentrations of aluminum and iron at a pH value of 5.05 drop to 15.8 and 0.2 mg/L, respectively (Table 6). Nevertheless, in comparison to the solvent extraction the amounts of remained impurities in the solution are higher, especially regarding aluminum.

Table 6.
Comparison of purity of the raffinate and the losses of lanthanum.
4. Conclusions
This paper investigates the following issues: (i) solvent extraction of aluminum, iron and lanthanum by saponified naphthenic acid; (ii) separation of aluminum and iron from lanthanum from binary-component solutions by solvent extraction with saponified naphthenic acid; (iii) separation of aluminum and iron from lanthanum from ternary-component solutions by solvent extraction with saponified naphthenic acid and by hydrolysis-precipitation.
The results show that the aluminum and iron removal by the solvent extraction with saponified naphthenic acid has limitations. Both can be simultaneously separated from REEs represented by lanthanum without emulsification and precipitation of metal oxides/hydroxides only from diluted solutions. Nevertheless, in comparison to the hydrolysis-precipitation method, the amounts of remaining impurities are lower, especially regarding aluminum. In case of the high concentrations of aluminum and iron in starting solutions, a high-purity REE solution can be produced in two stages. In a first step, the solution is pre-purified by hydrolysis-precipitation followed by the solvent extraction step with saponified naphthenic acid.
Author Contributions
Conceptualization, A.B.; methodology, A.B. and N.K.; validation, N.K., C.M. and M.A.R.; investigation, A.B.; resources, A.B.; data curation, A.B.; writing—original draft preparation, A.B.; writing—review and editing, N.K., C.M. and T.H.; supervision, M.A.R. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This research was funded by the BMBF (Federal Ministry of Education and Research, Germany); funding number: 033R132A.
Acknowledgments
The authors thank Stefanie Schubert (Helmholtz Institute Freiberg for Resource Technology) for the chemical analysis of liquid phases.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest. The funders had no role in the design of the study; in the collection, analyses, or interpretation of data; in the writing of the manuscript, or in the decision to publish the results.
Abbreviations
The following abbreviations are used in this manuscript:
| AN | acid number |
| mass concentration | |
| c | molar concentration |
| c | solubility |
| NA | naphthenic acid |
| REEs | rare earth elements |
| PR | phase ratio |
| SAP | saponification value |
| X | extraction yield |
References
- Charalampides, G.; Vatalis, K.I.; Apostoplos, B.; Ploutarch-Nikolas, B. Rare Earth Elements: Industrial Applications and Economic Dependency of Europe. Procedia Econ. Financ. 2015, 24, 126–135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hoshino, M.; Sanematsu, K.; Watanabe, Y. Chapter 279—REE Mineralogy and Resources. In Handbook on the Physics and Chemistry of Rare Earths; Jean-Claude, B., Pecharsky, V.K., Eds.; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2016; pp. 129–291. [Google Scholar]
- Mariano, A.N. Economic Geology of Rare Earth Minerals. Rev. Mineral. 1989, 21, 309–337. [Google Scholar]
- Massari, S.; Ruberti, M. Rare earth elements as critical raw materials: Focus on international markets and future strategies. Resour. Policy 2013, 38, 36–43. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pourret, O.; Tuduri, J. Continental shelves as potential resource of rare earth elements. Sci. Rep. 2017, 7, 5857. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Binnemans, K.; Jones, P.T.; Van Gerven, T.; Yang, Y.; Walton, A.; Buchert, M. Recycling of rare earths: A critical review. J. Clean. Prod. 2013, 51, 1–22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Krishnamurthy, N.; Gupta, C.K. Extractive Metallurgy of Rare Earths; CRC Press: Boca Raton, FL, USA, 2015. [Google Scholar]
- Yang, X.J.; Lin, A.; Li, X.-L.; Wu, Y.; Zhou, W.; Chen, Z. China’s ion-adsorption rare earth resources, mining consequences and preservation. Environ. Dev. 2013, 8, 131–136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Josso, P.; Roberts, S.; Teagle, D.A.H.; Pourret, O.; Herrington, R.; Ponce de Leon Albarran, C. Extraction and separation of rare earth elements from hydrothermal metalliferous sediments. Miner. Eng. 2018, 188, 106–121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fujimoto, J.; Tanaka, K.; Watanabe, N.; Takahashi, Y. Simultaneous recovery and separation of rare earth elements in ferromanganese nodules by using Shewanella putrefaciens. Hydrometallurgy 2016, 166, 80–86. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Balinski, A.; Atanasova, P.; Wiche, O.; Kelly, N.; Reuter, M.A.; Scharf, C. Recovery of REEs, Zr(+Hf), Mn and Nb by H2SO4 leaching of eudialyte concentrate. Hydrometallurgy 2019, 186, 176–186. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Emsbo, P.; McLaughlin, P.I.; Breit, G.N.; du Bray, E.A.; Koenig, A.E. Rare earth elements in sedimentary phosphate deposits: Solution to the global REE crisis? Gondwana Res. 2015, 27, 776–785. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vahidi, E.; Navarro, J.; Zha, F. An initial life cycle assessment of rare earth oxides production from ion-adsorption clays. Resour. Conserv. Recycl. 2016, 113, 1–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Balinski, A.; Atanasova, P.; Wiche, O.; Kelly, N.; Reuter, M.A.; Scharf, C. Selective Leaching of Rare Earth Elements (REEs) from Eudialyte Concentrate after Sulfation and Thermal Decomposition of Non-REE Sulfates. Minerals 2019, 9, 522. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bisaka, K.; Thobadi, I.C.; Pawlik, C. Extraction of rare earths from iron-rich rare earth deposits. J. South. Afr. Inst. Min. Metall. 2017, 117, 731–739. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, Y.; Yang, H.; Xue, X.-X.; Yuan, S. Separation and Recovery of Iron and Rare Earth from Bayan Obo Tailings by Magnetizing Roasting and (NH4)2SO4 Activation Roasting. Metals 2017, 7, 195. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qi, D. Chapter 2—Extractants Used in Solvent Extraction-Separation of Rare Earths: Extraction Mechanism, Properties, and Features In Hydrometallurgy of Rare Earths; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2018; pp. 187–389. [Google Scholar]
- Balinski, A.; Wiche, O.; Kelly, N.; Reuter, M.A.; Scharf, C. Separation of rare earth elements from contaminants and valuable components by in situ precipitation during hydrometallurgical processing of eudialyte concentrate. Hydrometallurgy 2020, 194, 105345. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Porvali, A.; Wilson, B.P.; Lundström, M. Lanthanide-alkali double sulfate precipitation from strong sulfuric acid NiMH battery waste leachate. Waste Manag. 2018, 71, 381–389. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chi, R.; Zhou, Z.; Xu, Z.; Hu, Y.; Zhu, G.; Xu, S. Solution-Chemistry Analysis of Ammonium Bicarbonate Consumption in Rare-Earth-Element Precipitation. Metall. Mater. Trans. B 2003, 34, 611–617. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gergoric, M.; Ravaux, C.; Steenari, B.-M.; Espegren, F.; Retegan, T. Leaching and Recovery of Rare-Earth Elements from Neodymium Magnet Waste Using Organic Acids. Metals 2018, 8, 721. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.; Huang, X.; Wang, L.; Wang, Q.; Yan, Y.; Zhao, N.; Cui, D.; Feng, Z. Kinetics study on the leaching of rare earth and aluminum from FCC catalyst waste slag using hydrochloric acid. Hydrometallurgy 2017, 171, 312–319. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, X.; Qiu, T. Influence of aluminum ions distribution on the removal of aluminum from rare earth solutions using saponified naphthenic acid. Sep. Purif. Technol. 2017, 186, 290–296. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Wang, Y.; Su, X.; Zhou, H.; Su, X. Complete separation of aluminium from rare earths using two-stage solvent extraction. Hydrometallurgy 2018, 179, 181–187. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, Z.; Zhang, Z.; Yu, J.; Xu, Z.; Chi, R. Process optimization of rare earth and aluminum leaching from weathered crust elution-deposited rare earth ore with compound ammonium salts. J. Rare Earths 2016, 34, 413–419. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Borra, C.R.; Blanpain, B.; Pontikes, Y.; Binnemans, K.; Van Gerven, T. Recovery of Rare Earths and Other Valuable Metals From Bauxite Residue (Red Mud): A Review. J. Sustain. Metall. 2016, 2, 365–386. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, F.; Feng, J.; Wang, Z.; Xu, Y.; Zhang, Z.; Chi, R. One step purification of impurities in the leachate of weathered crust elution-deposited rare earth ores. Physicochem. Probl. Miner. Process. 2017, 53, 1188–1199. [Google Scholar]
- Zeng, Q.-Y.; Zeng, Q.-Q.; Chang, Q.-Q. On the extraction and separation of rare earth and aluminium in naphthenic acid system. Nonferrous Met. Sci. Eng. 2012, 3, 17–19. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, Y.; Li, J.; Gao, Y.; Yang, Y.; Gao, Y.; Xu, Z. Removal of aluminum from rare-earth leaching solutions via a complexation-precipitation process. Hydrometallurgy 2020, 191, 105220. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, J.; Gao, Y.; Gao, Y.; Chen, Z.; Wang, R.; Xu, Z. Study on aluminum removal through 5-sulfosalicylic acid targeting complexing and D290 resin adsorption. Miner. Eng. 2020, 147, 106175. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, J.; Zhao, B.; Schreiner, B. Separation Hydrometallurgy of Rare Earth Elements; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2016. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, K.; Wang, Z.; Tang, X.; Lu, S. Extraction of yttrium using naphthenic acid with different acid numbers. Sep. Sci. Technol. 2016, 51, 2804–2814. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ling, C.; Liu, Z.; Yang, J.; Chen, H.; Han, Q. Method for Removing Aluminum from Rare-Earth Feed Liquid. Chinese Patent CN2010105477201A, 17 November 2010. [Google Scholar]
- Zhao, Z.; Xing, Q.; Liu, J.; Sang, X.; Guo, X.; Zhao, Z.; Zhang, W.; Li, X.; Wang, X.; Jiang, D.; et al. Method for Removing Aluminum in Rare-Earth Solution. Chinese Patent CN103146921B, 24 December 2014. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, D.; Wu, J.; Xu, D.; Yang, H.; Dong, B. Aggregation of organic phase of saponified naphthenic acid extraction system and its application in preparation of ultrafine particles. Sci. Technol. 1996, 32, 2393–2400. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Preston, J.S. Solvent extraction of metals by carboxylic acids. Hydrometallurgy 1985, 14, 177–188. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gindin, L.M.; Bobikov, P.I.; Kouba, E.F.; Bugaeva, A.V. On the Reactions of the Aluminium Ion with Water. Acta Chem. Scand. 1952, 6, 910–940. [Google Scholar]
© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).