Structural Characterization and Adsorption Capability of Carbonaceous Matters Extracted from Carbonaceous Gold Concentrate
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Sample
2.2. Reagents
2.3. Extraction of Carbonaceous Matters
2.3.1. Extraction of ECE
2.3.2. Extraction of HAE
2.4. Gold-Adsorbing Experiments
2.5. Analytical Methods
3. Result and Discussion
3.1. Quantification of Extracted ECE and HAE
3.2. Structural Characterization of Carbonaceous Matters
3.2.1. Elemental Analysis and Atomic Ratios
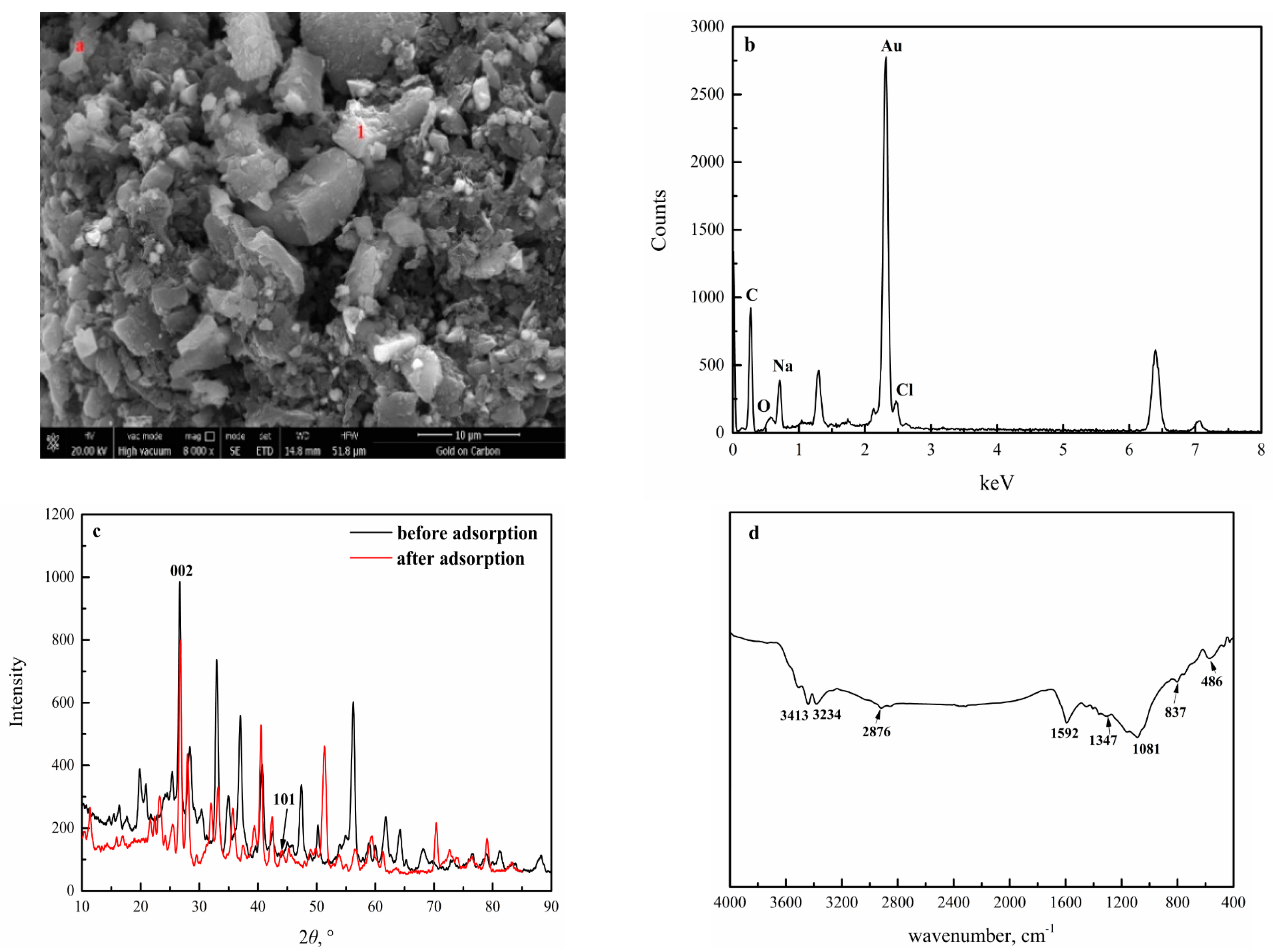
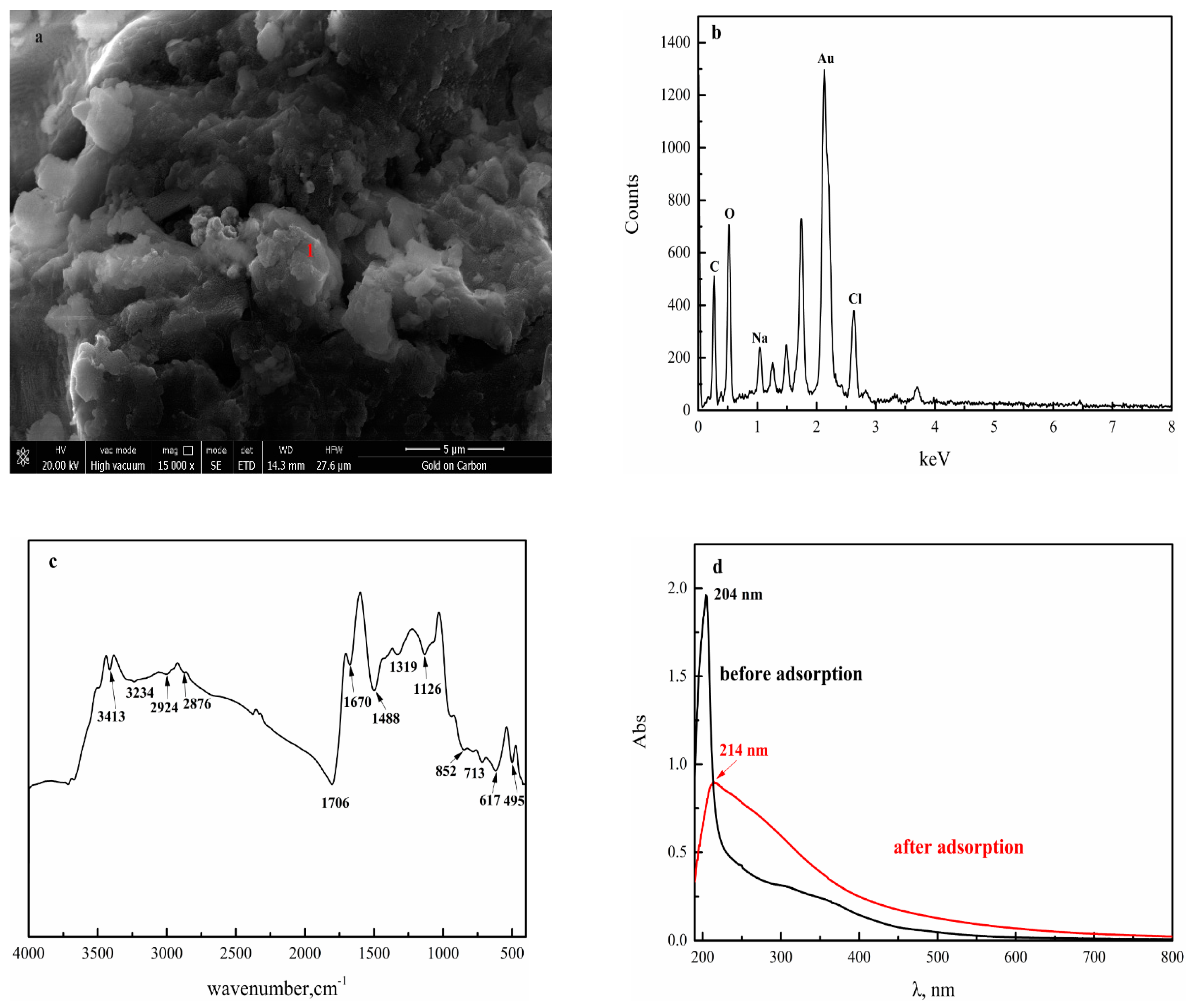
3.2.2. SEM Analysis
3.2.3. BET Area and Pore Analysis
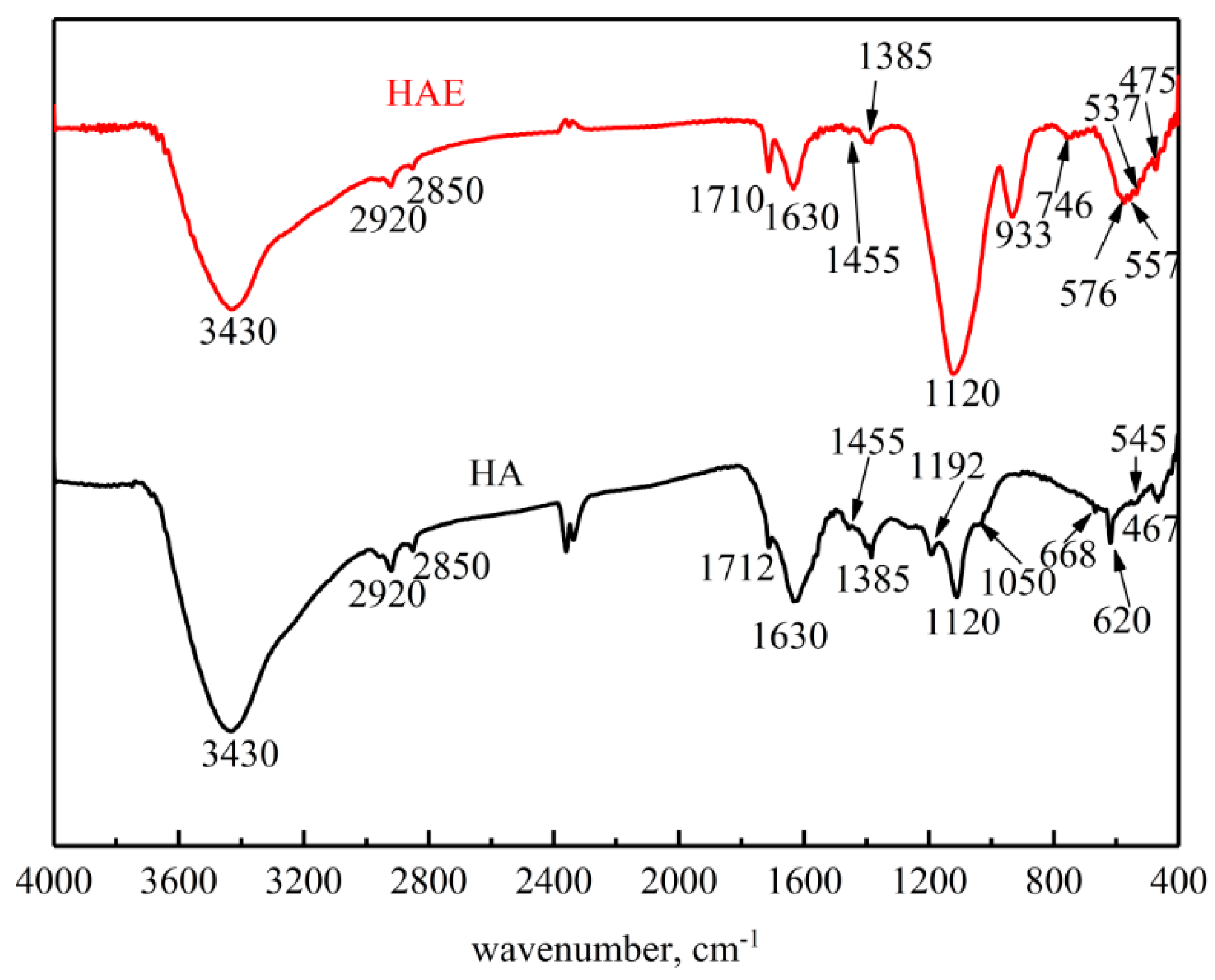
3.2.4. FTIR Analysis
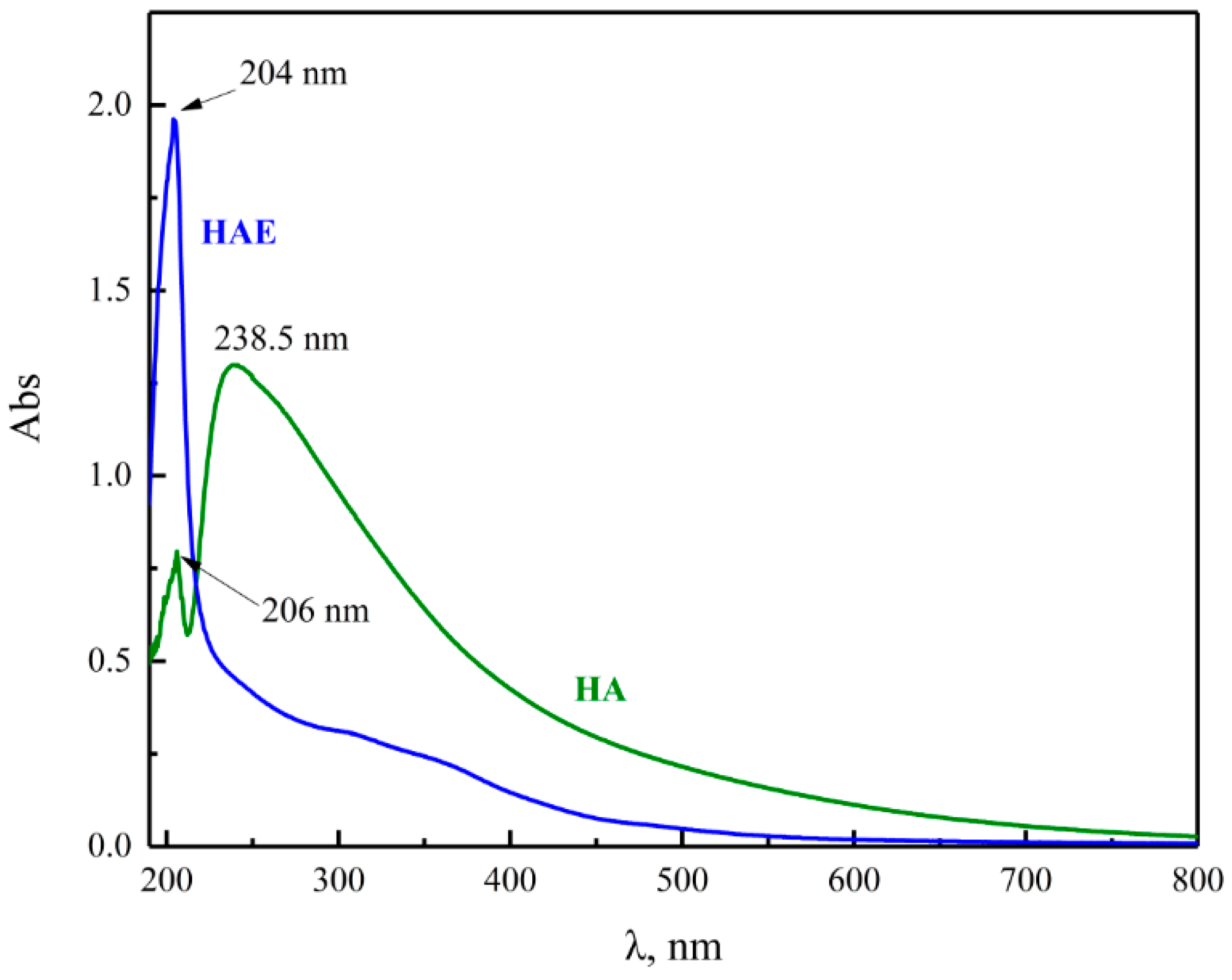
3.2.5. UV–VIS Analysis of HAE
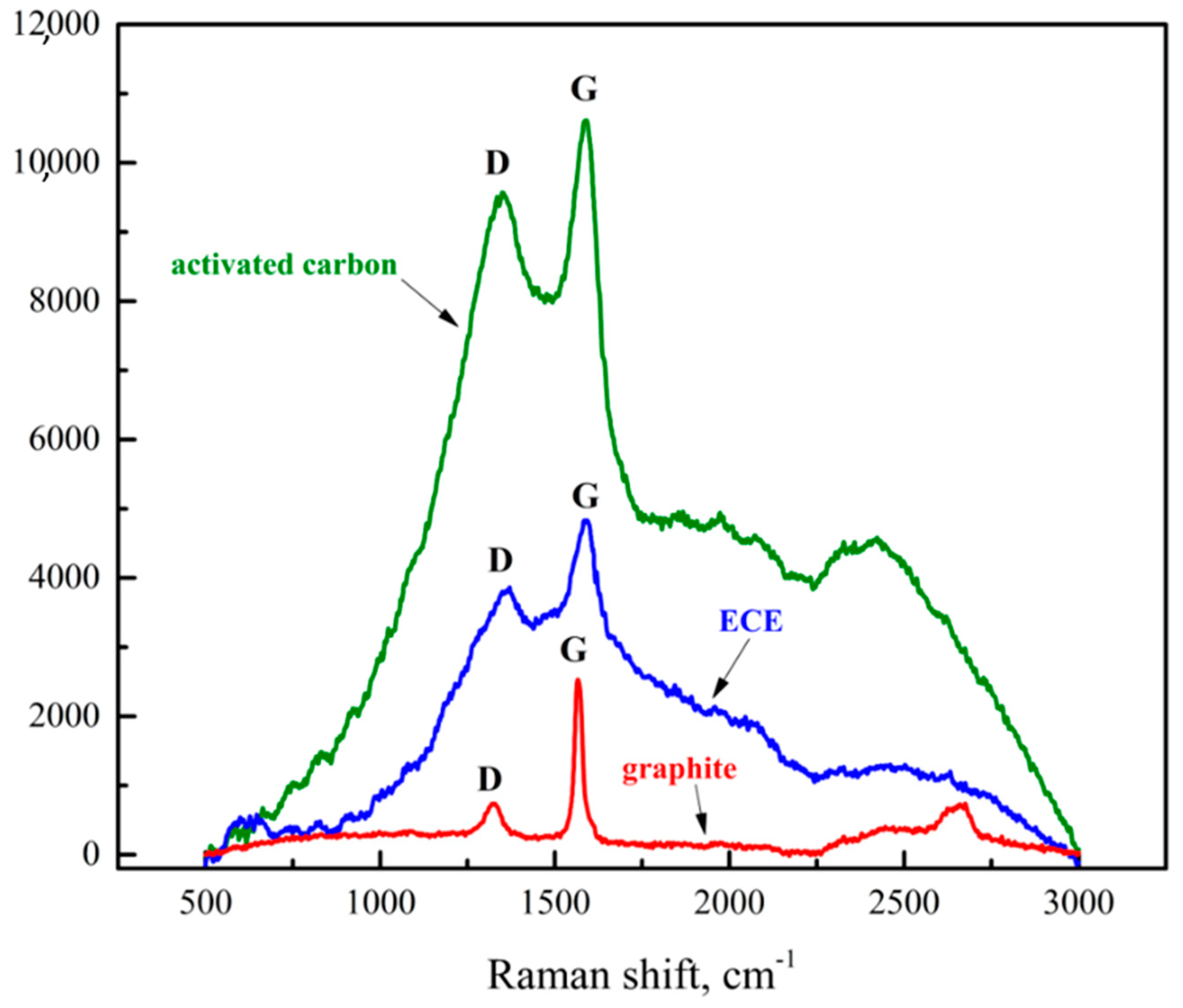
3.2.6. XRD and Raman Spectra Analysis of ECE
3.3. Gold-Adsorbing Experiments
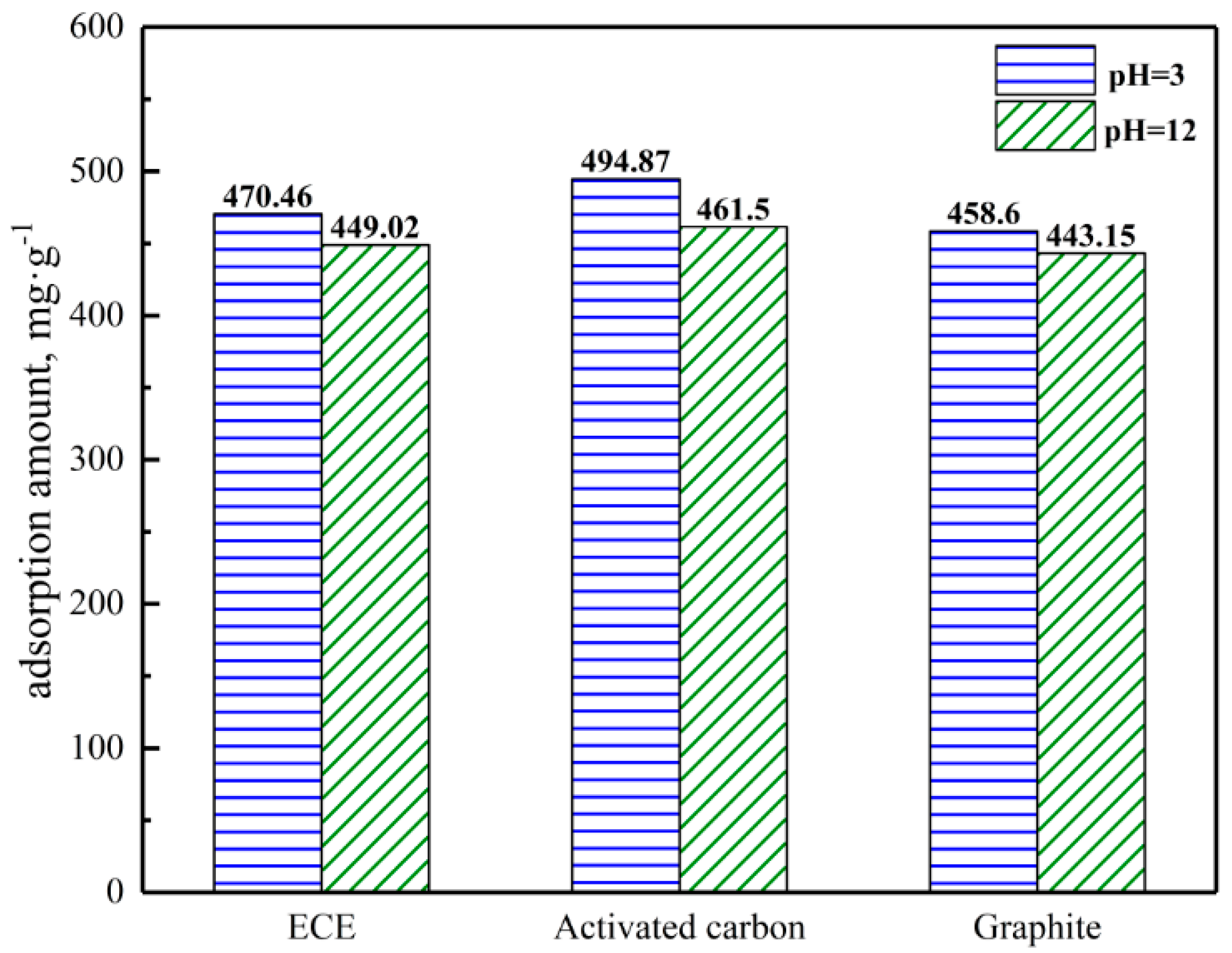
3.3.1. Gold-Adsorbing of ECE
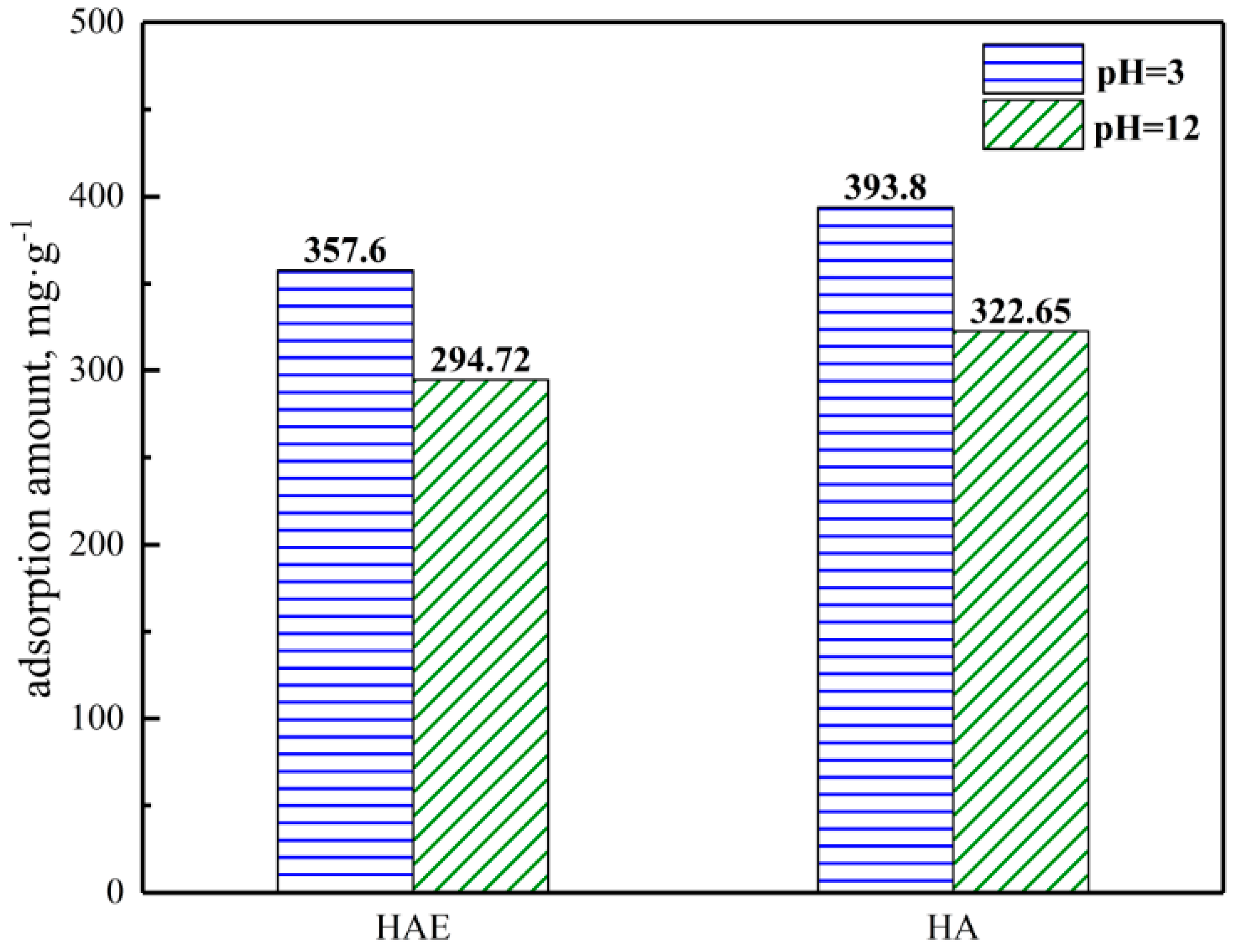
3.3.2. Gold-Adsorbing of HAE
3.3.3. Adsorption Process
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Rees, K.L.; Van Deventer, J.S.J. Preg-robbing phenomena in the cyanidation of sulphide gold ores. Hydrometallurgy 2000, 58, 61–80. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Q.; Yang, H.Y.; Tong, L.L.; Jin, Z.N.; Sand, W. Fungal degradation of elemental carbon in Carbonaceous gold ore. Hydrometallurgy 2016, 160, 90–97. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pyke, B.L.; Johnston, R.F.; Brooks, P. Characterisation and behaviour of carbonaceous material in a refractory gold bearing ore. Miner. Eng. 1999, 12, 851–862. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kwiecinska, B.; Suárez-Ruiz, I.; Paluszkiewicz, C.; Rodriques, S. Raman spectroscopy of selected carbonaceous samples. Int. J. Coal Geol. 2010, 84, 206–212. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Adams, M.D.; Swaney, S.J.; Friedl, J.J.; Wagner, F.E.J. Preg-robbing Minerals in Gold Ores and Residues. In Hidden Wealth; South African Inst of Mining & Metallurgy: Johannesburg, South Africa, 1996; pp. 163–172. [Google Scholar]
- Schmitz, P.A.; Duyvesteyn, S.; Johnson, W.P.; Enloe, L.; McMullen, J. Adsorption of aurocyanide complexes onto carbonaceous matter from preg-robbing Goldstrike ore. Hydrometallurgy 2001, 61, 121–135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martyniuk, H.; Wiȩckowska, J. Adsorption of metal ions on humic acids extracted from brown coals. Fuel Process. Technol. 2003, 84, 23–36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- HE, M.; SHI, Y.; LIN, C. Characterization of humic acids extracted from the sediments of the various rivers and lakes in China. J. Environ. Sci. 2008, 20, 1294–1299. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, C.; Wang, X.; Jiang, H.; Hu, W. Direct observation of macromolecular structures of humic acid by AFM and SEM. Colloids Surfaces A Physicochem. Eng. Asp. 2007, 302, 121–125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grinhut, T.; Hadar, Y.; Chen, Y. Degradation and transformation of humic substances by saprotrophic fungi: Processes and mechanisms. Fungal Biol. Rev. 2007, 21, 179–189. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rodríguez, F.J.; Schlenger, P.; García-Valverde, M. A comprehensive structural evaluation of humic substances using several fluorescence techniques before and after ozonation. Part I: Structural characterization of humic substances. Sci. Total Environ. 2014, 476–477, 718–730. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Doskočil, L.; Burdíková-Szewieczková, J.; Enev, V.; Kalina, L.; Wasserbauer, J. Spectral characterization and comparison of humic acids isolated from some European lignites. Fuel 2018, 213, 123–132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Uyguner, C.S.; Bekbolet, M. Evaluation of humic acid photocatalytic degradation by UV-vis and fluorescence spectroscopy. Catal. Today 2005, 101, 267–274. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Katsumata, H.; Sada, M.; Kaneco, S.; Suzuki, T.; Ohta, K.; Yobiko, Y. Humic acid degradation in aqueous solution by the photo-Fenton process. Chem. Eng. J. 2008, 137, 225–230. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Adams, M.D. The mechanism of adsorption of aurocyanide onto activated carbon, 1. Relation between the effects of oxygen and ionic strength. Hydrometallurgy 1990, 25, 171–184. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Giovanela, M.; Crespo, J.S.; Antunes, M.; Adamatti, D.S.; Fernandes, A.N.; Barison, A.; Da Silva, C.W.P.; Guégan, R.; Motelica-Heino, M.; Sierra, M.M.D. Chemical and spectroscopic characterization of humic acids extracted from the bottom sediments of a Brazilian subtropical microbasin. J. Mol. Struct. 2010, 981, 111–119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Garcia, C.; Hernandez, T.; Costa, F.; del Rio, J.C. Study of the lipidic and humic fractions from organic wastes before and after the composting process. Sci. Total Environ. 1989, 81–82, 551–560. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Du, J.; Zhang, F.; Yu, Y.; Zhang, J. Chemical characterization of humic substances isolated from mangrove swamp sediments: The Qinglan area of Hainan Island, China. Estuar. Coast. Shelf Sci. 2011, 93, 220–227. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, X.Q.; Hanna, J.V.; Johnson, W.D. Source indicators of humic substances: An elemental composition, solid state 13C CP/MAS NMR and Py-GC/MS study. Appl. Geochem. 2000, 15, 1019–1033. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Polak, J.; Sułkowski, W.W.; Bartoszek, M.; Papiez, W. Spectroscopic studies of the progress of humification processes in humic acid extracted from sewage sludge. J. Mol. Struct. 2005, 744, 983–989. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ofori-Sarpong, G.; Amankwah, R.K.; Osseo-Asare, K. Reduction of preg-robbing by biomodified carbonaceous matter-A proposed mechanism. Miner. Eng. 2013, 42, 29–35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saka, C. BET, TG-DTG, FT-IR, SEM, iodine number analysis and preparation of activated carbon from acorn shell by chemical activation with ZnCl2. J. Anal. Appl. Pyrolysis 2012, 95, 21–24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alvarez-Puebla, R.A.; Goulet, P.J.G.; Garrido, J.J. Characterization of the porous structure of different humic fractions. Colloids Surfaces A Physicochem. Eng. Asp. 2005, 256, 129–135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, Y.; Bustin, R.M. Micro-FTIR spectroscopy of liptinite macerals in coal. Int. J. Coal Geol. 1998, 36, 259–275. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Drobniak, A.; Mastalerz, M. Chemical evolution of Miocene wood: Example from the Belchatow brown coal deposit, central Poland. Int. J. Coal Geol. 2006, 66, 157–178. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Petersen, H.I.; Rosenberg, P.; Nytoft, H.P. Oxygen groups in coals and alginite-rich kerogen revisited. Int. J. Coal Geol. 2008, 74, 93–113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, H.; Yan, R.; Chen, H.; Lee, D.H.; Zheng, C. Characteristics of hemicellulose, cellulose and lignin pyrolysis. Fuel 2007, 86, 1781–1788. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Esteves, V.I.; Otero, M.; Duarte, A.C. Comparative characterization of humic substances from the open ocean, estuarine water and fresh water. Org. Geochem. 2009, 40, 942–950. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- See, J.H.; Bronk, D.A. Changes in C:N ratios and chemical structures of estuarine humic substances during aging. Mar. Chem. 2005, 97, 334–346. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Amir, S.; Jouraiphy, A.; Meddich, A.; El Gharous, M.; Winterton, P.; Hafidi, M. Structural study of humic acids during composting of activated sludge-green waste: Elemental analysis, FTIR and 13C NMR. J. Hazard. Mater. 2010, 177, 524–529. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gondar, D.; Lopez, R.; Fiol, S.; Antelo, J.M.; Arce, F. Characterization and acid-base properties of fulvic and humic acids isolated from two horizons of an ombrotrophic peat bog. Geoderma 2005, 126, 367–374. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, S.; Yuan, L.; Li, W.; Lin, Z.; Li, Y.; Hu, S.; Zhao, B. Characterization of pH-fractionated humic acids derived from Chinese weathered coal. Chemosphere 2017, 166, 334–342. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.; Yue, Q.; Gao, B. Adsorption kinetics and desorption of Cu(II) and Zn(II) from aqueous solution onto humic acid. J. Hazard. Mater. 2010, 178, 455–461. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, X.; Hou, Y.; Li, Z.; Yu, Z.; Tang, J.; Wang, Y.; Zhou, S. Hyperthermophilic composting of sewage sludge accelerates humic acid formation: Elemental and spectroscopic evidence. Waste Manag. 2020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huculak-Mączka, M.; Hoffmann, J.; Hoffmann, K. Evaluation of the possibilities of using humic acids obtained from lignite in the production of commercial fertilizers. J. Soils Sediments 2018, 18, 2868–2880. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Hanc, A.; Enev, V.; Hrebeckova, T.; Klucakova, M.; Pekar, M. Characterization of humic acids in a continuous-feeding vermicomposting system with horse manure. Waste Manag. 2019, 99, 1–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aranganathan, L.; Rajasree, S.R.R.; Suman, T.Y.; Remya, R.R.; Gayathri, S.; Jayaseelan, C.; Karthih, M.G.; Gobalakrishnan, M. Comparison of molecular characteristics of Type A humic acids derived from fish waste and sugarcane bagasse co-compost influenced by various alkaline extraction protocols. Microchem. J. 2019, 149, 104038. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peuravuori, J.; Pihlaja, K. Molecular size distribution and spectroscopic properties of aquatic humic substances. Anal. Chim. Acta 1997, 337, 133–149. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lipski, M.; Sławiński, J.; Zych, D. Changes in the Luminescent Properties of Humic Acids Induced by UV Radiation. J. Fluoresc. 1999, 9, 133–138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thomsen, M.; Lassen, P.; Dobel, S.; Hansen, P.E.; Carlsen, L.; Mogensen, B.B. Characterisation of humic materials of different origin: A multivariate approach for quantifying the latent properties of dissolved organic matter. Chemosphere 2002, 49, 1327–1337. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, J.; Gu, B.; LeBoeuf, E.J.; Pan, H.; Dai, S. Spectroscopic characterization of the structural and functional properties of natural organic matter fractions. Chemosphere 2002, 48, 59–68. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Klučáková, M.; Věžníková, K. Micro-organization of humic acids in aqueous solutions. J. Mol. Struct. 2017, 1144, 33–40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tan, H.; Feng, D.; Lukey, G.C.; Van Deventer, J.S.J. The behaviour of carbonaceous matter in cyanide leaching of gold. Hydrometallurgy 2005, 78, 226–235. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stenebråten, J.F.; Johnson, W.P.; McMullen, J. Characterization of Goldstrike ore carbonaceous material—Part 2: Physical characteristics. Miner. Metall. Process. 2000, 17, 7–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ofori-Sarpong, G.; Osseo-Asare, K.; Tien, M. Mycohydrometallurgy: Biotransformation of double refractory gold ores by the fungus, Phanerochaete chrysosporium. Hydrometallurgy 2013, 137, 38–44. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, S.; Evans, K.; Craw, D.; Rempel, K.; Bourdet, J.; Dick, J.; Grice, K. Raman characterization of carbonaceous material in the Macraes orogenic gold deposit and metasedimentary host rocks, New Zealand. Ore Geol. Rev. 2015, 70, 80–95. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Rantitsch, G.; Lämmerer, W.; Fisslthaler, E.; Mitsche, S.; Kaltenböck, H. On the discrimination of semi-graphite and graphite by Raman spectroscopy. Int. J. Coal Geol. 2016, 159, 48–56. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qiu, X.B.; Wen, J.K.; Huang, S.T.; Yang, H.Y.; Liu, M.L.; Wu, B. New insights into the extraction of invisible gold in a low-grade high-sulfur Carlin-type gold concentrate by bio-pretreatment. Int. J. Miner. Metall. Mater. 2017, 24, 1104–1111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cuesta, A.; Dhamelincourt, P.; Laureyns, J.; Martínez-Alonso, A.; Tascón, J.M.D. Comparative performance of X-ray diffraction and Raman microprobe techniques for the study of carbon materials. J. Mater. Chem. 1998, 8, 2875–2879. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Helm, M.; Vaughan, J.; Staunton, W.P.; Avraamides, J. An Investigation of the Carbonaceous Component of Preg-Robbing Gold Ores; The Southern African Institute of Mining and Metallurgy, Gauteng Johannesburg: Johannesburg, South Africa, 2009; pp. 139–141. [Google Scholar]
- Sibrell, P.L.; Miller, J.D. Significance of graphitic structural features in gold adsorption by carbon. Miner. Metall. Process. 1992, 9, 189–195. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Machesky, M.L.; Andrade, W.O.; Rose, A.W. Interactions of gold (III) chloride and elemental gold with peat-derived humic substances. Chem. Geol. 1992. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
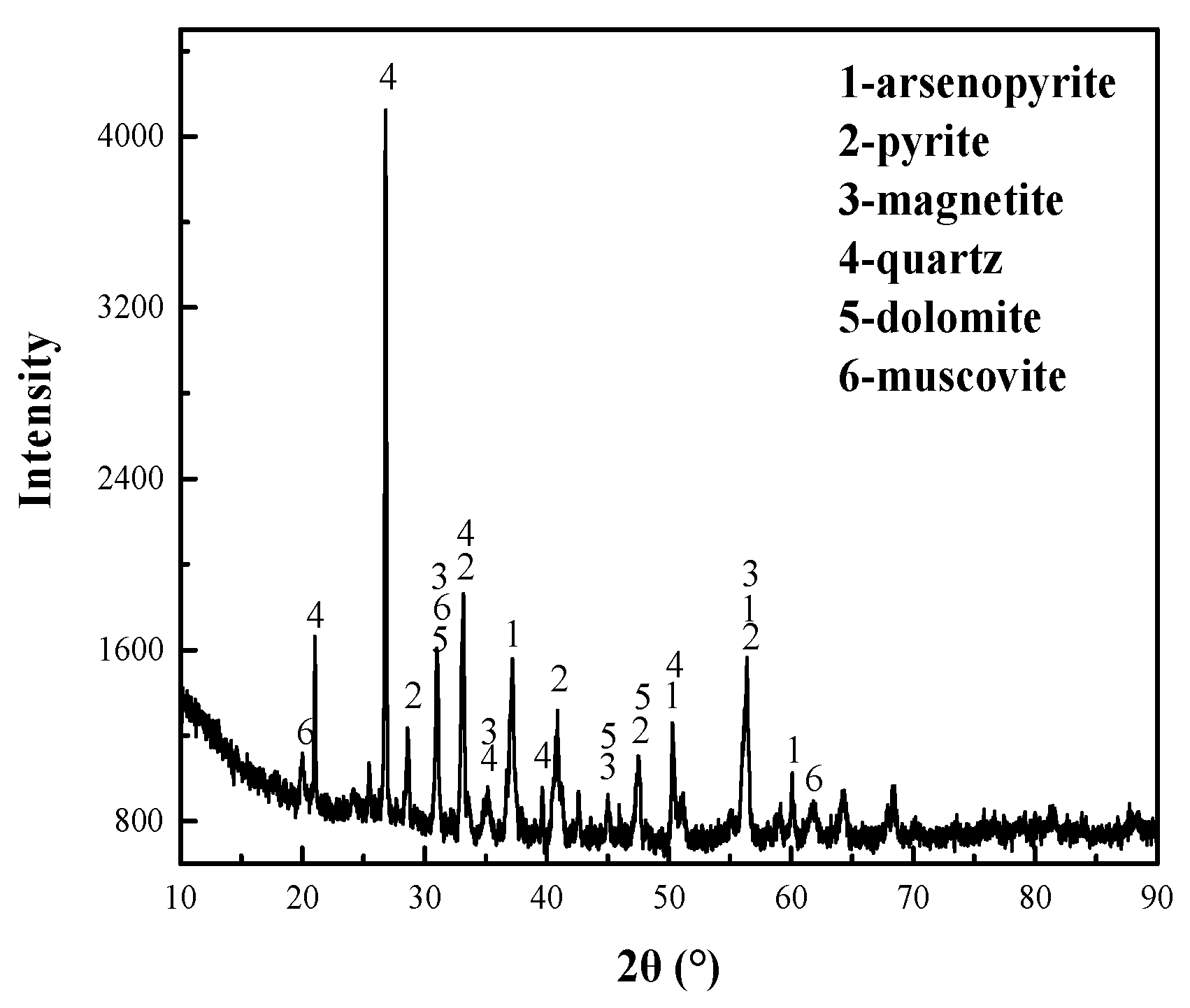
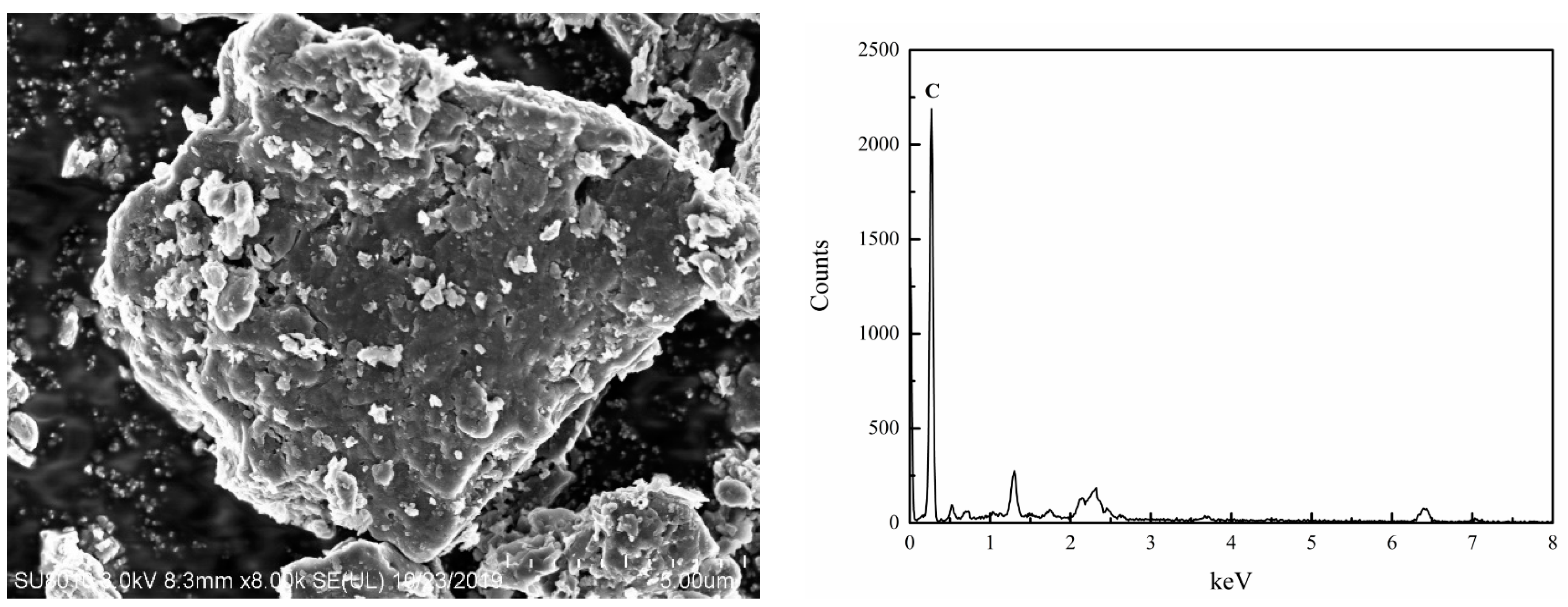
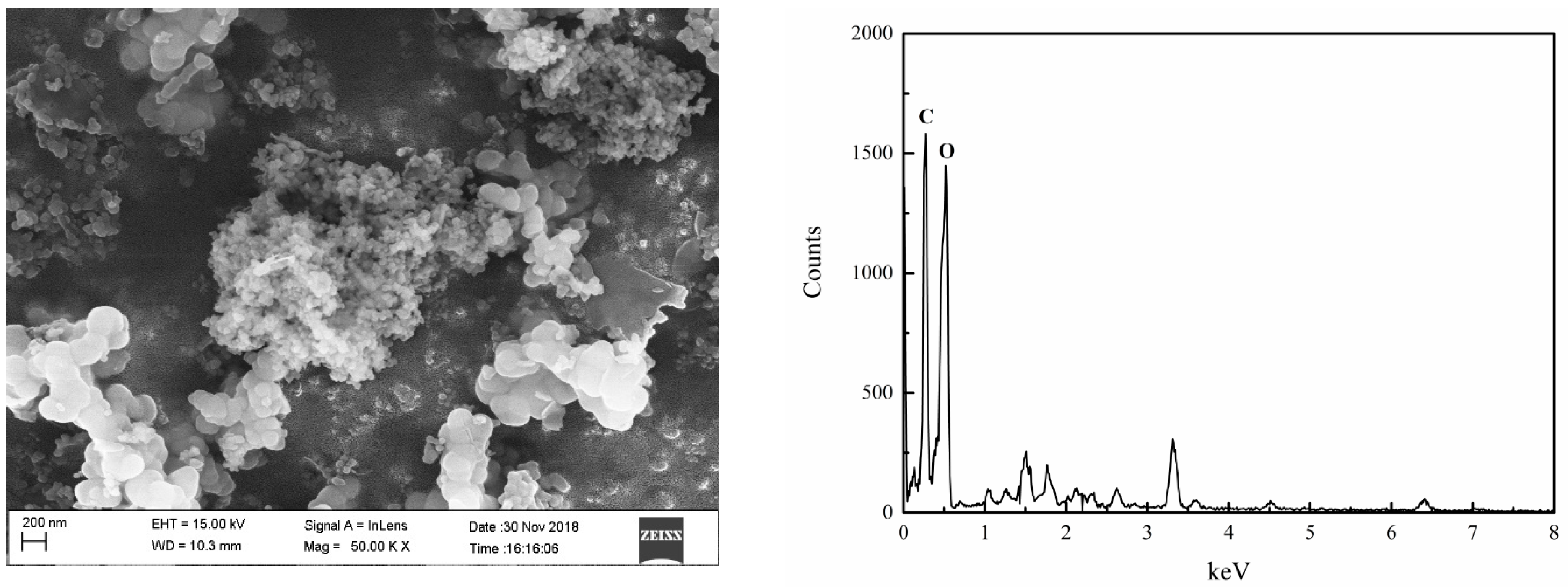
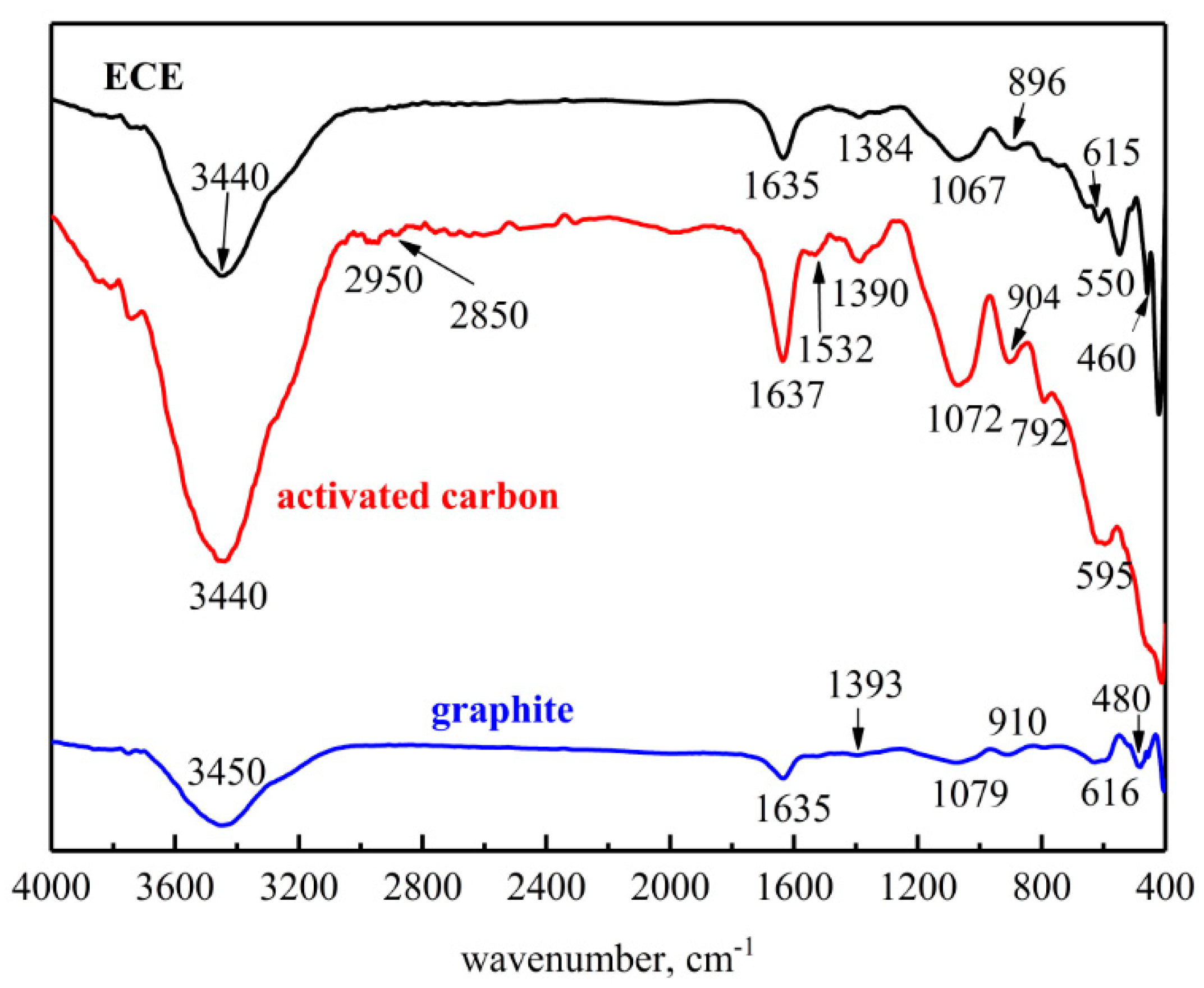

| Element | Au | Fe | S | As | Total Carbon | Inorganic Carbon | Organic Carbon |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Content | 15.9 g·t−1 | 23.17 | 24.7 | 3.41 | 6.06 | 1.70 | 4.36 |
| Experimental Conditions | ECE | Activated Carbon | Graphite | HAE | HA |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Initial Au concentration, mg·L−1 | 100 | 100 | 100 | 100 | 100 |
| pH | 3, 12 | 3, 12 | 3, 12 | 3, 12 | 3, 12 |
| Temperature, °C | 25 | 25 | 25 | 25 | 25 |
| Rotating speed, r·min−1 | 250 | 250 | 250 | 250 | 250 |
| Adsorption time, h | 5 | 5 | 5 | 5 | 5 |
| Carbonaceous Matters | Extraction Amount (mg·g−1) | Content Accounted for per ton of Gold Concentrate (g·t−1) |
|---|---|---|
| ECE | 14.84–38.50 | 0.90 × 103–2.33 × 103 |
| HAE | 11.55–28.05 | 0.79 × 103–1.67 × 103 |
| Component | C | H | O | N | Sum |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| ECE | 75.50 | 2.85 | 4.33 | 3.68 | 86.36 |
| Activated carbon | 93.50 | 1.10 | 3.45 | – | 98.05 |
| Graphite | 98.30 | 0.03 | 0.01 | – | 98.34 |
| HAE | 48.69 | 4.72 | 35.20 | 5.70 | 94.31 |
| HA | 50.37 | 4.25 | 32.98 | 5.54 | 93.14 |
| Atomic Ratio | C/N | H/C | O/C |
|---|---|---|---|
| HAE | 9.95 | 1.16 | 0.54 |
| HA | 10.61 | 1.01 | 0.49 |
| Carbonaceous Matters | SBET, m2·g−1 | DA, nm | VT, cm3·g−1 |
|---|---|---|---|
| ECE | 20.35 | 31.42 | 0.16 |
| Activated carbon | 745.60 | 25.45 | 1.89 |
| Graphite | 4.35 | 24.10 | 0.03 |
| HAE | 42.84 | 2.97 | 0.13 |
| HA | 27.45 | 3.13 | 0.09 |
| Characteristic Absorbance Ratios | E465/E665 | E270/E400 | E250/E365 |
|---|---|---|---|
| HAE | 4.98 | 2.42 | 2.08 |
| HA | 3.35 | 2.94 | 1.93 |
| Carbonaceous Matters | d002 (nm) | g (%) | R |
|---|---|---|---|
| ECE | 0.3361 | 91.86 | 0.8123 |
| Activated carbon | 0.3364 | 88.37 | 0.9137 |
| Graphite | 0.3358 | 95.35 | 0.2904 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Niu, H.; Yang, H.; Tong, L. Structural Characterization and Adsorption Capability of Carbonaceous Matters Extracted from Carbonaceous Gold Concentrate. Minerals 2021, 11, 23. https://doi.org/10.3390/min11010023
Niu H, Yang H, Tong L. Structural Characterization and Adsorption Capability of Carbonaceous Matters Extracted from Carbonaceous Gold Concentrate. Minerals. 2021; 11(1):23. https://doi.org/10.3390/min11010023
Chicago/Turabian StyleNiu, Huiqun, Hongying Yang, and Linlin Tong. 2021. "Structural Characterization and Adsorption Capability of Carbonaceous Matters Extracted from Carbonaceous Gold Concentrate" Minerals 11, no. 1: 23. https://doi.org/10.3390/min11010023
APA StyleNiu, H., Yang, H., & Tong, L. (2021). Structural Characterization and Adsorption Capability of Carbonaceous Matters Extracted from Carbonaceous Gold Concentrate. Minerals, 11(1), 23. https://doi.org/10.3390/min11010023




