Spatial Distribution and Pollution Assessment of Potentially Toxic Elements (PTEs) in Surface Sediments at the Drinking Water Source Channel of Taipu River in China
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Study Area and Sediment Sampling
2.2. Analysis of PTE Concentration in Sediments
2.3. Quality Control
2.4. Sediment Characterization
2.5. Risk Assessment Methods
2.5.1. Geoaccumulation Index ()
2.5.2. Enrichment Factor ()
2.5.3. Potential Ecological Risk Index ()
2.6. Data Analysis
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Sediment Characterization
3.2. PTEs Concentration
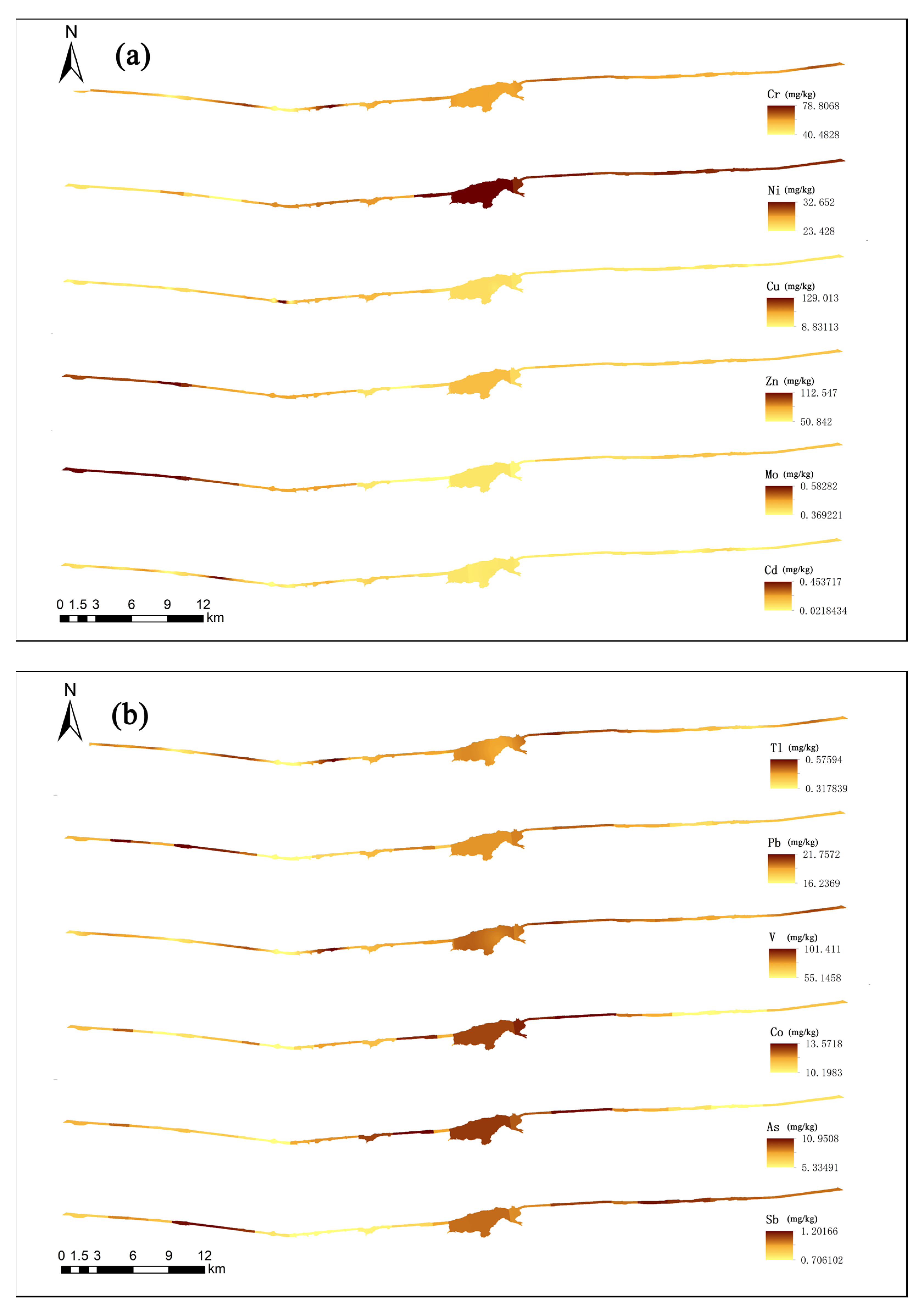
3.3. Spatial Distribution
3.4. Pollution and Risk Assessment
3.4.1. Pollution Degree Assessment
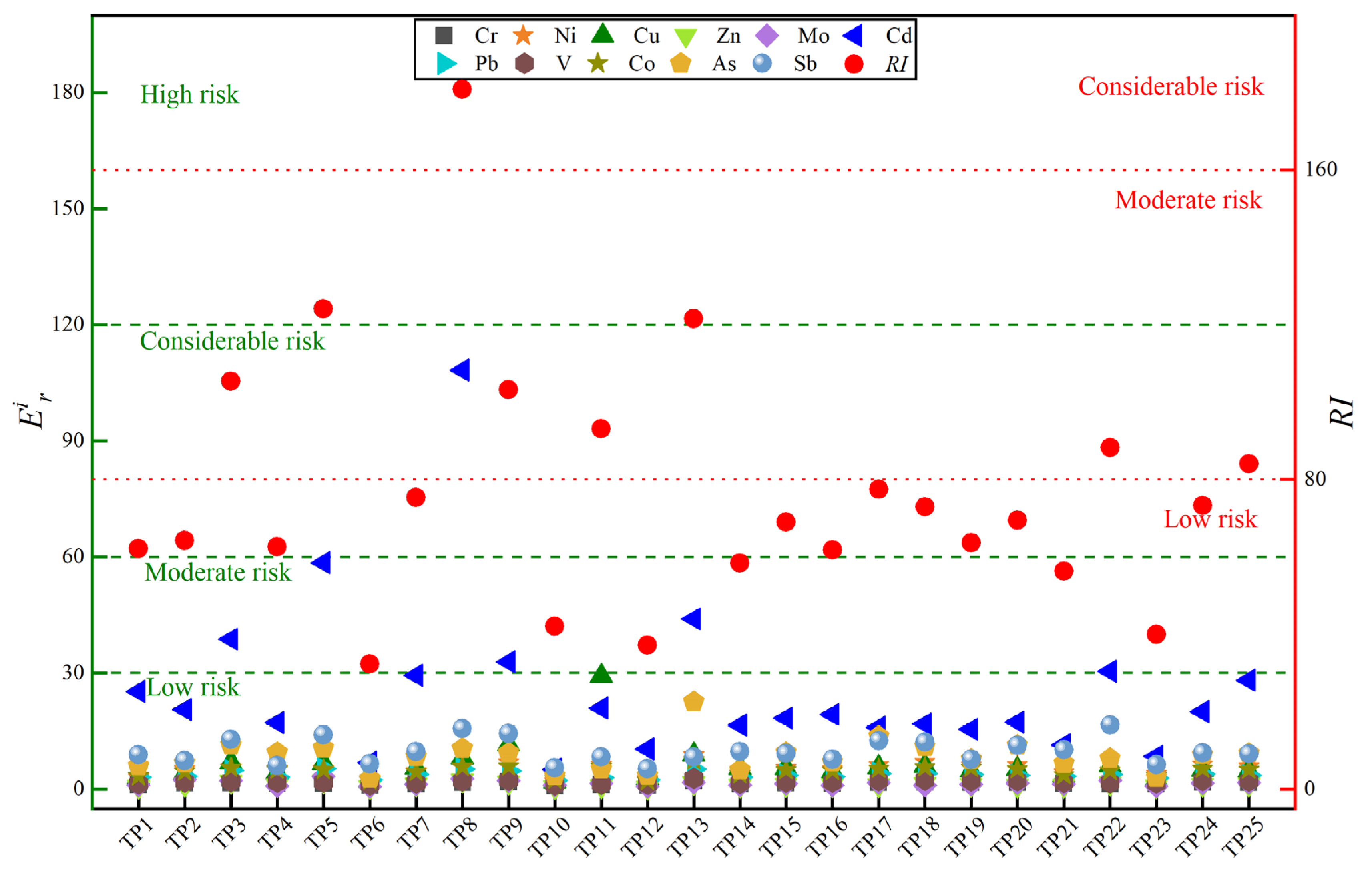
3.4.2. Environmental Risk Assessment
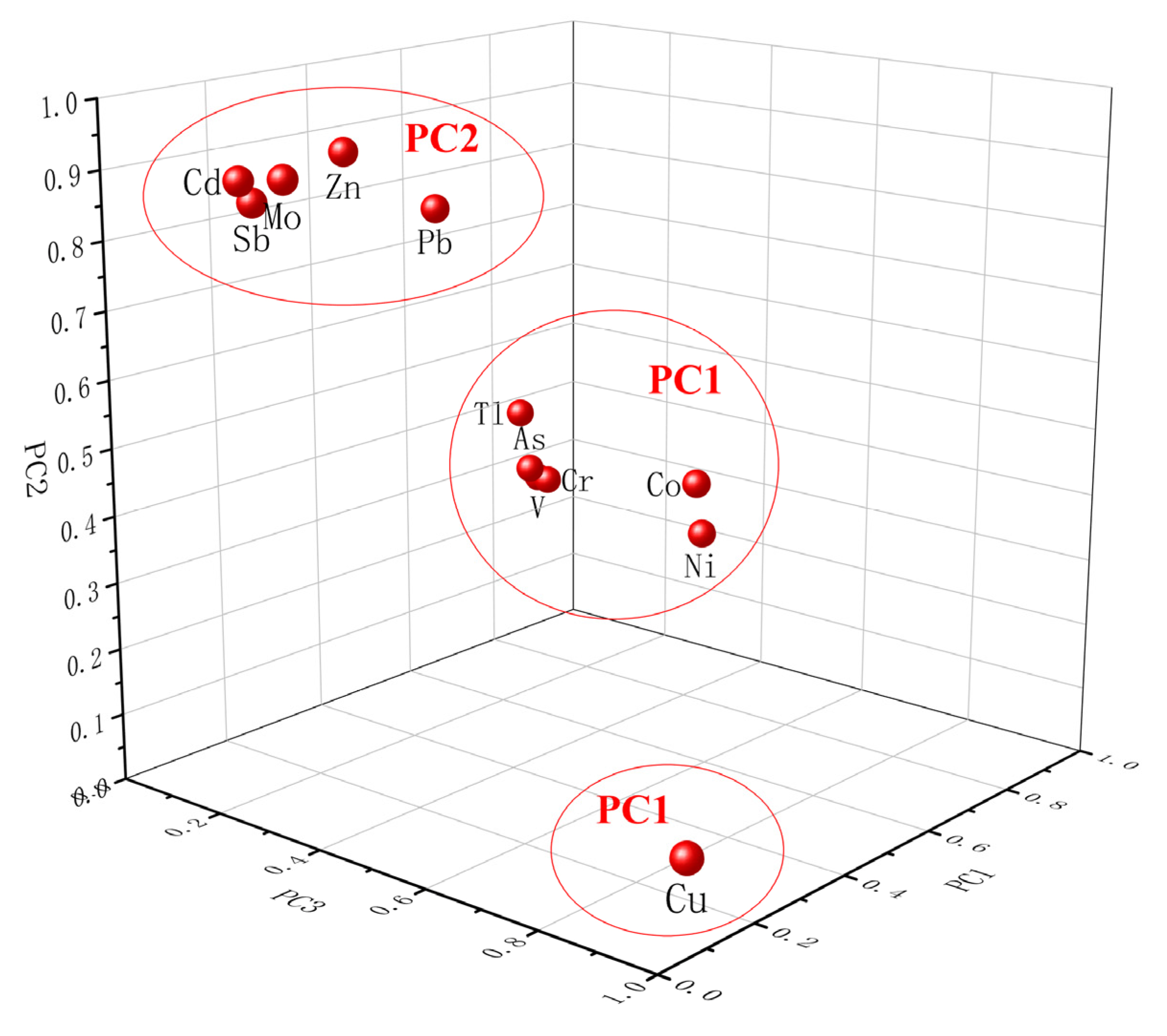
3.5. Source Apportionment
4. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Li, F.; Huang, J.; Zeng, G.; Yuan, X.; Li, X.; Liang, J.; Wang, X.; Tang, X.; Bai, B. Spatial risk assessment and sources identification of heavy metals in surface sediments from the Dongting Lake, Middle China. J. Geochem. Explor. 2013, 132, 75–83. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tam, N.F.Y.; Wong, Y.S. Spatial variation of heavy metals in surface sediments of Hong Kong mangrove swamps. Environ. Pollut. 2000, 110, 195–205. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ikem, A.; Egiebor, N.O.; Nyavor, K. Trace Elements in Water, Fish and Sediment from Tuskegee Lake, Southeastern USA. Water Air Soil Pollut. 2003, 149, 51–75. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Duncan, A.E.; de Vries, N.; Nyarko, K.B. Assessment of Heavy Metal Pollution in the Sediments of the River Pra and Its Tributaries. Water Air Soil Pollut. 2018, 229, 272. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Kalnejais, L.H.; Martin, W.R.; Signell, R.P.; Bothner, M.H. Role of Sediment Resuspension in the Remobilization of Particulate-Phase Metals from Coastal Sediments. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2007, 41, 2282–2288. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Audry, S.; Schäfer, J.; Blanc, G.; Jouanneau, J.M. Fifty-year sedimentary record of heavy metal pollution (Cd, Zn, Cu, Pb) in the Lot River reservoirs (France). Environ. Pollut. 2004, 132, 413–426. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, H. Distribution and control countermeasures for antimony in water source of Huangpu River upper stream. Water Purif. Technol. 2018, 37, 25–32. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, X.; Lu, Y.; Han, J.; He, G.; Wang, T. Identification of anthropogenic influences on water quality of rivers in Taihu watershed. J. Environ. Sci. 2007, 19, 475–481. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yao, H.; Qian, X.; Yin, H.; Gao, H.; Wang, Y. Regional Risk Assessment for Point Source Pollution Based on a Water Quality Model of the Taipu River, China. Risk Anal. 2015, 35, 265–277. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Guo, J.; Wang, L.; Yang, L.; Deng, J.; Zhao, G.; Guo, X. Spatial-temporal characteristics of nitrogen degradation in typical Rivers of Taihu Lake Basin, China. Sci. Total Environ. 2020, 713, 136456. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yao, H.; Zhuang, W.; Qian, Y.; Xia, B.; Yang, Y.; Qian, X. Estimating and Predicting Metal Concentration Using Online Turbidity Values and Water Quality Models in Two Rivers of the Taihu Basin, Eastern China. PLoS ONE 2016, 11, e0152491. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yao, H. Study on Regional Risk Assessment and Risk Governance Based on Water Quality Modelling—Exampled in the Multi-Provincial Boundary Region of the Taihu Basin, China; Nanjing University: Nanjing, China, 2015. [Google Scholar]
- Xue, B.; Yao, S. Recent sedimentation rates in lakes in lower Yangtze River basin. Quat. Int. 2011, 244, 248–253. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- China Environment Publishing Group. Soil-Determination of pH-Potentiometry; Ministry of Ecology and Environment of the People’s Republic of China, China Environment Publishing Group: Beijing, China, 2018. [Google Scholar]
- China Environment Publishing Group. Soil-Determination of Organic Carbon-Combustion Oxidation Nondispersive Infrared Absorption Method; Ministry of Ecology and Environment of the People’s Republic of China, China Environment Publishing Group: Beijing, China, 2014. [Google Scholar]
- National Standardization Administration of the People’s Republic of China. Specifications for Oceanographic Survey —Part 8: Marine Geology and Geophysics Survey; Inspection and Quarantine of the People’s Republic of China General Administration of Quality Supervision, National Standardization Administration of the People’s Republic of China: Beijing, China, 2008. [Google Scholar]
- Müller, G. Index of Geoaccumulation in Sediments of the Rhine River. GeoJournal 1969, 2, 108–118. [Google Scholar]
- Zoller, W.H.; Gladney, E.S.; Duce, R.A. Atmospheric Concentrations and Sources of Trace Metals at the South Pole. Science 1974, 183, 198. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sinex, S.A.; Wright, D.A. Distribution of trace metals in the sediments and biota of Chesapeake Bay. Mar. Pollut. Bull. 1988, 19, 425–431. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barbieri, M. The Importance of Enrichment Factor (EF) and Geoaccumulation Index (Igeo) to Evaluate the Soil Contamination. J. Geol. Geophys. 2016, 5, 1–4. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hakanson, L. An ecological risk index for aquatic pollution control.a sedimentological approach. Water Res. 1980, 14, 975–1001. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deng, J.; Zhang, J.; Yin, H.; Hu, W.; Zhu, J.; Wang, X. Ecological risk assessment and source apportionment of metals in the surface sediments of river systems in Lake Taihu Basin, China. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. Int. 2020, 27, 25943–25955. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Guozhong, Y. Background Value of Soil Elements in China; China Environmental Science Press: Beijing, China, 1991. [Google Scholar]
- Varol, M. Assessment of heavy metal contamination in sediments of the Tigris River (Turkey) using pollution indices and multivariate statistical techniques. J. Hazard. Mater. 2011, 195, 355–364. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reimann, C.; Garrett, R.G. Geochemical background—Concept and reality. Sci. Total Environ. 2005, 350, 12–27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mao, L.; Ye, H.; Li, F.; Yang, M.; Tao, H.; Wen, H. Enrichment assessment of Sb and trace metals in sediments with significant variability of background concentration in detailed scale. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. Int. 2019, 26, 2794–2805. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meklit, T.; Meirvenne, M.V.; Verstraete, S.; Bonroy, J.; Tack, F. Combining marginal and spatial outliers identification to optimize the mapping of the regional geochemical baseline concentration of soil heavy metals. Geoderma 2009, 148, 413–420. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhuang, S.; Lu, X.; Yu, B.; Fan, X.; Yang, Y. Ascertaining the pollution, ecological risk and source of metal(loid)s in the upstream sediment of Danjiang River, China. Ecol. Indic. 2021, 125, 107502. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Timofeev, I.; Kosheleva, N.; Kasimov, N. Contamination of soils by potentially toxic elements in the impact zone of tungstenmolybdenum ore mine in the Baikal region: A survey and risk assessment. Sci. Total Environ. 2018, 642, 63–76. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ke, X.; Gui, S.; Huang, H.; Zhang, H.; Wang, C.; Guo, W. Ecological risk assessment and source identification for heavy metals in surface sediment from the Liaohe River protected area, China. Chemosphere 2017, 175, 473–481. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shahab, A.; Zhang, H.; Ullah, H.; Rashid, A.; Rad, S.; Li, J.; Xiao, H. Pollution characteristics and toxicity of potentially toxic elements in road dust of a tourist city, Guilin, China: Ecological and health risk assessment. Environ. Pollut. 2020, 266 Pt 3, 115419. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ziwa, G.; Crane, R.; Hudson-Edwards, K.A. Geochemistry, Mineralogy and Microbiology of Cobalt in Mining-Affected Environments. Minerals 2020, 11, 22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Costa-Boddeker, S.; Hoelzmann, P.; Thuyen, L.X.; Huy, H.D.; Nguyen, H.A.; Richter, O.; Schwalb, A. Ecological risk assessment of a coastal zone in Southern Vietnam: Spatial distribution and content of heavy metals in water and surface sediments of the Thi Vai Estuary and Can Gio Mangrove Forest. Mar. Pollut. Bull. 2017, 114, 1141–1151. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tallkvist, J.; Oskarsson, A. Molybdenum. In Handbook on the Toxicology of Metals, 4th ed.; Nordberg, G.F., Fowler, B.A., Nordberg, M., Eds.; Academic Press: San Diego, CA, USA, 2015; pp. 1077–1089. [Google Scholar]
- Xue, H.B.; Sigg, L.; Gchte, R. Transport of Cu, Zn and Cd in a Small Agricultural Catchment. Water Res. 2000, 34, 2558–2568. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, F.X.; Hargreaves, J.A.; Kingery, W.L.; Huggett, D.B.; Schlenk, D.K. Accumulation, distribution, and toxicity of copper in sediments of catfish ponds receiving periodic copper sulfate applications. J. Environ. Qual. 2001, 30, 912–919. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Weng, H. The Determination of Environmental Geochemical Baseline of Heavy Metals in the Surface Sediments of Lake Taihu and Lake Dianchi; Nanchang University: Nanchang, China, 2011. [Google Scholar]
- Manman, W. Risk Assessment and Source Analysis of Heavy Metals in Typical Rivers of Taihu Lake Basin. Doctoral dissertation; Nanjing University: Nanjing, China, 2016. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, J.; Ren, T.; Pu, Y.; Duan, Y.; Zhi, W.; Tang, Y.; Zhang, H.; Luo, P. Pollution status and source analysis of heavy metals in the Huangpu River Basin. Environ. Tech. 2019, 032, 1–7. [Google Scholar]
- Chai, L.; Li, H.; Yang, Z.; Min, X.; Liao, Q.; Liu, Y.; Men, S.; Yan, Y.; Xu, J. Heavy metals and metalloids in the surface sediments of the Xiangjiang River, Hunan, China: Distribution, contamination, and ecological risk assessment. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. Int. 2016, 24, 874–885. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guoxin, L.; Wen, Z.; Yunpeng, X.; Xuemei, C. Evaluation of Heavy Metal Pollution and Estimation of Release Flux in Sediment of Dadu River. Environ Sci. Tech 2019, 42, 193–200. [Google Scholar]
- Fu, J.; Zhao, C.; Luo, Y.; Liu, C.; Kyzas, G.Z.; Luo, Y.; Zhao, D.; An, S.; Zhu, H. Heavy metals in surface sediments of the Jialu River, China: Their relations to environmental factors. J. Hazard. Mater. 2014, 270, 102–109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, N.; Tian, Y.; Zhang, J.; Zuo, W.; Zhan, W.; Zhang, J. Heavy metal contamination status and source apportionment in sediments of Songhua River Harbin region, Northeast China. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. Int. 2017, 24, 1–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tang, W.; Yu, Z.; Chao, W.; Shan, B.; Cui, J. Heavy metal contamination of overlying waters and bed sediments of Haihe Basin in China. Ecotoxicol. Environ. Saf. 2013, 98, 317323. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jian, Z. Risk Assessment of Heavy Metals in Sediments in Drinking Water Sources: A Case Study of Biliuhe Reservoir in Dalian. Doctoral Dissertation, Dalian University of Technology, Dalian, China, 2016. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, Z.; Li, J.; Mamat, Z.; Ye, Q.F. Sources identification and pollution evaluation of heavy metals in the surface sediments of Bortala River, Northwest China. Ecotoxicol. Environ. Saf. 2016, 126, 94–101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eqani, S. Geo-accumulation and enrichment of trace metals in sediments and their associated risks in the Chenab River, Pakistan. J. Geochem. Explor. 2016, 165, 62–70. [Google Scholar]
- Paramasivam, K.; Ramasamy, V.; Suresh, G. Impact of sediment characteristics on the heavy metal concentration and their ecological risk level of surface sediments of Vaigai river, Tamilnadu, India. Spectrochim. Acta A Mol. Biomol. Spectrosc. 2015, 137, 397–407. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rahman, M.S.; Saha, N.; Molla, A.H. Potential ecological risk assessment of heavy metal contamination in sediment and water body around Dhaka export processing zone, Bangladesh. Environ. Earth Sci. 2014, 71, 2293–2308. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barhoumi, B.; Beldean-Galea, M.S.; Ai-Rawabdeh, A.M.; Roba, C.; Martonos, I.M.; Balc, R.; Kahlaoui, M.; Touil, S.; Tedetti, M.; Driss, M.R. Occurrence, distribution and ecological risk of trace metals and organic pollutants in surface sediments from a Southeastern European river (Someu Mic River, Romania). Sci. Total Environ. 2019, 660, 660–676. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]


| Physicochemical Index | Max | Min | Median | Average | Standard Deviation | Variable Coefficient |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| pH | 8.81 | 6.48 | 7.86 | 7.65 | 0.56 | 0.074 |
| TOC(g/kg) | 49.23 | 3.73 | 10.21 | 12.60 | 9.66 | 0.77 |
| Clay (<4 μm) (%) | 75.47 | 7.35 | 18.09 | 24.93 | 18.40 | 0.74 |
| Silt (4–63 μm) (%) | 79.10 | 24.53 | 68.9 | 63.22 | 14.85 | 0.23 |
| Average | Median | Min–Max | Detection Limit | Standard Deviation | Variable Coefficient (%) | Background | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Cr | 58.2 | 57.9 | 35.6–85.3 | 0.11 | 11.88 | 20.4 | 77.8 |
| Ni | 27.6 | 28.1 | 10.88–46.9 | 0.67 | 8.26 | 30.0 | 26.7 |
| Cu | 27.5 | 23.3 | 8.53–130.2 | 0.06 | 23.3 | 83.7 | 22.3 |
| Zn | 71.7 | 67.1 | 26.8–143.1 | 0.05 | 28.7 | 40.1 | 62.6 |
| Mo | 0.460 | 0.433 | 0.222–0.963 | 0.02 | 0.19 | 41.9 | 0.3 |
| Cd | 0.107 | 0.081 | 0.021–0.455 | 0.09 | 0.087 | 81.5 | 0.126 |
| Tl | 0.435 | 0.423 | 0.291–0.617 | 0.08 | 0.088 | 20.2 | 0.439 |
| Pb | 19.1 | 18.4 | 12.03–27.5 | 0.03 | 4.41 | 23.1 | 26.2 |
| V | 77.1 | 77.2 | 45.8–116.5 | 0.12 | 17.1 | 22.2 | 83.4 |
| Co | 11.78 | 12.58 | 5.48–18.9 | 0.15 | 3.04 | 25.8 | 12.6 |
| As | 8.39 | 8.33 | 2.70–22.5 | 0.11 | 4.04 | 48.2 | 10 |
| Sb | 1.013 | 0.950 | 0.549–1.717 | 0.67 | 0.321 | 31.7 | 1.04 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Wang, Y.; Li, F.; Mao, L.; Chen, M.; Tao, H.; Li, J. Spatial Distribution and Pollution Assessment of Potentially Toxic Elements (PTEs) in Surface Sediments at the Drinking Water Source Channel of Taipu River in China. Minerals 2021, 11, 1202. https://doi.org/10.3390/min11111202
Wang Y, Li F, Mao L, Chen M, Tao H, Li J. Spatial Distribution and Pollution Assessment of Potentially Toxic Elements (PTEs) in Surface Sediments at the Drinking Water Source Channel of Taipu River in China. Minerals. 2021; 11(11):1202. https://doi.org/10.3390/min11111202
Chicago/Turabian StyleWang, Yue, Feipeng Li, Lingchen Mao, Mengmeng Chen, Hong Tao, and Jianhua Li. 2021. "Spatial Distribution and Pollution Assessment of Potentially Toxic Elements (PTEs) in Surface Sediments at the Drinking Water Source Channel of Taipu River in China" Minerals 11, no. 11: 1202. https://doi.org/10.3390/min11111202
APA StyleWang, Y., Li, F., Mao, L., Chen, M., Tao, H., & Li, J. (2021). Spatial Distribution and Pollution Assessment of Potentially Toxic Elements (PTEs) in Surface Sediments at the Drinking Water Source Channel of Taipu River in China. Minerals, 11(11), 1202. https://doi.org/10.3390/min11111202









