Origin of the Pd-Rich Pentlandite in the Massive Sulfide Ores of the Talnakh Deposit, Norilsk Region, Russia
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Geology of the Talnakh Ore Cluster
3. Materials and Methods
3.1. Sampling and Analytical Procedure
3.2. EDS Elemental Distribution Maps
3.3. Mapping of Pd Distribution in Pentlandite
4. Results
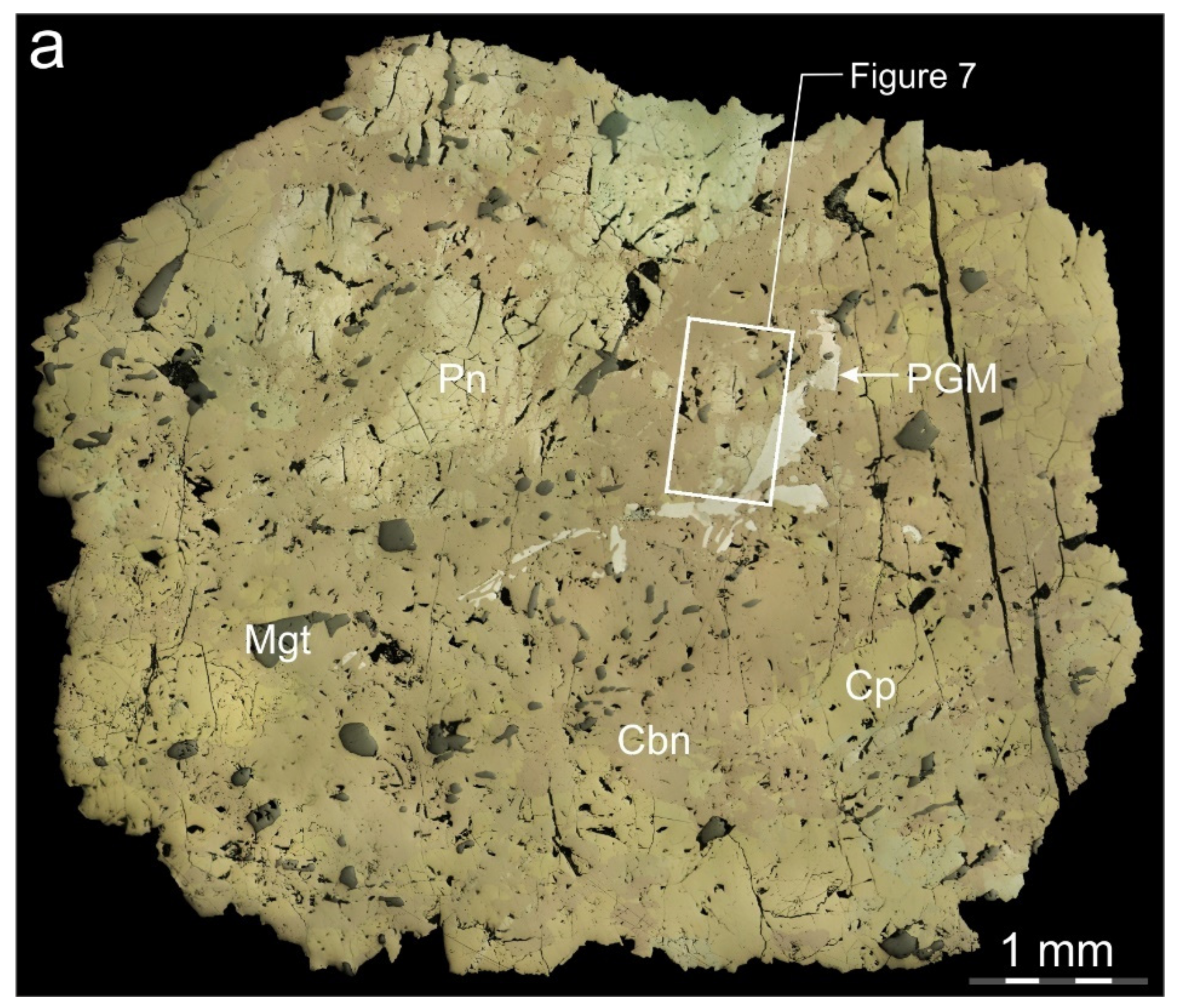
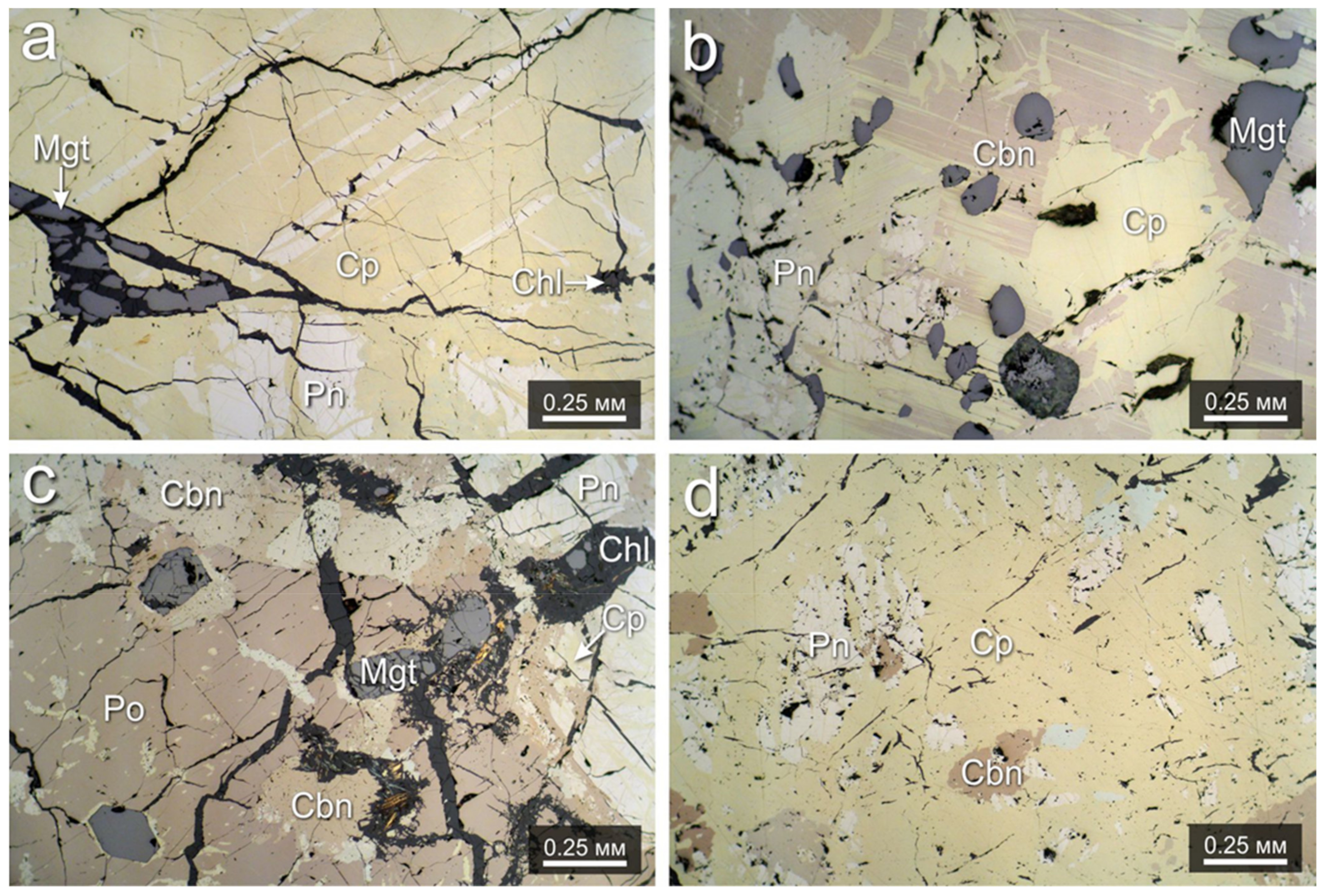
4.1. Structure and Mineral Assemblages of the Southern-2 Ore Body
4.2. Morphology of the Pentlandite
4.3. Compositional Variations of the Ore-Forming Pentlandite
4.4. Location and Composition of Pd-Rich Pentlandite
4.5. Distribution of Pd in Individual Grains of Pentlandite
5. Discussion
5.1. Position of Pd in the Pentlandite Structure
5.2. Genetic Constraints and Mechanisms for the Enrichment of Pd in Pentlandite
- Liquid immiscibility implies equilibrium between coexisting liquids and crystallizing phases. If separation of a PGE-semimetals liquid from a sulfide liquid ever occurs, PGE and semimetals would be concentrated in the former. Upon cooling, the separation of components between the liquids will also increase, and consequently, the partitioning of palladium from the PGE semimetal liquid back into the sulfide liquid or solid sulfide matrix is very unlikely.
- As opposed to the metamorphic reaction suggested for the J-M Reef, Stillwater, including Pd release [20], in our case, there is no single evidence of breakdown or dissolution of any PGM phases or multiphase PGM grains. Thus, a source of palladium from PGM grains is not manifested.
5.3. Origin of Pd-Rich Pentlandite in the Southern-2 Ore Body
6. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Cabri, L.J.; Laflamme, J.G. Analyses of minerals containing platinum-group elements. In Platinum-Group Elements: Mineralogy, Geology, Recovery; Cabri, L.J., Ed.; Canadian Insitute of Mining, Metallurgy and Petroleum: Montreal, QC, Canada, 1981; Volume 23, pp. 151–173. [Google Scholar]
- Czamanske, G.K.; Kunilov, V.E.; Zientek, M.L.; Cabri, L.J.; Likhachev, A.P.; Calk, L.C.; Oscarson, R.L. A proton microprobe study of magmatic sulfide ores from the Noril’sk-Talnakh district, Siberia. Can. Mineral. 1992, 30, 249–287. [Google Scholar]
- Chai, G.; Naldrett, A.J.; Rucklidge, J.C.; Kilius, L.R. In situ quantitative analyses for PGE and Au in sulfide minerals of the Jinchuan Ni-Cu deposit by accelerator mass spectrometry. Can. Mineral. 1993, 3l, 19–30. [Google Scholar]
- Distler, V.V.; Kulagov, E.A.; Sluzhenikin, S.F.; Laputina, I.P. The quench sulfide solid solutions in the ores of the Noril’sk deposit. Geol. Ore Depos. 1996, 38, 41–53. (In Russian) [Google Scholar]
- Cabri, L.J. The Geology, Geochemistry, Mineralogy and Mineral Beneficiation of Platinum-Group Elements; Canadian Institute of Mining, Metallurgy and Petroleum: Montreal, QC, Canada, 2002; Volume 54, p. 852. [Google Scholar]
- Gervilla, F.; Cabri, L.J.; Kojonen, K.; Oberthür, T.; Weiser, T.W.; Johanson, B.; Sie, S.H.; Campbell, J.L.; Teesdale, W.J.; Laflamme, J.G. Platinum-group element distribution in some ore deposits: Results of EPMA and micro-PIXE analyses. Microchim. Acta 2004, 147, 167–173. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Holwell, B.D.A.; McDonald, I. A review of the behavior of platinum group elements within natural magmatic sulfide ore systems. Platin. Met. Rev. 2010, 54, 26–36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Godel, B.; Barnes, S.-J.; Maier, W.D. Platinum-group elements in sulphide minerals, platinum-group minerals, and whole-rocks of the Merensky Reef (Bushveld Complex, South Africa): Implications for the formation of the Reef. J. Petrol. 2007, 48, 1569–1604. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Godel, B.; Barnes, S.-J. Platinum-group elements in sulfide minerals and the whole rocks of the J-M Reef (Stillwater Complex): Implication for the formation of the reef. Chem. Geol. 2008, 248, 272–294. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Osbahr, I.; Klemd, R.; Oberthür, T.; Brätz, H.; Schouwstra, R. Platinum-group element distribution in base-metal sulfides of the Merensky Reef from the eastern and western Bushveld Complex, South Africa. Miner. Depos. 2013, 48, 211–232. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Osbahr, I.; Oberthür, T.; Klemd, R.; Josties, A. Platinum-group element distribution in base-metal sulfides of the UG2 chromitite, Bushveld Complex, South Africa—A reconnaissance study. Miner. Depos. 2014, 49, 655–665. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brovchenko, V.D.; Sluzhenikin, S.F.; Kovalchuk, E.V.; Kovrigina, S.V.; Abramova, V.D.; Yudovskaya, M.A. Platinum Group Element Enrichment of Natural Quenched Sulfide Solid Solutions, the Norilsk 1 Deposit, Russia. Econ. Geol. 2020, 6, 1343–1361. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cabri, L.J.; Sylvester, P.J.; Tubrett, M.N.; Peregoedova, A.; Laflamme, J.H.G. Comparison of LAM–ICP–MS and micro-PIXE results for palladium and rhodium in selected samples of Noril’sk and Talnakh sulfides. Can. Mineral. 2003, 41, 321–329. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Keays, R.R.; Ross, J.R.; Woolrich, P. Precious metals in volcanic peridotite-associated nickel sulfide deposits in western Australia. II. Distribution within the ores and host rocks at Kambalda. Econ. Geol. 1981, 76, 1645–1674. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dare, S.A.S.; Barnes, S.-J.; Prichard, H.M. The distribution of platinum group elements (PGE) and other chalcophile elements among sulfides from the Creighton Ni–Cu–PGE sulfide deposit, Sudbury, Canada, and the origin of palladium in pentlandite. Miner. Depos. 2010, 45, 765–793. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Holwell, D.A.; McDonald, I. Distribution of platinum-group elements in the Platreef at OVerysel. Northern Bushveld Complex: A combined PGM and LA-ICP-MS study. Contrib. Mineral. Petrol. 2007, 154, 171–190. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Junge, M.; Wirth, R.; Oberthur, T.; Melcher, F.; Schreibr, A. Mineralogical siting of platinum-group minerals in pentlandite from the Bushveld Complex, South Africa. Miner. Depos. 2015, 50, 41–54. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Klemd, R.; Herderich, T.; Junge, M.; Oberthür, T.; Schouwstra, R.; Roberts, J. Platinum-group element concentrations in base-metal sulphides from the Platreef, Mogalakwena Platinum Mine, Bushveld Complex, South Africa. S. Afr. J. Geol. 2016, 119, 623–638. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cabri, L.J.; Blank, H.; El Goresy, A.; Laflamme, J.H.G.; Nobiling, R.; Sizgoric, M.B.; Traxel, K. Quantitative trace-element analyses of sulphides from Sudbury and Stillwater by proton microprobe. Can. Mineral. 1984, 22, 521–542. [Google Scholar]
- Li, C.; Ripley, E.M. Formation of Pt-Fe alloy by desulfurization of Pt-Pd sulfide in the J-M reef of the Stillwater Complex, Montana. Can. Mineral. 2006, 44, 895–903. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sinyakova, E.F.; Kosyakov, V.; Borisenko, A.S.; Karmanov, N.S. Behavior of noble metals during fractional crystallization of Cu–Fe–Ni–(Pt, Pd, Rh, Ir, Ru, Ag, Au, Te) sulfide melts. Russ. Geol. Geophys. 2019, 60, 642–661. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.; Brenan, J. Partitioning of platinum-group elements (PGE) and chalcogens (Se, Te, As, Sb, Bi) between monosulfide-solid solution (MSS), intermediate solid solution (ISS) and sulfide liquid at controlled fO2–fS2 conditions. Geochim. Cosmochim. Acta 2015, 159, 139–161. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Naldrett, A.J. Magmatic Sulphide Deposits: Geology, Geochemistry and Exploration; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany; New York, NY, USA, 2004; p. 727. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sluzhenikin, S.F.; Krivolutskaya, N.A.; Rad’ko, V.A.; Malitch, K.N.; Distler, V.V.; Fedorenko, V.A. Ultramafic-Mafic Intrusions, Volcanic Rocks and PGE-Cu-Ni Sulfide Deposits of the Norilsk Province, Polar Siberia Field Trip Guidebook; Zavaritsky Institute of Geology and Geochemistry of the Ural Branch (UB) of the Russian Academy of Sciences (RAS): Yekaterinburg, Russia, 2014; p. 87. [Google Scholar]
- Krivolutskaya, N.A. 2014 The Evolution of Trap Magmatism and Pt-Cu-Ni Ore Formation in the Norilsk Region; Tovarishhestvo nauchnyh izdanii KMK: Moscow, Russia, 2014; p. 305. [Google Scholar]
- Genkin, A.D.; Distler, V.V.; Gladyshev, G.D.; Filimonova, A.A.; Evstigneeva, T.L.; Kovalenker, V.A.; Laputina, I.P.; Smirnov, A.V.; Grokhovskaya, T.L. Sulfide Copper–Nickel Ores of the Norilsk Deposits; Nauka: Moscow, Russia, 1981; p. 374. [Google Scholar]
- Tolstykh, N.; Krivolutskaya, N.; Safonova, I.; Shapovalova, M.; Zhitova, L.; Abersteiner, A. Unique Cu-rich sulphide ores of the Southern-2 ore body in the Talnakh Intrusion, Noril’sk area (Russia): Geochemistry, mineralogy and conditions of crystallization. Ore Geol. Rev. 2020, 122, 103525. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vymazalová, A.; Laufek, F.; Sluzhenikin, S.F.; Stanley, C.J. Norilskite, (Pd,Ag)7Pb4, a new mineral from Noril’sk-Talnakh deposit, Russia. Mineral. Mag. 2017, 81, 531–541. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Knop, O.; Huang, C.-H.; Reid, K.I.G.; Carlow, J.S.; Woodhams, F.W.D. Chalkogenides of the Transition elements. X. X-Ray, Neutron, Mossbauer, and magnetic studies of pentlandite and the π phases π(Fe,Co,Ni,S), Co8MS8, and Fe4Ni4MS8 (M = Ru,Rh,Pd). J. Solid State Chem. 1976, 16, 97–116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Knop, O.; Ibrahim, M.A. Satarno chalcogenides of the transition elements; [Part] 4, Pentlandite, a natural pi phase. Can. Mineral. 1965, 8, 291–316. [Google Scholar]
- Hutchinson, D.; McDonald, I. Breaking the rules. Divergent behaviour of platinum and palladium in the northern limb of Bushveld Complex, R.S.A. In Proceedings of the 10th International Platinum Symposium, Oulu, Finland, 8–11 August 2005. [Google Scholar]
- Klemd, R.; Beinlich, A.; Kern, M.; Junge, M.; Martin, L.; Regelous, M.; Schouwstra, R. Magmatic PGE Sulphide Mineralization in Clinopyroxenite from the Platreef, Bushveld Complex, South Africa. Minerals 2020, 10, 570. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rajamani, V.; Prewitt, C.T. Crystal chemistry of natural pentlandites. Can. Mineral. 1973, 12, 178–187. [Google Scholar]
- Rajamani, V.; Prewitt, C.T. Thermal expansion of the pentlandite structure. Am. Mineral. 1975, 60, 39–48. [Google Scholar]
- Goldschmidt, V.M. Die Gesetze der Krystallochemie. Die Nat. 1926, 14, 477–485. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peregoedova, A.V.; Fedorova, Z.N.; Sinyakova, E.F. Physicochemical conditions of the pentlandite formation in Cu-bearing sulfide paragenesis (according to experimental data). Russ. J. Geol. Geophysics. 1995, 36, 91–98. [Google Scholar]
- Fedorova, Z.N.; Sinyakova, E.F. Experimental investigation of physicochemical conditions of pentlandite formation. Russ. J. Geol. Geophys. 1993, 34, 79–87. [Google Scholar]
- Sinyakova, E.F. Forms of palladium release under crystallization of sulfide melts of the Fe-Ni-S System at sulfur content 40–51 at.%. Russ. J. Geol. Geophys. 1998, 39, 634–647. [Google Scholar]
- Kolonin, G.R.; Orsoev, D.A.; Sinyakova, E.F.; Kislov, E.V. The Ni/Fe ratio in pentlandite as an indicator of sulfur fugacity during the formation of PGE-bearing sulfide mineralization of the Ioko–Dovyren Massif. Dokl. Earth Sci. 2000, 370, 75–79. [Google Scholar]
- Ballhaus, C.; Tredoux, M.; Spath, A. Phase relations in the Fe-Ni-Cu-PGE-S system at magmatic temperature and application to massive sulphide ores of the Sudbury igneous complex. J. Petrol. 2001, 42, 1911–1926. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Li, C.; Barnes, S.J.; Makovicky, E.; Rose-Hansen, J.; Makovicky, M. Partitioning of nickel, copper, iridium, rhenium, platinum, and palladium between monosulfide solid solution and sulfide liquid: Effects of composition and temperature. Geochim. Cosmochim. Acta 1996, 60, 1231–1238. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pina, R.; Gervilla, F.; Barnes, S.-J.; Ortega, L. Distribution of platinum-group and chalcophile elements in the Aguablanca Ni-Cu sulfide deposit (SW Spain): Evidence from a LA-ICP-MS study. Chem. Geol. 2012, 302–303, 61–75. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Mansur, E.T.; Barnes, S.J.; Duran, C.J. Textural and compositional evidence for the formation of pentlandite via peritectic reaction: Implications for the distribution of highly siderophile elements. Geology 2019, 47, 1–7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Makovicky, M.; Makovicky, E.; Rose-Hansen, J. Experimental studies on the solubility and distribution of platinum group elements in base metal sulphides in platinum deposits. In Metallurgy of Basic and Ultrabasic Rocks; Gallagher, M.J., Ixer, R.A., Neary, C.R., Prichard, H.M., Eds.; Institute of Mining and Metallurgy: London, UK, 1986; pp. 415–425. [Google Scholar]
- Mansur, E.T.; Barnes, S.J.; Duran, C.J.; Sluzhenikin, S.F. Distribution of chalcophile and platinum-group elements among pyrrhotite, pentlandite, chalcopyrite and cubanite from the Noril’sk-Talnakh ores: Implications for the formation of platinum-group minerals. Miner. Depos. 2020, 55, 1215–1232. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dutrizac, J.E. Reactions in cubanite and chalcopyrite. Can. Mineral. 1976, 14, 172–181. [Google Scholar]
- Sinyakova, E.F.; Kosyakov, V.I. Experimental modeling of zoning in copper-nickel sulfide ores. Dokl. Earth Sc. 2007, 417, 1380–1385. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sinyakova, E.F.; Kosyakov, V.I. The polythermal section of the Cu–Fe–Ni–S phase diagram constructed using directional crystallization and thermal analysis. J. Therm. Anal. Calorim. 2014, 117, 1085–1089. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kosyakov, F.I.; Sinyakova, E.F.; Distler, V.V. Experimental simulation of phase relationships and zoning of magmatic nickel-copper sulfide Ores, Russia. Geol. Ore Depos. 2012, 54, 179–208. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fleet, M.E.; Chryssoulis, S.L.; Stone, W.E.; Weisener, C.G. Partitioning of platinum-group elements and Au in the Fe−Ni−Cu−S system: Experiments on the fractional crystallization of sulfide melt. Contrib. Mineral. Petrol. 1993, 115, 36–44. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gervilla, F.; Leblanc, M.; Torres-Ruiz, J.; Fenoll Hach-Ali, P. Immiscibility between arsenide and sulfide melts: A mechanism for concentration of noble metals. Can. Mineral. 1996, 34, 485–502. [Google Scholar]
- Helmy, H.; Ballhaus, C.; Berndt, J.; Bockrath, C.; Wohlgemuth-Ueberwasser, C. Formation of Pt, Pd and Ni tellurides: Experiments in sulfide–telluride systems. Contrib. Mineral. Petrol. 2007, 153, 577–591. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Holwell, D.; McDonald, I. Petrology, geochemistry and the mechanisms determining the distribution of platinum-group element and base metal sulphide mineralisation in the Platreef at Overysel, northern Bushveld Complex, South Africa. Miner. Depos. 2006, 41, 575–598. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cabri, L.J.; Laflamme, J.H.G. The mineralogy of the platinum-group elements from some copper-nickel deposits of the Sudbury area, Ontario. Econ. Geol. 1976, 71, 1159–1195. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Prichard, H.M.; Hutchinson, D.; Fisher, P.C. Petrology and Crystallization History of Multiphase Sulfide Droplets in a Mafic Dike from Uruguay: Implications for the Origin of Cu-Ni-PGE Sulfide Deposits. Econ. Geol. 2004, 99, 365–376. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barnes, S.-J.; Cox, R.A.; Zientek, M.L. Platinum-group element, gold, silver and base metal distribution in compositionally zoned sulfide droplets from the Medvezky Creek Mine, Noril’sk, Russia. Contrib. Mineral. Petrol. 2006, 152, 187–200. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]












| Spectral Line | Spectrometer Crystal | Standard | Cmin, wt.%, Detection Limit |
|---|---|---|---|
| PdLα | PETJ | Pd-metal | 0.06 |
| NiKα | LIF | Alloy FeNiCo | 0.04 |
| CuKα | LIF | CuFeS2 | 0.04 |
| CoKα | LIFH | Alloy FeNiCo | 0.03 |
| PtLα | LIFH | Pt-metal | 0.08 |
| SKα | PETJ | CuFeS2 | 0.04 |
| FeKα | LIFL | CuFeS2 | 0.02 |
| No. | Depth, m | Number of Analyses | Ni | Cu | Co | S | Fe | Total | Mineral Formulas |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 69.6 | 18 | 38.75 | 0.23 | 0.65 | 33.04 | 27.32 | 99.97 | (Fe3.79Ni5.12Co0.08Cu0.02)9.01S7.99 |
| 2 | 70.1 | 13 | 40.58 | 0.40 | 0.60 | 32.86 | 25.46 | 99.90 | (Fe3.54Ni5.38Co0.08Cu0.04)9.04S7.96 |
| 3 | 71.2 | 7 | 39.06 | 0.46 | 0.53 | 33.47 | 26.91 | 100.44 | (Fe3.71Ni5.14Co0.07Cu0.04)8.96S8.04 |
| 4 | 72.3 | 5 | 38.48 | 0.40 | 0.49 | 32.10 | 27.09 | 98.56 | (Fe3.82Ni5.19Co0.07Cu0.04)9.12S7.88 |
| 5 | 73.3 | 9 | 38.36 | 0.23 | 0.59 | 33.10 | 27.82 | 100.10 | (Fe3.83Ni5.03Co0.08Cu0.07)9.01S7.99 |
| 6 | 73.8 | 18 | 38.71 | 0.37 | 0.48 | 32.73 | 27.26 | 99.54 | (Fe3.80Ni5.17Co0.07Cu0.02)9.06S7.94 |
| 7 | 75.0 | 8 | 37.98 | 0.37 | 0.56 | 33.32 | 27.90 | 100.13 | (Fe3.86Ni5.02Co0.07Cu0.02)8.98S8.02 |
| 8 | 75.6 | 4 | 37.07 | 0.32 | 0.75 | 33.57 | 28.98 | 100.69 | (Fe3.99Ni4.82Co0.10Cu0.08)8.99S8.01 |
| 9 | 76.5 | 18 | 34.30 | 0.44 | 0.68 | 33.72 | 31.41 | 100.55 | (Fe4.31Ni4.48Co0.09Cu0.05)8.93S8.07 |
| 10 | 76.7 | 11 | 34.51 | 0.15 | 0.40 | 33.53 | 31.71 | 100.30 | (Fe4.36Ni4.52Co0.05Cu0.02)8.95S8.05 |
| 11 | 76.9 | 6 | 34.15 | 0.42 | 0.68 | 33.58 | 31.76 | 100.60 | (Fe4.37Ni4.47Co0.09Cu0.05)8.98S8.02 |
| 12 | 77.2 | 8 | 34.21 | 0.08 | 0.45 | 33.45 | 32.07 | 100.27 | (Fe4.42Ni4.48Co0.06Cu0.01)8.97S8.03 |
| 13 | 77.9 | 13 | 33.24 | 0.41 | 1.24 | 33.47 | 32.10 | 100.46 | (Fe4.41Ni4.38Co0.16Cu0.03)8.98S8.02 |
| 14 | 78.6 | 11 | 33.23 | 0.51 | 1.19 | 33.69 | 31.85 | 100.46 | (Fe4.38Ni4.37Co0.16Cu0.04)8.95S8.05 |
| 15 | 78.9 | 13 | 33.20 | 0.12 | 4.46 | 33.66 | 29.57 | 101.01 | (Fe4.05Ni4.33Co0.58Cu0.01)8.97S8.03 |
| No. | Pd | Ni | Cu | Co | S | Fe | Total | Mineral Formulas |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 11.26 | 24.62 | 0.42 | 0.61 | 31.91 | 31.62 | 100.44 | (Fe4.58Ni3.39Pd0.86Co0.08Cu0.05)8.96S8.04 |
| 2 | 11.21 | 24.56 | 0.50 | 0.60 | 31.91 | 32.03 | 100.81 | (Fe4.62Ni3.37Pd0.85Co0.08Cu0.06)8.98S8.02 |
| 3 | 11.07 | 24.39 | 0.43 | 0.73 | 32.01 | 32.19 | 100.82 | (Fe4.64Ni3.34Pd0.84Co0.10Cu0.05)8.97S8.03 |
| 4 | 11.07 | 24.90 | 0.39 | 0.71 | 31.85 | 31.63 | 100.56 | (Fe4.60Ni3.32Pd0.85Co0.10Cu0.05)8.92S8.08 |
| 5 | 9.66 | 26.14 | 0.48 | 0.59 | 32.18 | 31.73 | 100.77 | (Fe4.54Ni3.56Pd0.73Co0.08Cu0.06)8.97S8.03 |
| 6 | 9.54 | 25.82 | 0.63 | 0.52 | 32.37 | 31.84 | 100.72 | (Fe4.55Ni3.51Pd0.72Co0.07Cu0.08)8.93S8.07 |
| 7 | 9.51 | 26.16 | 0.68 | 0.53 | 32.06 | 31.53 | 100.46 | (Fe4.53Ni3.57Pd0.72Co0.07Cu0.09)8.98S8.02 |
| 8 | 9.15 | 26.59 | 0.43 | 0.61 | 32.19 | 31.62 | 100.59 | (Fe4.53Ni3.62Pd0.69Co0.08Cu0.05)8.97S8.03 |
| 9 | 9.11 | 26.27 | 0.66 | 0.63 | 32.33 | 31.89 | 100.89 | (Fe4.55Ni3.57Pd0.68Co0.09Cu0.08)8.97S8.03 |
| No. | Pd | Ni | Cu | Co | S | Fe | Total | Mineral Formulas |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 4.32 | 30.38 | 0.34 | 0.66 | 32.74 | 31.84 | 100.28 | (Fe4.47Ni4.06Pd0.32Co0.09Cu0.04)8.98S8.02 |
| 2 | 4.80 | 29.83 | 0.27 | 0.57 | 32.98 | 32.08 | 100.53 | (Fe4.50Ni3.98Pd0.35Co0.08Cu0.03)8.94S8.06 |
| 3 | 1.44 | 33.39 | 0.10 | 0.58 | 33.29 | 31.64 | 100.44 | (Fe4.38Ni4.40Pd0.10Co0.08Cu0.01)8.97S8.03 |
| 4 | 1.06 | 33.79 | 0.09 | 0.58 | 33.74 | 31.74 | 101.00 | (Fe4.36Ni4.41Pd0.08Co0.08Cu0.01)8.09S8.07 |
| 5 | 0.99 | 33.84 | 0.14 | 0.60 | 33.53 | 31.64 | 100.74 | (Fe4.36Ni4.43Pd0.07Co0.08Cu0.02)8.96S8.04 |
| 6 | 0.98 | 33.55 | 0.43 | 0.59 | 33.52 | 31.74 | 100.81 | (Fe4.37Ni4.39Pd0.07Co0.08Cu0.05)8.96S8.04 |
| 7 | 0.65 | 34.34 | 0.13 | 0.57 | 33.75 | 31.50 | 100.95 | (Fe4.32Ni4.48Pd0.05Co0.07Cu0.02)8.94S8.06 |
| 8 | 0.47 | 34.63 | 0.09 | 0.58 | 33.53 | 31.44 | 100.74 | (Fe4.32Ni4.53Pd0.03Co0.08Cu0.01)8.97S8.03 |
| 9 | 0.25 | 34.61 | 0.08 | 0.64 | 34.08 | 31.43 | 101.10 | (Fe4.29Ni4.50Pd0.02Co0.08Cu0.01)8.90S8.10 |
| 10 | 0.22 | 34.23 | 0.14 | 0.57 | 33.00 | 31.23 | 99.40 | (Fe4.35Ni4.54Pd0.02Co0.08Cu0.02)9.01S8.01 |
| 11 | 0.17 | 34.96 | 0.05 | 0.54 | 33.67 | 31.58 | 100.95 | (Fe4.32Ni4.55Pd0.01Co0.07Cu0.01)8.96S8.03 |
| 12 | 0.16 | 34.86 | <0.04 | 0.53 | 33.57 | 31.51 | 100.66 | (Fe4.33Ni4.56Pd0.01Co0.07Cu0.00)8.97S8.03 |
| 13 | 0.14 | 34.99 | 0.06 | 0.53 | 33.54 | 31.46 | 100.72 | (Fe4.32Ni4.57Pd0.01Co0.07Cu0.01)8.98S8.02 |
| 14 | 0.27 | 35.02 | 0.09 | 0.54 | 33.49 | 31.43 | 100.84 | (Fe4.32Ni4.57Pd0.02Co0.07Cu0.01)8.99S8.01 |
| 15 | 0.20 | 34.55 | 0.14 | 0.57 | 33.54 | 31.46 | 100.46 | (Fe4.33Ni4.52Pd0.01Co0.07Cu0.02)8.95S8.04 |
| 16 | 0.24 | 34.78 | 0.12 | 0.53 | 33.57 | 31.54 | 100.78 | (Fe4.33Ni4.54Pd0.02Co0.07Cu0.01)8.97S8.03 |
| 17 | 0.55 | 34.63 | 0.12 | 0.50 | 33.61 | 31.78 | 101.19 | (Fe4.35Ni4.51Pd0.04Co0.06Cu0.01)8.97S8.02 |
| 18 | 0.67 | 34.19 | 0.31 | 0.48 | 33.73 | 31.69 | 101.06 | (Fe4.34Ni4.46Pd0.05Co0.06Cu0.04)8.95S8.05 |
| 19 | 0.49 | 34.46 | 0.12 | 0.50 | 33.54 | 31.55 | 100.66 | (Fe4.34Ni4.51Pd0.04Co0.07Cu0.01)8.97S8.04 |
| 20 | 0.80 | 33.93 | 0.13 | 0.58 | 33.43 | 31.71 | 100.58 | (Fe4.37Ni4.45Pd0.06Co0.08Cu0.02)8.98S8.03 |
| 21 | 0.39 | 34.06 | 0.10 | 0.65 | 33.58 | 31.50 | 100.28 | (Fe4.34Ni4.47Pd0.03Co0.08Cu0.01)8.93S8.06 |
| 22 | 0.86 | 33.97 | 0.07 | 0.58 | 33.49 | 31.50 | 100.46 | (Fe4.35Ni4.46Pd0.06Co0.08Cu0.01)8.96S8.05 |
| 23 | 0.93 | 33.67 | 0.10 | 0.62 | 33.46 | 31.63 | 100.41 | (Fe4.37Ni4.42Pd0.07Co0.08Cu0.01)8.95S8.05 |
| 24 | 2.24 | 32.54 | 0.17 | 0.60 | 33.23 | 31.90 | 100.69 | (Fe4.42Ni4.29Pd0.16Co0.08Cu0.02)8.97S8.02 |
| 25 | 2.91 | 31.68 | 0.47 | 0.55 | 32.94 | 31.95 | 100.50 | (Fe4.45Ni4.20Pd0.21Co0.07Cu0.06)8.99S8.00 |
| 26 | 2.79 | 31.74 | 0.36 | 0.61 | 33.03 | 32.02 | 100.55 | (Fe4.46Ni4.20Pd0.20Co0.08Cu0.04)8.98S8.01 |
| 27 | 2.80 | 31.45 | 0.48 | 0.59 | 33.04 | 32.12 | 100.47 | (Fe4.47Ni4.17Pd0.20Co0.08Cu0.06)8.98S8.02 |
| 28 | 3.47 | 31.19 | 0.30 | 0.59 | 33.01 | 32.16 | 100.73 | (Fe4.48Ni4.14Pd0.25Co0.08Cu0.04)8.99S8.01 |
| 29 | 3.64 | 31.04 | 0.27 | 0.57 | 33.39 | 32.06 | 100.97 | (Fe4.45Ni4.10Pd0.27Co0.07Cu0.03)8.92S8.08 |
| No. | Pd | Ni | Cu | Co | S | Fe | Total | Mineral Formulas |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 4.05 | 29.98 | 0.40 | 0.94 | 32.71 | 32.07 | 100.14 | (Fe4.51Ni4.01Pd0.30Co0.13Cu0.05)9.00S8.01 |
| 2 | 5.37 | 28.90 | 0.52 | 0.74 | 32.54 | 32.38 | 100.44 | (Fe4.57Ni3.88Pd0.40Co0.10Cu0.06)9.01S7.99 |
| 3 | 5.33 | 28.94 | 0.37 | 0.80 | 32.48 | 32.39 | 100.31 | (Fe4.57Ni3.89Pd0.40Co0.11Cu0.05)9.02S7.99 |
| 4 | 5.11 | 29.31 | 0.31 | 0.79 | 32.70 | 32.16 | 100.37 | (Fe4.53Ni3.93Pd0.38Co0.11Cu0.04)8.99S8.02 |
| 5 | 4.53 | 29.92 | 0.25 | 0.81 | 32.78 | 32.34 | 100.62 | (Fe4.53Ni3.99Pd0.33Co0.11Cu0.03)8.99S8.00 |
| 6 | 4.02 | 30.21 | 0.44 | 0.96 | 32.74 | 32.03 | 100.40 | (Fe4.49Ni4.03Pd0.30Co0.13Cu0.05)9.00S8.99 |
| 7 | 3.10 | 30.44 | 0.57 | 1.09 | 33.02 | 31.87 | 100.09 | (Fe4.46Ni4.05Pd0.23Co0.14Cu0.07)8.95S8.05 |
| 8 | 3.67 | 30.80 | 0.29 | 0.90 | 32.66 | 31.77 | 100.08 | (Fe4.46Ni4.12Pd0.27Co0.12Cu0.04)9.01S7.99 |
| 9 | 2.66 | 31.62 | 0.18 | 1.02 | 32.87 | 31.80 | 100.16 | (Fe4.44Ni4.20Pd0.20Co0.14Cu0.02)9.00S8.00 |
| 10 | 3.73 | 30.50 | 0.65 | 0.83 | 32.95 | 31.85 | 100.50 | (Fe4.45Ni4.06Pd0.27Co0.11Cu0.08)8.97S8.03 |
| 11 | 2.95 | 31.37 | 0.15 | 0.80 | 32.96 | 31.69 | 99.92 | (Fe4.44Ni4.18Pd0.22Co0.11Cu0.02)8.97S8.04 |
| 12 | 2.73 | 31.39 | 0.49 | 0.82 | 33.21 | 31.53 | 100.18 | (Fe4.40Ni4.17Pd0.20Co0.11Cu0.06)8.94S8.07 |
| 13 | 2.65 | 31.44 | 0.14 | 0.82 | 33.10 | 31.54 | 99.69 | (Fe4.42Ni4.19Pd0.19Co0.11Cu0.02)8.93S8.07 |
| 14 | 3.59 | 30.60 | 0.24 | 0.67 | 32.66 | 32.05 | 99.81 | (Fe4.51Ni4.10Pd0.27Co0.09Cu0.03)9.00S8.01 |
| 15 | 2.66 | 31.51 | 0.46 | 0.64 | 32.84 | 32.22 | 100.32 | (Fe4.50Ni4.18Pd0.19Co0.08Cu0.06)9.01S7.98 |
| 16 | 1.94 | 32.29 | 0.23 | 0.63 | 33.11 | 32.06 | 100.25 | (Fe4.46Ni4.27Pd0.14Co0.08Cu0.03)8.98S8.02 |
| 17 | 1.18 | 33.06 | 0.20 | 0.64 | 32.96 | 31.97 | 100.01 | (Fe4.45Ni4.37Pd0.09Co0.08Cu0.02)9.01S7.98 |
| 18 | 1.77 | 32.49 | 0.20 | 0.53 | 32.94 | 31.95 | 99.88 | (Fe4.46Ni4.31Pd0.13Co0.07Cu0.02)8.99S8.01 |
| 19 | 1.07 | 33.50 | 0.12 | 0.57 | 33.36 | 31.82 | 100.44 | (Fe4.40Ni4.40Pd0.08Co0.07Cu0.01)8.96S8.03 |
| 20 | 0.18 | 34.30 | 0.11 | 0.57 | 33.39 | 31.53 | 100.07 | (Fe4.36Ni4.51Pd0.01Co0.07Cu0.01)8.96S8.04 |
| 21 | 0.17 | 34.60 | 0.10 | 0.54 | 33.25 | 31.51 | 100.17 | (Fe4.35Ni4.55Pd0.01Co0.07Cu0.01)8.99S8.00 |
| 22 | 0.13 | 34.56 | 0.13 | 0.59 | 33.45 | 31.50 | 100.34 | (Fe4.34Ni4.53Pd0.01Co0.08Cu0.02)8.98S8.03 |
| 23 | 0.28 | 34.32 | 0.18 | 0.61 | 33.28 | 31.54 | 100.20 | (Fe4.36Ni4.51Pd0.02Co0.08Cu0.02)9.00S8.01 |
| 24 | 0.44 | 34.34 | 0.17 | 0.53 | 33.75 | 31.60 | 100.82 | (Fe4.33Ni4.48Pd0.03Co0.07Cu0.02)8.93S8.06 |
| 25 | 0.48 | 34.15 | 0.20 | 0.50 | 33.66 | 31.31 | 100.28 | (Fe4.32Ni4.48Pd0.03Co0.07Cu0.02)8.92S8.08 |
| 26 | 0.39 | 34.04 | 0.26 | 0.55 | 33.44 | 31.46 | 100.14 | (Fe4.35Ni4.47Pd0.03Co0.07Cu0.03)8.95S8.05 |
| 27 | 0.31 | 34.21 | 0.32 | 0.56 | 33.81 | 31.31 | 100.53 | (Fe4.30Ni4.47Pd0.02Co0.07Cu0.04)8.90S8.09 |
| 28 | 0.34 | 34.21 | 0.19 | 0.57 | 33.75 | 31.20 | 100.27 | (Fe4.30Ni4.48Pd0.02Co0.07Cu0.02)8.89S8.10 |
| 29 | 0.51 | 33.96 | 0.24 | 0.51 | 33.42 | 31.24 | 99.89 | (Fe4.33Ni4.48Pd0.04Co0.07Cu0.03)8.95S8.06 |
| 30 | 0.81 | 33.77 | 0.29 | 0.49 | 33.59 | 31.49 | 100.44 | (Fe4.34Ni4.43Pd0.06Co0.06Cu0.04)8.93S8.07 |
| 31 | 1.09 | 32.91 | 0.58 | 0.47 | 33.50 | 31.02 | 99.57 | (Fe4.31Ni4.36Pd0.08Co0.06Cu0.07)8.88S8.12 |
| Ni | Fe | Pd | Cu | Co | S | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Ni | - | −0.61 | −0.93 | −0.48 | −0.10 | 0.72 |
| Fe | −0.61 | - | 0.53 | 0.09 | −0.09 | −0.42 |
| Pd | −0.93 | 0.53 | - | 0.32 | 0.03 | −0.74 |
| Cu | −0.48 | 0.09 | 0.32 | - | 0.13 | −0.21 |
| Co | −0.10 | −0.09 | 0.03 | 0.13 | - | −0.03 |
| S | 0.72 | −0.42 | −0.74 | −0.21 | −0.03 | - |
| Deposit, Location | Shape | Host Mineral (s) | Parent Phase | Pd Content, wt.% | Distribution Pattern of Pd in the Grain | Proposed Mechanism of Pd Enrichment | Reference |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Bushveld, UG-2 (Karee Mine) | Granular Pn | Cp ± Po ± PGE-bismuthotelluride | ISS | 0.02–1.26 | Even | Not discussed | Junge et al., 2015 [17] |
| Bushveld, UG-2 | Granular Pn | Cp ± Po ± Pt-dominant PGM | ISS | 0.92–1003 (×10−4) | There is no information on the distribution of Pd in individual grains. Variation in Pd content in pentlandite along the section was noted | Pd partition into Pn during the exsolution of MSS. A high Pd content in the earlier MSS is suggested | Osbahr et al., 2014 [11] |
| Bushveld, Merensky Reef | Granular Pn and flames | Po + Cp ± Cbn ± Py ± Pt-dominant PGM | MSS | 3.61–1750 (×10−4) | There is no information on the distribution of Pd in individual grains. Variation in Pd content in pentlandite along the section was noted | Pd partition into Pn during the exsolution of MSS. A high Pd content in the earlier MSS is suggested | Osbahr et al., 2013 [10] |
| Bushveld, Merensky Reef | Granular Pn | Po | MSS | 7–600 (×10−4) | No information | Pd diffused into the Pn from ISS during exsolution of sulfides | Godel et al., 2007 [8] |
| Bushveld, Merensky Reef (Impala Mine) | Granular Pn and flames | Pn | High PnSS | 0.08–242 (×10−4) | Zonal. The core is enriched in Pd, the rim is depleted | Peritectic reaction MSS + L = PnSS | Mansur et al., 2019 [43] |
| Bushveld, Platreef (Mogalakwena Mine) | Granular Pn and flames | Po ± Cp ± PGE-bismuthotelluride | MSS | 0.04–0.07 | Even | Not discussed | Junge et al., 2015 [17] |
| Bushveld, Platreef (Mogalakwena Mine) | Granular Pn and flames | Po ± Cp ± Cbn ± PGE-bismuthotelluride | MSS | 3.1–636 (×10−4) | Even in the grain, uneven in the group of grains in the sample | Pentlandite is destroyed and re-deposited by alteration processes. Pentlandite from the different generations contain various concentrations of Pd | Klemd et al., 2016 [18] Klemd et al., 2020 [32] |
| Bushveld, Platreef | Granular Pn and flames | Po ± Cp ± PGE-bismuthotelluride | MSS | 70–200 (×10−4) | Even | High Pd/semimetal ratio. Part of Pd binds to Bi and Te. Excess Pd enters in MSS | Holwell and McDonald, 2007 [16] |
| Stillwater, J-M Reef | Granular Pn | Po ± Cp ± Pt-Fe alloy | MSS | 0.7–9.8 | No information | Pd is released from destructing Pd-Pt sulfide by a fluid and enters the newly formed Pn | Li and Ripley, 2006 [20] |
| Stillwater, J-M Reef | Granular Pn | Po ± Cp | MSS | 0.2–6700 (×10−4) | No information | Fluid transfer of Pd into Pn from outside | Godel and Barnes, 2008 [9] |
| Stillwater, West Fork | Pn grains from crushed samples | Po or Cp | MSS? | 0.19–1.36 | Even | Not discussed | Cabri et al., 1984 [19] |
| Norilsk-1, Mt. Rudnaya | Granular Pn and flames | Po ± Cp | High PnSS | 0.04–4.62 | Zonal. The core is enriched in Pd, the rim is depleted | Peritectic reaction MSS + L = PnSS | Brovchenko et al., 2020 [12] |
| Norilsk-1 | Granular Pn | CbSS + ISS ± MSS | ISS | 1.90–3.05 | Uneven | Not discussed | Distler et al., 1996 [4] |
| Norilsk-1 | Granular Pn | Pn | High PnSS | 0.04–0.10 | Even | Peritectic reaction MSS + L = PnSS | Mansur et al., 2019 [43] |
| Norilsk-1, Medvezhiy Creek Mine | Pn grains from crushed samples | Po or Cp | MSS? | 0.005–0.03 | No information | Not discussed | Cabri et al., 2003 [13] |
| Talnakh, Mayak Mine | Granular Pn and lamellae in Cbn and Cp | Cbn ± Cp | ISS | 0.06–11.26 | Uneven. One side of the grain is enriched in Pd | Fluid transfer of Pd into Pn from outside | This paper |
| Talnakh | Pn grains from crushed samples | Po or Cp | MSS? | 54.5–248 (×10−4) | No information | Not discussed | Cabri et al., 2003 [13] |
| Kharaelakh | Granular Pn and flames | Pn | High PnSS | 55–180 (×10−4) | (1) The core is enriched in Pd, the rim is depleted; (2) different Pd content on the contact with Po and Cp | Peritectic reaction MSS + L = PnSS | Mansur et al., 2019 [43] |
| Aguablanca | Granular Pn and flames | Po ± Cp | MSS | 0.5–7 (×10−4) | No information | Diffusion Pd from ISS | Piña et al., 2012 [42] |
| Jinchuan | Granular Pn and flames | Po ± Cp | MSS | 0.1–6 (×10−4) | Even | Pd diffused into the Pn during exsolution of MSS | Chai et al., 1993 [3] |
| Sudbury, Creighton Mine | Granular Pn and flames | Po ± Cp | MSS | 0.28–2.7 (×10−4) | Zonal. The core is enriched in Pd, the rim is depleted | Pd diffused into the Pn during exsolution of MSS | Dare et al., 2010 [15] |
| Kambalda | Pn grains from crushed samples | Po | MSS | 0.001–0.5 (×10−4) | No information | Stress-induced diffusion of Pd through MSS during cooling or metamorphism | Keays et al., 1981 [14] |
| Experiment at 500° C | No information | Po | MSS | 0–12.5 | Uneven | Pd diffused into the Pn during exsolution of MSS | Makovicky et al., 1986 [44] |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Kalugin, V.; Gusev, V.; Tolstykh, N.; Lavrenchuk, A.; Nigmatulina, E. Origin of the Pd-Rich Pentlandite in the Massive Sulfide Ores of the Talnakh Deposit, Norilsk Region, Russia. Minerals 2021, 11, 1258. https://doi.org/10.3390/min11111258
Kalugin V, Gusev V, Tolstykh N, Lavrenchuk A, Nigmatulina E. Origin of the Pd-Rich Pentlandite in the Massive Sulfide Ores of the Talnakh Deposit, Norilsk Region, Russia. Minerals. 2021; 11(11):1258. https://doi.org/10.3390/min11111258
Chicago/Turabian StyleKalugin, Valery, Viktor Gusev, Nadezhda Tolstykh, Andrey Lavrenchuk, and Elena Nigmatulina. 2021. "Origin of the Pd-Rich Pentlandite in the Massive Sulfide Ores of the Talnakh Deposit, Norilsk Region, Russia" Minerals 11, no. 11: 1258. https://doi.org/10.3390/min11111258
APA StyleKalugin, V., Gusev, V., Tolstykh, N., Lavrenchuk, A., & Nigmatulina, E. (2021). Origin of the Pd-Rich Pentlandite in the Massive Sulfide Ores of the Talnakh Deposit, Norilsk Region, Russia. Minerals, 11(11), 1258. https://doi.org/10.3390/min11111258







