Titanium: An Overview of Resources and Production Methods
Abstract
:1. Introduction
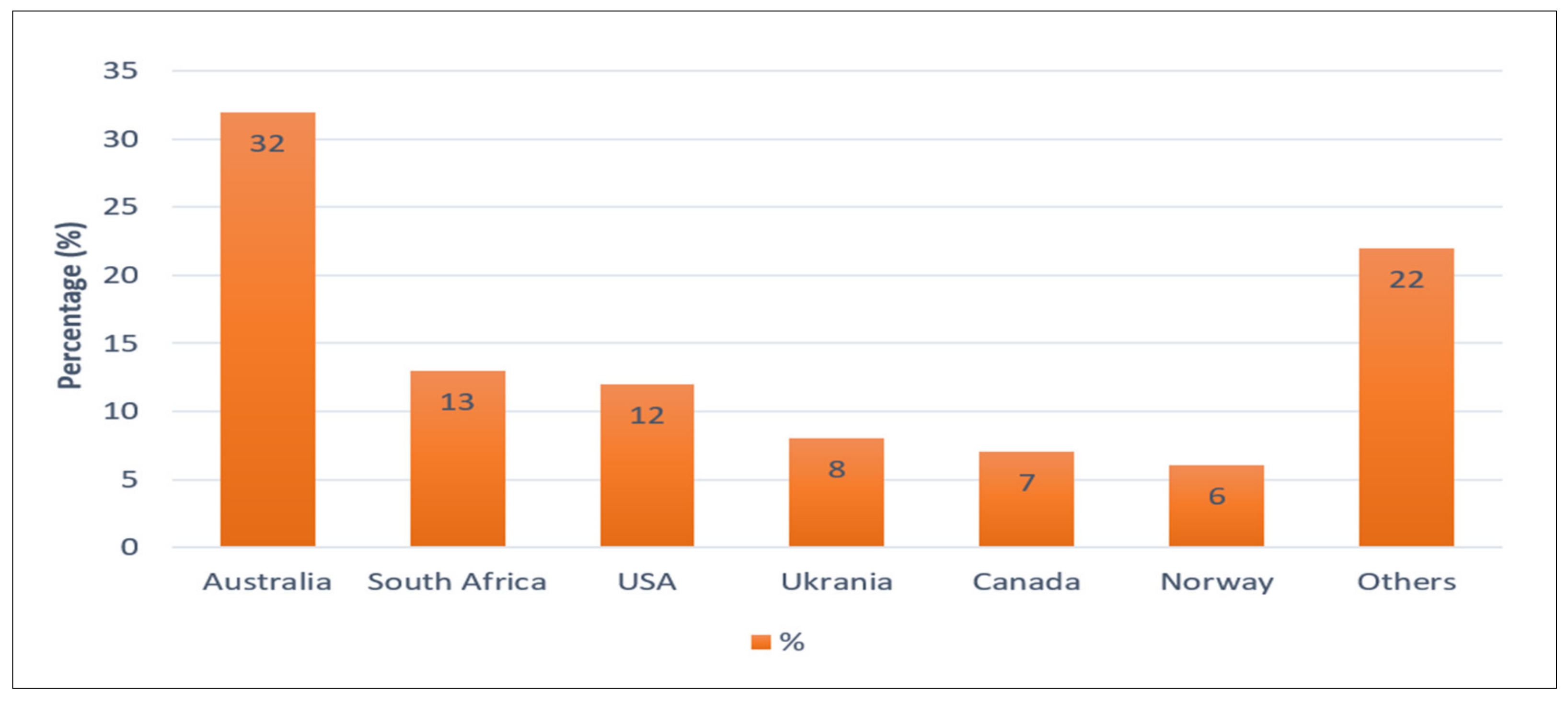
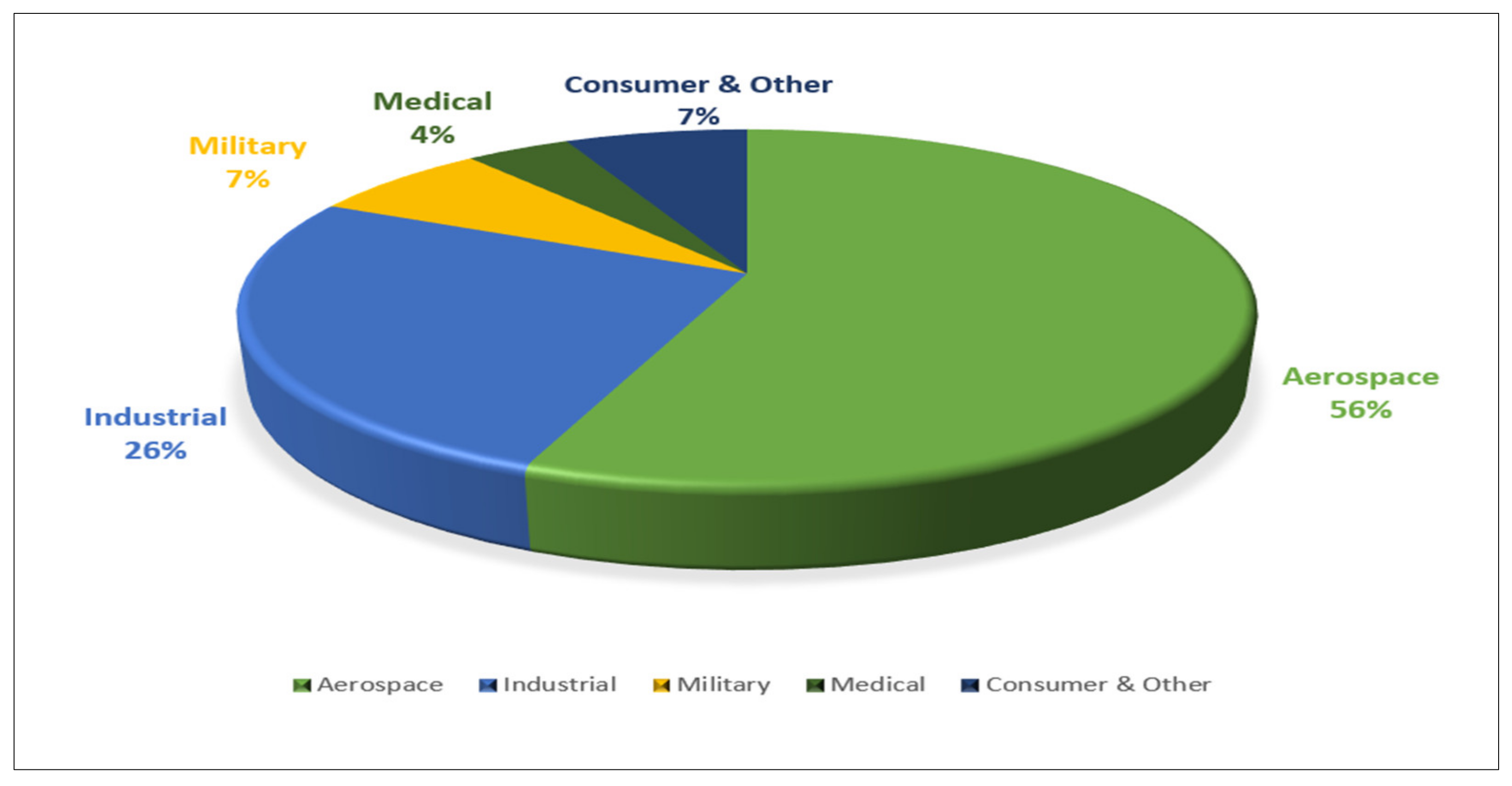
2. Titanium Usage and Market
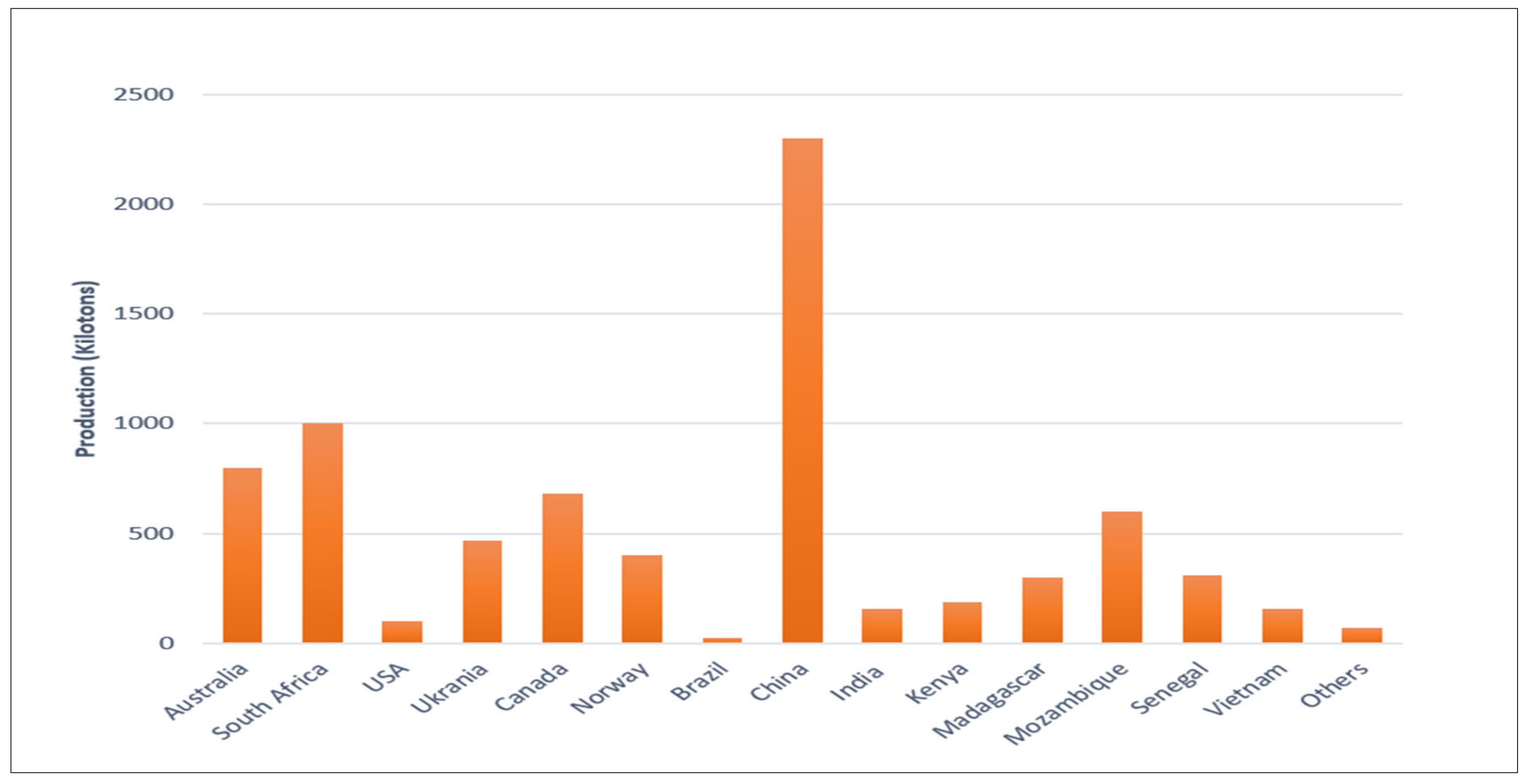
3. Resources
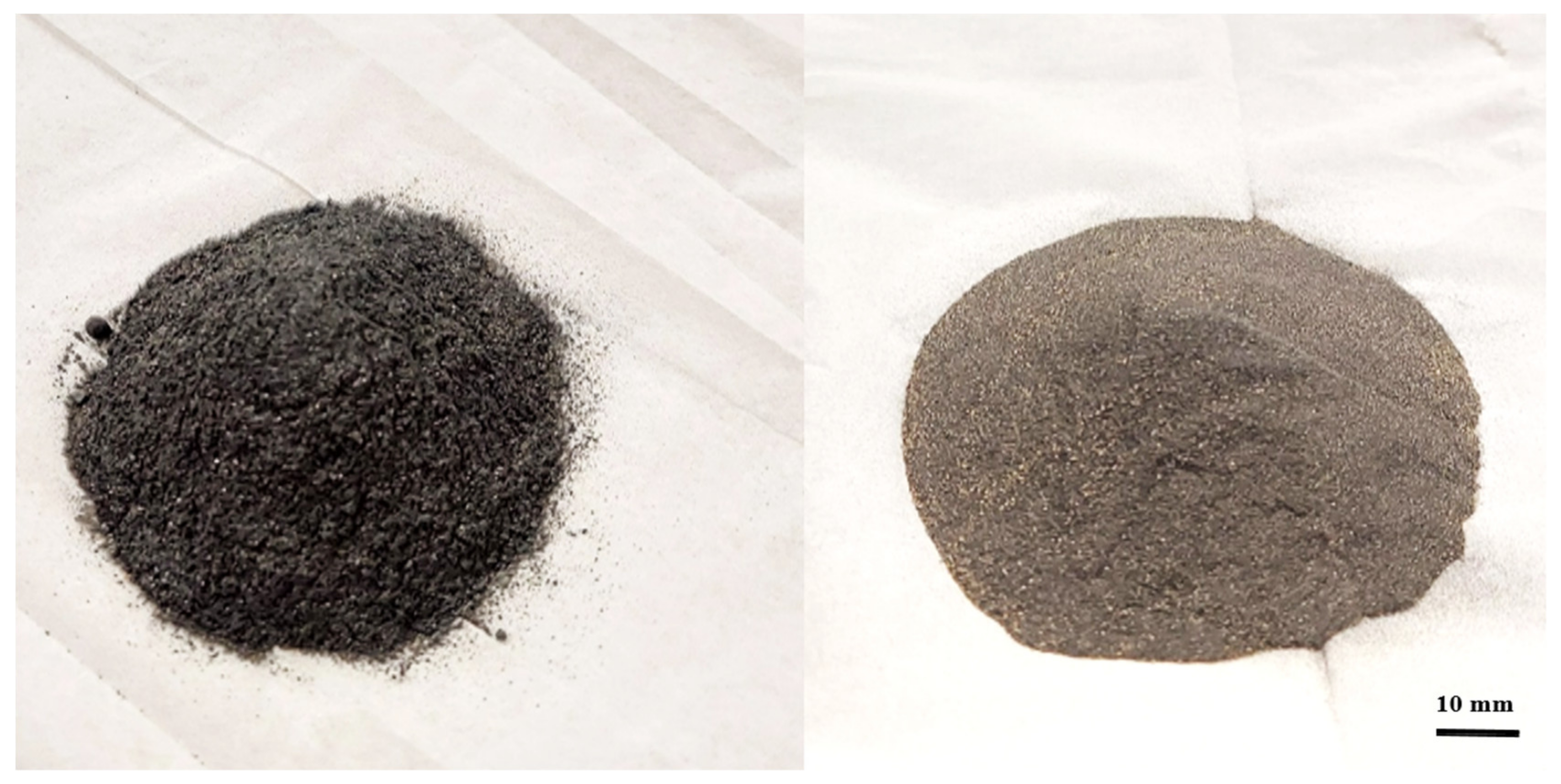
4. Mineral Ilmenite
5. Metallurgical Extraction of Titanium from Its Concentrates
5.1. Thermochemical Processes
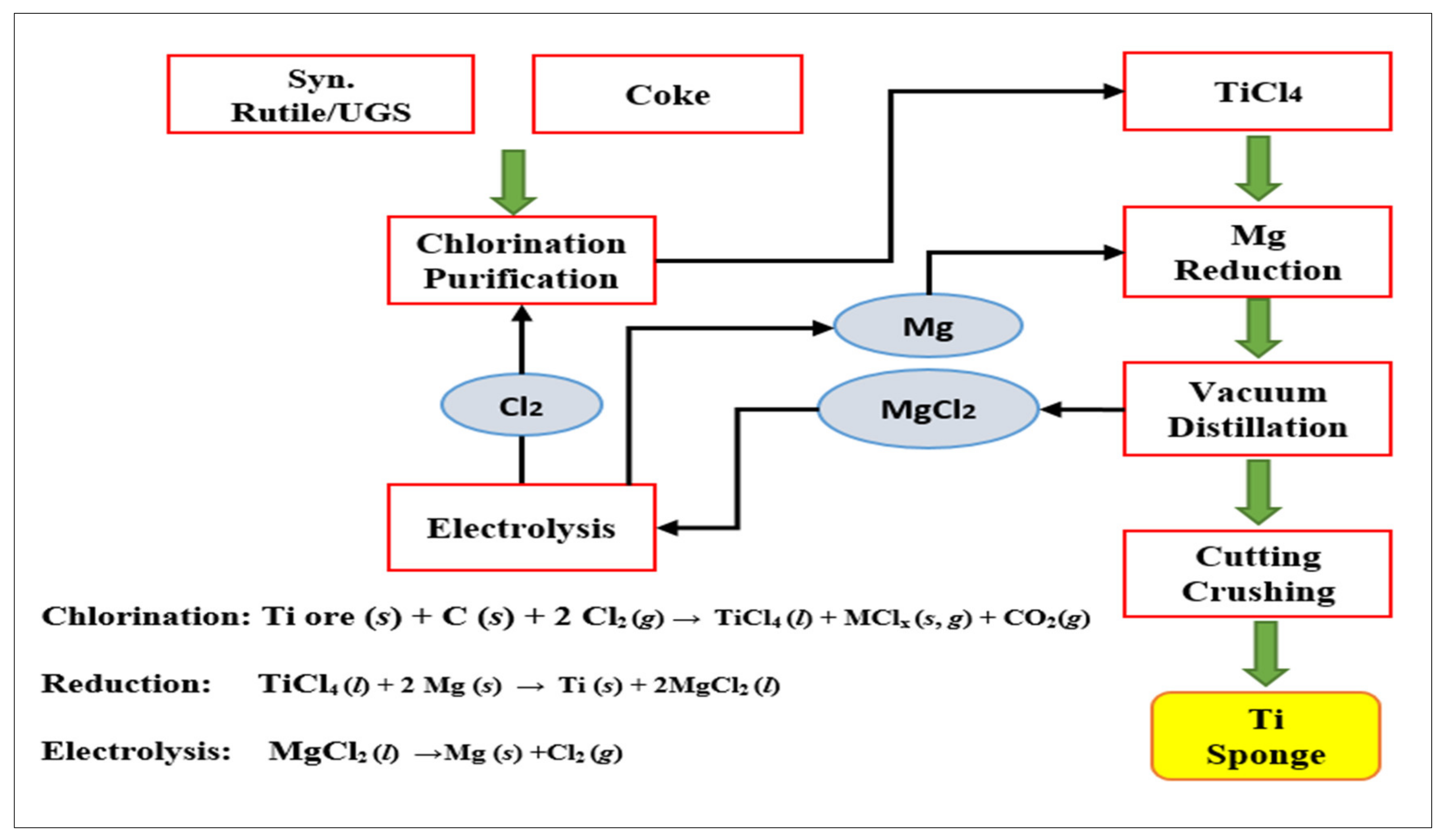
5.1.1. Kroll Process
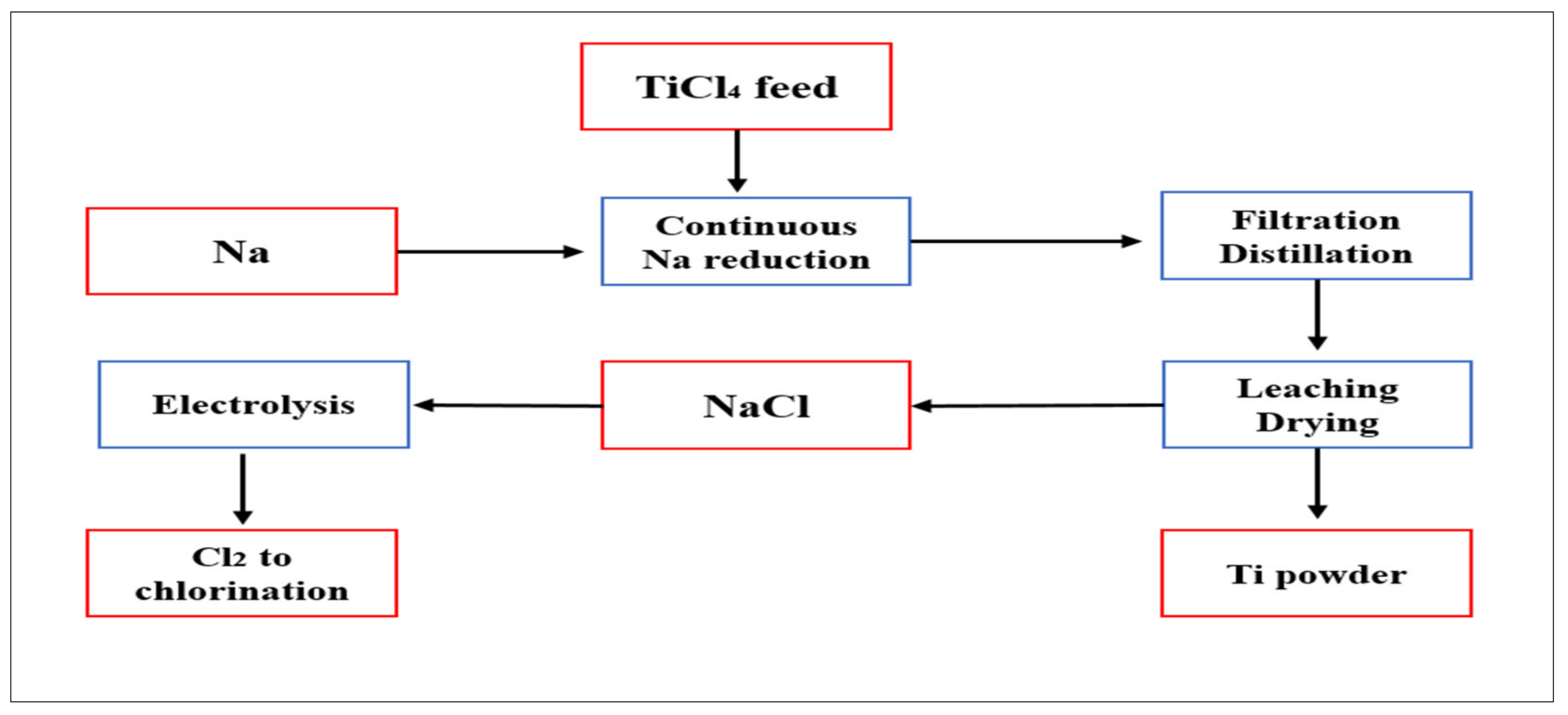
5.1.2. Hunter Process
5.1.3. Armstrong Process
5.1.4. TiRO Process
| Category | Process Identifier | Raw Material | Reducing Agent | Product Size and Morphology | Reported Chemical Product and Composition | Batch or Continuous: Reactions | Salt | Temp (°C) | Ref |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Reducing TiCl4 using Mg | Kroll | TiCl4 | Mg Liquid | Sponge | O∼0.06% | Batch; 2Mg + TiCl4→Ti + 2MgCl2 | No salt | 800–1000 | [13] |
| TiRO | TiCl4 | Mg Powder | Similar spherical shape but sintered to form large chunks | O ≥ 0.3%, Cl < 0.03% | Continuous; 2Mg + TiCl4→Ti + 2MgCl2(s) | No salt | 650–712 | [38] | |
| Vapor Phase Reduction | TiCl4 | Mg Vapor | Sub-micrometer, too fine to be captured | Low levels of Mg and Cl, but O ≥ 0.82%. | Continuous; 2Mg + TiCl4→Ti + 2MgCl2 | No salt | 1000 | [40] | |
| CSIR-Ti | TiCl4 | Mg | Irregular shape, size be ranging from 1 to 330 μm | Cl < 50 ppm, N < 50 ppm, O > 0.2% | Continuous; Mg + TiCl4→TiCl2 + MgCl2TiCl2 + Mg→Ti + MgCl2 | No salt | >900 | [41] | |
| Reducing TiCl4 using Na | Hunter | TiCl4 | Na | Sponge and powder | Purer than that produced by the Kroll process (99%) | Batch; 4Na + TiCl4→Ti + 4NaCl | No salt | >800 | [27,42] |
| Armstrong | TiCl4 | Na | Mini sponge, particulates with micro porosity | O: 0.12–0.23%, N: 0.009–0.026%, C: 0.013%, Fe: 0.012% | Continuous; 4Na + TiCl4→Ti + 4NaCl | No salt | 860 | [34,35] | |
| ARC | TiCl4 | Na | Powder, small aggregates | Oxide layer contributes a lot to the final high oxygen content | Continuous; 2Na + TiCl4→TiCl2 + 2NaCl TiCl2 + 2Na→Ti + 2NaCl | No salt | >800 | [43] |
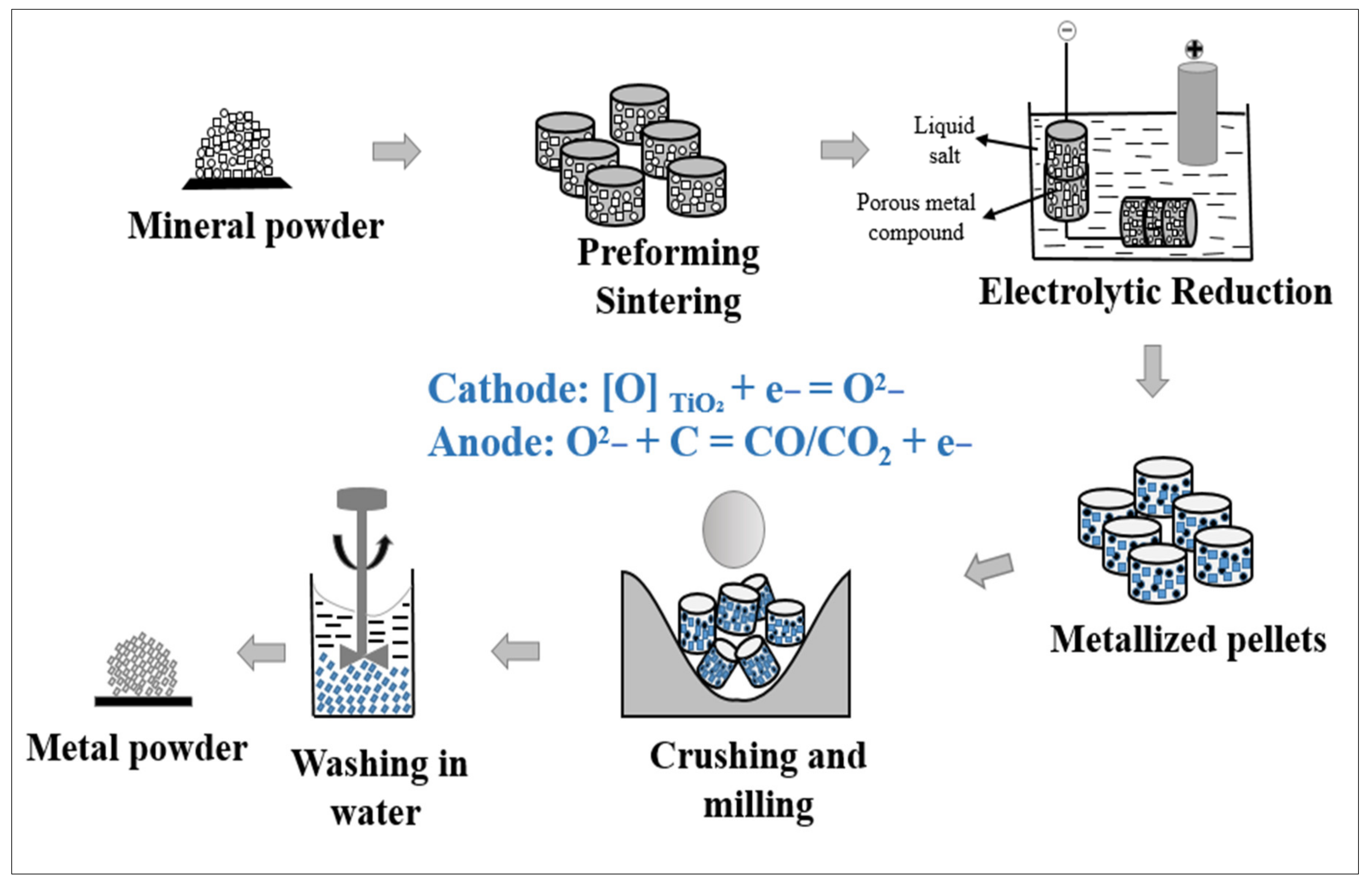
5.1.5. Metal Hydride Reduction (MHR) Process
5.1.6. Electronically Mediated Reduction (EMR) Process
5.1.7. Process for Reducing Preforms
5.1.8. Hydrogen-Assisted Magnesium Reduction (HAMR) Process
| Publication N° | Title | Advantages | Disadvantages | Reference |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| US 2016/0108497 A1 (2016) | Methods of producing a titanium product |
|
| [51] |
| US 9,963,796 B2 (2018) | Method of producing titanium metal with titanium-containing material |
|
| [71] |
| US 10,066,308 B2 (2018) | System and method for extraction and refining of titanium |
|
| [73] |
| US 9,067.264 B2 (2015) | Method of manufacturing pure titanium hydride powder and alloyed titanium hydride powders by combined hydrogen-magnesium reduction of metal halides |
|
| [74] |
| US 8,388,727 B2 (2013) | Continuous and semi-continuous process of manufacturing titanium hydride using titanium chlorides of different valency |
|
| [75] |
| Re. 34,598 (1994) | Highly pure titanium |
|
| [76] |
| US 4,923,531 (1990) | Deoxidation of titanium and similar metals using a deoxidant in a molten metal carrier |
|
| [72] |
| US 8,007,562 B2 (2011) | Semi-continuous magnesium-hydrogen reduction process for manufacturing of hydrogenated, purified titanium powder |
|
| [77] |
| US 10,689,730 B2 (2020) | Methods of producing a titanium product |
|
| [78] |
| US 583,492 B2 (2020) | Titanium powder production apparatus and method |
|
| [79] |
5.2. Electrochemical Processes
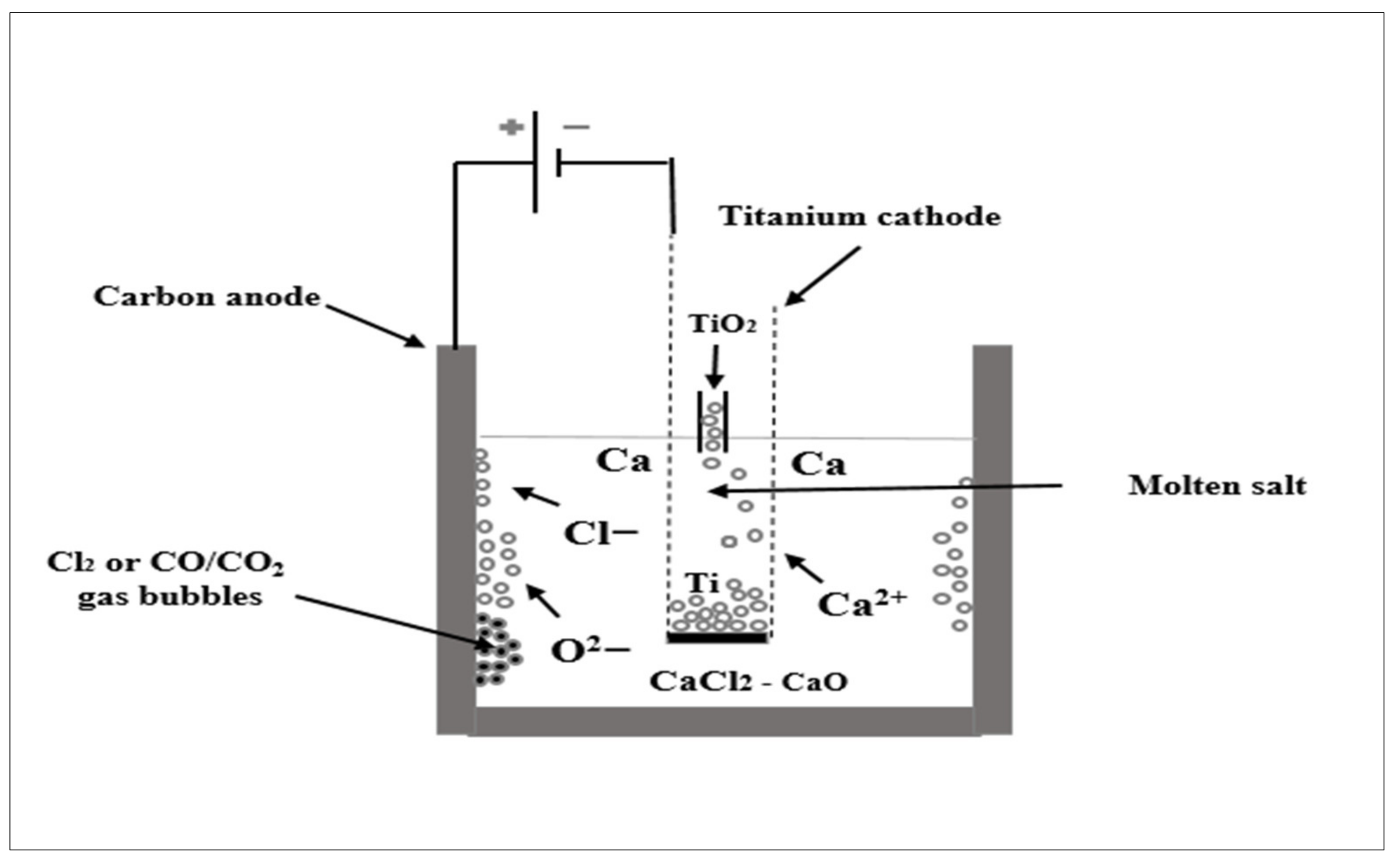
5.2.1. Cambridge FFC Method
5.2.2. Ono and Suzuki Process
5.2.3. Quebec Iron and Titane (QIT) Process
6. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Sibum, H. Titanium and titanium alloys—From raw material to semi-finished products. Adv. Eng. Mater. 2003, 5, 393–398. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Leyens, C.; Peters, M. Titanium and Titanium Alloys: Fundamentals and Applications; John Wiley & Sons: Hoboken, NJ, USA, 2003. [Google Scholar]
- Cui, C.; Hu, B.; Zhao, L.; Liu, S. Titanium alloy production technology, market prospects and industry development. Mater. Des. 2011, 32, 1684–1691. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mutava, T.D. Characterisation of a Titanium Precursor Salt and Study of Some of the Treatment Steps Used for the Extraction Process. Ph.D. Thesis, University of the Witwatersrand, Johannesburg, South Africa, 2009. [Google Scholar]
- Jackson, M.; Dring, K. A review of advances in processing and metallurgy of titanium alloys. Mater. Sci. Technol. 2006, 22, 881–887. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Force, E.R. Geology of Titanium-Mineral Deposits; Geological Society of America: Boulder, CO, USA, 1991; Volume 259. [Google Scholar]
- U.S. Geological Survey. Mineral Commodity Summaries 2021; U.S. Geological Survey: Reston, VA, USA, 2021; 200p.
- Force, E.R. Geology and Resources of Titanium; Geological Society of America: Boulder, CO, USA, 1976. [Google Scholar]
- Van Gosen, B.S.; Fey, D.L.; Shah, A.K.; Verplanck, P.L.; Hoefen, T.M. Deposit Model for Heavy-Mineral Sands in Coastal Environments: Chapter L in Mineral Deposit Models for Resource Assessment; US Geological Survey: Reston, VI, USA, 2014.
- Fadeel, B. Handbook of Safety Assessment of Nanomaterials: From Toxicological Testing to Personalized Medicine; Pan Stanford; CRC Press: Boca Raton, FL, USA, 2014. [Google Scholar]
- Fang, Z.Z.; Paramore, J.D.; Sun, P.; Chandran, K.R.; Zhang, Y.; Xia, Y.; Free, M. Powder metallurgy of titanium—Past, present, and future. Int. Mater. Rev. 2018, 63, 407–459. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, M.; Wang, D.; Wang, W.; Hu, X.; Jin, X.; Chen, G.Z. Extraction of titanium from different titania precursors by the FFC Cambridge process. J. Alloys Compd. 2006, 420, 37–45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kroll, W. The production of ductile titanium. Trans. Electrochem. Soc. 1940, 78, 35–47. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Berthaud, M. Étude du Comportement de L’alliage de Titane Ti6242S à Haute Température sous Atmosphères Complexes: Applications Aéronautiques. Ph.D. Thesis, Université Bourgogne Franche-Comté, Besançon, France, 2018. [Google Scholar]
- Samal, S. Thermal Plasma Processing of Ilmenite; Springer: Berlin/Heildelberg, Germany, 2017. [Google Scholar]
- Froes, F. Titanium: Physical Metallurgy, Processing, and Applications; ASM International: Novelty, OH, USA, 2015. [Google Scholar]
- Fang, Z.Z.; Lefler, H.D.; Froes, F.H.; Zhang, Y. Introduction to the development of processes for primary Ti metal production. In Extractive Metallurgy of Titanium; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2020; pp. 1–10. [Google Scholar]
- Biehl, V.; Wack, T.; Winter, S.; Seyfert, U.T.; Breme, J. Evaluation of the haemocompatibility of titanium based biomaterials. Biomol. Eng. 2002, 19, 97–101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bessinger, D.; Geldenhuis, J.M.A.; Pistorius, P.C.; Mulaba, A.; Hearne, G. The decrepitation of solidified high titania slags. J. Non Cryst. Solids 2001, 282, 132–142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nagesh, C.R.; Ramachandran, C.; Subramanyam, R. Methods of titanium sponge production. Trans. Indian Inst. Met. 2008, 61, 341–348. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vilakazi, A.Q. Hydrometallurgical Beneficiation of Ilmenite. Ph.D. Thesis, University of the Free State, Bloemfontein, South Africa, 2017. [Google Scholar]
- Wilson, N.C.; Muscat, J.; Mkhonto, D.; Ngoepe, P.E.; Harrison, N.M. Structure and properties of ilmenite from first principles. Phys. Rev. B 2005, 71, 075202. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Charlier, B.; Namur, O.; Bolle, O.; Latypov, R.; Duchesne, J.C. Fe–Ti–V–P ore deposits associated with Proterozoic massif-type anorthosites and related rocks. Earth-Sci. Rev. 2015, 141, 56–81. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Korneliussen, A.; McENROE, S.A.; Nilsson, L.P.; Schiellerup, H.; Gautneb, H.; Meyer, G.B.; Storseth, L.R. An overview of titanium deposits in Norway. Norges Geologiske Undersokelse 2000, 436, 27–38. [Google Scholar]
- Froes, F. Titanium powder metallurgy: A review-part 1. Adv. Mater. Process. 2012, 170, 16–22. [Google Scholar]
- McCracken, C.G.; Motchenbacher, C.; Barbis, D.P. Review of titanium powder production methods. Int. J. Powder Metall. 2010, 46, 19–25. [Google Scholar]
- Hunter, M. Metallic titanium. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 1910, 32, 330–336. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Florkiewicz, W.; Malina, D.; Tyliszczak, B.; Sobczak-Kupiec, A. Manufacturing of titanium and its alloys. In Sustainable Production: Novel Trends in Energy, Environment and Material Systems; Springer: Berlin, Heidelberg, 2020; pp. 61–74. [Google Scholar]
- Hartman, A.D.; Gerdemann, S.J.; Hansen, J.S. Producing lower-cost titanium for automotive applications. JOM 1998, 50, 16–19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kohli, R. Production of Titanium from Ilmenite: A Review; Lawrence Berkeley Lab.: Berkeley, CA, USA, 1981.
- Gambogi, J.; Gerdemann, S. Titanium metal: Extraction to application. In Review of Extraction, Processing, Properties & Applications of Reactive Metals; John Wiley & Sons: Hoboken, NJ, USA, 1999; pp. 175–210. [Google Scholar]
- Agripa, H.; Botef, I. Modern production methods for titanium alloys: A review. In Titanium Alloys-Novel Aspects of Their Processing; IntechOpen: London, UK, 2019. [Google Scholar]
- Kraft, E. Summary of Emerging Titanium Cost Reduction Technologies; EHK Technologies: Burlington, WA, USA, 2004. [Google Scholar]
- Crowley, G. How to extract low-cost titanium. Adv. Mater. Process. 2003, 161, 25–27. [Google Scholar]
- Chen, W.; Yamamoto, Y.; Peter, W.H. Investigation of pressing and sintering processes of CP-Ti powder made by Armstrong Process. In Key Engineering Materials; Trans Tech Publications: Stafa-Zurich, Switzerland, 2010. [Google Scholar]
- Araci, K.; Mangabhai, D.; Akhtar, K. Production of titanium by the Armstrong Process®. In Titanium Powder Metallurgy; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2015; pp. 149–162. [Google Scholar]
- Brooks, G.; Cooksey, M.; Wellwood, G.; Goodes, C. Challenges in light metals production. Miner. Process. Extr. Metall. 2007, 116, 25–33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Doblin, C.; Chryss, A.; Monch, A. Titanium powder from the TiRO™ process. In Key Engineering Materials; Trans Tech Publications: Stafa-Zurich, Switzerland, 2012. [Google Scholar]
- Van Vuuren, D.S. Direct titanium powder production by metallothermic processes. In Titanium Powder Metallurgy; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2015; pp. 69–93. [Google Scholar]
- Hansen, D.A.; Gerdemann, S.J. Producing titanium powder by continuous vapor-phase reduction. JOM 1998, 50, 56–58. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Van Vuuren, D.; Oosthuizen, S.; Heydenrych, M.D. Titanium production via metallothermic reduction of TiCl4in molten salt: Problems and products. J. S. Afr. Inst. Min. Metall. 2011, 111, 141–147. [Google Scholar]
- Mo, W.; Deng, G.; Luo, F. Titanium Metallurgy; Metallurgical Industry Press: Beijing, China, 1998. [Google Scholar]
- Mishra, B.; Kipouros, G.J. Titanium Extraction and Processing; The Minerals, Metals & Materials Society: Warrendale, PA, USA, 1997. [Google Scholar]
- Borok, B. Obtaining powders of alloys and steels by a complex reduction of oxide mixtures by CaH2. Trans. Cent. Res. Inst. Ferr. Met. 1965, 43, 69–80. [Google Scholar]
- Froes, F. The production of low-cost titanium powders. JOM J. Miner. Met. Mater. Soc. 1998, 50, 41–43. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Fang, Z.Z.; Sun, P.; Zheng, S.; Xia, Y.; Free, M. A Perspective on thermochemical and electrochemical processes for titanium metal production. JOM 2017, 69, 1861–1868. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Park, I.; Abiko, T.; Okabe, T.H. Production of titanium powder directly from TiO2 in CaCl2 through an electronically mediated reaction (EMR). J. Phys. Chem. Solids 2005, 66, 410–413. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Okabe, T.H.; Oda, T.; Mitsuda, Y. Titanium powder production by preform reduction process (PRP). J. Alloys Compd. 2004, 364, 156–163. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fray, D. Novel methods for the production of titanium. Int. Mater. Rev. 2008, 53, 317–325. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Fang, Z.Z.; Xia, Y.; Huang, Z.; Lefler, H.; Zhang, T.; Guo, J. A novel chemical pathway for energy efficient production of Ti metal from upgraded titanium slag. Chem. Eng. J. 2016, 286, 517–527. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Fang, Z.Z.; Zhang, Y.; Xia, Y.; Sun, P. Methods of Producing a Titanium Product. U.S. Patent 2016/0108497 A1, 23 June 2016. [Google Scholar]
- Froes, F.; Eylon, D. Powder metallurgy of titanium alloys. Int. Mater. Rev. 1990, 35, 162–184. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alexander, P.P. Production of Titanium Hydride. U.S. Patent 2,427,338, 16 September 1947. [Google Scholar]
- Suzuki, R.O.; Ono, K.; Teranuma, K. Calciothermic reduction of titanium oxide and in-situ electrolysis in molten CaCl2. Metall. Mater. Trans. B 2003, 34, 287–295. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abiko, T.; Park, I.; Okabe, T.H. Reduction of titanium oxide in molten salt medium. In Proceedings of the 10th World Conference on Titanium, Ti-2003, Hamburg, Germany, 13–18 July 2003. [Google Scholar]
- Won, C.; Nersisyan, H.; Won, H. Titanium powder prepared by a rapid exothermic reaction. Chem. Eng. J. 2010, 157, 270–275. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nersisyan, H.; Lee, J.; Won, C. Combustion of TiO2–Mg and TiO2–Mg–C systems in the presence of NaCl to synthesize nanocrystalline Ti and TiC powders. Mater. Res. Bull. 2003, 38, 1135–1146. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Fang, Z.Z.; Sun, P.; Zhang, T.; Xia, Y.; Zhou, C.; Huang, Z. Thermodynamic destabilization of Ti-O solid solution by H2 and deoxygenation of Ti using Mg. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2016, 138, 6916–6919. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lu, X.; Ono, T.; Takeda, O.; Zhu, H. Production of fine titanium powder from titanium sponge by the shuttle of the disproportionation reaction in molten NaCl–KCl. Mater. Trans. 2019, 60, 405–410. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Ardani, M.R.; Al Janabi, A.S.M.; Udayakumar, S.; Hamid, S.A.R.S.A.; Mohamed, A.R.; Lee, H.L.; Ibrahim, I. Reduction of TiCl4 to TiH2 with CaH2 in presence of Ni powder. In Rare Metal Technology 2019; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2019; pp. 131–144. [Google Scholar]
- Lei, X.; Xu, B.; Yang, G.; Shi, T.; Liu, D.; Yang, B. Direct calciothermic reduction of porous calcium titanate to porous titanium. Mater. Sci. Eng. C 2018, 91, 125–134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, C.; Ouchi, T.; Iizuka, A.; Taninouchi, Y.K.; Okabe, T.H. Deoxidation of titanium using Mg as deoxidant in MgCl2-YCl3 flux. Metall. Mater. Trans. B 2019, 50, 622–631. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Spreitzer, D.; Schenk, J. Iron ore reduction by hydrogen using a laboratory scale fluidized bed reactor: Kinetic investigation—Experimental setup and method for determination. Metall. Mater. Trans. B 2019, 50, 2471–2484. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Bolivar, R.; Friedrich, B. Magnesiothermic reduction from titanium dioxide to produce titanium powder. J. Sustain. Metall. 2019, 5, 219–229. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mojisola, T.; Ramakokovhu, M.M.; Raethel, J.; Olubambi, P.A.; Matizamhuka, W.R. In-situ synthesis and characterization of Fe–TiC based cermet produced from enhanced carbothermally reduced ilmenite. Int. J. Refract. Met. Hard Mater. 2019, 78, 92–99. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chae, J.; Oh, J.M.; Yoo, S.; Lim, J.W. Eco-friendly pretreatment of titanium turning scraps and subsequent preparation of ferro-titanium ingots. Korean J. Met. Mater. 2019, 57, 569–574. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ri, V.; Nersisyan, H.; Kwon, S.C.; Lee, J.H.; Suh, H.; Kim, J.G. A thermochemical and experimental study for the conversion of ilmenite sand into fine powders of titanium compounds. Mater. Chem. Phys. 2019, 221, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, Z.; Cheng, G.; Yang, H.; Xue, X.; Ri, J. Preparation of ferrotitanium using ilmenite with different reduction degrees. Metals 2019, 9, 962. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Zhang, G.; Gou, H.; Wu, K.; Chou, K. Carbothermic reduction of Panzhihua ilmenite in vacuum. Vacuum 2017, 143, 199–208. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, D.H.; Kim, T.S.; Heo, J.H.; Park, H.S.; Park, J.H. Influence of temperature on reaction mechanism of ilmenite ore smelting for titanium production. Metall. Mater. Trans. B 2019, 50, 1830–1840. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mu, H.; Mu, T.; Zhao, S.; Zhu, F.; Deng, B.; Peng, W.; Yan, B. Method of Producing Titanium Metal With Titanium-Containing Material. U.S. Patent 9,963,796, 8 May 2018. [Google Scholar]
- Fisher, R.L. Deoxidation of Titanium and Similar Metals Using a Deoxidant in a Molten Metal Carrier. U.S. Patent 4,923,531, 8 May 1990. [Google Scholar]
- Cox, J.R.; DeALWIS, C.L.; Kohler, B.A.; Lewis, M.G. System and Method for Extraction and Refining of Titanium. U.S. Patent 10,066,308, 4 September 2018. [Google Scholar]
- Moxson, V.S.; Duz, V.A.; Klevtsov, A.G.; Sukhoplyuyev, V.D.; Sopka, M.D.; Shuvalov, Y.V.; Matviychuk, M. Method of Manufacturing Pure Titanium Hydride Powder and Alloyed Titanium Hydride Powders by Combined Hydrogen-Magnesium Reduction of Metal Halides. U.S. Patent 9,067,264, 30 June 2015. [Google Scholar]
- Klevtsov, A.; Nikishin, A.; Shuvalov, J.; Moxson, V.; Duz, V. Continuous and Semi-Continuous Process of Manufacturing Titanium Hydride Using Titanium Chlorides of Different Valency. U.S. Patent 8,388,727, 5 March 2013. [Google Scholar]
- Shimotori, K.; Ochi, Y.; Ishihara, H.; Umeki, T.; Ishigami, T. Highly Pure Titanium. U.S. Patent RE34,598, 3 May 1994. [Google Scholar]
- Kasparov, S.A.; Klevtsov, A.G.; Cheprasov, A.I.; Moxson, V.S.; Duz, V.A. Semi-Continuous Magnesium-Hydrogen Reduction Process for Manufacturing of Hydrogenated, Purified Titanium Powder. U.S. Patent 8,007,562, 30 August 2011. [Google Scholar]
- Fang, Z.Z.; Zhang, Y.; Xia, Y.; Sun, P. Methods of Producing a Titanium Product. U.S. Patent 10,689,730, 23 June 2020. [Google Scholar]
- Hanusiak, W.M.; McBride, D.R. Titanium Powder Production Apparatus and Method. U.S. Patent 10,583,492, 10 March 2020. [Google Scholar]
- Chen, G.Z.; Fray, D.J.; Farthing, T.W. Direct electrochemical reduction of titanium dioxide to titanium in molten calcium chloride. Nature 2000, 407, 361. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, G.Z. The FFC Cambridge process and its relevance to valorisation of ilmenite and titanium-rich slag. Miner. Process. Extr. Metall. 2015, 124, 96–105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, K.; Wang, Y.; Gao, F. Electrochemical extraction of titanium from carbon-doped titanium dioxide precursors by electrolysis in chloride molten salt. Ionics 2019, 12, 6107–6114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Furuta, T.; Nishino, K.; Hwang, J.; Yamada, A.; Ito, K.; Osawa, S.; Kuramoto, S.; Suzuki, N.; Chen, R.; Saito, T. Development of multi functional titanium alloy, “Gum Metal”. In Ti-2003 Science and Technology; Lütjering, G., Albrecht, J., Eds.; Wiley-VCH: Weinheim, Germany, 2004. [Google Scholar]
- Cardarelli, F. Method for Electrowinning of Titanium Metal or Alloy from Titanium Oxide Containing Compound in the Liquid State. U.S. Patent 7,504,017, 17 March 2009. [Google Scholar]
- Mohanty, J.; Behera, P.K. Use of pre-treated TiO2 as cathode material to produce Ti metal through molten salt electrolysis. Trans. Indian Inst. Met. 2019, 72, 859–865. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, G.; Xu, B.; Wan, H.; Wang, F.; Yang, B.; Wang, Z. Effect of CaCl2 on microstructure of calciothermic reduction products of Ti2O3 to prepare porous titanium. Metals 2018, 8, 698. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Noguchi, H.; Natsui, S.; Kikuchi, T.; Suzuki, R.O. Reduction of CaTiO3 by electrolysis in the molten salt CaCl2-CaO. Electrochemistry 2018, 86, 82–87. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Zhu, F.; Qiu, K.; Sun, Z. Preparation of titanium from TiCl4 in a molten fluoride-chloride salt. Electrochemistry 2017, 85, 715–720. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Yang, G.; Xu, B.; Lei, X.; Wan, H.; Yang, B.; Liu, D.; Wang, Z. Preparation of porous titanium by direct in-situ reduction of titanium sesquioxide. Vacuum 2018, 157, 453–457. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, C.; Song, J.; Li, S.; Li, X.; Shu, Y.; He, J. An investigation on electrodeposition of titanium in molten LiCl-KCl. In Materials Processing Fundamentals 2019; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2019; pp. 193–202. [Google Scholar]
- Xia, Y.; Fang, Z.Z.; Zhang, Y.; Lefler, H.; Zhang, T.; Sun, P.; Huang, Z. Hydrogen assisted magnesiothermic reduction (HAMR) of commercial TiO2 to produce titanium powder with controlled morphology and particle size. Mater. Trans. 2017, 58, 355–360. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Zhu, H.; Wang, Q.; Jiao, S. Method for Electrowinning Titanium from Titanium-Containing Soluble Anode Molten Salt. U.S. Patent 10,081,874, 25 September 2018. [Google Scholar]
- Fray, D.J.; Farthing, T.W.; Chen, Z. Removal of Substances from Metal and Semi-Metal Compounds. U.S. Patent 7,790,014, 7 September 2010. [Google Scholar]
- Withers, J.C.; Loutfy, R.O. Thermal and Electrochemical Process for Metal Production. U.S. Patent 7,985,326, 26 July 2011. [Google Scholar]
- Withers, J.C.; Loutfy, R.O. Electrochemical Process for Titanium Production. U.S. Patent EP 2 322 693 B1, 18 August 2004. [Google Scholar]
- Withers, J.C.; Loutfy, R.O. Thermal and Electrochemical Process for Metal Production. U.S. Patent 2007/0029208A1, 8 February 2008. [Google Scholar]


| Parameter | Value |
|---|---|
| Atomic number | 22 |
| Atomic radius (Å) | 1.47 |
| Atomic weight | 47.9 |
| Boiling point (K) | 3273 |
| Chemical valence | 2, 3, 4 |
| Electrical resistivity | 42.06 × 10−6 |
| Ion radius (Å) Ti+2 | 0.9 |
| Ion radius (Å) Ti+4 | 0.68 |
| Melting point (K) | 2073 |
| Density (g/cm3) | 4.51 |
| Specific heat (J/kg–K) | 519 |
| Traction modulus × 103 (MPa) | 101 |
| Modulus of elasticity × 103 (MPa) | 103 |
| Hardness (1500 kg load) (HB) | 65 |
| Fatigue resistance | 0.5–0.6 |
| Property | Value |
|---|---|
| Chemical classification | Oxide |
| Color | Black |
| Luster | Metallic, sub-metallic |
| Mohs hardness | 5–6 |
| Specific weight | 4.7–4.8 g/cm3 |
| Crystalline structure | Hexagonal |
| Cleavage | Absent |
| Unit cell | a = b = 508.854 Å, c = 14.0924 Å |
| Kroll | Hunter |
|---|---|
| Batch | Does not last forever |
| 15–50% excess magnesium | A small excess of TiCl4 |
| Few fines | Up to 10% fines |
| Difficult to rectify | Easy to rectify |
| Heavy iron contamination from the walls of the autoclave | Little iron contamination from retort walls. |
| Sponge washed or vacuum distilled | Sponge leached |
| Retort contains mostly titanium | Retort contains 4 moles of NaCl for each mole of titanium |
| Process Identifier | Raw Material | Reducing Agent | Product Size and Morphology | Reported Chemical Product and Composition | Salt | Temperature (°C) | Ref |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| MHR | TiO2 | CaH2 | Irregular, sponge | O: 0.19 wt.%, H: 0.34 wt.%, C: 0.03 wt.%, N: 0.06 wt.% | No salt | 1100–1200 | [52,53] |
| Calciothermal reduction | TiO2 | Ca | Irregular, sponge | O: <0.2 wt.%, Ca: >0.1 wt.% | CaCl2 | 900–1200 | [54] |
| Process for reducing preforms | TiO2 | Ca | Irregular, sponge | O: 0.2–0.3 wt.% | CaCl2 | >900 | [48] |
| EMR | TiO2 | Ca | Irregular, sponge | O: 0.15–0.2 wt.% | CaCl2 or CaCl2 + CaO | >900 | [47,55] |
| Combustion synthesis | TiO2 | Mg + Ca | Irregular, sponge | O: 0.2–0.3 wt.% | Ca(OH)2 | 850–1000 | [56,57] |
| HAMR | UGS | Mg + Ca | Dense, globular powder | O: <0.15 wt.% | MgCl2 or MgCl2-KCl | <800 | [50,58] |
| Publication N° | Title | Advantages | Disadvantages | Reference |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| US 10, 081, 874 B2 (2018) | Method for electrowinning titanium from titanium-containing soluble anode molten salt |
|
| [92] |
| US 7,790,014 B2 (2010) | Removal of substances from metal and semi-metal compounds |
|
| [93] |
| US 7,504,017 B2 (2009) | Method for electrowinning of titanium metal or alloy from titanium oxide containing compound in the liquid state |
|
| [84] |
| US 7.410,562 B2 (2011) | Thermal and electrochemical process for metal production |
|
| [94] |
| EP 2 322 693 B1 (2004) | Electrochemical process for titanium production |
|
| [95] |
| US 2007/0029208A1 (2008) | Thermal and electrochemical process for metal production |
|
| [96] |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
El Khalloufi, M.; Drevelle, O.; Soucy, G. Titanium: An Overview of Resources and Production Methods. Minerals 2021, 11, 1425. https://doi.org/10.3390/min11121425
El Khalloufi M, Drevelle O, Soucy G. Titanium: An Overview of Resources and Production Methods. Minerals. 2021; 11(12):1425. https://doi.org/10.3390/min11121425
Chicago/Turabian StyleEl Khalloufi, Mohammed, Olivier Drevelle, and Gervais Soucy. 2021. "Titanium: An Overview of Resources and Production Methods" Minerals 11, no. 12: 1425. https://doi.org/10.3390/min11121425
APA StyleEl Khalloufi, M., Drevelle, O., & Soucy, G. (2021). Titanium: An Overview of Resources and Production Methods. Minerals, 11(12), 1425. https://doi.org/10.3390/min11121425