Removal of Impurities from Shungite Via a Combination of Physical and Chemical Treatments
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
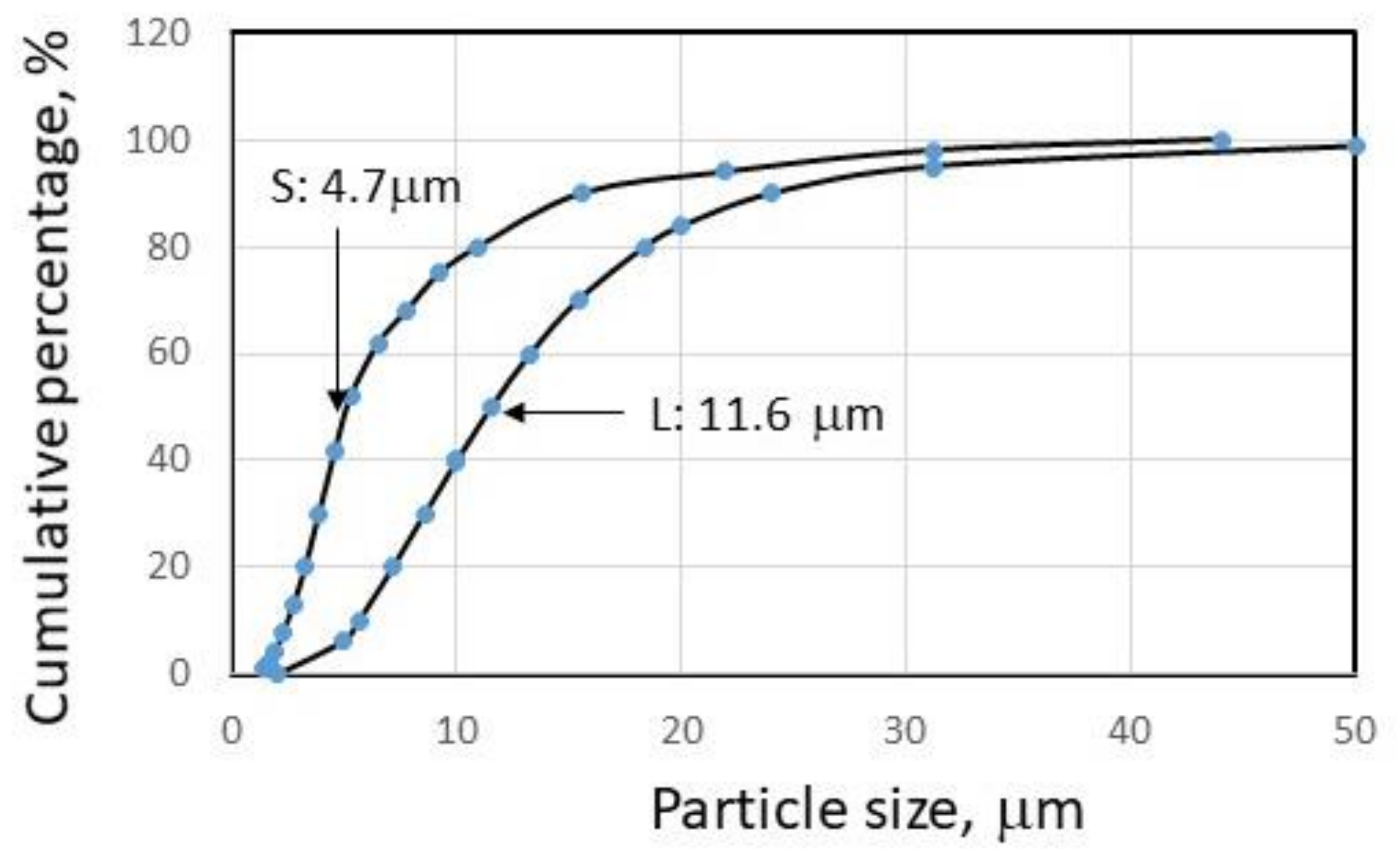
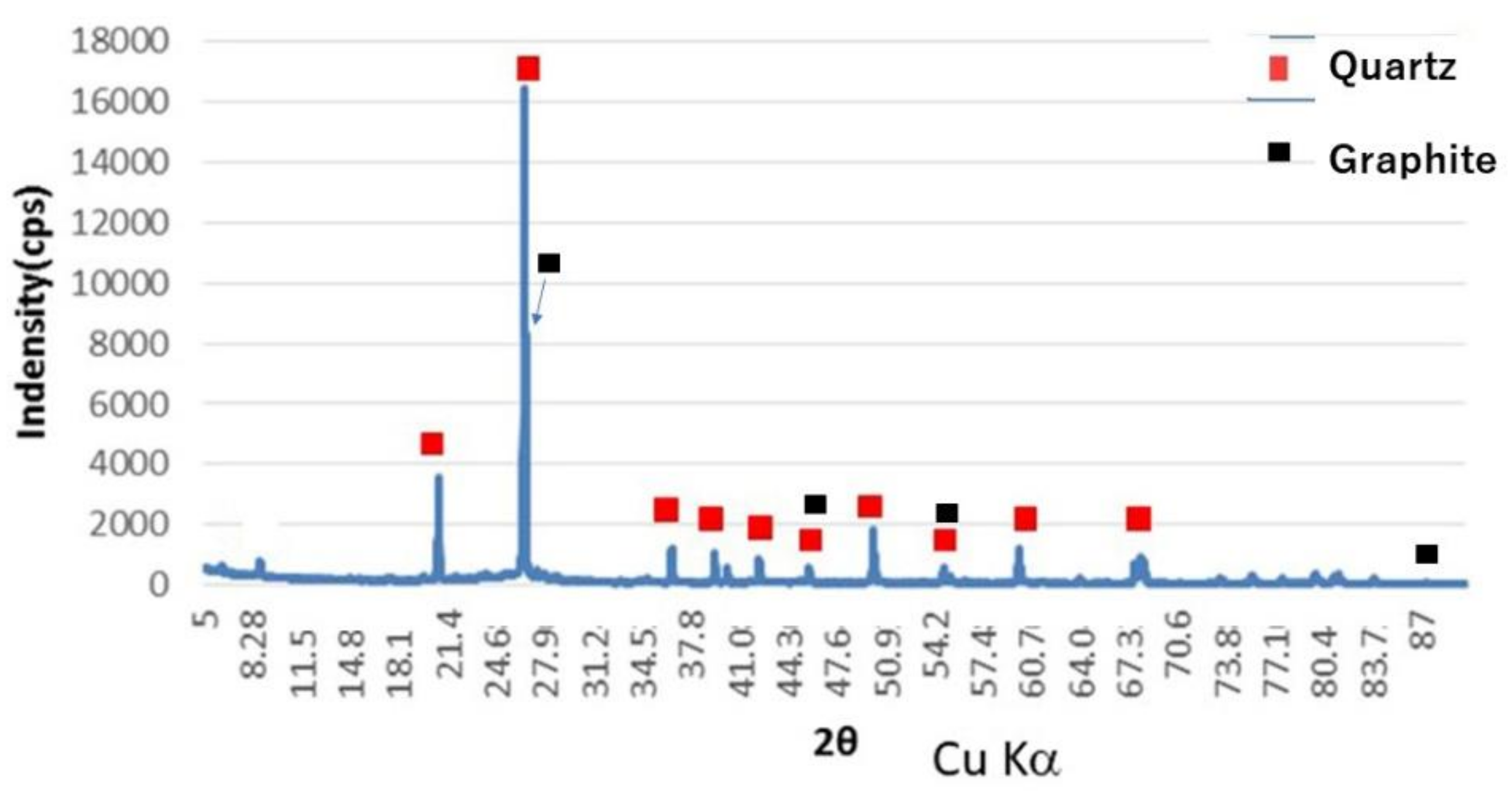
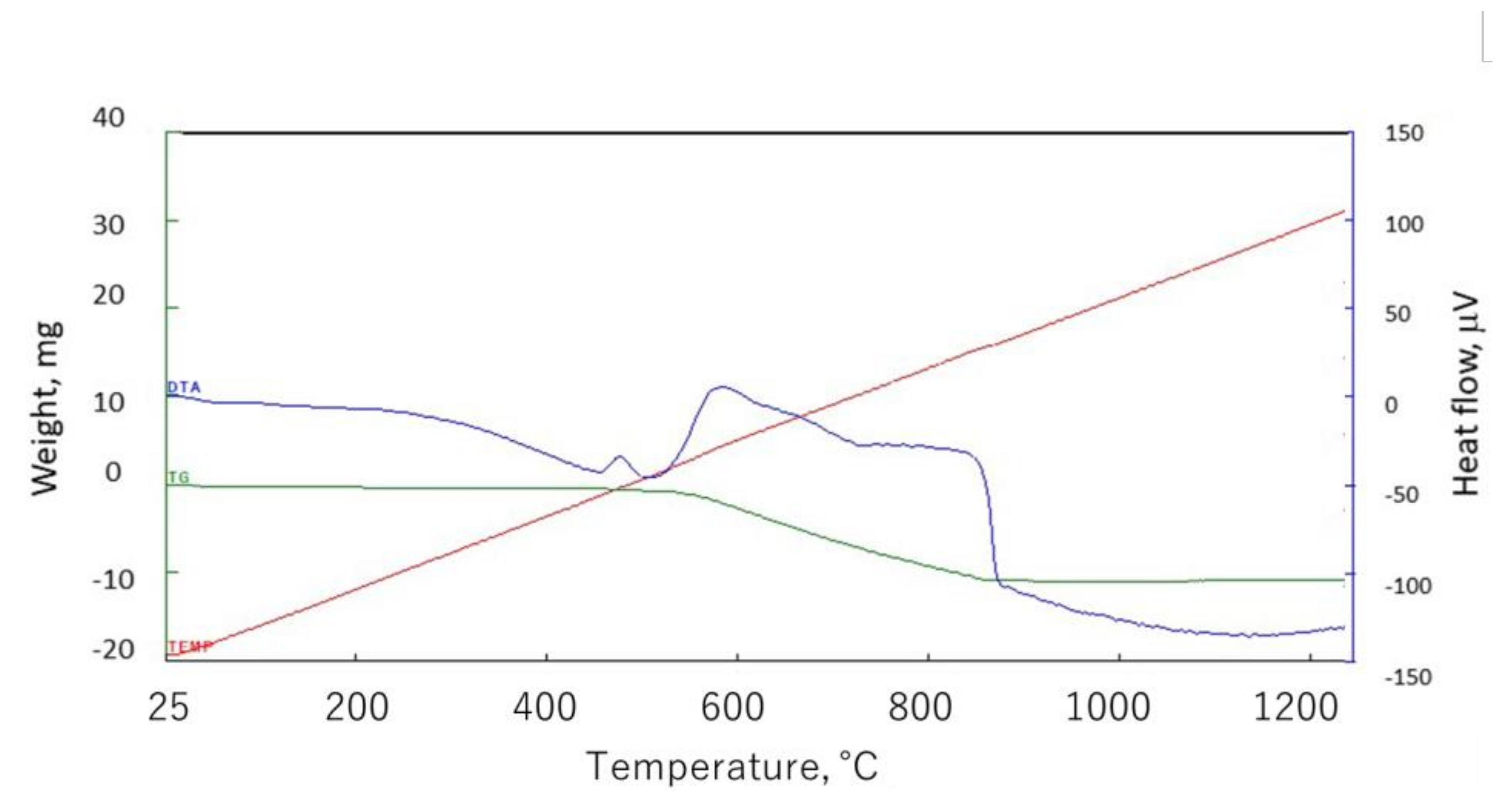
2.1. Materials
2.2. Experimental Method for Impurity Removal in Shungite
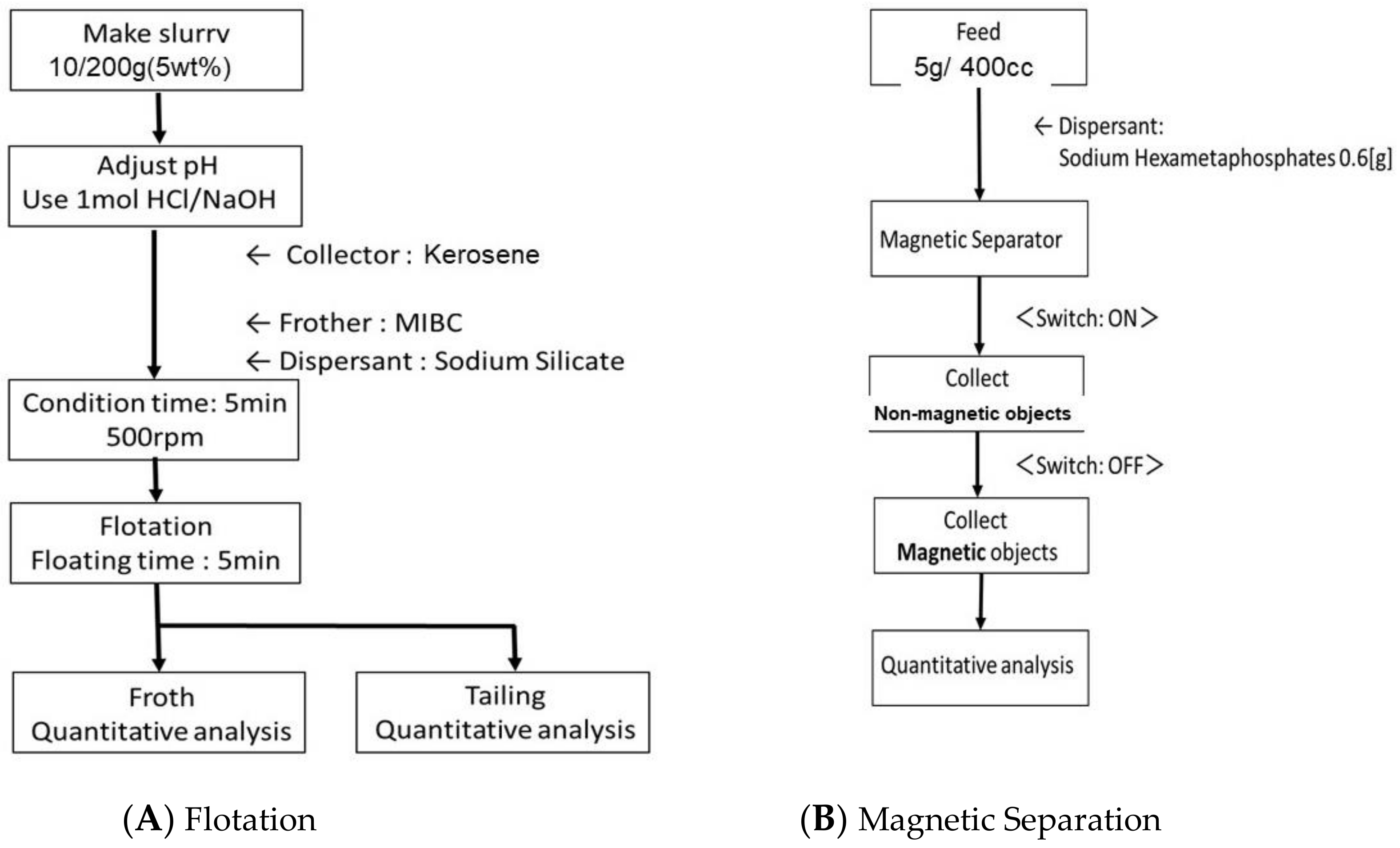
2.2.1. Flotation
2.2.2. Magnetic Separation
2.2.3. Microwave Irradiation
2.2.4. Leaching Using Chelating Reagent
2.2.5. Leaching Using Inorganic Acid
3. Results and Discussion
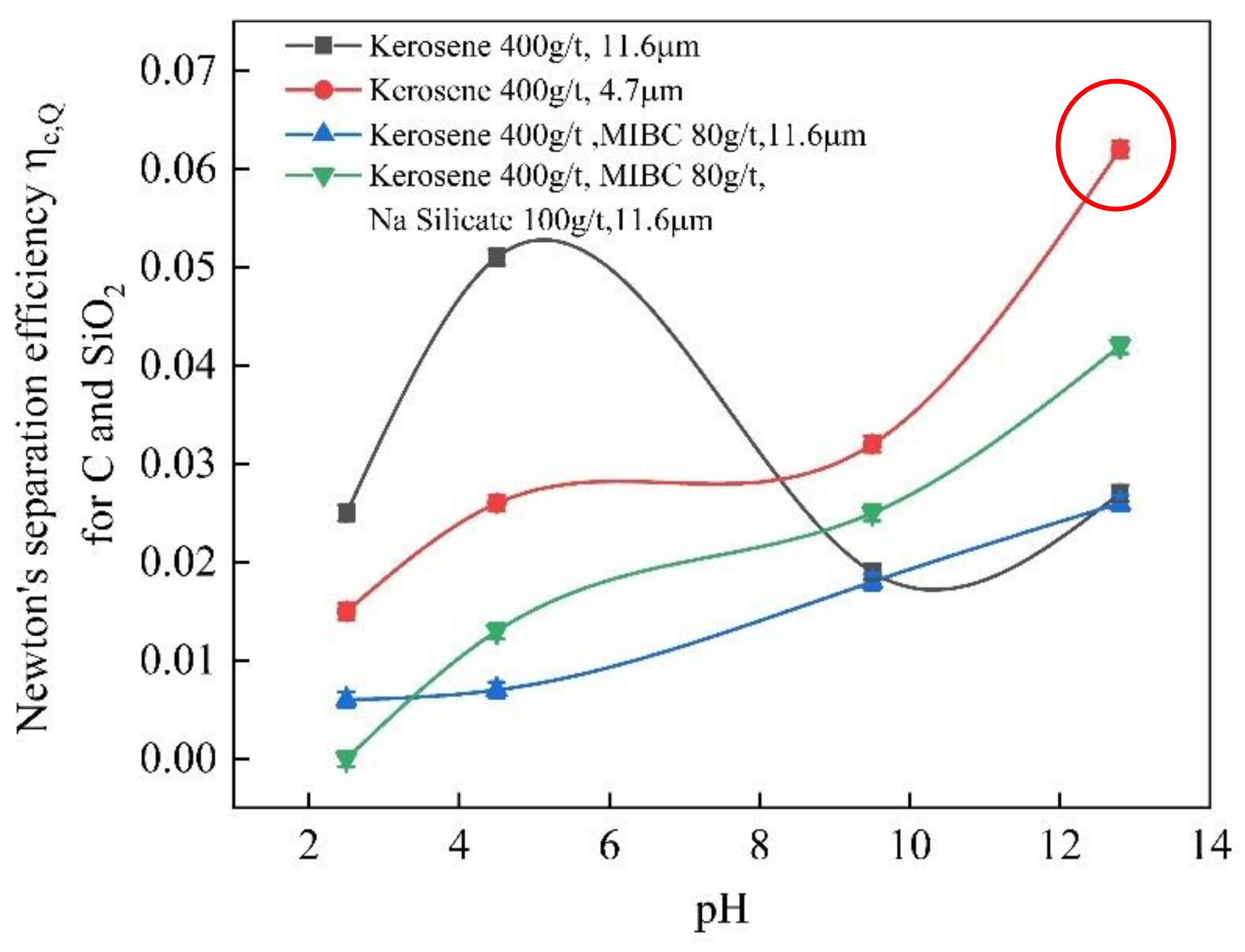
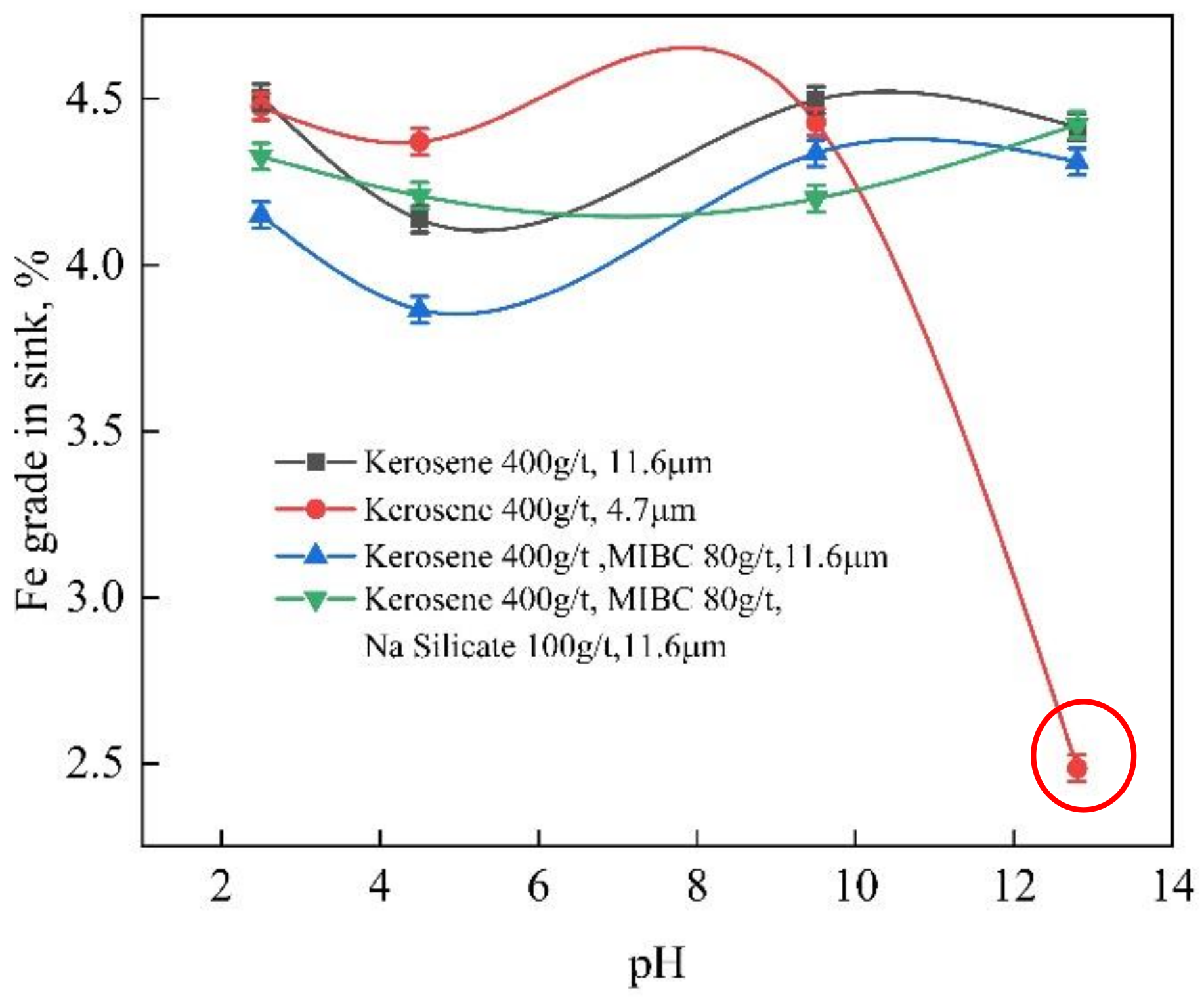
3.1. Flotation
3.2. Magnetic Separation
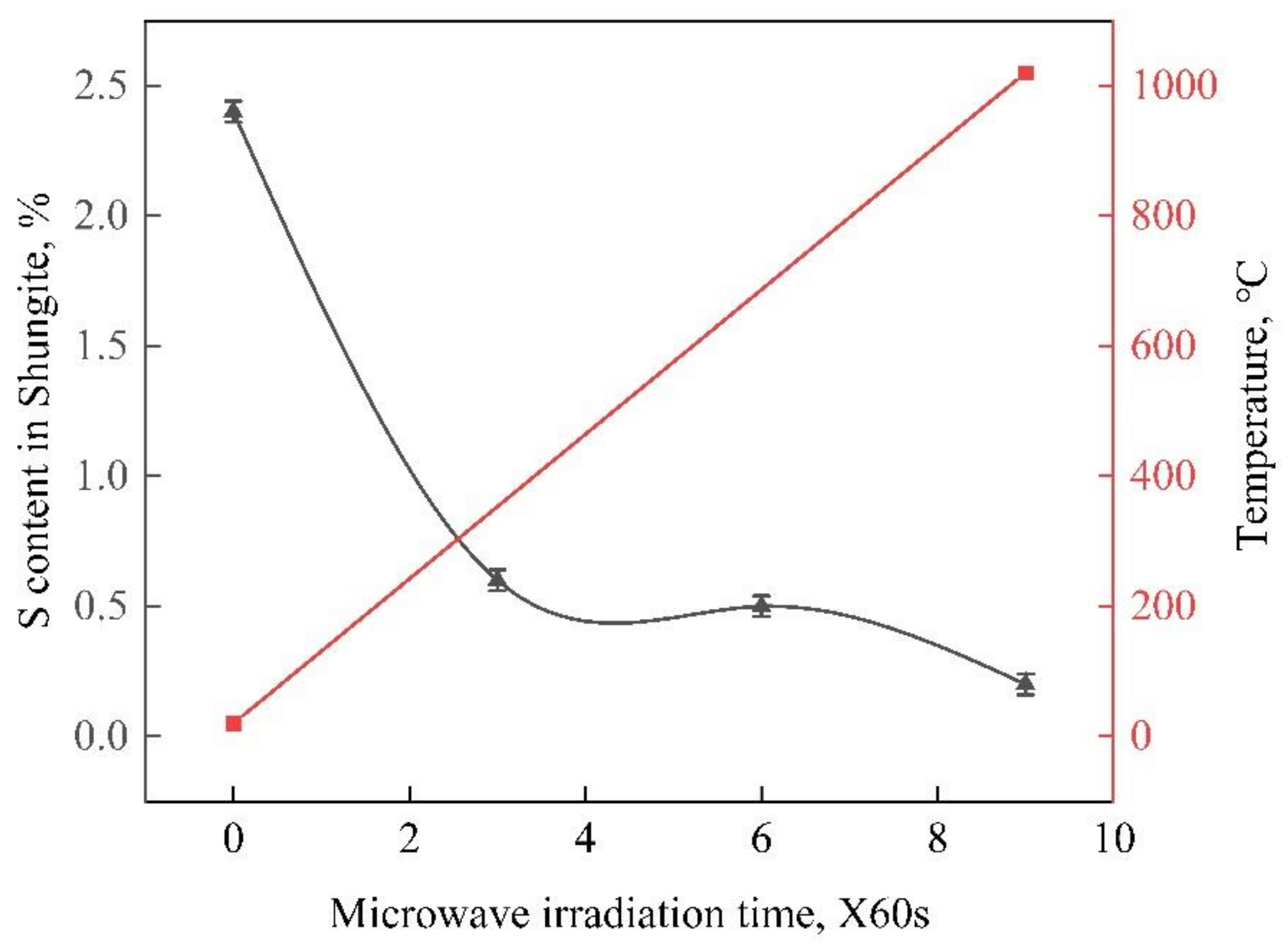
3.3. Microwave Irradiation
3.4. Leaching Using Chelating Reagent
3.5. Leaching Using Inorganic Acid
4. Conclusions
5. Patent
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Melezhik, V.A.; Filippov, M.M.; Romashkin, A.E. A giant Palaeopoerozoic deposit of shungite in NW Russia: Genesis and practical applications. Ore Geol. Rev. 2004, 135–154. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kweiecinska, B.; Pusz, S.; Krzesinska, M.; Pilawa, B. Physical properties of shungite. Int. J. Coal Geol. 2007, 71, 455–461. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kovalevski, V.V.; Buseck, P.R.; Cowley, J.M. Comparison of carbon in shungite rocks to other natural carbons: An X-ray and TEM study. Carbon 2001, 39, 243–256. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zenkiewicz, M.; Richert, J.; Rytlewski, P.; Richert, A. Comparative analysis of shungite and graphite effects on some properties of polylactide composites. Polym. Test. 2011, 30, 429–435. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mosin, O.; Ignaov, I. The structure and composition of natural carbonaceous fullerene containing mineral shungite. Int. J. Adv. Sci. Tech. Res. 2013, 6, 9–21. [Google Scholar]
- Moshnikov, I.A.; Kovalevski, V.V. Composite materials-based n nanostructured shungite filler. Mater. Today Proc. 2018, 5, 25971–25975. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Golubev, Y.A.; Antonets, I.V.; Shcheglov, V.I. Static and dynamic conductivity of nanostructured carbonaceous shungite geomaerials. Mater. Chem. Phys. 2019, 22, 19–203. [Google Scholar]
- Simsek, E.B.; Balta, Z.; Demircivi, P. Novel shungite based Bi2WO carbon catalyst with high photocatalytic degradation of tetracycline under visible light irradiation. J. Photochem. Photobiol. A Chem. 2019, 380, 11189. [Google Scholar]
- Chou, N.H.; Pierce, N.; Lei, Y.; Peea-Lopez, N.; Fujisawa, K.; Subamanian, S.; Robinson, J.A.; Chen, G.; Omichi, K.; Rozhkov, S.S.; et al. Carbon-rich shungite as a natural resource for efficient Li-ion battery electrodes. Carbon 2018, 130, 10–111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Popova, A. Crystallographic analysis of graphite by X-Ray diffraction. Coke Chem. 2017, 60, 361–365. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Obradović, N.; Gigov, M.; Đorđević, A.; Kern, F.; Dmitrović, S.; Matović, B.; Pavlović, V.B. Shungite—A carbon-mineral rock material: Its sinterability andpossible applications. Process. Appl. Ceram. 2019, 13, 89–97. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shalimov, A.S.; Kovalevskii, V.V.; Obrezkov, O.N.; Yaroslavtsev, A.B. Sorptive Properties of Shungite. Inorg. Mater. 2004, 40, 364–367. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheng, H.; Liu, Q.; Huang, M.; Zhang, S.; Frost, R.L. Application of TG-FTIR to study SO2 evolved during the thermal decomposition of coal-derived pyrite. Thermochim. Acta 2013, 555, 1–6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tani, K.; Kawabata, H.; Chang, Q.; Sato, K.; Tatsumi, Y. Quantitative analyses of silicate rock major and trace elements by X-ray fluores-cence spectrometer: Evaluation of analytical precision and sample preparation. Front. Res. Earth Evol.. 2005, 2, pp. 1–8.
- Morikawa, A. Rigaku Corporation. 2016. Available online: https://www.jaima.or.jp/jp/analytical/basic/xray/wds/ (accessed on 25 February 2021).
- Gao, Y.; Zhang, G.; Wang, M.; Liu, D. The Critical Role of Pulp Density on Flotation Separation of Nickel-Copper Sulfide from Fine Serpentine. Minerals 2018, 8, 317. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pradyumna, K.; Naik, P.; Reddy, S.R.; Misra, V.N. Interpretation of interaction effects and optimization of reagent dosages for fine coal flotation. Int. J. Miner. Process. 2005, 75, 83–90. [Google Scholar]
- Rao, D.S.; Kumar, T.; Rao, S.S.; Prabhakar, S.; Raju, G.B. Effectiveness of sodium silicate as gangue depressants in iron ore slimes flotation. Int. J. Miner. Metall. Mater. 2011, 18, 515–522. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aravamudhan, S.; Premkumar, N.; Yerrapragada, S.S.; Nani, B.P.; Viswanathan, K. Separation Based on Shape Part II: Newton’s Separation Efficiency. Powder Technol. 1984, 39, 93–98. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Higashitani, K.; Manino, H.; Matsusaka, S. Powder Technology Handbook, 4th ed.; CRC Press USA: Boca Raton, FL, USA, 2019. [Google Scholar]
- Svoboda, J.; Fujita, T. Recent Developments in Magnetic Methods of Material Separation. Miner. Eng. 2003, 16, 785–792. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oshima, K. Mechanism and Applications of Microwave Heating. Jpn. Soc. Color Mater. 1971, 44, 27–35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chandrasekaran, S.; Basak, T.; Srinivasan, R. Microwave heating characteristics of graphite based powder mixtures. Int. Commun. Heat Mass Transf. 2013, 48, 22–27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nanbu, S.; Nakamura, J.; Ito, H. Production Method of High Purity Carbon. Japanese Patent No. JP 4502618, 30 April 2010. [Google Scholar]
- Sulcek, Z.; Povondra, P. Methods of Decomposition in Inorganic Analysis, 1st ed.; CRC Press: Boca Raton, FL, USA, 1989; p. 27. [Google Scholar]




| Elemental | wt% | Elemental | wt% |
|---|---|---|---|
| C | 45.4 | MgO | 0.2 |
| SiO2 | 38.3 | Na2O | 0.1 |
| Fe | 4.6 | PbO | 0.1 |
| K2O | 2.5 | P2O5 | 0.1 |
| Al2O3 | 2.3 | Cl | 0.1 |
| S | 2.4 | Cr2O3 | 0.1 |
| TiO2 | 0.5 | MnO | 0.1 |
| CaO | 0.5 | NiO | 0.1 |
| ZnO | 0.3 | ZrO2 | 0.1 |
| CuO | 0.2 | V2O5 | 0.1 |
| Magnetic Field, T | Magnetics, % | Non-Magnetics, % | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Fe Grade | S Grade | Fe Grade | S Grade | |
| 0.5 | 5.4 | 2.6 | 2.9 | 2.0 |
| 1.0 | 5.7 | 3.1 | 2.8 | 1.9 |
| Fe, % | S, % | Weight Loss, % | |
|---|---|---|---|
| As-received | 4.6 | 2.4 | |
| NTA | 2.0 | 0.9 | 12.2 |
| EDTA | 2.9 | 1.0 | 9.3 |
| EDTA-2Na | 3.3 | 1.2 | 7.7 |
| Fe, % | S, % | Weight Loss, % | |
|---|---|---|---|
| As-received | 4.6 | 2.40 | |
| 3N HNO3 | 2.2 | 0.62 | 13.7 |
| 3N HNO3 75% + 4N H2SO4 25% | 1.7 | 0.68 | 15.6 |
| 3N HNO3 50% + 4N H2SO4 50% | 1.7 | 0.68 | 15.8 |
| 3N HNO3 25% + 4N H2SO4 75% | 1.8 | 0.78 | 14.4 |
| 4N H2SO4 | 3.2 | 1.12 | 6.8 |
| 13N HNO3 75% + 12N HCl 25% (Reverse aqua regia) | 0.9 | 0.23 | 22.4 |
| 6N HCl | 2.2 | 0.61 | 13.4 |
| 6N HCl 95% + 30 W/V% H2O2 5% | 0.8 | 0.34 | 21.7 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Fujita, T.; Aoki, T.; Ponou, J.; Dodbiba, G.; He, C.; Wang, K.; Ning, S.; Chen, H.; Wei, Y. Removal of Impurities from Shungite Via a Combination of Physical and Chemical Treatments. Minerals 2021, 11, 245. https://doi.org/10.3390/min11030245
Fujita T, Aoki T, Ponou J, Dodbiba G, He C, Wang K, Ning S, Chen H, Wei Y. Removal of Impurities from Shungite Via a Combination of Physical and Chemical Treatments. Minerals. 2021; 11(3):245. https://doi.org/10.3390/min11030245
Chicago/Turabian StyleFujita, Toyohisa, Taichi Aoki, Josiane Ponou, Gjergj Dodbiba, Chunlin He, Kaituo Wang, Shunyan Ning, Hao Chen, and Yuezou Wei. 2021. "Removal of Impurities from Shungite Via a Combination of Physical and Chemical Treatments" Minerals 11, no. 3: 245. https://doi.org/10.3390/min11030245
APA StyleFujita, T., Aoki, T., Ponou, J., Dodbiba, G., He, C., Wang, K., Ning, S., Chen, H., & Wei, Y. (2021). Removal of Impurities from Shungite Via a Combination of Physical and Chemical Treatments. Minerals, 11(3), 245. https://doi.org/10.3390/min11030245








