Intrusion-Associated Gold Systems and Multistage Metallogenic Processes in the Neoarchean Abitibi Greenstone Belt
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Geological Setting

3. Metallogenic Models
3.1. Magmatic-Hydrothermal Systems: Porphyries

3.2. Magmatic-Hydrothermal Systems: Porphyries Overprinted by OGS
3.3. Magmatic-Hydrothermal Systems: IRGS or Syntectonic Porphyries?
3.4. Multistage Processes: IRGS Overprinted by OGS
3.5. Intrusive Rocks and OGS
4. Discussion
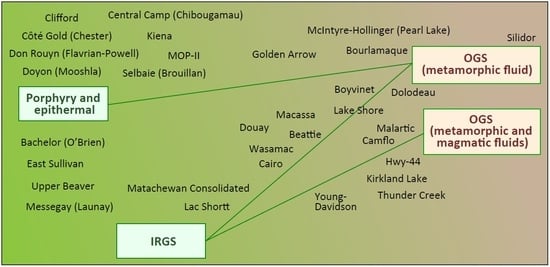
- Porphyry are base metal and gold-bearing deposits associated with large-volume plutons and can be characterized by zoned alteration and mineralization patterns;
- IRGS are gold deposits that may display a polymetallic signature and that can be associated with small-volume alkaline or other intrusions of the syntectonic period.
- 1
- Deformed porphyry (B1) or IRGS (B2): gold-bearing magmatic-hydrothermal systems that were subsequently deformed and overprinted by an OGS or by gold-barren metamorphic fluids, e.g., Beattie and Douay syenites;
- 2
- Multistage porphyry (B1) or IRGS (B2): gold-bearing or gold-barren magmatic-hydrothermal systems overprinted by an OGS, e.g., McIntyre-Hollinger, Malartic, and Lake Shore.
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Phillips, G.N.; Powell, R. Formation of gold deposits: A metamorphic devolatilization model. J. Metamorph. Geol. 2010, 28, 689–718. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Helt, K.M.; Williams-Jones, A.E.; Clark, J.R.; Wing, B.A.; Wares, R.P. Constraints on the genesis of the Archean oxidized, intrusion-related Canadian Malartic gold deposit, Quebec, Canada. Econ. Geol. 2014, 109, 713–735. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Souza, S.; Dubé, B.; McNicoll, V.; Dupuis, C.; Mercier-Langevin, P.; Creaser, R.A.; Kjarsgaard, I. Geology and hydrothermal alteration of the world-class Canadian Malartic gold deposit: Genesis of an Archean stockwork-disseminated gold deposit in the Abitibi greenstone belt. In Archean Base and Precious Metal Deposits, Southern Abitibi Greenstone Belt, Canada; Monecke, T., Mercier-Langevin, P., Dubé, B., Eds.; Society of Economic Geologists: Littleton, CO, USA, 2019; Volume 19, pp. 263–291. [Google Scholar]
- Robert, F. Syenite-associated disseminated gold deposits in the Abitibi greenstone belt, Canada. Miner. Depos. 2001, 36, 503–516. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hart, C.J.R. Reduced intrusion-related gold systems. In Mineral Deposits of Canada: A Synthesis of Major Deposit Types, District Metallogeny, the Evolution of Geological Provinces, and Exploration Methods; Goodfellow, W.D., Ed.; Geological Association of Canada, Mineral Deposits Division, Special Publication: St. John’s, NL, Canada, 2007; Volume 5, pp. 95–112. [Google Scholar]
- Meffre, S.; Large, R.R.; Steadman, J.A.; Gregory, D.D.; Stepanov, A.S.; Kamenetsky, V.S.; Ehrig, K.; Scott, R.J. Multi-stage enrichment processes for large gold-bearing ore deposits. Ore Geol. Rev. 2016, 76, 268–279. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mathieu, L.; Snyder, D.B.; Bedeaux, P.; Cheraghi, S.; Lafrance, B.; Thurston, P.; Sherlock, R. Deep into the Chibougamau Area, Abitibi greenstone belt: Structure of a Neoarchean crust revealed by seismic reflection profiling. Tectonics 2020, 39. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Palin, R.M.; Santosh, M.; Cao, W.; Li, S.-S.; Hernandez-Uribe, D.; Parsons, A. Secular change and the onset of plate tectonics. Earth-Sci. Rev. 2020, 207, 103172. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Laurent, O.; Martin, H.; Moyen, J.-F.; Doucelance, R. The diversity and evolution of late-Archean granitoids: Evidence for the onset of “modern-style” plate tectonics between 3.0 and 2.5 Ga. Lithos 2014, 205, 208–235. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- David, J.; Dion, C. Géochronologie D’échantillons Recueillis par Géologie Québec, Année 2009−2010; MRN report GM-64849; Ministère des Ressources Naturelles: Québec, QC, Canada, 2010.
- Madon, B.; Mathieu, L.; Marsh, J.H. Oxygen fugacity and volatile content of syntectonic magmatism in the Neoarchean Abitibi greenstone belt, Superior Province, Canada. Minerals 2020, 10, 966. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- van Breemen, O.; Heather, K.B.; Ayer, J.A. U-Pb Geochronology of the Neoarchean Swayze Sector of the Southern Abitibi Greenstone Belt; Current Research no. 2006-F1; Ontario Geological Survey: Sudbury, ON, Canada, 2006. [Google Scholar]
- Thurston, P.C.; Ayer, J.A.; Goutier, J.; Hamilton, M.A. Depositional gaps in Abitibi greenstone belt stratigraphy: A key to exploration for syngenetic mineralization. Econ. Geol. 2008, 103, 1097–1134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Leclerc, F.; Roy, P.; Pilote, P.; Bédard, J.H.; Harris, L.B.; McNicoll, V.J.; van Breemen, O.; David, J.; Goulet, N. Géologie de la Région de Chibougamau; MERN report RG 2015-03; Ministère de l’Énergie et des Ressources Naturelles: Québec, QC, Canada, 2017.
- Feng, R.; Kerrich, R. Single zircon age constraints on the tectonic juxtaposition of the Archean Abitibi greenstone belt and Pontiac subprovince, Quebec, Canada. Geochim. Cosmochim. Acta 1991, 55, 3437–3441. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mathieu, L.; Crépon, A.; Kontak, D.J. Tonalite-dominated magmatism in the Abitibi subprovince, Canada, and significance for Cu-Au magmatic-hydrothermal systems. Minerals 2020, 10, 242. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Moyen, J.-F. Archean granitoids: Classification, petrology, geochemistry and origin. Geol. Soc. London Spec. Publ. 2019, 489, 15–49. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- SIGÉOM Système d’information géominière du Québec; Ministère l’Énergie des Ressources Naturelles: Québec, QC, Canada, 2020.
- Katz, L.R.; Kontak, D.J.; Dubé, B.; McNicoll, V. The geology, petrology, and geochronology of the Archean Côté Gold large-tonnage, low-grade intrusion-related Au (±Cu) deposit, Swayze greenstone belt, Ontario, Canada. Can. J. Earth Sci. 2017, 54, 173–202. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Krogh, T.E. Improved accuracy of U-Pb zircon ages by the creation of more concordant systems using an air abrasion technique. Geochim. Cosmochim. Acta 1982, 46, 637–649. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pilote, P.; Robert, F.; Kirkham, R.; Daigneault, R.; Sinclair, W.D. Minéralisation de type porphyrique et filonienne dans le Complexe du lac Doré—le secteur du lac Clark et de l’île Merrill. In Géologie et Métallogénie du District Minier de Chapais-Chibougamau: Nouvelle Vision du Potentiel de Découverte; Pilote, P., Ed.; MRN report DV 98-03; Ministère des Ressources Naturelles: Québec, QC, Canada, 1998; pp. 71–90. [Google Scholar]
- David, J.; Parent, M. Géochronologie U-Pb du Projet Moyen-Nord; MRNF document GM 59903; Ministère des Ressources Naturelles et de la Faune: Québec, QC, Canada, 1997.
- Fraser, R.J. The Lac Troilus gold-copper deposit, northwestern Quebec; a possible Archean porphyry system. Econ. Geol. 1993, 88, 1685–1699. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Katz, L.R.; Kontak, D.J.; Dubé, B.; McNicoll, V.; Creaser, R.; Petrus, J.A. An Archean Porphyry-Type Gold Deposit: The Côté Gold Au (-Cu) Deposit, Swayze Greenstone Belt, Superior Province, Ontario, Canada. Econ. Geol. 2020, 116, 47–89. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Katz, L.R. Geology of the Archean Côté Gold Au (-Cu) Intrusion-Related Deposit, Swayze Greenstone Belt, Ontario. Ph.D. Thesis, Laurentian University, Sudbury, ON, Canada, 2016. [Google Scholar]
- Mathieu, L.; Racicot, D. Petrogenetic study of the multiphase Chibougamau pluton: Archaean magmas associated with Cu-Au magmato-hydrothermal systems. Minerals 2019, 9, 174. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Racicot, D.; Chown, E.H.; Hanel, T. Plutons of the Chibougamau-Desmaraisville belt: A preliminary survey. In Chibougamau, Stratigraphy and Mineralization; Guha, J., Chown, E.H., Eds.; Canadian Institute of Mining and Metallurgy: Westmount, QC, Canada, 1984; Volume 34, pp. 178–197. [Google Scholar]
- Guha, J.; Leroy, J.; Guha, D. Significance of fluid phases associated with shear zone Cu-Au mineralization in the Doré Lake complex, Chibougamau, Quebec. Bull. Mineral. 1979, 102, 569–576. [Google Scholar]
- Gosselin, P.; Dubé, B. Gold Deposits of the World: Distribution, Geological Parameters and Gold Content; Open File 4895; Geological Survey of Canada: Ottawa, ON, Canada, 2005. [Google Scholar]
- Barrie, C.T.; Krogh, T.E. U-Pb zircon geochronology of the Selbaie Cu-Zn-Ag-Au mine, Abitibi Subprovince, Canada. Econ. Geol. 1996, 91, 563–575. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Faure, S.; Jébrak, M.; Angelier, J. Structural evolution of Les Mines Selbaie, northern Abitibi Belt, Quebec, Canada. Explor. Min. Geol. 1996, 5, 215–230. [Google Scholar]
- McNicoll, V.; Goutier, J.; Dubé, B.; Mercier-Langevin, P.; Ross, P.-S.; Dion, C.; Monecke, T.; Legault, M.; Percival, J.; Gibson, H. U-Pb geochronology of the Blake River Group, Abitibi greenstone belt, Quebec, and implications for base metal exploration. Econ. Geol. 2014, 109, 27–59. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pearson, V.; Daigneault, R. An Archean megacaldera complex: The Blake River Group, Abitibi greenstone belt. Precambrian Res. 2009, 168, 66–82. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jébrak, M.; Harnois, L.; Carrier, A.; Lafrance, J. Le porphyre à Cu-Au de Don Rouyn. In Métallogénie et Évolution TECTONIQUE DE LA Région de Rouyn-Noranda; Couture, J.-F., Goutier, J., Eds.; MERN report MB 96-06; Ministère de l’Énergie et des Ressources Naturelles: Québec, QC, Canada, 1996; pp. 85–86. [Google Scholar]
- Goldie, R.; Kotila, B.; Seward, D. The Don Rouyn Mine; An Archean porphyry copper deposit near Noranda, Quebec. Econ. Geol. 1979, 74, 1680–1684. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Galley, A.G.; Lafrance, B. Setting and evolution of the Archean synvolcanic Mooshla intrusive complex, Doyon-Bousquet-LaRonde mining camp, Abitibi greenstone belt: Emplacement history, petrogenesis, and implications for Au metallogenesis. Econ. Geol. 2014, 109, 205–229. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ayer, J.A.; Thurston, P.C.; Bateman, R.; Gibson, H.L.; Hamilton, M.A.; Hathway, B.; Hocker, S.M.; Hudak, G.; Lafrance, B.; Ispolatov, V.O.; et al. Digital Compilation of Maps and Data from the Greenstone Architecture Project in the Timmins–Kirkland Lake Region; Miscellaneous Release—Data 155; Ontario Geological Survey: Sudbury, ON, Canada, 2005. [Google Scholar]
- MacDonald, P.J.; Piercey, S.J.; Hamilton, M.A. An Integrated Study of Intrusive Rocks Spatially Associated with Gold and Base Metal Mineralization in the Abitibi Greenstone Belt, Timmins Area and Clifford Township: Discover Abitibi Initiative; Open File Report 6160; Ontario Geological Survey: Greater Sudbury, ON, Canada, 2005; ISBN 0779476158. [Google Scholar]
- Taylor, B.E.; Timbale, A. Regional stable isotope studies in the Clifford–Ben Nevis area. In Project 94OE7: The Use of Regional-Scale Alteration Zones and Subvolcanic Intrusions in the Exploration for Volcanic-Associated Massive Sulphide Deposits; Canadian Mining Industry Research Organization: Sudbury, ON, Canada, 1998; pp. 123–130, unpublished. [Google Scholar]
- Morasse, S.; Wasteneys, H.A.; Cormier, M.; Helmstaedt, H.; Mason, R. A pre-2686 Ma intrusion-related gold deposit at the Kiena Mine, Val d’Or, Quebec, southern Abitibi Subprovince. Econ. Geol. 1995, 90, 1310–1321. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- MacDonald, P.J. The Geology, Lithogeochemistry and Petrogenesis of Intrusions Associated with Gold Mineralization in the Porcupine Gold Camp, Timmins, Canada. Master Thesis, University of Laurentia, Sudbury, ON, Canada, 2010. Unpublished. [Google Scholar]
- Mason, R.; Melnik, N. The Anatomy of an Archean Gold System; the McIntyre-Hollinger Complex at Timmins, Ontario, Canada. In Proceedings of the Gold ‘86: An international symposium on the geology of gold deposits, Toronto, ON, Canada, 28 September–1 October 1986; pp. 40–55. [Google Scholar]
- Smith, F.G. The ore deposition temperature and pressure at the McIntyre Mine, Ontario. Econ. Geol. 1948, 43, 627–636. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bateman, R.; Ayer, J.A.; Dubé, B.; Hamilton, M.A. The Timmins-Porcupine Gold Camp, Northern Ontario: The Anatomy of an Archaean Greenstone Belt and Its Gold Mineralization: Discover Abitibi Initiative; Open File report 6158; Ontario Geological Survey: Greater Sudbury, ON, Canada, 2005; ISBN 077947791X. [Google Scholar]
- Cameron, E.M.; Hattori, K. Archean gold mineralization and oxidized hydrothermal fluids. Econ. Geol. 1987, 82, 1177–1191. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McNeil, A.M.; Kerrich, R. Archean lamprophyre dykes and gold mineralization, Matheson, Ontario: The conjunction of LILE-enriched mafic magmas, deep crustal structures, and Au concentration. Can. J. Earth Sci. 1986, 23, 324–343. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lépine, S. Le gîte à Au-Cu-Mo de MOP-II (Chibougamau, Québec): Un porphyre archéen déformé. Master’s Thesis, Université du Québec à Montréal, Montréal, QC, Canada, 2009. Unpublished. [Google Scholar]
- Jébrak, M. Les gisements d’or des tonalites archéennes (Abitibi, Québec). Miner. Depos. 1992, 27, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jébrak, M.; LeQuentrec, M.F.; Mareschal, J.-C.; Blais, D. A gravity survey across the Bourlamaque massif, southeastern Abitibi greenstone belt, Québec, Canada: The relationship between the geometry of tonalite plutons and associated gold mineralization. Precambrian Res. 1991, 50, 261–268. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tremblay, A.; Ruffet, G.; Lemarchand, J. Timing and duration of Archean orogenic gold deposits in the Bourlamaque pluton, Val d’Or mining camp, Abitibi, Canada. Ore Geol. Rev. 2020, 127, 103812. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fayol, N.; Jébrak, M. Archean sanukitoid gold porphyry deposits: A new understanding and genetic model from the Lac Bachelor gold deposit, Abitibi, Canada. Econ. Geol. 2017, 112, 1913–1936. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Bigot, F. Les minéralisations à Cu-Au de type skarn du stock de East-Sullivan, ceinture de roches vertes de l’Abitibi, Canada. Master Thesis, UQAM University, Montréal, QC, Canada, 2020. [Google Scholar]
- Feick, K.E. An Evaluation of the Lithologies and Geochemistry of the Upper Beaver Deposit of the Kirkland Lake Area. Master Thesis, Western University, London, ON, Canada, 2016. [Google Scholar]
- Prud’homme, N. Caractérisation Pétrographique et Géochimique de la Carbonatite et de la Syénite de la Mine Lac Shortt. Master Thesis, Université du Québec à Chicoutimi, Chicoutimi, QC, Canada, 1990. [Google Scholar]
- Nadeau, O.; Stevenson, R.; Jébrak, M. The Archean magmatic-hydrothermal system of Lac Shortt (Au-REE), Abitibi, Canada: Insights from carbonate fingerprinting. Chem. Geol. 2014, 387, 144–156. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nadeau, O. Sources of fluids in Archean hydrothermal stockwork-disseminated gold deposits of Abitibi, Canada: Insights from Duquesne, Dolodau, Lac Shortt and Canadian Malartic. Ore Geol. Rev. 2019, 111, 102975. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bédard, L.P.; Chown, E.H. The Dolodau dykes, Canada: An example of an Archean carbonatite. Mineral. Petrol. 1992, 46, 109–121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pigeon, L. Mineralogy, Petrology and Petrogenesis of Syenitic Rocks of the Porcupine-Destor Fault Zone near Matheson, Ontario. Master Thesis, University of Ottawa, Ottawa, ON, Canada, 2003. Unpublished. [Google Scholar]
- Hattori, K.; Hart, S.R.; Shimizu, N. Melt and source mantle compositions in the Late Archaean: A study of strontium and neodymium isotope and trace elements in clinopyroxenes from shoshonitic alkaline rocks. Geochim. Cosmochim. Acta 1996, 60, 4551–4562. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rowins, S.M.; Lalonde, A.E.; Cameron, E.M. Magmatic oxidation in the syenitic Murdock Creek intrusion, Kirkland Lake, Ontario: Evidence from the ferromagnesian silicates. J. Geol. 1991, 99, 395–414. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jébrak, M.; Doucet, P. Geology and gold–molybdenum porphyry mineralisation of the Archean Taschereau–Launay plutons, Abitibi, Quebec. Precambrian Res. 2002, 115, 329–348. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kontak, D.; Dubé, B.; Benham, W. The Upper Beaver project, Kirkland Lake area: Investigation of a syenite-associated copper-gold deposit with magnetite-epidote-feldspar alteration. In Summary of Field Work and Other Activities 2008; Open File Report 6226; Ontario Geological Survey: Greater Sudbury, ON, Canada, 2008; pp. 12-1–12-12. [Google Scholar]
- Mathieu, L. Detecting magmatic-derived fluids using pyrite chemistry: Example of the Chibougamau area, Abitibi Subprovince, Québec. Ore Geol. Rev. 2019, 114, 103–127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gourcerol, B.; Kontak, D.J.; Thurston, P.C.; Petrus, J.A. Application of LA-ICP-MS sulfide analysis and methodology for deciphering elemental paragenesis and associations in addition to multi-stage processes in metamorphic gold settings. Can. Mineral. 2018, 56, 39–64. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Bourdeau, J. Petrology, Mineralogy and Geochemistry of the Beattie Syenite and Country Rocks, Abitibi Greenstone Belt, Québec. Master Thesis, University of Ottawa, Ottawa, ON, Canada, 2013. [Google Scholar]
- Côté-Lavoie, E. Métallogénie et Processus Minéralisateurs du Stock de Boyvinet, Desmaraisville, Abitibi, Québec. Master’s Thesis, UQAC University, Chicoutimi, QC, Canada, 2016. [Google Scholar]
- Mériaud, N.; Jébrak, M. From intrusion-related to orogenic mineralization: The Wasamac deposit, Abitibi Greenstone Belt, Canada. Ore Geol. Rev. 2017, 84, 289–308. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mathieu, L. Quantifying hydrothermal alteration with normative minerals and other chemical tools at the Beattie Syenite, Abitibi greenstone belt, Canada. Geochem. Explor. Environ. Anal. 2016, 16, 233–244. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bigot, L.; Jébrak, M. Gold mineralization at the syenite-hosted Beattie gold deposit, Duparquet, Neoarchean Abitibi Belt, Canada. Econ. Geol. 2015, 110, 315–335. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martin, R.D. Syenite-Hosted gold Mineralization and Hydrothermal Alteration at the Young-Davidson Deposit, Matachewan, Ontario. Master Thesis, University of Waterloo, Waterloo, ON, Canada, 2012. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, J.; Lin, S.; Linnen, R.; Martin, R. Structural setting of the Young-Davidson syenite-hosted gold deposit in the western Cadillac-Larder Lake deformation zone, Abitibi greenstone belt, Superior Province, Ontario. Precambrian Res. 2014, 248, 39–59. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Naderi, N. Stable Isotopes and XRD Investigation of Gold Mineralization at the Syenite-Hosted Young-Davidson Deposit, Matachewan, Ontario. Master Thesis, Western University, London, ON, Canada, 2012. [Google Scholar]
- Berger, B.R. Geological Synthesis along Highway 66 from Matachewan to Swastika; Open File report 6177; Ontario Geological Survey: Greater Sudbury, ON, Canada, 2006; ISBN 1424904005. [Google Scholar]
- Tesfaye, G. Ore-microscopic and geochemical characteristics of gold-tellurides-sulfide mineralization in the Macassa Gold Mine, Abitibi Belt, Canada. Miner. Depos. 1992, 27, 66–71. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kerrich, R.; Watson, G.P. The Macassa Mine Archean lode gold deposit, Kirkland Lake, Ontario; geology, patterns of alteration, and hydrothermal regimes. Econ. Geol. 1984, 79, 1104–1130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Still, A.C. Structural Setting and Controls of Gold Mineralization at the Macassa Mine, Kirkland Lake, Ontario. Master Thesis, Queen’s University, Kingston, ON, Canada, 2001. [Google Scholar]
- Hicks, K.D. Magmatic-Hydrothermal and Wall Rock Alteration at the Lake Shore Gold Deposit, Kirkland Lake, Ontario. Master Thesis, University of Ottawa, Ottawa, ON, Canada, 1990. [Google Scholar]
- Ispolatov, V.; Lafrance, B.; Dubé, B.; Hamilton, M.; Creaser, R. Geology, Structure, and Gold Mineralization, Kirkland Lake and Larder Lake Areas (Gauthier and Teck townships): Discover Abitibi Initiative; Open File report 6159; Ontario Geological Survey: Greater Sudbury, ON, Canada, 2005. [Google Scholar]
- El Rassi, D. Technical Report on the Douay Gold Project, Northwestern Québec, Canada; Technical report NI 43-101; Maple Gold Mines Ltd.: Toronto, ON, Canada, 2019. [Google Scholar]
- Burrows, D.R.; Spooner, E.T.C.; Wood, P.C.; Jemielita, R.A. Structural controls on formation of the Hollinger-McIntyre Au quartz vein system in the Hollinger shear zone, Timmins, southern Abitibi greenstone belt, Ontario. Econ. Geol. 1993, 88, 1643–1663. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brisbin, D.I. Geological Setting of Gold Deposits in the Porcupine Gold Camp, Timmins, Ontario. Ph.D. Thesis, Queen’s University, Kingston, ON, Canada, 1997. [Google Scholar]
- Campbell, R.A. Controls on Syenite-Hosted Gold Mineralization in the Western Timmins Camp. Master Thesis, University of Western Ontario, London, ON, Canada, 2014. [Google Scholar]
- Hattori, K. Diverse metal sources of Archaean gold deposits: Evidence from in situ lead-isotope analysis of individual grains of galena and altaite in the Ross and Kirkland Lake deposits, Abitibi greenstone belt, Canada. Contrib. Mineral. Petrol. 1993, 113, 185–195. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Robert, F.; Poulsen, K.H. World-class Archaean gold deposits in Canada: An overview. Aust. J. Earth Sci. 1997, 44, 329–351. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Perrouty, S.; Gaillard, N.; Piette-Lauziére, N.; Mir, R.; Bardoux, M.; Olivo, G.R.; Linnen, R.L.; Bérubé, C.L.; Lypaczewski, P.; Guilmette, C. Structural setting for Canadian Malartic style of gold mineralization in the Pontiac Subprovince, south of the Cadillac Larder Lake Deformation Zone, Québec, Canada. Ore Geol. Rev. 2017, 84, 185–201. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Helt, K. The Canadian Malartic Deposit: An Example of Oxidized, Intrusion-Related Gold Mineralization in the Abitibi Greenstone Belt, Québec, Canada. Master Thesis, McGill University, Montréal, QC, Canada, 2012. [Google Scholar]
- Zweng, P.L. Formation of Gold-Quartz Veins at Camflo, Malartic, Quebec, in Light of the Tectonic and THERMAL evolution of the Southern Abitibi Subprovince. Ph.D. Thesis, Stanford University, Stanford, CA, USA, 1994. [Google Scholar]
- Carrier, A.; Jébrak, M.; Angelier, J.; Holyland, P. The Silidor deposit, Rouyn-Noranda district, Abitibi belt: Geology, structural evolution, and paleostress modeling of an Au quartz vein-type deposit in an Archean trondhjemite. Econ. Geol. 2000, 95, 1049–1065. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Groves, D.I.; Goldfarb, R.J.; Gebre-Mariam, M.; Hagemann, S.G.; Robert, F. Orogenic gold deposits: A proposed classification in the context of their crustal distribution and relationship to other gold deposit types. Ore Geol. Rev. 1998, 13, 7–27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mathieu, L.; Madon, B.; Hamilton, M.A. Physico-chemical parameters of Neoarchean syntectonic magmatism: The example of the Muscocho Pluton, Abitibi Subprovince. Ore Geol. Rev. 2020, 125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sibson, R.H.; Robert, F.; Poulsen, K.H. High-angle reverse faults, fluid-pressure cycling, and mesothermal gold-quartz deposits. Geology 1988, 16, 551–555. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Phillips, G.N.; Evans, K.A. Role of CO2 in the formation of gold deposits. Nature 2004, 429, 860. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bedeaux, P.; Pilote, P.; Daigneault, R.; Rafini, S. Synthesis of the structural evolution and associated gold mineralization of the Cadillac Fault, Abitibi, Canada. Ore Geol. Rev. 2017, 82, 49–69. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]




| Deposit/Prospect | Intrusion | Area/Mining Camp (MC) |
|---|---|---|
| Lac Troilus | dykes | Opatica plutonic belt |
| Côté Gold | Chester intrusive complex | SW Abitibi greenstone belt |
| Central Camp | Chibougamau pluton | Chibougamau-Chapais MC |
| MOP-II | unnamed intrusion | |
| Dolodeau | Dolodeau stock | |
| Selbaie | Brouillan pluton | Selbaie MC |
| Douay | Douay syenite | NW Abitibi greenstone belt |
| Lac Shortt | unnamed intrusion | Desmaraiville |
| Boyvinet | Boyvinet stock | |
| Bachelor | O’Brien pluton | |
| Messegay | Launay | Taschereau |
| Don Rouyn | Flavrian-Powell intrusive complex | Rouyn Noranda MC |
| St-Jude breccia | Flavrian-Powell intrusive complex | |
| Silidor | Flavrian-Powell intrusive complex | |
| Doyon | Mooshla intrusive complex | Doyon-Bousquet-La Ronde MC |
| Clifford | Clifford stock | Blake River Group |
| Beattie | Beattie syenite | Porcupine-Destor fault zone |
| Wasamac | dykes | Francoeur-Wasa shear zone |
| Young-Davidson | Young-Davidson syenite | Matachewan |
| Matachewan Consolidated | syenite stock | |
| Cairo | Cairo stock | |
| Lake Shore | unnamed intrusion | Kirkland Lake MC |
| Macassa | unnamed intrusion | |
| Kirkland Lake deposit | Kirkland Lake intrusive complex | |
| Upper Beaver | unnamed intrusive suite | |
| Camflo-Malartic Hygrade | Camflo monzonite | Malartic MC |
| Canadian Malartic | dykes | |
| Kiena | dykes | Val d’Or MC |
| Several mineralization | Bourlamaque pluton | |
| East Sullivan | East Sullivan | |
| Hwy-44 property | unnamed intrusion | Timmins-Porcupine MC |
| Thunder Creek | unnamed intrusion | |
| McIntyre-Hollinger | Pearl Lake porphyry | |
| Golden (Canadian) Arrow | unnamed intrusion | Matheson |
| Kelore and Ross mines | unnamed intrusion |
| Clifford | Côté Gold | Central Camp | Troilus | Kiena | Don Rouyn | Doyon | Selbaie | McIntyre-Hollinger | Golden Arrow | MOP-II | Bourlamaque | Lac Shortt | Bachelor | East Sullivan | Upper Beaver | Launay | Wasamac | Beattie | Boyvinet | Young-Davidson | Ross | Kelore | Matachewan Consolidated | Cairo | Lake Shore | Macassa | Douay | Hwy-44 property | Thunder Creek | Kirkland Lake deposit | Canadian Malartic | Silidor | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Evidence for magmatic fluids1 | K-alteration | √ 6 | √ | √ | √ | √ | √ | √ | √ | √ | √ | √ | √ | √ | √ | √ | √ | √ | √ | √ | √ | √ | √ | √ | √ | |||||||||
| Hematization | √ | √ | √ | √ | √ | √ | √ | √ | √ | √ | √ | √ | √ | √ | √ | √ | √ | √ | √ | √ | √ | √ | ||||||||||||
| Sulfate (barite, anhydrite) | √ | √ | √ | √ | √ | √ | √ | √ | √ | √ | √ | |||||||||||||||||||||||
| Polymetallic signature | √ | √ | √ | √ | √ | √ | √ | √ | √ | √ | √ | √ | √ | √ | √ | |||||||||||||||||||
| Stable isotopes (O, S) | √ | √ | √ | √ | √ | √ | √ | √ | √ | √ | √ | √ | √ | √ | √ | √ | √ | |||||||||||||||||
| Au-telluride association | √ | √ | √ | √ | √ | √ | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Fluorite | √ | √ | √ | √ | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Base metals (Cu-Mo) | √ | √ | √ | √ | √ | √ | √ | √ | √ | √ | √ | √ | √ | √ | √ | √ | √ | √ | √ | √ | √ | √ | √ | √ | ||||||||||
| Zoning 4 | √ | √ | √ | √ | √ | √ | √ | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Evidence for metamorphic fluids2 | Fluid inclusions | √ | √ | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Stable isotopes (O, S) 5 | √ | √ | √ | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Non-specific characteristics3 | Structurally controlled | √ | √ | √ | √ | √ | √ | √ | √ | √ | √ | √ | √ | √ | √ | √ | √ | √ | √ | √ | √ | √ | √ | √ | √ | |||||||||
| Quartz-carbonate veins | √ | √ | √ | √ | √ | √ | √ | √ | √ | √ | √ | √ | √ | √ | √ | √ | √ | √ | √ | √ | ||||||||||||||
| Invisible gold in sulfide | √ | √ | √ | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Free gold | √ | √ | √ | √ | √ | √ | √ | √ | √ | √ | ||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Other characteristics | Disseminated sulfide | √ | √ | √ | √ | √ | √ | √ | √ | √ | √ | √ | √ | √ | √ | √ | √ | √ | √ | √ | √ | √ | √ | √ | √ | √ | √ | |||||||
| Silicification | √ | √ | √ | √ | √ | √ | √ | √ | √ | √ | √ | √ | √ | √ | √ | √ | √ | √ | √ | √ | √ | √ | √ | √ | √ | √ | √ | √ | √ | √ | ||||
| Breccia | √ | √ | √ | √ | √ | √ | √ | √ | √ | √ | √ | √ | √ | √ | √ | √ | √ | √ | √ | √ | √ | √ |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the author. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Mathieu, L. Intrusion-Associated Gold Systems and Multistage Metallogenic Processes in the Neoarchean Abitibi Greenstone Belt. Minerals 2021, 11, 261. https://doi.org/10.3390/min11030261
Mathieu L. Intrusion-Associated Gold Systems and Multistage Metallogenic Processes in the Neoarchean Abitibi Greenstone Belt. Minerals. 2021; 11(3):261. https://doi.org/10.3390/min11030261
Chicago/Turabian StyleMathieu, Lucie. 2021. "Intrusion-Associated Gold Systems and Multistage Metallogenic Processes in the Neoarchean Abitibi Greenstone Belt" Minerals 11, no. 3: 261. https://doi.org/10.3390/min11030261
APA StyleMathieu, L. (2021). Intrusion-Associated Gold Systems and Multistage Metallogenic Processes in the Neoarchean Abitibi Greenstone Belt. Minerals, 11(3), 261. https://doi.org/10.3390/min11030261