Batch and Continuous Chromate and Zinc Sorption from Electroplating Effluents Using Biogenic Iron Precipitates
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Biogenic Iron Precipitates
2.2. Encapsulation of Iron Precipitates in Alginate Beads
2.3. Batch Adsorption Experiments
2.4. Continuous Adsorption Experiments
2.5. Analytical and Characterization Techniques
3. Results and Discussions
3.1. Batch Experiments
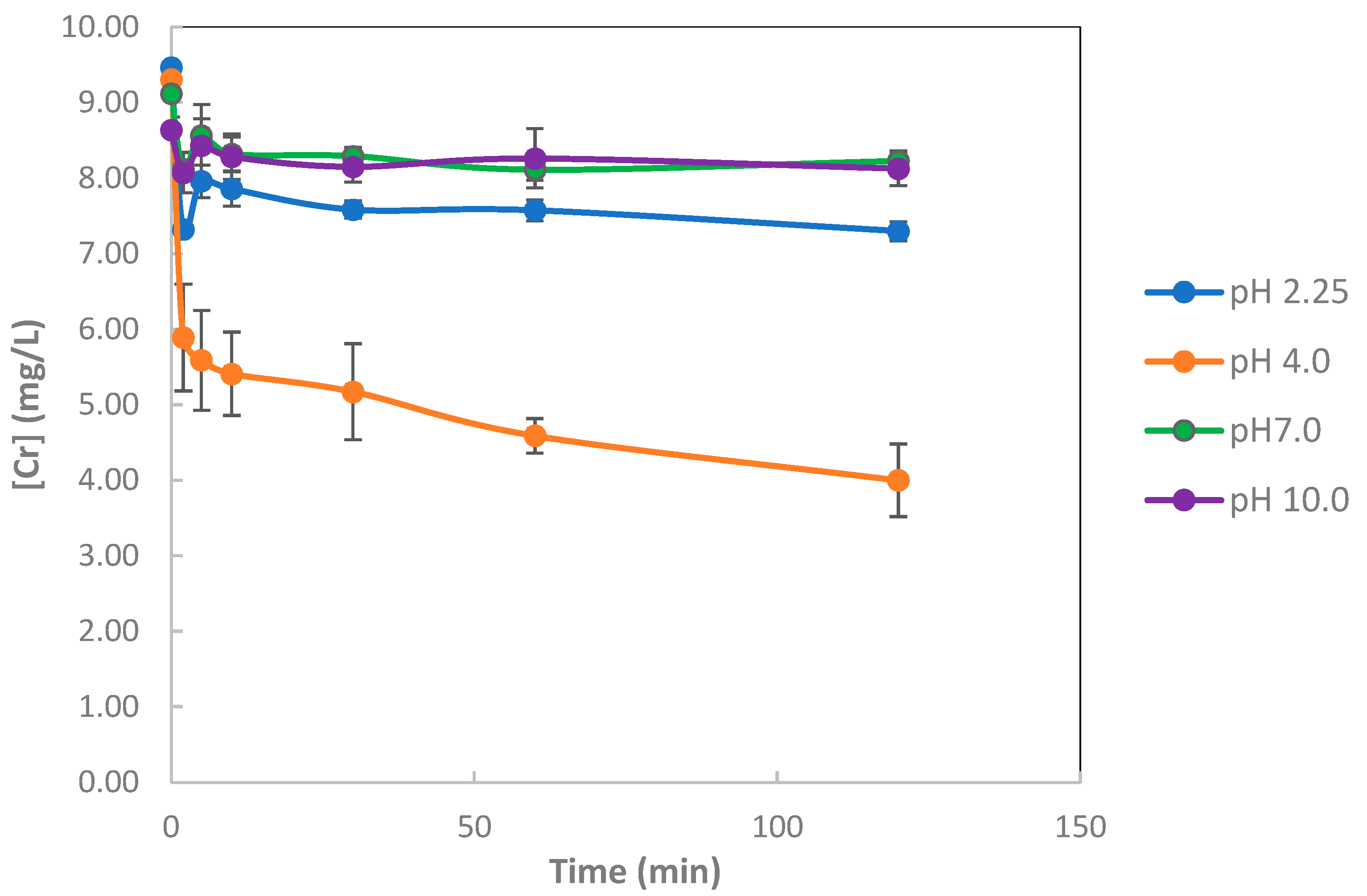
3.1.1. Metal Sorption Using Biogenic Iron Precipitates
3.1.2. Metal Adsorption Using Biogenic Iron Precipitates Encapsulated in Alginate Beads
3.2. Continuous Sorption
3.2.1. Influence of Flow Rate
3.2.2. Influence of Bed Height
3.2.3. Effect of Feeding System
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Xin, Z.; Wenchao, Z.; Zhenguang, Y.; Yiguo, H.; Zhengtao, L.; Xianliang, Y.; Xiaonan, W.; Tingting, L.; Liming, Z. Species Sensitivity Analysis of Heavy Metals to Freshwater Organisms. Ecotoxicology 2015, 24, 1621–1631. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- OECD. Environmental Outlook to 2030; Organization for Economic Cooperation and Development: Paris, France, 2008. [Google Scholar]
- WHO. Guidelines for Drinking Water Quality, Health Criteria and Other Supporting Information; World Health Organization: Geneva, Switzerland, 2004. [Google Scholar]
- Zhao, M.; Xu, Y.; Zhang, C.; Rong, H.; Zeng, G. New Trends in Removing Heavy Metals from Wastewater. Appl. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 2016, 100, 6509–6518. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- El-Sayed, M.E. Nanoadsorbents for Water and Wastewater Remediation. Sci. Total Environ. 2020, 739, 139903. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Castro, L.; Blázquez, M.L.; González, F.; Muñoz, J.A.; Ballester, A. Chapter 3. Biogenic Iron Compounds in Removing Heavy Metals from Polluted Waters. In Hydrometallurgy: Applications, Technology and Research; Cabrera, R., Ed.; Nova: Hauppage, NY, USA, 2017. [Google Scholar]
- Singh, P.; Itankar, N.; Patil, Y. Biomanagement of Hexavalent Chromium: Current Trends and Promising Perspectives. J. Environ. Manag. 2021, 279, 111547. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hennebel, T.; De Gusseme, B.; Boon, N.; Verstraete, W. Biogenic Metals in Advanced Water Treatment. Trends Biotechnol. 2009, 27, 90–98. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, C.; Jung, J.; Pawar, R.R.; Kim, M.; Lalhmunsiama; Lee, S.-M. Arsenate and Phosphate Removal from Water Using Fe-Sericite Composite Beads in Batch and Fixed-Bed Systems. J. Ind. Eng. Chem. 2017, 47, 375–383. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bordoloi, S.; Nath, S.K.; Gogoi, S.; Dutta, R.K. Arsenic and Iron Removal from Ground-Water by Oxidation–Coagulation at Optimized pH: Laboratory and Field Studies. J. Hazard. Mater. 2013, 260, 618–626. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, F.; Zhang, G.; Liu, S.; Fu, Z.; Chen, J.; Ma, C. Bioremoval of Arsenic and Antimony from Wastewater by a Mixed Culture of Sulfate-Reducing Bacteria Using Lactate and Ethanol as Carbon Sources. Int. Biodeterior. Biodegrad. 2018, 126, 152–159. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, J.; Zhou, L.; Dong, F.; Hudson-Edwards, K.A. Enhancing As(V) Adsorption and Passivation Using Biologically Formed Nano-Sized FeS Coatings on Limestone: Implications for Acid Mine Drainage Treatment and Neutralization. Chemosphere 2017, 168, 529–538. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Castro, L.; Blázquez, M.L.; González, F.; Muñoz, J.A.; Ballester, A. Removal of Arsenic from Aqueous Solution by Aeromonas hydrophila. Solid State Phenom. 2017, 262, 647–650. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thacher, R.; Ravindran, V.; Pirbazari, M. Modeling and Performance Prediction of Chromate Reduction by Iron Oxide Coated Sand in Adsorber Reactors. AIChE J. 2016, 62, 3717–3729. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nelson, Y.M.; Lion, L.W.; Shuler, M.L.; Ghiorse, W.C. Lead Binding to Metal Oxide and Organic Phases of Natural Aquatic Biofilms. Limnol. Oceanogr. 1999, 44, 1715–1729. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, T.; Zhang, S.-W.; Liu, L.-F.; Zhou, L. Green Rust Functionalized Geopolymer of Composite Cementitious Materials and Its Application on Treating Chromate in a Holistic System. Chemosphere 2021, 263, 128319. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dzieniszewska, A.; Kyziol-Komosinska, J.; Pająk, M. Adsorption and Bonding Strength of Chromium Species by Ferrihydrite from Acidic Aqueous Solutions. PeerJ 2020, 8, e9324. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, K.Y.; Tzou, Y.M.; Chan, Y.T.; Wu, J.J.; Teah, H.Y.; Liu, Y.T. Removal and Simultaneous Reduction of Cr(VI) by Organo-Fe(III) Composites Produced during Coprecipitation and Coagulation Processes. J. Hazard. Mater. 2019, 376, 12–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hilbrandt, I.; Ruhl, A.S.; Zietzschmann, F.; Molkenthin, M.; Jekel, M. Competition in Chromate Adsorption onto Micro-Sized Granular Ferric Hydroxide. Chemosphere 2019, 218, 749–757. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hajji, S.; Montes-Hernandez, G.; Sarret, G.; Tordo, A.; Morin, G.; Ona-Nguema, G.; Bureau, S.; Turki, T.; Mzoughi, N. Arsenite and Chromate Sequestration onto Ferrihydrite, Siderite and Goethite Nanostructured Minerals: Isotherms from Flow-through Reactor Experiments and XAS Measurements. J. Hazard. Mater. 2019, 362, 358–367. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, J.; Xu, K.; Yang, J.; Hao, Y.; Cheng, F. Nano Iron Oxide Impregnated in Chitosan Bead as a Highly Efficient Sorbent for Cr(VI) Removal from Water. Carbohydr. Polym. 2017, 173, 28–36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Iwahori, K.; Watanabe, J.-I.; Tani, Y.; Seyama, H.; Miyata, N. Removal of Heavy Metal Cations by Biogenic Magnetite Nanoparticles Produced in Fe(III)-Reducing Microbial Enrichment Cultures. J. Biosci. Bioeng. 2014, 117, 333–335. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Whitaker, A.H.; Peña, J.; Amor, M.; Duckworth, O.W. Cr(VI) Uptake and Reduction by Biogenic Iron (Oxyhydr) Oxides. Environ. Sci. Process. Impacts 2018, 20, 1056–1068. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, Z.Y.; Zhu, C.S.; Huang, J.B.; Gong, W.Q.; Chen, H.S.; Mu, S.B. A Study of Chromium Adsorption on Natural Goethite Biomineralized with Iron Bacteria. Acta Geol. Sin. Engl. 2006, 80, 597–603. [Google Scholar]
- Yu, C.; Zhang, J.; Wu, X.; Lan, Y.; Zhou, L. Cr(VI) Removal by Biogenic Schwertmannite in Continuous Flow Column. Geochem. J. 2014, 48, 1–7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ballester, A.; Castro, L.; Costa, M.C.; Carlier, J.; García-Roig, M.; Pérez-Galende, P.; Al-varez, A.; Bertagnolli, C.; Guibal, E. Design of Remediation Pilot Plants for the Treat-Ment of Industrial Metal-Bearing Effluents (Biometal Demo Project): Lab Tests. Hydrometallurgy 2017, 168, 103–115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Castro, L.; Blázquez, M.L.; González, F.; Muñoz, J.A.; Ballester, A. Biosorption of Zn(II) From Industrial Effluents Using Sugar Beet Pulp and F. Vesiculosus: From Laboratory Tests to a Pilot Approach. Sci. Total Environ. 2017, 598, 856–866. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Majcher, M.J.; Hoare, T. Applications of Hydrogels. In Functional Biopolymers; Jafar Mazumder, M.A., Sheardown, H., Al-Ahmed, A., Eds.; Springer International Publishing: Cham, Germany, 2019; pp. 453–490. [Google Scholar]
- Ukhurebor, K.E.; Aigbe, U.O.; Onyancha, R.B.; Nwankwo, W.; Osibote, O.A.; Paumo, H.K.; Ama, O.M.; Adetunji, C.O.; Siloko, I.U. Effect of Hexavalent Chromium on the Environment and Removal Techniques: A Review. J. Environ. Manag. 2021, 280, 111809. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Daradmare, S.; Xia, M.; Le, V.N.; Kim, J.; Park, B.J. Metal–Organic Frameworks/Alginate Composite Beads as Effective Adsorbents for the Removal of Hexavalent Chromium from Aqueous Solution. Chemosphere 2021, 270, 129487. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jiang, W.; Cai, Q.; Xu, W.; Yang, M.; Cai, Y.; Dionysiou, D.D.; O’Shea, K.E. Cr(VI) Adsorption and Reduction by Humic Acid Coated on Magnetite. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2014, 48, 8078–8085. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, T.; Zhang, L.; Li, C.; Yang, W.; Song, T.; Tang, C.; Meng, Y.; Dai, S.; Wang, H.; Chai, L.; et al. Synthesis of Core–Shell Magnetic Fe3O4@Poly(M-Phenylenediamine) Particles for Chromium Reduction and Adsorption. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2015, 49, 5654–5662. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Alam, M.S.; Bishop, B.; Chen, N.; Safari, S.; Warter, V.; Byrne, J.M.; Warchola, T.; Kap-pler, A.; Konhauser, K.O.; Alessi, D.S. Reusable Magnetite Nanoparticles–Biochar Composites for the Efficient Removal of Chromate from Water. Sci. Rep. 2020, 10, 19007. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Castro, L.; Blázquez, M.L.; González, F.; Muñoz, J.A.; Ballester, A. Heavy Metal Adsorption Using Biogenic Iron Compounds. Hydrometallurgy 2018, 179, 44–51. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tsezos, M. Biosorption: A Mechanistic Approach. Inhib. Cell Growth 2013, 141, 173–209. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gan, M.; Song, Z.; Jie, S.; Zhu, J.; Zhu, Y.; Liu, X. Biosynthesis of Bifunctional Iron Oxy-Hydrosulfate by Acidithiobacillus Ferroxidans and Their Application to Coagulation and Adsorption. Mater. Sci. Eng. C 2016, 59, 990–997. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rehm, B.H.A. Alginates: Biology and Applications; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2009. [Google Scholar]
- Mata, Y.; Blázquez, M.; Ballester, A.; González, F.; Muñoz, J. Optimization of the Continuous Biosorption of Copper with Sugar-Beet Pectin Gels. J. Environ. Manag. 2009, 90, 1737–1743. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sigdel, A.; Lim, J.; Park, J.; Kwak, H.; Min, S.; Kim, K.; Lee, H.; Nahm, C.H.; Park, P.-K. Immobilization of Hydrous Iron Oxides in Porous Alginate Beads for Arsenic Removal from Water. Environ. Sci. Water Res. Technol. 2018, 4, 1114–1123. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]






| Iron Compounds | Adsorption Capacity (mg/g) | pH | Reference |
|---|---|---|---|
| Green rust | 55.01 | 9 | [16] |
| Ferrihydrite | 83.73 | 3 | [17] |
| Organo-Fe (III) composites | 51.8 | 3 | [18] |
| Micro-sized granular ferric oxide | 5.8 | 7 | [19] |
| Ferrihydrite Siderite Goethite | 60 60 20 | 7.7 | [20] |
| Nano iron oxide impregnated in chitosan bead | 69.8 | 5 | [21] |
| pH 2.25 | pH 4 | pH 7 | pH 10 | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| [Cr]/mg·L−1 | 2064 | 1901 | 1827 | 1804 |
| [Zn]/mg·L−1 | 306.4 | 269.1 | 14.9 | 0 |
| [Fe]/mg·L−1 | 14.55 | 0 | 0 | 0 |
| pHinitial | pHfinal | Einitial (mV vs. Ag/AgCl) | Efinal (mV vs. Ag/AgCl) |
|---|---|---|---|
| 2.25 | 2.32 | 570 | 566 |
| 4.06 | 6.01 | 445 | 325 |
| 6.97 | 6.71 | 385 | 260 |
| 10.0 | 8.81 | 294 | 233 |
| Kinetic Model | Parameters | Cr (pH = 4) |
|---|---|---|
| Pseudo first-order (Lagergren) | q (mmol/g) | 0.153 |
| k1 (min−1) | 0.112 | |
| R2 | 0.841 | |
| Pseudo second-order | q (mmol/g) | 0.103 |
| k2 (q/mmol·min) | 2.274 | |
| R2 | 0.994 | |
| Elovich | α (g/mmol) | 8.366 |
| β (mmol/g·min) | 120.48 | |
| R2 | 0.920 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Castro, L.; Rocha, F.; Muñoz, J.Á.; González, F.; Blázquez, M.L. Batch and Continuous Chromate and Zinc Sorption from Electroplating Effluents Using Biogenic Iron Precipitates. Minerals 2021, 11, 349. https://doi.org/10.3390/min11040349
Castro L, Rocha F, Muñoz JÁ, González F, Blázquez ML. Batch and Continuous Chromate and Zinc Sorption from Electroplating Effluents Using Biogenic Iron Precipitates. Minerals. 2021; 11(4):349. https://doi.org/10.3390/min11040349
Chicago/Turabian StyleCastro, Laura, Fabiana Rocha, Jesús Ángel Muñoz, Felisa González, and María Luisa Blázquez. 2021. "Batch and Continuous Chromate and Zinc Sorption from Electroplating Effluents Using Biogenic Iron Precipitates" Minerals 11, no. 4: 349. https://doi.org/10.3390/min11040349
APA StyleCastro, L., Rocha, F., Muñoz, J. Á., González, F., & Blázquez, M. L. (2021). Batch and Continuous Chromate and Zinc Sorption from Electroplating Effluents Using Biogenic Iron Precipitates. Minerals, 11(4), 349. https://doi.org/10.3390/min11040349







