Pb Mineral Precipitation in Solutions of Sulfate, Carbonate and Phosphate: Measured and Modeled Pb Solubility and Pb2+ Activity
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Establishment of Reaction Systems
2.2. Determination of Pb Solubility and Pb2+ Activity
2.3. Mineralogical Analyses of Pb Precipitates
2.4. Data Analysis
3. Results and Discussion
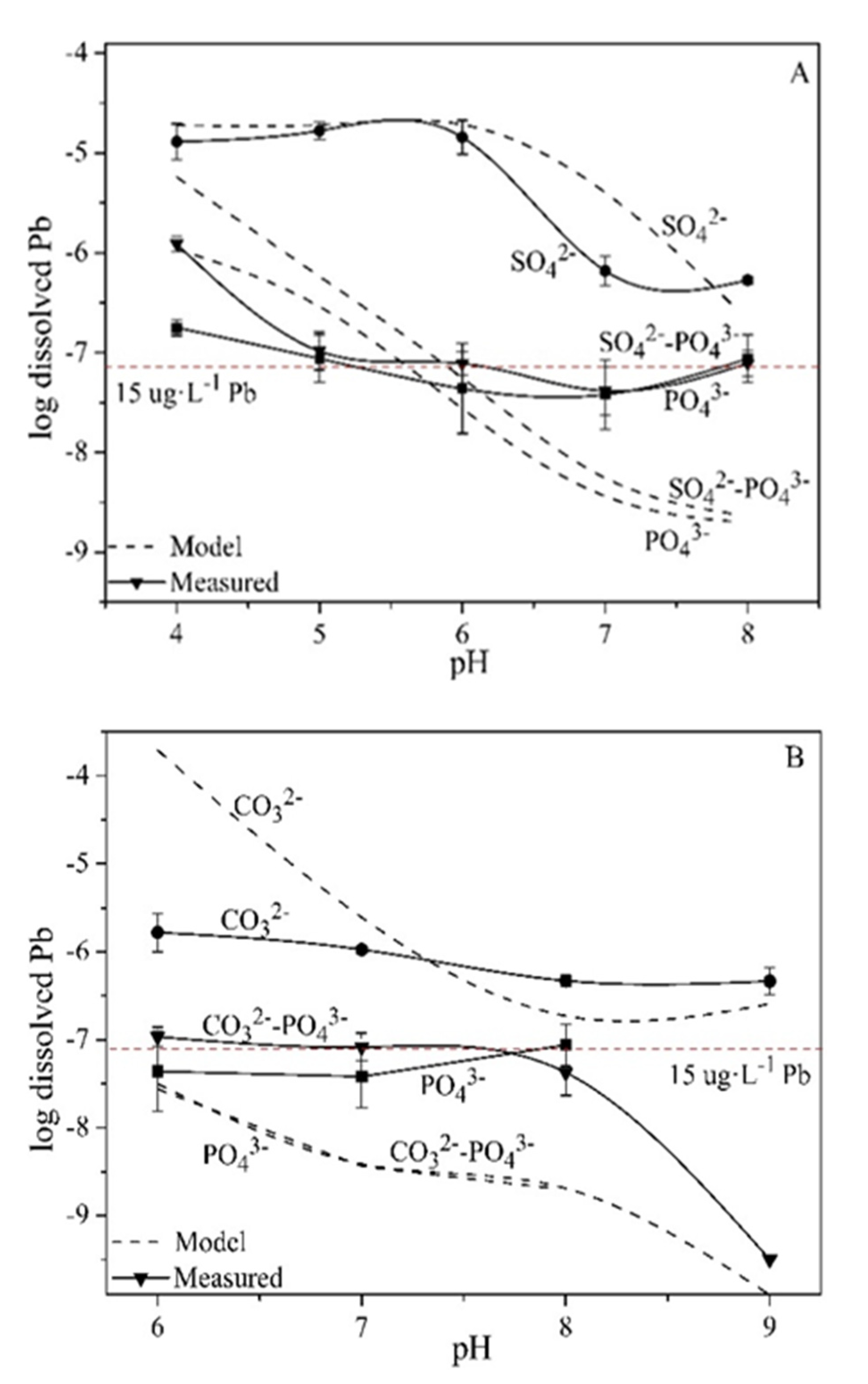
3.1. Effects of Sulfate, Carbonate and Phosphate on Pb Solubility
3.2. Effects of Sulfate, Carbonate and Phosphate on Pb2+ Activity
3.3. Effects of Pb Precipitation on Solution pH
3.4. FTIR Analysis of Precipitated Pb Minerals
3.5. XRD Analysis of Pb Precipitates
4. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Hemphill, C.P.; Ruby, M.V.; Beck, B.D.; Davis, A.; Bergstrom, P.D. The bioavailability of lead in mining wastes: Physical/chemical considerations. Chem. Spec. Bioavailab. 1991, 3, 135–148. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Chaney, R.L.; Mielke, H.W.; Sterrett, S.B. Speciation, mobility, and bioavailability of Soil Lead. Proc. Intern. Conf. Lead in Soils: Issues and Guidelines. Environ. Geochem. Health 1989, 11, 105–129. [Google Scholar]
- Harrison, R.M.; Laxen, D.H.P. Physicochemical speciation of lead in drinking water. Nature 1980, 286, 791–793. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Palumbo-Roe, B.; Wragg, J.; Cave, M.R.; Wagner, D. Effect of weathering product assemblages on Pb bioaccessibility in mine waste: Implications for risk management. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2013, 20, 7699–7710. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Ostergren, J.D.; Brown, G.E., Jr.; Parks, G.A.; Tingle, T.N. Quantitative speciation of lead in selected mine tailings from Leadville, CO. Environ. Sci. Technol. 1999, 33, 1627–1636. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Davis, A.; Drexler, J.W.; Ruby, M.V.; Nicholson, A. Micromineralogy of mine wastes in relation to lead bioavailability, Butte, Montana. Environ. Sci. Technol. 1993, 27, 1415–1425. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hayes, S.M.; Webb, S.M.; Bargar, J.R.; O’Day, P.A.; Maier, R.M.; Chorover, J. Geochemical weathering increases lead biaccessibility in semi-arid mine tailings. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2012, 46, 5834–5841. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Bao, Z.; Al, T.; Couillard, M.; Poirier, G.; Bain, J.; Shrimpton, H.K.; Finfrock, Y.Z.; Lanzirotta, A.; Paktunc, D.; Saurette, E.; et al. A crossscale investigation of galena oxidation and controls on mobilization of lead in mine waste rock. J. Hazard. Mater. 2021, 412, 125130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Iavazzo, P.; Adamo, P.; Boni, M.; Hillier, S.; Zampella, M. Mineralogy and chemical forms of lead and zinc in abandoned mine wastes and soils: An example from Morocco. J. Geochem. Explor. 2012, 113, 56–67. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abdul-Samad, F.A.; Thomas, J.H.; Williams, P.A.; Symes, R.F. Chemistry of formation of lanarkite, Pb2OSO4. Miner. Mag. 1982, 46, 499–501. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grey, I.E.; Shanks, F.L.; Wilson, N.C.; Mumme, W.G.; Birch, W.D. Carbon incorporation in plumbogummite-group minerals. Mineral. Mag. 2011, 75, 145–158. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Keim, M.F.; Gassmann, B.; Markl, G. Formation of basic lead phases during fire-setting and other natural and man-made processes. Am. Miner. 2017, 102, 1482–1500. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Essington, M.E.; Foss, J.E.; Roh, Y. The soil mineralogy of lead at Horace’s villa. Soil Sci. Soc. Am. J. 2004, 68, 979–993. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Henry, H.; Naujokas, M.F.; Attanyake, C.; Basta, N.T.; Cheng, Z.; Hettiarachchi, G.M.; Maddaloni, M.; Schadt, C.; Scheckel, K.G. Bioavailability-based in situ remediation to meet future lead (Pb) standards in urban soils and gardens. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2015, 49, 8948–8958. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grimes, S.M.; Johnston, S.R.; Batchelder, D.N. Lead carbonate-phosphate system: Solid-dilute solution exchange reactions in aqueous systems. Analyst 1995, 120, 2741–2746. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, L.; Putnis, C.V.; Ruiz-Agudo, E.; King, H.E.; Putnis, A. Coupled dissolution and precipitation at the cerussite-phosphate solution interface: Implications for immobilization of lead in soils. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2013, 47, 13502–13510. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Manecki, M.; Kwasniak-Kominek, M.; Majka, J.M.; Rakovan, J. Model of interface-coupled mechanism of pseudomorphic replacement reaction in aqueous solutions based on the system of cerrusite PbCO3 -pyromorphite Pb5(PO4)3Cl. Geochim. Cosmochim. Acta 2020, 289, 1–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chrysochoou, M.; Dermatas, D.; Grubb, D.G. Phosphate application to firing range soils for Pb immobilization: The unclear role of phosphate. J. Hazard. Mater. 2007, 144, 1–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Scheckel, K.G.; Ryan, J.A. Effects of aging and pH on dissolution kinetics and stability of chloropyromorphite. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2002, 36, 2198–2204. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dove, P.M.; Czank, C.A. Crystal chemical controls on the dissolution kinetics of the isostructural sulfates: Celestite, anglesite and barite. Geochim. Cosmochim. Acta 1995, 59, 1907–1915. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bilinski, H.; Schindler, P. Solubility and equilibrium constants of lead in carbonate solutions (25 °C, I = 0.3 mol dm−3). Geochim. Cosmochim. Acta 1982, 46, 921–928. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mercy, M.A.; Rock, P.A.; Casey, W.H.; Mokarram, M.M. Gibbs energies of formation for hydrocerussite [Pb(OH)2 Pb(CO3)2(s)] and hydrozincite [Zn(OH)2 Zn(CO3)2(s)] at 298 K and 1 bar from electrochemical cell measurements. Am. Miner. 1998, 83, 739–745. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marani, D.; Macchi, G.; Pagano, M. Lead precipitation in the presence of sulphate and carbonate: Testing of thermodynamic predictions. Water Res. 1995, 29, 1085–1092. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, P.; Ryan, J.A. Formation of chloropyromorphite from galena (PbS) in the presence of hydroxyapatite. Environ. Sci. Technol. 1999, 33, 618–624. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Xenidis, A.; Stouraiti, C.; Papassiopi, N. Stabilization of Pb and As in soils by applying combined treatment with phosphates and ferrous iron. J. Hazard. Mater. 2010, 177, 929–937. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sima, J.; Cao, X.; Zhao, L.; Luo, Q. Toxicity characteristic leaching procedure over-or under-estimates leachability of lead in phosphate-amended contaminated soils. Chemosphere 2015, 138, 744–750. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Santucci, R.J., Jr.; Scully, J.R. The pervasive threat of lead (Pb) in drinking water: Unmasking and pursuing scientific factors that govern lead release. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2020, 117, 23211–23218. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, J.; Giammar, D.E.; Pasteris, J.D.; Dai, C.; Bae, Y.; Hu, Y. Formation and aggregation of lead phosphate particles: Implications for lead immobilization in water supply systems. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2018, 52, 12612–12623. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bae, Y.; Pasteris, J.D.; Giammar, D.E. The ability of phosphate to prevent lead release from pipe scale when switching from free chlorine to monochloramine. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2020, 54, 879–888. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- McBride, M.B.; Kelch, S.E.; Schmidt, M.P.; Sherpa, S.; Martinez, C.E.; Aristilde, L. Oxalate-enhanced solubility of lead (Pb) in the presence of phosphate. Environ. Sci. Process. Impacts 2019, 21, 738. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Martinez, C.E.; Jacobson, A.R.; McBride, M.B. Lead phosphate minerals: Solubility and dissolution by model and natural ligands. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2004, 38, 5584–5590. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xie, L.; Giammar, D.E. Equilibrium solubility and dissolution rate of the lead phosphate chloropyromorphite. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2007, 41, 8050–8055. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Flis, J.; Manecki, M.; Bajda, T. Solubility of pyromorphite Pb5(PO4)3Cl-mimetite Pb5(AsO4)3Cl solid solution series. Geochim. Cosmochim. Acta 2011, 75, 1858–1868. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pan, H.B.; Darvell, B.W. Calcium phosphate solubility: The need for re-evaluation. Cryst. Growth Des. 2009, 9, 639–645. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Woosley, R.J.; Millero, F.J. Pitzer model for the speciation of lead chloride and carbonate complexes in natural waters. Mar. Chem. 2013, 149, 1–7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, Y.; Li, X.; McBride, M.B. Aqueous solubility of Pb at equilibrium with hydroxypyromorphite over a range of phosphate concentrations. Environ. Sci. Process. Impacts 2021, 23, 170. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Powell, K.J.; Brown, P.L.; Byrne, R.H.; Gajda, T.; Hefter, G.; Leuz, A.-K.; Sjoberg, S.; Wanner, H. Chemical speciation of environmentally significant metals with inorganic ligands. Part 3: The Pb2+ + OH−, Cl−, CO32−, SO42−, and PO43− systems. (IUPAC Technical Report). Pure Appl. Chem. 2009, 81, 2425–2476. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Traina, S.J.; Laperche, V. Contaminant bioavailability in soils, sediments and aquatic environments. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 1999, 96, 3365–3371. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Ruby, M.V.; Schoof, R.; Brattin, W.; Goldade, M.; Post, G.; Harnois, M.; Mosby, D.E.; Casteel, S.W.; Berti, W.; Carpenter, M.; et al. Advances in evaluating the oral bioavailability of inorganics in soil for use in human health risk assessment. Environ. Sci. Technol. 1999, 33, 3697–3705. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, Q.Y.; Logan, T.J.; Traina, S.J. Effects of NO3−, Cl−, F−, SO42−, and CO32− on Pb2+ immobilization by hydroxyapatite. Environ. Sci. Technol. 1994, 28, 408–418. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mirchell, M.J.; Jensen, O.E.; Cliffe, K.A.; Maroto-Valer, M.M. A model of carbon dioxide dissolution and mineral carbonation kinetics. Proc. R. Soc. A 2010, 466, 1265–1290. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, Y.; Zhu, Z.; Zhao, X.; Liang, Y.; Huang, Y. Characterization, dissolution and solubility of lead hydroxypyromorphite [Pb5(PO4)3OH] at 25–45 °C. J. Chem. 2015. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Taylor, P.; Lopata, V.J. Stability and solubility relationships between some solids in the system PbO-CO2-H2O. Can. J. Chem. 1984, 62, 395–402. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Baes, C.F.; Mesmer, R.E. The Hydrolysis of Cations; Wiley: New York, NY, USA, 1976. [Google Scholar]
- Ross, S.D. Sulphates and other oxy-anions of Group VI. In The Infrared Spectra of Minerals; Farmer, V.C., Ed.; Mineralogical Society: London, UK, 1974; pp. 423–444. [Google Scholar]
- Ross, S.D. Phosphates and other oxy-anions of Group V. In The Infrared Spectra of Minerals; Farmer, V.C., Ed.; Mineralogical Society: London, UK, 1974; pp. 383–422. [Google Scholar]
- Frost, R.L.; Martens, W.; Kloprogge, J.T.; Ding, Z. Raman spectroscopy of selected lead minerals of environmental significance. Spectrochim. Acta A 2003, 59, 2705–2711. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Griffith, W.P. Raman spectroscopy of minerals. Nature 1969, 224, 264–266. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- White, W.; Farmer, V.C. The infrared spectra of minerals. Miner. Soc. 1974, 4, 105–106. [Google Scholar]
- Bhatnagar, V.M. The preparation, X-ray and infra-red spectra of lead apatites. Arch. Oral Biol. 1970, 15, 469–480. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]




| System | pH = 4 | pH = 5 | pH = 6 | pH = 7 | pH = 8 | pH = 9 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| SO4 | 1.42 ± 0.63a | 1.71 ± 0.35a | 1.55 ± 0.60a | 0.07 ± 0.02b | 0.05 ± 0.01b | ND |
| CO3 | ND | ND | 0.19 ± 0.08a | 0.11 ± 0.01ab | 0.049 ± 0.02b | 0.047 ± 0.01b |
| PO4 | 0.018 ± 0.003a | 0.010 ± 0.005ab | 0.006± 0.007ab | 0.005 ± 0.004b | 0.010 ± 0.004ab | ND |
| SO4-PO4 | 0.12 ± 0.02a | 0.011 ± 0.004b | 0.008 ± 0.002b | 0.007 ± 0.002b | 0.008 ± 0.002b | ND |
| CO3-PO4 | ND | ND | 0.011 ± 0.003a | 0.009± 0.003ab | 0.005± 0.003ab | ND |
| System | pH | Predicted by Visual MINTEQ a | Identified by XRD |
|---|---|---|---|
| SO4 | 4.0 | PbSO4 | PbSO4 |
| 5.0 | PbSO4 [Pb2(OH)2SO4] | PbSO4 | |
| 6.0 | PbSO4 [Pb2(OH)2SO4] | PbSO4, Pb4(SO4)(CO3)2(OH)2 | |
| 7.0 | Pb2(OH)2SO4. [Pb3(OH)2(CO3)2] | Pb3(CO3)2(OH)2, Pb4(SO4)(CO3)2(OH)2 | |
| 8.0 | Pb3(OH)2(CO3)2 [Pb4(OH)6SO4] | Pb3(CO3)2(OH)2, Pb4(SO4)(CO3)2(OH)2 | |
| SO4-PO4 | 4.0 | PbHPO4 [Pb3(PO4)2] | Unidentified mineral, Pb3(PO4)2, Pb5(PO4)3(OH) |
| 5.0 | PbHPO4 [Pb3(PO4)2] | Unidentified mineral, Pb3(PO4)2, Pb5(PO4)3(OH) | |
| 6.0 | Pb3(PO4)2 [Pb5(PO4)3OH] | Pb3(PO4)2, Pb10(PO4)6O, Pb5(PO4)3(OH) | |
| 7.0 | Pb5(PO4)3OH [Pb3(PO4)2] | Pb3(PO4)2, Pb10(PO4)6O, Pb5(PO4)3(OH) | |
| 8.0 | Pb5(PO4)3OH [Pb3(PO4)2] | Pb3(PO4)2, Pb10(PO4)6O | |
| CO3 | 6.0 | Pb3(OH)2(CO3)2 [PbCO3] | PbCO3 |
| 7.0 | Pb3(OH)2(CO3)2 [PbCO3] | PbCO3 | |
| 8.0 | Pb3(OH)2(CO3)2 [PbCO3] | PbCO3 | |
| 9.0 | Pb3(OH)2(CO3)2 [Pb(OH)2] | Pb3(CO3)2(OH)2, PbCO3 | |
| CO3-PO4 | 6.0 | Pb3(PO4)2 [Pb5(PO4)3OH] | Pb10(PO4)6O, Pb3(PO4)2 |
| 7.0 | Pb5(PO4)3OH [Pb3(PO4)2] | Pb3(PO4)2, Pb10(PO4)6O | |
| 8.0 | Pb5(PO4)3OH [Pb3(PO4)2] | Pb3(PO4)2, Pb10(PO4)6O, Pb5(PO4)3(OH) | |
| 9.0 | Pb5(PO4)3OH [Pb3(PO4)2] | Pb3(PO4)2, Pb10(PO4)6O, Pb5(PO4)3(OH) |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Li, X.; Azimzadeh, B.; Martinez, C.E.; McBride, M.B. Pb Mineral Precipitation in Solutions of Sulfate, Carbonate and Phosphate: Measured and Modeled Pb Solubility and Pb2+ Activity. Minerals 2021, 11, 620. https://doi.org/10.3390/min11060620
Li X, Azimzadeh B, Martinez CE, McBride MB. Pb Mineral Precipitation in Solutions of Sulfate, Carbonate and Phosphate: Measured and Modeled Pb Solubility and Pb2+ Activity. Minerals. 2021; 11(6):620. https://doi.org/10.3390/min11060620
Chicago/Turabian StyleLi, Xinxin, Behrooz Azimzadeh, Carmen Enid Martinez, and Murray B. McBride. 2021. "Pb Mineral Precipitation in Solutions of Sulfate, Carbonate and Phosphate: Measured and Modeled Pb Solubility and Pb2+ Activity" Minerals 11, no. 6: 620. https://doi.org/10.3390/min11060620
APA StyleLi, X., Azimzadeh, B., Martinez, C. E., & McBride, M. B. (2021). Pb Mineral Precipitation in Solutions of Sulfate, Carbonate and Phosphate: Measured and Modeled Pb Solubility and Pb2+ Activity. Minerals, 11(6), 620. https://doi.org/10.3390/min11060620






