Abstract
Deformation microstructures of peak metamorphic conditions in ultrahigh-pressure (UHP) metamorphic rocks constrain the rheological behavior of deeply subducted crustal material within a subduction channel. However, studies of such rocks are limited by the overprinting effects of retrograde metamorphism during exhumation. Here, we present the deformation microstructures and crystallographic-preferred orientation data of minerals in UHP rocks from the Dabie–Shan to study the rheological behavior of deeply subducted continental material under UHP conditions. The studied samples preserve deformation microstructures that formed under UHP conditions and can be distinguished into two types: high-strain mafic–ultramafic samples (eclogite and garnet-clinopyroxenite) and low-strain felsic samples (jadeite quartzite). This distinction suggests that felsic rocks are less strained than mafic–ultramafic rocks under UHP conditions. We argue that the phase transition from quartz to coesite in the felsic rocks may explain the microstructural differences between the studied mafic–ultramafic and felsic rock samples. The presence of coesite, which has a higher strength than quartz, may result in an increase in the bulk strength of felsic rocks, leading to strain localization in nearby mafic–ultramafic rocks. The formation of shear zones associated with strain localization under HP/UHP conditions can induce the detachment of subducted crustal material from subducting lithosphere, which is a prerequisite for the exhumation of UHP rocks. These findings suggest that coesite has an important influence on the rheological behavior of crustal material that is subducted to coesite-stable depths.
1. Introduction
Since the discovery of coesite and micro-diamond in metamorphic rocks [1,2,3], the exhumation of deeply subducted continental material has been recognized as a common occurrence in continental collision zones. Ultrahigh-pressure (UHP) rocks contain coesite and diamond, which are indicators of UHP conditions. UHP rocks commonly record chemical and physical processes during subduction and subsequent exhumation.
Most previous studies of UHP rocks have relied on petrological, mineralogical, and geochemical investigations, with relatively few having focused on microstructural and rheological aspects, although the study of deformation microstructures should constrain the rheological behavior of deeply subducted crustal material under UHP conditions. However, in many cases, deformation microstructures that formed under UHP conditions have been overprinted by retrograde metamorphism related to fluid infiltration during exhumation, and this has limited our understanding of the rheological behavior of UHP rocks.
The Dabie–Sulu orogenic belt is a continental collision zone in eastern China that contains the world’s largest UHP metamorphic belt (>30,000 km2) [4,5]. The UHP rocks are estimated to have been subducted to depths of >80 km prior to rapid exhumation (e.g., [6,7,8]). The UHP metamorphic belt in the Dabie–Shan region of the Dabie–Sulu orogenic belt contains UHP mafic–ultramafic rocks that preserve the peak metamorphic assemblage [9]. In this study, we investigated UHP rocks from the Dabie–Shan region to understand the rheological behavior of deeply subducted continental material under UHP conditions by measuring deformation microstructures and crystallographic fabrics.
2. Geological Setting and Samples
The Dabie–Sulu orogenic belt is located in eastern China (Figure 1a) and was formed from the collision between the Sino-Korean and Yangtze cratons at 240–220 Ma (e.g., [10,11,12]). Since the discovery of coesite in the Dabie–Shan and Sulu regions (e.g., [13,14,15,16]), the Dabie–Sulu orogenic belt has been recognized as a continental collision zone that contains a UHP metamorphic belt.

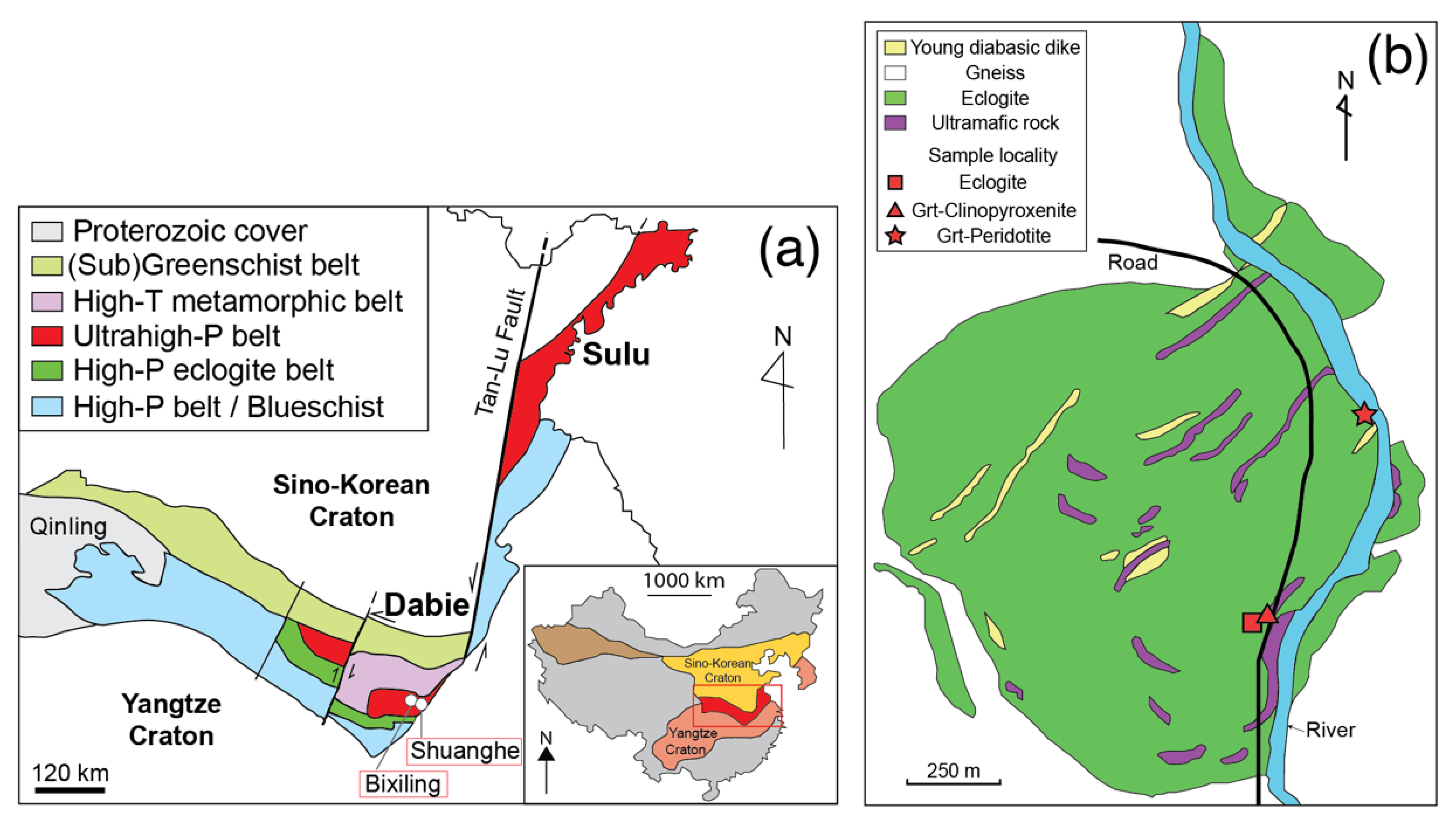
Figure 1.
(a) Simplified tectonic map of the Dabie–Sulu orogenic belt, modified after Zhang et al. [7]. The Dabie–Shan is divided into five belts according to metamorphic grade. Samples for the present study were obtained from the Bixiling Complex and the Shuanghe area. (b) Geological map of the Bixiling mafic–ultramafic complex. Red-colored symbols represent sample locations. Modified after Zhang et al. [17].
The Dabie–Sulu UHP belt is segmented into several blocks by NE–SW-trending faults that extend subparallel to the Tan–Lu Fault. The Dabie–Shan region is one of these segmented blocks (Figure 1a) and is further divided by E–W-trending faults into five belts [18,19], as follows (from south to north): (1) the Susong low-temperature–high-pressure (LT–HP) blueschist facies belt, (2) the south Dabie LT–HP eclogite belt, (3) the south Dabie medium-temperature–UHP eclogite belt, (4) the north Dabie HT–HP migmatite belt, and (5) the north Huaiyang LT–LP greenschist-facies belt. The Dabie UHP belt is composed mainly of quartzo-feldspathic gneiss interlayered with metapelite, jadeite quartzite, and marble [5]. Abundant coesite-bearing eclogite occurs as lenses, blocks, and layers within gneiss and marble [5,17]. Inclusions of micro-diamond have been reported in eclogitic garnet [20,21]. Coesite and quartz pseudomorphs after coesite have been found in zircon within country gneiss [22]. Consequently, the coesite-bearing eclogite and surrounding country rocks are thought to have been subjected to Triassic UHP metamorphism [23,24]. The age of UHP metamorphism in the UHP belt has been constrained to 218–210 Ma based on Sm–Nd isotopic analyses of garnet and omphacite in eclogite [25]. Most estimates of peak metamorphic conditions for Dabie coesite-bearing eclogite are in the range of 700 ± 50 °C and >2.8 GPa [5,12,17,26,27,28,29,30].
The Bixiling mafic–ultramafic metamorphic complex (Figure 1b) is the largest coesite-bearing mafic–ultramafic body (~1.5 km2 of outcrop) in the Dabie–Shan [17,31]. The complex is surrounded by foliated quartzo-feldspathic gneiss that contains plagioclase, K-feldspar, quartz, biotite, zoisite, titanite, and minor muscovite and zircon [17]. Younger diabasic dikes cut across the complex and gneissic country rocks. The complex consists chiefly of layered eclogites with about 20 elongated lenses of garnet-bearing ultramafic rocks. The meta-ultramafic rocks show gradational contacts with layered eclogite blocks [17,32,33]. Therefore, it has been suggested that the eclogites and meta-ultramafic rocks underwent the same UHP metamorphism. Field relationships and bulk compositions of various rocks suggest that the protoliths of the Bixiling mafic and ultramafic rocks were anorthitic plagioclase + olivine-rich gabbro cumulates that were derived from fractionation of basaltic magma at crustal levels [17].
In the Shuanghe area of the Dabie UHP belt, UHP metamorphic rocks occur as a thrusted slab within country gneiss [28,34]. The UHP metamorphic unit comprises biotite–feldspar gneiss, two-mica gneiss, eclogite, amphibolite, jadeite quartzite, marble, calc-silicate gneiss, serpentinite, and talc shist (Wang et al., 2010). Inclusions of coesite and polycrystalline quartz have been reported in eclogite and jadeite quartzite [28,34]. Petrological and mineralogical data indicate that UHP metamorphic rocks in the Shuanghe area underwent a complex polymetamorphic evolution and UHP coesite–eclogite records peak metamorphic conditions of 700 ± 50 °C and 27–28 kbar [28].
In this study, three samples were collected from the Bixiling complex (Figure 1b) and one from the Shuanghe area. Three samples of mafic–ultramafic rocks (i.e., eclogite, garnet clinopyroxenite, and garnet peridotite) were obtained from the Bixiling complex, with eclogite and garnet clinopyroxenite being obtained from road outcrops and garnet peridotite from the bed of a river flowing through the eastern part of the complex. Jadeite quartzite was obtained from the Shuanghe area.
3. Methods
For microstructural observations, where the foliation and lineation could be identified, thin-sections were made from rock sections cut parallel to the lineation (X) and perpendicular to the foliation (Z) (i.e., the XZ plane). The foliation and lineation were defined by compositional layering or elongated grains of constituent minerals in samples, full descriptions of which are presented in Section 4. Thin-sections with a thickness of ~30 µm were polished with 1 μm diamond paste. Thin-sections were also polished with colloidal silica to remove surface damage prior to analysis using the electron backscatter diffraction (EBSD) technique with a scanning electron microscope (SEM). Microstructures were analyzed in thin-sections under a polarizing microscope and in phase maps compiled from EBSD data using the Matlab MTEX 5.7.0 toolbox (https://mtex-toolbox.github.io/, accessed on 3 August 2021) [35]. The EBSD phase maps were used to depict structures of grain boundaries and subgrain boundaries over a thin-section on the basis of crystallographic orientations.
Chemical compositions of garnet and clinopyroxene in all four studied samples and of olivine in the garnet peridotite sample were analyzed using a JEOL electron microprobe (JXA-8800R) at the Rock and Mineral Laboratory of Nagoya University, Nagoya, Japan. Quantitative analyses were conducted with an accelerating voltage of 15 kV, a beam current of 12 nA, and a beam width of 5 µm. To prevent charging by the electron beam, thin-sections were coated with carbon.
Crystallographic orientations of major constituent minerals in four samples were analyzed using an EBSD system (Oxford Instruments INCA Synergy AZTEC v4.2 HKL-Channel5) attached to an SEM (HITACHI S-3400N Type II) at the Rock and Mineral Laboratory of Nagoya University. The measurements were conducted using an accelerating voltage of 20 kV, a working distance of 25–26 mm, and a sample tilt of 70° from the horizontal. Diffraction patterns were projected onto a phosphor screen and recorded by a CCD (Nordlys Nano, Oxford Instruments, High Wycombe, UK) camera. The images were processed and indexed in terms of crystal orientation using AZtec software v4.2 (Oxford Instruments, High Wycombe, UK). These data resulted in a series of maps with an analysis step size of 50 µm. Raw indexation data included non-indexed pixels, requiring the use of data treatments such as the reduction of noise, removal of wild spikes, and extrapolation of missing data. Modal compositions of the samples were calculated from the area fraction of indexed phases in the data after treatment. For observations of microstructures, EBSD phase maps were constructed for each sample using the Matlab MTEX 5.7.0 toolbox (https://mtex-toolbox.github.io/, accessed on 3 August 2021) [35]. In these phase maps, grain boundaries (represented by black lines) and subgrain boundaries (represented by white lines) were defined by misorientations of >10° and of 2–10°, respectively. Crystal-preferred orientations (CPOs) of garnet, clinopyroxene, quartz, and olivine were displayed in pole figures, presented on equal-area, lower-hemisphere stereographic projections. For thin-sections made on the XZ plane, the XY plane and Z-axis are parallel and perpendicular to the E–W direction in the pole figures, respectively. To avoid the influence of large grains, pole figures were constructed using one point per grain. To quantitatively evaluate the intensity of CPOs, the fabric strength was determined by calculating values of the J-index, which is the volume-averaged integral of squared orientation densities [36]. The J-index has a value ranging from 1 for a random distribution to infinity for a single crystal. In addition, the intensity of each pole figure was defined by the pfJ-index [37]. The generation of phase maps and pole figures, and the calculation of pfJ-indexes were performed using the software PFctf_PC.exe developed by D. Mainprice (Université Montpellier, Montpellier, France) and the calculation of J-index was used a MTEX function: textureindex.
4. Petrography and Microstructure
The lineation was defined by elongated grains of clinopyroxene in all samples. All samples contain clinopyroxene, including omphacite in eclogite, Ca-pyroxene in garnet clinopyroxenite and garnet peridotite, and jadeite in jadeite quartzite. Foliation was apparent in eclogite, garnet clinopyroxenite, and jadeite quartzite. In eclogite and garnet clinopyroxenite, the foliation was defined by slight compositional layering involving garnet and clinopyroxene, and by elongated grains of clinopyroxene. In jadeite quartzite, it was defined by elongated grains of jadeite. Thin-sections were made on the XZ plane for eclogite, garnet clinopyroxenite, and jadeite quartzite. Garnet peridotite shows no foliation, and therefore thin-sections of this rock were made parallel to the lineation. Petrographic and microstructural characteristics of each sample are described below.
4.1. Eclogite
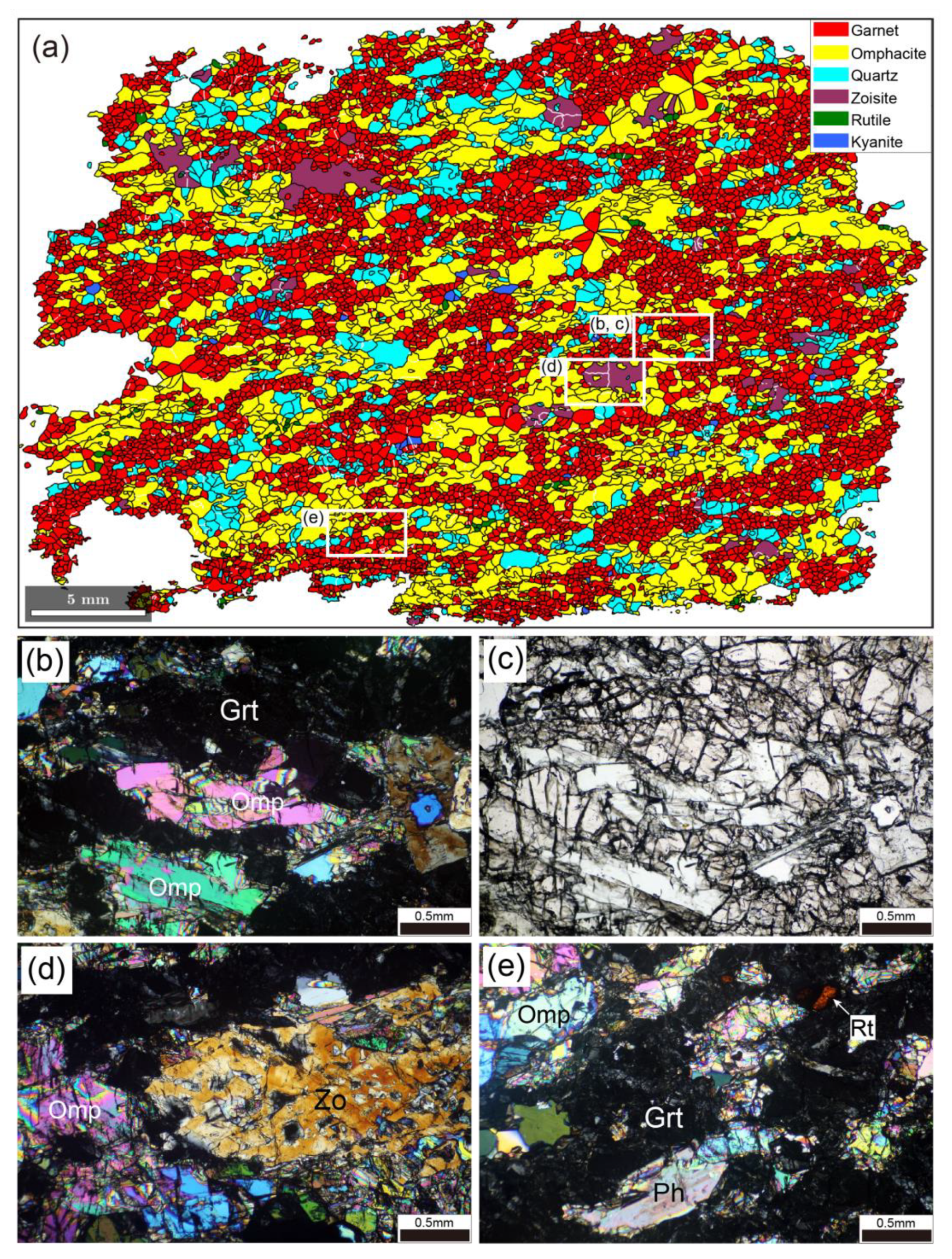
Figure 2 shows the microstructure of eclogite. The eclogite is composed of garnet (41.5 vol.%), omphacite (40.8 vol.%), quartz (13 vol.%), zoisite (4.2 vol.%), and minor amphibole, phengite, rutile, kyanite, and apatite. Garnet and omphacite are primary minerals and show a homogeneous texture in thin-section (Figure 2a–c). Garnet has a smaller grain size (mean = 240 µm) than omphacite (mean = 344 µm) and occurs in layers of fine-grained garnet aggregates. Elongated grains of omphacite with a mean aspect ratio of 2.12 show a shape-preferred orientation (SPO). Certain omphacite grains show weak undulose extinction and contain subgrain boundaries. Quartz grains have irregular shapes and show undulose extinction. Zoisite porphyroblasts (Figure 2d) commonly contain inclusions of garnet, omphacite, and quartz. Apatite grains occur as both interstitial grains and inclusions in omphacite. Amphibole typically forms by the replacement of omphacite in retrogressed eclogite. Amphibole is rarely found on rims of omphacite grains in eclogite. In addition, no coronas or symplectites are found on rims of garnet grains. Thus, eclogite appears to have been negligibly affected by retrograde metamorphism.
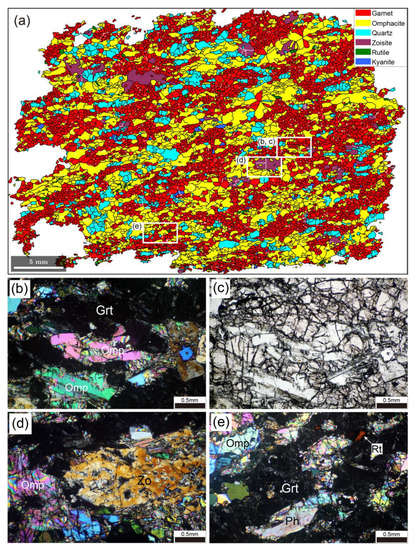
Figure 2.
Microstructure of eclogite. (a) EBSD phase map of entire thin-section. White areas in the map are non-indexed pixels. White lines represent subgrain boundaries. White rectangles indicate areas shown in (b–e). (b,d,e) Photomicrographs under cross-polarized light. (c) As in (b), but under plane-polarized light. Grt, garnet; Omp, omphacite; Qtz, quartz; Zo, zoisite; Rt, rutile; Ph, phengite.
4.2. Garnet Clinopyroxenite
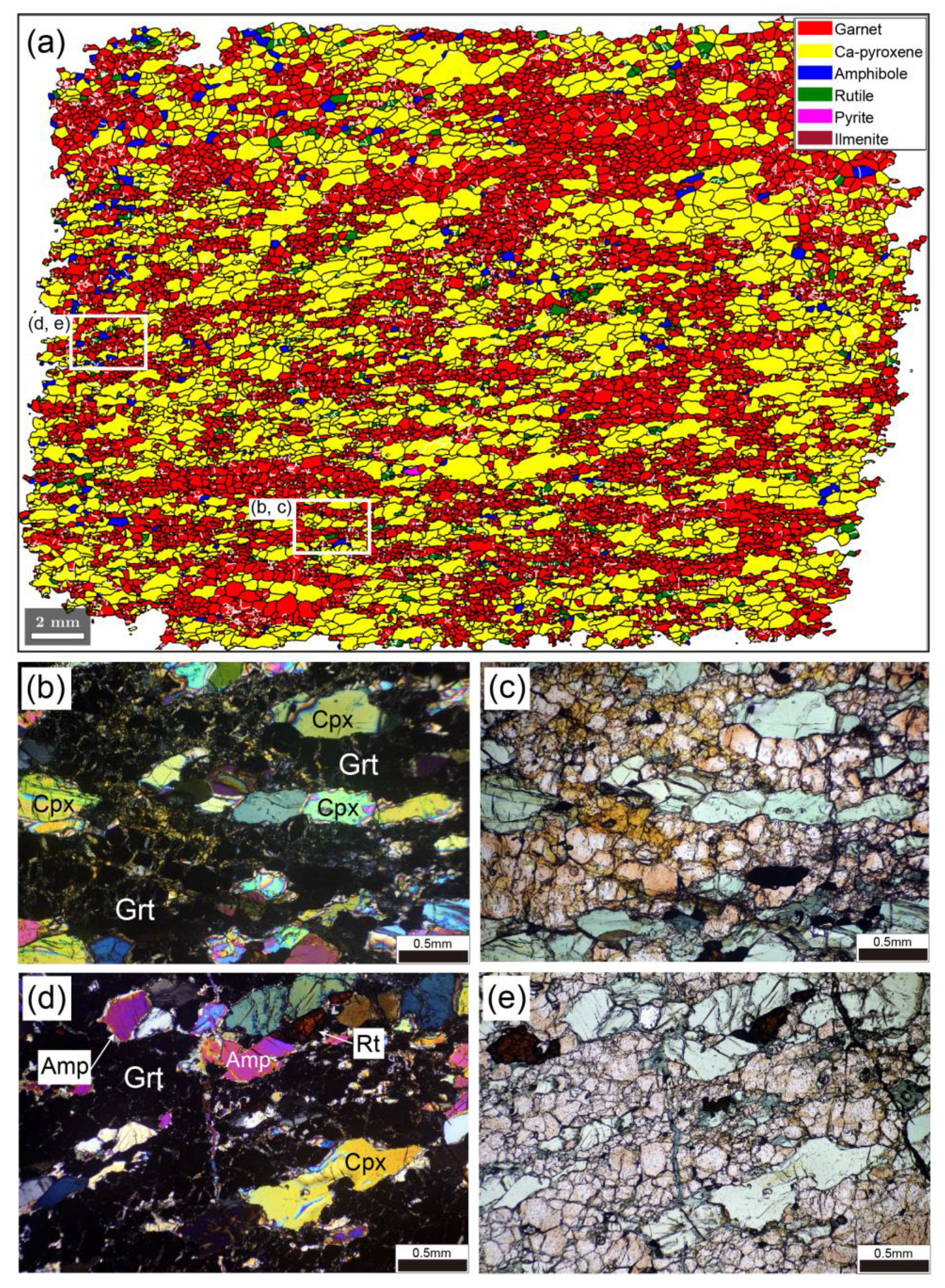
Figure 3 shows the microstructure of garnet clinopyroxenite. This rock is bimineralic, comprising garnet (40.7 vol.%) and Ca-pyroxene (57.2 vol.%). The microstructure of this sample is similar to that of eclogite in terms of the presence of layers of fine-grained garnet aggregates and the SPO of elongated clinopyroxene grains (Figure 3a–c). Garnet and Ca-pyroxene grains contain subgrain boundaries. Undulose extinction is rarely observed in Ca-pyroxene. Ca-pyroxene grains contain inclusions of garnet and rutile. Minor minerals are rutile, amphibole, ilmenite, and pyrite. Elongated grains of rutile show a SPO parallel to the lineation. Amphibole is commonly found along micro-fractures oriented sub-perpendicular to the foliation and lineation (Figure 3d,e). In most cases, there is no mineral transformation to amphibole around grains of garnet and Ca-pyroxene. The above observations suggest that garnet clinopyroxenite shows negligible signs of retrogression.

Figure 3.
Microstructures of garnet clinopyroxenite. (a) EBSD phase map of entire thin-section. White areas in the map are non-indexed pixels. White lines represent subgrain boundaries. White rectangles indicate areas shown in (b–e). (b,d) Photomicrographs under cross-polarized light. (c,e) As in (b,d), but under plane-polarized light, respectively. Grt, garnet; Cpx, Ca-pyroxene; Amp, amphibole; Rt, rutile.
4.3. Garnet Peridotite
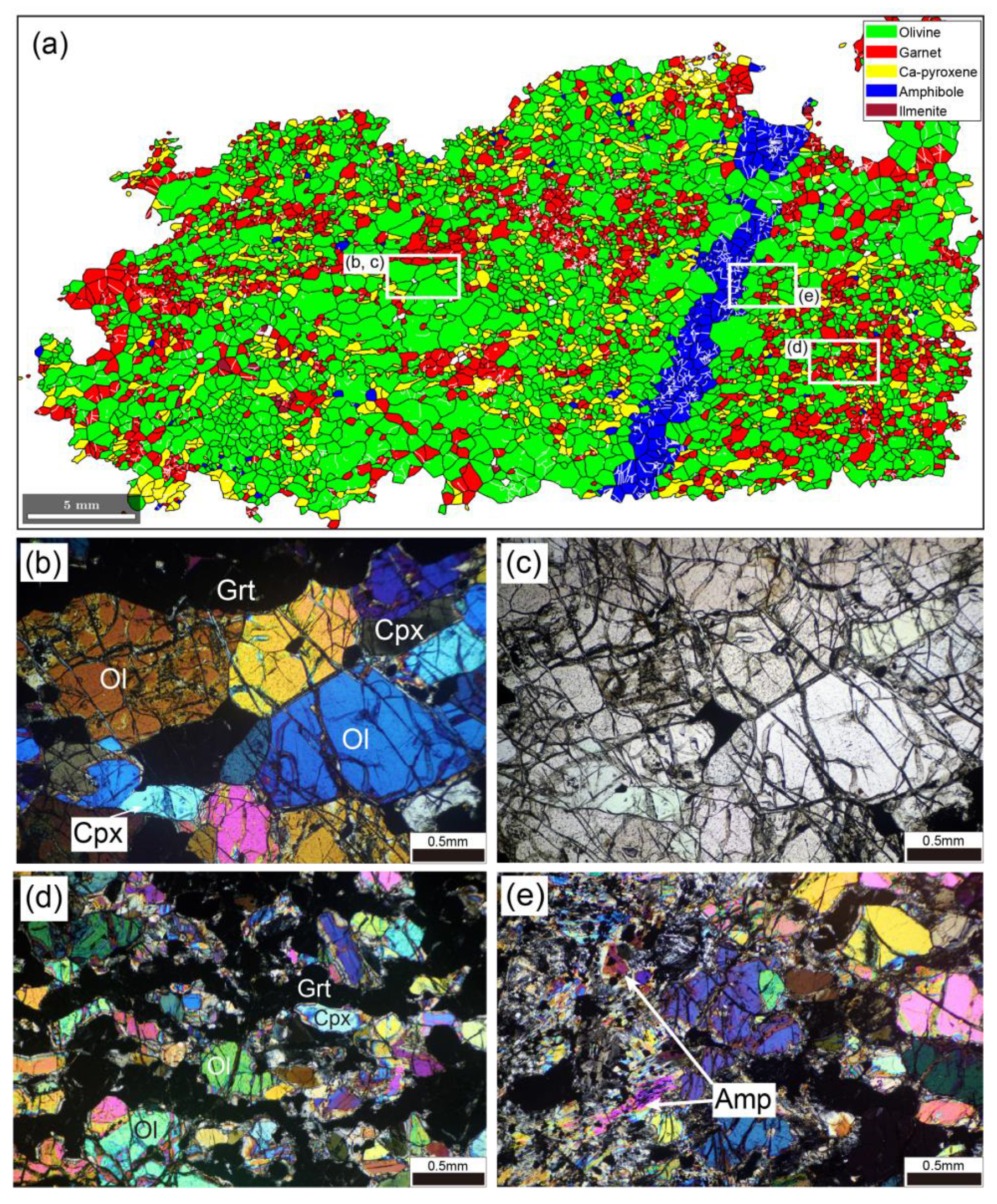
Figure 4 shows the microstructure of garnet peridotite. The sample contains olivine (63.9 vol.%), garnet (20.3 vol.%), Ca-pyroxene (13.1 vol.%), amphibole (2.2 vol.%), and trace ilmenite and Ti-clinohumite. Overall, the texture is heterogeneous (Figure 4a), showing both coarse-grained (Figure 4b,c) and fine-grained (Figure 4d) domains in thin-section. Weak serpentinization of olivine is observed. Olivine grains are anhedral and commonly show triple junction grain boundaries. Undulose extinction and subgrain boundaries are rare in olivine. Most garnet grains are locally concentrated and form aggregates. Ca-pyroxene grains are elongated (mean aspect ratio of 2.09) and define the lineation. Amphibole veins are sub-perpendicular to the lineation (Figure 4e). Garnet and amphibole contain subgrain boundaries. Based on the above observations, the mineral assemblage at peak metamorphic conditions is assumed to have been preserved, although olivine records serpentinization.
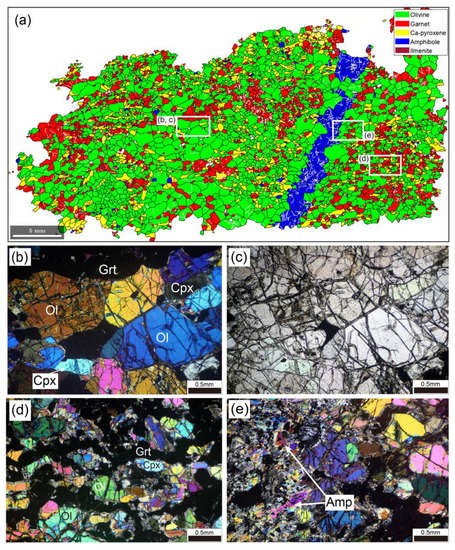
Figure 4.
Microstructures of garnet peridotite. (a) EBSD phase map of entire thin-section. White areas in the map are non-indexed pixels. White lines represent subgrain boundaries. White rectangles indicate areas shown in (b–e). (b,d,e) Photomicrographs under cross-polarized light. (c) As in (b), but under plane-polarized light. Ol, olivine; Grt, garnet; Cpx, Ca-pyroxene; Amp, amphibole.
4.4. Coesite Bearing Jadeite Quartzite
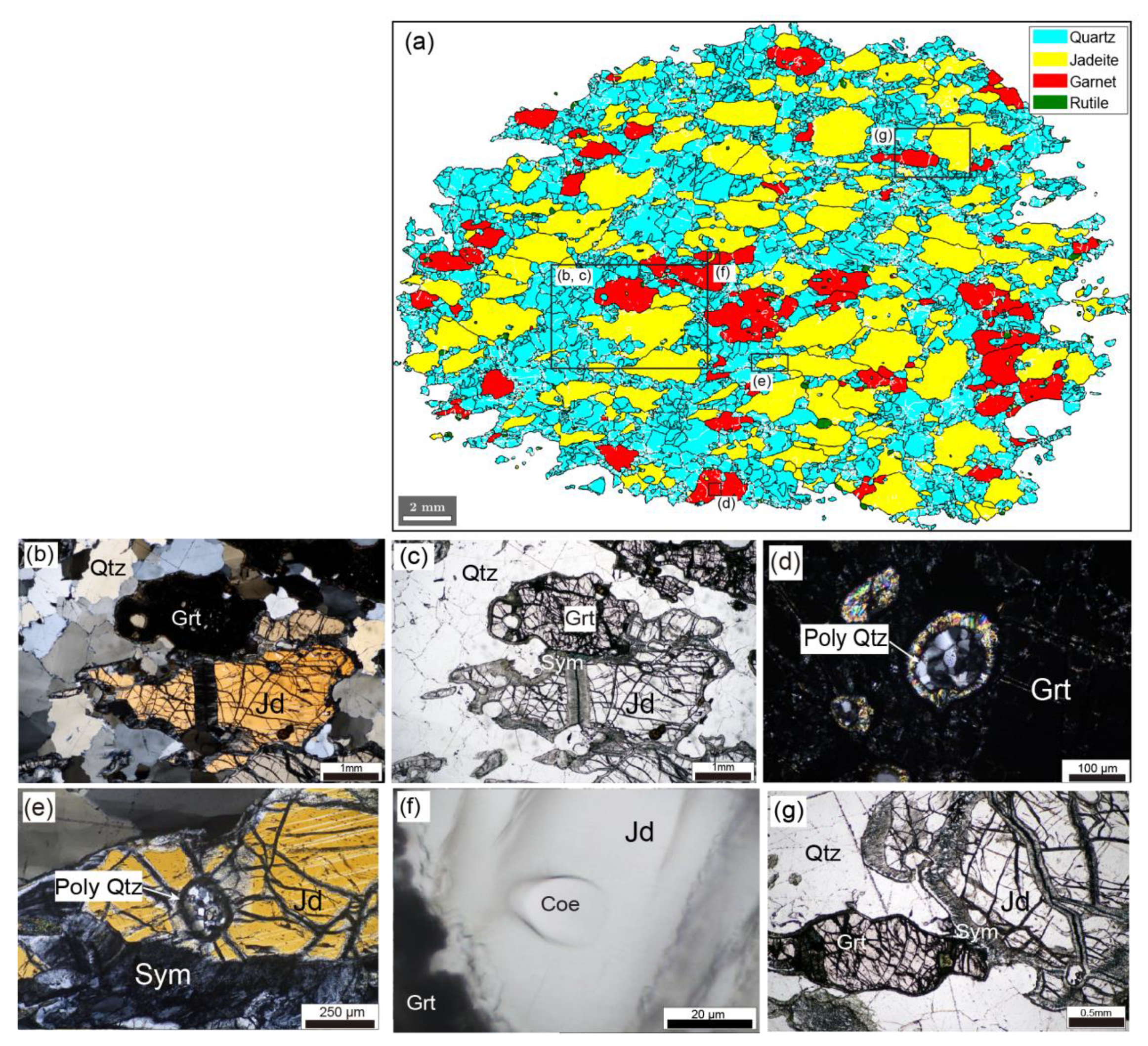
Figure 5 shows the microstructure of jadeite quartzite. The major minerals in this sample are quartz (46.6 vol.%), jadeite (39.3 vol.%), and garnet (13.9 vol.%). Garnet is coarse grained (mean grain size of 373 µm) and elongated (mean aspect ratio of 1.89) (Figure 5b,c) compared with garnet in the three mafic–ultramafic samples. Jadeite is also elongated and coarse grained. Quartz grains show irregular grain boundaries, strong development of subgrain boundaries, and intense undulose extinction. Inclusions of polycrystalline quartz after coesite are preserved in jadeite and garnet (Figure 5d,e). Coesite grain was found in Jadeite, one of the inclusion minerals of garnet. The diameter of the Coesite is ca. 30 µm and there are no radial cracks around the grain (Figure 5f). Rutile and zircon are minor minerals. Zircon inclusions are found in garnet, jadeite, and quartz.
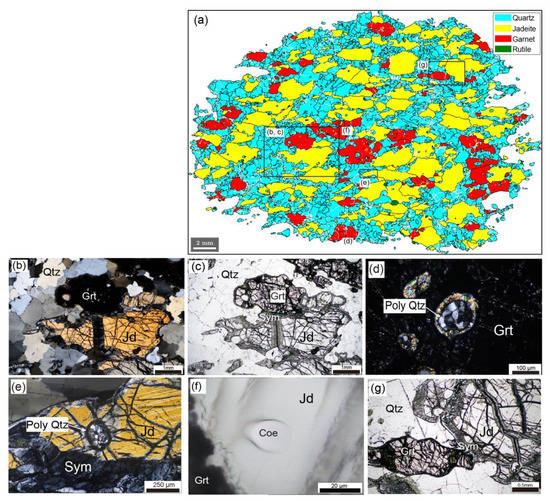
Figure 5.
Microstructures of jadeite quartzite. (a) EBSD phase map of entire thin-section. White areas in the map are non-indexed pixels. Black rectangles indicate areas shown in (b–g). (b,c) Photomicrographs of jadeite quartzite under cross-polarized light (left) and plane-polarized light (right). (d) Photomicrograph of polycrystalline quartz in garnet under cross-polarized light. (e) Photomicrograph of polycrystalline quartz in jadeite under cross-polarized light. (f) Photomicrograph of coesite inclusion in jadeite under cross-polarized light. (g) Photomicrograph of jadeite quartzite with symplectite under plane-polarized light. Qtz, quartz; Jd, jadeite; Grt, garnet; Sym, symplectite; Poly Qtz, polycrystalline quartz; Coe, coesite.
Garnet and jadeite grains are commonly surrounded by coronas of fine-grained amphibole and plagioclase. Symplectites are found in jadeite grains (Figure 5g) and are oriented mostly perpendicular to the lineation. The presence of coronas and symplectites reflects retrogression during exhumation to the surface.
5. Mineral Chemistry
Major-element compositions of garnet and clinopyroxene were analyzed for all samples, as well as the composition of olivine in garnet peridotite. For each mineral, analyses were conducted on two points in the grain core. Core compositions of the analyzed minerals are listed in Supplementary Materials (Table S1 (garnet), Table S2 (clinopyroxene), and Table S3 (olivine)).
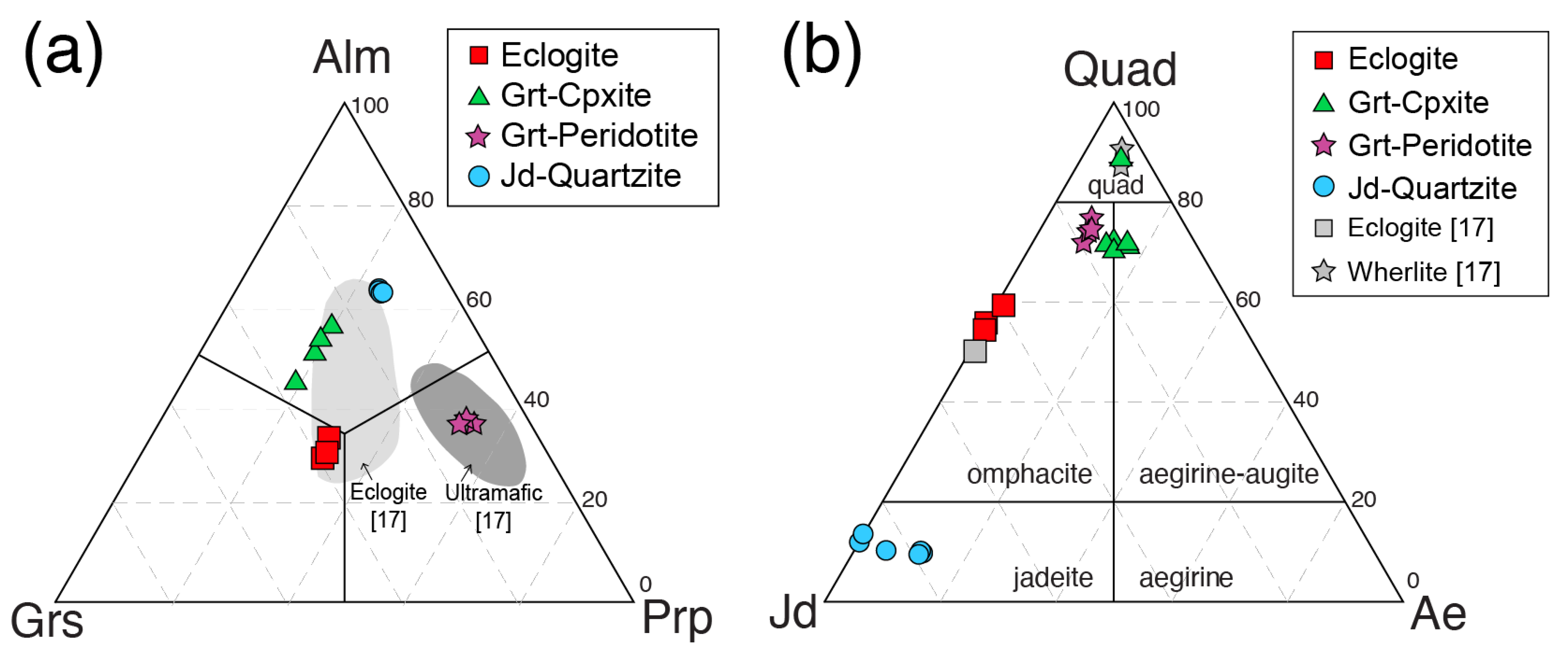
Garnet compositions differ among the samples (Figure 6a). The composition of garnet in eclogite is within the range of that for eclogite in the Bixiling complex, as analyzed by Zhang et al. [17]. In garnet clinopyroxenite, although garnet is rich in almandine relative to that in eclogite, the compositions of garnet are in the range of those for garnet in eclogite, as reported by Zhang et al. [17]. Garnet peridotite has similar garnet compositions to those of ultramafic rocks studied by Zhang et al. [17]. Garnet in jadeite quartzite has the highest almandine component of all of the studied samples.

Figure 6.
(a) Chemical compositions of garnet. Gray areas represent garnets in eclogite and ultramafic samples from the Bixiling complex reported by Zhang et al. [17]. (b) Chemical compositions of clinopyroxene. Gray symbols represent clinopyroxenes in eclogite and wherlite from the Bixiling complex reported by Zhang et al. [17]. Alm, almandine; Grs, grossular; Prp, pyrope, Quad, quadruplet pyroxenes that is the field of the clinopyroxenes classified in the Ca-Mg-Fe diagram; Jd, jadeite; Ae, aegirine.
Figure 6b presents the chemical compositions of clinopyroxene for each sample. Omphacite in eclogite has a similar composition to that of eclogitic garnet reported by Zhang et al. [17]. Garnet clinopyroxenite and garnet peridotite have similar Ca-rich clinopyroxene compositions but differ from those of wherlite analyzed by Zhang et al. [17]. Although the clinopyroxenes of these two samples are termed Ca-pyroxene in this study, they are omphacitic. Jadeite contents in jadeite quartzite are in a range between 78.14 and 88.07.
Ten grains of olivine were measured in garnet peridotite and have uniform compositions, with Mg# = Mg/(Mg + Fe) of 84.23–84.96. These Mg# values are lower than those of typical lithospheric mantle-derived peridotites [33,38].
6. Crystallographic Preferred Orientations
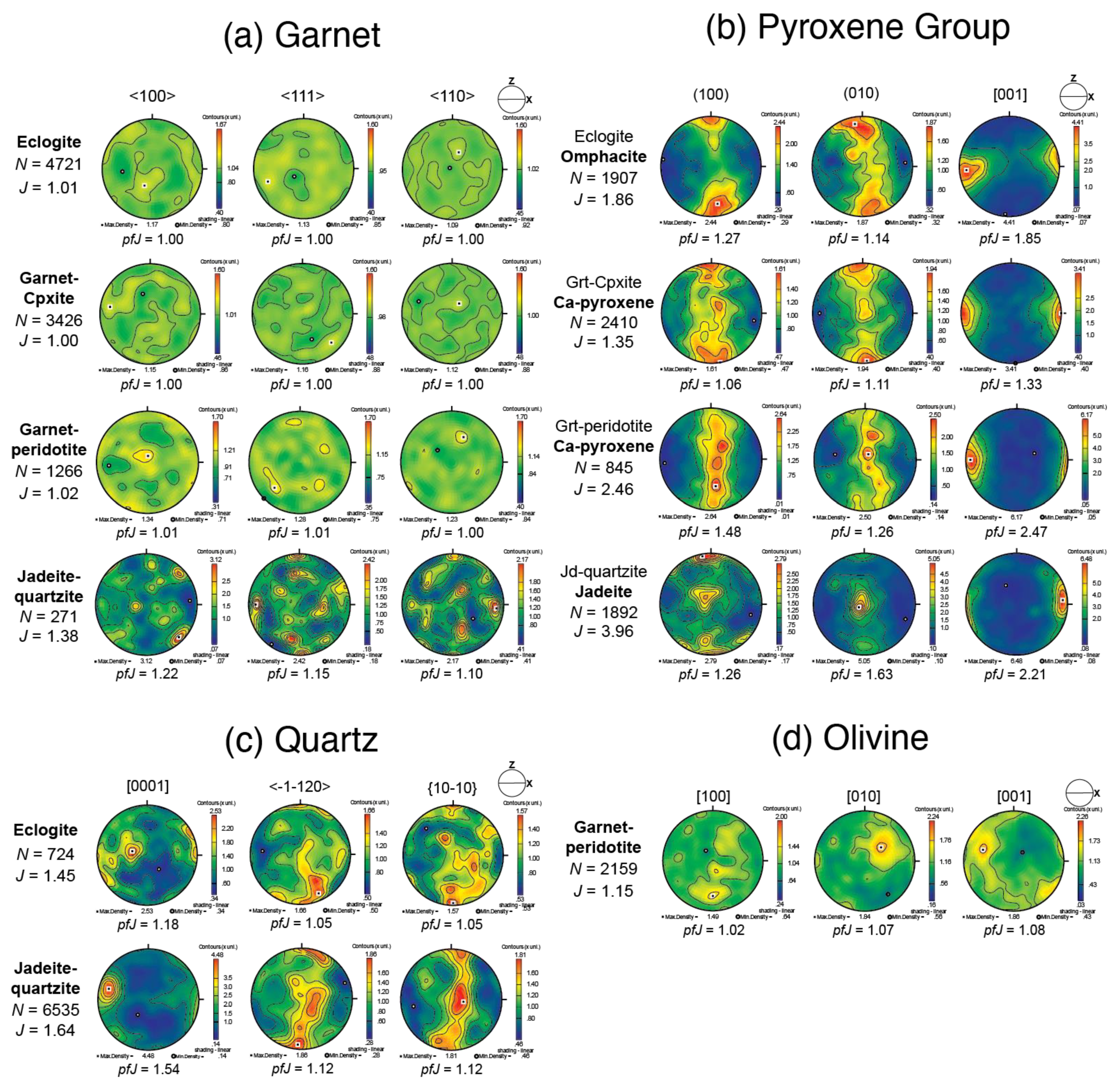
Pole figures of garnet and their fabric strength data are presented in Figure 7a. Eclogite, garnet clinopyroxenite, and garnet peridotite show random CPOs of garnet, with J-index values of 1.00–1.02. In contrast, jadeite quartzite shows a weak CPO of garnet with a J-index value of 1.38. Values of pfJ show that the intensity of [100] is the strongest of the three axes. The CPO pattern is sufficiently complicated that the slip system cannot be identified.
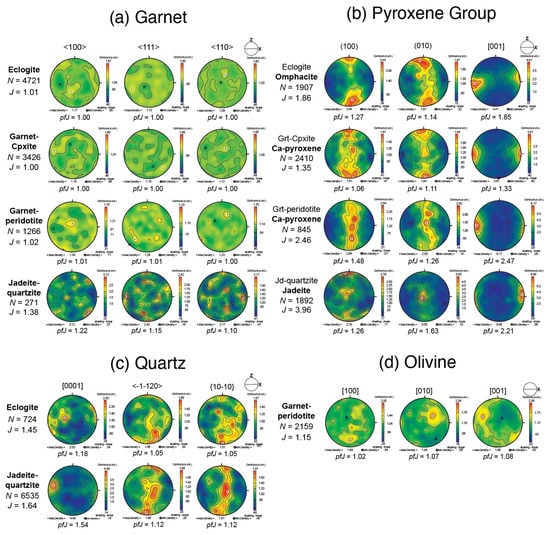
Figure 7.
(a) Crystal-preferred orientation of garnet in each sample based on one point per grain and presented on equal-area, lower-hemisphere projections. The foliation is on the XY plane, and the lineation is on the X-axis (E–W). N is the number of grains. J is the J-index calculated by a Mtex function: textureindex. (b) For pyroxene minerals. (c) Quartz in eclogite and jadeite quartzite. (d) Olivine in garnet peridotite.
As illustrated in Figure 7b, clinopyroxene shows clear CPO patterns characterized by the concentration of [001] subparallel to the lineation (X). Poles of [010] form girdle concentrations normal to the lineation in eclogite, garnet clinopyroxenite, and garnet peridotite. In jadeite quartzite, [010] poles of jadeite are concentrated predominantly on the Y-axis. Except for garnet peridotite, in which clinopyroxene does not occur as a primary mineral, the fabric strength of clinopyroxene increases with increasing Na content (i.e., from Ca-pyroxene to omphacite to jadeite).
Figure 7c shows quartz CPOs. In eclogite and jadeite quartzite, quartz displays moderate CPO patterns. Eclogite shows two c-axis concentrations: subparallel to the lineation (X) and close to the Y-axis. In jadeite quartzite, the c-axis concentration is subparallel to the lineation (X). The fabric strength is slightly higher in jadeite quartzite than in eclogite.
Olivine was analyzed only in garnet peridotite, and CPO data are shown in Figure 7d. The pattern shows mostly no CPO, with a J-index of 1.15. [001] shows a concentration slightly inclined to the lineation (X), with a pfJ value of 1.08. [010] is aligned approximately normal to the [001] direction.
7. Discussion
7.1. Deformation Mechanism
7.1.1. Garnet
Garnet is a stable mineral in many metamorphic rocks under a wide range of P–T conditions and becomes more abundant with increasing depth in the lithosphere. The physical properties and deformation mechanisms of garnet are important in understanding the rheological behavior of deeply subducted lithosphere. Garnet generally shows an approximately isometric texture, on which basis it is inferred to have a high flow strength in many crustal rocks. Furthermore, garnet is optically isotropic owing to its cubic structure, indicating that measurements of its CPO cannot be conducted by using a U-stage [39]. However, EBSD techniques can be used to examine the crystallographic orientation of garnet.
The plastic deformation regime of garnet is limited to high temperatures [39,40,41,42,43,44]. Microstructures indicating the plastic deformation of garnet can be classified into two types. The first is elongated grains with a weak CPO. The predominant deformation mechanism of these garnets is dislocation creep [39,40]. The second is layers of fine-grained garnet aggregates, with no CPO. Terry and Heidelbach [45] demonstrated that fine-grained garnet in high-pressure shear zones deforms by grain boundary sliding. Therefore, both dislocation creep and grain boundary sliding with diffusion are important deformation mechanisms of garnet under conditions of high P–T.
In this study, eclogite, garnet clinopyroxene, and garnet peridotite show random CPOs of garnet (Figure 7a). In eclogite and garnet clinopyroxenite, garnet forms layers of fine-grained aggregates (Figure 2 and Figure 3). These microstructures are similar to those reported by Terry and Heidelbach [45] in a study of mylonite shear zones, except the garnet grain size was only tens of micrometers, compared with a mean of ~240 µm in the present study. However, based on the similar microstructures and random CPOs, a deformation mechanism involving grain boundary sliding is inferred, following Terry and Heidelbach [45]. We consider that the dominant deformation mechanism of garnet in the studied eclogite and garnet clinopyroxenite samples was grain-size-sensitive (GSS) creep, including diffusion creep and grain boundary sliding. The garnet peridotite did not contain garnet layers (Figure 4a). However, fine garnet grains form aggregates in parts of the studied thin-section. Thus, garnet in garnet peridotite might have deformed by GSS creep.
In contrast, the jadeite quartzite shows a weak CPO with a J-index value of 1.38 (Figure 7a), as well as subgrain boundaries (Figure 5a). Given that garnet has cubic symmetry and several slip systems [46], if garnet deformed by dislocation creep, the intensity of the garnet CPO would be weaker relative to that of low-symmetry minerals. In the jadeite quartzite, garnet is coarser grained (about 373 µm) than in the other three studied samples and is elongated parallel to the lineation (Figure 5a–c). The elongated garnet grains are similar to those reported by Kleinschrodt and McGrew [39] and Kleinschrodt and Duyster [40], who suggested that the garnet grains had been deformed by a diffusion-assisted dislocation creep on the basis of the presence of subgrains and the weak CPO. Therefore, the dominant deformation mechanism of garnet in jadeite quartzite is inferred to be dislocation creep. However, as noted above, details of its slip system cannot be established.
7.1.2. Clinopyroxene
All of the studied samples include clinopyroxene that varies in composition among the samples (Figure 6b). Omphacite is a Na-rich clinopyroxene stable at high pressures and a major mineral in eclogite. Its composition ranges between the calcic end-member diopside (CaMgSi2O6) and the sodic end-member jadeite (NaAlSi2O6). In natural eclogite, omphacite commonly shows evidence of plastic deformation whereby the foliation and lineation of eclogite are defined by a strong CPO and SPO of omphacite grains. Therefore, the rheological behavior of eclogite is dominated by the mechanical behavior of omphacite [44,47]. Omphacite analyzed in this study shows a clear CPO (Figure 7b) and SPO in eclogite (Figure 2). Thus, the omphacite is considered to have deformed by dislocation creep.
Garnet clinopyroxenite and garnet peridotite contain Ca-pyroxene that is more calcic than that in omphacite (Figure 6b). Clinopyroxene, along with plagioclase, is a constituent mineral in the lower crust. The rheological properties of clinopyroxene influence the creep strength of the lower crust [48]. In this study, Ca-pyroxene shows clear CPO (Figure 7b) and SPO in both garnet clinopyroxene and garnet peridotite (Figure 3 and Figure 4). In general, clinopyroxene CPOs are observed in both natural samples and experimental samples with [001] parallel to the lineation and [010] normal to the foliation [47]. The CPOs of Ca-pyroxene analyzed in the present study are consistent with general CPO patterns of clinopyroxene. Therefore, the dominant deformation mechanism is inferred to have been dislocation creep.
Jadeite is the sodic end-member of clinopyroxene and is stable under high-pressure conditions. Jadeite in the studied jadeite-quartzite shows elongated grains (Figure 5) and a strong CPO (Figure 7b). Jadeite CPOs have been reported in both natural samples [34] and experimental samples [49]. In this study, the observed CPO pattern of jadeite is generally similar to that of clinopyroxene, and jadeite fabric development is strong. These characteristics suggest the dominant deformation mechanism was dislocation creep.
7.1.3. Quartz
The deformation mechanism of quartz is complicated. The dominant slip system activated during dislocation creep varies as a function of temperature, differential stress, strain rate, and water content [50]. Quartz c-axes show different CPO patterns with increasing temperature [51]. Periphery maxima in c-axis data indicate basal <a> slip at low temperatures, maxima between the periphery and the center of a pole figure indicate rhomb <a> slip at intermediate temperatures, and point maxima parallel to the Y-axis indicate prism <a> slip at intermediate–high temperatures [51,52]. Point maxima parallel to the lineation (X) indicate prism <c> slip, suggesting high-temperature (>700 °C) and possibly hydrous conditions [51,52,53].
In this study, quartz fabrics were analyzed in eclogite and jadeite quartzite (Figure 7c). Quartz in eclogite shows c-axis concentrations around the Y-axis and parallel to the lineation (X). The CPO pattern is consistent with prism <a> and prism <c> slip. Jadeite quartzite exhibits a quartz c-axis fabric parallel to the lineation, indicating that the dominant slip system was prism <c> slip. According to these observations, quartz fabrics in these two samples may have been formed by dislocation creep under high temperatures. Furthermore, high pressures and temperatures favor prism <c> slip [54,55]. As eclogite and jadeite quartzite in this study were obtained from a UHP belt, the observed c-axis fabrics would have been caused by high pressure as well as high temperature conditions.
7.1.4. Olivine
Olivine is a major mineral in Earth’s mantle. Deformation microstructures such as CPOs are assumed to reflect the deformation conditions in the crust and mantle. Based on results of simple shear deformation experiments at high P–T conditions, olivine crystallographic fabrics have been divided into five types (A–E) [56,57,58]. These fabric types are related to temperature, differential stress, water content, pressure, and the presence of melt during plastic flow. In addition, deformation in cumulate olivine has been reported [59,60]. Whereas olivine cumulates are widely distributed, magmatic olivine fabrics in nature are uncommon because of overprinting by deformation, emplacement, and late-stage alteration [61]. However, weak B-type-like CPO patterns have been documented for olivine, probably related to compaction and shearing during the crystallization and accumulation of magmatic olivine [61,62].
The garnet peridotite in this study is interpreted to be derived from magma, based on results of previous studies [17] and the low Mg# of olivine analyzed in this study. Olivine CPOs are nearly random in the garnet peridotite sample (Figure 7d), probably because pre-existing cumulative fabrics in olivine were overprinted by subduction and subsequent exhumation of the Bixiling complex. Alternatively, a weak CPO may suggest a diffusion creep, or at least GSS creep, particularly with B-type fabric [63,64], although it is difficult to infer the deformation mechanism of olivine in more detail. Given the difficulty in estimating the microstructural evolution of garnet peridotite, we exclude this rock from the discussion below.
7.2. Preservation of Deformation Microstructures during UHP Metamorphism
In most cases, the presence of coesite implies that coesite-bearing metamorphic rocks were subducted to deeper levels than those corresponding to the quartz–coesite transition. The Bixiling complex is thought to have reached UHP conditions during subduction on the basis of the presence of coesite [17]. Coesite and its pseudomorphs found in zircon from country gneiss in the Dabie UHP belt [22] also demonstrate that not only coesite eclogite but also country rocks reached UHP conditions [23,24].
In this study, although we did not identify any coesite in eclogite and garnet clinopyroxenite, these samples are inferred to have undergone UHP metamorphism on the basis of coesite reported from the Bixiling eclogite by Zhang et al. [17]. Microstructures of these samples (Figure 2 and Figure 3) show that they were negligibly affected by retrogression. Therefore, these samples preserve the deformation microstructures that formed during UHP metamorphism.
We have identified coesite as well as polycrystalline quartz inclusions in jadeite quartzite (Figure 5). Hence, this sample could also have undergone UHP metamorphism. However, the development of coronas was observed at many grain boundaries of jadeite and garnet (Figure 5). In addition, jadeite grains show symplectites oriented perpendicular to the direction of elongation (Figure 5b,c). These characteristics of retrogression are assumed to be unrelated to the main deformation because symplectites cut jadeite grains normal to the lineation [34]. Nevertheless, quartz has irregular grain boundaries, contains subgrains, and shows intense undulose extinction. In many cases, quartz fabrics in high-grade metamorphic rocks are interpreted to have formed at the later stage during exhumation [44], as quartz is easily deformed at temperatures as low as 300 °C. Thus, despite possible retrogression during exhumation, these observations suggest that deformation microstructures that formed under UHP metamorphic conditions are mostly preserved in jadeite and garnet. Rapid exhumation is presumed to result in the preservation of mineral assemblages and deformation microstructures formed under UHP conditions [65]. In contrast, the quartz fabric in the studied jadeite quartzite is considered to have formed after UHP metamorphism.
7.3. Microstructural Evolution of UHP Metamorphic Rocks in the Dabie–Shan Region
The microstructures and CPOs of eclogite and garnet clinopyroxenite imply plastic deformation of both garnet and clinopyroxene under UHP conditions. The characteristic layers of fine-grained garnet aggregates differ from garnet in crustal rocks, which show an isometric and relatively coarse-grained texture. The dominant deformation mechanism of garnet in the eclogite and the garnet-clinopyroxenite is proposed to have been GSS creep. Terry and Heidelbach [45] reported fine-grained garnet deformed by grain boundary sliding in shear zones. Storey and Prior [41] suggested a transition in the deformation mechanism of garnet whereby dislocation creep and recovery caused the deformation of garnet porphyroclasts, followed by dynamic recrystallization, and then GSS creep (diffusion-accommodated grain boundary sliding) by finer grains that formed by dynamic recrystallization. Furthermore, Bestmann et al. [66] suggested that new garnet grains, previously formed by subgrain rotation, are able to deform by grain boundary sliding, which leads to a weakening of garnet CPOs. These changes in the deformation mechanism of garnet are associated with strain localization. With increasing strain, dynamic recrystallization induces grain-size reduction and associated strain localization, which increases the contribution of GSS creep [41,66,67]. Consequently, a weakening of the garnet CPO is expected to occur. In this study, garnet shows a random CPO in eclogite and garnet clinopyroxenite, consistent with GSS creep that resulted from strain localization. Therefore, it is reasonable to infer that deformation microstructures in these two samples were formed under higher strain and UHP metamorphic conditions compared with typical crustal rocks under the conditions of amphibolite- or granulite-facies metamorphism.
In contrast to the eclogite and garnet clinopyroxenite, the garnet in jadeite quartzite is relatively coarse-grained and elongated. As described above, the dominant deformation mechanism of garnet and jadeite during UHP conditions is proposed to be dislocation creep. A difference is noted in the deformation mechanism and microstructure of garnet between mafic–ultramafic (eclogite and garnet clinopyroxenite) and relatively felsic (jadeite quartzite) samples. This difference suggests that jadeite quartzite accommodates smaller strain than mafic–ultramafic samples under UHP conditions. This point is discussed below with respect to the quartz matrix in jadeite quartzite.
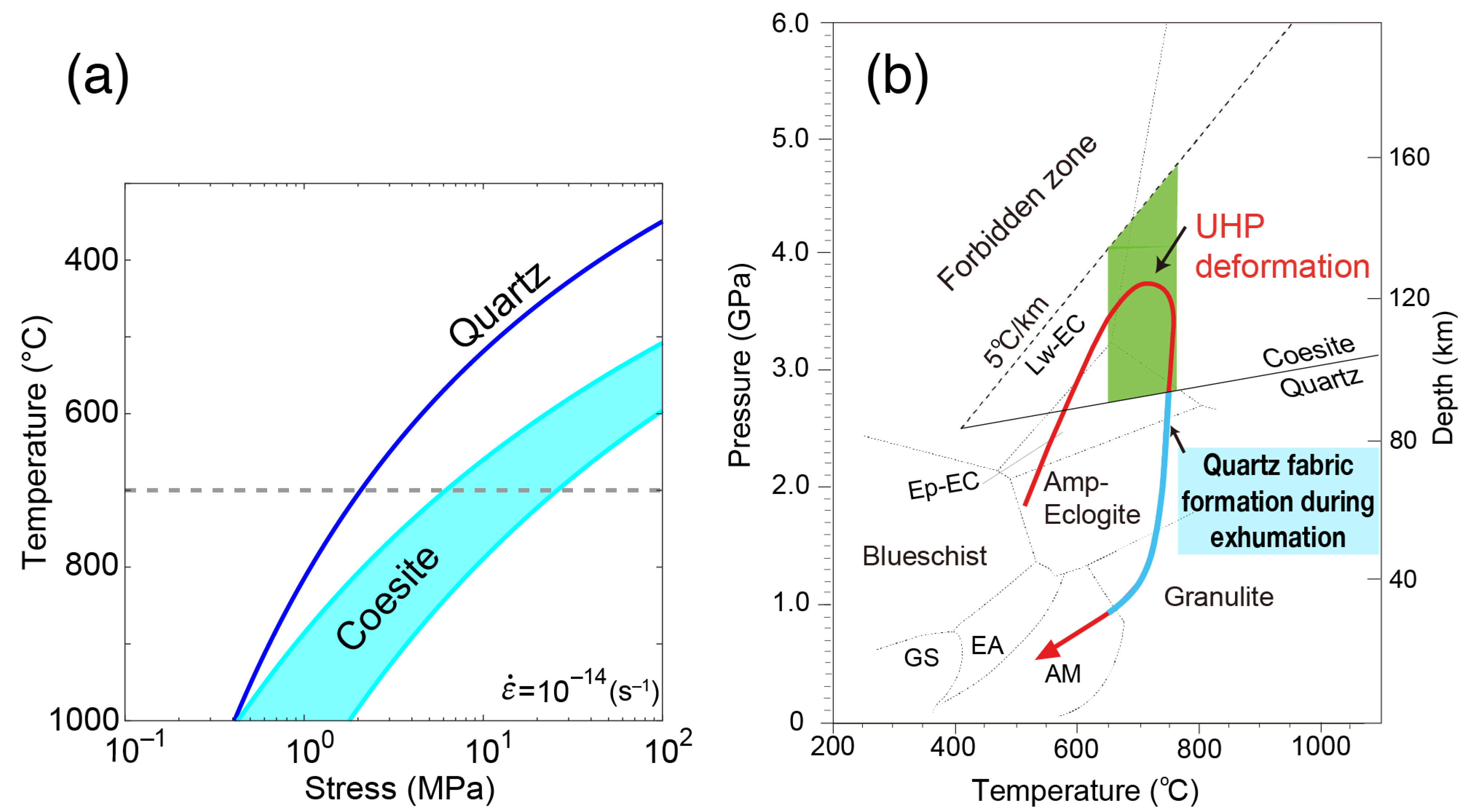
Jadeite quartzite contains inclusions of coesite and polycrystalline quartz after coesite in garnet and jadeite (Figure 5). As jadeite quartzite is estimated to have been subducted under UHP conditions, it is supposed that a phase transition from quartz to coesite occurred in the matrix. Thus, it is inferred that the mineral assemblage for jadeite quartzite under UHP conditions is mainly coesite, jadeite, and garnet. Figure 8a compares the flow strengths of coesite and quartz. The flow law for mineral dislocation creep is as follows:
where is the strain rate, A is a pre-exponential factor, σ is the flow stress, n is the stress exponent, Q is activation energy, R is the gas constant, and T is absolute temperature. As shown in Figure 8a, coesite is about an order of magnitude stronger than quartz at 700 °C.
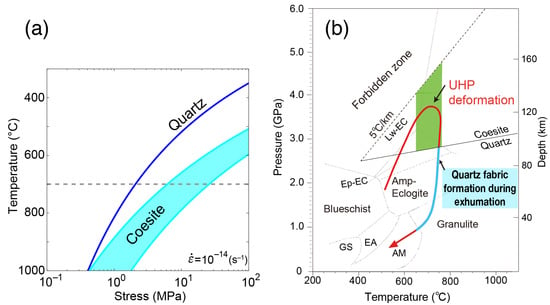
Figure 8.
(a) Flow strength comparison between quartz and coesite at a natural strain rate of 10−14 s−1. Flow law parameters for quartz: A = 5.1 × 10−4 MPa−4s−1, n = 4, Q = 223 kJ/mol. Flow law parameters for coesite: lnA = −8.0 to −3.7 MPa−3s−1, n = 3, Q = 275 kJ/mol. Mean values are used, with parameters for quartz (~0.15 wt.% H2O) taken from Gleason and Tullis [68] calibrated by Holyoke and Kronenberg [69], and for coesite (~500 to 1000 × 10−6 H/Si) from Renner et al. [70]. For coesite, the error range of the preexponential factor (A) is large. The dashed line at a temperature of 700 °C shows the estimated peak temperature for the Dabie coesite-bearing eclogite [5]. (b) Simplified P–T–deformation path for the Dabie UHP belt. In mafic–ultramafic rocks, deformation microstructures that were formed under UHP conditions have been preserved during exhumation. In felsic rocks, coesite transitioned to quartz during exhumation. Quartz fabrics in felsic rocks were formed during exhumation under quartz-stable pressure conditions. P–T path is from Carswell and Zhang [71] modified after Zhang et al. [5]. P–T boundaries represent metamorphic facies: GS, greenschist; EA, epidote-amphibolite; AM, amphibolite; Amp-Eclogite, amphibole-eclogite; Ep-EC, epidote-eclogite; Lw-EC, lawsonite-eclogite.
Under the estimated conditions for the Dabie UHP belt, the flow strength of the major SiO2 phase (about 47 vol.%) in jadeite quartzite is assumed to increase owing to the phase transition to coesite. It is expected that an increase in flow strength of the SiO2 phase results in a strengthening of the bulk rock. It is therefore inferred that the jadeite quartzite may be weakly or locally strained because the presence of coesite in the matrix led to an increase in the bulk strength of jadeite quartzite under UHP metamorphic conditions. As a result, garnet and jadeite preserve coarse-grained and elongated textures in jadeite quartzite (Figure 5).
After deformation and metamorphism under UHP conditions, coesite transitions to quartz during exhumation. The strength of SiO2 decreases accordingly, indicating that most strain during exhumation is expected to localize in quartz, which can deform easily at low temperature. In this study, quartz shows irregular grain boundaries, numerous subgrain boundaries, and intense undulose extinction in jadeite quartzite (Figure 5). Therefore, it is inferred that the quartz fabric was formed by localized strain in quartz during exhumation (Figure 8b). Moreover, the CPO pattern of quartz indicates prism <c> slip (Figure 7c). Similar quartz fabrics have been documented in HP/UHP eclogite from the Sulu region in China [54] and from the Western Gneiss Region in Norway [55]. Thus, it is inferred that the quartz fabric in jadeite quartzite developed during deformation under high-pressure conditions near the quartz–coesite transition at high temperature (Figure 8b). However, this is limited to the case in which subsequent deformation and recrystallization did not overprint the quartz fabric that had previously formed under high-P–T conditions.
8. Conclusions
Microstructures and crystallographic orientations of UHP rocks from the Dabie–Shan region of the Dabie–Sulu orogenic belt were analyzed to investigate the rheological behavior of deeply subducted continental material within a subduction channel under UHP conditions. Except for quartz in jadeite quartzite, major minerals preserve deformation microstructures that formed under peak metamorphic conditions. Microstructural differences between mafic–ultramafic and felsic rock samples suggest a difference in the degree of strain, whereby jadeite quartzite is less strained than eclogite and garnet pyroxenite. This strain difference is unexpected, as felsic minerals appear usually to have lower viscosity than mafic minerals under typical crustal conditions [72]. We propose that the difference is related to the phase transition of quartz to coesite in felsic rocks under UHP conditions. As the presence of coesite, which has higher strength than quartz, is expected to result in an increase in the bulk strength of felsic rocks, strain localization may occur in mafic–ultramafic rocks. Strain localization is associated with the formation of shear zones, and shear zones under HP/UHP conditions favor the detachment of subducted crustal material from subducting lithosphere, which is necessary for the exhumation of UHP rocks [73]. The differences in microstructures between the studied felsic and mafic rock samples may demonstrate strain localization and subsequent formation of shear zones in mafic–ultramafic rocks along a subduction zone under UHP conditions.
Supplementary Materials
The following are available online at https://www.mdpi.com/article/10.3390/min11080842/s1: Table S1: Chemical compositions of garnet, Table S2: Chemical compositions of clinopyroxenes, Table S3: Chemical compositions of olivine.
Author Contributions
K.M. proposed the topic, conceived, and designed the study. K.A. analyzed the data and prepared the original manuscript. T.T. used Raman spectrometry to find and analyze coesite in the samples. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This work was supported by a research grant awarded to K.M. by the Japan Society for the Promotion of Science (Kiban-S 16H06347).
Data Availability Statement
Not Applicable.
Acknowledgments
We would like to thank Yui Kouketsu for her helpful support with EPMA analyses and Yuki Kakihata for her assistance with SEM-EBSD and EPMA analyses and three reviewers for their useful comments. K.M. acknowledge Bing Yi, Chao Wang, Lu Wang and Zhenmin Jin for their kind hospitality during the Dabie-Shan field excursion in May 2019. This study was supported by a research grant awarded to K.M. by the Japan Society for the Promotion of Science (Kiban-S 16H06347).
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
References
- Chopin, C. Coesite and pure pyrope in high-grade blueschists of the Western Alps: A first record and some consequences. Contrib. Mineral. Petrol. 1984, 86, 107–118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Smith, C.D. Coesite in clinopyroxene in the Caledonides and its implications for geodynamics. Nature 1984, 310, 641–644. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sobolev, N.V.; Shatsky, V.S. Diamond inclusions in garnets from metamorphic rocks: A new environment for diamond formation. Nature 1990, 343, 742–746. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, Z.; Wang, Q.; Tang, Z.; Chen, F. Fabric kinematics of the ultrahigh-pressure metamorphic rocks from the main borehole of the Chinese Continental Scientific Drilling Project: Implications for continental subduction and exhumation. Tectonophysics 2009, 475, 235–250. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, R.Y.; Liou, J.G.; Ernst, W.G. The Dabie-Sulu continental collision zone: A comprehensive review. Gondwana Res. 2009, 16, 1–26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nakamura, D.; Hirajima, T. Granulite-facies overprinting of ultrahigh-pressure metamorphic rocks, northeastern Su-Lu region, eastern China. J. Petrol. 2000, 41, 563–582. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Zhang, R.Y.; Liou, J.G.; Yang, J.S.; Yui, T.-F. Petrochemical constraints for dual origin of garnet peridotites form the Dabie-Sulu UHP terrane, eastern-central China. J. Metamorph. Geol. 2000, 18, 149–166. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, X.W.; Jin, Z.-M.; Green, H.W. Clinoenstatite exsolution in diopsidic augite of Dabieshan: Garnet peridotite from depth of 300 km. Am. Mineral. 2007, 92, 546–552. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cong, B.L. Ultrahigh-Pressure Metamorphic Rocks in the Dabieshan-Sulu Region of China; Science Press: Beijing, China, 1996; 226p. [Google Scholar]
- Hacker, B.R.; Ratschbacher, L.; Webb, L.; Ireland, T.; Walker, D.; Dong, S. U/Pb zircon ages constrain the architecture of the ultrahigh-pressure Qinling-Dabie Orogen, China. Earth Planet. Sci. Lett. 1998, 161, 215–230. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hacker, B.R.; Ratschbacher, L.; Webb, L.; McWilliams, M.O.; Ireland, T.; Calvert, A.; Shuwen, D.; Wenk, H.-R.; Chateigner, D. Exhumation of ultrahigh-pressure continental crust in East-central China: Late Triassic-Early Jurassic tectonic unroofing. J. Geophys. Res. 2000, 105, 13339–13364. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Li, X.P.; Zheng, Y.-F.; Wu, Y.B.; Chen, F.K.; Gong, B.; Li, Y.L. Low-T eclogite in the Dabie terrane of China: Petrological and isotopic constraints on fluid activity and radiometric dating. Contrib. Mineral. Petrol. 2004, 148, 443–470. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Okay, A.I.; Xu, S.; Sengör, A.M.C. Coesite from the Dabie Shan eclogites, central China. Eur. J. Mineral. 1989, 1, 595–598. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.M.; Liou, J.G.; Mao, H.K. Coesite-bearing eclogites from the Dabie mountains in central China. Geology 1989, 17, 1085–1088. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hirajima, T.; Ishiwatari, A.; Cong, B.; Zhang, R.Y.; Banno, S.; Nozaka, T. Identification of coesite in Mengzhong eclogite from Donghai county, northeastern Jiangsu Province, China. Mineral. Mag. 1990, 45, 579–583. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Zhang, R.Y.; Liou, J.G. Coesite-bearing eclogite in Henan Province, central China: Detailed petrography, glaucophane stability and PT-path. Eur. J. Mineral. 1994, 6, 217–234. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Zhang, R.Y.; Liou, J.G.; Cong, B.L. Talc-, Magnesite- and Ti-Clinohumite-Bearing Ultrahigh-Pressure Meta-Mafic and Ultramafic Complex in the Dabie Mountains, China. J. Petrol. 1995, 36, 1011–1037. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, Y.-F.; Fu, B.; Gong, B.; Li, L. Stable isotope geochemistry of ultrahigh pressure metamorphic rocks from the Dabie-Sulu orogen in China: Implications for geodynamics and fluid regime. Earth Sci. Rev. 2003, 62, 105–161. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, Y.-F.; Zhou, J.-B.; Wu, Y.-B.; Xie, Z. Low-grade metamorphic rocks in the Dabie-Sulu orogenic belt: A passive-margin accretionary wedge deformed during continent subduction. Int. Geol. Rev. 2005, 47, 851–871. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, S.T.; Okay, A.I.; Ji, S.; Sengör, A.M.C.; Wen, S.; Liu, Y.C.; Jiang, L.L. Diamond from the Dabie Shan Metamorphic Rocks and Its implication for Tectonic Setting. Science 1992, 256, 80–82. [Google Scholar]
- Okay, A.I. Petrology of a diamond and coesite-bearing metamorphic terrain: Dabie Shan, China. Eur. J. Mineral. 1993, 5, 659–675. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sobolev, N.V.; Shatskii, V.S.; Vavilov, M.A.; Goryainov, S.V. Zircon from high-pressure metamorphic rocks of folded regions as an unique container of inclusions of diamond, koesite and coexisting minerals. Dokl. Akad. Nauk 1994, 334, 488–492. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, R.Y.; Hirajima, T.; Banno, S.; Cong, B.; Liou, J.G. Petrology of ultrahigh-pressure rocks from the southern Su-lu region, eastern China. J. Metamorph. Geol. 1995, 13, 659–675. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carswell, D.A.; Wilson, R.N.; Zhai, M. Metamorphic evolution, mineral chemistry and thermobarometry of schists and orthogneisses hosting ultra-high pressure eclogites in the Dabieshan of central China. Lithos 2000, 52, 121–155. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chavagnac, V.; Jahn, B.-M. Coesite-bearing eclogites from the Bixiling Complex, Dabie Mountains, China: Sm-Nd ages, geochemical characteristics and tectonic implications. Chem. Geol. 1996, 133, 29–51. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Okay, A.I. Paragonite eclogites from Dabie Shan, China: Re-equilibrations during exhumation. J. Metamorph. Geol. 1995, 13, 449–460. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.M.; Zhang, R.Y.; Liou, J.G. UHPM Terrane in East Central China. In Ultrahigh Pressure Metamorphism; Coleman, R.G., Wang, X., Eds.; Cambridge University Press: Cambridge, UK, 1995; pp. 356–390. [Google Scholar]
- Cong, B.L.; Zhai, M.G.; Carswell, D.A.; Wilson, R.N.; Wang, Q.C.; Zhao, Z.Y.; Windley, B.F. Petrogenesis of ultrahigh-pressure rocks and their country rocks at Shuanghe in the Dabie Mountains, Central China. Eur. J. Mineral. 1995, 7, 119–138. [Google Scholar]
- Carswell, D.A.; O’Brien, P.J.; Wilson, R.N.; Zhai, M. Thermobarometry of phengite-bearing eclogites in the Dabie Mountains of central China. J. Metamorph. Geol. 1997, 15, 239–252. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, Y.; Wang, Q. Variation in peak P-T conditions across the upper contact of the UHP terrane, Dabieshan, China: Gradational or abrupt? J. Metamorph. Geol. 2006, 24, 803–822. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liou, J.G.; Zhang, R.Y. Significance of ultrahigh-P talc-bearing eclogite assemblages. Mineral. Mag. 1995, 59, 93–102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiao, Y.L.; Hoefs, J.; van den Kerkhof, A.M.; Fiebig, J.; Zheng, Y.F. Fluid history of UHP metamorphism in Dabie Shan, China: A fluid inclusion and oxygen isotope study on the coesite-bearing eclogite from Bixiling. Contrib. Mineral. Petrol. 2000, 139, 1–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, J.P.; Sun, M.; Griffin, W.L.; Zhou, M.F.; Zhao, G.C.; Robinson, P.; Tang, H.Y.; Zhang, Z.H. Age and geochemistry of contrasting peridotite types in the Dabie UHP belt, eastern China: Petrogenetic and geodynamic implications. Chem. Geol. 2008, 247, 282–304. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, L.; Jin, Z.M.; Kusky, T.; Xu, H.J.; Liu, X.W. Microfabric characteristics and rheological significance of ultra-high-pressure metamorphosed jadeite-quartzite and eclogite from Shuanghe, Dabie Mountains, China. J. Metamorph. Geol. 2010, 28, 163–182. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bachmann, F.; Hielscher, R.; Schaeben, H. Texture Analysis with MTEX–Free and Open Source Software Toolbox. Solid State Phenom. 2010, 160, 63–68. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Bunge, H.J. Texture Analysis in Materials Science; Butterworths: London, UK, 1982; 593p. [Google Scholar]
- Michibayashi, K.; Mainprice, D. The role of pre-existing mechanical anisotropy on shear zone development within oceanic mantle lithosphere: An example from the Oman ophiolite. J. Petrol. 2004, 45, 405–414. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Arai, S. Characterization of spinel peridotites by olivine-spinel compositional relationships: Review and interpretation. Chem. Geol. 1994, 113, 191–204. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kleinschrodt, R.; McGrew, A. Garnet plasticity in the lower continental crust: Implications for deformation mechanisms based on microstructures and SEM electron channeling pattern analysis. J. Struct. Geol. 2000, 22, 795–809. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kleinschrodt, R.; Duyster, J.P. HT-deformation of garnet: An EBSD study on granulites from Sri Lanka, India and the Ivrea Zone. J. Struct. Geol. 2002, 24, 1829–1844. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Storey, C.D.; Prior, D.J. Plastic deformation and recrystallization of garnet: A mechanism to facilitate diffusion creep. J. Petrol. 2005, 46, 2593–2613. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Vollbrecht, A.; Pawlowski, J.; Lesiss, B.; Heinrichs, T.; Seidel, M.; Kronz, A. Ductile deformation of garnet in mylonitic gneisses from the Münchberg Massif (Germany). Tectonophysics 2006, 427, 153–170. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Puelles, P.; Bbalos, B.; Gil Ibarguchi, J.I. Transposed high-pressure granulite fabrics (Cabo Ortegal, NW Spain): Implications on the scales of deformation localization. J. Struct. Geol. 2009, 31, 776–790. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Keppler, R. Crystallographic preferred orientations in eclogites—A review. J. Struct. Geol. 2018, 115, 284–296. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Terry, M.P.; Heidelbach, F. Superplasticity in garnet from eclogite facies shear zones in the Haram Gabbro, Haramsøya, Norway. Geology 2004, 32, 281–284. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mainprice, D.; Bascou, J.; Cordier, P.; Tommasi, A. Crystal preferred orientations of garnet: Composition between numerical simulations and electron back-scattered diffraction (EBSD) measurements in naturally deformed eclogites. J. Struct. Geol. 2004, 26, 2089–2102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, J.; Green, H.W.; Bozhilov, K. Rheology of omphacite at high temperature and pressure and significance of its lattice preferred orientations. Earth Planet. Sci. Lett. 2006, 246, 432–443. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, S.; Hiraga, T.; Kohlstedt, D.L. Water weakening of clinopyroxene in the dislocation creep regime. J. Geophys. Res. 2006, 111, B08203. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Orzol, J.; Stockhert, B.; Trepmann, C.A.; Rummel, F. Experimental deformation of synthetic wet jadeite aggregates. J. Geophys. Res. 2006, 111, B06205. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Tullis, J. Deformation of granitic rocks: Experimental studies and natural examples. Rev. Mineral. Geochem. 2002, 51, 51–95. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Passchier, C.W.; Trouw, R.A.J. Microtectonics, 2nd ed.; Revised and Enlarged Edition; Springer: Berlin, Germany, 2005; 366p. [Google Scholar]
- Blumefeld, P.; Mainprice, D.; Bouchez, J.L. C-slip in quartz from subsolidus deformed granite. Tectonophysics 1986, 127, 96115. [Google Scholar]
- Mainprice, D.; Bouchez, J.L.; Blumenfeld, P.; Tubié, J.M. Dominant c slip in naturally deformed quartz: Implications for dramatic plastic softening at high temperature. Geology 1986, 14, 819–822. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, J.F.; Shi, F.; Xu, H.J.; Wang, L.; Feng, S.Y.; Liu, W.L.; Wang, Y.F.; Green, H.W. Petrofabric and strength of SiO2 near the quartz-coesite phase boundary. J. Metamorph. Geol. 2013, 31, 83–92. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Renedo, R.N.; Nachlas, W.O.; Whitney, D.L.; Teyssier, C.; Piazolo, S.; Gordon, M.S.; Fossen, H. Fabric development during exhumation from ultrahigh-pressure in an eclogite-bearing shear zone, Western Gneiss Region, Norway. J. Struct. Geol. 2015, 71, 58–70. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jung, H.; Karato, S. Water-induced fabric transitions in olivine. Science 2001, 293, 1460–1463. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Katayama, I.; Jung, H.; Karato, S. New type of olivine fabric at modest water content and low stress. Geology 2004, 32, 1045–1048. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Karato, S.; Jung, H.; Katayama, I.; Skemer, P.A. Geodynamic significance of seismic anisotropy of the upper mantle: New insights from laboratory studies. Annu. Rev. Earth Planet. Sci. 2008, 36, 59–95. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Li, C.; Thakurta, J.; Ripley, E.M. Low-Ca contents and kink-banded textures are not unique to mantle olivine: Evidence from the Duke Island Complex, Alaska. Mineral. Petrol. 2012, 104, 147–153. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jenkins, M.C.; Mungall, J.E. Genesis of the peridotite zone, Stillwater Complex, Montana, USA. J. Petrol. 2018, 59, 2157–2189. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yao, Z.; Qin, K.; Wang, Q.; Xue, S. Weak B-type Olivine Fabric Induced by Fast Compaction of Crystal Mush in a Crustal Magma Reservoir. J. Geophys. Res. Solid Earth 2019, 124, 3530–3556. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cao, Y.; Jung, H.; Song, S. Olivine fabrics and tectonic evolution of fore-arc mantles: A natural perspective from the Songshugou dunite and harzburgite in the Qinling orogenic belt, central China. Geochem. Geophys. Geosys. 2017, 18, 907–934. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sundberg, M.; Cooper, R.F. Crystallographic preferred orientation produced by diffusion creep of harzburgite: Effect of chemical interactions among phases during plastic flow. J. Geophys. Res. 2008, 113, B12208. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Précigout, J.; Hirth, G. B-type olivine fabric induced by grain boundary sliding. Earth Planet. Sci. Lett. 2014, 395, 231–240. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Ji, S.; Saruwatari, K.; Mainprice, D.; Wirth, R.; Xu, Z.; Xia, B. Microstructures, petrofabrics and seismic properties of ultra high-pressure eclogites from Sulu region, China: Implications for rheology of subducted continental crust and origin of mantle reflections. Tectonophysics 2003, 370, 49–76. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bestmann, M.; Habler, G.; Heidelbach, F.; Theni, M. Dynamic recrystallization of garnet and related diffusion processes. J. Struct. Geol. 2008, 30, 777–790. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bestmann, M.; Prior, D.J. Intragranular dynamic recrystallization in naturally deformed calcite marble: Diffusion accommodated grain boundary sliding as a result of subgrain rotation recrystallization. J. Struct. Geol. 2003, 25, 1597–1613. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gleason, G.C.; Tullis, J. A flow law for dislocation creep of quartz aggregates determined with the molten salt cell. Tectonophysics 1995, 247, 1–23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Holyoke, C.W.; Kronenberg, A.K. Accurate differential stress measurement using the molten salt cell and solid salt assemblies in the Griggs apparatus with applications to strength, piezometers and rheology. Tectonophysics 2010, 494, 17–31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Renner, J.; Stöckhert, B.; Zerbian, A.; Röller, K.; Rummel, F. An experimental study into the rheology of synthetic polycrystalline coesite aggregates. J. Geophys. Res. 2001, 106, 19411–19429. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carswell, D.A.; Zhang, R.Y. Petrographic characteristics and metamorphic evolution of ultrahigh-pressure eclogites in plate-collision belts. Inter. Geol. Rev. 1999, 41, 781–798. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jin, Z.-M.; Zhang, J.; Green, H.W., II; Jin, S. Eclogite rheology: Implications for subducted lithosphere. Geology 2001, 29, 667–670. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Warren, C.J. Exhumation of (ultra-)high-pressure terranes: Concepts and mechanisms. Solid Earth 2013, 4, 75–92. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).