Microstructural Characteristics of Graphite Microcrystals in Graphitized Coal: Insights from Petrology, Mineralogy and Spectroscopy
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Geological Setting
3. Samples and Analytical Procedures
3.1. Sampling
3.2. Analytical Methods
3.2.1. Proximate and Ultimate Analyses
3.2.2. Optical Microscopy
3.2.3. Scanning Electron Microscopy
3.2.4. Raman Spectroscopy
4. Results and Discussions
4.1. Geochemistry Characterization of Graphitized Coal
4.2. Petrography Characterization of Graphite Microcrystals
4.3. Mineralogy Characterization of Graphite Microcrystals
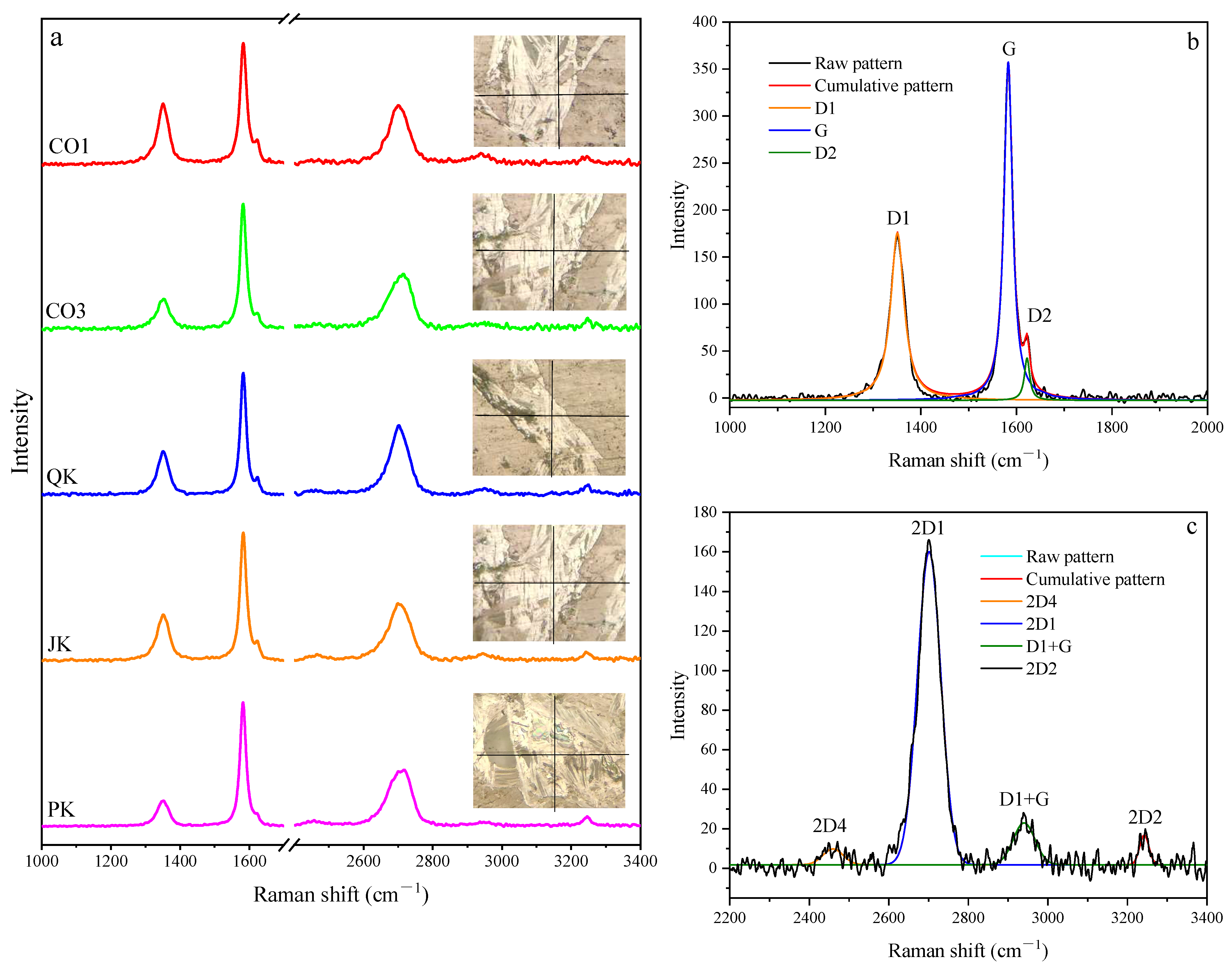
4.4. Raman Characterization of Graphite Microcrystals
5. Conclusions
- (1)
- Graphite microcrystals are characterized by filling microcracks and cell cavities in graphitized coal, with the morphology of flake, needle and aggregates. The volume proportion of graphite microcrystals is between 2.39% and 7.32%, and the optical anisotropy is stronger than that of coal macerals. Under polarized light with a retarder plate of 1λ, graphite microcrystals show the color of primary yellow and secondary blue, and the two kinds of color appear alternately when rotating the microscope stage. The isochromatic zone of flake-like graphite microcrystals with a diameter of 10−50 μm shows an arrangement order along the microcracks;
- (2)
- The morphology of graphite microcrystals filled with microcracks shows a rough and irregular edge, flow-like or bubble film-like structures along with several pores, indicating a formation mode similar to vapor deposition as cooling crystallization after softening and melting of carbon-containing substances. Moreover, flake-like graphite microcrystals that developed interlayer pores with a clear outline of loose stacking were also observed. The elemental composition was almost pure carbon, and a small amount of oxygen was related to oxygen-containing functional groups or structural defects;
- (3)
- The micro-Raman spectra of graphite microcrystals show low-intensity D1 and D2 bands and high-intensity G bands in the first-order region and a higher intensity of the 2D1 band and a lower intensity of the other three bands in the second-order region. The parameters R1 and R2 range from 0.21−0.39 and 0.60−0.74, respectively, and the parameter R3 proposed in this paper ranges between 0.78 and 0.86, both of them indicate a higher percentage of graphene plane with a highly internal crystallographic structure.
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Dai, S.; Ren, D. Effects of magmatic intrusion on mineralogy and geochemistry of coals from the Fengfeng−Handan Coalfield, Hebei, China. Energy Fuels 2007, 21, 1663–1673. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, K.; Rimmer, S.M.; Liu, Q.; Zhang, Y. Micro-Raman spectroscopy of microscopically distinguishable components of naturally graphitized coals from central Hunan Province, China. Energy Fuels 2019, 33, 1037–1048. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, L.; Cao, D.; Peng, Y.; Ding, Z.; Li, Y. Strain-induced graphitization mechanism of coal-based graphite from Lutang, Hunan Province, China. Minerals 2019, 9, 617. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, Y.; Li, K.; Wang, Z.; Hu, M.; Cao, H.; Liu, Q. Fluctuations in graphitization of coal seam-derived natural graphite upon approaching the Qitianling granite intrusion, Hunan, China. Minerals 2021, 11, 1147. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yuan, L.; Liu, Q.; Li, K.; Quan, Y.; Li, X.; Mathews, J.P. The evolution of coal, examining the transitions from anthracite to natural graphite: A spectroscopy and optical microscopy evaluation. Front. Earth Sci. 2022, 1–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, J. Composition and Optical Proporty Evolution of Macerals in Meta-Anthracite from Yongan, Fujian, China. Master’s Thesis, China University of Mining and Technology, Xuzhou, China, 2019. [Google Scholar]
- Li, J.; Qin, Y.; Chen, Y.; Luo, Q.; Deng, R.; Guo, S.; Zhong, N.; Chen, Q. Differential graphitization of organic matter in coal: Some new understandings from reflectance evolution of meta-anthracite macerals. Int. J. Coal Geol. 2021, 240, 103747. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cao, D.; Zhang, H.; Dong, Y.; Wu, G.; Ning, S.; Mo, J.; Li, X. Research status and key orientation of coal-based graphite mineral geology. Front. Earth Sci. 2017, 24, 317–327. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, S.; Liu, Q.; Zhang, H.; Ma, R.; Li, K.; Wu, Y.; Teppen, B.J. Structural order evaluation and structural evolution of coal derived natural graphite during graphitization. Carbon 2020, 157, 714–723. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, H.; Wang, S.; Zhang, X.; Zhang, X.; Zhao, Y.; Zhang, H. A study of chemical structural evolution of thermally altered coal and its effect on graphitization. Fuel 2021, 283, 119295. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, Y.; Zang, W.; Nan, D.; Huang, Z.; Liu, X.; Zheng, Y.; Shen, W. Preparation of graphitized Taixi coal and its electrochemical properties. J. China Coal Soc. 2012, 37, 1925–1929. [Google Scholar]
- Shen, K.; Cao, X.; Huang, Z.H.; Shen, W.; Kang, F. Microstructure and thermal expansion behavior of natural microcrystalline graphite. Carbon 2021, 177, 90–96. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Suarez-Ruiz, I.; Crelling, J.C. Applied Coal Petrology: The Role of Petrology in Coal Utilization; Academic Press: New York, NY, USA, 2008; pp. 180–186. [Google Scholar]
- Taylor, G.; Teichmüller, M.; Davis, A.; Diessel, G.F.K.; Littke, R.; Robert, P. Organic Petrology; Gebruder Borntraeger: Berlin, Germany, 1998; pp. 162–174. [Google Scholar]
- Li, K.; Rimmer, S.M.; Liu, Q. Geochemical and petrographic analysis of graphitized coals from Central Hunan, China. Int. J. Coal Geol. 2018, 195, 267–279. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stach, E.; Mackowsky, M.-H.; Teichmüller, M.; Taylor, G.H.; Chandra, D.; Teichmüller, R. Stach’s Textbook of Coal Petrology; Gebruder Borntraeger: Berlin, Germany, 1982. [Google Scholar]
- Qin, Y. Micropetrology and Structural Evolution of High-Rank Coals in China; China University of Mining and Technology Press: Xuzhou, China, 1994. [Google Scholar]
- Qin, Y.; Jiang, B. Coalification jumps, stages and mechanism of high-rank coals in China. In Geology of Fossil Fuels–Coal; CRC Press: Boca Raton, FL, USA, 2020; pp. 99–122. [Google Scholar]
- Beyssac, O.; Goffé, B.; Chopin, C.; Rouzaud, J.N. Raman spectra of carbonaceous material in metasediments: A new geothermometer. J. Metamorph. Geol. 2002, 20, 859–871. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oberlin, A. Carbonization and graphitization. Carbon 1984, 22, 521–541. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, Z.; Zhang, J.; Huang, J.Y. Observations of microstructure and reflectivity of coal graphites for two locations in China. Int. J. Coal Geol. 1996, 30, 277–284. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mathews, J.P.; Fernandez-Also, V.; Jones, A.D.; Schobert, H.H. Determining the molecular weight distribution of Pocahontas No. 3 low-volatile bituminous coal utilizing HRTEM and laser desorption ionization mass spectra data. Fuel 2010, 89, 1461–1469. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Q.; Yuan, L.; Li, K.; Cui, X.; Yu, L. Structure characteristics of different metamorphic grade coal-based graphites. Earth Sci. 2018, 43, 1663–1669. [Google Scholar]
- Li, K.; Liu, Q.; Hou, D.; Wang, Z.; Zhang, S. Quantitative investigation on the structural characteristics and evolution of high-rank coals from Xinhua, Hunan Province, China. Fuel 2021, 289, 119945. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, J.; Qin, Y.; Chen, Y.; Song, Y.; Wang, Z. HRTEM observation of morphological and structural evolution of aromatic fringes during the transition from coal to graphite. Carbon 2022, 187, 133–144. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marsh, H. Introduction to Carbon Science; Butterworth Publishers: London, UK, 1989. [Google Scholar]
- Kwiecinska, B.; Suarez-Ruiz, I.; Paluszkiewicz, C.; Rodriques, S. Raman spectroscopy of selected carbonaceous samples. Int. J. Coal Geol. 2010, 84, 206–212. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, K.; Rimmer, S.M.; Presswood, S.M.; Liu, Q. Raman spectroscopy of intruded coals from the Illinois Basin: Correlation with rank and estimated alteration temperature. Int. J. Coal Geol. 2020, 219, 103369. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wopenka, B.; Pasteris, J.D. Structural characterization of kerogens to granulitefacies graphite: Applicability of Raman microprobe spectroscopy. Am. Mineral. 1993, 78, 533–557. [Google Scholar]
- Zu, F.; Shu, L.; Li, C. Evolution features of depositional and tectonic setting from late Paleozoic to Meso–Cenozoic in the Yong’an Basin. Int. Geol. Rev. 2012, 50, 126–148. [Google Scholar]
- Chen, Q.; Deng, R.; He, Z.; Wang, R. Occurrence Characteristics and Coal Prospecting Mode of Deep Coal Resources in Permian Coal-Bearing Area of Fujian Province; Geological Publishing House: Beijing, China, 2016; pp. 35–41. [Google Scholar]
- Shu, L.; Faure, M.; Wang, B.; Zhou, X.; Song, B. Late Palaeozoic–early Mesozoic geological features of South China: Response to the Indosinian collision events in Southeast Asia. Compt. Rendus Geosci. 2008, 340, 151–165. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, N. The characteristics of sedimentary structure of Lower Permian series Tongzi petrofabic of Permian system in Fujian and the range of coal–finding. J. Jiaozuo Inst. Technol. 1998, 17, 34–38. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, L.; Cao, D.; Ding, Z.; Chen, Q.; Deng, R.; Lin, X.; Li, Y.; Du, X. Controlling factors and metallogenic belts of coal-based graphite in the South-weatern Fujian province. J. China Coal Soc. 2020, 45, 2865–2871. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, Z.; Zuo, R. Tectonic Evolution of southwestern Fujian Province and spatial–temporal distribution regularity of mineral deposits. Acta Petrol. Sin. 2015, 31, 217–229. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, Y.; Xu, X.; Jia, D.; Shu, L. Deformation record of the change from Indosinian collision-related tectonic system to Yanshanian subduction-related tectonic system in South China during the Early Mesozoic. Front. Earth Sci. 2009, 16, 234–247. [Google Scholar]
- GB/T 482-2008; Sampling of Coal Seams. Standardization Administration of the P.R.C.: Beijing, China, 2008.
- GB/T 3521-2008; Method for Chemical Analysis of Graphite. Standardization Administration of the P.R.C.: Beijing, China, 2008.
- GB/T 31391-2015; Ultimate Analysis of Coal. Standardization Administration of the P.R.C.: Beijing, China, 2015.
- GB/T 8899-2013; Determination of Maceral Group Composition and Minerals in Coal. Standardization Administration of the P.R.C.: Beijing, China, 2013.
- GB/T 5751-2009; Chinese Classification of Coals. Standardization Administration of the P.R.C.: Beijing, China, 2009.
- Kwiecińska, B.; Petersen, H.I. Graphite, semi-graphite, natural coke, and natural char classification—ICCP system. Int. J. Coal Geol. 2004, 57, 99–116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pasteris, J.D.; Wopenka, B. Raman spectra of graphite as indicators of degree of metamorphism. Can. Mineralog. 1991, 29, 1–9. [Google Scholar]
- Tuinstra, F.; Koenig, J.L. Raman Spectrum of Graphite. J. Chem. Phys. 1970, 53, 1126–1130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ammar, M.R.; Galy, N.; Rouzaud, J.N.; Toulhoat, N.; Vaudey, C.E.; Simon, P.; Moncoffre, N. Characterizing various types of defects in nuclear graphite using Raman scattering: Heat treatment, ion irradiation and polishing. Carbon 2015, 95, 364–373. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, S.; Song, B.; Cao, C.; Zhang, H.; Liu, Q.; Li, K.; Teppen, B.J. Structural evolution of high-rank coals during coalification and graphitization: X-ray diffraction, Raman spectroscopy, high-resolution transmission electron microscopy, and reactive force field molecular dynamics simulation study. Energy Fuels 2021, 35, 2087–2097. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bernard, S.; Beyssac, O.; Benzerara, K.; Findling, N.; Tzvetkov, G.; Brown, G.E. XANES, Raman and XRD Study of Anthracenebased Cokes and Saccharose-based Chars Submitted to HighTemperature Pyrolysis. Carbon 2010, 48, 2506–2516. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pocsik, I.; Hundhausen, M.; Koós, M.; Ley, L. Origin of the D Peak in the Raman Spectrum of Microcrystalline Graphite. J. Non-Cryst. Solids 1998, 227–230, 1083–1086. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pimenta, M.A.; Dresselhaus, G.; Dresselhaus, M.S.; Cancado, L.G.; Jorio, A.; Saito, R. Studying Disorder in Graphite-Based Systems by Raman Spectroscopy. Phys. Chem. Chem. Phys. 2007, 9, 1276–1290. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ferrari, A.C.; Robertson, J. Interpretation of Raman spectra of disordered and amorphous carbon. Phys. Rev. B 2000, 61, 14095–14107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nemanich, R.J.; Solin, S.A. First- and second-order Raman scattering from finite-size crystals of graphite. Phys. Rev. B. 1979, 20, 392–401. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sato, Y.; Kamo, M.; Setaka, N. Raman spectra of carbons at 2600–3300 cm−1 region. Carbon 1978, 16, 279–280. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, H.; Li, K.; Sun, J.; Sun, Z.; Yuan, L.; Liu, Q. The structural evolution and mutation of graphite derived from coal under the influence of natural igneous plutonic intrusion. Fuel 2022, 322, 124066. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, S.; Li, T.; Wu, L.; Zhang, L.; Dong, L.; Hu, X.; Li, C. Second-order Raman spectroscopy of char during gasification. Fuel Process. Technol. 2015, 135, 105–111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rodrigues, S.; Marques, M.; Suárez-Ruiz, I.; Camean, I.; Flores, D.; Kwiecinska, B. Microstructural investigations of natural and synthetic graphites and semi-graphites. Int. J. Coal Geol. 2013, 111, 67–79. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rantitsch, G.; Lämmerer, W.; Fisslthaler, E.; Mitsche, S.; Kaltenböck, H. On the discrimination of semi-graphite and graphite by Raman spectroscopy. Int. J. Coal Geol. 2016, 159, 48–56. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sadezky, A.; Muckenhuber, H.; Grothe, H.; Niessner, R.; Pöschl, U. Raman microspectroscopy of soot and related carbonaceous materials: Spectral analysis and structural information. Carbon 2005, 43, 1731–1742. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lünsdorf, N.K.; Dunkl, I.; Schmidt, B.C.; Rantitsch, G.; Eynatten, H. Towards a higher comparability of geothermometric data obtained by raman spectroscopy of carbonaceous material. Part 2: A revised geothermometer. Geostand. Geoanal. Res. 2017, 41, 593–612. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]





| Samples | Reflectance/% | Proximate Analysis/% | Ultimate Analysis/% | Maceral Composition/% | |||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| VRmax | s.d. | GMmax | s.d. | GMmin | s.d. | Mad | Ad | Vdaf | Cdaf | Hdaf | Odaf | Ndaf | V | I | L | GM | |
| CO1 | 7.94 | 0.42 | 10.21 | 0.54 | 0.87 | 0.16 | 2.24 | 21.90 | 8.79 | 89.25 | 0.94 | nd | 0.14 | 90.11 | 1.68 | 0.90 | 7.32 |
| CO3 | 7.17 | 0.52 | 10.83 | 0.46 | 0.85 | 0.16 | 6.88 | 22.51 | 5.29 | 93.87 | 0.00 | 5.76 | 0.26 | 87.98 | 6.71 | 2.12 | 3.18 |
| QK | 8.95 | 0.47 | nd | nd | nd | nd | 7.26 | 13.95 | 1.55 | 96.19 | 0.09 | nd | 0.27 | 86.15 | 9.74 | 1.73 | 2.39 |
| JK | 7.01 | 0.43 | 8.49 | 0.44 | 1.33 | 0.25 | 12.90 | 14.54 | 2.61 | 96.88 | 0.00 | 2.94 | 0.15 | 90.21 | 6.11 | 0.00 | 3.68 |
| PK | 7.32 | 0.39 | 9.75 | 0.47 | 1.25 | 0.19 | 9.62 | 11.64 | 2.85 | 96.66 | 0.01 | 2.98 | 0.15 | 89.37 | 4.55 | 1.82 | 4.26 |
| Samples | D1/cm−1 | G/cm−1 | D2/cm−1 | R1 | R2 | |||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Position | s.d. | FWHM | s.d. | Position | s.d. | FWHM | s.d. | Position | s.d. | FWHM | s.d. | |||
| CO1 | 1351 | 1.48 | 34 | 1.97 | 1583 | 1.86 | 22 | 1.52 | 1622 | 1.34 | 13 | 1.66 | 0.39 | 0.64 |
| CO3 | 1351 | 1.26 | 37 | 1.39 | 1582 | 1.25 | 20 | 1.19 | 1624 | 1.09 | 7 | 0.81 | 0.21 | 0.74 |
| QK | 1351 | 1.55 | 34 | 1.84 | 1583 | 2.03 | 20 | 1.87 | 1624 | 0.75 | 9 | 0.97 | 0.36 | 0.60 |
| JK | 1351 | 2.18 | 35 | 1.08 | 1583 | 1.17 | 21 | 1.59 | 1623 | 1.16 | 11 | 1.62 | 0.35 | 0.62 |
| PK | 1350 | 1.13 | 33 | 1.52 | 1582 | 1.28 | 20 | 1.64 | 1622 | 0.92 | 8 | 1.06 | 0.21 | 0.74 |
| Samples | 2D4/cm−1 | 2D1/cm−1 | D1+G/cm−1 | 2D2/cm−1 | R3 | ||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Position | s.d. | FWHM | s.d. | Position | s.d. | FWHM | s.d. | Position | s.d. | FWHM | s.d. | Position | s.d. | FWHM | s.d. | ||
| CO1 | 2460 | 2.26 | 60 | 1.26 | 2701 | 1.96 | 69 | 1.36 | 2940 | 2.16 | 65 | 1.09 | 3242 | 2.26 | 28 | 0.93 | 0.83 |
| CO3 | 2461 | 1.85 | 54 | 1.58 | 2707 | 2.25 | 82 | 1.86 | 2947 | 1.85 | 70 | 1.26 | 3248 | 1.92 | 37 | 1.16 | 0.78 |
| QK | 2455 | 1.61 | 56 | 1.86 | 2703 | 1.54 | 69 | 1.08 | 2945 | 1.67 | 66 | 1.65 | 3246 | 2.16 | 38 | 1.35 | 0.84 |
| JK | 2464 | 2.08 | 51 | 1.67 | 2704 | 1.71 | 78 | 0.94 | 2947 | 1.39 | 64 | 1.38 | 3246 | 1.66 | 29 | 0.86 | 0.86 |
| PK | 2454 | 2.59 | 59 | 2.24 | 2705 | 1.63 | 80 | 1.39 | 2946 | 2.04 | 75 | 1.24 | 3245 | 1.59 | 33 | 0.97 | 0.86 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Li, J.; Qin, Y.; Chen, Y.; Shen, J. Microstructural Characteristics of Graphite Microcrystals in Graphitized Coal: Insights from Petrology, Mineralogy and Spectroscopy. Minerals 2022, 12, 1189. https://doi.org/10.3390/min12101189
Li J, Qin Y, Chen Y, Shen J. Microstructural Characteristics of Graphite Microcrystals in Graphitized Coal: Insights from Petrology, Mineralogy and Spectroscopy. Minerals. 2022; 12(10):1189. https://doi.org/10.3390/min12101189
Chicago/Turabian StyleLi, Jiuqing, Yong Qin, Yilin Chen, and Jian Shen. 2022. "Microstructural Characteristics of Graphite Microcrystals in Graphitized Coal: Insights from Petrology, Mineralogy and Spectroscopy" Minerals 12, no. 10: 1189. https://doi.org/10.3390/min12101189
APA StyleLi, J., Qin, Y., Chen, Y., & Shen, J. (2022). Microstructural Characteristics of Graphite Microcrystals in Graphitized Coal: Insights from Petrology, Mineralogy and Spectroscopy. Minerals, 12(10), 1189. https://doi.org/10.3390/min12101189







