Abstract
The only example and reference of Ptolemaic Alexandrian tombs, with clear integrations of Egyptian-style scenes and decorations, is considered an endangered archaeological site due to different coastal environmental risks in Alexandria and the absence of maintenance. Anfushi’s Necropolis is located near the western harbour (Island of Pharos) and dates back to the 2nd century BC. Sea level rises, earthquakes, flooding, storminess, variations in temperature, rainfall, and wind are the factors that have the largest effect on the destruction and decay of Anfushi’s Necropolis building materials. This paper’s main objectives were to characterize this necropolis’s building materials and assess its durability problems and risks regarding the coastal environment. Additionally, the vector mapping of its architectural and structural elements was applied for documentation and recording purposes for the necropolis. To achieve these aims, field (recording and photographs), desk (engineering drawing and mapping), and laboratory works (X-ray diffraction, X-ray fluorescence, binocular microscopy, polarizing microscopy, and scanning electron microscopy) were carried out. The results confirmed the probabilistic risk of sea level rises and its impact on the submergence of Anfushi’s Necropolis. The structural deficiencies of the tombs were caused by the effect of earthquake tremors along with anthropogenic factors. In addition, chemical and microscopic investigations showed that salt weathering (halite and gypsum) induced the decay of the building materials.
1. Introduction
The resilience and durability of historical buildings near marine areas are reduced due to the dynamics of coastal environments [1]. Due to the importance of preserving heritage, for example, in 2022, a database was constructed for 213 natural and 71 cultural African heritage sites affected by coastal environmental changes for their sustainable management. In this regard, by 2050, the number of archaeological sites that will be subjected to severe effects due to coastal flooding and erosion will increase more than three times [2]. Sea level rise (SLR), coastal flooding, coastal erosion, extreme rainfall, high winds, storm surge, temperatures, and soil moisture are the most relevant issues related to the sustainability problems of archaeological buildings near coasts [3]. Sea level rise is considered a major threat to coastal areas and is recognized as a powerful indicator of climate change and coastal dynamics [4,5]. Sea level rise occurs due to increasing global mean temperature, leading to oceanic thermal expansion and the loss of continental ice [6]. Accordingly, global sea levels will rise between 1 and 5 m by 2100, submerging most archaeological sites worldwide [7].
Globally, many desktop and field studies have been performed to evaluate and assess the threats and sustainability problems of archaeological sites and their built heritage sites in the coastal context [8,9,10,11]. In New Zealand, the heritage sites in Whangarei District near the harbour have been destroyed due to sea level rises, extreme rainfall, and storminess [12]. In Ireland, Westley et al. [13] studied and assessed the impact of coastal erosion on archaeological sites and showed the collapse of archaeological buildings at Derryoge town due to cliff erosion. In the United States, Anderson et al. [14] studied the impact of SLR on the archaeological sites, buildings, and cultural landscapes of the Gulf and Atlantic coasts of the southeastern United States, reporting that a 1 m rise in sea level will lead to the loss of over >13,000 recorded archaeological sites there. In the United Kingdom, Harkin et al. [15] mentioned that the rate of regional sea level rise is between 1 and 2 mm according to tide gauge records, which causes potential damage to the heritage on its coastline. In Cyprus, Andreou [16] studied endangered areas using the Digital Shoreline Analysis System (DSAS) to monitor the areas most vulnerable to coastal erosion and flooding. Accordingly, archaeological sites in the south-central zone are experiencing a high rate of coastal erosion. Furthermore, Andreou et al. [17] started to work on endangered coastal archaeological sites in the Middle East and North Africa to show that sea waves and storm effects produced coastal erosion and caused damage to archaeological buildings in Libya, Yemen, and Jordan.
On the other hand, sea spray (marine aerosol), rising dampness, and coastal/flash flooding can cause salt decay in archaeological building materials near the marine environment [18]. In this context, Morillas et al. [19] said that one of the most aggressive deterioration aspects of sea spray is salt precipitation, which is composed of inorganic salts (sulphates, nitrates, and mainly chlorides) and organic matter. In addition, sea spray exists in a range of particles named using different terms because of their physical characteristics, such as film drops, jet drops, seawater drops, brine drops, hygroscopic salt drops, sea salt nuclei, and sea salt particles. These drops are composed of bubbles in which a large amount of air and water are blended, and they reflect the chemical context in the atmosphere [18,20,21]. Sea spray could cause the accumulative deposition of ions on stones’ surfaces and penetrates inside the stone pores through ionic diffusion, leading to degeneration [22]. Moreover, wind can increase the possibility of the aggressiveness of sea spray’s impact on stone by carrying sea spray and directly depositing it on stone surfaces [23]. Cardell et al. [24] demonstrated that most of the decayed stones in their case studies (SW coast of France) were observed on the medium–high parts of the buildings because the stones did not receive saline water from groundwater, but the stones received salt from sea spray. Therefore, the mechanism of the salt crystallization of sea spray is different from salt crystallization from groundwater through capillary action. In this sense, salt from sea spray and groundwater can be considered a significant factor in the decay of building stones near coasts [25].
In Egypt, some studies have been conducted to evaluate climate changes and marine environmental impacts on archaeological sites, including Alexandria. For instance, El-Raey [26] carried out an assessment study using GIS maps and remote sensing to evaluate the impact of SLR on Egypt. He reported that many historical sites will be affected and flooded when the water reaches 50 cm and upwards. Elsharkawy et al. [27] conducted a study on SLR impacts and observed that SLR can increase soil salinity due to saltwater intrusion in the delta and Alexandria. In this sense, SLR affected the Library of Alexandria, one of Alexandria’s landmarks, in 2005. Moreover, Bekheet et al. [28] and El-Raey and RCDRR [29] mentioned that Egypt is considered among the top five countries that will be in danger due to an SLR of 1 m, specifically in Alexandria, which is considered among the 20 top cities in the world that will be in danger due to SLR. In addition, they explained that permanent coastal flooding results in the loss of dry land and saltwater intrusion into the surface and groundwater by submergence. The European Institute of Underwater Archaeology (EIUA) allowed us to see the submerged port structures of the Great Harbour of Alexandria using new methods (sonar scanning and magnetic surveys) [30]. Ivanov [31] revealed the remains of the submerged ancient breakwater using historical satellite images at Anfushi, which reflects the sea level rise’s impact in Alexandria. Furthermore, Abdelnaby and Elnashai [32] studied the impact of the historical earthquake of 1303 AD in damaging the historical buildings in Alexandria, concluding that the historical earthquakes felt in Alexandria caused structural cracks, failures, and the partial and total collapse of most of the ancient buildings in Alexandria. Hemeda et al. [33] studied the geohazard-related problems at the Necropolis of Mustafa Kamil in Alexandria and showed how the susceptibility of the necropolis rocks with regard to saline water and the seismic analysis response upon the necropolis revealed that the tombs are not structurally safe for PGA (peak ground acceleration) values greater than 0.07-0.08 G. Moreover, Hemeda [34] studied climate change at archaeological sites in Alexandria using satellite images and geotechnical modelling and concluded that flooding is a key factor in the damage to most built heritage in Alexandria. According to a recent study [35], the Qaitbay Citadel was found to be the most vulnerable site to SLR after carrying out four SLR scenarios based on representative concentration pathways (RCPs) and shared socioeconomic pathways (SSPs).
The present study was conducted to evaluate the coastal environment’s impact on Anfushi’s Necropolis and the building materials’ decay sources, which led to severe damage to the structural and architectural elements of the tombs. To achieve these aims, satellite images and Google Earth maps were integrated into the research paper to evaluate the vulnerability of Anfushi’s Necropolis to coastal dynamics (SLR, earthquakes, flooding, and climate). In addition, multianalytical techniques (X-ray diffraction, X-ray fluorescence, Raman spectroscopy, digital microscopy, optical polarizing microscopy, and scanning electron microscopy) were applied to assess the durability and sustainability problems related to Anfushi’s Necropolis’s building materials in the context of the coastal environment.
2. The Geographical and Archaeological Context of Anfushi’s Necropolis
Anfushi’s Necropolis is located on the Island of Pharos (western harbour), north of Marriot Lake and 300 m from the Mediterranean Sea with coordinates N 31° 12′ and E 29° 52′ (Figure 1A,B). The necropolis is situated around 1 m above the sea level and around 3 m from the ground level of the tombs to the soil surface. Anfushi’s Necropolis is considered one of the endangered coastal archaeological sites in North Africa that has not been studied before in terms of material characterization and problems of conservation. Figure 2A presents a general risk map for all marine archaeological sites in North Africa, and Figure 2B,C) show the study area (zoomed-in risk map) as part of these endangered sites due to the coastal environment. Giuseppe Botti, who was the director of the Greco-Roman Museum in Alexandria, revealed Anfushi’s Necropolis in 1901. After Giuseppe’s death, Evaristo Breccia and Achille Adriani continued their work on this archaeological site and published research about it [36]. Anfushi’s Necropolis is considered an elite Egyptian tomb for a blessed afterlife and represents a distinguished style for the tombs that emerged from the 2nd century BC. This necropolis is the only example and reference of a Ptolemaic Alexandrian tomb with extensive integrations of Egyptian-style scenes and decorations; it was also the right place for a mummified body to be preserved and resurrected (Figure 1C) [36]. The architectural features of the necropolis’s tombs reflect the mentioned importance and role of the necropolis, which only consists of five tombs from the overall complex that is visible, which is currently in a bad state of preservation (Figure 1B). Each tomb consists of an open courtyard with burial units with attached rooms for burial purposes and descending stairs from the ground level to the underground court (Figure 3A). The first room of the burial unit depicts scenes in the Egyptian style. For instance, it represents the dead person as an Egyptian priest between the god Horus and a Pharaonic couple, standing in front of the enthroned Osiris to offer him a jar as a clear effect of Egyptian art. From the previous room, we can see a doorframe in the Egyptian style leading us to the burial chamber and an Egyptian motif interrupted by larger tiles with painted Egyptian crowns (Figure 1C). As shown in Figure 3A,B, tombs were engraved in the bedrock of the Pharos Island ridge and were covered with two plastering layers (coarse and fine) as preparation layers for the painting (Figure 3C). Some Egyptian scenes may have been over Greek decorative plastered elements [37,38].
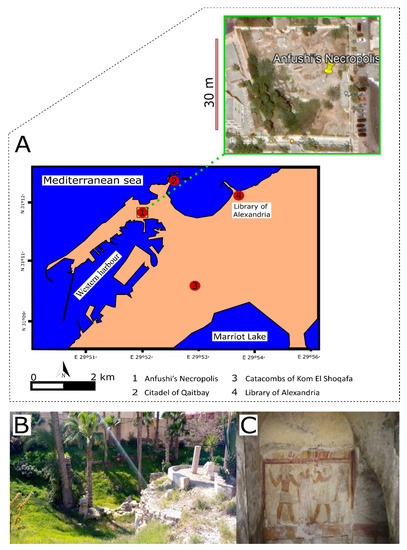
Figure 1.
(A) The geographical location of Anfushi’s Necropolis on the coast of the Mediterranean Sea. (B) The general view and the current state of preservation of Anfushi’s Necropolis. (C) Ancient Egyptian-style scene.
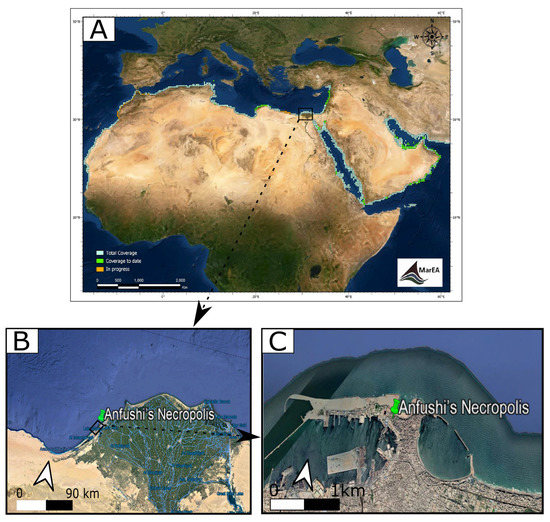
Figure 2.
(A) General map of the endangered coastal archaeological sites in North Africa and the Middle East. From [17]. (B) Zoomed-in risk map of the delta (including Alexandria), and the green pin shows the case study of Anfushi’s Necropolis as an endangered coastal archaeological site in North Africa, Egypt (Alexandria). (C) Zoomed-in map of endangered Anfushi’s Necropolis and its surrounding coastal environment.
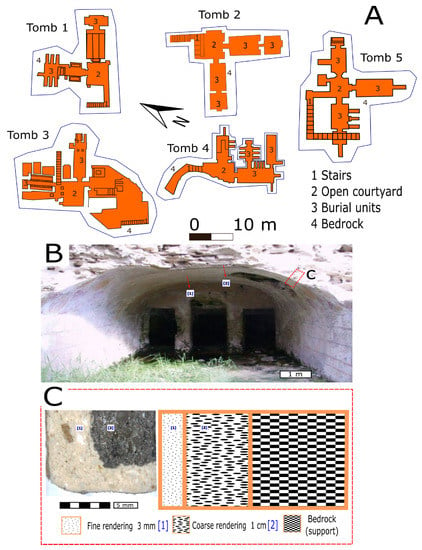
Figure 3.
(A) Schematic plans for the five tombs of Anfushi’s Necropolis and their architectural elements of the rock-cut tombs and their elements. (B) General view the ground level of the tomb No 4 leads to the burial units and attached rooms. Numbers in square brackets and red rectangles refer to the image (C). (C) Cross-section for mortar of the tombs, which consists of the support wall (bedrock), coarse rendering mortar, and fine rendering mortar for painting.
3. Geological Context and Ancient Quarries in Alexandria
Egypt covers 1,000,000 km2 and consists of four major morphological regions: the Nile valley and Nile delta, the western desert, the eastern desert, and the Sinai Peninsula. Geologically, Egypt is mainly composed of five kinds of lithologies with unconsolidated Quaternary sediments (Figure 4A) [39]. The western desert is composed of thick deposits of loose sediments, mainly sand dunes, while the Nile valley is composed of floodplains, silt, and clay. The eastern desert and Sinai are mainly composed of sand and gravel, while the northwest is composed of sandstone and conglomerate. Moreover, the western and eastern deserts are mainly composed of limestone with some formations of sandstone from the Upper Cretaceous age and sandstone, shale, and basement rocks. In the eastern and south-eastern deserts, there are crystalline basements from igneous and metamorphic rocks [39,40]. The coastline of Alexandria is characterized as an unconformity surface composed of soil sediments, oolitic sand and clay, oolitic limestone (Middle Miocene), grey shelly dolomite, marly dolomite, oncolitic limestone and dolomite, and shelly limestone. In addition, it largely comprises bioclastic (shelly) and muddy carbonate sand strata interbedded with fine-grained sandy silt (arid loamy soil), silty mud, and dark, organic-rich layers (Figure 4B,C) [41,42,43,44]. On the other hand, the ridge of the Abusir between south-western Alexandria and Abu Kir in the east dates back to the Pleistocene age, which reaches a height of 35 m in its western part and 6 m in Abu Kir, and it was formed by poorly to moderately cemented sandy carbonate [45]. The Island of Pharos is formed of limestone (the bedrock of Anfushi’s Necropolis). A thin layer of clay with different thicknesses and consolidation states is overlaid on the slopes of this limestone ridge [46].
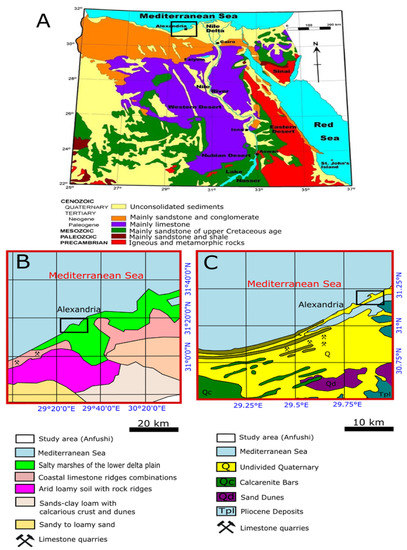
Figure 4.
(A) Geological map of Egypt (black rectangle refers to Alexandria) from [39]. Detailed maps for soil units (B) and geological map (C) of Alexandria, edited after [43]. Black rectangles refer to the study area.
Ancient Egyptians used different kinds of stones (limestone, sandstone, granite, basalt, etc.) from different quarries along Egypt, from south to north and from east to west. The extracted stone blocks were used to build temples and tombs in different periods in Egypt for architectural and ornamental purposes [47,48,49]. Alexandria was a source of quarried limestone blocks from the Quaternary ages along the Nile delta’s Mediterranean coast [50]. Abusir and Al Max west of Alexandria are considered quarries that were used from the Ptolemaic era to the Roman era (Figure 5). The limestone of these quarries is light-coloured, and their deposits belong to the Pleistocene Alexandria Formation. Ancient and recent quarries are observed on the Alexandria-Marsa Matrouh Road in a 21 km area [51,52].
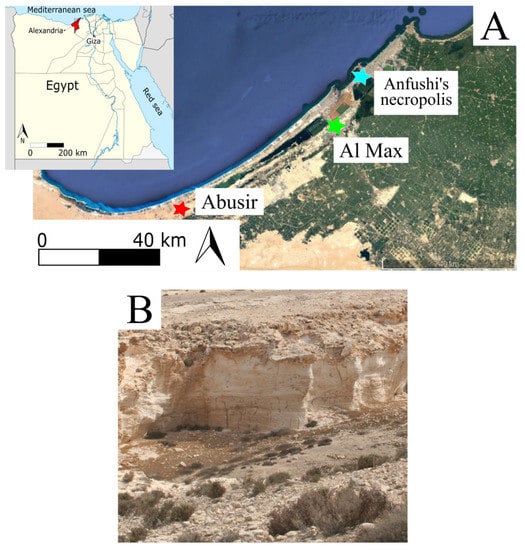
Figure 5.
(A) Ancient quarries in Alexandria (green and red stars) with an example of the light-coloured of limestone outcrop (B).
4. Coastal Geodynamics Context
4.1. Sea Level Rise
Globally, sea levels are rising due to global warming; from 1995 to 2020, the water has risen to approximately 102.3 mm, and in January 2022, it reached 102 ± 4 mm according to satellite sea level observations [53]. Alexandria is susceptible to the SLR effect as one of the marine dynamics. From 1906 to 2020, the annual linear SLR in Alexandria was 2.6 mm/year; from 1906 to 1980, the SLR increased by 51%; from 1981 to 2000, the SLR increased by 20%; and from 2001 to 2020, the SLR increased by 78% [54]. Figure 6 shows the change in the average water level from November 2021 to February 2022. In November 2021, the sea level rise reached +88 mm (maximum), but in February 2022, the sea level rise returned to −88 mm (minimum), which reflects the considerable variation in the sea level in Alexandria.
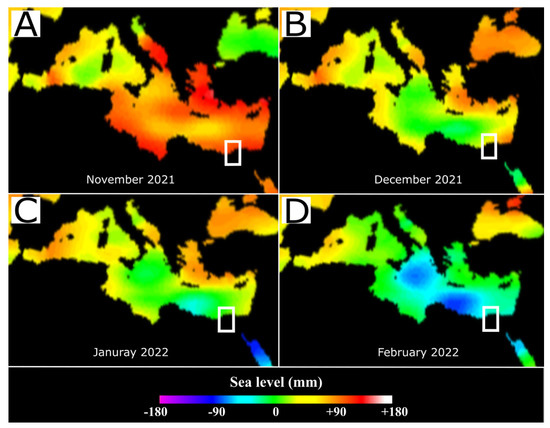
Figure 6.
(A–D) Satellite images for the average monthly sea level rise variations; the pinkish rectangle refers to Alexandria. From https://climate.nasa.gov/, accessed on 13 May 2022.
Furthermore, Alexandria is also vulnerable to SLR because of its low elevation and local land subsidence. The land approximately 50 km in front of the sea is less than 2 m from the sea’s water level, and a sand belt formed by sediments charged from Nile branches protects this land with its buildings. After building a high dam, the discharge of these sediments decreased, and the safe sand belt started to be eroded [55]. El-Raey and RCDRR [29] studied two scenarios of SLR’s impact on the loss of land and socioeconomic activities in Alexandria and the whole delta after [56,57]. In this regard, they proposed that an SLR of 0.5 m would affect 3.8 million people and 1800 km2 of land, while it was assumed that an increase of a 1.0 m SLR would influence 6.1 million people and 4500 km2 of land use (Figure 7A,B). Another scenario has been studied with a 1.5 m SLR, which put Anfushi Bay (approximately 300 m from Anfushi’s Necropolis) in the risk zone of the future SLR (Figure 7C) [28].
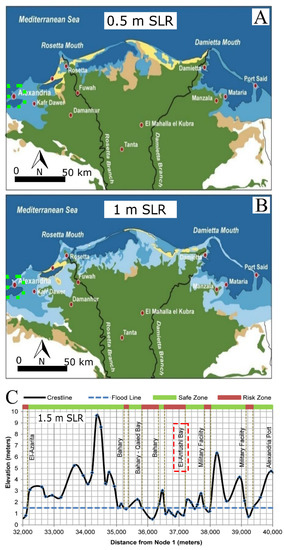
Figure 7.
(A,B) Two scenarios for possible water increases of 0.5 m and 1 m, respectively, and their impact on territory. Alexandria and the research area are represented in the green dotted square, after [29]. (C) Longitudinal profile of the flood line and safe and risk zones for the SLR scenario of 1.5 m. The study area is represented in black rectangle as a risk zone, after [28].
4.2. Earthquakes and Land Subsidence
Generally, Egypt has many seismotectonic sources, such as those in the Gulf of Suez–Northern Eastern Desert, Southwest Cairo (Dahshour), the Northern Red Sea, the Gulf of Aqaba, and Aswan zones [58]. Historically, Alexandria was subjected to 25 severe earthquakes between 320 and 2000 AD with large and moderate magnitudes. Alexandria was subjected to a very strong earthquake that affected the ancient buildings in 702 AD, and the earthquake of 726 AD caused the collapse of many structures, especially the lighthouse of Alexandria [43]. A recent study confirmed that the historical record of earthquakes in Egypt is from 2200 BC to 1889 AD. Recently, there have been various earthquakes of different sizes, such as the Aswan earthquake in 1981 (moderate magnitude, 5.8), the Cairo earthquake in 1992 (moderate magnitude, 5.8), the Aqaba earthquake in 1995 (great magnitude, 7.2), and the El Alamein earthquake in 2015 (moderate magnitude, 4.5), and most earthquake activities are focused in northern Egypt. In this regard, the Hellenic Arc, Red Sea, and Aqaba earthquakes gave less than 100 cm/s2 peak ground acceleration with a duration of more than 3 min, which affected the ancient buildings in Alexandria [59,60,61]. In addition, Figure 8A presents the distributions of historical earthquakes in Egypt from 2200 BC to 2015 AD. Due to their closeness to the two major faults, Egypt’s Eastern Mediterranean–Cairo–Fayoum fault and Suez–Cairo–Alexandria fault have severely affected the ancient buildings of Alexandria. The second reason for Alexandria’s vulnerability to earthquakes is the mechanical and physical characterizations of the soil [60]. In Figure 8B, the historical epicentres in Egypt are shown, and most of these earthquake epicentres affected many buildings structurally in Alexandria with magnitudes from 4.5 to 6.5, since with a magnitude of 6.7, the offshore area gives a peak ground acceleration of up to 300 cm/s2 [59].
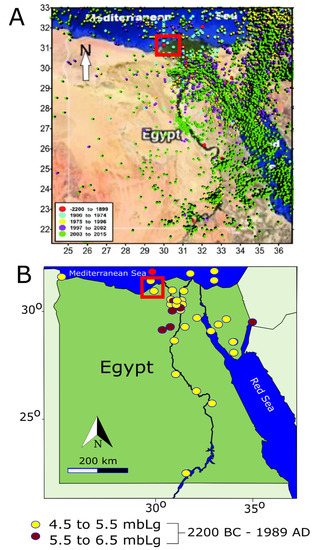
Figure 8.
(A) General distribution of the historical record of earthquakes in Egypt (2200 BC to 2015 AD). (B) Map of historical earthquakes with their magnitudes from 2200 BC to 1989 AD, after [61]. Red squares represent the Alexandria area.
Additionally, Alexandria’s land subsidence ranges from 0 to −5 mm yearly. From 2017 to 2020, the vertical displacement/deformations in Alexandria were −60 mm with an average of −12.5 mm and a mean displacement rate of −1.73 mm/yr [62]. Moreover, another study suggested that Alexandria was subjected to 0.4 mm/yr on average and up to 2 mm/yr locally over the last decade after analysis using GPS and persistent scattered interferometry data [63]. It was mentioned that the subsidence rate in Alexandria during the last 60 years was 2 mm/year. In addition, the average rates of land subsidence in Alexandria from 0.9 to 4.3 mm/year, from the west to the east along the northern delta coast, vary irregularly with an average of ~2.5 mm/year [45]. SLR, earthquakes, and other natural hazards from the Ptolemaic era until the Arabic era caused land subsidence and affected the archaeological landscape, such as the ancient Royal Port in Alexandria, which is 1 km from Anfushi’s Necropolis [64].
4.3. Environmental Factors
4.3.1. Storminess
Alexandria experiences approximately 16 strong storms yearly with strong winds, high waves, and heavy rains, especially in the winter season [65]. In 2010, storm waves were measured with heights of 7.7 and 6.8 m [66]. Most heavy storms (Nawat, local name) occur between September and March each year, with a minimum of two days and a maximum of eight days (Table 1).

Table 1.
Some recorded heavy storms in Alexandria with expected dates and durations. From [65].
4.3.2. Flooding
Heavy rainfall and tidal actions are the main reasons for flash and coastal flooding in Alexandria [67]. On 25 October and 4 November 2015, Alexandria experienced a rare rainfall storm with 100 mm/h, which led to the worst flooding for decades because 60% of the city was covered by water from 0.5 to 1 m [68]. Accordingly, Alexandria is considered one of the five coastal cities that have the risk of flash flooding and coastal flooding [69]. Young [70] said that rainfalls with a 50 mm event would have a higher severity, as well as rainfalls with 20 mm rainfall, resulting in significant flooding. In 2020, the maximum tide in Alexandria occurred on 1 January at 0.40 m, and the minimum tide occurred on February 29 at 0.25 m. In 2022, the minimum tidal action was 0.03 cm, and the maximum was 0.29 cm from 18 May to 31 May 2022 (https://www.seatemperatu.re/middle-east/egypt/alexandria/tides.html, accessed on 31 August 2022). Flooding in Alexandria occurs each winter and has an insufficient drainage system and infrastructure [71]. For this reason, the archaeological sites in Alexandria will be under the permanent impact of wetting and flooding each year as well.
4.3.3. Meteorological Context
Alexandria is considered warm, arid, and clear in the summer, but it is cool, rainy, and windy in the winter. In the summer, the average temperature degree is above 30 °C from June to the end of September. On the other hand, the temperature in the winter is a 5 °C minimum and 18 °C maximum from December to mid-March (Figure 9A) [72]. From the automated weather station at the western harbour (approximately 1 km from Anfushi’s Necropolis), the maximum relative humidity from 2007 to 2018 was 99%, and the minimum relative humidity was 11% [73]. In 2021, the maximum relative humidity was 71%, and the minimum relative humidity was 65% (Figure 9B). Furthermore, the average rainfall in the summer is approximately 30 mm, while the average rainfall in the winter is 166 mm [68]. Hafez [72] said that the average annual rainfall is approximately 200 mm but can reach more than 400 mm. Figure 9C shows the average days of rainfall in Alexandria, and Figure 9D shows the monthly average rainfall in Alexandria in 2021. Due to rapid climatic change, Alexandria has only two seasons: a hot summer from April to September and a moderate winter from October to March. Daytime temperature and wind patterns are the main factors for the difference between the two seasons [74]. In 2021, the maximum wind speed was 44 km/h or 24 kts (strong), and the minimum speed was 7 km/h or 3.78 kts (weak). Wind forces represent 70% of the total dynamic in both sea level, and current and tidal actions represent 30% of the sea level and its current energy (Table 2) [75]. Currently, snow is part of the marine dynamics in Alexandria that affect ancient building materials. After decades, Alexandria was subjected to snowfall in December 2021, and this was considered a rare snow occurrence (Figure 10A,B). However, from time to time, Egypt experiences a cold snap, with low temperatures reaching 2 °C. Bibliographical studies of snowfalls in Egypt and Alexandria are not available; however, it said that Egypt experienced snowfalls in 1639, 1855, and 1934.
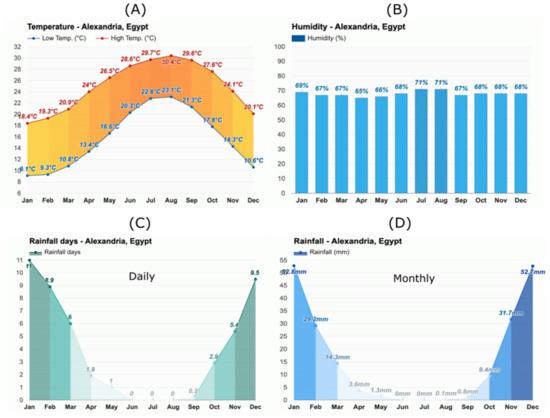
Figure 9.
(A–D) Hyetographs for meteorological average data in Alexandria 2021 of temperature ((A), in °C), relative humidity ((B), in %), rainfall days ((C), in number of days) and rainfall ((D), in mm). After https://www.weather-atlas.com/en/egypt/alexandria-climate. Accessed on 19 May 2022.

Table 2.
Wind dynamics in Alexandria, monthly in 2021 (after https://www.timeanddate.com/weather/egypt/alexandria/historic?month=12&year=2021, accessed on 23 May 2022).

Figure 10.
(A,B) Rare snow falls over Alexandria in December 2021.
4.4. Anthropogenic Damage
In 1899, Guiseppe Batti noticed and explained that many archaeological structures had been destroyed due to mining, quarrying, and other infrastructure activities in the district of El-Mafrouza, a road between El Mex and Anfushi. Some Egyptianizing façades, cornices, a frieze with a winged solar disc, and an architrave had been damaged in one of the hypogea at El-Mafrouza. In addition, some of the funeral structures at Anfushi’s Necropolis were damaged [76]. Currently, the lack of maintenance and the neglect of this important site are considered anthropogenic factors for damage as well.
5. Materials and Methods
To evaluate the impact of environmental dynamics in Alexandria over Anfushi’s Necropolis, in situ visits were carried out to take photographs of the architectural and structural defects and degradation. In addition, deskwork was performed to sketch and map the decay and durability problems of the construction materials through engineering drawings. Satellite images were collected to monitor the problem of sea level rise and its impact on Anfushi’s Necropolis.
Highly weathered fallen archaeological samples were collected from the different parts of Anfushi’s Necropolis (construction materials and rendering mortars) to carry out the assessment study of the decay through analysis and microscopic examination from the construction. Samples of the construction materials were divided into samples from the casing stone and the bedrock with light colour and crust over the surface (Figure 11A,B). The rendering mortar samples were coarse and fine mortars from the first and second layers with blackish and yellowish colours, respectively (Figure 11C). The samples ranged from 3 cm to 7 cm3 in size. In addition, some of the samples had been ground to be ready for analysis purposes.
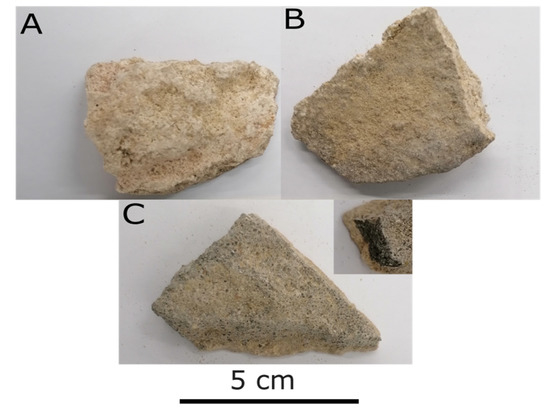
Figure 11.
(A,B) Construction stones (casing and bedrock). (C) Coarse and fine rendering mortars.
To detect the morphological features of the construction materials, a digital microscope was used, and thin sections were prepared and studied using an Olympus BH-2 (Shinjuku-ku, Tokyo, Japan) polarized optical microscope to identify the different minerals, altered phases and textures of the samples. Small fragments were used to detect the durability problems and alterations through the textural features of the samples under high resolution using a scanning electron microscope (TESCAN-performance at 20.00 kV, WD: 17.73 mm and Vac: HiVac, Brno—Kohoutovice, Czech Republic). In addition, an EDS detector (EDAX 60 mm2 Octane Super) was utilized for salt phase detection, degradation patterns, and elemental analysis for the detected salts. X-ray diffraction was utilized to identify the mineralogy of the stones and mortars. For this, a Bruker D-8 Advance ECO diffractometer equipped with a Lynxeye high-speed measurement detector was used under the following conditions: CuKα radiation filtered by Ni, a graphite monochromator, fixed slots, and a 2theta 5° to 60° scanning angle; diffractograms were interpreted with the software software Diffrac. EVA V.3.0 (Bruker-AXS) (Bruker Corporation, Billerica, MA, USA). A Bruker AXS M-4 Tornado sequential dispersive wave X-ray spectrometer with an Rh tube operating at 4000 W (XRF) was used to recognize the major and trace elements.
6. Results
6.1. In-Situ Recordings
Over the years, earthquakes in Alexandria have affected the archaeological site of Anfushi’s Necropolis and its structural stability. During ground motion, the accelerations of the earthquake go through the foundation and bedrock to the building structures. Accordingly, earthquake-induced damages are recorded and monitored, such as (1) the horizontal displacement of some blocks; (2) vertical and horizontal wall displacements; (3) cracks and fractures (approximately from 2 to 4 mm of space); (4) collapsed ashlars and walls; (5) opened joints between blocks; and (6) chippings in most of the built structures (Figure 12A,B). The bedrock has its own geotechnical problems because the unconsolidated limestone presents many cavities, which affect the durability of the tombs and accelerate the ground motion of the earthquakes to be transmitted rapidly from the bedrock to the tomb structures (Figure 12C,D). Moreover, water reaching the ground level of the necropolis was monitored, which is considered a damaging factor for the necropolis as well. In this case, water could cause cavities in the bedrock and be responsible for the deterioration of the architectural and structural elements of the necropolis (red arrows, Figure 12C,D). In general, it has been observed that trees and vegetation around the necropolis and near the tomb structures could be an additional factor as a mechanical force (Figure 12A,C), and salt weathering, biological attack, discolouration, cracking, loss of material, and flaking are the main decay patterns for the walls and ceilings with decorative motives due to dampness. Finally, Figure 12E shows the accumulation of water inside room number four of tomb number five. It is observed that the level of water rise reached to more than 50 cm over the painted walls.
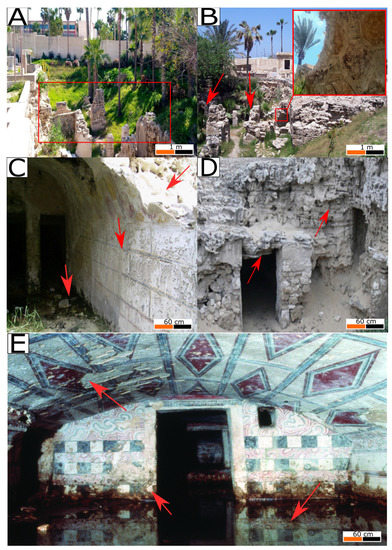
Figure 12.
(A,B) Structural damage aspects due to earthquakes. (A) The red rectangle refers to the deformations in the structures. (B) The red arrows refer to collapse and displacement of the blocks and opened joints, and the red square refers to the damage to walls with chipping. (C) Water intrusion impact on the architectural and structural elements of Anfushi’s Necropolis. Red arrows refer to biological growth, salt accumulation, and degradation of the stone and painting layers. (D) Geotechnical problems and unconsolidated bedrock with many cavities, as shown by the red arrows. (E) Dampness impact over the structural and decorative elements of tomb No 5 (burial unit) at Anfushi’s Necropolis. Red arrows refer to flaking, salt erosion, and biological attack on the tomb’s construction materials [77].
Moreover, many aspects of decay were recorded, such as alveolarization, exfoliation, flaking, salt erosion (efflorescence and subflorescence), discolouration, blistering, spalling and cracking. In this sense, Figure 13A shows the severe state of preservation due to the degradation that occurs in the side room for one of the tombs of Anfushi’s Necropolis. In that room, the degradation aspects are efflorescence and subflorescence, discolouration, blistering, eroded edges, chipping, paint layer removal, and cracking. In addition, we can see the horizontal displacement and cracking on the front wall from approximately 2 to 5 mm. In Figure 13B, the main degradation aspects include exfoliation, flaking, peeling, spalling, blistering, pitting, rising damps, subflorescence, discolouration, and loss of the painting layer. In addition, Figure 13C shows the alveolarization, chipping, and pitting decay forms in the front of the wall, but on the ceiling, the main degradation patterns are efflorescence and subflorescence, discolouration, and paint layer removal. Figure 13D,E show two historical photos that date back to 2010 and 2018 for the same area, respectively, where Figure 13D shows a complete ritual scene with its painting layer in a good state. On the other hand, Figure 13E shows the same scene after the loss of most of the painting layers and salt attachment due to marine conditions. In both photos of Figure 13D,E show a displacement of the wall can be observed (out of plane) above the Egyptian-style scene which was estimated by approximately 10 mm. Finally, after taking different photographs, digital recordings were taken to monitor and evaluate the deterioration patterns in different areas for different architectural elements of Anfushi’s Necropolis, showing that salt erosion, the loss of materials, the loss of painting layers, flaking, and cracks are the most dominant decay aspects over the surfaces (Figure 14A–C).
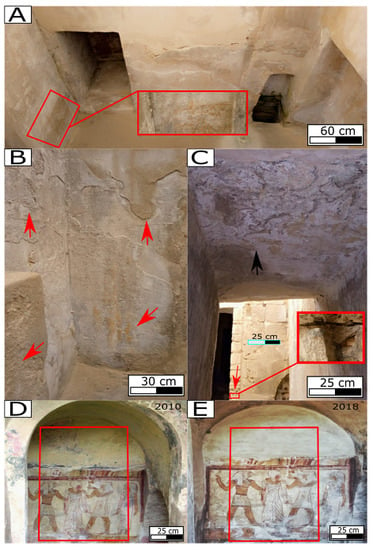
Figure 13.
(A–C) Different kinds of decay patterns due to the marine environment the walls are in. (A) The red rectangle refers to areas with efflorescence, subflorescence, edge eroding, flaking, and loss of the painting layer in the courtyard of tomb No 4. (B) The red arrows refer to flaking, exfoliation, salt erosion, surface disintegration, and loss of the painting layer in the courtyard of tomb No 4. (C) Red squares refer to honeycomb and loss of material decay patterns, and black arrows refer to salt precipitation and loss of the painting layer in the corridor to the burial units of tomb No 4. (D) A ritual scene in the necropolis and its state of preservation state in 2010 from tomb No. 2 (back wall of the burial chamber) (from https://mapsus.net/EG/necropolis-of-anfushi-5577, accessed on 1 June 2022). (E) The same ritual scene after 8 years, with a worsened state of preservation, where a large loss of the painting layer and renderings occurred due to the salt attack (from https://www.meretsegerbooks.com/gallery/581/anfushi-necropolis, accessed on 1 June 2022).
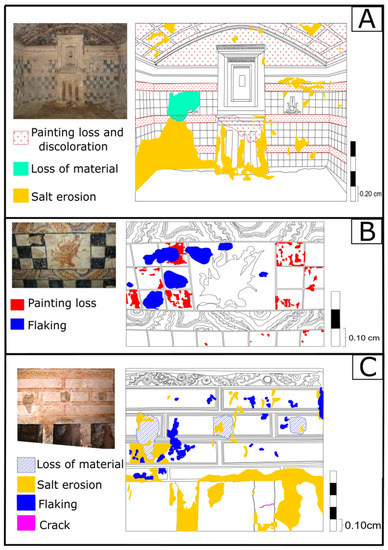
Figure 14.
(A–C) Different decay patterns for various architectural elements of Anfushi’s Necropolis, where salt erosion is the main decay pattern on the surfaces in tomb No 2 rooms 1 and 2.
6.2. Sea Level Rise Impact (SRL) and Future Scenarios
Currently, SLR is considered the main hazard for the archaeological sites in Alexandria. Accordingly, the probabilistic analysis and assessment of the future impacts of SLR were carried out through satellite image observations from the accessible Climatic Central Analysis (CCA) (http://sealevel.climatecentral.org, accessed on 10 June 2022). Different topographical scenarios with an SLR ranging between 0.5 and 3 m were evaluated. The results showed that the morphological scenario of 0.5 m SLR would not cover Anfushi’s Necropolis with water (Figure 15A), but the 1 to 3 m SLR scenarios would submerge it completely (Figure 15B–F).
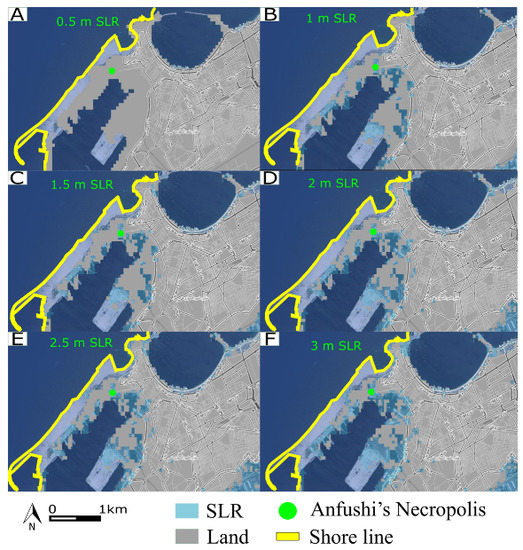
Figure 15.
(A–F) Various scenarios for SLR influence on Anfushi’s Necropolis.
6.3. Construction Materials Characterization
6.3.1. Petrographic Description
The thin section of the bedrock sample (BR, Figure 16A,B) shows a creamy oolitic limestone with recrystallized sparitic cement (early gravitational cement) and late geopetal micritic infills. Significant pores with rhombohedral calcite crystals exist due to their formation in the absence of coccolithophorids. In addition, this kind of stone is made up of large intraclasts and sand-sized spheres (ooids/oosparite) of calcium carbonate. Fossil allochemical fragments of echinoderms, corals, red algae, bryozoans, gastropods, and foraminifera are present and distributed in the matrix with carbonate in peloid and pellet shapes. Rare subangular to rounded quartz grains are presented. Casing stone (CS, Figure 16C,D) is considered a creamy fossiliferous micritic limestone. Calcite is embedded in a micrite matrix rich in benthic foraminifera (Pseudochrtsalidina Conica), nummulites, bivalves, molluscs, ostracods, sponge spicules, and other bioclasts. Rare subangular to angular quartz grains are also present. Coarse-grained rendering mortar is present after the stone casing layer (CRM, Figure 16E,F), and from the morphological features, the main constituent of the mortar is quartz, which is poorly sorted, polycrystalline, and angular to subangular. In addition, some quartz grains have undulatory extinction, and others are monocrystalline with normal extinction and a maximum diameter of 2 mm. Quartz grains are embedded in a micritic matrix with rock fragments, chert, plagioclase, and opaque minerals (iron oxides). Figure 16G,H represent the fine-grained rendering mortar (FRM) before painting layer application. Subangular to rounded quartz grains are well sorted, and the maximum grain size is 0.5 mm in diameter and embedded in a micritic matrix.
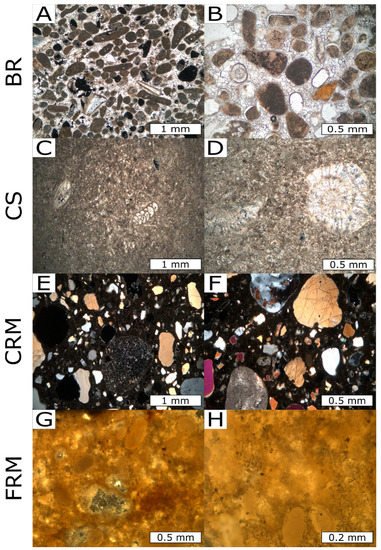
Figure 16.
Photomicrographs of the geological and archaeological prepared thin sections. (A,B) Bedrock (BR) oolitic limestone with recrystallized sparitic calcite cement and sand-sized spheres (ooids/oosparite). (C,D) Casing stone (CS), creamy fossiliferous micritic limestone, and calcite embedded in a micrite matrix rich in benthic foraminifera. (E,F) Coarse-grained rendering mortar (CRM) with quartz grains which are poorly sorted, polycrystalline, and angular to subangular; grains embedded in a micritic matrix with rock fragments. (G,H) Fine-grained rendering mortar (FRM) has well-sorted quartz grains, subangular to rounded, and these grains are embedded in a micritic matrix.
6.3.2. Mineralogical and Chemical Characterization
Semiquantitative mineralogical analysis using XRD (Table 3) revealed that the BR consists of calcite (very abundant), aragonite (abundant) and halite (rare) (degradation compound). The CS is composed of calcite (very abundant), halite (abundant), and gypsum (rare), where halite and gypsum are considered degradation compounds. Regarding the mortar samples, the CRM is composed of quartz (very abundant), calcite (abundant), and halite (rare), while the FRM consists of calcite (very abundant) with minimum amounts of quartz, gypsum, and aragonite.

Table 3.
Mineralogical analysis of Anfushi’s Necropolis samples. BR: bedrock; CS casting stone; CRM: coarse-grained rendering mortar; FRM: fine-grained rendering mortar; Cal: calcite; Qz: quartz; Gp: gypsum; Ar: aragonite and Hal: halite (+++ very abundant; ++ abundant; + rare, − not detected).
Elemental analysis via XRF and EDX was carried out to confirm the results of the mineralogical interpretation (Table 4). The results responded well to the XRD results. The BR is mainly composed of calcium (93%) and chloride, silica, potassium, sulphates, and strontium as scarce elements. The CS is mainly composed of calcium (83%), and sodium, chloride, sulphates, iron, magnesium, potassium, and strontium are detected as rare. The CRM is mainly composed of silica (54%) and calcium (36%), with sulphates, chloride, aluminium, potassium, magnesium, and iron as scarce elements. Finally, the FRM is composed of calcium (70%) and silica (18%), plus sulphates, chloride, iron, sodium, potassium, and strontium. Chloride was detected in all samples as a degradation element. In addition, strontium is considered a significant trace element that is a signature of the coastal environment’s impact on buildings because seawater contains approximately 8 mg/L strontium [52]. Moreover, halite and gypsum were detected in all samples with different ratios. For this, the content of halite and gypsum salts was calculated by dividing the total molecular weight of each salt on the molecular weight of the Cl and SO3 on for all samples. In the BR sample, the content of halite is 3.5% and gypsum is 0.6%. In the CS sample, the halite content is 5% and gypsum is 3%. In the CRM sample, halite is 1.8% and gypsum 2.3%. Finally, in the FRM sample, halite is 3.5 and gypsum is 2.3%. In this sense, it is clear that the two main decay salts are halite and gypsum, and they were detected with high content in the CS and FRM samples. In the FRM, gypsum could be an additive component to the preparation layer of paintings.

Table 4.
Elemental analysis of major and minor elements, expressed in oxides (wt. %), for the Anfushi’s Necropolis samples. BR: bedrock; CS casting stone; CRM: coarse-grained rendering mortar; FRM: fine-grained rendering mortar.
6.3.3. Macroscopic and Microscopic Investigation
Binocular microscopy was used to examine the textural and morphological features, detecting the alterations and weathering aspects on the surfaces due to the marine environment impact. Figure 17 represents the BR sample, where salt attack (efflorescence) is well observed on the surface and disintegration of the stone surface is seen. Figure 17B shows the morphological texture of the CS, and salt erosion is considered the main feature of decay for the stone surface. Furthermore, Figure 17C represents the coarse-grained rendering mortar, where quartz grains are well shown with different sizes in the lime matrix. Disintegrated quartz grains and some gaps are detected. Figure 17D shows a homogenous surface of the fine-grained rendering mortar and yellowish colour due to the high amount of lime with a minor amount of gypsum. In addition, there are a few quartz grains in the matrix. From textural observations, salt covers most of the mortar surface.
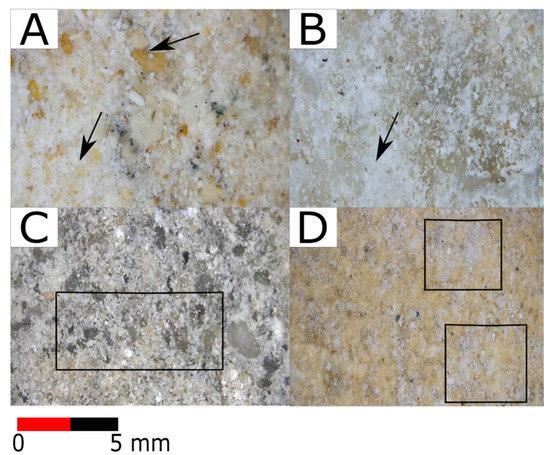
Figure 17.
(A–D) Photomicrographs under a binocular microscope for the bedrock (BR), casting stone (CS), coarse-grained rendering mortar (CRM), and fine-grained rendering mortar (FRM). Black arrows and rectangles show the ooids, quartz grains, disintegration, and salt crusts on different samples. Apparently, salt erosion is the main feature of deterioration for all samples.
On the other hand, microscopically, the building materials were examined under a scanning electron microscope (SEM) with high resolution to evaluate the impact of marine dynamics on the building materials and their alterations/byproducts. For the BR, Figure 18A shows the morphological texture of the BR with a wide large-angle view for the bedrock sample. Euhedral to anhedral halite crystals with changeable habits and different growth phases are present due to the inhomogeneous absorption of the aqueous solution (Figure 18B). The initial state of gypsum nucleation formed in needle-like crystals along with halite crystals and gaps are observed as well (Figure 18B). Figure 18C,D represent the morphological features and decay of the casing stone, where Figure 18C shows the surface filled with pores and gaps, and Figure 18D shows the distribution of the mesostructured halite, which is integrated with the stone surface. Microfissures and pores are present on the surface. Figure 18E–H display the decayed surface of the coarse-grained rendering mortar. In Figure 18E,D, the textural features exhibit the disintegration of the mortar, with many gaps and pores and the precipitation of the salt enveloping the quartz grains and filling the pores intensively. Furthermore, in Figure 18G, quartz grains are distributed with different sizes in the white lime matrix. Figure 18H shows the textural features of the mortar mixed with the precipitation of halite crystals (cubic and amorphous phases) and gypsum (needle habit). Finally, for the FRM, Figure 18I shows a lime–gypsum matrix with many pores and pitting in between. In Figure 18J, the precipitation of halite crystals is observed, and the needle habit of gypsum is present as an additive to the rendering mortar before the painting layer. Finally, an EDS detector was utilized to detect and carry out elemental analysis for the salts on the surface for one of the selected samples of bedrock (BR) (Figure 19A–C).

Figure 18.
Micromorphological features of the construction building materials of Anfushi’s Necropolis. (A,B) The oolitic limestone (BR, bedrock) surface texture with halite cubic crystals and needle-like gypsum. (C,D) The fossiliferous micritic limestone (CS, casing stone) morphological texture with halite crystal perceptions, pores and microfissures. (E–H) The coarse-grained rendering mortar (CRM) textural features with disintegrated grains, precipitation of halite (cubes), gypsum (needles), and detection of gaps and pitting. (I,J) Fine-grained rendering mortar (FRM) textural aspects with depositing halite mixed with needle-like crystals of gypsum, in addition to gaps and pitting. Red squares and rectangles refer to the disintegration feature of the samples due to salt weathering impact. Scales are expressed in microns. BR: bedrock; CS casting stone; CRM: coarse-grained rendering mortar; FRM: fine-grained rendering mortar; Hl: halite; Cal: calcite; Qz: quartz; Gp: gypsum.
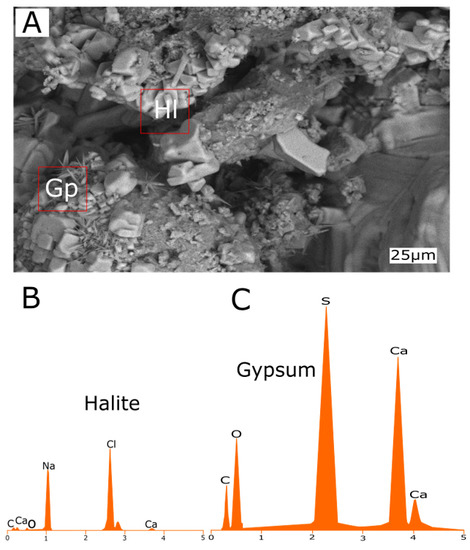
Figure 19.
(A) Micromorphological feature of bedrock (BR) with halite cubic crystals and needle-like gypsum, and the red squares were analysed elementally using EDS. (B,C) EDS elemental analysis results for halite and gypsum salts for one of selected samples from bedrock of the necropolis.
6.4. Digital Mapping
The heritage digitalization approach is considered a reproduction of physical interactions and interventions. Remote recontextualization and interactive models for heritage are necessary since the world of conservation and restoration should follow up all advanced technologies to help protect world heritage. Indeed, the virtual recording and mapping of monuments will decrease the physical interventions to the monuments and increase their authenticity and value [78]. In addition, using computer mapping methods can reduce the mistakes of intervention by restorers, which will help save money for the budgets of restoration projects [79]. In this regard, mapping of the architectural and structural elements was carried out to preserve the archaeological site of Anfushi’s Necropolis using AutoCad 2020. The process is important for virtual archiving to protect our heritage for the next generation, and some maps were made for virtual retouching with the original tones of colours of the paintings and the significant motifs of Anfushi’s Necropolis, and this will help in future restoration work. Geometrical surveys, documentation, data processing, interpretation, the creation of 2D models/maps, editing, and rendering were taken into consideration in the work during the digital restoration, as shown in Figure 20A–D.
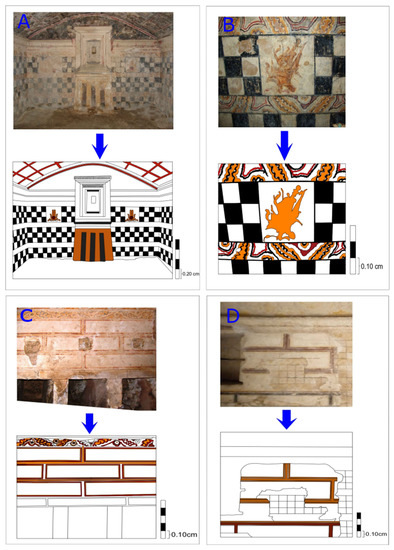
Figure 20.
(A–D) Digital restoration of some selected structural and architectural elements in Anfushi’s Necropolis (walls of tomb No 2, rooms 1 and 2) using AutoCAD 2020.
7. Discussion
Anfushi’s Necropolis is considered a rock cut in oolitic limestone as the bedrock and is placed near the shore. Different aspects of marine dynamics have affected Anfushi’s Necropolis, such as SLR, coastal and flash flooding, storminess, earthquakes, and various climate factors (temperature variations, rainfall, humidity, and wind), in addition to all anthropogenic factors that can affect historical buildings. The consequences of the marine dynamics led to the resilience/durability weakness of the Necropolis construction elements.
Historical pieces of evidence confirmed the sudden increasing rate of SLR. In this sense, this research has depended on some historical satellite images that enabled us to monitor the SLR rate through submergence phenomena. Figure 21A,B) shows two historical satellite images (2012 and 2013) that display the submergence of an ancient structure (old breakwater) in the eastern harbour (Island of Pharos). Figure 21C displays an old photo of the same area before its submergence in 1916. Figure 21D shows a recent Google Earth image (2022) with anthropogenic intervention via artificial nourishment using sands. Accordingly, Stanley et al. [80] confirmed that many ancient port structures and old coastal structures were submerged due to SLR. For these reasons, this research presented different SLR scenarios (Figure 15) on Anfushi’s Necropolis through satellite image observations from climatic central analysis (CCA), and the results showed us that a rise of more than 1 m would submerge Anfushi’s Necropolis completely. In this regard, Bekheet et al. [28] put the Anfushi area in the risk zone of the 1.5 m SLR scenario, and Shaltout et al. [81] confirmed that Alexandria was subjected to an observable SLR of 0.5 cm yearly before a High Dam was built, and after this was built, it became subject to 0.2 cm SLR yearly. Moreover, in their report about climate change, the World Bank [82] reported that the SLR will reach +0.20 m by 2030, and regardless of the scenario of SLR, the SLR will increase during the next few decades and the next century by more than the currently observed rates. This yearly increase in SLR has had a negative impact on the durability of Anfushi’s Necropolis. For example, the water level reached 30 cm on the ground of the necropolis as a result of water infiltration inside the tombs and caused salt weathering and deformations to the most of the walls and their valuable paintings.
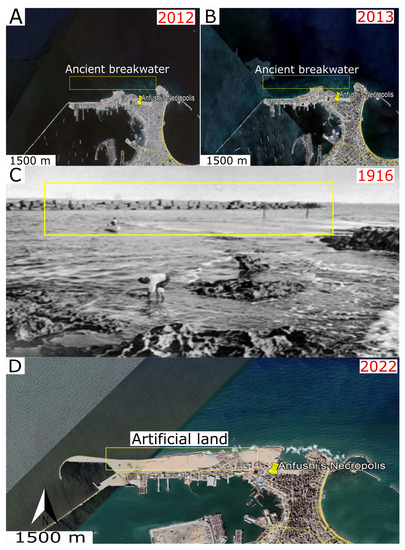
Figure 21.
(A,B) show two satellite images (2012 and 2013) confirming the submergence of the ancient structures. (C) Old photo (1916) of the same area before the submergence of the ancient structures, from [83], and a recent Google Earth image (D) for the same area with nourishment interventions.
Structural deficiencies were photographed and recorded due to the historical earthquakes’ effect on Anfushi’s Necropolis. These structural deformations are erosion, collapses, and horizontal displacements. Kázmér [84] explained that these earthquake-induced damages are caused to ancient structures as well. In addition, the geotechnical problems and the unconsolidated limestone of the bedrock of the tombs accelerated the impact of earthquakes in damaging the necropolis because the low-quality bedrock could amplify the ground motions during the earthquakes, which made the structure of the tomb more vulnerable to earthquake damage. In this sense, Hemeda et al. [33] observed that the tombs of the Necropolis of Mustafa Kamil in Alexandria are not structurally safe for PGA (peak ground acceleration) values greater than 0.07-0.08 g. Furthermore, Mohamed et al. [43] confirmed that 25 strong earthquakes hit Alexandria from 320 to 2000 AD. These earthquakes definitely affected the structural states of the buildings, and the response at some sites was strong and damaging due to the site effect and unconsolidated deposits (soil problems/geotechnical problems). In this sense, Hamouda et al. [64] established that the ancient royal port of Alexandria approximately 1 km from Anfushi’s Necropolis was influenced by land subsidence due to SLR, earthquakes, tsunamis, and sediment mass failure, where all these environmental actions caused land subsidence in Alexandria from the Ptolemaic era until now.
Alexandria is vulnerable to both flooding by rains and SLR, especially in the last two years in the winter season, due to the high dynamics of the coastal environment of Alexandria and rapid climate change. Alexandria is subjected to approximately 16 storms yearly during the winter season accompanied by strong winds, high waves, and heavy rains [65,67]. Accordingly, the in-situ observation confirmed the gathering of water in the chambers due to flash flooding and storminess with high waves of the sea (Figure 12E). The water inside Anfushi’s Necropolis reached 30 cm over the ground, causing dampness in the architectural and structural elements through capillary actions. Thus, the main observed deterioration aspects were salt erosion, spalling, layering, disintegration, and structural deformations.
The chemical analysis showed that halite is the main alteration compound and appeared in all compositional and elemental analyses. Halite is a soluble salt that becomes present in buildings mainly from sea spray precipitation. Additionally, it could come from gathered water from flooding in the ground, saline rainwater, or even condensed atmospheric humidity. Efflorescence and subflorescence are considered the main decay patterns of salt erosion in most architectural and structural elements. Examination using a scanning electron microscope for the building materials (stones and mortars) showed interaction between the stones and mortar surfaces with halite crystals, which nucleated heterogeneously and severely eroded the surfaces in their crystalline form or in the brine inside the pores or on the surface. The crystallization and recrystallization process of the halite salt led to the bleeding of the stone with many pores and pitting (disintegration), as shown in the microscopic results. In this regard, Benavente et al. [85] reported that salt crystallization in porous stones mainly occurs on the surface of the porous stone (efflorescence) and within the porous media of stone (subflorescence), and they confirmed that the halite salt source is mainly attached to sea spray. In addition, halite crystallization could exist as result of humidity fluctuations under and above 75% RH. In this sense, Sato and Hattanji [86] said that halite is deliquescence salt and has the affinity to absorb moisture from the surrounding environment, causing severe salt weathering to stones. Finally, the calculations of halite content from the elemental chemical analysis revealed that the casing stone (CS) contains the highest content from all the samples with 5%, but in the bedrock (BR) and fine rendering layer, the content is 3.5%. Thus, it is easy to find degradation features such as spalling, flaking and powdering in many parts of the necropolis as a result of salt weathering along with climatic factors.
Gypsum is detected in the fine-grained rendering mortar as an additive to the mortar constituents with lime and quartz. In addition, gypsum is present in the casing stones behind the rendering layers with 3% as decay salt from the elemental chemical analysis result. In this case, gypsum could be delivered to the stone via immigration from the rendering mortar, causing salt attack on the stone [25]. The examination via SEM confirmed the existence of needle-like gypsum salt along with the crystals of halite. Charola et al. [87] mentioned that gypsum has low solubility and is less aggressive, but damage due to gypsum occurs in the case of dehydration–hydration reactions causing internal forces and cracks. In addition, strontium is detected in most of the samples as a significant trace element that is a signature of the marine environment’s impact on buildings because seawater contains approximately 8 mg/L strontium [52].
Furthermore, the content ratio of the existing salts is considered reasonable a value for salt weathering for the stone surfaces and the paintings, especially with halite, which has been estimated to be 5% in the casing stone sample. Compared with the previous study of [86], they confirmed the erosive role of 0.5, 5.3, and 7.7 of halite content (gram weights of salt in a 100 g salt-free rock specimen) in stone degradation.
The dynamics of climate, such as variations in temperatures, wind, humidity, and rainfall, have affected the building materials of Anfushi’s Necropolis. Fluctuations in temperature degrees daily and seasonally led to expansions and shrinkages in the building materials [88]. This thermal differentiation could lead to the cracking of surfaces and rendering layers’ separations due to the various thermal coefficients between the minerals (calcite, quartz, gypsum, and halite) in the construction materials and their alterations. Mart et al. [89] explained the destructive impact of the mismatched thermal expansion values between salt (halite) and stone (calcite), where halite thermal stress is 35 GPa and could cause changes in the tensile strength of the stone with daily and seasonal changes in temperature degrees. When the stone hosts a high amount of halite, the higher thermal stresses will lead to cracks and flaking decay patterns, as observed in this necropolis. In addition, the changes in temperatures could cause severe damage because of phase changes for the salts and microclimate. In this context, Grossi et al. [90] said that halite salt can crystallize at a fixed humidity regardless of the temperature, and gypsum can be susceptible to crystallization due to changes in humidity and temperature. Moreover, wind power is considered one of the causes of the necropolis building materials’ decay, especially the wind speed in Alexandria, which reaches 44 km/h (strong), and wind power is considered to be 70% of the total dynamic in both sea level and current [75]. The wind is considered a way of transferring halite salt (marine spray) from the sea to construction materials. In addition, wind is responsible for the formation of alveolar weathering (honeycomb) in the stones because hollows that are filled with salt are washed away by the wind [91]. As an exceptional and recent case, very low temperatures could be considered a new and future environmental phenomenon in Alexandria. Last year, Alexandria experienced rare snowfalls that could affect the construction materials of Anfushi’s Necropolis (Figure 10). Snow can deteriorate the construction materials by soaking water inside the pores of building materials, followed by cooling, which causes delamination and spalling as decay patterns. Moreover, probable subsequent and repeated freezing events in the following years could deteriorate the material if the water content from rainfall or a high-humidity environment is higher than the critical degree of saturation for the material at the time of freezing [92].
Anthropogenic actions are considered one of the damaging factors to the structures of Anfushi’s Necropolis due to ancient mining, quarrying, and other infrastructure activities around the necropolis in 1899 [76]. Recently, neglect of the archaeological site without any preservation interventions has also been regarded as an anthropogenic factor. From field observations, trees and shrubs around the tombs of the necropolis affected the tombs mechanically and biologically, especially the trees, which can cause mechanical damage to structures through roots during growth. In this sense, Loperte et al. [93] mentioned that the roots of trees could cause direct and indirect damage to structures of historic buildings in the case of direct contact between tree roots and the building or through shrinkable soil indirectly, as is happening in this site.
From all of the above and field observations, the various marine dynamics factors (coastal surrounding environment and salt decay) have resulted in much structural and architectural decay in Anfushi’s Necropolis, such as the displacement of walls, cracking, collapse, block chipping, salt erosion (fluorescence and subflorescence), flacking, spalling, the loss of material, alveolarization, layering, disintegration, pitting, and the loss of painting layers.
Finally, this study presented a digital reconstruction and restoration of the architectural and structural elements of Anfushi’s Necropolis through engineering drawings. In this regard, this part of digitalization is considered a significant contribution to safeguarding this important necropolis for the next generation as part of world heritage, especially with the new world of digitalization. We believe this virtual restoration and reconstruction is essential for any upcoming restoration project for this site. In addition, these maps and models will help to achieve low-cost restoration projects with minimum physical interventions. This archaeological site of Anfushi’s Necropolis is urgently requiring restoration, conservation, and site management.
8. Conclusions
The research presented the durability problems regarding the construction materials of Anfushi’s Necropolis and the impact of environmental dynamics in Alexandria on the necropolis tombs. The tombs were excavated in the oolitic limestone ridge and covered by fossiliferous limestone. This necropolis was painted on two different preparation mortars. The first preparation mortar is coarse-grained, and the second preparation layer is fine-grained. These construction materials have been subjected to different factors of damage and decay, such as SLR, coastal and flash flooding, storminess, earthquakes, and various climate factors (temperature variations, rainfall, humidity, and wind).
The main decay patterns are structural cracks, horizontal displacement for the walls, block chipping, and collapses. These are in addition to flaking, spalling, salt erosion, the loss of materials, delimitations, alveolarization, and the discolouration of the painting layer due to marine dynamics (earthquakes, flooding, windstorms, sea spray, and climatic conditions). Moreover, SLR is considered a future risk for the necropolis that will lead to the full submergence of the necropolis at 1m SLR during the next few decades. Halite, as an aggressive soluble salt, is considered the main decay factor for architectural elements and their surfaces. The efflorescent and subflorescent precipitation of halite and gypsum were observed on all surfaces of Anfushi’s Necropolis and were detected via analytical and microscope investigation in all samples. The water level inside Anfushi’s Necropolis reached 30 cm over the ground as a result of flooding and heavy rains, causing dampness of the architectural and structural elements through capillary actions. The main observed deterioration aspects related to this are salt erosion, spalling, layering, disintegration, and structural deformations. The responsibility for the destruction and poor state of preservation of the necropolis lies not only with marine dynamics and environmental conditions but also anthropogenic interventions which played a role in the destruction of some structural elements, along with the recent failure to give due care to this important heritage site. Finally, this paper participated in the mapping and recording of some selected architectural and structural elements of Anfushi’s Necropolis through vector sketches with the retouching of original tones of colours for the paintings to help in the retouching and restoration works in the future.
Author Contributions
A.F., E.M.-P., J.M.-L. and S.D.-B. contributed to the conception and design of this study. A.F., E.M.-P. and S.D.-B. carried out the laboratory tests. A.F. wrote the first draft of the manuscript. E.M.-P., J.M.-L. and S.D.-B. contributed to the discussion of the results and collaborated in the writing of the different sections of the manuscript. E.M.-P. and S.D.-B. contributed to the funding acquisition. P.M. took part in the scanning electron microscopy and thin section preparations. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This research received no external funding.
Data Availability Statement
Data sharing is not applicable to this article, as no datasets were generated or analysed during the current study.
Acknowledgments
A. Fahmy acknowledges SCiCYT and UGEA-PHAM at Cadiz of University for carrying out the main part of the archaeometrical analysis. E. Molina Piernas acknowledges co-funding from the European Social Fund (D1113102E3) and Junta de Andalucía. We acknowledge Philip Machev from the Faculty of Geology and Geography at Sofia University (Bulgaria) for carrying out scanning electron microscope imaging and preparing the thin sections. We acknowledge Francois Olivier for providing us with the photographs of Anfushi’s Necropolis in Figure 1C, Figure 2B and Figure 12C,D.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
References
- Sullivan, S.; Mackay, R. Archaeological Sites: Conservation and Management; J. Paul Getty Trust: Los Angeles, CA, USA, 2012; Available online: https://www.getty.edu/publications/resources/virtuallibrary/9781606061244.pdf (accessed on 5 May 2022).
- Vousdoukas, M.I.; Clarke, J.; Ranasinghe, R.; Reimann, L.; Khalaf, N.; Duong, T.M.; Ouweneel, B.; Sabour, S.; Iles, C.E.; Trisos, C.H.; et al. African Heritage Sites Threatened as Sea-Level Rise Accelerates. Nat. Clim. Chang. 2022, 12, 256–262. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cassar, M.; Pender, R. The impact of climate change on cultural heritage: Evidence and response. In Proceedings of the 14th Triennial Meeting, The Hague, The Netherlands, 12–16 September 2005; pp. 610–616. Available online: https://discovery.ucl.ac.uk/id/eprint/5059/ (accessed on 12 May 2022).
- Gehrels, R.; Garrett, E. Rising sea levels as an indicator of global change. In Climate Change; Elsevier B.V.: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2021; pp. 205–217. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nicholls, R.J. Adapting to Sea-Level Rise. Resilience; Elsevier Inc.: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2018; pp. 13–30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marzeion, B.; Levermann, A. Loss of Cultural World Heritage and Currently Inhabited Places to Sea-Level Rise. Environ. Res. Lett. 2014, 9, 034001. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.; Jia, X.; Liu, Z.; Zhao, L.; Sheng, P. The potential impact of rising sea levels on China’s coastal cultural heritage: A GIS risk assessment. Antiquity 2022, 96, 406–421. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lewis, R. Sea-Level Rise and Subsidence Effects on Gulf Coast Archaeological Site Distributions. Am. Antiq. 2000, 65, 525–541. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Daly, C. Climate Change and the Conservation of Archaeological Sites: A Review of Impacts Theory. Conserv. Manag. Archaeol. Sites 2011, 12, 293–310. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dawson, T.; Hambly, J.; Kelley, A.; Lees, W.; Miller, S. Coastal heritage, global climate change, public engagement, and citizen science. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2020, 117, 8280–8286. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fluck, H.; Dawson, M. The Historic Environment: Policy & Practice Climate Change and the Historic Environment. Hist. Environ. Policy Pract. 2021, 12, 263–270. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bickler, S.; Clough, R.; Macready, S. The Impact of Climate Change on the Archaeology of New Zealand’s Coastline A Case Study from the Whangarei District; Publishing Team. Department of Conservation: Wellington, New Zealand, 2013. Available online: https://www.doc.govt.nz/documents/science-and-technical/sfc322high_res.pdf (accessed on 16 May 2022).
- Westley, K.; Mcneary, R. Assessing the Impact of Coastal Erosion on Archaeological Sites: A Case Study from Northern Ireland Assessing the Impact of Coastal Erosion on Archaeological Sites: A Case Study from Northern Ireland. Conserv. Manag. Archaeol. Sites 2014, 16, 185–211. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Anderson, D.G.; Bissett, T.G.; Yerka, S.J.; Wells, J.J.; Kansa, C.; Kansa, S.W.; Myers, K.N.; Demuth, R.C.; White, D.A. Sea-level rise and archaeological site destruction: An example from the southeastern United States using DINAA (Digital Index of North American Archaeology). PLoS ONE 2017, 12, e0188142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Harkin, D.; Davies, M.; Hyslop, E.; Fluck, H.; Wiggins, M.; Merritt, O. Impacts of climate change on cultural heritage. MCCIP Sci. Rev. 2020, 16, 24–39. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Andreou, G.M. Monitoring the impact of coastal erosion on archaeological sites: The Cyprus Ancient Shoreline Project. Antiquity 2018, 92, e4. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Andreou, G.; Blue, L.; Breen, C.; Safadi, C.; El Huigens, H.O.; Nikolaus, J.; Ortiz-Vazquez, R.; Westley, K. Maritime endangered archaeology of the Middle East and North Africa: The MarEA project. Antiquity 2020, 94, e36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bolton, J. An Assessment of the Vulnerability of Coastal Stone Monuments in Ireland. Doctoral Thesis, Technological University Dublin, Dublin, Ireland, 2009. Available online: https://arrow.tudublin.ie/builtdoc/9/ (accessed on 19 May 2022).
- Morillas, H.; França, F.; Filho, D.M.; Derluyn, H.; Maguregui, M.; Grégoire, D.; Manuel, J. Decay processes in buildings close to the sea induced by marine aerosol: Salt depositions inside construction materials. Sci. Total Environ. 2020, 721, 137687. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Morillas, H.; Maguregui, M.; García-Florentino, C.; Marcaida, I.; Madariaga, J.M. Study of particulate matter from Primary/Secondary Marine Aerosol and anthropogenic sources collected by a self-made passive sampler for the evaluation of the dry deposition impact on built heritage. Sci. Total Environ. 2016, 550, 285–296. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chameides, W.L.; Stelson, A.W. Aqueous-phase chemical processes in deliquescent sea salt aerosols: A mechanism that couples the atmospheric cycles of S and sea salts. J. Geophys. Res.-Atmos. 1992, 97, 20565–20580. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hossain, K.M.A.; Easa, S.M.; Lachemi, M. Evaluation of the effect of marine salts on urban built infrastructure. Build. Environ. 2009, 44, 713–722. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Silva, A.; Neves, L.C.; Gaspar, P.L.; De Brito, J. Probabilistic transition of condition: Render facades. Build. Res. Inf. 2016, 44, 301–318. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cardell, C.; Delalieux, F.; Roumpopoulos, K.; Moropoulou, A.; Auger, F.; Van Grieken, R. Salt-induced decay in calcareous stone monuments and buildings in a marine environment in SW France. Constr. Build. Mater. 2003, 17, 165–179. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fahmy, A.; Molina-Piernas, E.; Martínez-López, J.; Domínguez-Bella, S. Salt weathering impact on Nero/Ramses II Temple at El-Ashmonein archaeological site (Hermopolis Magna), Egypt. Herit. Sci. 2022, 10, 125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- El-Raey, M. Vulnerability assessment of the coastal zone of the Nile delta of Egypt, to the impacts of sea level rise. Ocean. Coast. Manag. 1998, 37, 29–40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Elsharkawy, H.; Rashed, H.; Rached, I. Climate Change: The Impacts of Sea Level Rise on Egypt. In Proceedings of the 45th ISOCARP Congress, Porto, Portugal, 18–22 October 2009; pp. 1–11. Available online: https://www.isocarp.net/data/case_studies/1456.pdf (accessed on 3 May 2022).
- Bekheet, R.A.; El Raey, M.; Yassin, A. The crest line approach for assessing the development of coastal flooding due to sea level rise. Mitig. Adapt. Strateg. Glob. Chang. 2017, 22, 1113–1130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- El-Raey, M.; Regional Center for Disaster Risk Reduction (RCDRR). Impact of Sea Level Rise on the Arab Region; UNDP Regional Bureau for the Arab States (UNDP-RBAS): Cairo, Egypt, 2010; Available online: https://research.fit.edu/media/site-specific/researchfitedu/coast-climate-adaptation-library/africa/morocco-algeria-tunisia/El-Raey.-2010.-SLR-Impacts-on-Arab-Region.pdf (accessed on 5 May 2022).
- Belov, A. Navigational Aspects of Calling to the Great Harbour of Alexandria. 2014. Available online: https://halshs.archives-ouvertes.fr/halshs00845524/file/Belov.A._forthcoming_Navigational_aspects_of_calling_to_the_Great_Harbour_of_Alexandria.pdf (accessed on 22 May 2022).
- Ivanov, S.V. Russian underwater archaeological mission to Alexandria. General report (2003–2015). Egypt Neigbouring Ctries. 2019, 3, 1–31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abdelnaby, A.E.; Elnashai, A.S. Integrity assessment of the Pharos of Alexandria during the AD 1303 earthquake Integrity assessment of the Pharos of Alexandria during the AD 1303 earthquake. Eng. Fail. Anal. 2013, 33, 119–138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hemeda, S.; Pitilakis, K.; Bandis, S. Geotechnical, geophysical investigations and seismic response analysis of the underground tombs in Mustafa Kamil Necropolis, Alexandria, Egypt. Mediterr. Archaeol. Archaeom. 2015, 15, 191–207. [Google Scholar]
- Hemeda, S. Geotechnical modelling of the climate change impact on world heritage properties in Alexandria, Egypt. Herit. Sci. 2021, 9, 73. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kamal, I.; Fekri, M.; Abou, I. Mapping the impacts of projected sea-level rise on Cultural heritage sites in Egypt: Case study (Alexandria). J. Fac. Tour. Hostel. Univ. Sadat City 2021, 5, 1–20. Available online: https://mfth.journals.ekb.eg/article_190350_9dbe1272982c21ec55d603fe0787213f.pdf (accessed on 10 June 2022).
- Sousa, R.; Céu Fialho, M.; Haggag, M.; Rodrigues, N. Alexandrea ad Aegyptvm the Legacy of Multiculturalism in Antiquity. 2013. Available online: https://ler.letras.up.pt/uploads/ficheiros/16940.pdf (accessed on 9 May 2022).
- Kyriakos, S. Alexandrea in Aegyptvm. The Role of the Egyptian Tradition in the Hellenistic and Roman Periods: Ideology, Culture, Identity, and Public Life. Doctoral Thesis, Faculty of Archaeology, Universiteit Leiden, Leiden, The Netherlands, 2011. Available online: https://scholarlypublications.universiteitleiden.nl/handle/1887/16395 (accessed on 10 May 2022).
- Kyriakos, S. The Polyvalent Nature of the Alexandrian Elite Hypogea: A case Study in the Greco-Egyptian Cultural Interaction in the Hellenistic and Roman Periods. Porto. 2013. Available online: https://digitalis-dsp.uc.pt/handle/10316.2/36162 (accessed on 9 May 2022).
- Hosny, A.; Ali, S.M.; Abed, A. Study of the 26 December 2011 Aswan earthquake, Aswan area, South of Egypt. Arab. J. Geosci. 2014, 7, 4553–4562. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- El-Sharkawi, M.; Hamimi, Z.; El-Barkooky, A.; Martínez Frías, J.; Fritz, H.; Abd El-Rahman, Y. The Geology of Egypt. Regional Geology Reviews; Springer: Cham, Switzerland, 2020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ibrahim, M.I.A.; Mansour, A.M.S. Biostratigraphy and palaeoecological interpretation of the Miocene–Pleistocene sequence at El-Dabaa, north-western Egypt. J. Micropalaeontol. 2002, 21, 51–65. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stanley, J.D.; Jorstad, T.F.; Goddio, F. Human impact on sediment mass movement and submergence of ancient sites in the two harbours of Alexandria, Egypt. Nor. Geol. Tidsskr. 2006, 86, 337–350. [Google Scholar]
- Mohamed, A.A.; Helal, A.M.A.; Mohamed, A.M.E.; Shokry, M.M.F.; Ezzelarab, M. Effects of surface geology on the ground-motion at New Borg El-Arab City, Alexandria, Northern Egypt. NRIAG J. Astron. Geophys. 2016, 5, 55–64. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Torab, M.M. Paleo-geomorphological map of Alexandria site, Egypt by using submerged archaeological and other evidence. In Proceedings of the International Conference on Agriculture, Science and Engineering, Umunze, Nigeria, 21–26 April 2013; Federal College of Education: Umunze, Nigeria, 2013. Available online: http://www.damanhour.edu.eg/pdf/artsfac/PALEO-GEOMORPHOLOGICAL%20MAP%20OF%20ALEXANDRIA%20SITE,%20EGYPT%20BY%20USING%20SUBMERGED%20ARCHAEOLOGICAL%20AND%20OTHER%20EVIDENCE2.pdf (accessed on 21 May 2022).
- Evelpidou, N.; Repapis, C.; Zerefos, C.; Tzalas, H.; Synolakis, C. Geophysical Phenomena and the Alexandrian Littoral. Geophys. Phenom. Alex. Littoral 2019, 10, 1–146. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arthur, D.G. The four harbours of Alexandria. J. Inst. Civ. Eng. 1940, 1. Available online: https://www.ancientportsantiques.com/wp-content/uploads/Documents/PLACES/Egypt-Libya/Alexandria/Alexandria-Tyr-Savile1940.pdf (accessed on 10 May 2022).
- Fahmy, A.; Molina-Piernas, E.; Domínguez-Bella, S.; Martínez-López, J.; Helmi, F. Geoenvironmental investigation of Sahure’s pyramid, Abusir archaeological site, Giza, Egypt. Herit. Sci. 2022, 10, 61. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hemeda, S.; Fahmy, A.; Sonbol, A. Geo-Environmental and Structural Problems of the First Successful True Pyramid, (Snefru Northern Pyramid) in Dahshur, Egypt. Geotech. Geol. Eng. 2019, 37, 2463–2484. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hemeda, S.; Fahmy, A.; Moustafa, A.; Abd, M.; Hafez, E. The Early Basilica Church, El-Ashmonein Archaeological Site, Minia, Egypt: Geo-Environmental Analysis and Engineering Characterization of the Building Materials. Open J. Geol. 2019, 9, 91162. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Harrell, J.A.; Storemyr, P. Ancient Egyptian quarries—An illustrated overview. In Quarry Scapes: Ancient Stone Quarry Landscapes in the Eastern Mediterranean; Abu-Jaber, N., Bloxam, E.G., Degryse, P., Heldal, T., Eds.; Geological Survey of Norway Special Publication: Trondheim, Norway, 2009; Volume 12, pp. 7–50. Available online: https://www.ngu.no/upload/Publikasjoner/Special%20publication/SP12_s7-50.pdf (accessed on 12 June 2022).
- Akarish, A.; Dessandier, D. Characterization and Source of Sedimentary Rocks of the Alexandria Lighthouse Archaeological Objects, Egypt. J. Appl. Sci. 2011, 11, 2513–2524. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Dessandier, D.; Akarish, A.; Antonelli, F.; Lazzarini, L.; Leroux, A. Atlas of the Stones of Alexandria Light House (Egypt). Final Report BRGM/RP-56218-FR. 2008. Available online: https://www.lrmh.fr/Default/doc/SYRACUSE/50575/atlas-of-the-stones-of-alexandria-lighthouse-egypt-final-report?_lg=fr-FR (accessed on 16 June 2022).
- Global Climate Change. Available online: https://climate.nasa.gov/vital-signs/sea-level/ (accessed on 13 May 2022).
- Dawod, G.; Resrach, W.; Mohamed, H.F.; Haggag, G.G. Mean Sea Level and Tides Variations at Alexandria, Egypt Over 1906–2020. J. Eng. Sci. 2022, 50, 175–188. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eldeberky, Y. Coastal adaptation to sea level rise along the Nile delta, Egypt. Coast. Process. II 1996, 149, 41–52. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fitzgerald, D.M.; Fenster, M.S.; Argow, B.A.; Buynevich, I.V. Coastal Impacts Due to Sea-Level Rise. Annu. Rev. Earth Planet. Sci. 2008, 36, 601–647. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Agrawala, S.; Moehner, A.; El Raey, M.; Conway, D.; Aalst, M.; Van Hagenstad, M.; Smith, J. Development and climate change in Egypt: Focus on coastal resources and the Nile. Organ. Econ. Co-Oper. Dev. 2004, 1, 1–68. Available online: http://www.oecd.org/env/cc/33330510.pdf (accessed on 31 August 2022).
- Sawires, R.; Peláez, J.; Fat-Helbary, R.; Ibrahim, H.; García Hernández, M. An Updated Seismic Source Model for Egypt. In Earthquake Engineering—From Engineering Seismology to Optimal Seismic Design of Engineering Structures; Intech Open: London, UK, 2015. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- El-Sayed, A.; Korrat, I.; Hussein, H.M. Pure and Applied Geophysics Seismicity and Seismic Hazard in Alexandria (Egypt) and Its Surroundings; Birkhäuser Basel: Basel, Switzerland, 2004; Volume 161, pp. 1003–1019. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Badawy, A.; Gaber, H.; Ibrahim, H. Earthquake risk assessment of Alexandria, Egypt. J. Seismol. 2015, 19, 159–170. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fergany, E.; Omar, K.; Mohammed, G.A.; Fergany, E.; Omar, K.; Mohammed, G.A. Evolution in seismic monitoring system and updating seismic zones of Egypt. NRIAG J. Astron. Geophys. 2020, 9, 548–557. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Darwish, N.; Kaiser, M.; Koch, M. Assessing the Accuracy of ALOS/PALSAR-2 and Sentinel-1 Radar Images in Estimating the Land Subsidence of Coastal Areas: A Case Study in Alexandria City, Egypt. Remote Sens. 2021, 13, 1838. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wöppelmann, G.; Le Cozannet, G.; De Michele, M.; Raucoules, D.; Cazenave, A.; Garcin, M.; Hanson, S.; Marcos, M. Is land subsidence increasing the exposure to sea level rise in Alexandria, Egypt? Geophys. Res. Lett. 2013, 40, 2953–2957. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hamouda, A.Z.; El-gharabawy, S.M.; Fekry, A.; Nassar, M.A.; Salah, M. Subsidence model of the ancient Alexandria Royal port linked to sea-level rise and natural hazards using integrated geophysical methods. Egypt. J. Aquat. Res. 2021, 47, 283–292. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zaghloul, E.A. Physical Geology and Historical Settlement in North Western Nile Delta Region, Egypt. 2016. Available online: https://www.researchgate.net/publication/305950323_PHYSICAL_geology_and_historical_settlement_in_North_Western_Nile_delta_Region_Egypt (accessed on 11 August 2022).
- Frihy, O.E.; Deabes, E.A.; Gindy, A.A.E. Wave Climate and Nearshore Processes on the Mediterranean Coast of Egypt. J. Coast. Res. 2010, 26, 103–112. Available online: http://www.jstor.org/stable/27752790 (accessed on 31 August 2022). [CrossRef]
- Sea Level Rise Projection Map—Alexandria. Available online: https://earth.org/data_visualization/sea-level-rise-by-the-end-of-the-century-alexandria/ (accessed on 31 August 2022).
- Zevenbergen, C.; Bhattacharya, B.; Wahaab, R.A.; Elbarki, W.A.I.; Busker, T.; Rodriguez, C.N.A.S. In the aftermath of the October 2015 Alexandria Flood Challenges of an Arab city to deal with extreme rainfall storms. Nat. Hazards 2017, 86, 901–917. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bhattacharya, B.; Zevenbergen, C.; Wahaab, R.A.W.R.A.; Elbarki, W.A. Characterization of Flooding in Alexandria in October 2015 and Suggested Mitigating Measures. EGU Gen. Assem. Conf. Abstr. 2017, 19, 14230. Available online: https://ui.adsabs.harvard.edu/abs/2017EGUGA.1914230B/abstract (accessed on 18 August 2022).
- Young, A. A rainfall threshold-based approach to early warnings in urban data-scarce regions: A case study of pluvial flooding in Alexandria, Egypt. J. Flood Risk Manag. 2021, 14, e12702. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ali, N.A. Alexandria Drowns: A Philosophical Reading of Flood Management in Post-Revolution Egypt. Online Report. 2015. Available online: https://doi.org/10.13140/RG.2.1.2635.9129 (accessed on 31 August 2022).
- Hafez, M.E. Assessment of Climate Change Impact on Urban Heavy Rainfall Extremes Alexandria, Egypt Case Study. 2017. Available online: https://journals.ekb.eg/article_154964_3faef7daa2e9bac56a7a241cb0586400.pdf (accessed on 12 May 2022).
- Mohamed, B.; Navy, T.E.; Osman, A.; Saber, S.A.; Allah, H.M. Assessment of weather and climate variability over Western Harbor of the climate. Egypt. J. Aquat. Biol. Fish. 2020, 24, 323–339. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- El-Geziry, T.M. Analysis of long-term rainfall and air temperature patterns in Alexandria (Egypt). Arab. J. Geosci. 2021, 14, 1199. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khedr, A.M.; Abdelrahman, S.M.; El-din, K.A.A. Currents and Sea Level Variability of Alexandria Coast in Association with Wind Forcing Currents and Sea Level Variability of Alexandria Coast in Association with Wind Forcing. J. King Abdulaziz Univ. 2018, 28, 27–42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Amr, A. Alexandria in Antiquity A Topographical Reconstruction. Ph.D. Thesis, The Autonomous University of Barcelona, Departament de Ciències de l’Antiguitat i de l’Edat Mitjana, Barcelona, Spain, 1996. Available online: https://www.tesisenred.net/bitstream/handle/10803/670088/amab1de5.pdf?sequence=1&isAllowed=y (accessed on 17 May 2022).
- Venit, M. Egypt as Metaphor: Visual Bilingualism in the Monumental Tombs of Ancient Alexandria. In Visualizing the Afterlife in the Tombs of Graeco-Roman Egypt; Cambridge University Press: Cambridge, UK, 2015; pp. 50–86. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ioannides, M.; Fink, E.; Cantoni, L.; Champion, E.; Goos, G. Digital Heritage. Progress in Cultural Heritage: Documentation, Preservation, and Protection. In Proceedings of the 8th International Conference, EuroMed 2020, Virtual Event, 2–5 November 2020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jozef, L.; Oostwegel, N.; Jaud, Š.; Muhič, S.; Rebec, K.M. Digitalization of culturally significant buildings: Ensuring high—Quality data exchanges in the heritage domain using Open BIM. Herit. Sci. 2022, 10, 10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stanley, J.D.; Carslon, R.W.; Van Beek, G.; Jorstad, T.F.; Landau, E.A. Alexandria, Egypt, before Alexander the Great: A multidisciplinary approach yields rich discoveries. GSA Today 2007, 17, 4–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shaltout, M.; Tonbol, K.; Omstedt, A. Sea-level change and projected future flooding along the Egyptian Mediterranean coast. Oceanologia 2015, 57, 293–307. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- The World Bank. Climate Change Adaptation and Natural Disasters Preparedness in the Coastal Cities of North Africa Phase 1: Risk Assessment for the Present Situation and Horizon 2030—Alexandria Area. 2011. Available online: http://web.worldbank.org/archive/website01418/WEB/IMAGES/ALEXANDR.PDF (accessed on 20 May 2022).
- Jondet, G. Les Portssubmergés de l’Ancienneîle de Pharos. Le Caire. 1916. Available online: https://www.ancientportsantiques.com/wp-content/uploads/Documents/PLACES/Egypt-Libya/AlexPharos-Jondet1916/JONDET-Texteintegral.pdf (accessed on 10 May 2022).
- Kázmér, M. Damage to Ancient Buildings from Earthquakes. Encyclopedia of Earthquake Engineering; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2014. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Benavente, D.; García del Cura, M.A.; García- Guinea, J.; Sanchez-Moral, S.; Ordonez, S. Role of pore structure in salt crystallization in unsatured porous stone. J. Cryst. Growth 2004, 260, 532–544. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sato, M.; Hattanji, T. A laboratory experiment on salt weathering by humidity change: Salt damage induced by deliquescence and hydration. Prog. Earth Planet. Sci. 2018, 5, 84. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Charola, A.E.; Puhringer, J.; Steiger, M. Gypsum: A review of its role in the deterioration of building materials. Environ. Geol. 2007, 52, 339–352. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zurbriggen, R.; Herwegh, M. Daily and seasonal thermal stresses in tilings: A field survey combined with numeric modeling. Mater. Struct. 2016, 49, 1917–1933. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mart, J.; Arizzi, A.; Benavente, D. The Role of Calcite Dissolution and Halite Thermal Expansion as Secondary Salt Weathering Mechanisms of Calcite-Bearing Rocks in Marine Environments. Minerals 2021, 11, 911. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grossi, C.M.; Brimblecombe, P.; Menéndez, B.; Benavente, D.; Harris, I.; Déqué, M. Science of the Total Environment Climatology of salt transitions and implications for stone weathering. Sci. Total Environ. 2011, 409, 2577–2585. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Doehne, E.; Price, C.A. Stone Conservation: An Overview of Current Research; Getty Conservation Insitute: Los Angeles, CA, USA, 2010. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Robert, K.; Kvande, T.; Olav, H.; Vincent, J.; Harstveit, K. A frost decay exposure index for porous, mineral building materials. Build. Environ. 2007, 42, 3547–3555. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Loperte, A.; National, I.; Proto, M.; National, I.; Bavusi, M. Geosciences Building damage caused by tree roots: Laboratory experiments of GPR and ERT surveys. Adv. Geosci. 2010, 24, 133–137. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).