Eclogite Varieties and Their Positions in the Cratonic Mantle Lithosphere beneath Siberian Craton and Archean Cratons Worldwide
Abstract
:1. Introduction
1.1. Eclogite Mantle Xenoliths
1.2. Eclogite Thermobarometry
2. Analytical Methods and Data Sets
3. Subdivisions of Mantle Eclogites
4. Distributions of Different Eclogite Groups in the Lithospheric Mantle Beneath Siberia
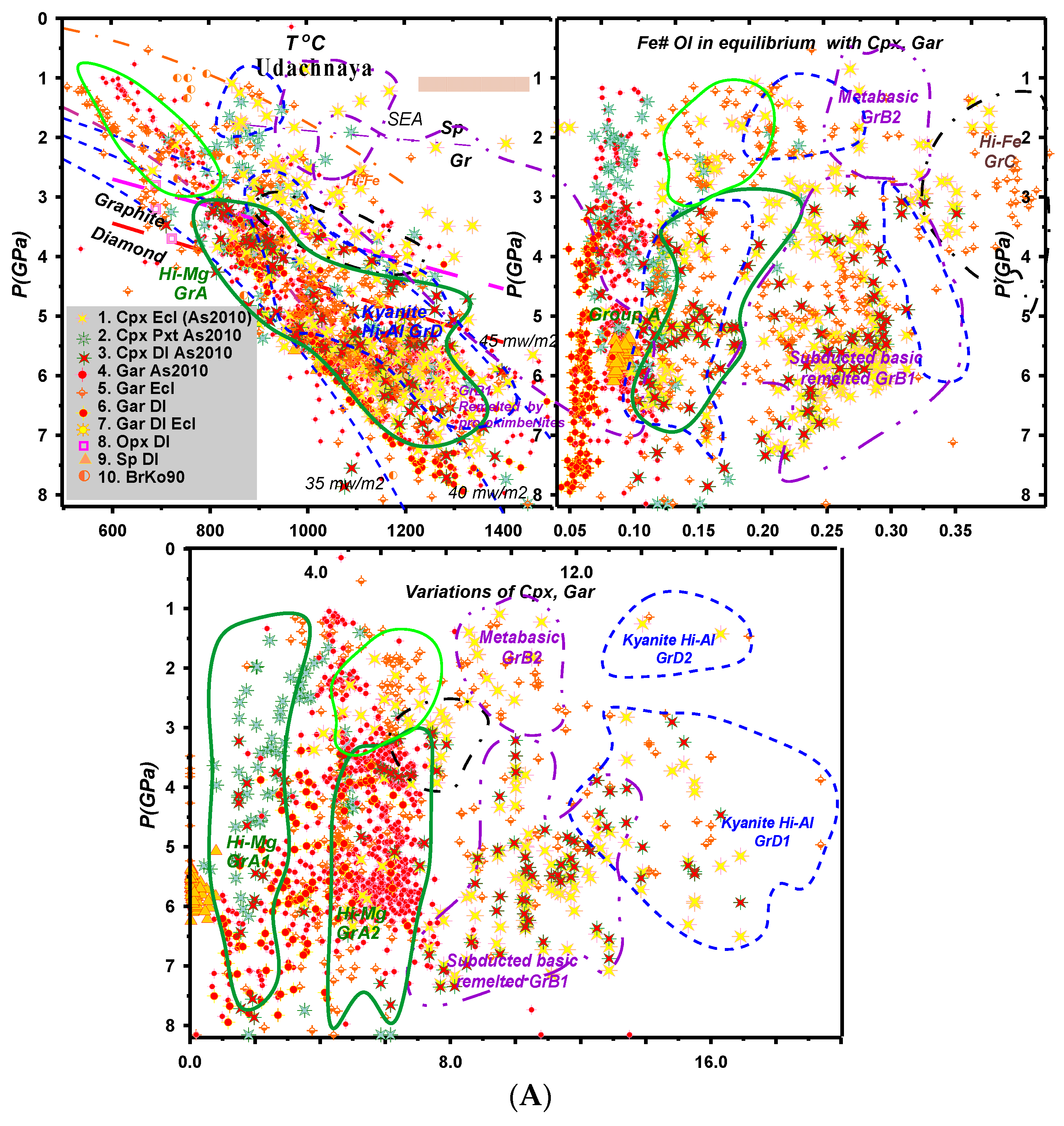
4.1. Udachnaya Pipe
4.2. Mir Pipe
4.3. Sytykanskaya Pipe
4.4. Komsomolskaya Pipe
4.5. Obnazhennaya Pipe
4.6. Bumerang and Khardakh Pipes
5. Characteristics of Distributions of Different Eclogite Groups in the Lithospheric Mantle Worldwide
5.1. Colorado, Wyoming Craton Montana
5.2. Lac de Gras Cluster, Slave Craton
5.3. KL-4 pipe, Dharwar Craton, India
5.4. Catoca pipe, Congo Kasai Craton, Africa
5.5. Roberts Victor pipe, Kaapvaal Craton, Africa
5.6. Orapa Pipe, Limpopo Belt, Africa
6. Geochemistry of Trace Elements of Studied Eclogites
6.1. Udachnaya Eclogites, Trace Element Distributions for Pyroxenes and Garnets
6.2. Sytykanskaya Eclogites, Trace Element Distributions for Pyroxenes and Garnets
6.3. Komsomolskaya Eclogites
6.4. Obnazhennaya Eclogites
6.5. Ary Mastakh Field
6.6. Dharwar Craton, Wajrakarur Field, Kl-4 Pipe
6.7. Wyoming Craton, Sloan Pipe
7. Discussion
7.1. General Regularities of Eclogite Distribution in the SCLM
7.2. Role of Eclogites in the Reconstruction of Mantle Layering
7.3. Geochemical Application of Eclogites for the Reconstruction of Geodynamic Processes
7.4. Influence of Protokimberlites on Eclogite Compositions
8. Conclusions
- Eclogite thermobarometry for clinopyroxenes and garnets allows us to determine the position of eclogites in the mantle sections beneath kimberlite pipes in some detail, showing high-T conditions for protokimberlite-related and melt-metasomatized eclogites and low-T for subducted eclogites.
- Most eclogites have been remelted during subduction and later plume events.
- The division of the sub-cratonic mantle lithosphere into an upper and lower part is probably marked by the presence of Fe-rich eclogites.
- Ca-rich kyanite eclogites are common in the middle part of the SCLM in the Precambrian kimberlites and became more frequent in the LSCLM beneath Phanerozoic kimberlites.
- Different groups of eclogites commonly have individual positions and geothermal gradients in the mantle section beneath kimberlites from different cratons and terranes.
- Trace elements for Fe-rich and high-Ca eclogites commonly demonstrate their derivation from a silicic LILE-enriched substrate. The MORB basalt-like protoliths show derivation from a HFSE- and LILE-depleted source. Common type B (metabasaltic) protoliths show the strong influence of volatile-rich melts and fluid produced by different types of magmatic differentiation. The MgO-rich eclogites show Nb anomalies and participation of rutile in the source rocks.
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Sobolev, V.N.; Sobolev, N.V. Nd and Sr isotopes from diamondiferous eclogites, Udachnaya kimberlite pipe, Yakutia, Siberia: Evidence of differentiation in the early Earth? Earth Planet Sci. Lett. 1993, 118, 91–100. [Google Scholar]
- Jagoutz, E.; Lowry, D.; Mattey, D.; Kudrjavtseva, G. Diamondiferous eclogites from Siberia: Remnants of Archean oceanic crust. Geochim. Cosmochim. Acta 1994, 58, 5195–5207. [Google Scholar]
- Jacob, D.E. Nature and origin of eclogite xenoliths from kimberlites. Lithos 2004, 77, 295–316. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Heaman, L.M.; Creaser, R.A.; Cookenboo, H.O.; Chacko, T. Multistage modification of the northern Slave mantle lithosphere evidence from zircon- and diamond-bearing eclogite xenoliths entrained in Jericho Kimberlite, Canada. J. Petrol. 2006, 47, 821–858. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schmidberger, S.S.; Simonetti, A.; Heaman, L.M.; Creaser, R.A.; Cookenboo, H.O.; Whiteford, S. Lu–Hf, in-situ Sr and Pb isotope and trace element systematics for mantle eclogites from the Diavik diamond mine: Evidence for Paleoproterozoic subduction beneath the Slave craton, Canada. Earth Planet. Sci. Lett. 2007, 254, 55–68. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Smart, K.A.; Heaman, L.M.; Chacko, T.; Simonetti, A.; Kopylova, M.; Mah, D.; Daniels, D. The origin of high-MgO diamond eclogites from the Jericho Kimberlite, Canada. Earth Planet. Sci. Lett. 2009, 284, 527–537. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aulbach, S.; Pearson, N.J.; O’Reilly, S.Y.; Doyle, B.J. Origins of Xenolithic Eclogites and Pyroxenites from the Central Slave Craton, Canada. J. Petrol. 2007, 48, 1843–1873. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Riches, A.J.V.; Liua, Y.; Day, J.M.D.; Spetsius, Z.V.; Taylor, L.A. Subducted oceanic crust as diamond hosts revealed by garnets of mantle xenoliths from Nyurbinskaya, Siberia. Lithos 2010, 120, 368–378. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Spetsius, Z.V.; de Vries, W.D.F.; Davie, G.R. Combined C isotope and geochemical evidence for a recycled origin for diamondiferous eclogite xenoliths from kimberlites of Yakutia. Lithos 2009, 112, 1032–1042. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Godard, G. Eclogites and their geodynamic interpretation. J. Geodyn. 2001, 32, 165–203. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carlson, R.W.; Boyd, F.R.; Shirey, S.B.; Janney, P.E.; Grove, T.J.; Bowring, S.A.; Schmitz, M.D.; Dann, J.C.; Bell, D.R.; Gurney, J.J.; et al. Continental growth, preservation, and modification in Southern Africa. GSA Today 2000, 10, 24. [Google Scholar]
- Rudnick, R.L.; Barth, M.G.; Horn, I.; McDonough, W.F. Rutile-bearing refractory eclogites: Missing link between continents and depleted mantle. Science 2000, 287, 278–281. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Pearson, D.G.; Snyder, G.A.; Shirey, S.B.; Taylor, L.A.; Carlson, R.W.; Sobolev, N.V. Archaean Re–Os age for Siberian eclogites and constraints on Archaean tectonics. Nature 2005, 374, 711–713. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pearson, D.G. The age of continental roots. Lithos 1999, 48, 171–194. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aulbach, S.; Jacob, D.E.; Cartigny, P.; Stern, R.A.; Viljoen, K.S. Eclogite xenoliths from Orapa: Ocean crust recycling, mantle metasomatism and carbon cycling at the western Zimbabwe craton margin. Geochim. Cosmochim. Acta 2017, 213, 574–592. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aulbach, S.; Viljoen, K.S. Eclogite xenoliths from the Lace kimberlite, Kaapvaal craton: From convecting mantle source to palaeo-ocean floor and back. Earth Planet. Sci. Lett. 2015, 431, 274–286. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shchukina, E.V.; Agashev, A.M.; Soloshenko, N.G.; Streletskaya, M.V.; Zedgenizov, D.A. Origin of V. Grib pipe eclogites (Arkhangelsk region, NW Russia): Geochemistry, Sm-Nd and Rb-Sr isotopes and relation to regional Precambrian tectonics. Mineral. Petrol. 2019, 113, 593–612+617. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bebout, G.E.; Bebout, A.E.; Graham, C.M. Cycling of B, Li, and LILE (K, Cs, Rb, Ba, Sr) into subduction zones: SIMS evidence from micas in high-P/T metasedimentary rocks. Chem. Geol. 2007, 239, 284–304. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Becker, H.; Jochum, K.P.; Carlson, R.W. Trace element fractionation during dehydration of eclogites from high-pressure terranes and the implications for element fluxes in subduction zones. Chem. Geol. 2000, 163, 65–99. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shchipansky, A.A.; Khodorevskaya, L.I.; Konilov, A.N.; Slabunov, A.I. Eclogites from the Belomorian Mobile Belt (Kola Peninsula): Geology and petrology. Russ. Geol. Geophys. 2012, 53, 1–21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kempton, P.D.; Downes, H.; Sharkov, E.V.; Vetrin, V.R.; Ionov, D.A.; Carswell, D.A.; Beard, A. Petrology and geochemistry of xenoliths from the Northern Baltic shield: Evidence for partial melting and metasomatism in the lower crust beneath an Archaean terrane. Lithos 1995, 36, 157–184. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Slabunov, A.I.; Volodichev, O.I.; Skublov, S.G.; Berezin, A.V. Main stages of the formation of Paleoproterozoic eclogitized gabbro-norite: Evidence from U–Pb (SHRIMP) dating of zircons and study of their genesis. Dokl. Earth Sci. 2011, 437, 396–400. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Snyder, G.A.; Taylor, L.A.; Crozaz, G.; Halliday, A.N.; Beard, B.L.; Sobolev, V.N. The Origins of Yakutian Eclogite Xenoliths. J. Petrol. 1997, 38, 85–113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sobolev, N.V.; Sobolev, V.N.; Snyder, G.A.; Yefimova, E.S.; Taylor, L.A. Significance of eclogitic and related parageneses of natural diamonds. Int. Geol. Rev. 1999, 41, 129–140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Smit, K.V.; Stachel, T.; Luth, R.W.; Stern, R.A. Evaluating mechanisms for eclogitic diamond growth: An example from Zimmi Neoproterozoic diamonds (West African craton). Chem. Geol. 2019, 520, 21–32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.; Taylor, L.A.; Sarbadhikari, A.B.; Valley, J.W.; Ushikubo, T.; Spicuzza, M.J.; Kita, N.; Ketcham, R.A.; Carlson, W.; Shatsky, V.S.; et al. Metasomatic origin of diamonds in the world’s largest diamondiferous eclogites. Lithos 2009, 112, 1014–1024. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Beard, B.L.; Fraracci, K.N.; Clayton, R.N.; Mayeda, T.K.; Snyder, G.A.; Taylor, L.A.; Sobolev, N.V. Petrography and geochemistry of eclogites from the Mir kimberlite, Yakutia, Russia. Contrib. Mineral. Petrol. 1996, 125, 293–310. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kopylova, M.G.; Russell, J.K.; Cookenboo, H. Petrology of peridotite and pyroxenite xenoliths from the Jericho kimberlite: Implications for the thermal state of the mantle beneath the Slave craton, northern Canada. J. Petrol. 1999, 40, 79–104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Smart, K.A.; Cartigny, P.; Tappe, S.; O’Brien, H.; Kemme, S. Lithospheric diamond formation as a consequence of methane-rich volatile flooding: An example from diamondiferous eclogite xenoliths of the Karelian craton (Finland). Geochim. Cosmochim. Acta 2017, 206, 312–342. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Horodyskyj, U.N.; Lee, C.-T.A.; Ducea, M.N. Similarities between Archean high MgO eclogites and Phanerozoic arc-eclogite cumulates and the role of arcs in Archean continent formation. Earth Planet. Sci. Lett. 2007, 256, 510–520. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barth, M.G.; Foley, S.F.; Horn, I. Partial melting in Archean subduction zones: Constraints from experimentally determined trace element partition coefficients between eclogitic minerals and tonalitic melts under upper mantle conditions. Precambrian Res. 2002, 113, 323–340. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jacob, D.E.; Viljoen, K.S.; Grassineau, N.; Jagoutz, E. Remobilization in the cratonic lithosphere recorded in polycrystalline diamond. Science 2000, 289, 1182–1185. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jerde, E.A.; Taylor, L.A.; Crozaz, G.; Sobolev, N.V.; Sobolev, V.S. Diamondiferous eclogites from Yakutia, Siberia: Evidence for a diversity of protoliths. Contrib. Mineral. Petrol. 1993, 114, 189–192. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Spetsius, Z.V.; Taylor, L.A.; Valley, J.W.; Ivanov, A.S.; Banzeruk, V.I. Diamondiferous xenoliths from crustal subduction: Garnet oxygen isotopes from the Nyurbinskaya pipe, Yakutia. Eur. J. Mineral. 2008, 20, 375–385. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Spetsius, Z.V.; Belousova, E.A.; Griffin, W.L.; O’Reilly, S.Y.; Pearson, N.J. Archean sulfide inclusions in Paleozoic zircon megacrysts from the Mir kimberlite, Yakutia: Implications for the dating of diamonds. Earth Planet. Sci. Lett. 2002, 199, 111–126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Taylor, L.A.; Anand, M. Diamonds: Time capsules from the Siberian Mantle. Chem. Der. Erde. 2004, 64, 1–74. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Taylor, L.A.; Anand, M.; Promprated, P.; Floss, C.; Sobolev, N.V. The significance of mineral inclusions in large diamonds from Yakutia, Russia. Am. Mineral. 2003, 88, 912–920. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liou, J.G.; Tsujimori, T.; Yang, J.; Zhang, R.Y.; Ernst, W.G. Recycling of crustal materials through study of ultrahigh-pressure minerals in collisional orogens, ophiolites, and mantle xenoliths. J. Asian Earth Sci. 2014, 96, 386–420. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Spetsius, Z.V.; Ivanov, A.S.; Mityukhin, S.I. Diamondiferous xenoliths and megacrysts from the Nyurbinskaya kimberlite pipe (Nakynsky field, Yakutia). Dokl. Earth Sci. 2006, 409, 779–783. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Spetsius, Z.V. Petrology of highly aluminous xenoliths from kimberlites of Yakutia. Lithos 2004, 77, 525–538. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Holland, T.J.B.; Powell, R. An internally consistent thermodynamic data set for phases of petrological interest. J. Metamorph. Geol. 1998, 16, 309–343. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ducheune, S.; Albarede, F. Simulated garnet-clinopyroxene geothermometry of eclogites. Contrib. Mineral. Petrol. 1999, 135, 75–91. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nowlan, E.U.; Schertl, H.-P.; Schreyer, W. Garnet–omphacite–phengite thermobarometry of eclogites from the coesite-bearing unit of the southern Dora-Maira Massif, Western Alps. Lithos 2000, 52, 197–214. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Krogh Ravna, E.J.; Terry, M.P. Geothermobarometry of UHP and HP eclogites and schists—An evaluation of equilibria among garnet–clinopyroxene–kyanite–phengite–coesite/quartz. J. Metamorph. Geol. 2004, 22, 579–592. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Beyer, C.; Frost, D.J.; Miyajima, N. Experimental Calibration of a Garnet-Clinopyroxene Geobarometer for Mantle clogites. Contrib. Mineral. Petrol. 2015, 169, 18–21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ashchepkov, I.V.; Pokhilenko, N.P.; Vladykin, N.V.; Logvinova, A.M.; Kostrovitsky, S.I.; Afanasiev, V.P.; Pokhilenko, L.N.; Kuligin, S.S.; Malygina, L.V.; Alymova, N.V.; et al. Structure and evolution of the lithospheric mantle beneath Siberian craton, thermobarometric study. Tectonophysics 2010, 485, 17–41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ashchepkov, I.V.; Ntaflos, T.; Logvinova, A.M.; Spetsius, Z.V.; Downes, H.; Vladykin, N.V. Monomineral universal clino-pyroxene and garnet barometers for peridotitic, eclogitic and basaltic systems. Geosci. Front. 2017, 8, 775–795. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Dongre, A.N.; Jacob, D.E.; Stern, R.A. Subduction-related origin of eclogite xenoliths from the Wajrakarur kimberlite field, Eastern Dharwar craton, Southern India: Constraints from petrology and geochemistry. Geochim. Cosmochim. Acta 2015, 166, 165–188. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mikhailenko, D.S.; Aulbach, S.; Korsakov, A.V.; Golovin, A.V.; Malygina, E.V.; Gerdes, A.; Stepanov, A.S.; Xu, Y.G. Origin of Graphite-Diamond-Bearing Eclogites from Udachnaya Kimberlite Pipe. J. Petrol. 2021, 62, 1–32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mikhailenko, D.S.; Stagno, V.; Korsakov, A.V.; Andreozzi, G.B.; Marras, G.; Cerantola, V.; Malygina, E.V. Redox state determination of eclogite xenoliths from Udachnaya kimberlite pipe (Siberian craton), with some implications for the graphite/diamond formation. Contrib. Mineral. Petrol. 2020, 175, 107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mikhailenko, D.S.; Golovin, A.V.; Korsakov, A.V.; Aulbach, S.; Gerdes, A.; Ragozin, A.L. Metasomatic Evolution of Coesite-Bearing Diamondiferous Eclogite from the Udachnaya Kimberlite. Minerals 2020, 10, 383. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kolesnichenko, M.V.; Zedgenizov, D.A.; Ragozin, A.L.; Litasov, K.D.; Shatsky, V.S. The role of eclogites in the redistribution of water in the subcontinental mantle of the Siberian craton:esults of determination of the water content in minerals from the Udachnaya pipe eclogites. Russ. Geol. Geophys. 2018, 59, 763–779. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ragozin, A.L.; Zedgenizov, D.A.; Shatskii, V.S.; Orihashi, Y.; Agashev, A.M.; Kagi, H. U–Pb Age of Rutile from the Eclogite Xenolith of the Udachnaya Kimberlite Pipe. Dokl. Earth Sci. 2014, 457, 861–886. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shatsky, V.; Ragozin, A.; Zedgenizov, D.; Mityukhin, M. Evidence for multistage evolution in a xenolith of diamond-bearing eclogite from the Udachnaya kimberlite pipe. Lithos 2008, 105, 289–300. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stepanov, A.S.; Korsakov, A.V.; Yuryeva, O.P.; Nadolinniy, V.A.; Perraki, M.; de Gussem, K. Diamondiferous subcontinental lithospheric mantle of the northeastern Siberian Craton: Evidence from mineral inclusions in alluvial diamonds. Gondwana Res. 2008, 28, 106–120. [Google Scholar]
- Vandenabeele, P. Brown diamonds from an eclogite xenolith from Udachnaya kimberlite, Yakutia, Russia. Spectrochim. Acta Part A Mol. Biomol. Spectrosc. 2011, 80, 41–48. [Google Scholar]
- Logvinova, A.M.; Taylor, L.A.; Fedorova, E.N.; Yelisseyev, A.P.; Wirth, R.; Howarth, G.; Reutsky, V.N.; Sobolev, N.V. A unique diamondiferous peridotite xenolith from the Udachnaya kimberlite pipe, Yakutia: Role of subduction in diamond formation. Russ. Geol. Geophys. 2015, 56, 306–320. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ashchepkov, I.V.; Ntaflos, T.; Kuligin, S.S.; Malygina, E.V.; Agashev, A.M.; Logvinova, A.M.; Mityukhin, S.I.; Alymova, N.V.; Vladykin, N.V.; Palessky, S.V.; et al. Deep-Seated Xenoliths from the Brown Breccia of the Udachnaya Pipe, Siberia. In Proceedings of 10th International Kimberlite Conference; Springer: New Delhi, India, 2013; Volume 1, pp. 59–74. [Google Scholar]
- Ionov, D.A.; Doucet, L.S.; Ashchepkov, I.V. Composition of the Lithospheric Mantle in the Siberian Craton: New Constraints from Fresh Peridotites in the Udachnaya-East Kimberlite. J. Petrol. 2010, 51, 2177–2210. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Stepanov, A.S.; Shatsky, V.S.; Zedgenizov, D.A.; Ragozin, A.L. Chemical heterogeneity in the diamondiferous eclogite xenolith from the Udachnaya kimberlite pipe. Doklady Earth Sciences 2008, 419, 308–311. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Misra, K.C.; Anand, M.; Taylor, L.A.; Sobolev, N.V. Multi-stage metasomatism of diamondiferous eclogite xenoliths from the Udachnaya kimberlite pipe, Yakutia, Siberia. Contrib. Mineral. Petrol. 2004, 146, 696–714. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Snyder, G.A.; Taylor, L.A.; Sobolev, V.N.; Beard, B.L.; Sobolev, N.V. A diversity of origins for diamondiferous eclogites; isotopic studies from the Mir Kimberlite, Siberia. EOS Trans. Am. Geophys. Union 1996, 77, 816. [Google Scholar]
- Alifirova, T.A.; Pokhilenko, L.N.; Korsakov, A.V. Apatite, SiO2, rutile and orthopyroxene precipitates in minerals of eclogite xenoliths from Yakutian kimberlites, Russia. Lithos 2015, 226, 31–49. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Taylor, L.A.; Snyder, G.A.; Crozaz, G.; Sobolev, V.N.; Yefimova, E.S.; Sobolev, N.V. Eclogitic inclusions in diamonds: Evidence of complex mantle processes over time. Earth Planet. Sci. Lett. 1996, 142, 535–551. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sobolev, N.V.; Pustyntsev, V.I.; Kuznetsova, I.K.; Khar’kiv, A.D. New data on the mineralogy of the diamond-bearing eclogites from the “Mir” pipe (Yakutia). Int. Geol. Rev. 1970, 12, 657–659. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bulanova, G.P.; Wiggers de Vries, D.F.; Pearson, D.G.; Beard, A.; Mikhail, S.; Smelov, A.P.; Davies, G.R. An eclogitic diamond from Mir pipe (Yakutia), recording two growth events from different isotopic sources. Chem. Geol. 2014, 381, 40–54. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sobolev, N.V.; Logvinova, A.M.; Zedgenizov, D.A.; Yefimova, E.S.; Taylor, L.A.; Promprated, P.; Koptil, V.I.; Zinchuk, N.N. Mineral Inclusions in Diamonds from Komsomolskaya and Krasnopresnenskaya Pipes, Yakutia: Evidence for Deep Lithospheric Heterogeneities in Siberian Craton. In International Kimberlite Conference: Extended Abstracts; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2003; Volume 8. [Google Scholar]
- Pernet-Fisher, J.F.; Howarth, G.H.; Liu, Y.; Barry, P.H.; Carmody, L.; Valley, J.W.; Bodnar, R.J.; Spetsius, Z.V.; Taylor, L.A. Komsomolskaya diamondiferous eclogites: Evidence for oceanic crustal protoliths. Contrib. Mineral. Petrol. 2014, 167, 981. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ashchepkov, I.V.; Vladykin, N.V.; Ntaflos, T.; Downes, H.; Mitchel, R.; Smelov, A.P.; Rotman, A.Y.; Stegnitsky, Y.; Smarov, G.P.; Makovchuk, I.V.; et al. Regularities of the mantle lithosphere structure and formation beneath Siberian craton in comparison with other cratons. Gondwana Res. 2013, 23, 4–24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ashchepkov, I.V.; Ivanov, A.S.; Kostrovitsky, S.I.; Vavilov, M.A.; Babushkina, S.A.; Vladykin, N.V.; Tychkov, N.S.; Medvedev, N.S. Mantle terranes of the Siberian craton: Their interaction with plume melts based on thermobarometry and geochemistry of mantle xenocrysts. Geodyn. Tectonophys. 2019, 10, 197–245. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Ashchepkov, I.V.; Logvinova, A.M.; Ntaflos, T.; Vladykin, N.V.; Downes, H. Alakit and Daldyn kimberlite fields, Siberia, Russia: Two types of mantle sub-terranes beneath central Yakutia? Geosci. Front. 2017, 8, 671–692. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Ashchepkov, I.; Ntaflos, T.; Medvedev, N.; Yudin, D.; Makovchuk, I.; Salikhov, R. The multistage metasomatized mantle beneath Alakit: Evidence from mantle xenoliths from Komsomolskaya kimberlite pipe, Yakutia, stages of mantle evolution. In Proceedings of the EGU General Assembly Conference, Vienna, Austria, 23–27 May 2022. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ashchepkov, I.V.; Logvinova, A.M.; Reimers, L.F.; Ntaflos, T.; Spetsius, Z.V.; Vladykin, N.V.; Downes, H.; Yudin, D.S.; Travin, A.V.; Makovchuk, I.V.; et al. The Sytykanskaya kimberlite pipe: Evidence from deep-seated xenoliths and xenocrysts for the evolution of the mantle beneath Alakit, Yakutia, Russia. Geosci. Front. 2015, 6, 687–714. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Reimers, L.F.; Pokhilenko, N.P.; Yefimova, E.S.; Sobolev, N.V. Ultramafic Mantle Assemblages from Sytykanskaya Kimberlite Pipe (Yakutia). In Seventh International Kimberlite Conference: Extended Abstracts; Elsevier: Cape Town, South Africa, 1998; pp. 730–732. [Google Scholar]
- Spetsius, Z.V.; Koptil, V.I. Associations with the diamond from the kimberlite pipe Sytykanskaya, Yakutia. Geol. Razved. 2008, 2008, 23–28. [Google Scholar]
- Bulanova, G.P.; Griffin, W.L.; Kaminsky, F.V.; Davies, R.; Ryan, C.G.; Andrew, A.; Spetsius, Z.V.; Zahkarchenko, O.D. Diamonds from Zarnitsa and Dalnaya kimberlites (Yakutia): Their nature, growth history, and lithospheric mantle source. In International Kimberlite Conference: Extended Abstracts; Gurney, J.J., Gurney, J.L., Pascoe, M.D., Richardson, S.H., Eds.; Red Roof Design: Cape Town, South Africa, 1998; pp. 21–24. [Google Scholar]
- Ashchepkov, I.V.; Vladykin, N.N.; Ntaflos, T.; Kostrovitsky, S.I.; Prokopiev, S.A.; Downes, H.; Smelov, A.P.; Agashev, A.M.; Logvinova, A.M.; Kuligin, S.S.; et al. Layering of the lithospheric mantle beneath the Siberian Craton: Modeling using thermobarometry of mantle xenolith and xenocrysts. Tectonophysics 2014, 634, 55–75. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ater, P.C.; Eggler, D.H.; Mc Callum, M.E. Petrology and Geochemistry of Mantle Eclogite Xenoliths from Colorado-Wyoming Kimberlites: Recycled Ocean Crust? Dev. Petrol. 1984, 11, 309–318. [Google Scholar]
- Ashchepkov, I.V.; Downes, H.; Mitchell, R.; Vladykin, N.V.; Coopersmith, H.; Palessky, S.V. Wyoming Craton Mantle Lithosphere: Reconstructions Based on Xenocrysts from Sloan and Kelsey Lake Kimberlites. In Proceedings of 10th International Kimberlite Conference; Pearson, G., Ed.; Springer: New Delhi, India, 2013; Volume 1, pp. 13–27. [Google Scholar]
- Aulbach, S.; Stachel, T.; Heaman, L.M.; Carlson, J.A. Microxenoliths from the Slave craton: Archives of diamond formation along fluid conduits. Lithos 2011, 126, 419–434. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Davies, R.M.; Griffin, W.L.; O’Reilly, S.Y.; Doyle, B.J. Mineral inclusions and geochemical characteristics of microdiamonds from the DO27, A154, A21, A418, DO18, DD17 and Ranch Lake kimberlites at Lac de Gras, Slave Craton, Canada. Lithos 2004, 77, 39–55. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aulbach, S.; Creaser, R.A.; Stachel, T.; Heaman, L.M.; Chinn, I.L.; Kong, J. Diamond ages from Victor (Superior Craton): Intra-mantle cycling of volatiles (C, N, S) during supercontinent reorganization. Earth Planet. Sci. Lett. 2018, 490, 77–87. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Patel, S.C.; Ravi, S.; Anilkumar, Y.; Naik, A.; Thakur, S.S.; Pati, J.K.; Nayak, S.S. Mafic xenoliths in Proterozoic kimberlites from Eastern Dharwar Craton, India: Mineralogy and P–T regime. J. Asian Earth Sci. 2009, 34, 336–346. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Naganjaneyulu, K.; Santosh, M. The nature and thickness of lithosphere beneath the Archean Dharwar Craton, southern India: A magnetotelluric model. J. Asian Earth Sci. 2012, 49, 349–361. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ustinov, V.N.; Feijo Bartolomeu, A.M.; Zagainy, A.K.; Felix, J.T.; Mikoev, I.I.; Stegnitskiy, Y.B.; Lobkova, L.P.; Kukui, I.M.; Nikolaeva, E.V.; Antonov, S.A. Kimberlites distribution in Angola and prospective areas for new discoveries. Miner. Petrol. 2018, 112, 383–396. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ashchepkov, I.V.; Rotman, A.Y.; Somov, S.V.; Afanasiev, V.P.; Downes, H.; Logvinova, A.M.; Nossyko, S.; Shimupi, J.; Palessky, S.V.; Khmelnikova, O.S.; et al. Composition and thermal structure of the lithospheric mantle beneath kimberlite pipes from the Catoca cluster, Angola. Tectonophysics 2012, 530, 128–151. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nikitina, L.P.; Korolev, N.M.; Zinchenko, V.N.; Felix, J.T. Eclogites from the upper mantle beneath the Kasai Craton (Western Africa): Petrography, whole-rock geochemistry and U-Pb zircon age. Precambrian Res. 2014, 249, 13–32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Korolev, N.; Nikitina, L.P.; Goncharov, A.; Dubinina, E.O.; Melnik, A.; Müller, D.; Chen, Y.-X.; Zinchenko, V.N. Three Types of Mantle Eclogite from Two Layers of Oceanic Crust: A Key Case of Metasomatically-Aided Transformation of Low-to-High-Magnesian Eclogite. J. Petrol. 2021, 62, 1–38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jacob, D.E.; Bizimis, M.; Salters, V.J.M. Lu–Hf and geochemical systematics of recycled ancient oceanic crust: Evidence from Roberts Victor eclogites. Contrib. Mineral. Petrol. 2005, 148, 707–720. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Korolev, N.M.; Kopylova, M.; Bussweiler, Y.; Pearson, D.G.; Gurney, J.; Davidson, J. The uniquely high-temperature character of Cullinan diamonds: A signature of the Bushveld mantle plume? Lithos 2018, 304, 362–373. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jacob, D.E.; Viljoen, K.S.; Grassineau, N.V. Eclogite xenoliths from Kimberley, South Africa—A case study of mantle metasomatism in eclogites. Lithos 2009, 112, 1002–1013. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, Y.; Li, D.; Chen, Y.; Kang, H.; Geng, H.; Xu, S.; Wang, Y.; Sun, M. Mantle cooling and cratonization of Archean lithosphere by continuous plate subduction: Constraints from TTGs, sanukitoids, and high-K granites, eastern North China Craton. Precambrian Res. 2021, 353, 106042. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hopp, J.; Trieloff, M.; Brey, G.P.; Woodland, A.B.; Simon, N.S.C.; Wijbrans, J.R.; Siebel, W.; Reitter, E. 40Ar/39Ar-ages of phlogopite in mantle xenoliths from South African kimberlites: Evidence for metasomatic mantle impregnation during the Kibaran orogenic cycle. Lithos 2008, 106, 351–364. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Appleyard, C.M.; Viljoen, K.S.; Dobbe, R. A study of eclogitic diamonds and their inclusions from the Finsch kimberlite pipe, South Africa. Lithos 2004, 77, 317–332. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Smyth, J.R. A coesite-sanidine grospydite from the Roberts Victor kimberlite. Earth Planet. Sci. Lett. 1977, 34, 284–290. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gréau, Y.; Huang, J.-X.; Griffin, W.L.; Renac, C.; Alard, O.; O’Reilly, S.Y. Type I eclogites from Roberts Victor kimberlites: Products of extensive mantle metasomatism. Geochim. Cosmochim. Acta 2011, 75, 6927–6954. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, J.-X.; Griffin, W.L.; Gréau, Y.; Pearson, N.J.; O’Reilly, S.Y.; Cliff, J.; Martin, L. Unmasking xenolithic eclogites: Progressive metasomatism of a key Roberts Victor sample. Chem. Geol. 2014, 364, 56–65. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, J.-X.; Li, P.; Griffin, W.L.; Xia, Q.-K.; Greau, Y.; Pearson, N.J.; O’Reilly, S.Y. Water contents of Roberts Victor xenolithic eclogites: Primary and metasomatic controls. Contrib. Mineral. Petrol. 2014, 168, 1092. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schulze, D.J.; Valley, J.W.; Spicuzza, M.J. Coesite eclogites from the Roberts Victor kimberlite, South Africa. Lithos 2000, 54, 23–32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dludla, S.; le Roex, A.P.; Gurney, J.J. Eclogite xenoliths from the Premier kimberlite, South Africa: Geochemical evidence for a subduction origin. South Afr. J. Geol. 2006, 109, 353–368. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Viljoen, F.; Dobbe, R.; Harris, J.; Smit, B. Trace element chemistry of mineral inclusions in eclogitic diamonds from the Premier (Cullinan) and Finsch kimberlites, South Africa: Implications for the evolution of their mantle source. Lithos 2010, 118, 156–168. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Phillips, D.; Onstott, T.C.; Harris, J.W. 40Ar/39Ar laser-probe dating of diamond inclusions from the Premier kimberlite. Nature 1989, 340, 460–462. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kiselev, A.I.; Yarmolyuk, V.V.; Ivanov, A.V.; Egorov, K.N. Middle Paleozoic basaltic and kimberlitic magmatism in the northwestern shoulder of the Vilyui Rift, Siberia: Relations in space and time. Russ. Geol. Geophys. 2014, 55, 144–152. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Radu, I.B.; Harris, C.; Moine, B.N.; Cottin, J.-Y. Subduction relics in the subcontinental lithospheric mantle evidence from variation in the δ 18 O value of eclogite xenoliths from the Kaapvaal craton. Contrib. Mineral. Petrol. 2019, 174, 19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rollinson, H. Eclogite xenoliths in west African kimberlites as residues from Archaean granitoid crust formation. Nature 1997, 389, 173–176. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deines, P.; Harris, J.W. New insights into the occurrence of 13C-depleted carbon in the mantle from two closely associated kimberlites: Letlhakane and Orapa, Botswana. Lithos 2004, 77, 125–142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pyle, J.M.; Haggerty, S.E. Eclogites and the Metasomatism of Eclogites from the Jagersfontein Kimberlite: Punctuated Transport and Implications for Alkali Magmatism. Geochim. Cosmochim. Acta 1998, 62, 1207–1231. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Phillips, D.; Harris, J.W.; Viljoen, K.S. Mineral chemistry and thermobarometry of inclusions from De Beers Pool diamonds, Kimberley, South Africa. Lithos 2004, 77, 155–179. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Albarede, F. How deep do common basaltic magmas form and differentiate. J. Geophys. Res. 1992, 97, 10997–11009. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dawson, J.B. Kimberlites and Their Xenoliths; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 1980; 252p. [Google Scholar]
- Nimis, P.; Taylor, W. Single clinopyroxene thermobarometry for garnet peridotites. Part, I. Calibration and testing of a Cr-in-Cpx barometer and an enstatite-in-Cpx thermometer. Contrib. Mineral. Petrol. 2000, 139, 541–554. [Google Scholar]
- O’Neill, H.S.C.; Wood, B.J. An experimental study of Fe-Mg- partitioning between garnet and olivine and its calibration as a geothermometer. Contrib. Mineral. Petrol. 1979, 70, 59–70. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Krogh, E.J. The garnet-clinopyroxene Fe-Mg geothermometer—A reinterpretation of existing experimental data. Contrib. Mineral. Petrol. 1988, 99, 44–48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lavrent’ev, Y.G.; Korolyuk, V.; Usova, L.; Nigmatulina, E. Electron probe microanalysis of rock-forming minerals with a JXA-8100 electron probe microanalyzer. Russ. Geol. Geophys. 2015, 56, 1428–1436. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ashchepkov, I.V.; André, L.; Downes, H.; Belyatsky, B.A. Pyroxenites and megacrysts from Vitim picrite-basalts (Russia): Polybaric fractionation of rising melts in the mantle? J. Asian Earth Sci. 2011, 42, 14–37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wyman, D.; Kerrich, R. Plume and arc magmatism in the Abitibi subprovince: Implications for the origin of Archean continental lithospheric mantle. Precambrian Res. 2009, 168, 4–22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Neal, C.R.; Taylor, L.A.; Davidson, J.P.; Holden, P.; Halliday, A.N.; Nixon, P.H.; Paces, J.B.; Clayton, R.N.; Mayeda, T.K. Eclogites with oceanic crustal and mantle signatures from the Bellsbank kimberlite, South Africa, Part 2: Sr, Nd, and O isotope geochemistry. Earth Planet. Sci. Lett. 1990, 99, 362–379. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Herzberg, C.; Rudnick, R. Formation of cratonic lithosphere: An integrated thermal and petrological model. Lithos 2012, 149, 4–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rosenthal, A.; Yaxley, G.M.; Green, D.H.; Hermann, J. Continuous eclogite melting and variable refertilisation in upwelling heterogeneous mantle. Sci. Rep. 2014, 4, 6099. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Griffin, W.L.; O’Reilly, S.Y.; Abe, N.; Aulbach, S.; Davies, R.M.; Pearson, N.J.; Doyle, B.J.; Kivi, K. The origin and evolution of the Archean lithospheric mantle. Precambrian Res. 2003, 127, 19–41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ashchepkov, I.V.; Alymova, N.V.; Logvinova, A.M.; Vladykin, N.V.; Kuligin, S.S.; Mityukhin, S.I.; Downes, H.; Stegnitsky, Y.B.; Prokopiev, S.A.; Salikhov, R.F.; et al. Picroilmenites in Yakutian kimberlites: Variations and genetic models. Solid Earth 2014, 5, 915–938. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Pollack, H.N.; Chapman, D.S. On the regional variation of heat flow, geotherms and lithospheric thickness. Tectonophysics 1977, 38, 279–296. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Kennedy, C.S.; Kennedy, G.C. The equilibrium boundary between graphite and diamond. J. Geophys. Res. 1976, 81, 2467–2470. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Day, H.W. A revised diamond-graphite transition curve. Am. Mineral. 2012, 97, 52–62. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brey, G.P.; Kohler, T. Geothermobarometry in four-phase lherzolites. II. New thermobarometers, and practical assessment of existing thermobarometers. J. Petrol. 1990, 31, 1353–1378. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, J.; Rudnick, R.L.; Kostrovitsky, S.; Kalashnikova, T.; Kitajima, K.; Li, R.; Shu, Q. The origin of low-MgO eclogite xenoliths from Obnazhennaya kimberlite, Siberian craton. Contrib. Mineral. Petrol. 2020, 175, 25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Taylor, L.A.; Gregory, A.; Keller, S.R.; Remley, D.A.; Anand, M.; Wiesli, R.; Valley, J.; Sobolev, N.V. Petrogenesis of group A eclogites and websterites: Evidence from the Obnazhennaya kimberlite, Yakutia. Contrib. Mineral. Petrol. 2003, 145, 424–443. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ovchinnikov, Y.I. Deep Seated Xenoliths from Obnazhennaya Pipe Yakutia and Alkaline Basalts from Minusa Depression. Ph.D. Thesis, United Institute of Geology, Geophysics and Minerology, Novosibirsk, Russia, 1991; p. 195. [Google Scholar]
- Ashchepkov, I.V.; Kuligin, S.S.; Vladykin, N.V.; Downes, H.; Vavilov, M.A.; Nigmatulina, E.N.; Babushkina, S.A.; Tychkov, N.S.; Khmelnikova, O.S. Comparison of mantle lithosphere beneath early Triassic kimberlite fields in Siberian craton reconstructed from deep-seated xenocrysts. Geosci. Front. 2016, 7, 639–662. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Griffin, W.L.; Natapov, L.M.; O’Reilly, S.Y.; van Achterbergh, E.; Cherenkova, A.F.; Cherenkov, V.G. The Kharamai kimberlite field, Siberia: Modification of the lithospheric mantle by the Siberian Trap event. Lithos 2005, 81, 167–187. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiao, Y.; Niu, Y.; Li, H.; Wang, H.; Liu, X.; Davidson, J. Trace element budgets and (re-) distribution during subduction-zone ultrahigh pressure metamorphism: Evidence from Western Tianshan, China. Chem. Geol. 2014, 365, 54–68. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Zhou, L.-G.; Xia, Q.-X.; Zheng, Y.-F.; Chen, R.-X. Multistage growth of garnet in ultrahigh-pressure eclogite during continental collision in the Dabie orogen: Constrained by trace elements and U–Pb ages. Lithos 2011, 127, 101–127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McDonough, W.F.; Sun, S.-S. The composition of the Earth. Chem. Geol. 1995, 120, 223–253. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Richardson, S.H.; Shirey, S.B.; Harris, J.W.; Carlson, R.W. Archean subduction recorded by Re–Os isotopes in eclogitic sulfide inclusions in Kimberley diamonds. Earth Planet. Sci. Lett. 2001, 191, 257–266. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Erdman, M.E.; Lee, C.-T.A. Oceanic- and continental-type metamorphic terranes: Occurrence and exhumation mechanisms. Earth-Sci. Rev. 2014, 139, 33–46. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Afanasyev, V.P.; Agashev, A.M.; Orihashi, Y.; Pokhilenko, N.P.; Sobolev, N.V. Paleozoic U–Pb Age of Rutile Inclusions in Diamonds of the V–VII Variety from Placers of the Northeast Siberian Platform. Dokl. Earth Sci. 2009, 428, 1151–1155. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Laiginhas, F.; Pearson, D.G.; Phillips, D.; Burgess, R.; Harris, J.W. Re–Os and 40Ar/39Ar isotope measurements of inclusions in alluvial diamonds from the Ural Mountains: Constraints on diamond genesis and eruption ages. Lithos 2009, 112, 714–723. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shu, Q.; Brey, G.P.; Gerdes, A.; Hoefer, H.E. Mantle eclogites and garnet pyroxenites—The meaning of two-point isochrons, Sm–Nd and Lu–Hf closure temperatures and the cooling of the subcratonic mantle. Earth Planet. Sci. Lett. 2014, 389, 143–154. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rogers, J.J.W.; Santosh, M. Continents and Supercontinents; Oxford University Press: New York, NY, USA, 2004; Volume 289, p. 1204. [Google Scholar]
- Gerya, T. Precambrian geodynamics: Concepts and models. Gondwana Res. 2014, 25, 442–463. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pokhilenko, N.P.; Sobolev, N.V.; Kuligin, S.S.; Shimizu, N. Peculiarities of distribution of pyroxenite paragenesis garnets in Yakutian kimberlites and some aspects of the evolution of the Siberian craton lithospheric mantle. In Proceedings of the 7th International Kimberlite Conference; Red Roof Design: Cape Town, South Africa, 1999; pp. 690–707. [Google Scholar]
- Regelous, M.; Collerson, K.D. 147Sm/143Nd, 146Sm/142Nd systematics of early Archaean rocks and implications for crust-mantle evolution. Geochim. Cosmochim. Acta 1996, 60, 3513–3520. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Z.; Wang, L.; Brown, M.; Johnson, T. Partial Melting of Bimineralic Eclogite by Clinopyroxene Breakdown. In Proceedings of the EGU General Assembly 2021, Online, 13–30 April 2021. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ashchepkov, I.V.; Vladykin, N.V.; Ivanov, A.; Babushkina, S.; Vavilov, M.; Medvedev, N. Problems of Mantle Structure and Compositions of Various Terranes of Siberian Craton. In Alkaline Rocks, Kimberlites and Carbonatites: Geochemistry and Genesis; Vladykin, N., Ed.; Springer: Cham, Switzerland, 2021; Volume 95, pp. 15–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cherepanova, Y.; Artemieva, I.M. Density heterogeneity of the cratonic lithosphere: A case study of the Siberian Craton. Gondwana Res. 2015, 28, 1344–1360. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dobosi, G.; Kurat, G. Trace element abundances in garnets and clinopyroxenes from diamondites a signature of carbonatitic fluids. Mineral. Petrol. 2002, 76, 21–38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- John, T.; Scherer, E.E.; Haase, K.; Schenk, V. Trace element fractionation during fluid-induced eclogitization in a subducting slab: Trace element and Lu-Hf-Sm-Nd isotope systematics. Earth Planet. Sci. Lett. 2004, 227, 441–456. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Radu, I.B.; Moine, B.N.; Bolfan-Casanova, N.; Ionov, D.A.; Devidal, J.L.; Deloule, E.; Korsakov, A.V.; Golovin, A.V.; Oleinikov, O.B.; Cottin, J.Y. Zoisite in cratonic eclogite xenoliths - Implications for water in the upper mantle. Lithos 2022, 418–419, 106681. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hart, S.R.; Dunn, T. Experimental cpx/melt partitioning of 24 trace elements. Contrib. Mineral. Petrol. 1993, 113, 1–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Harte, D.; Kirkley, M.B. Partitioning of trace elements between clinopyroxene and garnet: Data from mantle eclogites. Chem. Geol. 1997, 136, 1–24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Condie, K.C.; Cox, J.; O’Reilly, S.Y.; Griffin, W.L.; Kerrich, R. Distribution of high field strength and rare earth elements in mantle and lower crustal xenoliths from the Southwestern United States: The role of grain-boundary phases. Geochim. Cosmochim. Acta 2004, 68, 3919–3942. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schmidt, A.; Weyer, S.; John, T.; Brey, G.P. HFSE systematics of rutile-bearing eclogites: New insights into subduction zone processes and implications for the earth’s HFSE budget. Geochim. Cosmochim. Acta 2009, 73, 455–468. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zack, T.; Tomascak, P.B.; Rudnick, R.L.; Dalpé, C.; McDonough, W.F. Extremely light Li in orogenic eclogites: The role 836 of isotope fractionation during dehydration in subducted oceanic crust. Earth Planet. Sci. Lett. 2003, 208, 279–290. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kamenetsky, V.S.; Kamenetsky, M.B.; Sobolev, A.V.; Golovin, A.V.; Sharygin, V.V.; Pokhilenko, N.P.; Sobolev, N.V. Can pyroxenes be liquidus minerals in the kimberlite magma? Lithos 2009, 112, 213–222. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Afanasiev, V.P.; Ashchepkov, I.V.; Verzhak, V.V.; O’Brien, H.; Palessky, S.V. PT conditions and trace element variations of picroilmenites and pyropes from the Arkhangelsk region. J. Asian Earth Sci. 2013, 70, 45–63. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]



















Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Ashchepkov, I.; Logvinova, A.; Spetsius, Z.; Downes, H.; Ntaflos, T.; Ivanov, A.; Zinchenko, V.; Kostrovitsky, S.; Ovchinnikov, Y. Eclogite Varieties and Their Positions in the Cratonic Mantle Lithosphere beneath Siberian Craton and Archean Cratons Worldwide. Minerals 2022, 12, 1353. https://doi.org/10.3390/min12111353
Ashchepkov I, Logvinova A, Spetsius Z, Downes H, Ntaflos T, Ivanov A, Zinchenko V, Kostrovitsky S, Ovchinnikov Y. Eclogite Varieties and Their Positions in the Cratonic Mantle Lithosphere beneath Siberian Craton and Archean Cratons Worldwide. Minerals. 2022; 12(11):1353. https://doi.org/10.3390/min12111353
Chicago/Turabian StyleAshchepkov, Igor, Alla Logvinova, Zdislav Spetsius, Hilary Downes, Theodoros Ntaflos, Alexandr Ivanov, Vladimir Zinchenko, Sergey Kostrovitsky, and Yury Ovchinnikov. 2022. "Eclogite Varieties and Their Positions in the Cratonic Mantle Lithosphere beneath Siberian Craton and Archean Cratons Worldwide" Minerals 12, no. 11: 1353. https://doi.org/10.3390/min12111353
APA StyleAshchepkov, I., Logvinova, A., Spetsius, Z., Downes, H., Ntaflos, T., Ivanov, A., Zinchenko, V., Kostrovitsky, S., & Ovchinnikov, Y. (2022). Eclogite Varieties and Their Positions in the Cratonic Mantle Lithosphere beneath Siberian Craton and Archean Cratons Worldwide. Minerals, 12(11), 1353. https://doi.org/10.3390/min12111353







