Abstract
The Daocaowan antimony (Sb) deposit is a newly discovered Sb deposit located outside the northeast Xikuangshan ore field. In the absence of geochemical data, the metallogenic mechanism of the Daocaowan Sb deposit and its relationship with the Xikuangshan ore field remains unclear. Using high-resolution LA-ICP-MS technique, this study quantitatively determined the in-situ S isotope values and trace element composition of stibnite from the Daocaowan Sb deposit in South China to investigate the source of ore-forming materials and genesis of this deposit. The trace element compositions of stibnite from the Daocaowan Sb deposit revealed the form of occurrence and substitution mechanism of trace elements in stibnite, providing new constraints for explaining the genesis of Sb deposits. The relatively smooth LA-ICP-MS profiles indicate that As, Cu, Hg, and Pb primarily occur as solid solutions in stibnite. Therefore, we speculate that the substitution 3Sb3+↔As3+ + 2Cu+ + Hg2+ + Pb2+ may be the reason for the enrichment of As, Cu, Hg, and Pb in stibnite. A comparison with the Xikuangshan Sb deposit reveals the metallogenic mechanism of the Daocaowan Sb deposit, and the relationship between the two. With the exception of higher content of Fe in Stibnite from the Daocaowan deposit as compared to the Xikuangshan deposit, other trace elements are similar between the two deposits. The results show that the Daocaowan and Xikuangshan Sb deposits may have the same source of ore-forming fluids. We propose that the ore-forming fluid flowed through the Xikuangshan Sb deposit along the F75 fault and dissolved pyrite in the wall rock. Subsequently this fluid containing a high concentration of Fe precipitated and mineralized at Daocaowan. Meanwhile, the S isotope value of the Daocaowan Sb deposit (+6.65 to +9.29‰) is consistent with that of the Xikuangshan, proving that the ore-forming materials of the two deposits are from the same source, probably the basement strata. We propose that the Daocaowan Sb deposit is part of the Xikuangshan ore field, indicating a great prospecting potential in the northeast of the Xikuangshan ore field.
1. Introduction
Sb, as a non-renewable strategic mineral resource, is widely used in flame retardants, battery alloy materials, and military fields, and is listed as a strategic key metal by major countries such as China and the United States [1,2,3]. China is rich in Sb reserves and production, leading the world in Sb production and trade [2]. China accounted for 55% of global Sb production in 2021, followed by Russia (23%) and Tajikistan (12%) [3,4]. Stibnite (Sb2S3), due to its stable physical and chemical properties [5], is the main, or even the only, ore mineral in most Sb deposits (e.g., Xikuangshan Sb deposit) [2,6,7,8,9,10].
The composition of mineral trace elements is generally related to fluid characteristics (such as redox state, pressure, temperature, fluid source area, etc.), and is widely used to clarify the genesis and metallogenic processes of various hydrothermal deposits [11,12,13,14]. At present, there are few quantitative studies on trace elements in stibnite [9,15], and the distribution mechanism of trace elements in stibnite is not clear. Therefore, the study of trace element composition and precipitation mechanism of stibnite can potentially clarify the genesis of Sb deposits. In addition, S isotope can directly constrain the source of sulfur in hydrothermal deposits. Although bulk-rock analysis methods for sulfur isotopes can produce high precision analyses, recent studies have shown that laser ablation multi-collector inductively coupled plasma mass spectrometry (LA-MC-ICP-MS) for in-situ sulfur isotope analysis has a higher accuracy and spatial resolution (10–100 μm) than the bulk-rock analysis method [16,17]. Therefore, in-situ sulfur isotope analysis can accurately trace the source of sulfur in hydrothermal minerals.
The central Hunan metallogenic province, which belongs to the South China low-temperature metallogenic domain, is the largest Sb ore concentration area in China, with abundant mineral resources and more than 100 Sb deposits [7,18]. The Xikuangshan Sb deposit, the world’s largest Sb deposit, is located in the central Hunan metallogenic province. Its proven reserves of Sb resources exceed 2 million tons with an average grade of 4% [7,19]. However, with the long-term high-intensity mining, the reserves of Sb metal in the Xikuangshan Sb deposit have been greatly depleted, causing a serious resource depletion crisis. Additional reserves need to be urgently identified to ensure sustainable production. In recent years, a new Sb deposit in Daocaowan has been discovered outside the northern margin of the Xikuangshan ore field. The total proven metal reserves of Sb resources in the Daocaowan Sb deposit are about 70,000 tons, with an average grade of 1.82%. Some scholars have comparatively analyzed the geological characteristics of the Xikuangshan and Daocaowan Sb deposits, which showed the same ore-controlling characteristics, and proposed that the Daocaowan Sb deposit is a part of the Xikuangshan ore field [20,21]. It is notable that the study on geochemistry of the Daocaowan Sb deposit is still unknown. To address these lacunae, this paper reports the LA-ICP-MS study of trace elements and in-situ S isotope in stibnite from the Daocaowan Sb deposit. The objectives of this study are to (1) reveal and improve the distribution and substitution mechanism of trace elements in stibnite; (2) determine the source and mechanism of Sb ore-forming materials in the Daocaowan Sb deposit; (3) clarify the relationship between the Daocaowan and Xikuangshan Sb deposit from the perspective of geochemistry; (4) elucidate the mechanism of Sb mineralization in the Xikuangshan ore field. The results of this study will provide new insights in the genesis of the deposit and propose a basis for further deep mineral exploration.
2. Regional and Deposit Geology
The South China Block is composed of the Yangtze Block and the Cathaysia Block, which were amalgamated along the Jiangnan orogenic belt [7,22]. The central Hunan metallogenic province is located at the junction of Yangtze Block and Cathaysia Block (Figure 1a), which is composed of the central Hunan basin and the Xuefengshan uplift belt (Figure 1b). The basement of this region comprises low-grade metasedimentary rocks of Late Proterozoic and Early Paleozoic age, whereas the overlying non-metamorphosed sedimentary rocks consist of mainly Upper Paleozoic to Mesozoic carbonate and clastic rocks [23,24].
There are more than 170 Sb-(Au-W) deposits and prospects in the central Hunan Sb metallogenic belt [7,25]. The proven Sb metal reserves in this area exceed 2.7 million tons, accounting for more than 50% of the world’s total reserves [7,26]. Most Sb deposits in this area occur in the Paleozoic and Precambrian strata, especially in the Cambrian and Devonian strata [18,27]. The magmatic activity in the area is intense, but the distribution of Sb deposits is generally far away from magmatic rocks. The relationship between magma and Sb mineralization is not clear. Structure and stratum lithology are important factors controlling the distribution of Sb deposits in this area. Sb deposits in the area can be divided into two groups: Sb-only deposits and Sb-polymetallic deposits. The Xikuangshan Sb deposit is the largest and most representative Sb-only deposit in this region. The geological features of the Xikuangshan have been described in previous literature [7,9,25,28,29,30,31], the most important of which are summarized below.
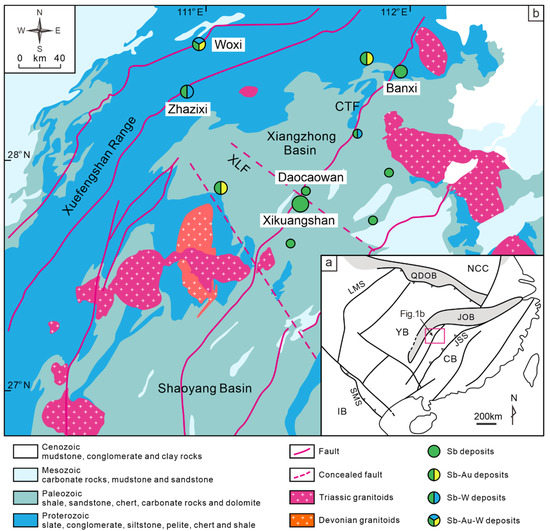
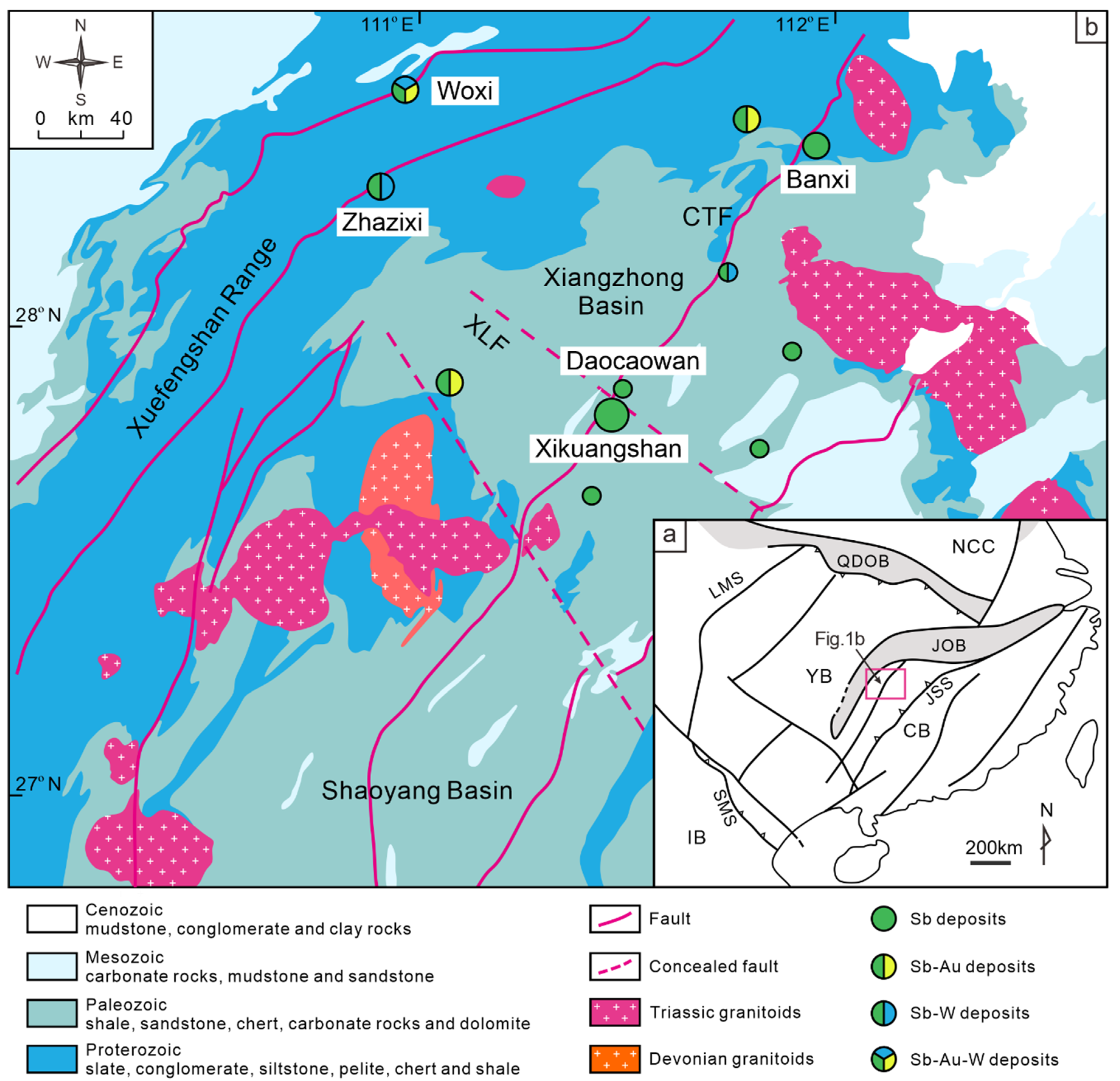
Figure 1.
(a) Tectonic framework of the South China Block (Modified from [7,30]). Abbreviations: NCC = North China Craton, QDOB = Qinling-Dabie Orogen Belt, LMS = Longmenshan Fault, JOB = Jiangnan Orogen Belt, YB = Yangtze Block, JSS = JiangShao Suture, CB = Cathaysia Block, SMS = Song-MA Suture, IB = Indochina Block. (b) Regional geological map and distribution of some antimony ores in Central Hunan (Modified from [7,30]). XLF = Xinhua-Lianyuan Fault, CTF = Chengbu-Taojiang Fault.
Figure 1.
(a) Tectonic framework of the South China Block (Modified from [7,30]). Abbreviations: NCC = North China Craton, QDOB = Qinling-Dabie Orogen Belt, LMS = Longmenshan Fault, JOB = Jiangnan Orogen Belt, YB = Yangtze Block, JSS = JiangShao Suture, CB = Cathaysia Block, SMS = Song-MA Suture, IB = Indochina Block. (b) Regional geological map and distribution of some antimony ores in Central Hunan (Modified from [7,30]). XLF = Xinhua-Lianyuan Fault, CTF = Chengbu-Taojiang Fault.
2.1. The Xikuangshan Sb Deposit
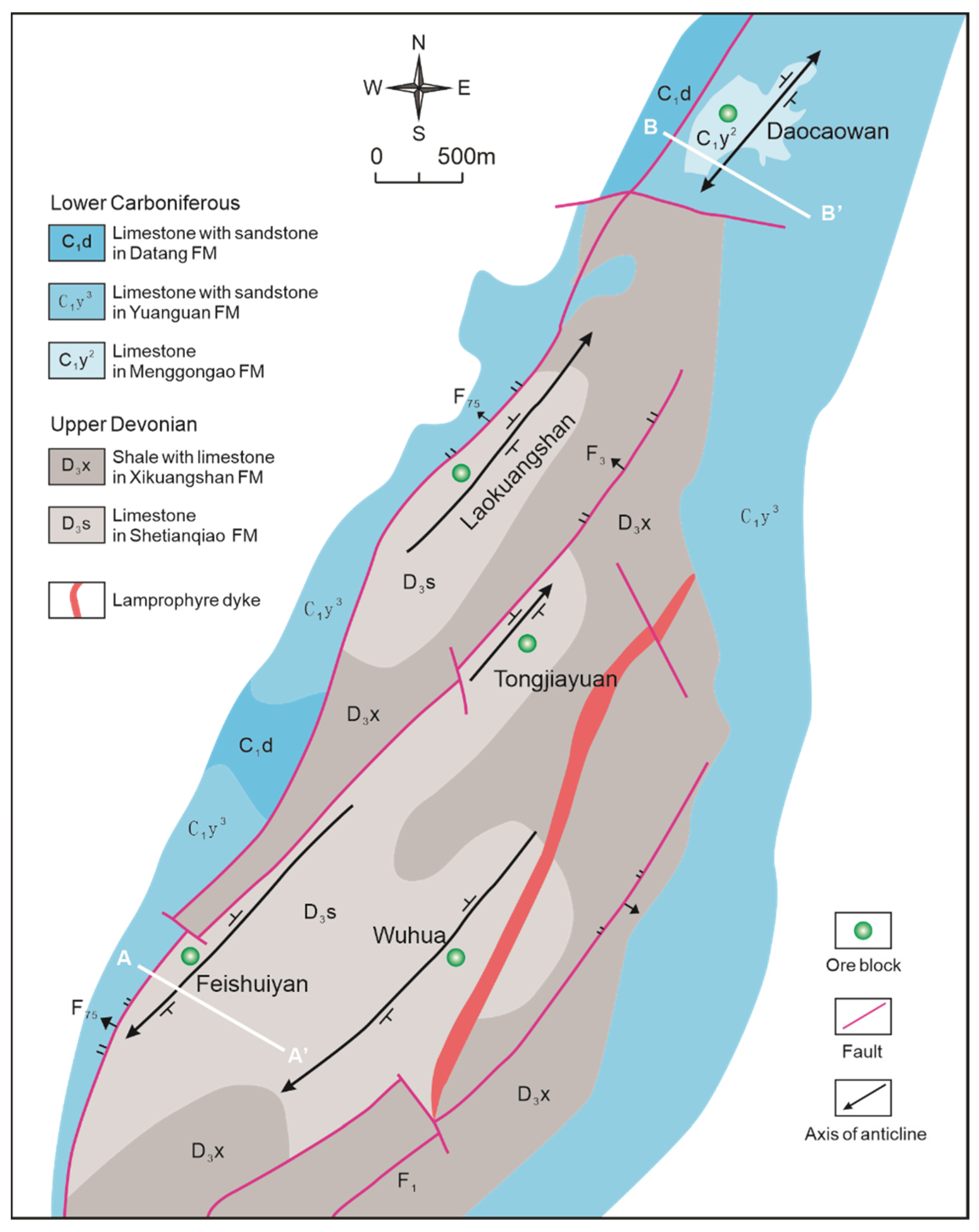
The Xikuangshan Sb deposit is located at the intersection of the NE-striking Taojiang-Chengbu crust-scaled fault and NW-striking Xinhua-Lianyuan basement fault (Figure 1b). On a local scale, the Xikuangshan complex ‘box-type’ anticline is the first-order structure, and a series of secondary folds are developed within this range. The northwest limb of the anticline is cut by the fault F75, and the east wing is cut by a lamprophyre vein [25,32,33]. F75 is the main primary ore-controlling fault in Xikuangshan. Almost all orebodies occur in the lower plate of F75, so the fault is also considered to be the main channel for the migration of mineralized fluid [7,34]. Anticline structure is the main host structure. Sb mineralization is mainly controlled by secondary anticlines and faults. From north to south, four secondary anticlines, Laokuangshan, Tongjiayuan, Feishuiyan, and Wuhua, controlled the output of the four ore sections of the Xikuangshan Sb deposit (Figure 2) [28,29]. The combination of anticline + NE-trending fault + ore-bearing lithology constitutes the regional ore-controlling regularity of ‘anticline plus one knife’. The lamprophyre vein [25] exposed in the east is the only magmatic rock known in Xikuangshan, which is usually considered to be the eastern boundary of Sb mineralization [27].
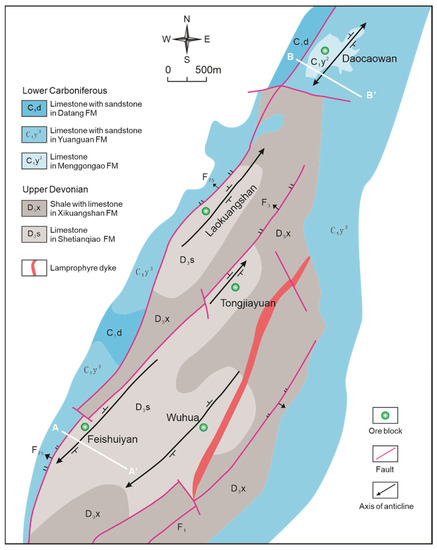
Figure 2.
Geological map of the Xikuangshan ore field (Modified from [31]). The Daocaowan Sb deposit is located outside the northern margin of the Xikuangshan Sb deposit.
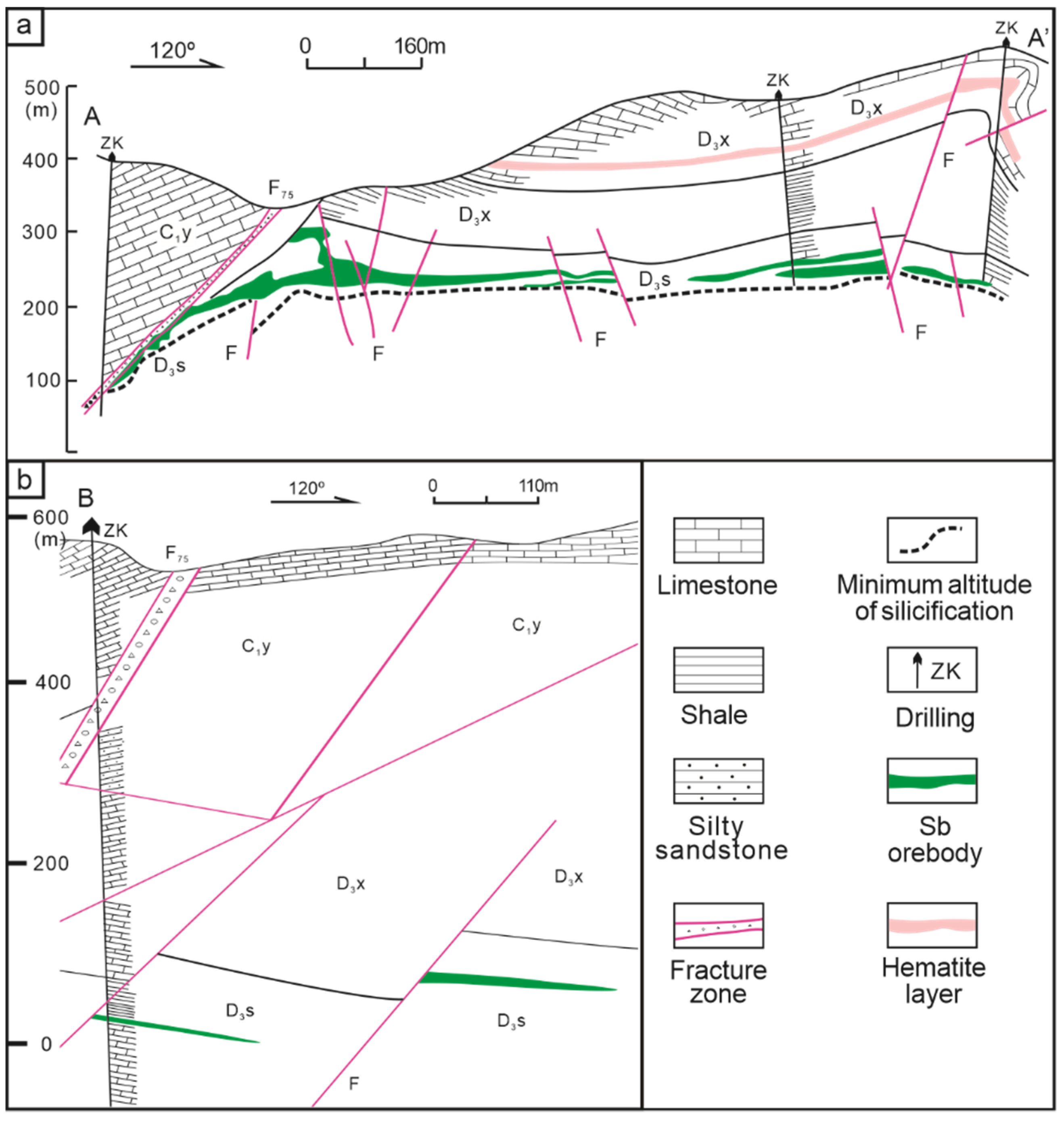
The strata exposed in the ore district are mainly Carboniferous and Upper Devonian carbonate. The wall rock alteration, stronger in the shallow position, is mainly silicification. The main ore-bearing strata are the Upper Devonian Shetianqiao Formation. The Shetianqiao Formation is divided into shale, limestone, and sandstone sections from top to bottom. The Sb orebodies are dominantly hosted in silicified rock of limestone section. Most Sb orebodies occur below the shale, which is considered to be a barrier to ascending ore fluids in the Xikuangshan Sb deposit [19,35]. The Sb orebodies in the Xikuangshan Sb deposit are chiefly stratiform in shape, parallel to the host Devonian strata (Figure 3a), generally extending from 30 m to 600 m along the strike, and 1300–1800 m down dip with a thickness of 1–5 m (locally up to 20 m).
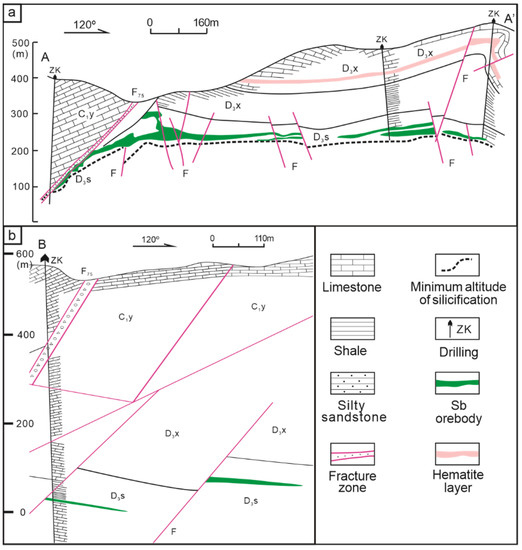
Figure 3.
(a) A typical profile map of the Xikuangshan Sb deposit (Modified from [25]). (b) A typical profile map of the Daocaowan Sb deposit.
The Sb ores in Xikuangshan are distributed in massive, net-veins and disseminated forms. The ores have a simple mineral association with stibnite as the only economic metallic mineral; the gangue minerals are mainly quartz, calcite, and a small amount of barite and fluorite [25,28,29]. Sparse disseminated pyrite affected by late hydrothermal fluid exists in host rock of Sb orebodies. According to mineral paragenesis, the mineralization can be divided into three stages: pre-mineralization, mineralization, and post-mineralization [7,25]. The ore types are mainly quartz-stibnite type, quartz–calcite stibnite type, and calcite–stibnite type.
Although many studies have been carried out in Xikuangshan, the source of ore-forming materials and mechanism is still controversial. Fluid inclusion data show that the ore-forming fluids homogenization temperature, and the salinity between stibnite and gangue minerals in Xikuangshan are significantly different. The homogenization temperature of stibnite inclusions is 112 °C~324 °C, and the salinity range is 0.2~15.4 wt% NaCl equiv [25]. Different from the two mineralization ages (Sm–Nd isotopic compositions of syn-sulfide calcites, 155.5 ± 1.1 Ma, 124.1 ± 3.7 Ma) [29], the in-situ U-Pb data of calcite associated with stibnite show that mineralization occurred in the Eocene (58.1 ± 0.9 Ma, 50.4 ± 5.0 Ma) [31]. At the same time, isotope data in recent years show that the source of ore-forming materials of Xikuangshan may be the Proterozoic basement [9,19,30].
2.2. The Daocaowan Sb Deposit
The Daocaowan Sb deposit is located outside the northern margin of the Xikuangshan Sb deposit (Figure 2), with excellent metallogenic geological conditions. Two groups of faults are mainly developed in the Daocaowan Sb deposit. A group of faults is the north-east longitudinal faults, of which the regional Chengbu-Taojiang deep fault F75 is the primary ore-controlling fault in the Daocaowan Sb deposit, extending northeastward through the west of the ore district. The other group, F74, F71, F72, etc., is the east-west extension of secondary faults. Similar to the Xikuangshan Sb deposit, Sb mineralization in the Daocaowan Sb deposit is mainly controlled by secondary anticline and fault. The Daocaowan anticline, a secondary anticline of the Xikuangshan complex ‘box-type’ anticline, is the main ore-hosting structure of Sb orebodies, controlling the mineralization of the Daocaowan Sb deposit (Figure 2). The ore-controlling combination of ‘anticline + NE fault + ore–host rock’ in the Daocaowan Sb deposit forms the ore-controlling regularity of ‘anticline plus one blade’ similar to the Xikuangshan Sb deposit.
The strata exposed in the ore district are mainly the Lower Carboniferous Datang Stage (C1d) and the Yanguan Stage (C1y). The Xikuangshan Formation (D3x) and Shetianqiao Formation (D3s) of Upper Devonian are revealed in the borehole. The limestone member of the Shetianqiao Formation (D3s2) is the main ore-bearing strata. There is no magmatic rock mass exposed in the ore district. Silicification is the most closely related wall rock alteration due to mineralization in this area, which is distributed on the footwall side of the NE-trending fault. Among them, the silicification of the Shetianqiao Formation (D3s2) is accompanied by Sb mineralization, which is closely related. The Sb orebodies of the Daocaowan Sb deposit are chiefly stratiform in shape (Figure 3b and Figure 4a). The integrity of the Sb orebodies is good and is mainly controlled by the anticline structure of the stratum. Thick and rich Sb orebodies generally occur at stratigraphic uplifts, where the silicification thickness increases. In synclines, silicification is generally weak, mineralization is discontinuous, and even non-mineralized sections appear. The Sb orebodies are divided into I-1, I-2, and I-3, of which I-2 is the main orebodies in the Daocaowan Sb deposit. The thickness of the I-2 is 0.46–4.35 m, and the ore grade is 0.47–6.62% [20].

Figure 4.
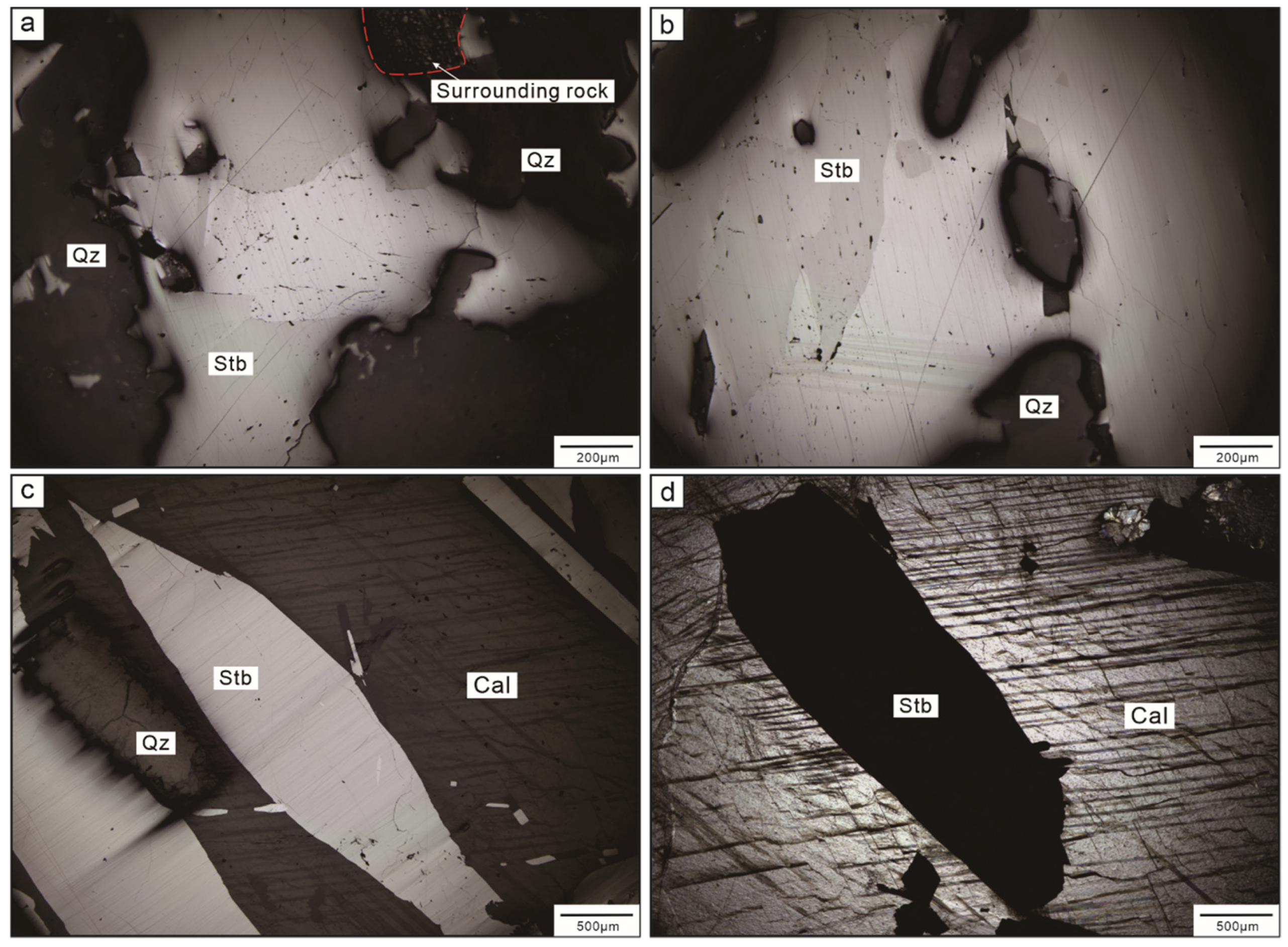
Representative photographs of orebodies and Sb ores in the Daocaowan Sb deposit. (a,b) Vein-type orebodies hosted by silicified limestone; (c) Quartz–stibnite ores; (d) Massive stibnite ores; (e) Calcite–stibnite ore; (f) Miarolitic structure. Qz = quartz, Cal = calcite, Stb = stibnite.
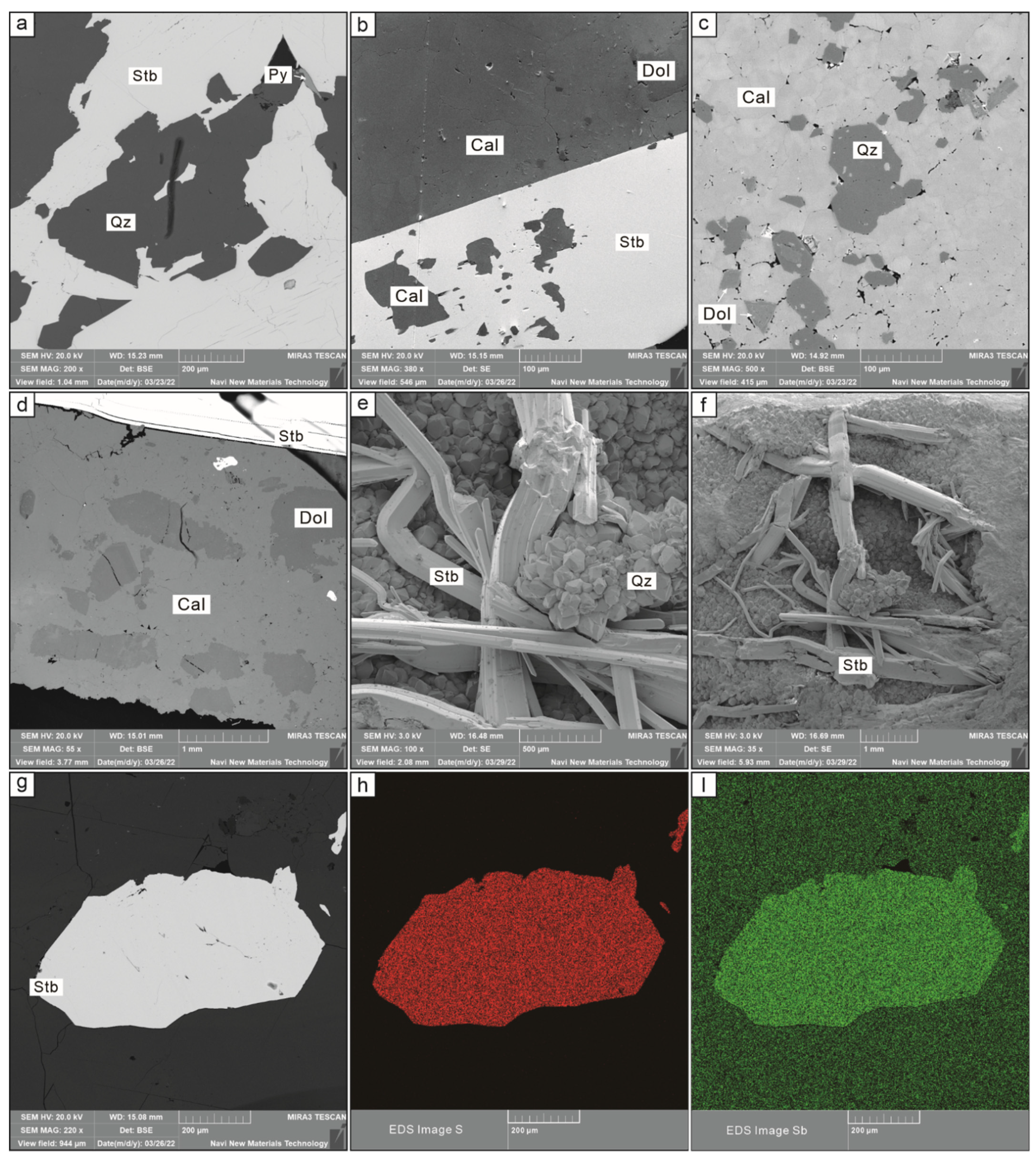
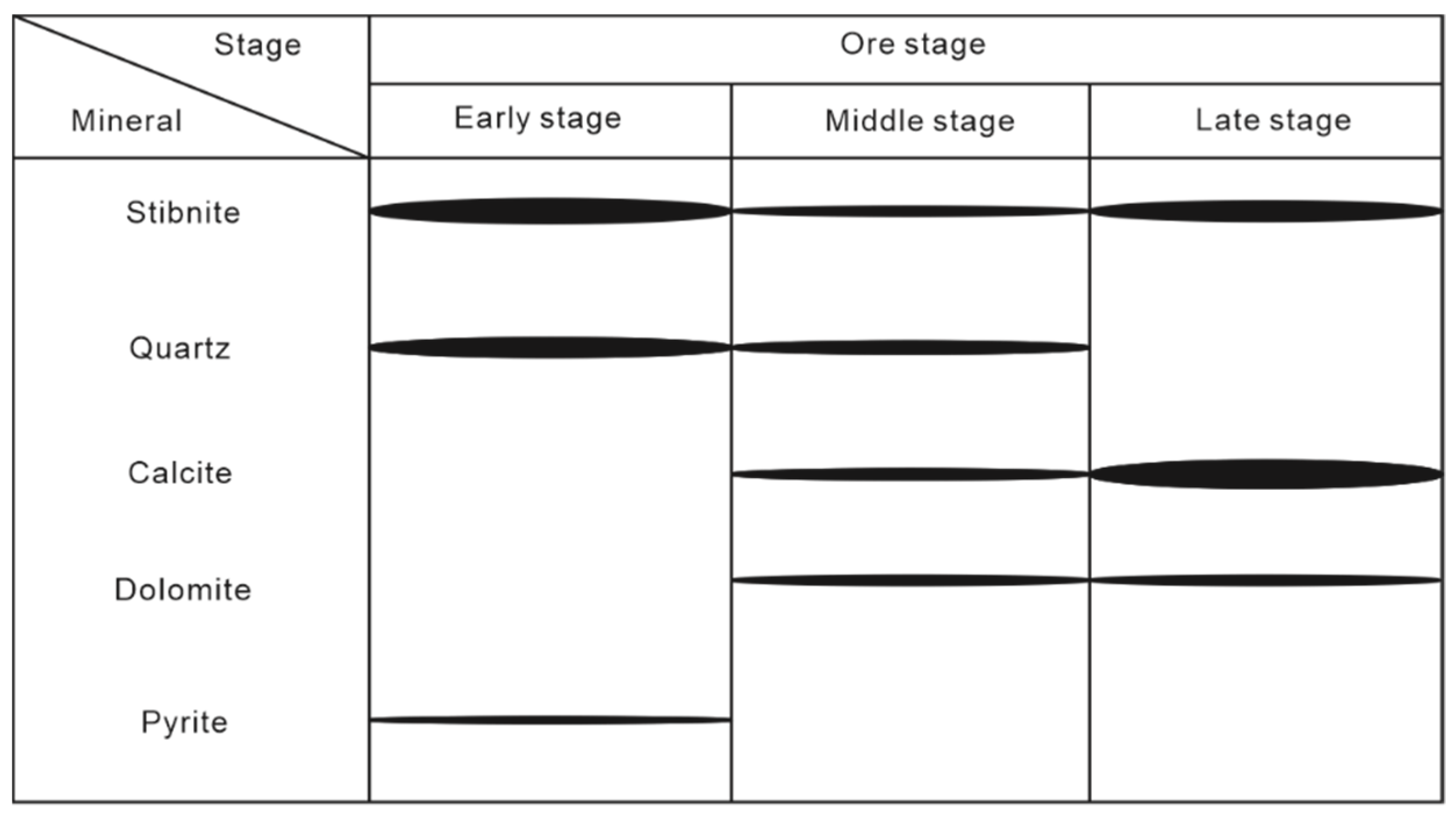
The Daocaowan Sb deposit has a simple mineral assemblage. The main metal minerals are stibnite and pyrite, and gangue minerals are mainly calcite, quartz, and dolomite (Figure 4, Figure 5 and Figure 6). The ore structure is dominated by a disseminated and veined structure. It is worth noting that crystal hole structures can be found (Figure 6e,f). The mineralization of Daocaowan can simply divided into three stages according to field interpenetration and mineral paragenesis (Figure 7). The ore types are mainly quartz–stibnite type, quartz–calcite–stibnite type, and calcite–stibnite type.
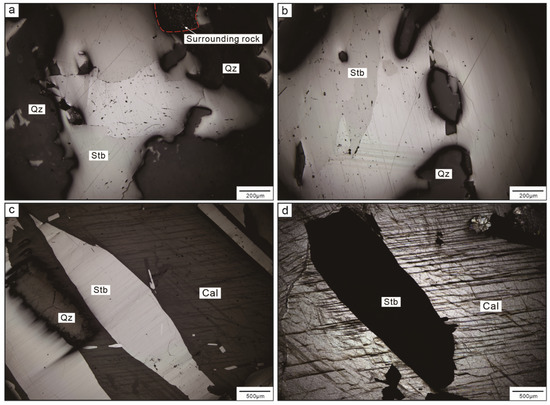
Figure 5.
Representative microscopic photographs of the Daocaowan Sb deposit. (a,b) Quartz–stibnite ores; (c) Quartz–calcite–stibnite ores; (d) Calcite–stibnite ore.
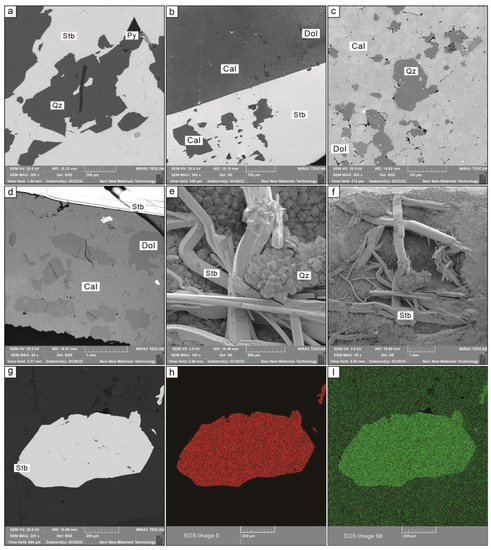
Figure 6.
Scanning electron microscopy images of the Daocaowan Sb deposit. (a) Pyrite growing in quartz–stibnite ores; (b,d) Dolomite growth in calcite–stibnite ore; (c) Quartz–calcite–stibnite ores showing the association between calcite and quartz; (e,f) Quartz and stibnite in crystal cavity; (g–i) Energy spectrum scanning of stibnite showing that there is no obvious structure in stibnite particles.
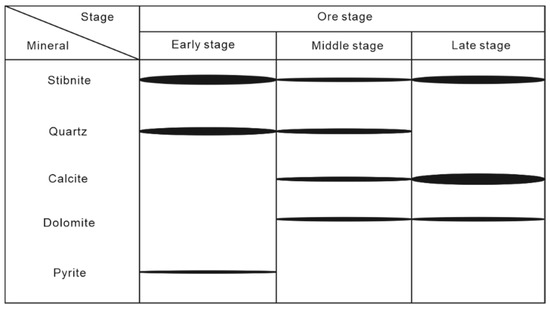
Figure 7.
Paragenetic sequence at the Daocaowan Sb deposit.
At present, there are few studies of the Daocaowan Sb deposit. Previous scholars have only briefly summarized the geological features of the Daocaowan Sb deposit [20,21]. Despite a lack of geological and geochemical evidence, the Daocaowan Sb deposit is con-sidered to be the fourth largest ore block in the Xikuangshan ore field. At the same time, the ore-forming material source, fluid evolution, and metallogenic mechanism of the Daocaowan Sb deposit are still unclear.
3. Samples and Analytical Methods
3.1. Samples
In this study, all samples were fresh ores collected from underground exposures. Field photographs of samples are shown in Figure 4a,b. Systematic sampling and numbering of ores from three mineralization stages in the Daocaowan Sb deposit (Figure 4c–e): (1) Quartz–Stibnite type (DCW-1-2); (2) Quartz–Calcite–Stibnite type (DCW-1-1); (3) Calcite–Stibnite type (DCW-1-3, DCW-2). The in-situ trace elements (DCW-1-1, DCW-1-1, DCW-1-3, DCW-2) and S isotopes (DCW-1-2 and DCW-2) of stibnite were tested for representative ores in different metallogenic stages.
3.2. LA-ICP-MS Analyses
Trace elements of stibnite were determined by NWR 193 nm ArF Excimer laser-ablation system coupled to an iCAP RQ (ICPMS) at the Guangzhou Tuoyan Analytical Technology Co., Ltd., Guangzhou, China. In order to obtain a lower oxide production rate, the ICPMS was tuned using NIST 610 standard glass The 0.7 l/min He carrier gas was passed into the cup, followed by mixing the aerosol with 0.89 l/min Ar make-up gas. The laser fluence was 5 J/cm2, and the repetition frequency was 6 Hz. The spot size was 30 μm with the analysis time of 40 s, and the background measurement time was 45 s. Measured isotopes were selected to avoid isobaric and polyatomic interferences, and the following isotopes were measured: 34S, 51V, 53Cr, 55Mn, 70Ge, 126Te, 57Fe, 59Co, 60Ni, 65Cu, 66Zn, 71Ga, 75As, 77Se, 85Rb, 88Sr, 95Mo, 105Pd, 107Ag, 111Cd, 115In, 118Sn, 197Au, 202Hg, 208Pb, 209Bi, and 238U, all of which have a residence dwell time of 10 ms, corresponding to a total dwell time of 280 ms. The raw isotope data were reduced using the “TRACE ELEMENTS” data reduction scheme (DRS), which runs in the freeware IOLITE software of Paton et al. [36]. In IOLITE, user-defined time intervals are established for the baseline correction process in order to calculate session-wide baseline-corrected values for each isotope. In the analytical session, the elements were calibrated using NIST 610, GE7b, and the sulfide reference material MASS-1 (formerly known as PSD-1) [37]. The external calibration was performed against the different standards (NIST 610, GE7b, or MASS-1) for different elements, and the others were analyzed to monitor the analytical accuracy. The determination of five to eight unknown samples was performed for two standards (one NIST 610 and one GE7b) and one MASS-1 sulfide standard analysis. Analytical accuracy for most elements is expected to be better than 20%. The raw analytical data in each spot is plotted as a time-resolved depth spectrum and the integration time for background and sample signal selected. The counts were then corrected for instrument drift and converted to concentration values using the 121Sb (Sb = 71%) as an internal standard. The detection limits for the major elements were S (358 ppm), Cu (0.124 ppm), Hg (0.061 ppm), As (0.759 ppm), Pb (0.002 ppm), Zn (0.114 ppm), and Fe (598 ppm).
3.3. In-Situ Sulfur Isotope Analysis
In-situ sulfur isotopic compositions of stibnite in ore samples were analyzed by LA-MC-ICP-MS at the State Key Laboratory of Continental Dynamics, Northwest University, China. The instrument used for in situ S isotope analysis consists of a laser ablation system (RESOlution M-50) connected to MC-ICP-MS (Nu Plasma 1700). An excimer laser (193 nm), a two-volume laser ablation cell (Laurin Technic S155, 155 mm × 105 mm), a squid leveling device, and a computer-controlled high-precision X-Y stage make up the laser ablation system. The Nu 1700 MC-ICP-MS system is equipped with 16 Faraday cups and 3 ion counters for the determination of the sulfur isotopic composition of the PSPTs. The configuration of sulfur cups varies, with H5 cups for 34S, Ax cups for 33S, and L4 cups for 32S.
Helium was used as a carrier gas (0.28 L/min) during the laser ablation process and entered the cell body at its bottom to fill the cell. Prior to the squid signal smoothing device, helium was mixed downstream from the bottom and top into the MC-ICP-MS through a funnel cell containing sample aerosol and argon (0.98 L/min). Details of the method are given by Chen et al. [38]. To monitor the accuracy of the data during the analysis, the instrument mass bias was corrected using the SSB method with repeated measurements of the standard reference (IAEA-S-1, Ag2S) before and after each sample. The internal standard Cpy-1/GC (δ34S = −0.7 ± 0.3‰) was also analyzed for every eight unknown points. The analytical uncertainty of δ34S is < 0.1‰.
4. Results
4.1. Trace Element Composition of Stibnite
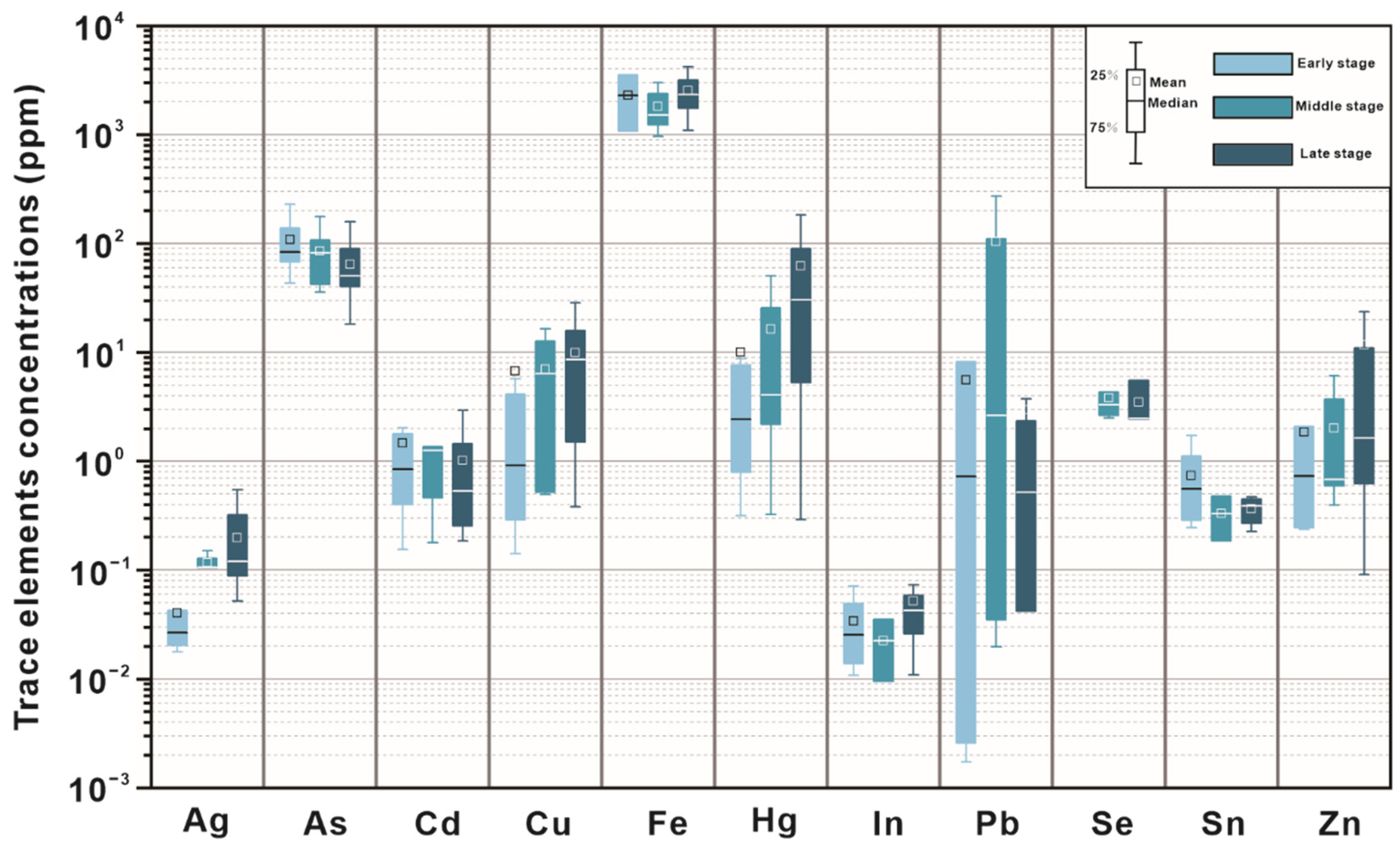
A total of 50 spots by LA-ICP-MS in-situ analysis of three representative stibnite samples from the Daocaowan Sb deposit were analyzed, and the results are shown in Table S1 and Figure 8. As many elements were detected at extremely low concentration or even below detection limit, Figure 8 shows only some elements with elevated concentrations. However, the entire LA-ICP-MS dataset is reported in Electronic Supplement Table S1. Stibnite, the main ore mineral in the Daocaowan Sb deposit, did not display zonation in backscattered electron images (BSE) (Figure 6a,g). Sb was also found to be very uniform in stibnite particles by EDS energy spectrum scanning (Figure 6i).
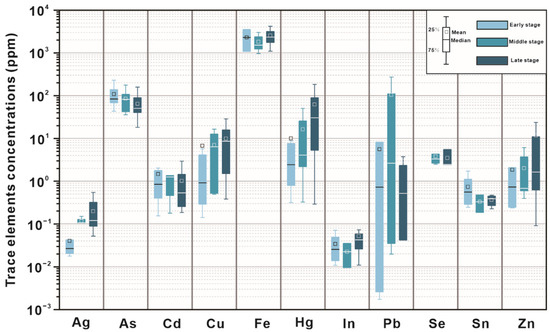
Figure 8.
Trace element data of stibnite in the three mineralization stages of the Daocaowan Sb deposit determined by LA-ICP-MS. All values are in ppm.
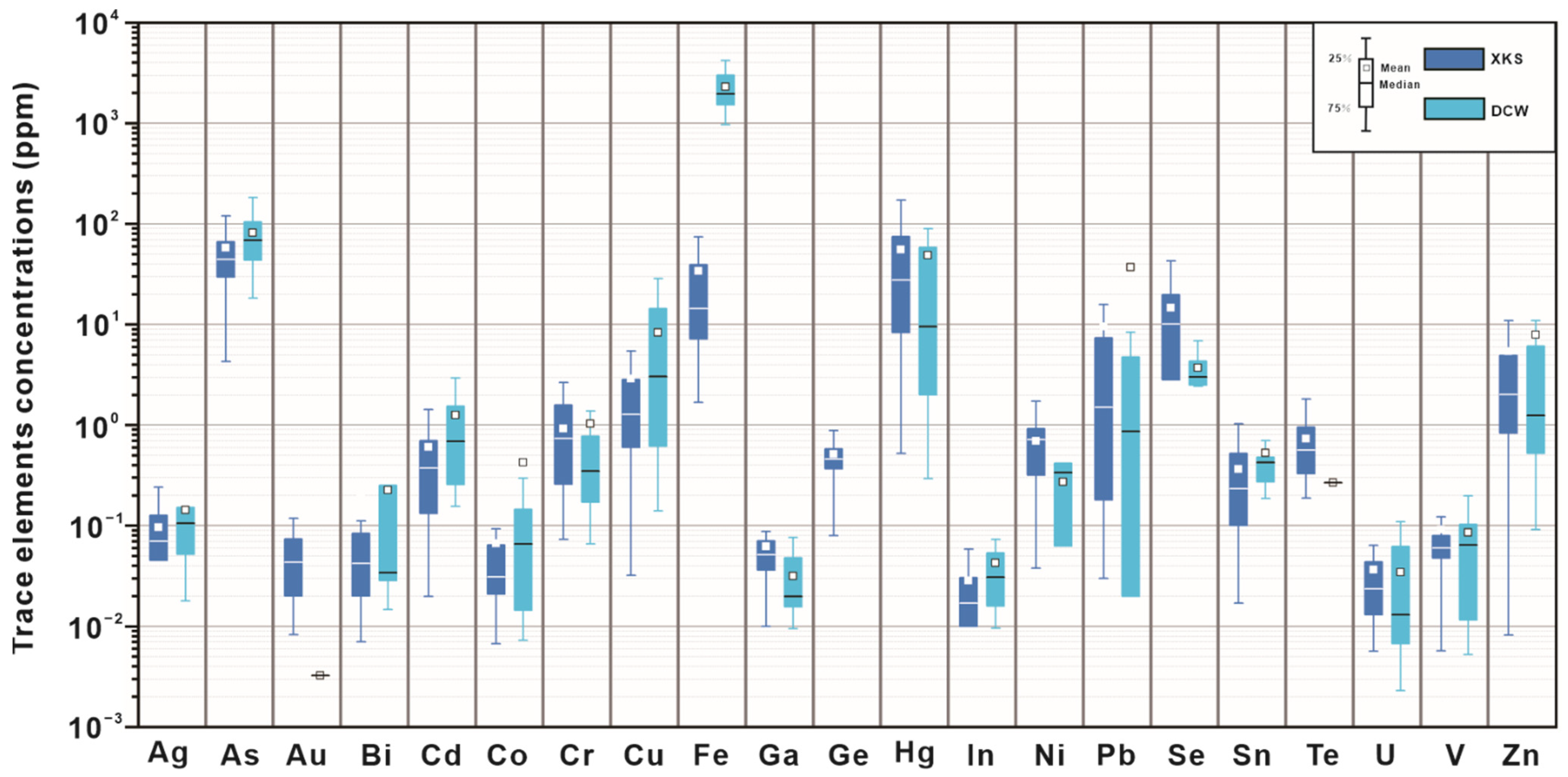
Figure 8 shows a comparison of the major trace element concentration in the three ore types in the stibnite samples of the Daocaowan Sb deposit. In general, As, Cu, Pb, Hg, Fe, and Zn are the most abundant trace elements in stibnite. Meanwhile, different types of stibnite have similar trace element composition. A comparison of the trace elements of stibnite in the Daocaowan and Xikuangshan Sb deposits shows similar trace element content characteristics. However, the Fe content (>103 ppm) in the Daocaowan Sb deposit is generally one order of magnitude higher than that in the Xikuangshan (>100–300 ppm) (Figure 9). In addition to Fe, other comparable trace elements have similar concentrations, such as: As (10–100 ppm), Hg (1–100 ppm), Cu (0.1–10 ppm), Pb (0.01–10 ppm), and Zn (0.1–10 ppm). Other trace elements in stibnite, such as Au, Ag, Mo, Bi, Sn, Cr, V, Mn, Co, Ni, Sr, Se, Te, Ge, Ga, Rb, Pd, In, Cd, and U, are similar in both the deposits but have extremely low concentrations (Table S1 and Figure 9).
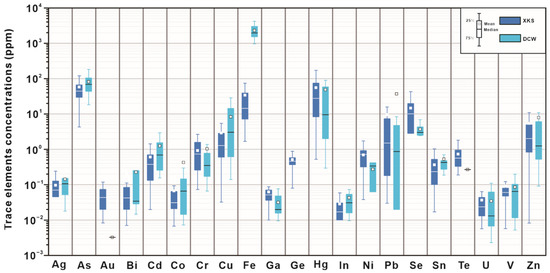
Figure 9.
Trace element data for the stibnite measured by LA-ICP-MS from the Xikuangshan and Daocaowan Sb deposits. All values are in ppm.
4.2. Sulfur Isotopic Compositions
In order to determine the source of S in the mineralization process of the Daocaowan Sb deposit, a total of 20 spots were analyzed in stibnite from the Daocaowan deposit with S isotope in-situ analyses methods. The results are shown in Table 1. The δ34S values of stibnite are distributed in a relatively narrow range (+6.65 to +9.29‰), with an average of +8.8 ± 0.2‰ (n = 20, 2σ). The stibnite in different mineralization stages has similar δ34S values (Table 1). The range of δ34S values in quartz–stibnite type of early stage of mineralization extends from +6.65 to +9.28‰, and the δ34S values of stibnite in calcite–stibnite type of late mineralization stage displays values between +8.75 to +9.29‰ (Table 1).

Table 1.
In-situ sulfur isotopic compositions of sulfide minerals in the Daocaowan Sb deposit in central Hunan province.
5. Discussion
5.1. Distribution and Substitution Mechanism of Trace Elements in Stibnite
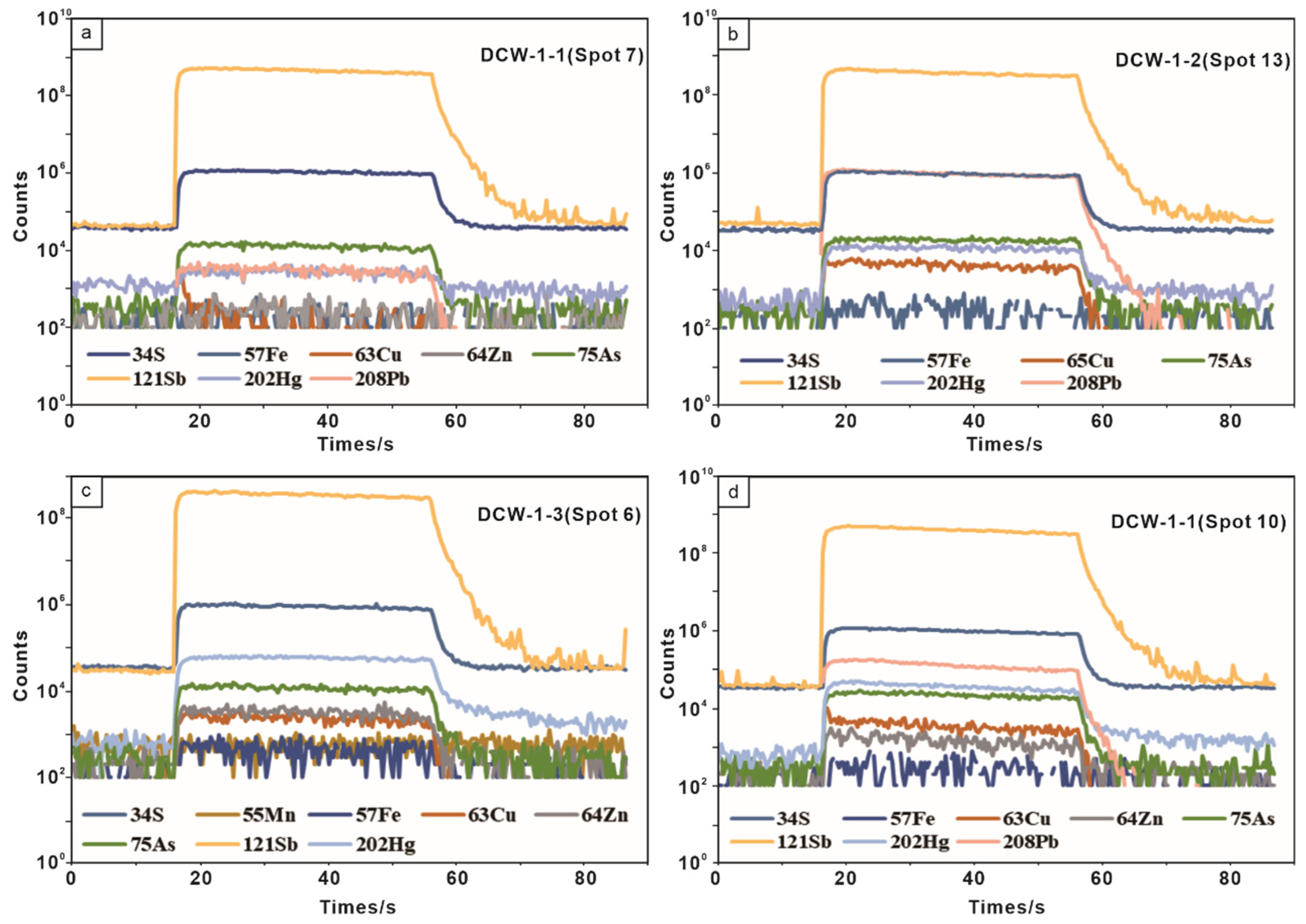
As a common constituent in a range of ore systems of hydrothermal mineralization, stibnite is the main ore mineral of most Sb deposits [6,7,8,9,10]. However, there are few studies on the composition characteristics of trace elements in stibnite [9,15,39], leading to a lack of clarity on the distribution mechanism of trace elements in stibnite. Previous studies have shown that trace elements in sulfide minerals (e.g., pyrite, sphalerite, galena) generally exist as solid solutions or nanoparticles in the mineral structure, and partly as microscopic inclusions or visible fluid or mineral inclusions [11,12,14,40,41]. The representative single-point LA-ICP-MS depth profiles (Figure 10) of the stibnite in the Daocaowan Sb deposit can provide evidence for trace element distribution.
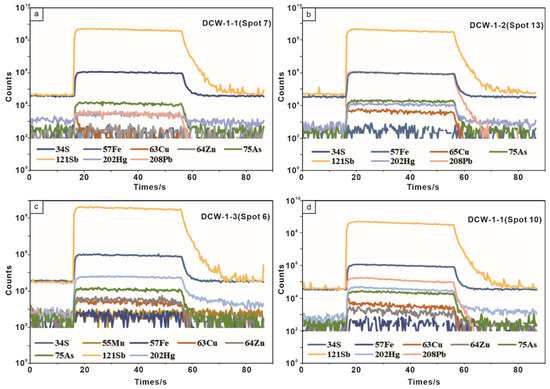
Figure 10.
Representative single-spot LA-ICP-MS depth profiles of selected elements in stibnite from the Daocaowan Sb deposit. (a) DCW-1-1 (Spot 7). (b) DCW-1-2 (Spot 13). (c) DCW-1-3 (Spot 6). (d) DCW-1-1 (Spot 10).
In this study, the LA-ICP-MS depth profiles for As, Hg, Cu, and Pb are relatively smooth and consist of a series of comparable peaks, which are similar to the signal distribution form of Sb (Figure 10), while Fe, Mn, and Zn have irregular depth profiles (Figure 10a,b,d). Part of the depth profiles of Zn are similar to those of As, Hg, and Cu (Figure 10c). No visible mineral inclusions were found in the BSE images (Figure 6a,b,g). These depth profiles indicate that As, Hg, Cu, and Pb may primarily occur as solid solutions in in the mineral structure or as invisible nanoparticles, while Fe, Mn, and Zn may be present in micro-inclusions in stibnite, partially as invisible nanoparticles. This is consistent with the occurrence form of trace elements in the Woxi stibnite [9]. Since most of the trace elements measured in stibnite are below or slightly above the minimum detection limits, the following discussion focuses on the correlation and substitution mechanism for As, Hg, Cu, Zn, and Pb, whose concentrations are much higher than the detection limit and may exist in stibnite in the form of isomorphism.
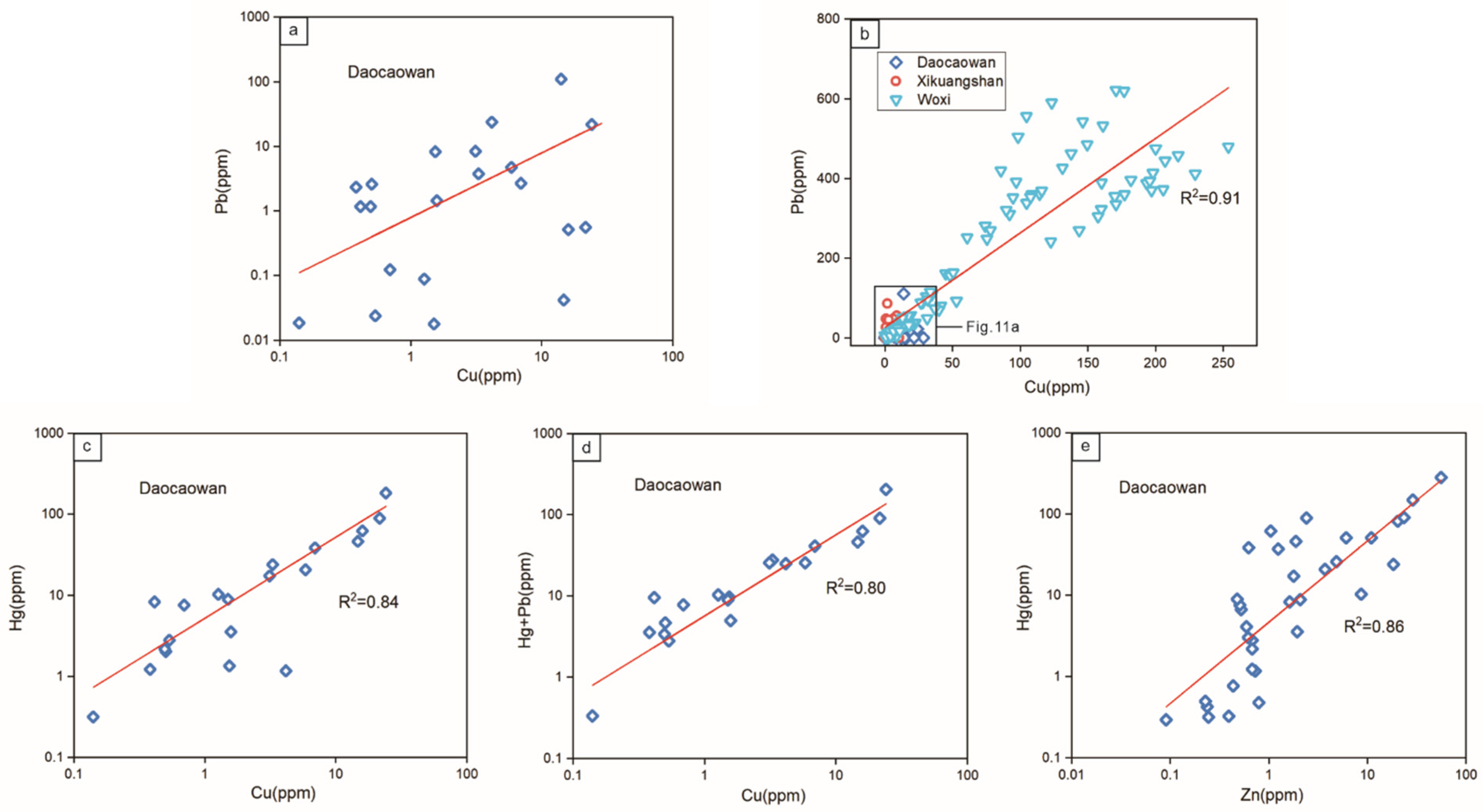
The data of stibnite from the Daocaowan Sb deposit show a significant correlation between Cu and Pb (Figure 11a). The trend of correlation is not significant due to the low content of Cu and Pb in the Daocaowan Sb deposit, but the correlation is quite significant (R2 = 0.91) in the high content (>100 ppm) stibnite at Woxi (Figure 11b). This correlation is consistent with the expected coupled substitution mechanism Sb3+↔Cu+ + Pb2+ [9,39]. In an ideal coupled substitution, Cu and Pb would be present in equal proportions in stibnite, but data from the Woxi and the Daocaowan show that the molar percentages of Cu are higher than the molar percentages of Pb in stibnite [9]. Therefore, it is suggested that there may be other substitution mechanisms besides the substitution of Cu into the mineral structure. It should be noted that the concentration of Hg in stibnite from the Daocaowan Sb deposit is high, and both Sb and Hg are sulfophilic elements with similar chemical properties [7,42,43], suggesting that Hg generally has the same or similar origin as Sb. Therefore, it is believed that Hg can replace Sb during the formation of stibnite [44]. The trace element data of stibnite in the Daocaowan Sb deposit show a good correlation between Cu and Hg (Figure 11c) and Cu and Hg + Pb (Figure 11d), indicating that Cu and Hg may be involved in a coupling substitution of Sb (Sb3+↔Cu+ + Hg2+). Therefore, it is plausible to propose that the substitution of Sb3+ by Cu+ + Pb2+/Hg2+ is the main mechanism leading to the enrichment of Cu, Pb, and Hg in stibnite. Meanwhile, the LA-ICP-MS data of stibnite reveal an additional positive correlation (Figure 11e) between Hg and Zn, suggesting that although most of Zn exists in the form of invisible nanoparticles or micro-inclusions (Figure 10), it may also be partially involved in a coupled replacement with Hg.
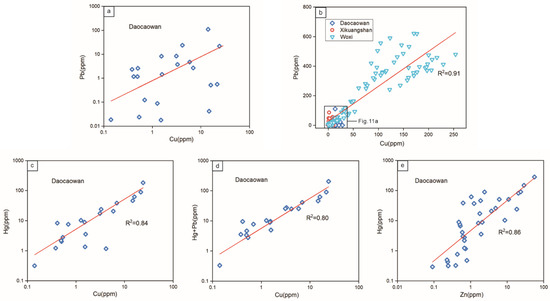
Figure 11.
Correlation plots of (a,b) Cu vs. Pb, (c) Cu vs. Hg, (d) Cu vs. Hg + Pb, and (e) Zn vs. Hg in stibnite determined by LA-ICP-MS. The stibnite data of Xikuangshan and Woxi from [9].
It is noteworthy that As, the most abundant trace element in stibnite, was found not to correlate well with any of the other trace elements. However, As is mainly present in the form of solid solution in stibnite (Figure 10), and As and Sb are similar in ionic radius and chemical properties [44,45], so there is likely a simple substitution (Sb3+↔As3+). Thus, the main substitution mechanism of trace elements in stibnite can be reasonably inferred (3Sb3+↔As3+ + 2Cu+ + Hg2+ + Pb2+).
5.2. Sources of Sulfur in Ore Fluids
Sulfur isotopes can indicate the origin of sulfide minerals [46,47]. Stibnite is the principal sulfide in the ores of the Daocaowan Sb deposit. Compared with sulfide, the contents of other sulfate minerals (Barite and Pyrite) are negligible. Stibnite typically forms at relatively low temperatures, low fO2, and in an acidic to neutral environment [48,49,50]. Under these conditions, the S isotope fractionation between fluid and sulfide is minimal [46,51]. Thus, the δ34S value of stibnite can approximately represent the initial S isotope compositions for the ore fluid [52].
Despite the high precision and accuracy of the sulfur isotope data obtained by the bulk powder method used in previous decades, there are still some problems [53], such as the δ34S values of stibnite from Xikuangshan acquired by LA-ICP-MS (+6.8 to +10.2‰) [17] being more concentrated than previous results using a traditional bulk powder method (−3.3 to +16.8‰) [19,54,55,56]. Therefore, we used an in-situ analysis method to determine the δ34S values of stibnite in different mineralization stages of Daocaowan.
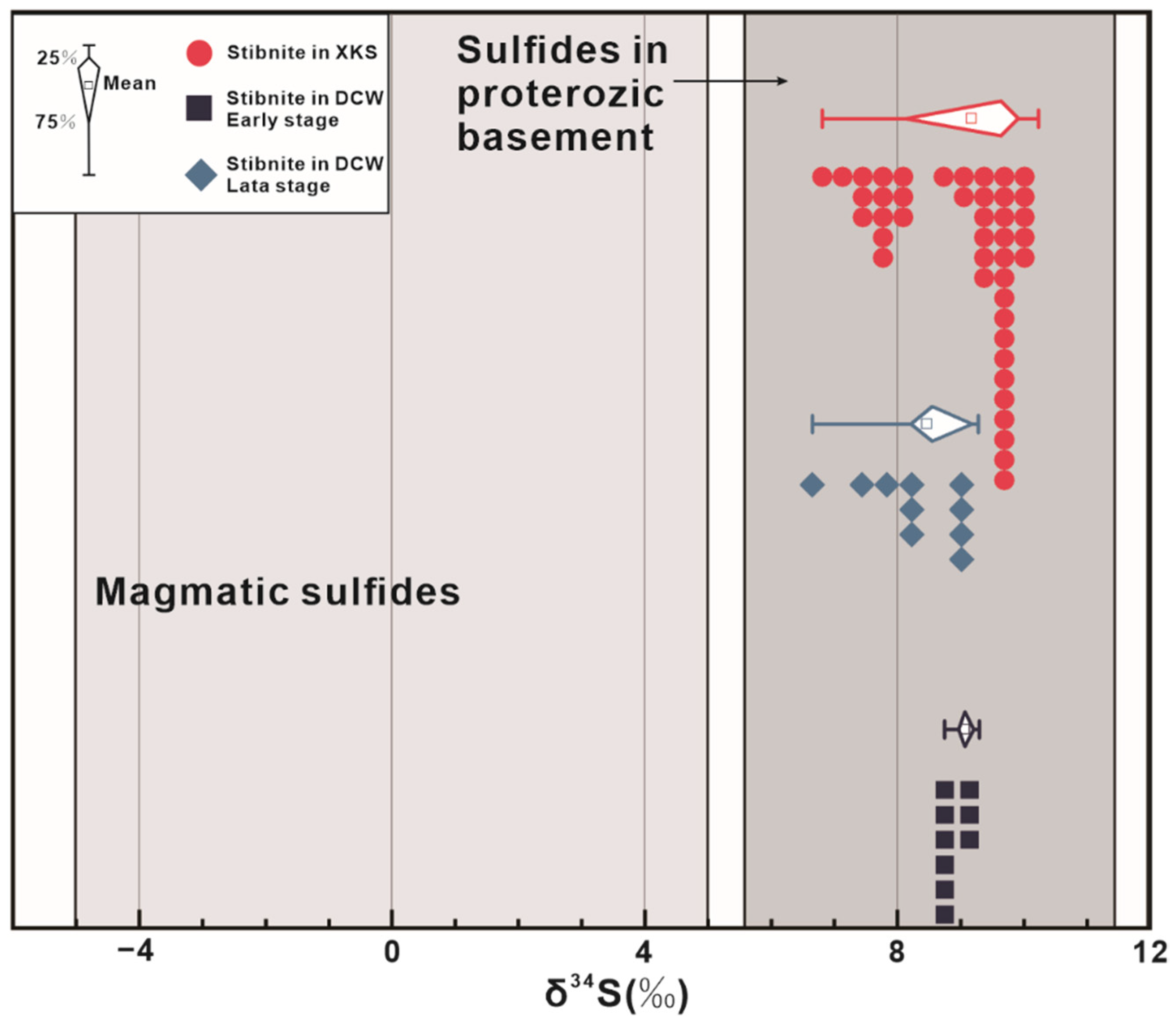
In this study, the δ34S values of stibnite in Daocaowan by LA-ICP-MS were concentrated in a narrow range (+6.65 to +9.29‰; Figure 12), indicating that sulfur in ore-forming fluids at different mineralization stages of the Daocaowan Sb deposit had a common source or comes from the same source area. Otherwise, stibnite from the Daocaowan Sb deposit show a relatively homogeneous appearance in high-contrast BSE images (Figure 6a,b,g,i), indicating a stable fluid composition. The δ34S values of stibnite in the Daocaowan and Xikuangshan Sb deposit are consistent, indicating that they possibly have similar or identical S sources. These values are different from the δ34S values of pyrite in lamprophyre dikes (−6.9 to −3.9‰) [57] in the mining area, indicating that the dominant sulfur in ore-forming fluids is unlikely to have been sourced from the lamprophyre dikes or the upper mantle. In addition, the δ34S values of pyrite in the Devonian host rocks (−26.0 to +21.9‰) [17] encompass a wide range. If the sulfur component of the ore-forming fluid is mainly derived from the host rock, the δ34S value of the ore-forming fluid should be consistent with that of Devonian initial seawater sulfate (+12.2 to +17.2‰) [19,46]. However, these δ34S values are much heavier than the values of ore fluids obtained in this study, indicating that the contribution of Devonian host rocks to sulfur is not significant.
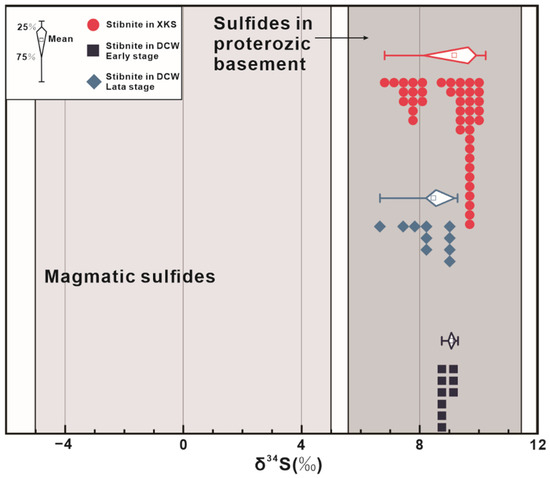
Figure 12.
Sulfur isotopic composition of sulfide minerals from the Daocaowan Sb deposit and potential source rocks. Data sources: magmatic sulfides from [58,59]; sulfides in basement metamorphic rocks from [54,60,61]; stibnite in the Xikuangshan from [17].
Additionally, the δ34S values in this study are significantly higher than those of magmatic sulfur (0 ± 5‰) [58,59], but are comparable to the average δ34S values of sulfide in the Proterozoic basement rocks (+5.6 to + 11.5‰) [54,60,61]. Analogously, the results of Hg and Sb isotopes show that these basement rocks are likely to be the Sb source of South China Sb deposit [9,30]. Notably, the results of Sb partition coefficient between magmatic fluids and silicate melts conducted by Fu et al. [62] indicate that the Sb budget for large hydrothermal Sb deposits is likely not directly derived from magmatic fluids. Similarly, the latest age of Xikuangshan also indicates that Sb mineralization may not be directly related to magmatism [31]. In general, it is reasonable to speculate that the Proterozoic ore–host rocks or underlying basement sequence may be the main source of sulfur and Sb for the ore-forming fluids of the Daocaowan and Xikuangshan Sb deposits.
5.3. Implications for Ore Genesis of Sb Deposits
As a newly discovered Sb deposit, Daocaowan is considered to be a part of Xikuangshan ore field from the perspective of geological characteristics [20,21]. Consistent with Xikuangshan, the most representative Sb-only deposits in central Hunan, the major ore mineral in the Daocaowan Sb deposit is stibnite. In this study, the LA-ICP-MS data show that the trace element characteristics of stibnite in the Daocaowan and Xikuangshan Sb deposit are largely consistent (Figure 9). Our results on the similar trace element characteristics and consistent δ34S values indicate that the stibnite from the Daocaowan and Xikuangshan Sb deposits is generated by fluids from the same source, confirming that the Daocaowan Sb deposit is a part of the Xikuangshan ore field.
Consistent with Xikuangshan, concentrations of almost all trace elements in stibnite of Daocaowan are relatively low, suggesting that the initial Sb-bearing fluid in Daocaowan may lack base metals and other metals [9]. It is worth noting that the stibnite from the Daocaowan Sb deposit has a higher concentration of Fe than that in Xikuangshan Sb deposit. Additionally, pyrite associated with stibnite can be seen in the Daocaowan Sb deposit (Figure 6a). However, pyrite in Xikuangshan is mainly disseminated in silicified surrounding rocks. At the same time, F75 fault is the main fluid migration pathway in the Xikuangshan ore field. Therefore, it is inferred that the high Fe content in stibnite from Daocaowan may be due to the northeastward migration of the ore-forming fluid along the F75 fault. Partial fluid was mineralized in the Devonian strata of the Xikuangshan. The remaining ore-forming fluid dissolved part of the pyrite in the surrounding rock and migrated northeastward to participate in the mineralization at the Daocaowan anticline. It is considered that there is still great prospecting potential outside the northeast of the Xikuangshan ore field.
The metallogenic mechanism of the Xikuangshan ore field is still controversial. The main points of debate are the source of the huge Sb metal in the large Sb deposit and whether the thermal events (heat flow) of fluid migration and Sb deposit deposition are caused by magmatism.
Previous studies indicate that the Sb content in the Devonian ore–host strata of Xikuangshan is low (0.7–2.3 ppm) [63]. Therefore, ore–host strata are unlikely to be a source of Sb. Some scholars have speculated that the ore-forming material for Sb deposits in South China may have been derived from the basement strata [2,7,9,10,17,30] due to its high Sb abundance (7.8–27.2 ppm) [24,64]. In addition, hydrothermal leaching experiments show that 20–90% of Sb can be transferred from such rocks to fluids at 200 °C [24,65,66], suggesting that the ore-forming materials in Xikuangshan may have been derived from the basement strata.
In this study, the δ34S values of stibnite in the Daocaowan Sb deposit and the previous Hg and Sb isotope data of stibnite in Xikuangshan further support that Proterozoic basement rocks may be the main Sb source of Xikuangshan ore field [17,30]. Therefore, this study of the geochemical characteristics of the stibnite in the Daocaowan Sb deposit supports the metallogenic model of Xikuangshan ore field currently accepted by most researchers.
The model proposes that the deep circulation of meteoric water drives Sb and S, which were mobilized from basement metamorphic rocks underlying the central Hunan basin. The hydrothermal fluid rises along the deep fault, followed by the deposition of Sb deposit in favorable structural traps [2,9,10,17]. However, a critical issue is that the heat source of Sb leaching in the basement strata is still controversial [31,67], mainly due to the controversy over the age of the Xikuangshan ore field. Therefore, it is necessary to further constrain the mineralization age of Xikuangshan ore field and the migration mechanism of Sb in the hydrothermal system.
6. Conclusions
(1) Trace element characteristics of stibnite in the Daocaowan Sb deposit indicate that the substitution 3Sb3+↔As3+ + 2Cu+ + Hg2+ + Pb2+ is the most important mechanism for the incorporation of Cu, Pb, Hg, and As within the stibnite lattice.
(2) The characteristics of trace elements and S isotope of stibnite in the Daocaowan Sb deposit are consistent with those in the Xikuangshan Sb deposit, indicating that the ore-forming fluids of the two deposits may have the same fluid source region. It also confirms that the Daocaowan Sb deposit is a part of the Xikuangshan ore field.
(3) In-situ δ34S values of stibnite indicate that the source of ore-forming materials in the Xikuangshan ore field is indeed from basement strata.
Supplementary Materials
The following supporting information can be downloaded at: https://www.mdpi.com/article/10.3390/min12111407/s1, Table S1: Full dataset of trace element composition in stibnite from Daocaowan deposits in sourthern China (All elements are in ppm).
Author Contributions
Conceptualization, X.S., J.L., J.X. and X.L.; data curation, X.S., J.L. and J.X.; formal analysis, X.S. and X.L.; funding acquisition, J.X. and J.L.; investigation, X.S., J.L., J.X. and X.L.; methodology, X.S. and J.X.; project administration, J.X. and J.L.; resources, X.S. and J.L.; software, X.S.; supervision, X.S., J.X. and J.L.; visualization, X.S. and J.L.; writing–original draft, X.S.; writing–review & editing, X.S., J.L., B.L., H.H., J.S., C.W. (Chaofei Wang), C.W. (Chunhua Wen) and Y.W. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This research is financially supported by the National Key Research and Development Plan of China (2017YFC0602402), the National key research and development program of Hunan province (2019SK2261).
Data Availability Statement
Not applicable.
Acknowledgments
The staff of Shanxing Antimony Company and Second Team of Hunan Nonferrous Metals Geological Exploration Bureau are thanked for their help during field work.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
References
- Schulz, K.J.; DeYoung, J.H.; Seal, R.R.; Bradley, D.C. Critical Mineral Resources of the United States-Economic and Environmental Geology and Prospects for Future Supply; U.S. Geological Survey: Reston, VA, USA, 2017; pp. 1–797.
- Ding, J.; Zhang, Y.; Ma, Y.; Wang, Y.; Zhang, J.; Zhang, T. Metallogenic characteristics and resource potential of antimony in China. J. Geochem. Explor. 2021, 230, 106834. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- U.S. Geological Survey. Mineral Commodity Summaries 2022; U.S. Geological Survey: Reston, VA, USA, 2022; pp. 1–202.
- Kyono, A.; Hayakawa, A.; Horiki, M. Selenium substitution effect on crystal structure of stibnite (Sb2S3). Phys. Chem. Miner. 2015, 42, 475–490. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Williams-Jones, A.E.; Normand, C. Controls of mineral parageneses in the system Fe-Sb-S-O. Econ. Geol. 1997, 92, 308–324. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dill, H.; Melcher, F.; Botz, R. Meso- to epithermal W-bearing Sb vein-type deposits in calcareous rocks in western Thailand; with special reference to their metallogenetic position in SE Asia. Ore Geol. Rev. 2008, 34, 242–262. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, R.; Fu, S.; Huang, Y.; Zhou, M.-F.; Fu, S.; Zhao, C.; Wang, Y.; Bi, X.; Xiao, J. The giant South China Mesozoic low-temperature metallogenic domain: Reviews and a new geodynamic model. J. Southeast Asian Earth Sci. 2017, 137, 9–34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, H.; Wu, Q.-H.; Evans, N.J.; Zhou, Z.-K.; Kong, H.; Xi, X.-S.; Lin, Z.-W. Geochemistry and geochronology of the Banxi Sb deposit: Implications for fluid origin and the evolution of Sb mineralization in central-western Hunan, South China. Gondwana Res. 2018, 55, 112–134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fu, S.; Hu, R.; Bi, X.; Sullivan, N.A.; Yan, J. Trace element composition of stibnite: Substitution mechanism and implications for the genesis of Sb deposits in southern China. Appl. Geochem. 2020, 118, 104637. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fu, S.; Lan, Q.; Yan, J. Trace element chemistry of hydrothermal quartz and its genetic significance: A case study from the Xikuangshan and Woxi giant Sb deposits in southern China. Ore Geol. Rev. 2020, 126, 103732. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cook, N.J.; Ciobanu, C.L.; Pring, A.; Skinner, W.; Shimizu, M.; Danyushevsky, L.; Saini-Eidukat, B.; Melcher, F. Trace and minor elements in sphalerite: A LA-ICPMS study. Geochim. Cosmochim. Acta 2009, 73, 4761–4791. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ciobanu, C.; Cook, N.; Kelson, C.; Guerin, R.; Kalleske, N.; Danyushevsky, L. Trace element heterogeneity in molybdenite fingerprints stages of mineralization. Chem. Geol. 2013, 347, 175–189. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reich, M.; Deditius, A.; Chryssoulis, S.; Li, J.-W.; Ma, C.-Q.; Parada, M.A.; Barra, F.; Mittermayr, F. Pyrite as a record of hydrothermal fluid evolution in a porphyry copper system: A SIMS/EMPA trace element study. Geochim. Cosmochim. Acta 2013, 104, 42–62. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- George, L.; Cook, N.; Ciobanu, C.L.; Wade, B.P. Trace and minor elements in galena: A reconnaissance LA-ICP-MS study. Am. Miner. 2015, 100, 548–569. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cook, N.J.; Ciobanu, C.L.; Giles, D.; Wade, B. Correlating textures and trace elements in ore minerals. Mineral deposit research for a high-tech world. In Proceedings of the 12th Biennial SGA Meet, Uppsala, Sweden, 12–15 August 2013; pp. 288–291. [Google Scholar]
- Craddock, P.R.; Rouxel, O.J.; Ball, L.A.; Bach, W. Sulfur isotope measurement of sulfate and sulfide by high-resolution MC-ICP-MS. Chem. Geol. 2008, 253, 102–113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fu, S.; Hu, R.; Yin, R.; Yan, J.; Mi, X.; Song, Z.; Sullivan, N.A. Mercury and in situ sulfur isotopes as constraints on the metal and sulfur sources for the world’s largest Sb deposit at Xikuangshan, southern China. Miner. Depos. 2019, 55, 1353–1364. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, R.-Z.; Zhou, M.-F. Multiple Mesozoic mineralization events in South China—An introduction to the thematic issue. Miner. Depos. 2012, 47, 579–588. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, D.-S.; Shimizu, M.; Shimazaki, H.; Li, X.-H.; Xie, Q.-L. Sulfur Isotope Geochemistry of the Supergiant Xikuangshan Sb Deposit, Central Hunan, China: Constraints on Sources of Ore Constituents. Resour. Geol. 2006, 56, 385–396. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, S.B.; Tang, D.W.; Wei, J.J. Ore-controlling characteristics and prospecting potential of Daocaowan antimony deposit in Lengshuijiang City, Hunan Province. World Nonferrous Met. 2020, 7, 75–76, (In Chinese with English Abstract). [Google Scholar]
- Tang, D.W.; Wei, J.J.; Liu, S.B.; Zhao, Z.J.; Tan, M.L.; Zhou, L.Q.; Xiao, L.M. Important prospecting breakthrough and new understanding of geological characteristics in the north plunging end of Xikuangshan antimony ore field. Miner Explor. 2021, 12, 1750–1757, (In Chinese with English Abstract). [Google Scholar]
- Yao, J.; Shu, L.; Cawood, P.A.; Li, J. Delineating and characterizing the boundary of the Cathaysia Block and the Jiangnan orogenic belt in South China. Precambrian Res. 2016, 275, 265–277. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- BGMRHN Bureau of Geology and Mineral Resource in Hunan Province. Regional Geology of the Hunan Province; Geological Publishing House: Beijing, China, 1988; pp. 286–507, (In Chinese with English Abstract). [Google Scholar]
- Ma, D.S.; Pan, J.Y.; Xie, Q.L.; He, J. Ore source of Sb (Au) deposits in Center Hunan: I. Evidences of trace elements and experimental geochemistry. Miner. Depos. 2002, 3, 366–376, (In Chinese with English Abstract). [Google Scholar]
- Hu, A.X.; Peng, J.T. Fluid inclusions and ore precipitation mechanism in the giant Xikuangshan mesothermal antimony deposit, South China: Conventional and infrared microthermometric constraints. Ore Geol. Rev. 2018, 95, 49–64. [Google Scholar]
- Peng, Y.; Gu, X.; Zhang, Y.; Liu, L.; Wu, C.; Chen, S. Ore-forming process of the Huijiabao gold district, southwestern Guizhou Province, China: Evidence from fluid inclusions and stable isotopes. J. Southeast Asian Earth Sci. 2014, 93, 89–101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, M.K.; Fu, B.Q.; Jin, X.X.; Zhou, X.C. Antimony Metallogeny in the Central Part of Hunan Province. Changsha; Hunan Press of Science Technology: Changsha, China, 1993; pp. 1–149, (In Chinese with English Abstract). [Google Scholar]
- Hu, X.W.; Pei, R.F.; Zhou, S. Sm-Nd dating for antimony mineralization in the Xikuangshan deposit, Hunan, China. Resour. Geol. 1996, 4, 227–231. [Google Scholar]
- Peng, J.T.; Hu, R.Z.; Burnard, P.G. Samarium-neodymium isotope systematics of hydrothermal calcites from the Xikuangshan deposits (Hunan, China): The potential of calcite as a geochronometer. Chem. Geol. 2003, 200, 129–136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhai, D.; Mathur, R.; Liu, S.-A.; Liu, J.; Godfrey, L.; Wang, K.; Xu, J.; Vervoort, J. Antimony isotope fractionation in hydrothermal systems. Geochim. Cosmochim. Acta 2021, 306, 84–97. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, J.W.; Liu, X.H.; Lai, J.Q.; He, H.S.; Song, X.F.; Zhai, D.G.; Li, B.; Wang, Y.H.; Shi, J.; Zhou, X. In Situ U-Pb Geochronology of Calcite from the World’s Largest Antimony Deposit at Xikuangshan, Southern China. Minerals 2022, 12, 899. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xie, G.Q.; Peng, J.T.; Hu, R.Z.; Jia, D.C. Geochemical characteristics of lamprophyres in the Xikuangshan antimony ore deposits Hunan province. Acta Petrol. Sin. 2001, 17, 629–636, (In Chinese with English Abstract). [Google Scholar]
- Hu, A.X.; Peng, J.T. Mesozoic lamprophyre and its origin in the Xikuangshan mining district, central Hunan. Acta Petrol. Sin. 2016, 32, 2041–2056, (In Chinese with English Abstract). [Google Scholar]
- Liu, G.; Jian, H. Geological characteristics of the Xikuangshan antimony ore field. Miner. Depos. 1983, 3, 43–50, (In Chinese with English Abstract). [Google Scholar]
- Jin, J.F.; Tao, Y.; Zeng, L.J. The ore-forming fluid of Xikuangshan-type antimony deposits. Bull. China Soc. Miner Petrol. Geochem. 2001, 3, 156–164, (In Chinese with English Abstract). [Google Scholar]
- Paton, C.; Hellstrom, J.; Paul, B.; Woodhead, J.; Hergt, J. Iolite: Freeware for the visualisation and processing of mass spectrometric data. J. Anal. At. Spectrom. 2011, 26, 2508–2518. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wilson, S.A.; Ridley, W.I.; Koenig, A.E. Development of sulfide calibration standards for the laser ablation inductively-coupled plasma mass spectrometry technique. J. Anal. At. Spectrom. 2002, 17, 406–409. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, L.; Chen, K.; Bao, Z.; Liang, P.; Sun, T.; Yuan, H. Preparation of standards for in situ sulfur isotope measurement in sulfides using femtosecond laser ablation MC-ICP-MS. J. Anal. At. Spectrom. 2016, 32, 107–116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhaanbaeva, A.; Peng, K.; Oyebamiji, A.; Asilbekov, K. Source characteristics and genesis of Sb mineralization from the Au and Sb deposits of the Youjiang Basin, SW China: Constraints from stibnite trace element and isotope geochemistry. Acta Geochim. 2021, 40, 659–675. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deditius, A.P.; Utsunomiya, S.; Reich, M.; Kesler, S.E.; Ewing, R.C.; Hough, R.; Walshe, J. Trace metal nanoparticles in pyrite. Ore Geol. Rev. 2011, 42, 32–46. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, J.; Li, L.; Gilbert, S.; Liu, J.-J.; Shi, W.-S. LA-ICP-MS and EPMA studies on the Fe-S-As minerals from the Jinlongshan gold deposit, Qinling Orogen, China: Implications for ore-forming processes. Geol. J. 2014, 49, 482–500. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arehart, G.B. Characteristics and origin of sediment-hosted disseminated gold deposits: A review. Ore Geol. Rev. 1996, 11, 383–403. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nevolko, P.; Hnylko, O.; Mokrushnikov, V.; Gibsher, A.; Redin, Y.; Zhimulev, F.; Drovzhak, A.; Svetlitskaya, T.; Fomynikh, P.; Karavashkin, M. Geology and geochemistry of the Kadamzhai and Chauvai gold-antimony-mercury deposits: Implications for new province of Carlin-type gold deposits at the Southern Tien Shan (Kyrgyzstan). Ore Geol. Rev. 2018, 105, 551–571. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rytuba, J.J. Mercury from mineral deposits and potential environmental impact. Environ. Earth Sci. 2003, 43, 326–338. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wilson, S.C.; Lockwood, P.V.; Ashley, P.M.; Tighe, M. The chemistry and behaviour of antimony in the soil environment with comparisons to arsenic: Acritical review. Environ. Pollut. 2010, 158, 1169–1181. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ohmoto, H.; Rye, R.O. Isotopes of sulfur and carbon. In Geochemistry of Hydrothermal Ore Deposits; Wiley: New York, NY, USA, 1979; pp. 509–567. [Google Scholar]
- Hoefs, J. Stable Isotope Geochemistry, 7th ed.; Springer International Publishing: Cham, Switzerland, 2015; p. 97. [Google Scholar]
- Zotov, A.; Shikina, N.; Akinfiev, N. Thermodynamic properties of the Sb(III) hydroxide complex Sb(OH)3(aq) at hydrothermal conditions. Geochim. Cosmochim. Acta 2003, 67, 1821–1836. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Obolensky, A.; Gushchina, L.; Borisenko, A.; Borovikov, A.; Pavlova, G. Antimony in hydrothermal processes: Solubility, conditions of transfer, and metal-bearing capacity of solutions. Russ. Geol. Geophys. 2007, 48, 992–1001. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Biver, M.; Shotyk, W. Stibnite (Sb2S3) oxidative dissolution kinetics from pH 1 to 11. Geochim. Cosmochim. Acta 2012, 79, 127–139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ohmoto, H.; Yamaguchi, K.E.; Ono, S. Questions Regarding Precambrian Sulfur Isotope Fractionation. Science 2001, 292, 1959. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Seal, R.R. Sulfur isotope geochemistry of sulfide minerals. Rev. Mineral. Geochem. 2006, 61, 633–677. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, W.; Cook, N.J.; Xie, G.-Q.; Mao, J.-W.; Ciobanu, C.L.; Fu, B. Complementary Textural, Trace Element, and Isotopic Analyses of Sulfides Constrain Ore-Forming Processes for the Slate-Hosted Yuhengtang Au Deposit, South China. Econ. Geol. 2021, 116, 1825–1848. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zou, T.X. Geochemica characteristics and ore-forming mechanism of the antimony ore field of Xikuangshan, Hunan. J. Guilin Coll. Geol. 1988, 8, 187–195, (In Chinese with English Abstract). [Google Scholar]
- Ma, D.S.; Pan, J.Y.; Xie, Q.L. Ore sources of Sb (Au) deposits in CenterHunan: II. Evidence of isotopic geochemistry. Miner. Depos. 2003, 21, 78–87, (In Chinese with English Abstract). [Google Scholar]
- Fan, D.; Zhang, T.; Ye, J. The Xikuangshan Sb deposit hosted by the Upper Devonian black shale series, Hunan, China. Ore Geol. Rev. 2004, 24, 121–133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, S.Q. On inquiry about the genesis of Hunan antimony deposit and prospecting direction. Hunan Geol. 1986, 4, 12–25, (In Chinese with English Abstract). [Google Scholar]
- Ohmoto, H. Stable isotopes in high temperature geological process. Rev. Mineral. Geochem. 1986, 16, 491–559. [Google Scholar]
- Chaussidon, M.; Albarede, F.; Sheppard, S.M. Sulphur isotope variations in the mantle from ion microprobe analyses of micro-sulphide inclusions. Earth Planet. Sci. Lett. 1989, 92, 144–156. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, Z.Y.; Wei, L.M.; Chen, M.Y. Sulfur isotopic study of sulfides from sedimentary strata and strata-bound deposits in Hunan. Guangdong Guangxi South. China Geochem. 1990, 19, 117–126, (In Chinese with English Abstract). [Google Scholar]
- Gu, X.; Zhang, Y.; Schulz, O.; Vavtar, F.; Liu, J.; Zheng, M.; Zheng, L. The Woxi W–Sb–Au deposit in Hunan, South China: An example of Late Proterozoic sedimentary exhalative (SEDEX) mineralization. J. Southeast Asian Earth Sci. 2012, 57, 54–75. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fu, S.L.; Zajacz, Z.; Tsay, A.; Hu, R.Z. Can magma degassing at depth donate the metal budget of large hydrothermal Sb deposits? Geochim. Cosmochim. Acta. 2020, 290, 1–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peng, J.T.; Hu, R.Z.; Deng, H.L.; Su, W.C. Strontium isotope geochemistry of Xikuangshan antimony deposit, center Hunan. Geochemistry 2001, 3, 248–256, (In Chinese with English Abstract). [Google Scholar]
- Lu, X.W.; Ma, D.S.; Xie, Q.L.; Wang, W.Y. Trace element geochemical characteristics of Neoproterozoic-Paleozoic strata in western and central Hunan. Geol. Geochem. 2001, 29, 24–30, (In Chinese with English Abstract). [Google Scholar]
- Niu, H.C.; Ma, D.S. Experimental geochemistry of gold, antimony and tungsten during water-rock interactions under low-temperature, open system. Chin. J. 1991, 36, 1879–1881, (In Chinese with English Abstract). [Google Scholar]
- He, J.; Ma, D.S. Leaching experiment of gold, antimony, mercury and arsenic from the strata under epithermal-mesothermal conditions in sulfur- and chlorine-bearing solutions. Geol. Rev. 1996, 42, 76–85, (In Chinese with English Abstract). [Google Scholar]
- Yan, J.; Fu, S.; Liu, S.; Wei, L.; Wang, T. Giant Sb metallogenic belt in South China: A product of Late Mesozoic flat-slab subduction of paleo-Pacific plate. Ore Geol. Rev. 2022, 142, 104697. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).