Abstract
The aim of this work is to investigate the causes of the El Descargador tailings dam failure, at the mine district Cartagena–La Unión (SE Spain), in October 1963. Dam stability back analyses have been carried out by applying a geotechnical and geophysical approach. The failure occurred in the form of several landslides in five different points along the dam structure. The rise in the pore pressure and the steeped slopes of the tails, scaling up to 40° in some sectors, were the main causal preparatory factors. Here we propose that static liquefaction is the most plausible cause of the tailings dam flow failure. The presence of sand dikes and sand volcanoes with atypical stratigraphic architecture, both in the lagoon and at the surfaces exposed in the landslide areas, as well as the evidence of conspicuous sand fraction on the surface support the occurrence of the liquefaction processes. Major landslides were located near the drainage pipe and the flow directions were controlled by its position. Our results reveal that the liquefaction processes were triggered and aggravated by the poor drainage capability of the tailings dam structure.
1. Introduction
El Descargador tailings dam failed catastrophically at 7:45 on Monday, 14 October 1963, causing an environmental disaster in the Cartagena–La Unión mining district, in the province of Murcia, Spain (Figure 1 and Figure 2). The Cartagena–La Unión mining district is part of the easternmost foothills of the Betic mountain ranges, and it is well known as a highly productive area of metals such as lead, zinc, iron, manganese and silver since ancient times [1]. The tailings dam was part of a large underground mining complex that had been in operation for more than nine years in La Unión municipality. The El Descargador tailings dam stored tailings from the Belleza mining group. This group is integrated by the following Fortuna, Felicidad, Maestra, Belleza, Resucitada, Pronta, Virgendel Carmen, Convención and Ferrocarril mining concessions. The activity of the Belleza group included the exploitation of pyrite (12%), sphalerite (10%) and galena (7%). The flotation process of the mine had a capacity of 300 tons of mineral per day. The 75% of the ore entering the flotation process was discharged into the dam as tailings. Considering the volume of daily production, half a million tons were stored at the time of the dam failure. The confining embankment was conceived in the original design as an upstream construction using the tailings themselves. The method of tailings discharge was hydraulic backfill.
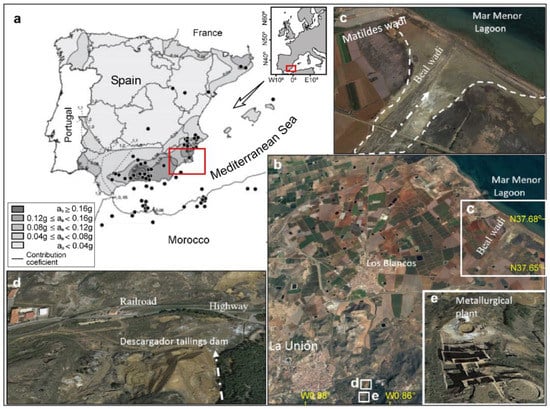
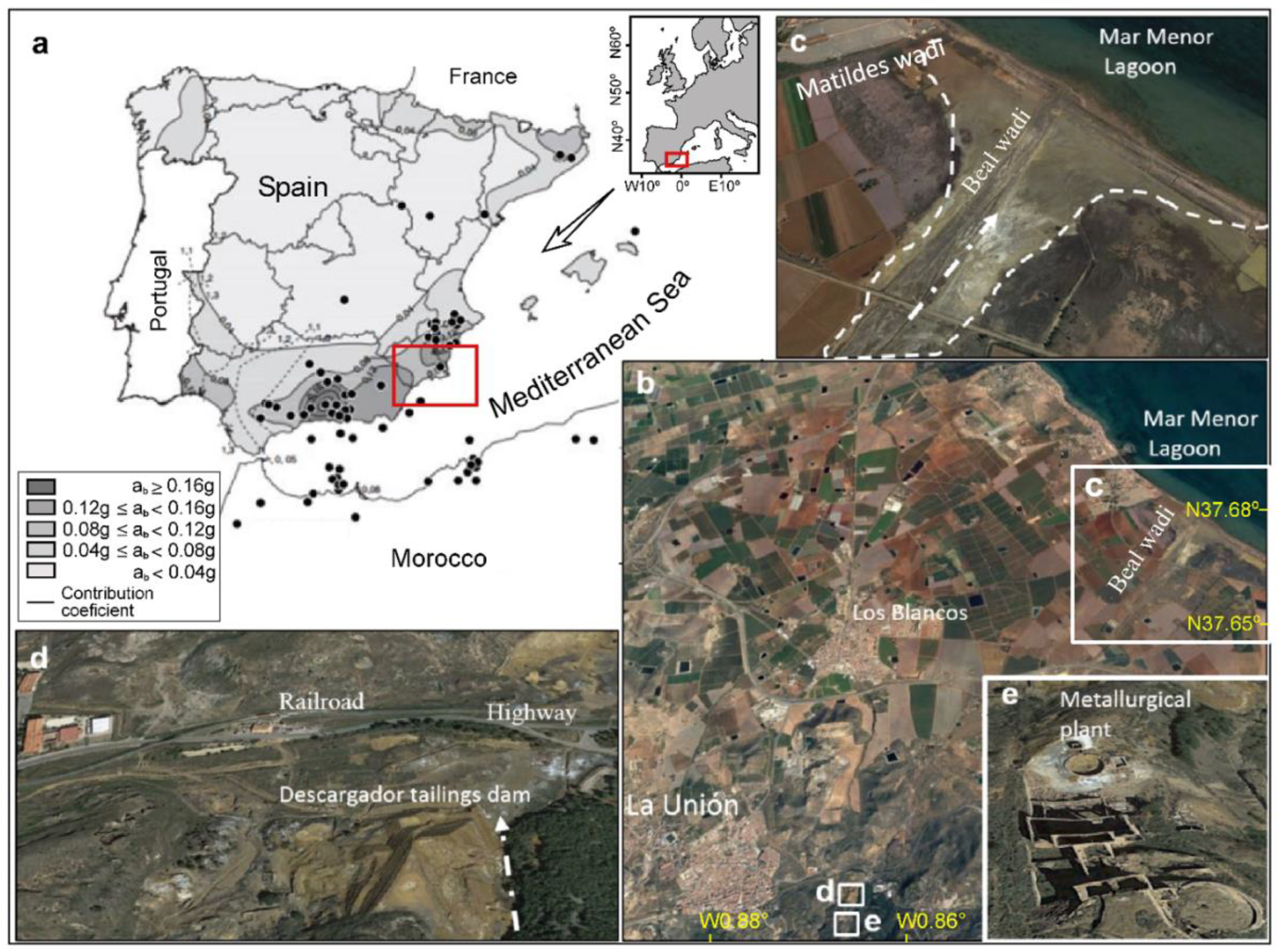
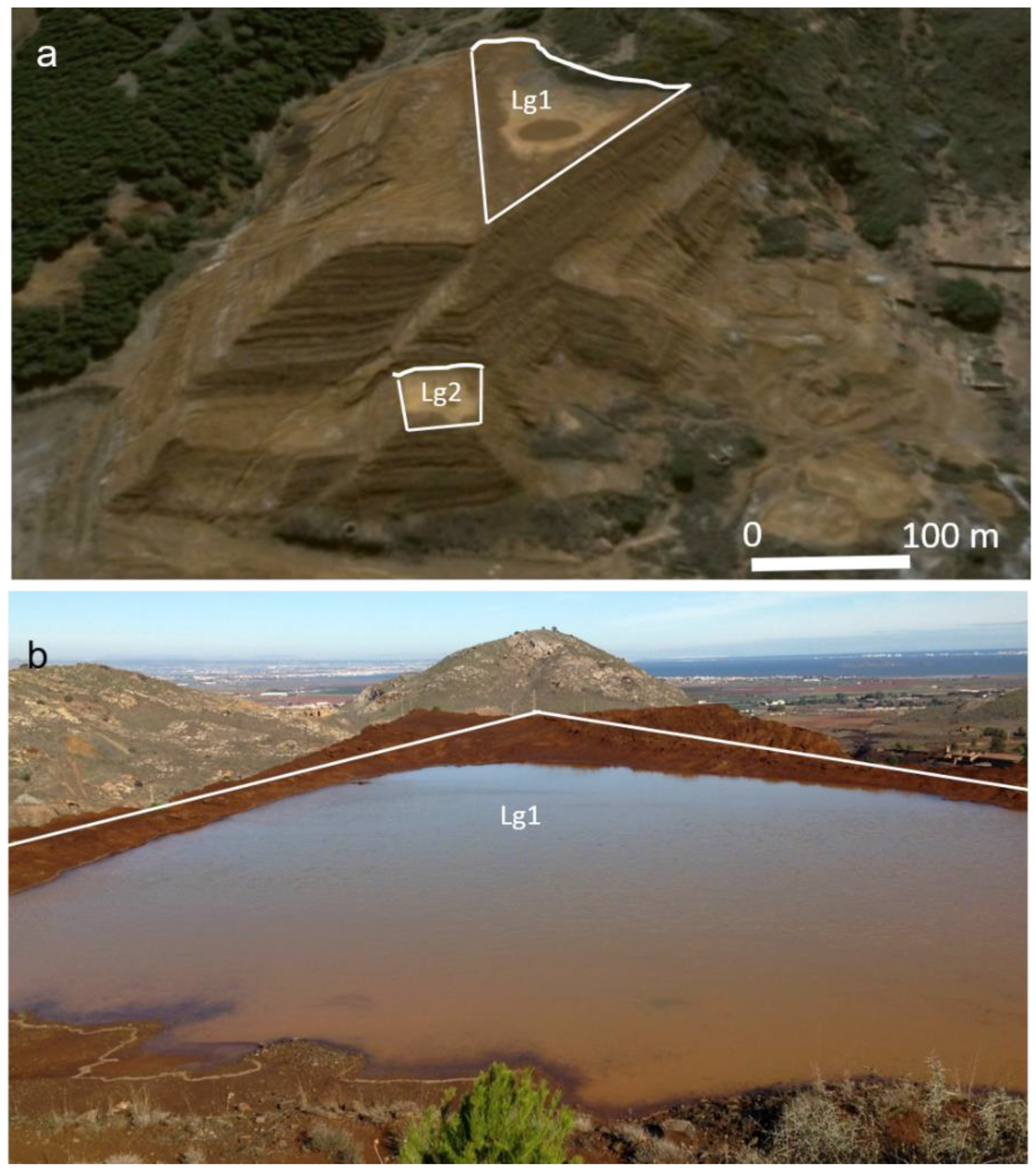
Figure 1.
(a) Location of studied area on the Spanish seismic base map; source: NCSR-2 (2004) at Region of Murcia, (b) El Descargador tailings dam and its area of influence, (c) Beal wadis and the oxidation products of sulphides can be seen in white color in the area covered by tailings, (d) Cartagena–Cabo de Palos highway and the Cartagena–Los Blancos railroad affected by flow failure and (e) abandoned metallurgical plant. The discontinuous arrow indicates the direction of the runoff. Base maps orthorectified aerial photographs; source Spanish National Geographic Institute (IGN). Schemes follow the same formatting.
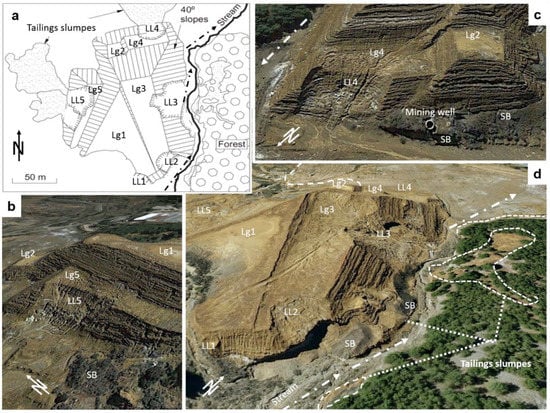
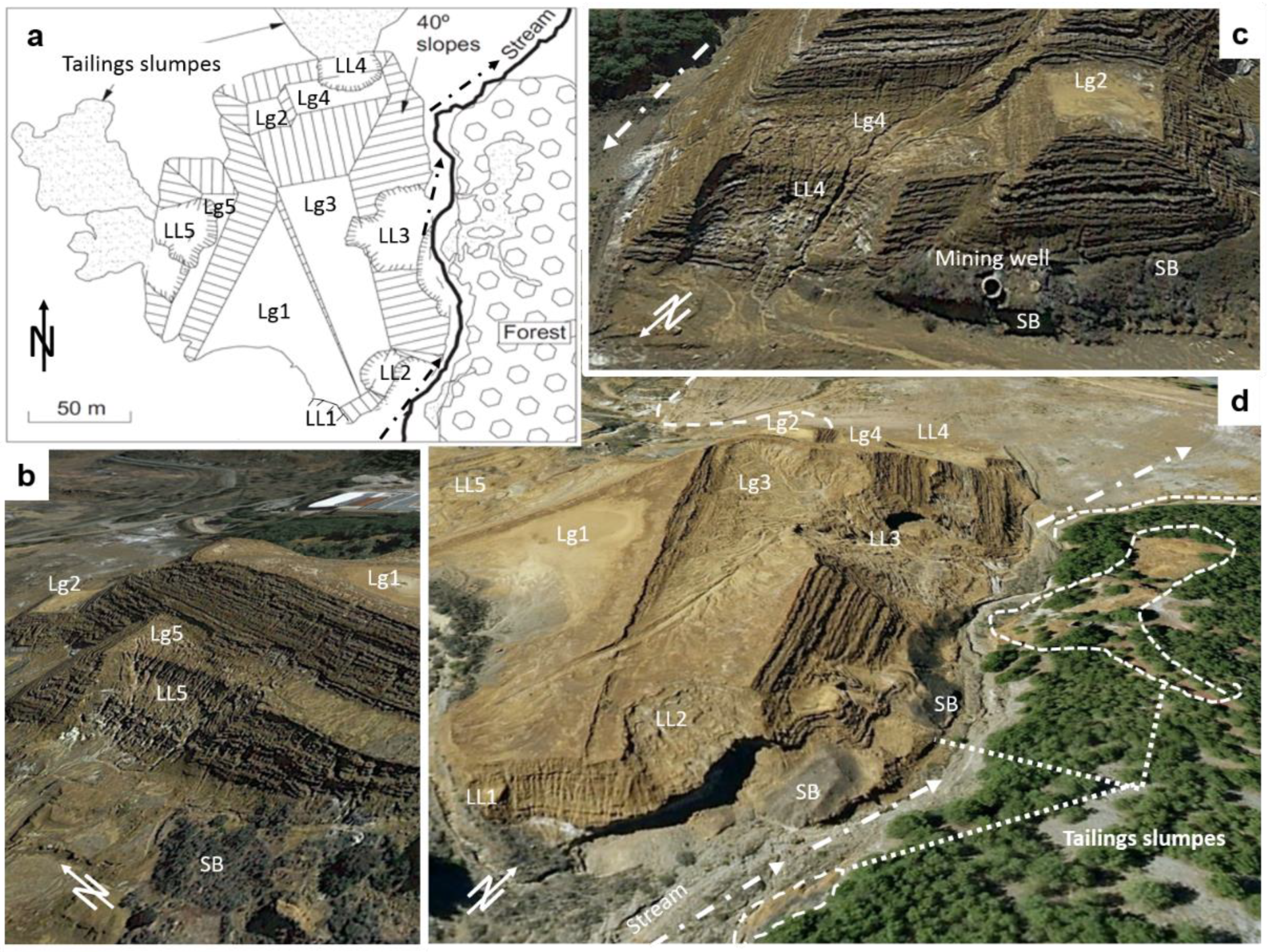
Figure 2.
(a) Layout of El Descargador tailings dam depicting the localization of different landslides (LL), lagoons (Lg), and fragments of breakwater (SB) and some are affected for flow failure. The discontinuous arrow indicates the direction of the runoff, (b–d) Obliquus aerial views of the dam from different perspectives; source Spanish National Geographic Institute-IGN and Google Earth©. Schemes follow the same formatting.
The tailings dam construction began in November 1953 and it was 42 m height at the time of the failure. The flow failure developed in five different landslide points (labeled LL; Figure 2). The height of the main landslide (LL3, Figure 3) was 27 m. 66,000 m3 of tailings and high acidic waters were released into the environment affecting: (1) an area of 4 km2; (2) different infrastructures (Cartagena–Cabo de Palos highway, the Cartagena–Los Blancos railroad); (3) the watercourse of Beal wadis stream; and (4) the El Mar Menor lagoon, an area of great ecological and patrimonial value in the Mediterranean Sea. Catastrophic mine tailings dam failures are increasing globally [2,3,4,5,6,7,8,9,10,11,12]. However, while the study of its ecological and socioeconomic consequences has been widely addressed in the literature [11,12,13,14,15,16,17] studies, attempts to address the hydro-geomechanical factors that caused the failures are scarce [18,19,20]. There is still more uncertainty regarding historical failures of dams that happened many decades ago, as is the case of El Descargador. This is an important gap of knowledge, since more than 80 uncontrolled old dams have been inventoried in this mining region [20]. The study of the causes that triggered and controlled the failure and collapse of ancient tailings dams such as El Descargador can provide valuable information to be considered in the design and management of such installations and its associated hazards, which are instrumental for the success of any mining operation.
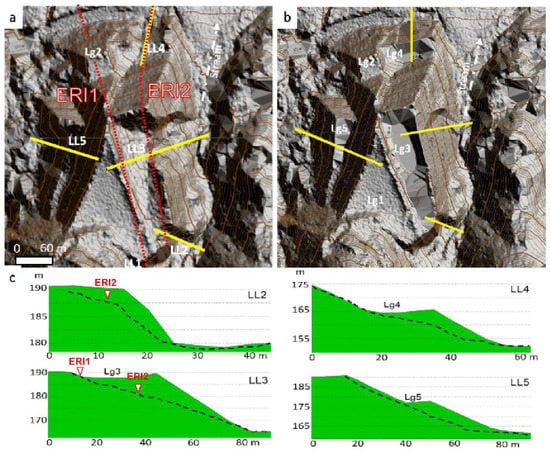
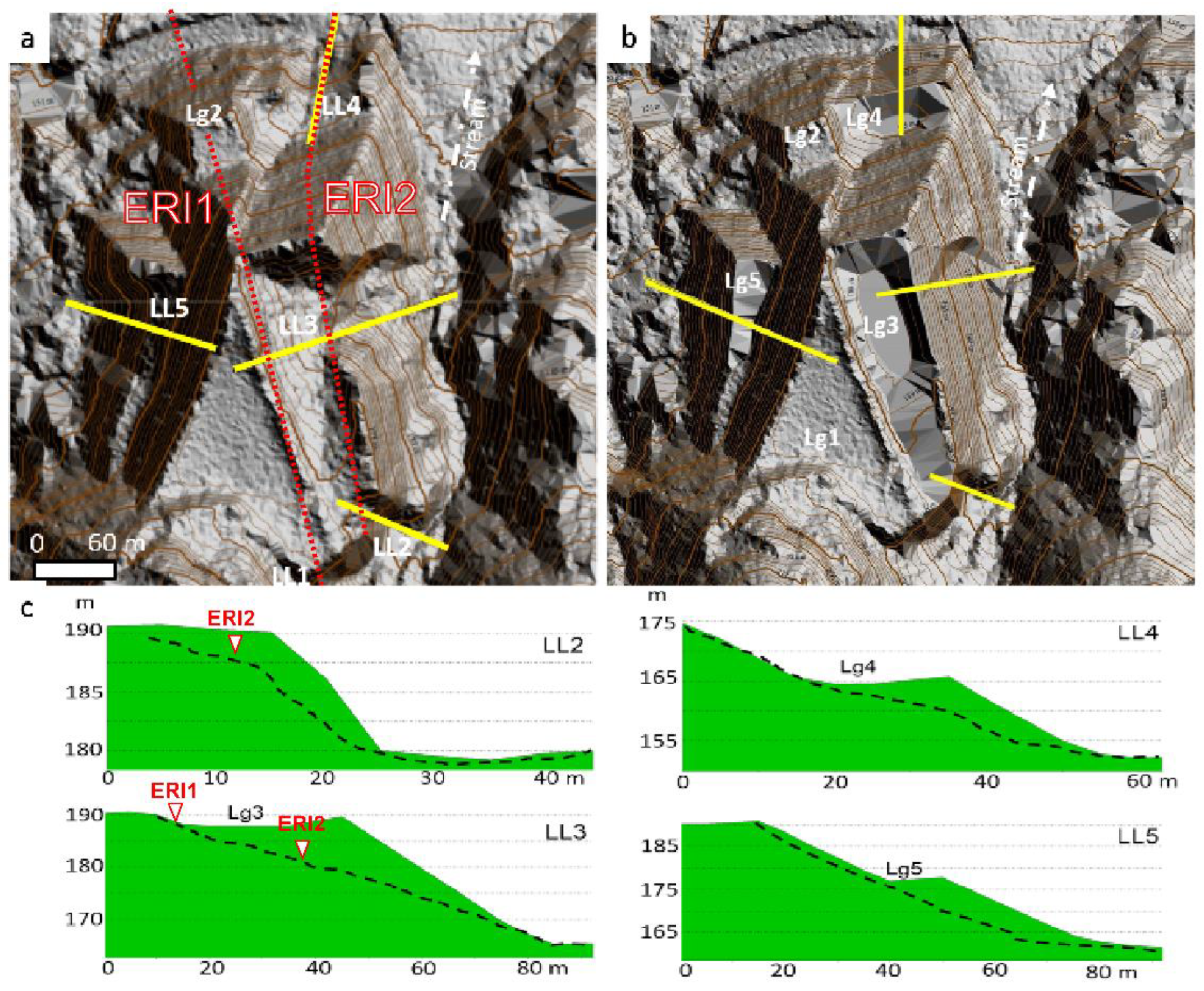
Figure 3.
(a) ERI profiles layout on a hill shaded elevation models of El Descargador tailings dam; (a) actual state; (b) tentative reconstruction of the relief before the 1963′s failure; and (c) Representative topographic profiles of the main landslide before (green) and actual surface of failure dashed lines. The white dashed arrow indicates the stream runoff direction.
Here we aim to stress the hypothesis that the El Descargador tailings dam failed due to static liquefaction. To meet the goal, a geotechnical characterization of the different elements of the tailings dam and a back-analysis of the failure by geophysical and geotechnical modeling have been carried out. The failure of a sloping ground due to static liquefaction occurs when the shear stress applied by a monotonic triggering load exceeds the undrained yield (peak) shear strength of the saturated liquefiable cohesionless soil. Triggering mechanisms for this type of tailings dam failure in contractive and saturated granular materials are usually: (1) slope instability; (2) a rise in the hydraulic head; (3) toe erosion due to piping (seepage, internal erosion, runoff erosion); (4) overtopping; (5) rapid application of surface loading due to the discharge of new materials; and (6) important storage volume of water on the surface or as a result of other mechanisms [1,20,21,22]. According to existing reviews and databases on tailings dam failures, static liquefaction is not considered relevant as one of the fundamental mechanisms of failure [1,12,22,23]. Unfortunately, an important number of tailings dam failures due to static liquefaction have been misinterpreted as other failure modes, and only few case studies have been correctly interpreted due to static liquefaction [20,24]. Static liquefaction phenomena and the resulting land sliding and tailings liquefaction have been commonly related to the more hazardous historic tailings dam flow failures. Noticeable incidents of destructive mudflows caused by tailings dam breaching are: (1) the Befokeng platinum ring-dike tailings dam failed as a result of overtopping after a large storm [17,25]; (2) Merriespruit, Harmony Mine, South Africa ring-dike gold tailings dam failed in 1994 in many similar aspects to Bafokeng failure. The failure occurred after a significant rainfall event [26]; (3) active iron pond tailings impoundment at the Sullivan Mine, Canada, failed in August of 1991 due to static liquefaction [27]. (4) The two tailings dams in a fluorite mine located near Stava (northern Italy) suddenly failed and released approximately 240,000 m3 of liquefied tailings. The failure occurred on 19 July 1985. This was perhaps the most tragic tailings dam failure in history. The liquefied mass moved up to a speed of 60 km/h obliterating everything in its path for a length of ~4 km. The failure was initiated not because of increasing shear stresses and undrained loading but because of the decreasing effective stress due to the rising phreatic surface under drained conditions [28]; and (5) tailings dam Los Frailes mine, Spain, 1998, which is possibly the most reported tailings dam failure. A shallow foundation failure led to the release of more than 3 million m3 of processed water and tailings from one of the two adjacent ponds within an overall impoundment [18]. According to different studies, these five cases are clear examples of static liquefaction [1,18,20,21].
The importance of modeling the mechanical behavior of earth dams is the knowledge on their geotechnical features. Geotechnical characterization of large earth structures is a challenging issue. Numerical solutions require selecting many parameters, and sometimes-geological models are oversimplified to achieve simpler numerical models. Direct observations by means of boreholes and laboratory tests offer valuable information, but they have several economical and logistical constraints and sometimes they fail to be enough representatives of the characteristics of such large structures. In this regard, more extensive geophysical surveying techniques, although they are penalized by a lower resolution, may be useful to construct more representative geological models at field-scale. Electrical resistivity imaging (ERI) has experienced major improvements in recent decades [27]. Among other applications, ERI has been increasingly used for geotechnical characterization of tailings dams and their emplacements [28,29,30,31,32,33,34]. Bulk resistivity of materials is mainly controlled by porosity, fluid content, hydrochemistry and mineralogy. Therefore, ERI has strong capabilities to characterize the stratigraphy of the tailings dams, resistivity and the groundwater flow conditions [11,30]. A tailings dam should be considered as a complex multilayer aquifer system, in which there are different hydraulic relationships between the waters stored in the lagoons and the groundwater that flows through sedimentary layers of tailings [11,28,29,30,31,32,33,34,35,36]. In addition, studies of ERT work on mine tailings dams that assess environmental risk and groundwater flow are relatively abundant [11,28,29,30,31,32,33,34,35,36]. However, combined ERT and geotechnical studies are more limited [18]. The main limitation of ERT studies is that they do not determine the key parameters for the stability of tailings dams: gravimetric moisture, volumetric water content, degree of saturation, density, etc. Hence, ERI data combined with geotechnical and hydrogeological information may be useful for modeling the flow conditions that could have triggered and controlled the assumed static liquefaction phenomenon.
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Characterization of the Tailings Dam
Geotechnical mapping of the tailings dam was performed by fieldwork and inspection of the aerial photographs and satellite images and topographical data (resolution 1 m × 1 m; source: Instituto Geográfico Nacional) [36,37,38]. The topographical model was constructed by Global Mapper software (V.18.1; Figure 3a). A tentative reconstruction of the previous topography of the tailings dam failure was carried out by AutoCAD (Autodesk) software, V 10 (Figure 3b). Such pre-failure topographical reconstruction was used as a base model for the numerical stability back-analysis (Figure 3c).
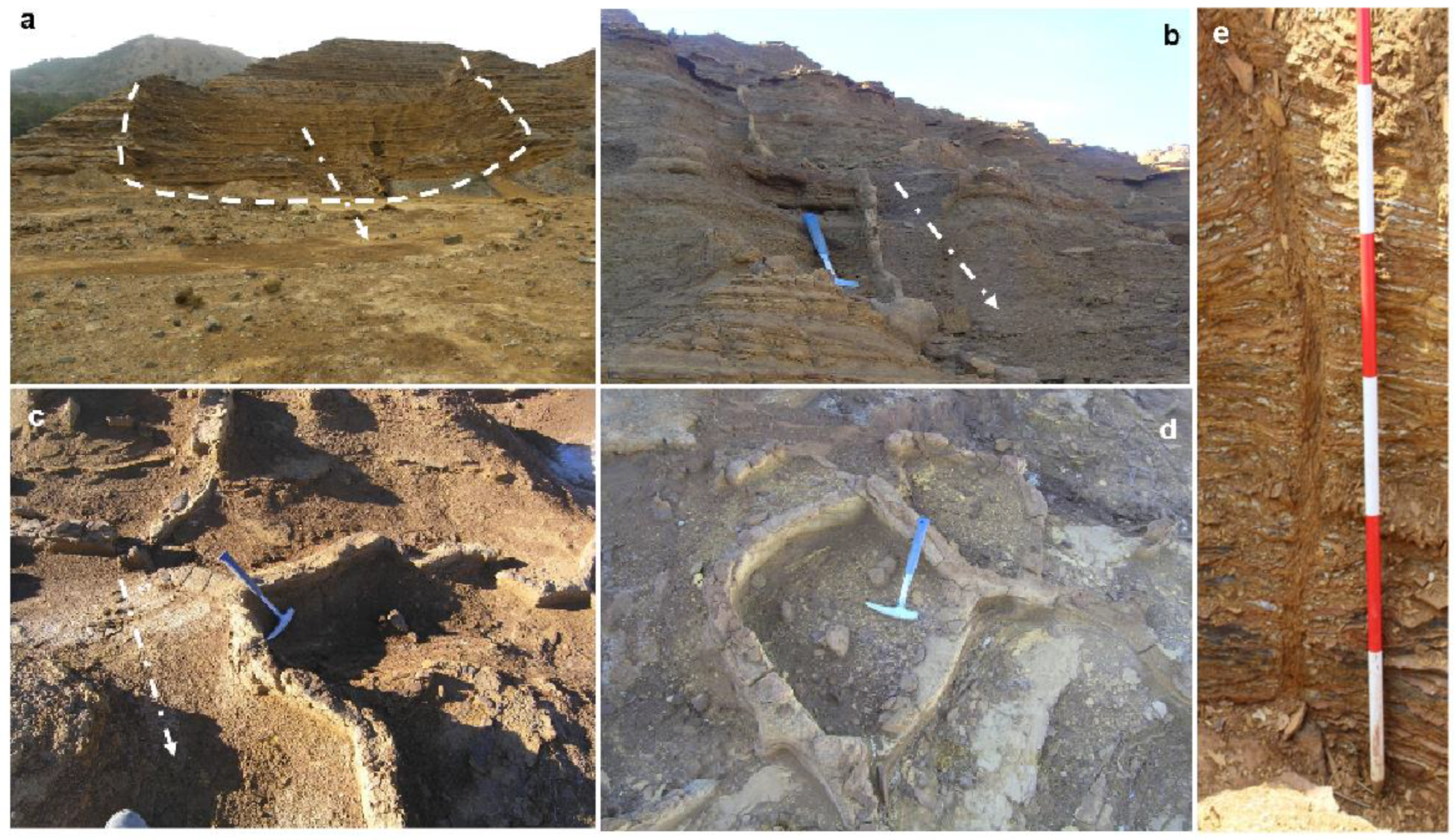
A sampling campaign was performed in May 2015 in two different zones: trial-pit profile and sampling of the sand dikes (Figure 4). The sampling aimed at comparing both unaltered and liquefacted materials. Up to nine representative tailings beds were sampled on the left side of a trial pit (1.7 m high and 1 m wide), which was dug in the northern sector of the East wall of the base of the tailings dam (Figure 2). Around 2 kg samples were collected, P1 being the lowest and P9 the shallowest sampling points. Once collected, they were preserved in sealed plastic bags to avoid quick oxidation. An additional 13 samples were extracted from several subvertical sand dikes crosscutting the fault plane in the north wall of the dam (Figure 4), W1 being the bottom and W13 being the top sample (Figure 4b).
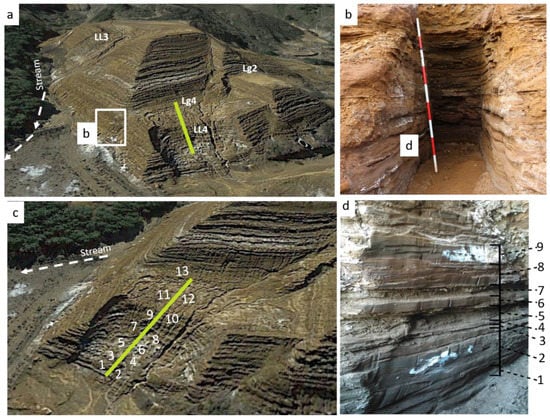
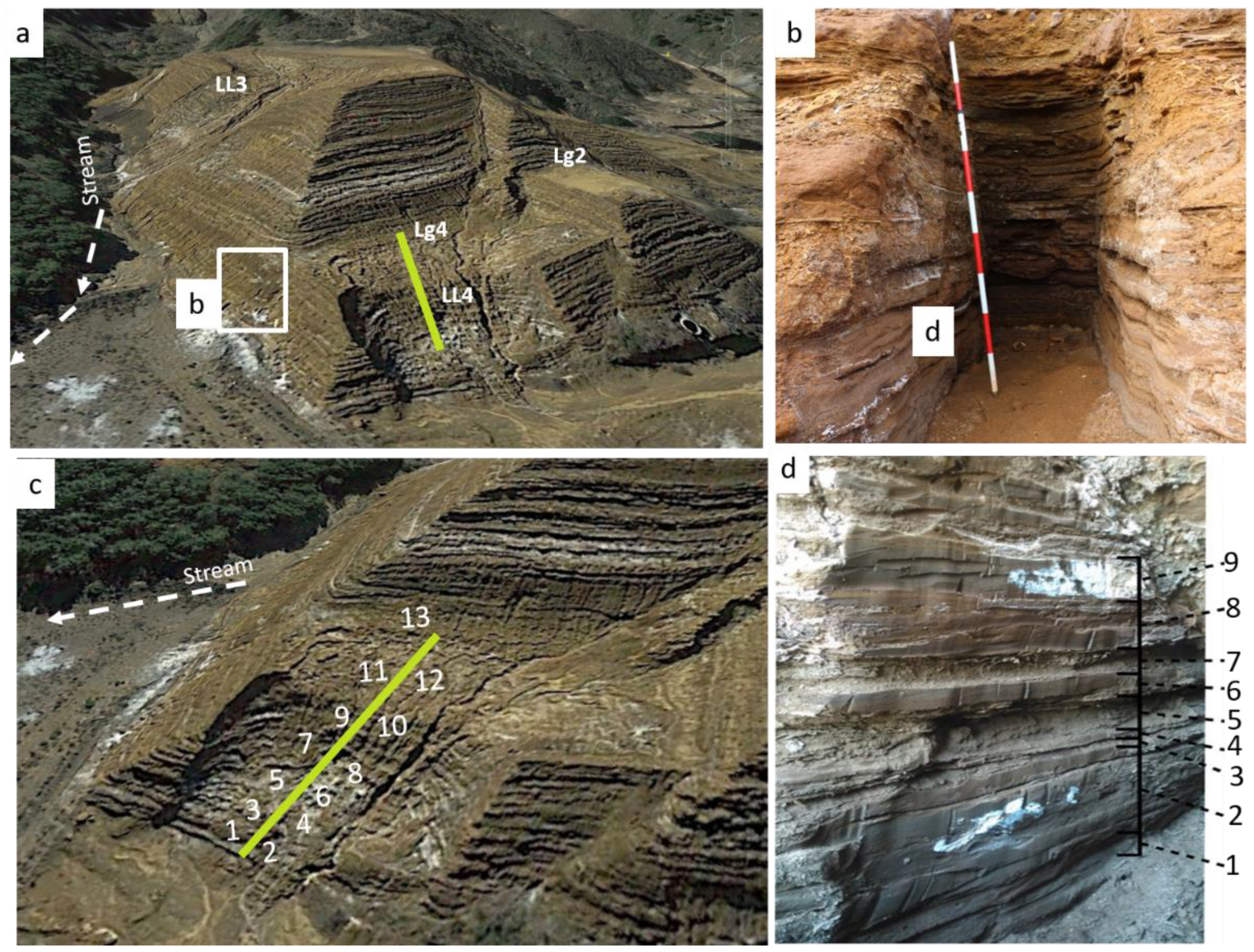
Figure 4.
(a) El Descargador tailings dam, (b) trial pit excavated in the East wall, (c) sampling points of sand dikes exposed on the surface of the landslide four (LL4), (d) detail sedimentary layer and sampling points by different layer in vertical profile. The white color indicates the precipitation of the different types of sulphates that contribute to the cementation of the tailings in the dam. The discontinuous arrow indicates the direction of the stream runoff.
2.2. Particle Size Distribution
The particle size disftribution (PSD) was determined by a Mastersizer 2000LF (Malvern Instruments Ltd. [39]), a coarse grain-size analyzer with a coupled dispersant unit (Hydro 2000 G). The analyzer covers a measurement range from 0.02 to 2000 µm with two light sources: the red light (633 nm) comes from a He-Ne laser and the blue light (466 nm) comes from a solid-state light source. Laser diffraction (LD) technique bases on the modeled PSD calculation from an angular pattern of equivalent scattered light intensities, which provides a volume-based size distribution of a group of spherical particles. In this case, the LD system analyzed the dispersed dry soil fraction in water, performing the measurements off-line. A medium-to-low particulate concentration is required to have enough signal-to-noise ratios to avoid multiple scattering. Obscuration—the percentage of incident light removed by particles—indicates the suitable concentration limits. An ideal obscuration range for this type of suspensions is 5%–15%.
2.3. Electrical Resistivity Imaging (ERI)
ERI is a non-invasive geophysical method devoted to capture the resistivity distribution in the subsoil by multielectrode schemes [25,40,41]. The moisture content and the hydrochemistry of the pore fluids are probably the dominant factors controlling the bulk resistivity of sediments in many cases [28,29,30,31,32,33,34,35,36]. Mild changes in such parameters cause rough variations in resistivity, which can reach up to several magnitude orders. Since tailings typically exhibit significant changes in moisture, hydrochemistry and textural features, ERI is postulated as a useful technique for tailings dam exploration [11,29,30,31,32,33,34,35].
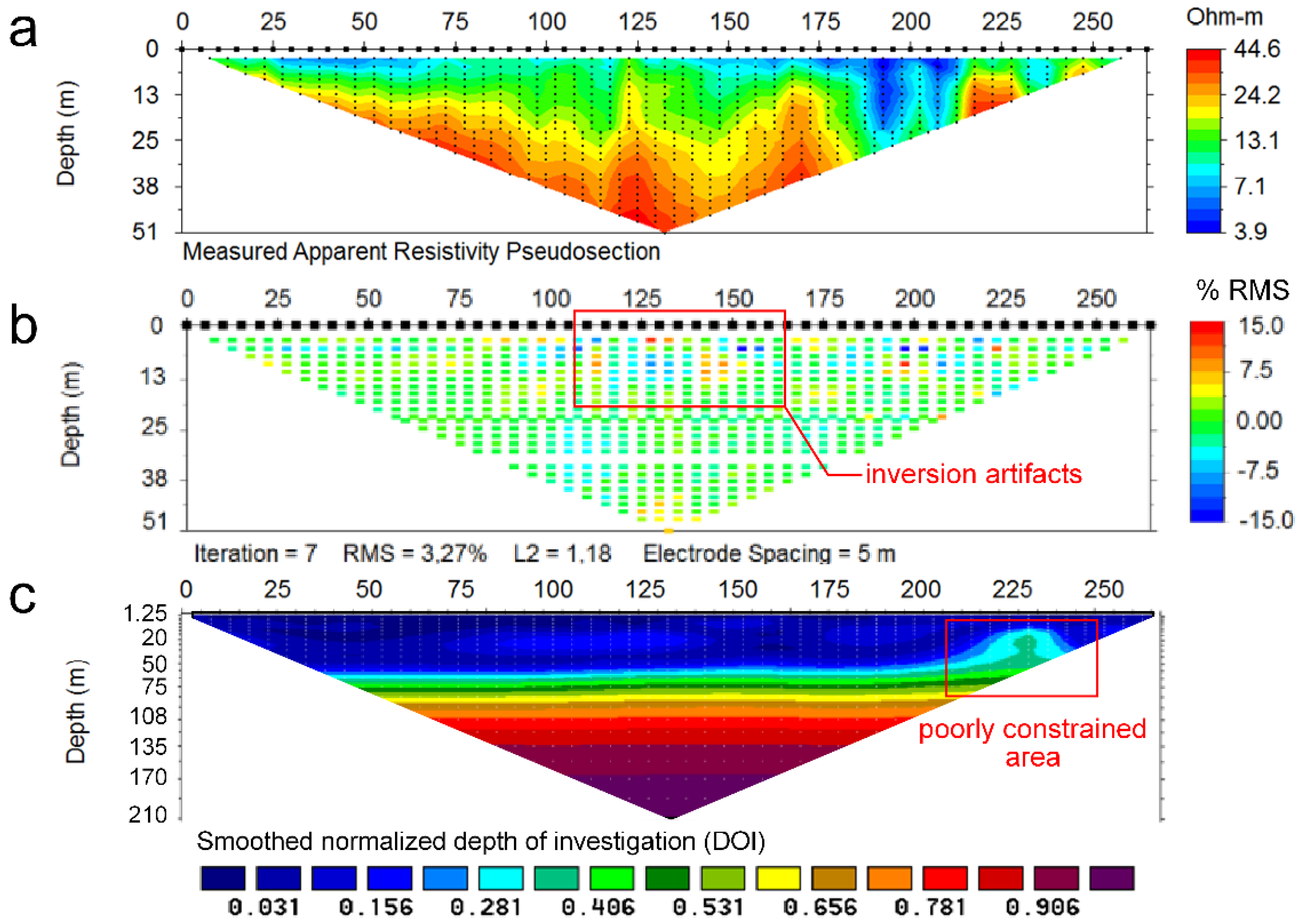
The ERI survey was conducted in April 2004. A Syscal R1 Plus (IRIS Instruments) resistivity meter, equipped with 75 electrodes, spaced every 5 m was used to gather two parallel ERI profiles, oriented N-S (Figure 3). Several reverse measuring cycles and long current injection periods were set to deal with self-potential cancellation. The hybrid Wenner–Schlumberger array was selected as the collecting array since it provides enhanced data coverage compared to Wenner, while it maintains an analogous high signal-to-noise ratio [42,43,44,45,46,47,48,49,50,51,52]. The apparent resistivity records (pseudosection) (Figure 5a) were inverted to construct “real” resistivity images (best fitted models) by EarthImager2D software (Advanced Geosciences, Inc.). The numerical solutions were solved by the least-square smoothness-damping constrained method (Occam’s inversion) [52,53,54,55]. A smoothed inversion was selected due to its stability and consistency, and a homogeneous half-space with a resistivity equal to the average of the recorded resistivity datasets was used as the starting model [56]. Several quality control criteria were considered prior to the geological interpretation of the resistivity images. On the one hand, potential noisy data were excluded from the inversion based on the root mean square (RMS) of the residuals from a preliminary inversion, considering a cutoff threshold of ±15% RMS (Figure 5b). Overall, just some noticeable data points exhibited significant RMS in the central part of the images.
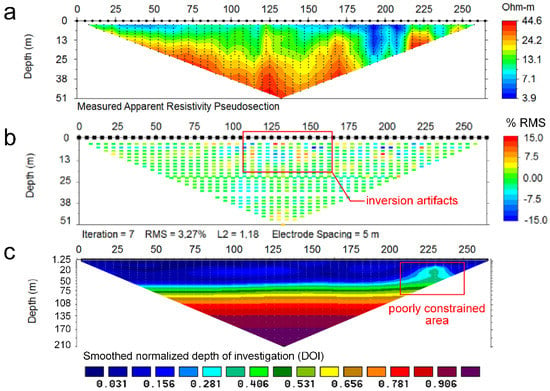
Figure 5.
Quality assessment of the ERI1 profile, (a) recorded pseudosection, (b) Data misfit pseudosection representing the relative data error between the calculated and the measured apparent resistivity records (model residuals), (c) Depth of investigation index (DOI) computed as the difference between subsequent inversions setting the starting models to 1.7 and 170 Ωm, respectively.
More rigorous cutoff criteria were not imposed, since some features are interpreted as inversion artifacts that could offer relevant information on the presence of fractures [28,57,58,59]. The final model residuals do not exceed an RMS of 5%. On the other hand, the DOI-index was computed with Res2DInv software (Geotomo) to identify the depth at which the resistivity images were poorly constrained by the data [60]. Two constant resistivity-starting models of 0.1 and 10 times the average of the measured apparent resistivity were used for the calculation. The average of apparent resistivities was 17 Ωm (ERI1) and 16 Ωm (ERI2) in this case. Several authors advise a DOI cutoff value of 0.1 to 0.2 or, alternatively, considering the limit according to the maximum gradient [60,61]. Based on both criteria, it is possible to identify poorly constrained sectors, as those located in the northern sector of ERI1, at position x = 250 m (Figure 5c), which should be interpreted with extreme caution.
2.4. Numerical Slope Stability Modeling
The modeling of the stability factors was performed by means of a coupled hydro-mechanical fine element formulation, considering different scenarios and boundary conditions (Tables S2 and S3). The computation was made by the software Slide (Rock Science). Slide is a 2D slope stability analysis software that uses limit equilibrium methods for stability computation. This includes the following calculation methods: simplified Bishop method (1955); simplified Janbu method (1954), Janbu corrected method (1968) and GLE/Morgenstern–Price method (1965). These methods are based on the Mohr–Coulomb failure criterion that considers a linear relationship between normal and shear stresses at failure planes (Equation (1)), which has proven to be a robust hypothesis to model earth slope failures. Geotechnical parameters for the computation were set according to the results obtained (Table S2) and values proposed by [12,62,63].
where τ is the shear stress, σ is the normal stress on the sliding plane, u is the pore water pressure, φ is the internal friction angle, c is the cohesion, and s is suction.
τ = (σ − u) × tang φ + c + s
The last two variables in Equation (1) are the shear stress interparticle components that are characteristics of the mine tailings material. The value of cohesion in the mine tailings studied is zero. If they are saturated, the suction is zero. In our case, 13 boundary conditions have been considered for the calculation of the safety factors (Table S3).
3. Results
3.1. Geotechnical and Geophysical Features of the Tailings Dam
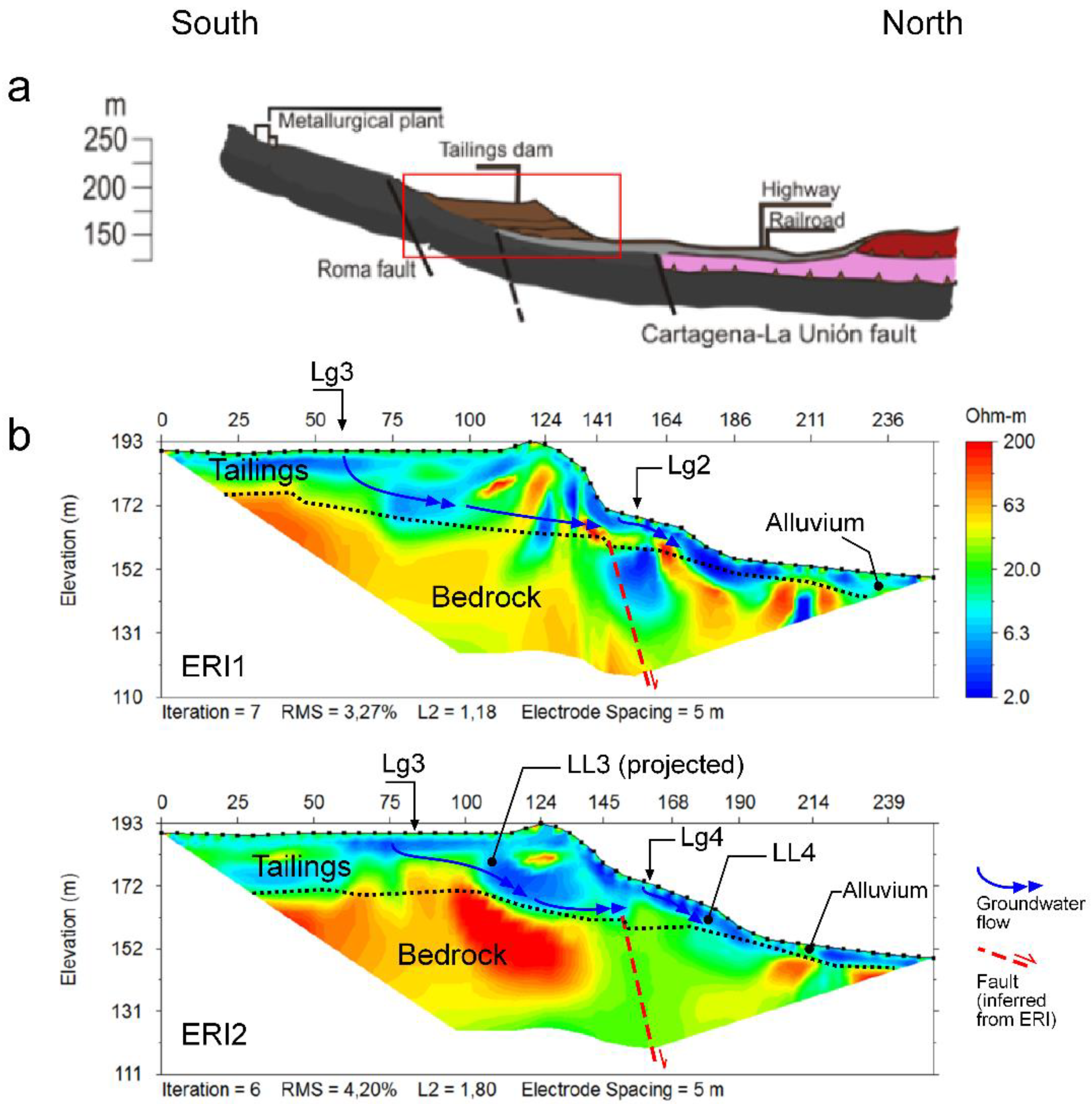
In general, the tailings dam is an irregular pyramidal structure, with platforms and lagoons distributed at different elevations. The local relief is slightly more than 40 m (Figure 2 and Figure 3). The dam settles on two different geological materials, with contrasted geomechanical features. While the northern sector overlies quaternary alluvial sediments (sandstone, limestone, and conglomerate), whose thickness may exceed 20 m, the southern sector already settles on the local Betics complex bedrock are formed by micaschists, white quartzites, marbles and ‘‘green” rocks [10,64,65]) (Figure S1). Such bedrock is shown in resistivity images as medium-resistivity materials (ρ > 50 Ωm; Figure 6). A different pattern is observed from north to south on both ERI profiles. While the resistivity is similar in the southern sector (ρ > 50 Ωm), it is more heterogeneous and lower toward the north, where the metamorphic bedrock is overlain by quaternary alluviums. On the other hand, noticeable inversion artifacts are shown beneath the midpoint of the profiles. It should be noted that these features are shown in an area well-constrained by the data, according to the computed DOI-indexes (Figure 5b).
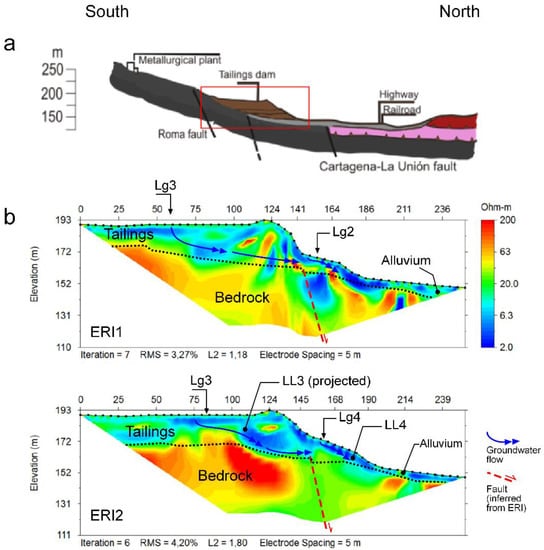
Figure 6.
(a) Modeled geological profile S–N oriented along the El Descargador tailings dam emplacement. (b) Inverted resistivity images and tentative of geological interpretation of ERI1 and ERI2 collected by Wenner–Schlumberger array on the dam structure (see emplacements ERI1 and ERI2 in Figure 3a).
Therefore, we interpret the inversion artifacts as model misfits caused by rough resistivity variation gradients, which are awkwardly solved by the smoothed-constrained inversion method. Such rough gradients have been frequently related to fault areas, in different geomorphological contexts [28,58,59]. The direct observation of the fault was not possible since the area is covered by the tailings and the alluvial fans sedimented by the two ravines bordering the tailings dam. However, the break in the slope that occurs in the area—even a possible degraded fault facet is observed in the NW–sector—as well as the accommodation of the alluvial fans themselves are considered as the possible geomorphic expression of the fault imaged by ERI, and which would form part of the East-trending fault system already mapped (e.g., Roma fault) (Figure 6a).
The mine wastes are shown as low-resistivity materials (ρ < 20 Ωm). The internal structure of the sedimentary layer of tailings could be observed on the walls of the test pit. The pit exposed an interbedded sequence of sands and a very fine-grained dark gray material (Figure 4a). The tailings layers thickness ranged from a few mimileters to several centimeters. Coarse- to medium-grained dark gray materials are coated by red-to-white hydrated sulphates, iron hydroxisulphates, and iron oxyhydroxides precipitation compounds. All sediments were completely or almost completely saturated in water regardless of their texture. It should be noted that the apparent cohesion of materials disappears when they become dry. The resistivity is even lower (ρ < 5 Ωm) beneath the lagoons, up to at least 10 m-depth (Figure 6) and within the slid mass, at the foot of the northern sector of the tailings dam. These low-resistivity zones are interpreted as the geophysical signature of the materials saturated in saline waters related to acid mine drainage processes, which are characterized by extremely low resistivity. The ERI profiles image the preferential groundwater flow paths as anomalous low-resistivity areas. Groundwater is recharged preferentially by the lagoons (e.g., Lg2, Lg3 and Lg4), and the preferential flow pathways are controlled by the local hydraulic gradients, induced by the geometry of the basin and the dam itself, stratification and desiccation cracks. Noticeable is that the landslide areas (e.g., LL3 and LL4) also show low-resistivity features, even decades after 1963 (Figure 6). This is because the tailings saturate quickly but dry very slowly due to their low permeability and suction [18]. The very low-resistivity values in the vertical profile below the lagoon are consistent with other work [11,18,29,30,31,32,33,34,35].
3.2. Landslides Geometry
The reconstructed topographic model prior to the dam failure restores the localization of the pre-existent five decantation ponds (Figure 2 and Figure 3b). The flow failure directly affected four of these lagoons (Lg1, Lg3, Lg4 and Lg5), which stored a large amount of water at the time of collapse. The lagoons had a little freeboard not exceeding 2 m (Figure 3). The flow failure of the tailings dam took place in five different points (Figure 2 and Figure 3). Landslide LL1 (Figure 2) caused a breach in the wall of the impoundment 10 m wide and 6 m high, through which about 2000 m3 of tailings slurry were released to the stream. LL1 affected a small section of lagoon 1 (Lg1, Figure 2). The water runoff eroded the slope and part of the foot of the dam, where it is still possible observing the contact between tailings and underlain quaternary and metamorphic materials. The landslide LL2 (Figure 2 and Figure 3) breached the impoundment wall along 30 m wide and 15 m high, and 5.000 m3 of slurries reached the stream. Here, whitish precipitation compounds produced by the oxidation of the sulphides, mainly magnesium sulphates, still coat some sectors of the exposed slope surfaces. Landslide LL3 (Figure 2, Figure 3, Figure 9 and Figure 10) was the biggest and the only one where a drainage pipe was installed. The movement of the sliding mass from LL3 came to obstruct temporarily the stream channel. LL3 caused a breach 60 m wide and 27 m height, and ca 50,000 m3 tailings flowed up to temporarily dam the stream channel and buried the drainage pipe. The inspection in 2015 revealed that a drainage pipe was filled with tailings, before the sliding, suggesting that the obstruction and failure of the drainage system contributed to the dam slope destabilization. Some noticeable stratigraphic unconformities characterize LL3 deformation upstream. In LL3, some up to 30° dip-tilted tailings beds are juxtaposed to subhorizontal other ones. It should be noted that settling slopes for tailings dams are majorly in the order of 1 to 2°. In the north, LL4 breached the impoundment along 35 m wide (Figure 2, Figure 3 and Figure 11) and released ca. 6000 m3 of tailings. The lack of topographic impediments favored the flowing and sedimentation of mining slurries along a surface of 0.2 km2. Landslide LL5, in the west, depicted a similar behavior compared to LL4, with a breach of 40 m wide and the mobilization of ca. 3000 m3 of tailings along 0.3 km2. In general, the tailings dam is an irregular pyramidal structure, with platforms and lagoons distributed at different elevations.
3.3. Sand Dikes
The subhorizontal interbedded sequences of tailings are crosscut by sand dikes, which are typical water-escape structures. Clastic dikes depart from the dam’s foot, with a sheet thickness of 5–10 mm that expanded up to 10–20 cm during the upwelling. Interconnected sand dikes forming irregular polygonal shapes (quadrilaterals, pentagons, or hexagons), as well as sand volcanoes, are observable on the exposed surfaces along the fault planes (Figure 7, Figure 8, Figure 9, Figure 10 and Figure 11). The textural characteristics of the tailings present in the sand dikes are very similar to the sands exposed in the trial pit. There are no sand dams and sand volcanoes in Lg2; it is because the liquefied tailings were released by Lg4, placed at the downstream, while the presence of sand volcanoes has been related to tailings dam failures [13,18,21,66,67,68], to our knowledge. The manifestation of sand dikes of this magnitude has not been previously reported in the literature [1,2,20,21]. The reconstructed topographic model prior to the dam failure restores the localization of the pre-existent five decantation ponds (Figure 2 and Figure 3b).
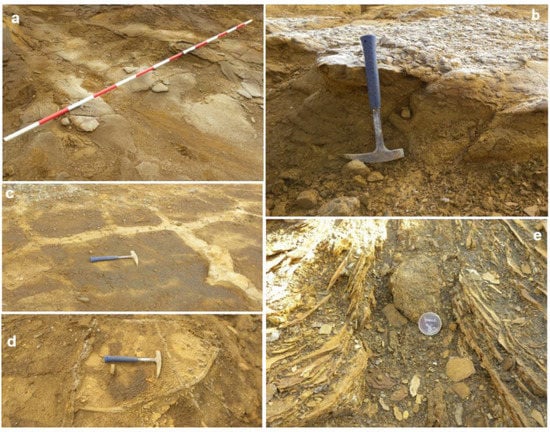

Figure 7.
(a) Massive sandy layer in the lagoon one (Lg1). (b) Detail of the atypical stratification of sand volcanoes compared with stratigraphic signature of mining tailings. (c) Sand dikes in lagoon one (Lg1). (d) Sand dikes in landslide one (LL1). (e) Detail of the sand dike emplacement, which cut crosses the subhorizontal tailings bedding.
Figure 7.
(a) Massive sandy layer in the lagoon one (Lg1). (b) Detail of the atypical stratification of sand volcanoes compared with stratigraphic signature of mining tailings. (c) Sand dikes in lagoon one (Lg1). (d) Sand dikes in landslide one (LL1). (e) Detail of the sand dike emplacement, which cut crosses the subhorizontal tailings bedding.
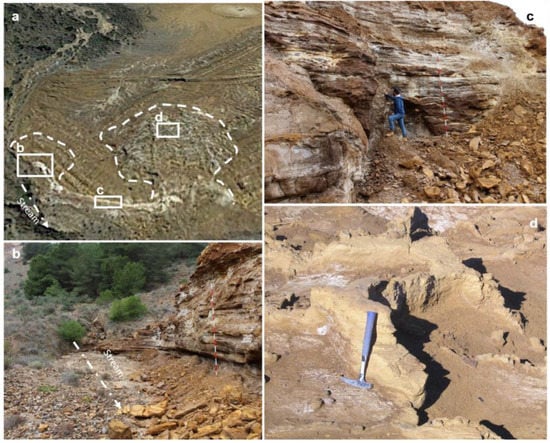


Figure 8.
(a) Obliquus view of landslide one (LL1) and two (LL2); the discontinuous arrow indicates the direction of the stream runoff; source Spanish National Geographic Institute-IGN and Google Earth© landslide one. Detailed views landslide one (LL1) (b) and landside 2 (LL2) (c). (d) Sand dikes exposed on the surface of landslide two (LL2).
Figure 8.
(a) Obliquus view of landslide one (LL1) and two (LL2); the discontinuous arrow indicates the direction of the stream runoff; source Spanish National Geographic Institute-IGN and Google Earth© landslide one. Detailed views landslide one (LL1) (b) and landside 2 (LL2) (c). (d) Sand dikes exposed on the surface of landslide two (LL2).
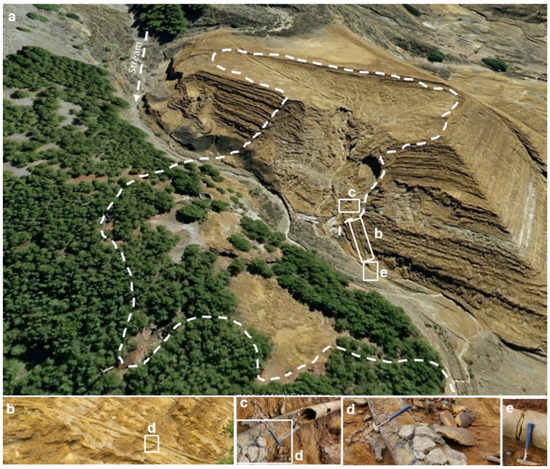


Figure 9.
(a) Obliquus view of landslide three (LL3); source: Spanish National Geographic Institute-IGN and Google Earth©. Note that the slid mass reached the opposite bank of the stream up to 20 m height from the channel bottom. The obstruction dammed the stream, hindering the mudflow to expand downstream. (b) Remains of the existing drainage pipe at the time of the failure. (c) Close-up views of the broken pipeline that is filled of tailings. (d) Pipeline degradation and collapse due to the inside tailings oxidation. (e) Drainage pipeline decoupling.
Figure 9.
(a) Obliquus view of landslide three (LL3); source: Spanish National Geographic Institute-IGN and Google Earth©. Note that the slid mass reached the opposite bank of the stream up to 20 m height from the channel bottom. The obstruction dammed the stream, hindering the mudflow to expand downstream. (b) Remains of the existing drainage pipe at the time of the failure. (c) Close-up views of the broken pipeline that is filled of tailings. (d) Pipeline degradation and collapse due to the inside tailings oxidation. (e) Drainage pipeline decoupling.


Figure 10.
(a) View of landslide three (LL3) from lagoon one (Lg1). (b) View of the dam slide deposit remnants on the opposite stream bank, which caused the stream obstruction. (c) View of the tilted tailings bedding in the right margin of the landslide LL3, which is in contrast with the subhorizontal bedding of mining tailings. (d) View of the almost horizontal bedding characteristic of the tailings deposition, in the left margin of the landslide. The discontinuous arrow indicates the direction of the runoff.
Figure 10.
(a) View of landslide three (LL3) from lagoon one (Lg1). (b) View of the dam slide deposit remnants on the opposite stream bank, which caused the stream obstruction. (c) View of the tilted tailings bedding in the right margin of the landslide LL3, which is in contrast with the subhorizontal bedding of mining tailings. (d) View of the almost horizontal bedding characteristic of the tailings deposition, in the left margin of the landslide. The discontinuous arrow indicates the direction of the runoff.
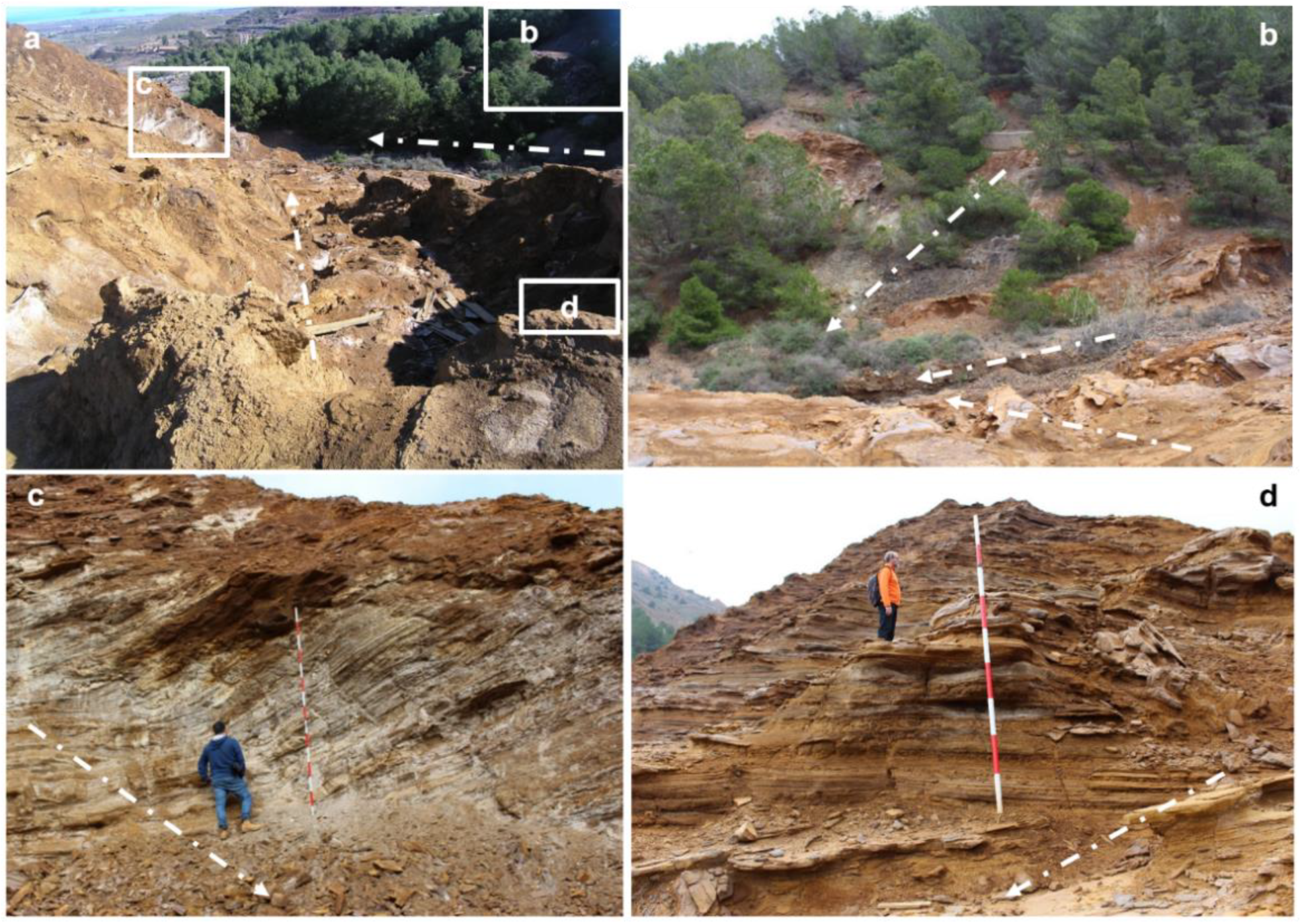


Figure 11.
(a) View of the breach in the wall of the impoundment in landslide four (LL4). (b) Close-up view of a sand dike cross cutting the subhorizontal tailings bedding. Plan view of the polygonal arrangement of sand dikes on the LL4 surface (c) and lagoon four (Lg4) (d). (e) View of a sand dike exposed on the breach plane of landslide five (LL5). The discontinuous arrow indicates the direction of the runoff.
Figure 11.
(a) View of the breach in the wall of the impoundment in landslide four (LL4). (b) Close-up view of a sand dike cross cutting the subhorizontal tailings bedding. Plan view of the polygonal arrangement of sand dikes on the LL4 surface (c) and lagoon four (Lg4) (d). (e) View of a sand dike exposed on the breach plane of landslide five (LL5). The discontinuous arrow indicates the direction of the runoff.

4. Discussion
The El Descargador tailings dam failure in 1963 caused significant damages that have lasted until nowadays. More than 65,000 m3 were released by landslides that covered an area of ca. 4 km2 in the periurban area of La Unión town, affecting different infrastructures such as the Cartagena–Cabo de Palos highway and the Cartagena–Los Blancos railroad), and the Beal wadis stream. A large amount of released acidic waters polluted the El Mar Menor coastal lagoon, which currently shows concentrations of metals and other mining pollutants well above the quality standards [63,69,70]. The impacts of the dam flow failure could have been of greater magnitude if LL3 had not dammed the stream flow in the early stages of the tailing slurries releasing.
4.1. Failure of the Tailings Dam: Conceptual Model
Several causal factors should be considered in the analysis of the tailings dam failure. According to [71], distinct groups of factors may concatenate in the development of landslides. The mechanical contact between the pre-existent terrain and the previous dip slope around 10° toward the plain is considered as predisposing factors in El Descargador site. Several dynamic preparatory factors concurred in El Descargador, which shifted the dam from stable to marginally stable state. The geometric arrangement of the materials that reached very steep slopes of up to 40°, higher than the internal fiction angle of the sandy tailings (32°), was one of the most influential [70]. However, even more influential were the rapid raising of the tailings dam (4.2 m/years) and its poor drainage conditions, which was not able to relieve the pore-fluid overpressures. Pore-fluid overpressurization minimizes the shear strength of earths and, therefore, compromises the resisting efforts within the dam [17,70]. Noticeable is that El Descargador lacked any water drainage system, except for the drainage from the lagoon Lg3 by siphon method.
The samples taken from the trial pit were already saturated (Table S2), indicating that mine tailings remain fully saturated and for a long time after their deposition. The El Descargador area is a semiarid climate and rainwater recharge is just seasonal (300 mm/year), with a precipitation deficit of 900 mm/year. However, the low resistivity of tailings recorded by ERI revealed that tailings keep on saturated down to more than 10 m-depth beneath the lagoons, and that the two active decantation ponds continue recharging the tailings deposit at present by their rainwater storage (Figure 6). According to these results, an important volume of tailings could have remained saturated almost 45 years after the flow failure. This also points to the low drainage capacity of these materials, although being deposited in a semiarid climate. The endorheic nature of the lagoons and the almost non-existence of the drainage systems increase infiltration to the detriment of surface runoff and evacuation of water outside the dam. Consequently, any contribution of water by direct infiltration from the surface, or from the alluvial systems underlain the dam, may favor overpressures due to the drainage deficiencies of the tailings dam. It should be noted that ERI has been very useful to image the areas of preferential groundwater recharging and groundwater flow paths. Such areas were characterized by their anomalous low resistivity (ρ < 5 Ωm), which is consistent with tailings saturated in briny acidic mining lixiviates. This information is very difficult to obtain through direct observations or other geophysical techniques; hence, this work illustrates that ERI has strong capabilities to support tailings dam investigations. ERI also enabled imaging the tailings slid mass, which depicts analogous low-resistivity geophysical signature.
However, this rainwater stored in the lagoons would have contributed to the groundwater recharge and the rise in pore pressure and flowing, which favored the liquefaction processes. The groundwater recharge increases the saturation of the tailings and the granular material forming the foundation. The saturation of the porous material and the rapid increase of load by tailings discharge sustained over time (300 ton/day) in a small area (23,500 m2), and the rapid raising of the tailings dam (more than 4.2 m/years), caused the rise in the pore pressure and the static liquefaction of the sandy tailings (Figure 12 stage 2). The liquefied materials ascended vertically crosscutting strata of different textural and sedimentary features and filled the decantation lagoons (Figure 12 stage 3). This implied the collapse of the structure and the overtopping of the three lagoons (1, 3 and 4) affected by landslides. The expulsion of the pore water and sediment from the beds caused an excessive water table rising in the lagoons. Consequently, the embankment overtopping and the toe of the dam become unstable by the erosion, altering the equilibrium of forces and eventually releasing the stress by the mass sliding (Figure 12, stage 4).
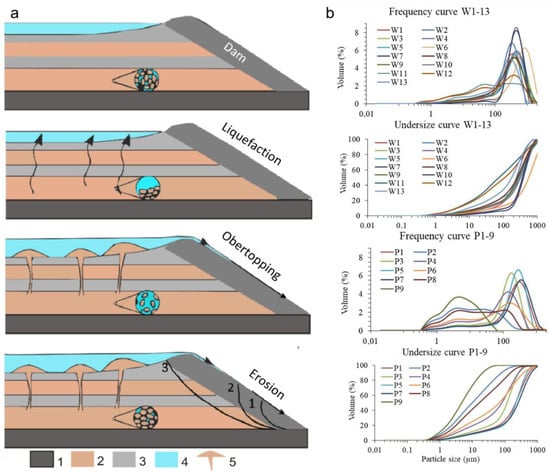
Figure 12.
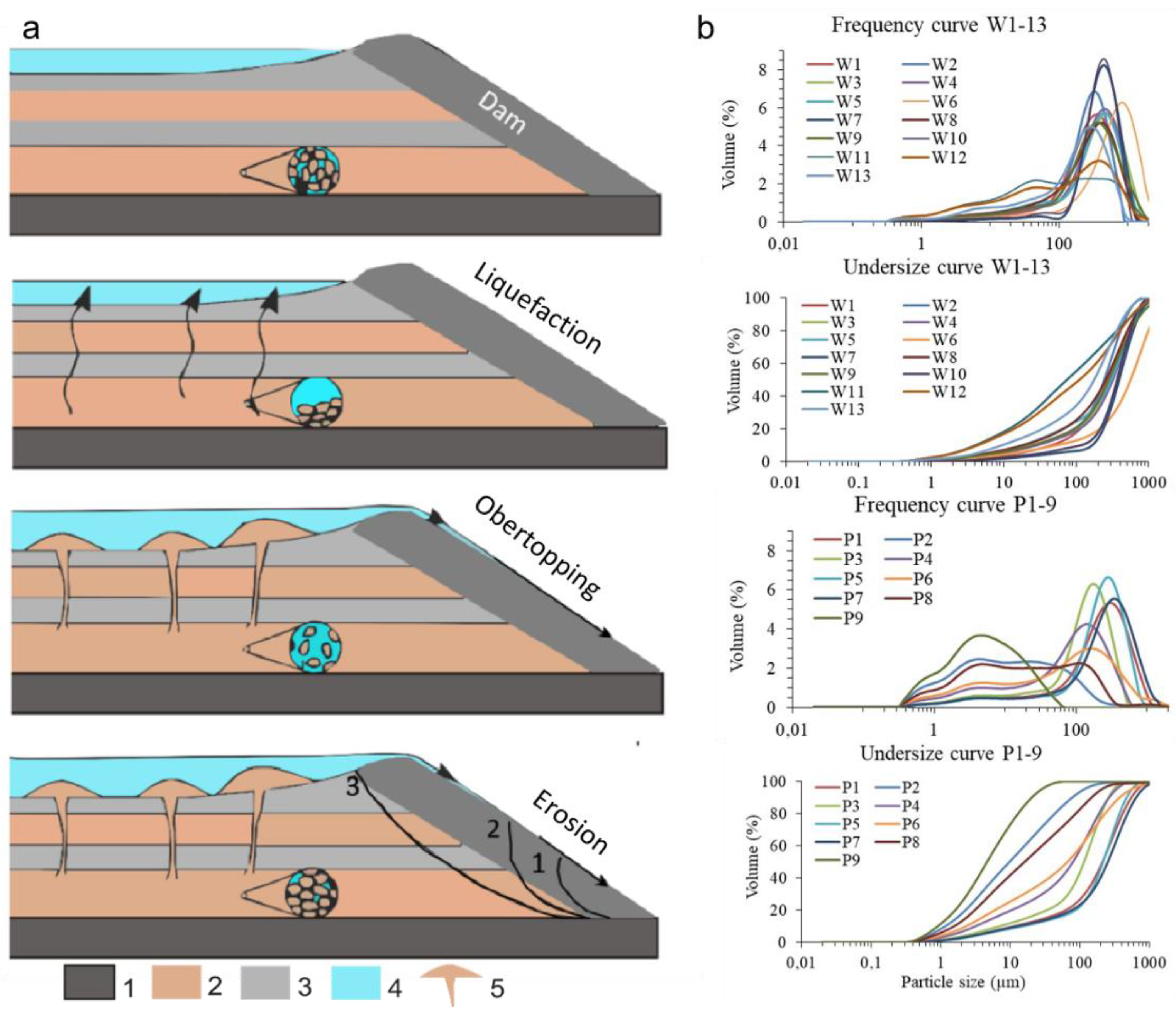
(a) Conceptual model of the “El Descargador” tailings dam flow failure. The model proposes a history of static liquefaction favored by the gain size of tailings at base levels and the rise in the hydraulic head by the effective groundwater recharge from the lagoons (stage 2). The upwelling of sands and water caused the clogging of the lagoons and the freeboards overtopping (stage 3). The flowing of tailings and water on the slopes together with the internal erosion and the pore-fluid over pressuring of the tailings mass triggered the land sliding (stage 4). 1. Basement; 2. Sandy tailings layers; 3. Silty tailings layers; 4. Water and 5. Sand dikes and volcanoes. (b) Textural features of mine tailings: samples P1 to P9, collected from the trial-pit profile and W1 to W11, collected from the sand dike from bottom to top on the surface of landslide four (see Figure 4 and Table S2).
Sediment extrusion structures, such as the sand dikes identified both in the five landslides and the sand dikes and sand volcanoes in Lg1 (Figure 7, Figure 8 and Figure 11), together with the conspicuous sand fraction on the surface (Figure 7a,b) do not present typical stratification of tailings, and support the occurrence of liquefaction processes. SEM observations of the mine wastes from El Descargador exhibited quite different shapes, depending on the degree of weathering and liquefaction. Differences are in the irregularity (major for P9 than W11) and surface roughness (major for W11 than P9) of samples P9 and W11 [17,71]. P9 was extracted from the test pit and is a fine-grained material (Figure 13a) with a structure unaltered since its deposition (see Figure 9b; more information in [52]). W11 is coarse-grained material (Figure 13b) from the sand dike cutting the surface of the landslide four (LL4) see Figure 9a in [71]. Therefore, W11 is a weathered post-flotation waste with a shear history of liquefaction because of a previous severe mudslide.
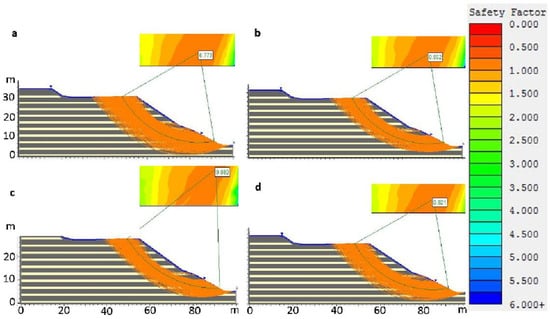
Figure 13.
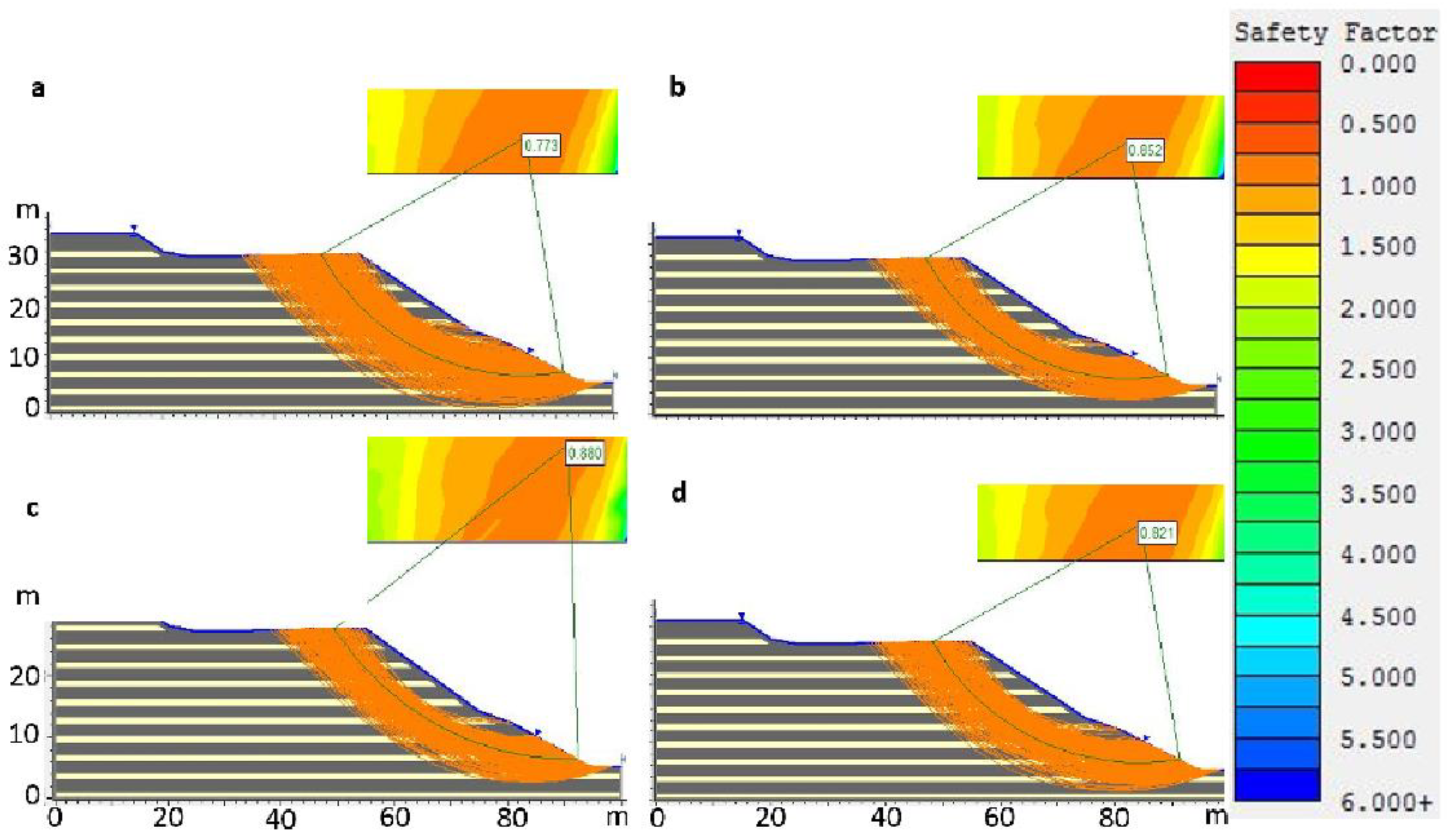
The graph shows all possible circular failure surfaces with a safety factor of less than one in orange; look at the vertical scale on the right and the most critical of all is marked in green. Numerical modeling of the stability factors based on the reconstruction of the topography conditions before the failure (back-analysis), considering static scenarios, with the hydraulic head set at the surface. (a) Janbu Method, (b) simplified Bishop Method, (c) GLE/Morgenstern–Price Method and (d) Janbu corrected Method.
4.2. Numerical Modeling
The slope stability analysis using the reconstructed topography before the failure shows that the dam broke under static and pseudostatic for 13 boundary conditions (Table S3). The layers and dam with different thicknesses were considered. The calculation acceleration used was 0.18 PGA. The article does not show the images of the results of the pseudo-static analysis, but it does show the results in Table S3 and Figure S2. The geotechnical parameters as specific weight, cohesion, frictional angle of mining tailings were set according to Table S2 and [71]. Figure 13 shows the results of the static stability calculation for the LL4 slip. Four materials have been considered: silty tailings with the internal fraction angle of 27 °C, sandy tailings with the internal fraction angle of 29 °C (see Table S2), dam with the internal fraction angle of 37 °C and foundation with the internal fraction angle of 41 °C. The cohesion is zero. The water head was considered at the tailings dam surface, reproducing the hydraulic condition of liquefaction. This is considered a minimum since the hydraulic head could have reached even an elevation higher than that of the lagoons. The achieved numerical simulations are consistent with the hypothesis that the tailings mass sliding occurred due to a combination a dysfunction of the drainage system and static liquefaction. This concatenation of factors caused the ascent of liquefied material to the lagoon and the overflow. The debris caused the erosion of the slope and its foot which altered the stress equilibrium, leading to the tailings dam failure. The geometry of failure is, according to the model, a subcircular type landslide with stability factors ranging from 0.773 to 0.880 (less than one is considered as unstable condition; Figure 13). This geometry is consistent with a failure within the mass of tailings, which can be considered as a reasonably homogeneous material for modeling purposes. Part of the liquefied tailings can be seen on the left side of the stream (Figure 9 and Figure 10). The released tailings caused the obstruction of the valley and the invasion of the national highway. In this regard, the damming of the stream valley had a positive impact from a hazard’s perspective since it minimized the ability of the mine wastes to flow and spread downstream of the basin.
This work illustrates why static liquefaction should not be underestimated as a triggering factor of tailings dams’ failures, with respect to seismicity or extreme weather events that have been more frequently invoked. It also shows that a multidisciplinary investigation approach, by integrating geotechnical, hydrogeological and geophysical characterization and modeling, is required to not misinterpret the main causes of a dam failure. The new acquired knowledge on the El Descargador tailings dam failure could be replicated in other regions worldwide, which may contribute to a better design and management of these critical mining operations and their side impacts.
5. Conclusions
- The work is a unique case study. Its contribution lies in the magnitude and nature of the static liquefaction. This phenomenon has not been reported in this way before. In no case in the literature or in the databases has a tailings dam been reported to develop simultaneous flow failure at five points [1,2,5,6,7,8,9,10,11,18].
- The geophysical–geotechnical characterization and modeling of the El Descargador tailings dam supported that the static liquefaction was the most plausible cause of its flow failure in 1963. This occurred in the form of five different landslides along the dam structure, which mobilized 66,000 m3 on 4 km2 of the La Unión periurban area.
- The rapid growing of the tailings dam, exceeding 4.2 m/year, the steeped slopes of the tails, scaling up to 40°, the saturation of tailings due to recharge from the lagoons, the failure of the drainage system and the rise in the hydraulic head were the main causal preparatory factors for flow failure (Figure 2, Figure 3, Figure 4, Figure 7, Figure 8, Figure 9, Figure 10, Figure 11, Figure 12, Figure 13 and Figure 14).
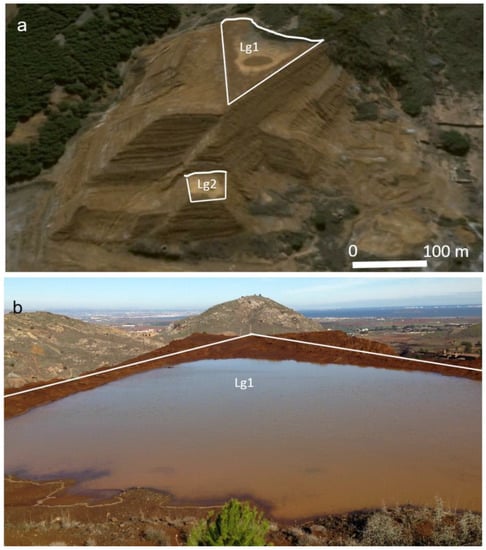 Figure 14. (a) Lagoon Lg1 and Lg3 after a rainstorm and (b) detail an Lg1 (October 2015). The spatio-temporal evolution of drying and wetting of the lagoons can be seen in the Google Earth clock (Since June 2002).
Figure 14. (a) Lagoon Lg1 and Lg3 after a rainstorm and (b) detail an Lg1 (October 2015). The spatio-temporal evolution of drying and wetting of the lagoons can be seen in the Google Earth clock (Since June 2002). - The dysfunction of the drainage system and the static liquefaction caused the dam’s lagoons overtopping and the erosion of the slope and the foot of the structure, which triggered mechanism the flow failure the El Descargador tailings dam.
- Geophysical modeling of the tailings dam revealed that the materials remain saturated beneath the lagoons to a 10 m depth or more, even decades after the dam failure. This observation highlights the relevant role of the lagoons in the groundwater recharge in tailings dam (Figure 14).
Supplementary Materials
The following supporting information can be downloaded at: https://www.mdpi.com/article/10.3390/min12121488/s1, Figure S1. The image shows the contact between the different geological materials and tailings. The discontinuous arrow indicates the direction of the runoff. Figure S2. Factors of safety for the 13 boundary conditions analyzed, (a) in static conditions and (b) in pseudo-static conditions. Table S1. Local magnitude (Richter scale) of the seismic events during 1967 over 500 km ratio from El Descargador tailings dam; source: Spanish National Geographic Institute (IGN); Table S2. Particle size distribution (PSD) of the tailings’ samples collected in the trial pit (P1–P9) and the sand dikes (W1–W13). D10, D30, D50, D60, D90 are the particle size at the 10, 30, 50, 60, 90% point of the cumulative undersize PSD, Cu is the coefficient of uniformity, Cc is the coefficient of curvature, Sr is degree of saturation, e is void ratio, w is gravimetric water content, n is porosity; Table S3. Safety factors for different calculation hypotheses. Fs is phreatic surface, BS is Bishop simplify method, MP is Morgenstem–Price Method, JS is Janbu simplify method, JC is Janbu simplify method. Sp is that the height of the water table is at the surface of the dam and Md is at the middle and D means that the dam of tailings dam is dry. * In scenario 13, the lagoons are considered full of water.
Author Contributions
Conceptualization, R.R.-P. and M.Z.; methodology, R.R.-P., A.V.C., M.Z., A.A., R.R.-P., I.C. and C.R.; software, R.R.-P. and M.Z.; validation, R.R.-P. and M.Z.; formal analysis, R.R.-P., I.C., C.R. and M.Z.; investigation, R.R.-P., A.V.C., A.A., P.M.-P., M.A.M.-S., C.G.-G., Á.F., I.C., C.R. and M.Z.; resources, R.R.-P., A.A. and Á.F.; data curation, R.R.-P., A.V.C., A.A., M.Z., I.C. and C.R.; writing—original draft preparation, R.R.-P. and M.Z.; writing—review and editing, R.R.-P., I.C., C.R. and M.Z.; visualization, R.R.-P. and M.Z.; supervision, R.R.-P. and M.Z.; project administration, R.R.-P. and C.G.-G.; funding acquisition, R.R.-P., A.A., C.G.-G. and Á.F. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This research received no external funding.
Data Availability Statement
Not applicable.
Acknowledgments
This research was supported by the Spanish Ministry of Industry, Commerce and Tourism and from a management entrustment with the Spanish Ministry of Agriculture, Food and Environment. Authors thanks the anonymous reviewers for their work.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest. The funders had no role in the design of the study; in the collection, analyses, or interpretation of data; in the writing of the manuscript; or in the decision to publish the results.
References
- Oldecop, L.; Rodríguez, R. Estabilidad y seguridad de depósitos de residuos mineros. In Los Residuos Minero Metalúrgicos en el Medio Ambiente; Rodríguez, R., García-Cortés, A., Eds.; Instituto Geológico y Minero de España (IGME): Madrid, Spain, 2006; pp. 197–243. [Google Scholar]
- Rico, M.; Benito, G.; Salgueiro, A.R.; Díez-Herrero, A.; Pereira, H.G. Reported tailings dam failures: A review of the European incidents in the worldwide context. J. Hazard. Mater. 2008, 152, 846–852. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Owen, J.R.; Kemp, D.; Lèbre, É.; Svobodova, K.; Pérez Murillo, G. Catastrophic tailings dam failures and disaster risk disclosure. Int. J. Disaster Risk Reduct. 2020, 42, 101361. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- López-Pamo, E.; Barettino, D.; Antón-Pacheco, C.; Ortiz, G.; Arránz, J.C.; Gumiel, J.C.; Martínez-Pledel, B.; Aparicio, M.; Montouto, O. The extent of the Aznalcóllar pyritic sludge spill and its effects on soils. Sci. Total Environ. 1999, 242, 57–88. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- ICOLD; UNEP. Tailings Dams–Risk of Dangerous Occurrences, Lessons Learnt from Practical Experiences (Bulletin 121); Commission Internationale des Grands Barrages: Paris, France, 2001; Volume 155. [Google Scholar]
- Available online: https://www.wise-uranium.org (accessed on 24 August 2022).
- Available online: https://tailings.info/ (accessed on 24 August 2022).
- Available online: http://www.csp2.org/technical-reports (accessed on 24 August 2022).
- Available online: http://www.csp2.org/ (accessed on 24 August 2022).
- Available online: https://worldminetailingsfailures.org/ (accessed on 24 August 2022).
- Martín-Crespo, T.; Gómez-Ortiz, D.; Martín-Velázquez, S.; Martínez-Pagán, P.; De Ignacio, C.; Lillo, J.; Faz, A. Geoenvironmental characterization of unstable abandoned mine tailings combining geophysical and geochemical methods (Cartagena-La Unión district, Spain). Eng. Geol. 2018, 232, 135–146. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Simón, M.; Ortiz, I.; García, I.; Fernández, E.; Fernández, J.; Dorronsoro, C.; Aguilar, J. Pollution of soils by the toxic spill of a pyrite mine (Aznalcollar, Spain). Sci. Total Environ. 1999, 242, 105–115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ayala-Carcedo, F.J. La rotura de la balsa de residuos mineros de Aznalcóllar (España) de 1998 y el desastre ecológico consecuente del Río Guadiamar: Causas, efectos y lecciones. Boletín Geológico Min. 2004, 115, 711–738. [Google Scholar]
- Robles-Arenas, V.M.; Rodríguez, R.; García, C.; Candela, L. Sulphide-miningimpacts in thephysicalenvironment: Sierra de Cartagena-La Unión (SE Spain) case study. Environ. Geol. 2006, 51, 47–64. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- do Carmo, F.F.; Kamino, L.H.Y.; Junior, R.T.; de Campos, I.C.; do Carmo, F.F.; Silvino, G.; Mauro, M.L.; Rodrigues, N.U.A.; de Souza Miranda, M.P.; Pinto, C.E.F. Fundão tailings dam failures: The environment tragedy of the largest technological disaster of Brazilian mining in global context. Perspect. Ecol. Conserv. 2017, 15, 145–151. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alonso, E.E.; Gens, A. Aznalcóllar dam failure. Part 1: Field observations and material properties. Géotechnique 2006, 56, 165–183. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alonso, E.E.; Zabala, F. Progressive failure of Aznalcóllar dam using the material point method. Géotechnique 2011, 61, 795–808. [Google Scholar]
- Rodríguez, R.; Muñoz-Moreno, A.; Caparrós, A.V.; García-García, C.; Brime-Barrios, A.; Arranz-González, J.C.; Rodríguez-Gómez, V.; Fernández-Naranjo, F.J.; Alcolea, A. How to Prevent Flow Failures in Tailings Dams. Mine Water Envion. 2021, 40, 83–112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Davies, M.P.; McRoberts, E.C.; Martin, T.E. Static Liquefaction of Tailings–Fundamentals and Case Histories. In Proceedings of the Tailings Dams 2002, ASDSO/USCOLD, Las Vegas, NV, USA, 29 April–1 May 2002. [Google Scholar]
- Nichols, G. Sedimentology and Stratigraphy; John Wiley & Sons: New York, NY, USA, 2009; Volume 99, pp. 1–432. [Google Scholar]
- Zandarín, M.T.; Oldecop, L.A.; Rodríguez, R.; Zabala, F. The role of capillary water in the stability of tailing dams. Eng. Geol. 2009, 105, 108–118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Azam, S.; Li, Q. Tailings dam failures: A review of the last one hundred years. Geotech. News 2010, 28, 50–54. [Google Scholar]
- Fourie, A.B.; Blight, G.E.; Papageorgiou, G. Static liquefaction as a possible explanation for the Merriespruit tailings dam failure. Can. Geotech. J. 2001, 38, 707–719. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jennings, J.E. The failure of a slimes dam at Bafokeng. Mechanisms of failure and associated design considerations. Civil. Eng. S. Afr. 1979, 21, 135–141. [Google Scholar]
- Blight, G.B.; Fourie, A.B. A review of catastrophic flow failures of deposits of mine waste and municipal refuse. In Proceedings of the International Workshop on: Occurrence and Mechanisms of Flows in Natural Slopes and Earth Fills (IW-Flows 2003), Associazione Geotecnica Italiana (AGI), Sorrento, Italy, 14–16 May 2003; pp. 1–17. [Google Scholar]
- Davies, M.P.; Dawson, B.B.; Chin, B.G. Static Liquefaction Slump of Mine Tailings—A Case History. In Proceedings of the 51st Canadian Geotechnical Conference, Edmonton, AB, Canada, 4–7 October 1998. [Google Scholar]
- Morgenstern, N. Geotechnics and mine waste management–update. In Proceedings of the Seminar Proceedings, Safe Tailings Dam Constructions, Gallivare, Sweden, 20–21 September 2001. [Google Scholar]
- Gómez-Ortiz, D.; Martín-Velázquez, S.; Martín-Crespo, T.; De Ignacio-San, J.C.; Lillo-Ramos, J. Application of electrical resistivity tomography to the environmental characterization of abandoned massive sulphide mine ponds (Iberian Pyrite Belt, SW Spain). Near Surf. Geophys. 2010, 8, 65–74. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martín-Crespo, T.; Martín-Velázquez, S.; Gómez-Ortiz, D.; De Ignacio-San, J.C.; Lillo, J. A geochemical and geophysical characterization of sulfide mine ponds at the Iberian Pyrite Belt (Spain). Water Air Soil Pollut. 2011, 217, 387–405. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martín-Crespo, T.; De Ignacio-San, J.C.; Gómez-Ortiz, D.; Martín-Velázquez, S.; Lillo, J. Monitoring study of the mine pond reclamation of Mina Concepción, Iberian Pyrite Belt (Spain). Environ. Earth Sci. 2010, 54, 1275–1284. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martín-Crespo, T.; Gómez-Ortiz, D.; Martín-Velázquez, S.; Esbrí, J.M.; de Ignacio-San José, C.; Sánchez-García, M.J.; Montoya-Montes, I.; Martín-González, F. Abandoned mine tailings in cultural itineraries: Don Quijote route (Spain). Eng. Geol. 2015, 197, 82–93. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martín-Crespo, T.; Gómez-Ortiz, D.; Martínez-Pagán, P.; De Ignacio-San José, C.; Martín-Velázquez, S.; Lillo, J.; Faz, A. Geoenvironmental characterization of riverbeds affected by mine tailings in the Mazarrón district (Spain). J. Geochem. Explor. 2012, 119–120, 6–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oyarzun, R.; Lillo, J.; López-García, J.A.; Esbrí, J.M.; Cubas, P.; Llanos, W.; Higueras, P. The Mazarrón Pb-(Ag)-Zn mining district (SE Spain) as a source of heavy metal contamination in a semiarid realm: Geochemical data from mine wastes, soils, and stream sediments. J. Geochem. Explor. 2011, 109, 113–124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martín-Crespo, T.; Gómez-Ortiz, D.; Martín-Velázquez, S. Geoenvironmental characterization of sulfide mine tailings. In Applied Geochemistry with Case Studies on Geological Formations, Exploration Techniques and Environmental Issues; Mazadiego, L.F., De Miguel Garcia, E., Barrio-Parra, F., Izquierdo-Díaz, M., Eds.; IntechOpen: London, UK, 2020; pp. 1–26. [Google Scholar]
- Martín-Velázquez, S.; Rodríguez-Santalla, I.; Ropero-Szymañska, N.; Gomez-Ortiz, D.; Martín-Crespo, T.; de Ignacio-San José, C. Geomorphological mapping and erosion of abandoned tailings in the hiendelaencina Mining District (Spain) from Aerial Imagery and LiDAR Data. Remote Sens. 2022, 14, 4617. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martínez, J.; Hidalgo, M.C.; Rey, J.; Garrido, J.; Kohfahl, C.; Benavente, J.; Rojas, D. A multidisciplinary characterization of a tailings pond in the Linares–La Carolina mining district, Spain. J. Geochem. Explor. 2016, 162, 62–71. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martínez, J.; Rey, J.; Hidalgo, M.C.; Garrido, J.; Rojas, D. Influence of measurement conditions on the resolution of electrical resistivity imaging: The example of abandoned mining dams in the La Carolina District (Southern Spain). Int. J. Miner. Process. 2014, 133, 67–72. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rey, J.; Martínez, J.; Hidalgo, M.C.; Rojas, D. Heavy metal pollution in the Quaternary Garza basin: A multidisciplinary study of the environmental risks posed by mining (Linares, southern Spain). Catena 2013, 110, 234–242. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Available online: https://www.malvernpa (accessed on 24 August 2022).
- Loke, M.H.; Chambers, J.E.; Rucker, D.F.; Kuras, O.; Wilkinson, P.B. Recent developments in the direct-current geoelectrical imaging method. J. Appl. Geophys. 2013, 95, 135–156. [Google Scholar]
- Zarroca, M.; Linares, R.; Velásquez-López, P.C.; Roqué, C.; Rodríguez, R. Application of electrical resistivity imaging (ERI) to a tailings dam project for artisanal and small-scale gold mining in Zaruma-Portovelo, Ecuador. J. Appl. Geophys. 2015, 113, 103–113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gabarrón, M.; Martínez-Pagán, P.; Martínez-Segura, M.A.; Bueso, M.C.; Martínez-Martínez, S.; Faz, A.; Acosta, J.A. Electrical Resistivity Tomography as a Support Tool for Physicochemical Properties Assessment of Near-Surface Waste Materials in a Mining Tailing Pond (El Gorguel, SE Spain). Minerals 2020, 10, 559. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martínez, J.; Mendoza, R.; Rey, J.; Sandoval, S.; Hidalgo, M.C. Characterization of Tailings Dams by Electrical Geophysical Methods (ERT, IP): Federico Mine (La Carolina, Southeastern Spain). Minerals 2021, 11, 145. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Griffiths, D.H.; Barker, R.D. 2-Dimensional resistivity imaging and modeling in areas of complex geology. J. Appl. Geophys. 1993, 29, 211–226. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Archie, G.E. The electrical resistivity log as an aid in determining some reservoir characteristics. Pet. Trans. AIME 1942, 146, 54–62. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zarroca, M.; Bach, J.; Linares, R.; Pellicer, X.M. Electrical methods (VES and ERT) for identifying, mapping and monitoring different saline domains in a coastal plain region (Alt Empordà, northern Spain). J. Hydrol. 2011, 409, 407–422. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zarroca, M.; Linares, R.; Rodellas, V.; Garcia-Orellana, J.; Roqué, C.; Bach, J.; Masqué, P. Delineating coastal groundwater discharge processes in a wetland area by means of electrical resistivity imaging, 224Ra and 222Rn. Hydrol. Process. 2014, 28, 2382–2395. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pazdirek, O.; Blaha, V. Examples of resistivity imaging using ME-100 resistivity field acquisition system. In Proceedings of the EAGE 58th Conference and Technical Exhibition Extended Abstracts, Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 7 June 1996. [Google Scholar]
- Dahlin, T.; Zhou, B. A numerical comparison of 2D resistivity imaging with 10 electrode arrays. Geophys. Prospect. 2004, 52, 379–398. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Loke, M.H.; Kiflu, H.; Wilkinson, P.B.; Harro, D.; Kruse, S. Optimized arrays for 2-D resistivity surveys with combined surface and buried arrays. Near Surf. Geophys. 2015, 13, 505–517. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Constable, S.; Parker, R.L.; Constable, C.G. Occam’s inversion: A practical algorithm for generating smooth models from electromagnetic sounding data. Geophysics 1987, 52, 289–300. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- La Brecque, D.; Miletto, M.; Daily, W.; Ramirez, A.; Owen, E. The effects of noise on Occam’s inversion of resistivity tomography data. Geophysics 1996, 61, 538–548. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Labuz, J.F.; Zang, A. Mohr–Coulomb Failure Criterion. Rock Mech. Rock Eng. 2012, 45, 975–979. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Loke, M.H. Electrical resistivity surveys and data interpretation. In Solid Earth Geophysics Encyclopedia, 2nd ed.; Gupta, H., Ed.; Electrical & Electromagnetic; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2020; pp. 276–283. [Google Scholar]
- Loke, M.H.; Acworth, I.; Dahlin, T. A comparison of smooth and blocky inversion method in 2D electrical tomography surveys. Explor. Geophys. 2003, 34, 182–187. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zarroca, M.; Linares, R.; Bach, J.; Roqué, C.; Moreno, V.; Font, L.; Baixeras, C. Integrated geophysics and soil gas profiles as a tool to characterize active faults: The Amer fault example (Pyrenees, NE Spain). Environ. Earth Sci. 2012, 67, 889–910. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zarroca, M.; Comas, X.; Gutiérrez, F.; Carbonel, D.; Linares, R.; Roqué, C.; Mozafari, M.; Guerrero, J.; Pellicer, X.M. The application of GPR and ERI in combination with exposure logging and retrodeformation analysis to characterize sinkholes and reconstruct their impact on fluvial sedimentation. Earth Surf. Process. Landf. 2017, 42, 1049–1064. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oldenburg, D.W.; Li, Y. Estimating depth of investigation in dc resistivity and IP surveys. Geophysics 1999, 64, 403–416. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oldenborger, G.A.; Routh, P.S.; Knoll, M.D. Model reliability for 3D electrical resistivity tomography: Application of the volume of investigation index to a time-lapse monitoring experiment. Geophysics 2007, 72, F167–F175. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Caterina, D.; Beaujean, J.; Robert, T.; Nguyen, F. A comparison study of image appraisal tools for electrical resistivity tomography. Near Surf. Geophys. 2013, 11, 639–657. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- García, C. Impacto y Riesgo Ambiental de los Residuos Minero-Metalúrgicos de la Sierra de Cartagena-La Unión (Murcia-España). Ph.D. Thesis, Universidad Politécnica de Cartagena, Cartagena, Spain, 7 November 2004. [Google Scholar]
- Alcolea, A.; Vázquez, M.; Caparrós, A.; Ibarra, I.; García, C.; Linares, R.; Rodríguez, R. Heavy metal removal of intermittent acid mine drainage with an open limestone channel. Miner. Eng. 2012, 1, 86–98. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alcolea, A.; Fernández-López, C.; Vázquez, M.; Caparrós, A.; Ibarra, I.; García, C.; Zarroca, M.; Rodríguez, R. An assessment of the influence of sulfidic mine wastes on rainwater quality in a semiarid climate (SE Spain). Atmos. Environ. 2015, 107, 85–94. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dobry, R.; Alvarez, L. Seismic failures of Chilean tailings dam. Journal of the Soil mechanics and Foundations Division. Proc. Am. Soc. Civ. Eng. 1967, 93, 237–260. [Google Scholar]
- Okusa, S.; Anma, S. Slope failures and tailings dam damage in the 1988 Izu-Ohshima-Kinkai earthquake. Eng. Geol. 1980, 16, 195–224. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Conesa, H.M.; Jiménez-Cárceles, F.J. The Mar Menor lagoon (SE Spain): A singular natural ecosystem threatened by human activities. Mar. Pollut. Bull. 2007, 54, 839–849. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- García, G.; Muñoz-Vera, A. Characterization and evolution of the sediments of a Mediterranean coastal lagoon located next to a former mining area. Mar. Pollut. Bull. 2015, 100, 249–263. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Glade, T.; Crozier, M.J. The nature of landslide hazard impact. In Landslide Hazard and Risk; Glade, T., Anderson, M., Crozier, M., Eds.; Wiley Online Library: Chichester, UK, 2005; pp. 43–74. [Google Scholar]
- Caparrós, A.V. Rheology of Pb-Zn Post-Flotation Waste in the Sierra de Cartagena-La Unión (SE Spain). Ph.D. Thesis, Universidad Politécnica de Cartagena, Cartagena, Spain, July 2017. [Google Scholar]
- Oldecop, L.; Garino, L.; Muñoz, J.; Rodríguez Pacheco, R.; García-García, C. Unsaturated behaviour of mine tailings in low precipitation areas. In Unsaturated Soils; Alonso, E., Gens, A., Eds.; Taylor & Francis Group: London, UK, 2011; Volume 2, pp. 1425–1430. [Google Scholar]
- Tergazhi, K. Der grundbruch a stauwerken and seine verhiltung. Die Wasserkr. 1922, 17, 445–449. [Google Scholar]
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).