Total vs. Partial Acid Digestion Methods for Trace Element Analysis in Archaeological Sediments
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
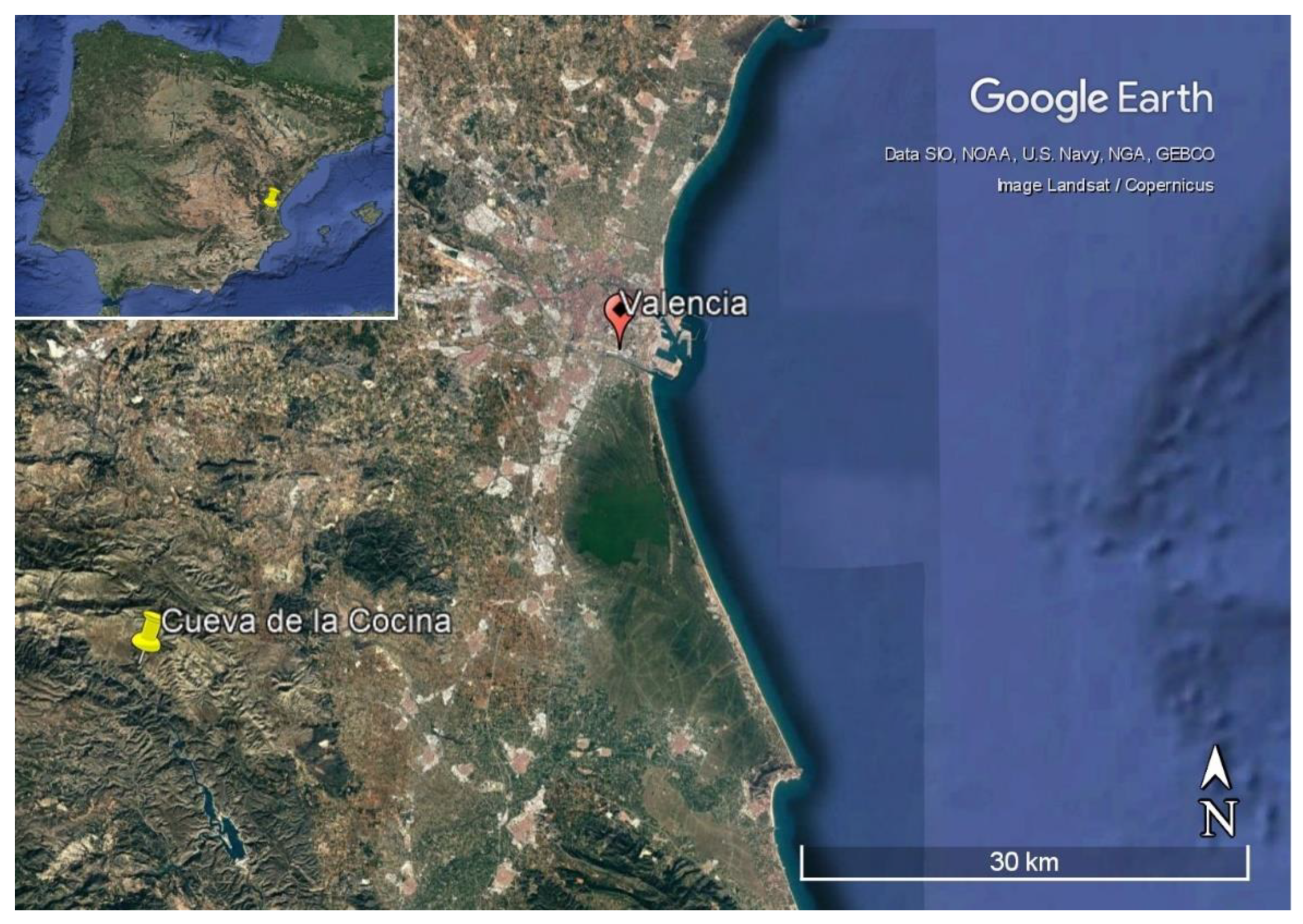
2.1. The Sediments
2.2. Analytical Techniques
2.3. Data Analysis
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Trace Elements
3.2. Rare-Earth Elements (REEs)
4. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Pastor, A.; Gallello, G.; Cervera, M.L.; de la Guardia, M. Mineral Soil Composition Interfacing Archaeology and Chemistry. TrAC Trends Anal. Chem. 2016, 78, 48–59. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kennedy, S.A.; Kelloway, S.J. Identifying Metallurgical Practices at a Colonial Silver Refinery in Puno, Peru, Using Portable X-Ray Fluorescence Spectroscopy (PXRF). J. Archaeol. Sci. Rep. 2020, 33, 102568. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Save, S.; Kovacik, J.; Demarly-Cresp, F.; Issenmann, R.; Poirier, S.; Sedlbauer, S.; Teyssonneyre, Y. Large-scale Geochemical Survey by PXRF Spectrometry of Archaeological Settlements and Features: New Perspectives on the Method. Archaeol. Prospect. 2020, 27, 203–218. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Williams, R.; Errickson, D.; Taylor, G. Mapping an Archaeological Site: Interpreting Portable X-Ray Fluorescence (PXRF) Soil Analysis at Boroughgate, Skelton, UK. J. Archaeol. Sci. Rep. 2021, 38, 103109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Holliday, V.T.; Gartner, W.G. Methods of Soil P Analysis in Archaeology. J. Archaeol. Sci. 2007, 34, 301–333. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Theden-Ringl, F.; Gadd, P. The Application of X-Ray Fluorescence Core Scanning in Multi-Element Analyses of a Stratified Archaeological Cave Deposit at Wee Jasper, Australia. J. Archaeol. Sci. Rep. 2017, 14, 241–251. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Butler, D.H.; Lopez–Forment, A.; Dawson, P.C. Multi-Element and Biomolecular Analyses of Soils as a Means of Sustainable Site Structure Research on Hunter–Gatherer Sites: A Case Study from the Canadian Arctic. J. Archaeol. Sci. Rep. 2018, 17, 973–991. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Asare, M.O.; Afriyie, J.O. Tracing the Past from the Analysis of Cu, Zn, Mn, Sr, and Rb in Archaeological Dark Earth Soils from the Tropics and Temperate Zone. Quat. Int. 2020, 562, 13–26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Asare, M.O.; Horák, J.; Šmejda, L.; Janovský, M.; Hejcman, M. A Medieval Hillfort as an Island of Extraordinary Fertile Archaeological Dark Earth Soil in the Czech Republic. Eur. J. Soil Sci. 2021, 72, 98–113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gallello, G.; Pastor, A.; Diez, A.; La Roca, N.; Bernabeu, J. Anthropogenic Units Fingerprinted by REE in Archaeological Stratigraphy: Mas d’Is (Spain) Case. J. Archaeol. Sci. 2013, 40, 799–809. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gallello, G.; Pastor, A.; Diez, A.; Bernabeu, J. Lanthanides Revealing Anthropogenic Impact within a Stratigraphic Sequence. J. Archaeol. 2014, 2014, 767085. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Gallello, G.; Ferro-Vázquez, C.; Chenery, S.; Lang, C.; Thornton-Barnett, S.; Kabora, T.; Hodson, M.E.; Stump, D. The Capability of Rare Earth Elements Geochemistry to Interpret Complex Archaeological Stratigraphy. Microchem. J. 2019, 148, 691–701. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gallello, G.; Bernabeu, J.; Diez-Castillo, A.; Escriba, P.; Pastor, A.; Lezzerini, M.; Chenery, S.; Hodson, M.E.; Stump, D. Developing REE Parameters for Soil and Sediment Profile Analysis to Identify Neolithic Anthropogenic Signatures at Serpis Valley (Spain). Atti Della Soc. Toscana Sci. Nat. Resid. Pisa Mem. Ser. A 2020, 126, 13–32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gallello, G.; Ramacciotti, M.; García-Puchol, O.; Chenery, S.; Cortell-Nicolau, A.; Cervera, M.L.; Diez-Castillo, A.; Pastor, A.; McClure, S.B. Analysis of Stratigraphical Sequences at Cocina Cave (Spain) Using Rare Earth Elements Geochemistry. Boreas 2021, 50, 1190–1208. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Middleton, W.D. Identifying Chemical Activity Residues on Prehistoric House Floors: A Methodology And Rationale For Multi-Elemental Characterization of a Mild Acid Extract of Anthropogenic Sediments. Archaeometry 2004, 46, 47–65. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oonk, S.; Slomp, C.P.; Huisman, D.J.; Vriend, S.P. Effects of Site Lithology on Geochemical Signatures of Human Occupation in Archaeological House Plans in the Netherlands. J. Archaeol. Sci. 2009, 36, 1215–1228. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vyncke, K.; Degryse, P.; Vassilieva, E.; Waelkens, M. Identifying Domestic Functional Areas. Chemical Analysis of Floor Sediments at the Classical-Hellenistic Settlement at Düzen Tepe (SW Turkey). J. Archaeol. Sci. 2011, 38, 2274–2292. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fulton, K.A.; Wells, E.C.; Storer, D.A. Ritual or Residential? An Integrated Approach to Geochemical Prospection for Understanding the Use of Plaza Spaces at Palmarejo, Honduras. Archaeol. Anthropol. Sci. 2017, 9, 1059–1076. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Storozum, M.J.; Goldstein, S.T.; Contreras, D.A.; Gidna, A.O.; Mabulla, A.Z.P.; Grillo, K.M.; Prendergast, M.E. The Influence of Ancient Herders on Soil Development at Luxmanda, Mbulu Plateau, Tanzania. CATENA 2021, 204, 105376. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dirix, K.; Muchez, P.; Degryse, P.; Kaptijn, E.; Mušič, B.; Vassilieva, E.; Poblome, J. Multi-Element Soil Prospection Aiding Geophysical and Archaeological Survey on an Archaeological Site in Suburban Sagalassos (SW-Turkey). J. Archaeol. Sci. 2013, 40, 2961–2970. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kanthilatha, N.; Boyd, W.; Chang, N. Multi-Element Characterization of Archaeological Floors at the Prehistoric Archaeological Sites at Ban Non Wat and Nong Hua Raet in Northeast Thailand. Quat. Int. 2017, 432, 66–78. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Linderholm, J.; Geladi, P.; Gorretta, N.; Bendoula, R.; Gobrecht, A. Near Infrared and Hyperspectral Studies of Archaeological Stratigraphy and Statistical Considerations. Geoarchaeology 2019, 34, 311–321. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sulas, F.; Kristiansen, S.M.; Wynne-Jones, S. Soil Geochemistry, Phytoliths and Artefacts from an Early Swahili Daub House, Unguja Ukuu, Zanzibar. J. Archaeol. Sci. 2019, 103, 32–45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brenko, T.; Borojević Šoštarić, S.; Ružičić, S.; Sekelj Ivančan, T. Evidence for the Formation of Bog Iron Ore in Soils of the Podravina Region, NE Croatia: Geochemical and Mineralogical Study. Quat. Int. 2020, 536, 13–29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- García-Puchol, O.; McClure, S.B.; Juan-Cabanilles, J.; Diez-Castillo, A.A.; Bernabeu-Aubán, J.; Martí-Oliver, B.; Pardo-Gordó, S.; Pascual-Benito, J.L.; Pérez-Ripoll, M.; Molina-Balaguer, L.; et al. Cocina Cave Revisited: Bayesian Radiocarbon Chronology for the Last Hunter-Gatherers and First Farmers in Eastern Iberia. Quat. Int. 2018, 472, 259–271. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ramacciotti, M.; García-Puchol, O.; Cortell-Nicolau, A.; Gallello, G.; Morales-Rubio, A.; Pastor, A. Moving to the Land: First Archaeometric Study of Chert Procurement at Cueva de La Cocina (Eastern Iberia). Geoarchaeology 2022, 37, 544–559. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fumanal, M.P. Estudio sedimentológico de la Cueva de la Cocina. Dos Aguas (Valencia). Cuad. Geogr. Univ. Valencia 1979, 24, 79–98. [Google Scholar]
- Fumanal, M.P. Sedimentología y clima en el País Valenciano: Las cuevas habitadas en el Cuaternario reciente; Diputación Provincial de Valencia, Servicio de Investigación Prehistórica: Valencia, Spain, 1986; ISBN 978-84-505-4294-3. [Google Scholar]
- García Puchol, O.; Pardo Gordó, S.; Diez Castillo, A.Á.; Cortell Nicolau, A.; Juan Cabanilles, J.; McClure, S.B.; Ramacciotti, M. Actuación Arqueológica En Los Depósitos Mesolíticos de Cueva de La Cocina (Dos Aguas, Valencia): Valoración Preliminar. SAGVNTVM 2018, 50, 249–256. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Radojevic, M.; Bashkin, V. Practical Environmental Analysis; Royal Society of Chemistry: Cambridge, UK, 2007; ISBN 978-0-85404-594-5. [Google Scholar]
- R Core Team. R: A Language and Environment for Statistical Computing; R Core Team: Vienna, Austria, 2021. [Google Scholar]
- Laveuf, C.; Cornu, S. A Review on the Potentiality of Rare Earth Elements to Trace Pedogenetic Processes. Geoderma 2009, 154, 1–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pattan, J.N.; Pearce, N.J.G.; Mislankar, P.G. Constraints in Using Cerium-Anomaly of Bulk Sediments as an Indicator of Paleo Bottom Water Redox Environment: A Case Study from the Central Indian Ocean Basin. Chem. Geol. 2005, 221, 260–278. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, Z.; Haneklaus, S.; Sparovek, G.; Schnug, E. Rare Earth Elements in Soils. Commun. Soil Sci. Plant Anal. 2006, 37, 1381–1420. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Coppin, F.; Berger, G.; Bauer, A.; Castet, S.; Loubet, M. Sorption of Lanthanides on Smectite and Kaolinite. Chem. Geol. 2002, 182, 57–68. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]



| Sample | Type | Sample | Type | Sample | Type |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| S4a1 | Disturbed | S4b6 | Disturbed | S4d3 | Archaeological |
| S4a2 | Disturbed | S4b7 | Disturbed | S4d4 | Archaeological |
| S4a3 | Disturbed | S4b8 | Disturbed | S4d5 | Archaeological |
| S4a4 | Disturbed | S4c1 | Natural | S4d6 | Archaeological |
| S4a5 | Disturbed | S4c2 | Natural | S4e1 | Disturbed |
| S4a6 | Disturbed | S4c3 | Archaeological | S4e2 | Disturbed |
| S4a7 | Disturbed | S4c4 | Archaeological | S4e3 | Disturbed |
| S4a8 | Disturbed | S4c5 | Archaeological | S4e4 | Disturbed |
| S4b1 | Disturbed | S4c6 | Archaeological | S4f1 | Disturbed |
| S4b2 | Disturbed | S4c7 | Archaeological | S4f2 | Disturbed |
| S4b3 | Disturbed | S4c8 | Archaeological | S4f3 | Disturbed |
| S4b4 | Disturbed | S4d1 | Archaeological | S4f4 | Disturbed |
| S4b5 | Disturbed | S4d2 | Archaeological | S4f5 | Disturbed |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Gallello, G.; Ramacciotti, M.; Puchol, O.G.; Lezzerini, M.; McClure, S.B.; Pastor, A. Total vs. Partial Acid Digestion Methods for Trace Element Analysis in Archaeological Sediments. Minerals 2022, 12, 685. https://doi.org/10.3390/min12060685
Gallello G, Ramacciotti M, Puchol OG, Lezzerini M, McClure SB, Pastor A. Total vs. Partial Acid Digestion Methods for Trace Element Analysis in Archaeological Sediments. Minerals. 2022; 12(6):685. https://doi.org/10.3390/min12060685
Chicago/Turabian StyleGallello, Gianni, Mirco Ramacciotti, Oreto García Puchol, Marco Lezzerini, Sarah B. McClure, and Agustín Pastor. 2022. "Total vs. Partial Acid Digestion Methods for Trace Element Analysis in Archaeological Sediments" Minerals 12, no. 6: 685. https://doi.org/10.3390/min12060685
APA StyleGallello, G., Ramacciotti, M., Puchol, O. G., Lezzerini, M., McClure, S. B., & Pastor, A. (2022). Total vs. Partial Acid Digestion Methods for Trace Element Analysis in Archaeological Sediments. Minerals, 12(6), 685. https://doi.org/10.3390/min12060685








