MSWI Fly Ash Multiple Washing: Kinetics of Dissolution in Water, as Function of Time, Temperature and Dilution
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Sampling and Subsampling Preparation
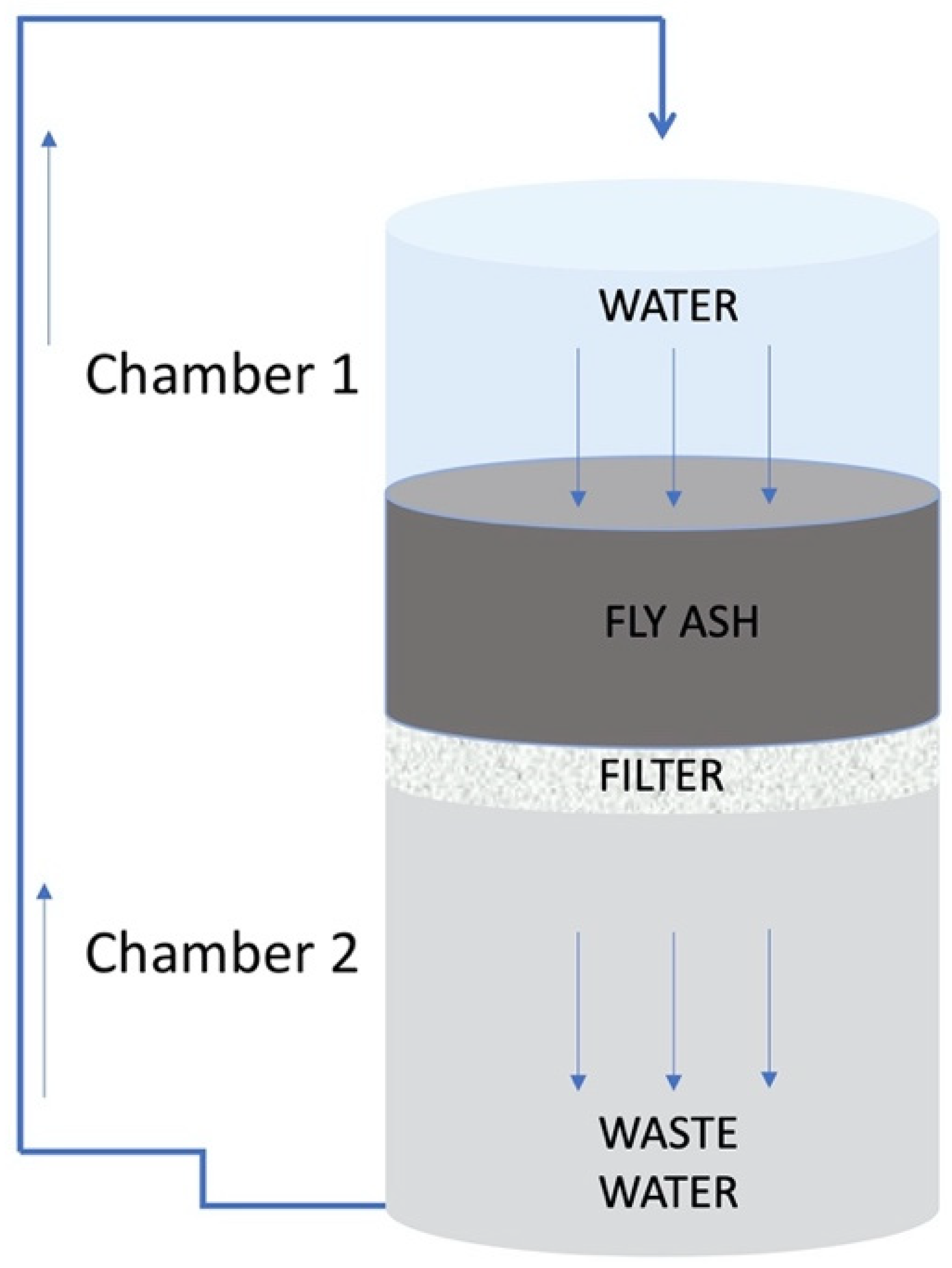
2.2. Falling Head Water Washing Implementation
2.3. X-ray Powder Diffraction (XRPD)
2.4. Washing and Leaching Tests
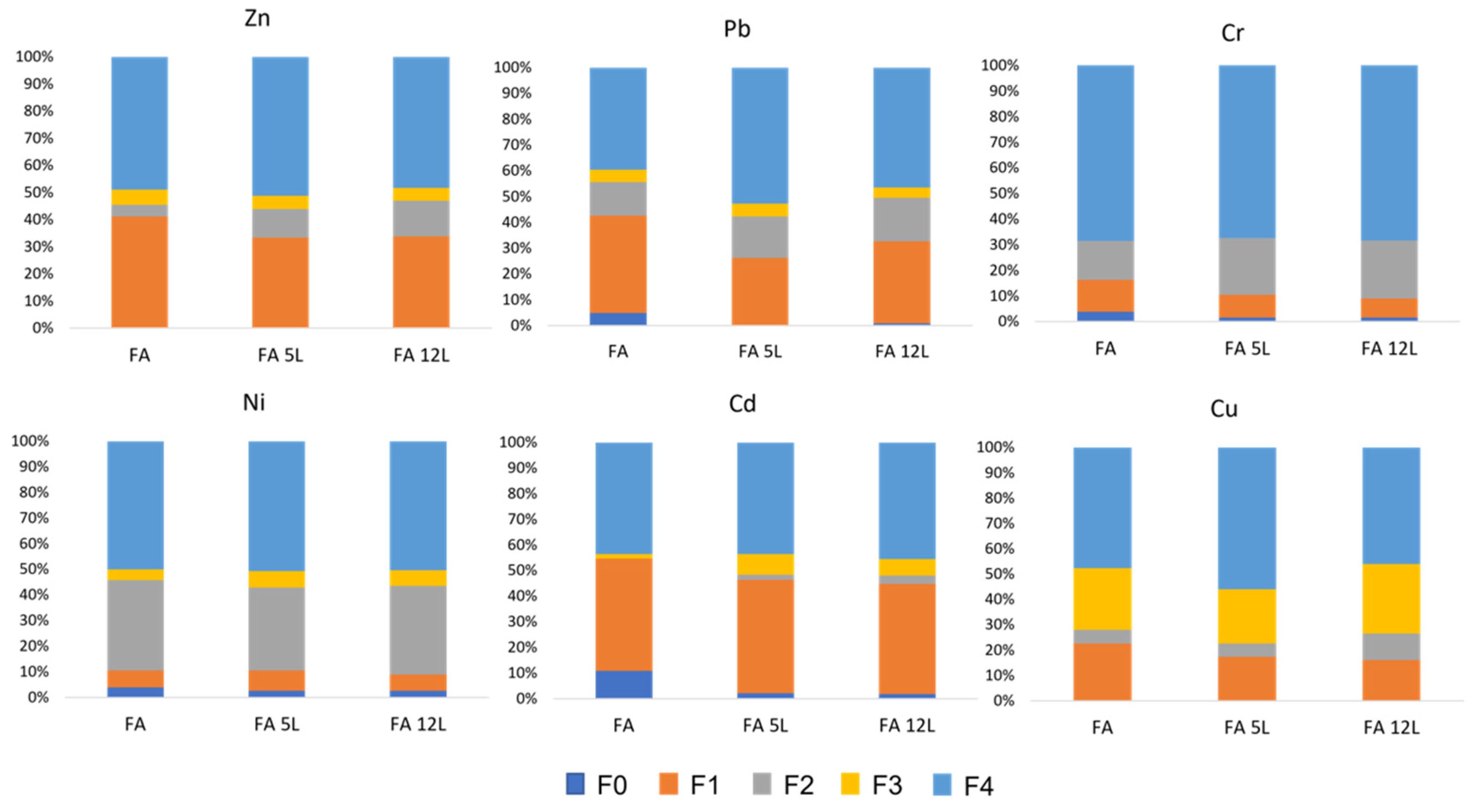
2.5. Sequential Extraction Method
3. Results
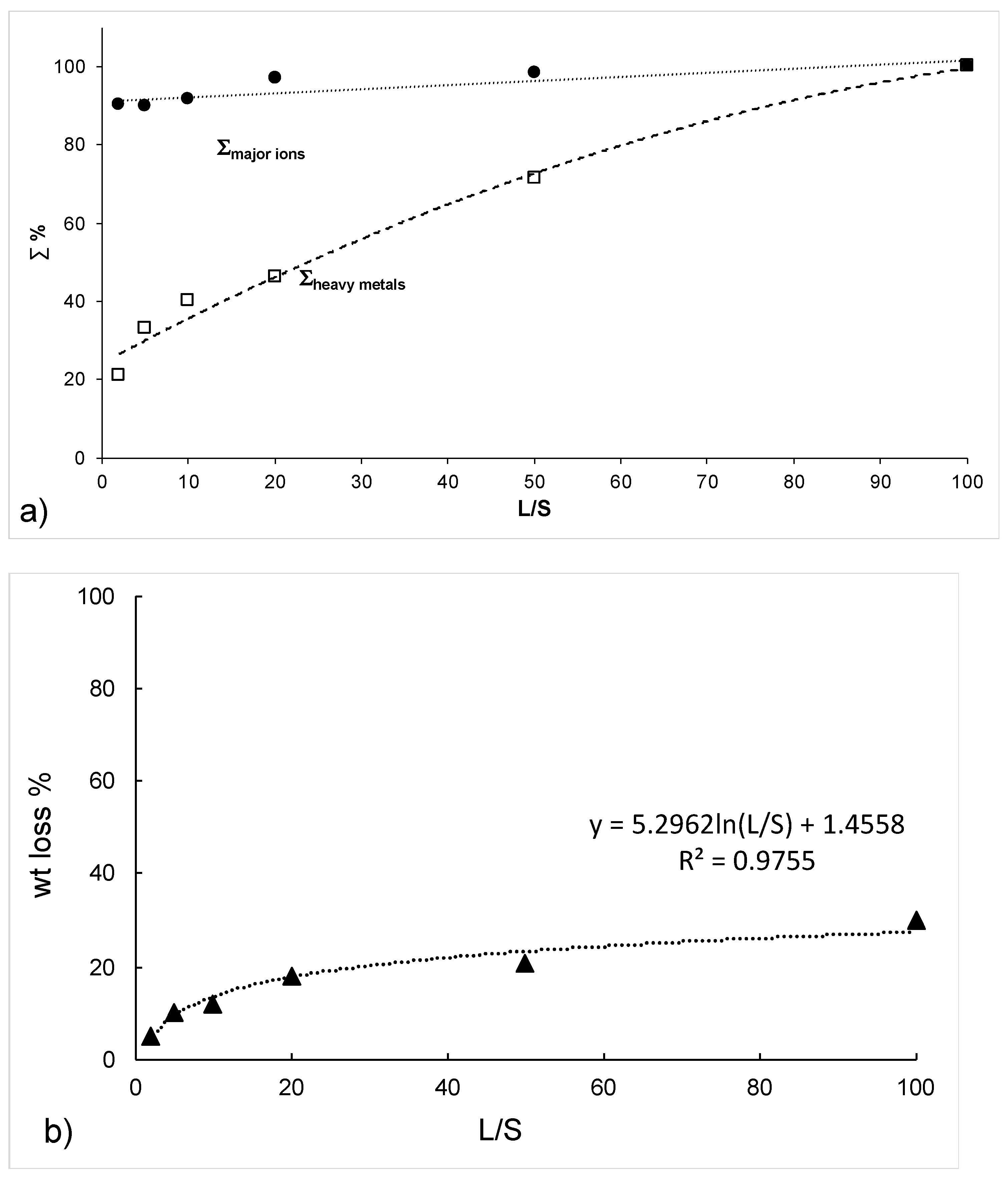
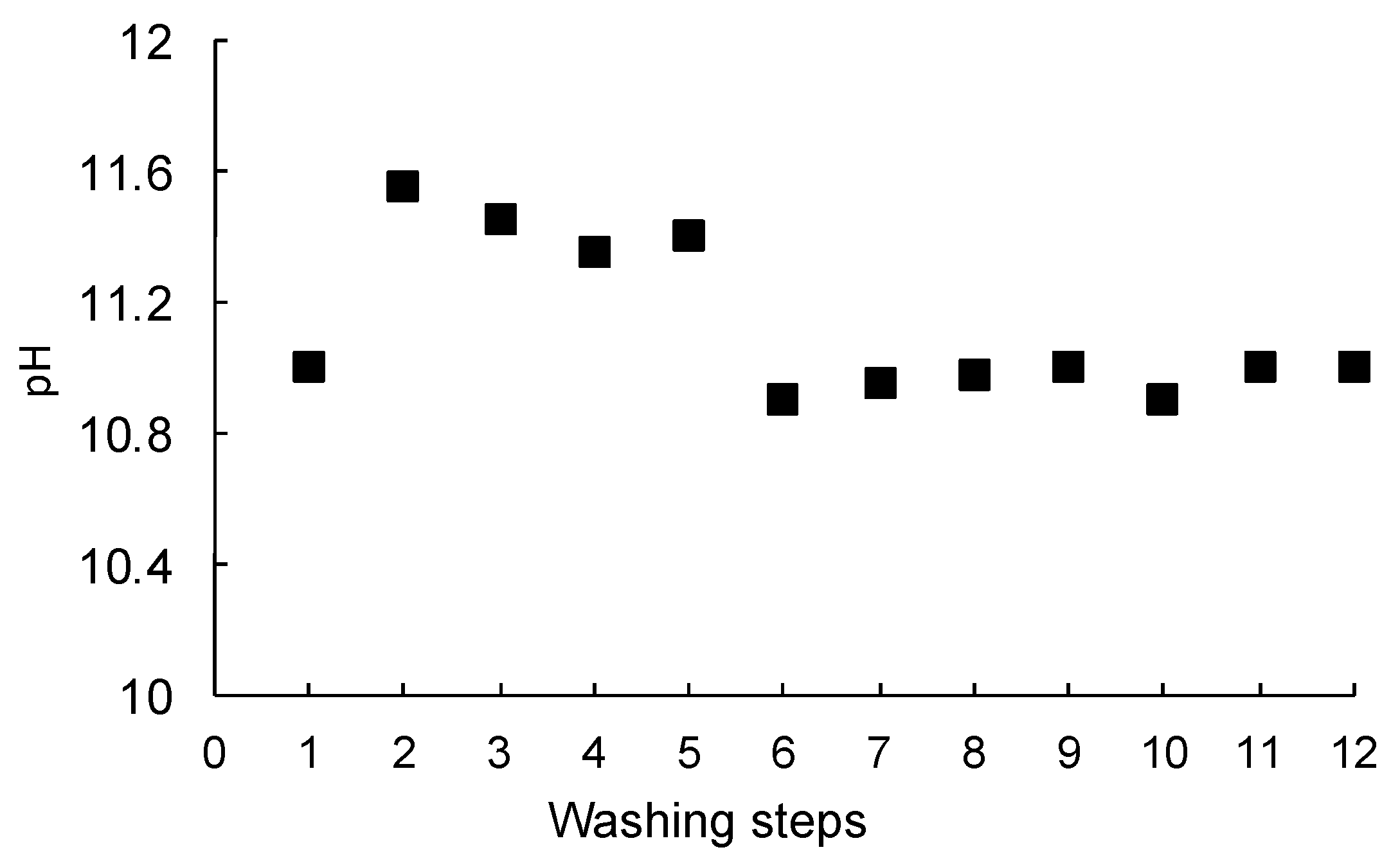
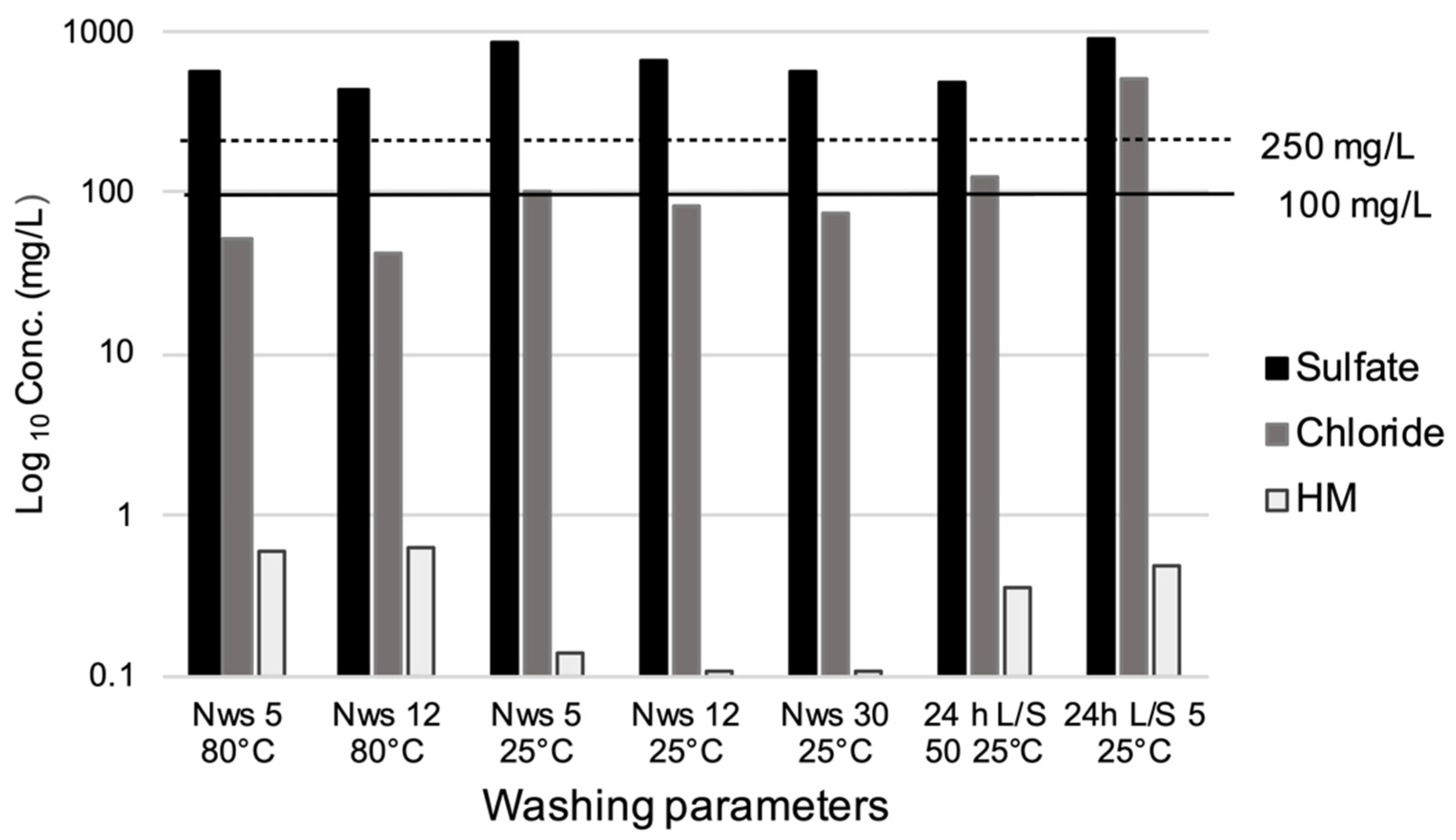
3.1. Washing Tests
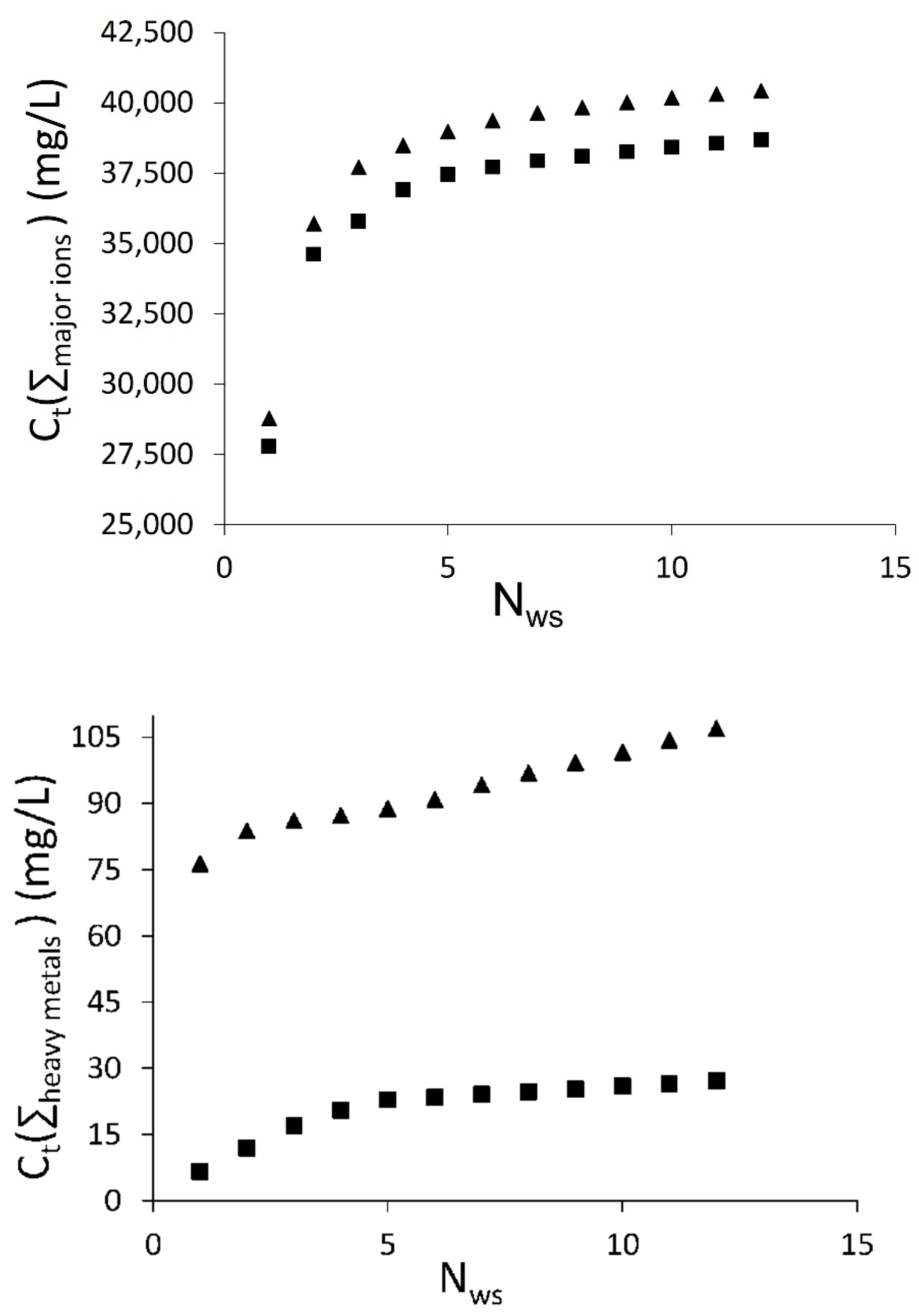
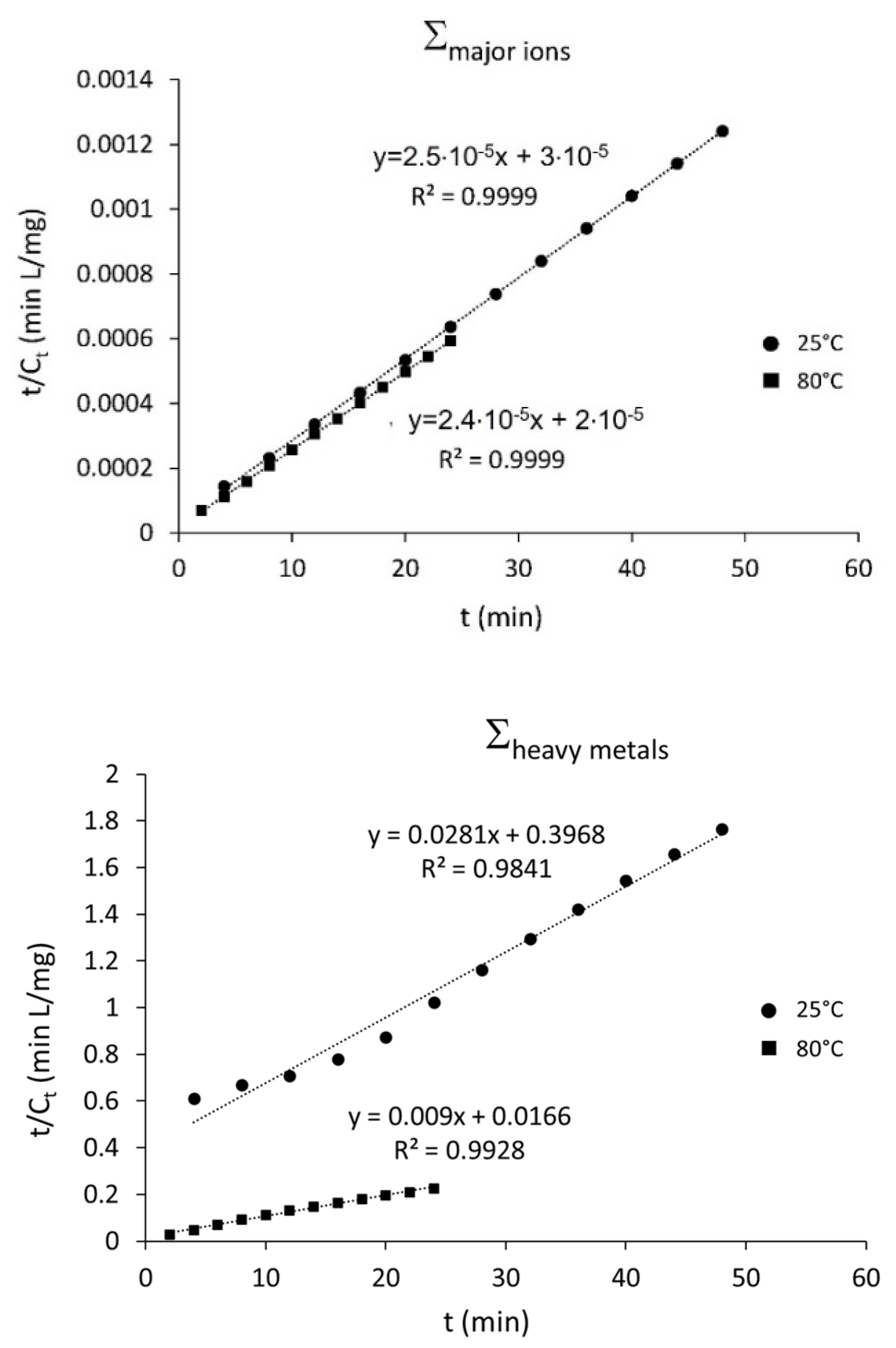
3.2. Falling Head Water Washing (FH-WW)
3.3. Leaching Tests
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Quina, M.J.; Bontempi, E.; Bogush, A.; Schlumberger, S.; Weibel, G.; Braga RFunari, V.; Hyks, J.; Rasmussen, E.; Lederer, J. Technologies for the management of MSW incineration ashes from gas cleaning: New perspectives on recovery of secondary raw materials and circular economy. Sci. Total Environ. 2018, 635, 526–542. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Parashar, C.K.; Das, P.; Samanta, S.; Ganguly, A.; Chatterjee, P.K. Municipal Solid Wastes—A Promising Sustainable Source of Energy: A Review on Different Waste-to-Energy Conversion Technologies. In Energy Recovery Processes from Wastes; Ghosh, S., Ed.; Springer: Singapore, 2020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Joseph, A.M.; Snellings, R.; Van den Heede, P.; Matthys, S.; De Belie, N. The Use of Municipal Solid Waste Incineration Ash in Various Building Materials: A Belgian Point of View. Materials 2018, 11, 141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lam, C.H.; Ip, A.W.; Barford, J.P.; McKay, G. Use of incineration MSW ash: A review. Sustainability 2010, 2, 1943–1968. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Directive 2008/98/EC of the European Parliament and of the Council of 19 November 2008 on Waste and Repealing Certain Directives. Available online: https://eur-lex.europa.eu/legal-content/EN/TXT/?uri=CELEX%3A02008L0098-20180705 (accessed on 9 April 2022).
- Dontriros, S.; Likitlersuang, S.; Janjaroen, D. Mechanisms of chloride and sulfate removal from municipal-solid-waste-incineration fly ash (MSWI FA): Effect of acid-base solutions. Waste Manag. 2020, 101, 44–53. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, K.; Hu, Y.; Tian, Y.; Chen, D.; Feng, Y. Chlorine removal from MSWI fly ash by thermal treatment: Effects of iron/aluminum additives. J. Environ. Sci. 2020, 88, 112–121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ni, P.; Xiong, Z.; Tian, C.; Li, H.; Zhao, Y.; Zhang, J.; Zheng, C. Influence of carbonation under oxy-fuel combustion flue gas on the leachability of heavy metals in MSWI fly ash. Waste Manag. 2017, 67, 171–180. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, H.Y.; Liu, H.; Shen, W.Q.; Luo, G.Q.; Li, A.J.; Lu, Z.L.; Yao, H. Comparison of CaO’s effect on the fate of heavy metals during thermal treatment of two typical types of MSWI fly ashes in China. Chemosphere 2013, 93, 590–596. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nikravan, M.; Ramezanianpour, A.A.; Maknoon, R. Study on physiochemical properties and leaching behavior of residual ash fractions from a municipal solid waste incinerator (MSWI) plant. J. Environ. Manag. 2020, 260, 110042. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Loginova, E.; Proskurnin, M.; Brouwers, H.J.H. Municipal solid waste incineration (MSWI) fly ash composition analysis: A case study of combined chelatant-based washing treatment efficiency. J. Environ. Manag. 2019, 235, 480–488. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bernasconi, D.; Caviglia, C.; Destefanis, E.; Agostino, A.; Boero, R.; Marinoni, N.; Bonadiman, C.; Pavese, A. Influence of speciation distribution and particle size on heavy metal leaching from MSWI fly ash. Waste Manag. 2022, 138, 318–327. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ginés, O.; Chimenos, J.M.; Vizcarro, A.; Formosa, J.; Rosell, J.R. Combined use of MSWI bottom ash and fly ash as aggregate in concrete formulation: Environmental and mechanical considerations. J. Hazard. Mater. 2009, 169, 643–650. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Colangelo, F.; Messina, F.; Cioffi, R. Recycling of MSWI fly ash by means of cementitious double step cold bonding pelletization: Technological assessment for the production of lightweight artificial aggregates. J. Hazard. Mater. 2015, 299, 181–191. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yakubu, Y.; Zhou, J.; Ping, D.; Shu, Z.; Chen, Y. Effects of pH dynamics on solidification/stabilization of municipal solid waste incineration fly ash. J. Environ. Manag. 2018, 207, 243–248. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ferraro, A.; Farina, I.; Race, M.; Colangelo, F.; Cioffi, R.; Fabbricino, M. Pre-treatments of MSWI fly-ashes: A comprehensive review to determine optimal conditions for their reuse and/or environmentally sustainable disposal. Rev. Environ. Sci. Biotechnol. 2019, 18, 453–471. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, Y.; Gencturk, B.; Willam, K.; Attar, A. Carbonation-induced and chloride-induced corrosion in reinforced concrete structures. J. Mater. Civ. Eng. 2015, 27, 04014245. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cho, B.H.; Nam, B.H.; An, J.; Youn, H. Municipal Solid Waste Incineration (MSWI) Ashes as Construction Materials—A Review. Materials 2020, 13, 3143. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Ma, Z.; Fang, Z.; Qian, Y.; Zhong, P.; Yan, J. Review of harmless treatment of municipal solid waste incineration fly ash. Waste Dispos. Sustain. Energy 2020, 2, 1–25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Assi, A.; Bilo, F.; Zanoletti, A.; Ponti, J.; Valsesia, A.; La Spina, R.; Zacco, A.; Bontempi, E. Zero-waste approach in municipal solid waste incineration: Reuse of bottom ash to stabilize fly ash. J. Clean. Prod. 2020, 245, 118779. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yin, K.; Ahamed, A.; Lisak, G. Environmental perspectives of recycling various combustion ashes in cement production—A review. Waste Manag. 2018, 78, 401–416. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, W.; Klupsch, E.; Kirkelund, G.M.; Jensen, P.E.; Ottosen, L.M.; Dias-Ferreira, C. Recycling of MSWI fly ash in clay bricks-effect of washing and electrodialytic treatment. In WASTES—Solutions, Treatments and Opportunities II; Taylor & Francis: Abingdon, UK, 2017; pp. 183–189. [Google Scholar]
- Kang, D.; Son, J.; Yoo, Y.; Park, S.; Huh, I.-S.; Park, J. Heavy-metal reduction and solidification in municipal solid waste incineration (MSWI) fly ash using water, NaOH, KOH, and NH4OH in combination with CO2 uptake procedure. Chem. Eng. J. 2020, 380, 122534. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nordmark, D.; Lagerkvist, A. Controlling the mobility of chromium and molybdenum in MSWI fly ash in a washing process. Waste Manag. 2018, 76, 727–733. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, X.; Bi, Y.; Zhang, H.; Wang, J. Chlorides Removal and Control through Water-washing Process on MSWI Fly Ash. Procedia Environ. Sci. 2016, 31, 560–566. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huber, F.; Blasenbauer, D.; Mallow, O.; Lederer, J.; Winter, F.; Fellner, J. Thermal co-treatment of combustible hazardous waste and waste incineration fly ash in a rotary kiln. Waste Manag. 2016, 58, 181–190. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gomes, H.I.; Funari, V.; Ferrari, R. Bioleaching for resource recovery from low-grade wastes like fly and bottom ashes from municipal incinerators: A SWOT analysis. Sci. Total Environ. 2020, 715, 136945. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kirkelund, G.M.; Skevi, L.; Ottosen, L.M. Electrodialytically treated MSWI fly ash use in clay bricks. Constr. Build. Mater. 2020, 254, 119286. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, T.; Zhou, L.; Liu, L.; Xia, M. Ultrasound-enhanced electrokinetic remediation for removal of Zn, Pb, Cu and Cd in municipal solid waste incineration fly ashes. Waste Manag. 2018, 75, 226–235. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Boom, A.; Aubert, J.E.; Degrez, M. Carbonation of municipal solid waste incineration electrostatic precipitator fly ashes in solution. Waste Manag. Res. 2014, 32, 406–413. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhan, X.; Wang, L.; Wang, L.; Wang, X.; Gong, J.; Yang, L.; Bai, J. Enhanced geopolymeric co-disposal efficiency of heavy metals from MSWI fly ash and electrolytic manganese residue using complex alkaline and calcining pre-treatment. Waste Manag. 2019, 98, 135–143. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, L.; Wang, C.; Wang, W.; Shi, Y.; Gao, X. Immobilization of MSWI fly ash through geopolymerization: Effects of water-wash. Waste Manag. 2011, 31, 311–317. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Phua, Z.; Giannis, A.; Dong, Z.L.; Lisak, G.; Ng, W.J. Characteristics of incineration ash for sustainable treatment and reutilization. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2019, 26, 16974–16997. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kanhar, A.H.; Chen, S.; Wang, F. Incineration Fly Ash and its treatment to possible utilization: A review. Energies 2020, 13, 6681. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, L.; Steefel, C.I.; Yang, L. Scale dependence of mineral dissolution rates within single pores and fractures. Geochim. Cosmochim. Acta 2008, 72, 360–377. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Atangana, A. Chapter 2: Principle of Groundwater Flow. In Fractional Operators with Constant and Variable Order with Application to Geo-Hydrology; Atangana, A., Ed.; Academic Press: Cambridge, MA, USA, 2018; pp. 15–47. ISBN 9780128096703. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, L.; Kang, Q.; Viswanathan, H.S.; Tao, W.Q. Pore-scale study of dissolution-induced changes in hydrologic properties of rocks with binary minerals. Water Resour. Res. 2014, 50, 9343–9365. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Toby, B.H.; Van Dreele, R.B. GSAS-II: The genesis of a modern open-source all purpose crystallography software package. J. Appl. Cryst. 2013, 46, 544–549. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bruder-Hubscher, V.; Lagarde, F.; Leroy, M.J.F.; Coughanowr, C.; Enguehard, F. 523 Application of a sequential extraction procedure to study the release of elements from municipal solid waste incineration bottom ash. Anal. Chim. Acta 2002, 451, 285–525. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ministerial Decree n. 186 Dated 5 April 2006. Regulatory That Modified Ministerial Decree Dated 5 February 1998. Official Gazette n. 115. 19 May 2006. Available online: http://www.gazzettaufficiale.it/eli/gu/2010/12/01/281/sg/pdf (accessed on 9 April 2022).
- G.U. Ministerial Decree 27/09/2010-Definition of the Criteria of Admissibility of Landfill Waste. Serie Generale n-281. 1 December 2010. Available online: https://www.gazzettaufficiale.it/eli/id/2010/12/01/10A14538/sg (accessed on 9 April 2022).
- Gharabaghi, M.; Irannajad, M.; Azadmehr, A. Leaching kinetics of nickel extraction from hazardous waste by sulphuric acid and optimization dissolution conditions. Chem. Eng. Res. Des. 2013, 91, 325–331. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Levenspiel, O. Chemical Reaction Engineering, 3rd ed.; Wiley: New York, NY, USA, 1998. [Google Scholar]
- Souza, A.D.; Pina, P.S.; Lima, E.V.O.; da Silva, C.A.; Leão, V.A. Kinetics of sulphuric acid leaching of a zinc silicate calcine. Hydrometallurgy 2007, 89, 337–345. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, I.H.; Wang, Y.J.; Chern, J.M. Extraction kinetics of heavy metal-containing sludge. J. Hazard. Mater. 2005, 123, 112–119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sakultung, S.; Pruksathorn, K.; Hunsom, M. Simultaneous recovery of valuable metals from spent mobile phone battery by an acid leaching process. Korean J. Chem. Eng. 2007, 24, 272–277. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ho, Y.S.; Harouna-Oumarou, H.A.; Fauduet, H.; Porte, C. Kinetics and model building of leaching of water-soluble compounds of Tilia sapwood. Sep. Purif. Technol. 2005, 45, 169–173. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mbogoro, M.; Snowden, E.; Edwards, M.; Peruffo, M.; Unwin, P. Intrinsic Kinetics of Gypsum and Calcium Sulfate Anhydrite Dissolution: Surface Selective Studies under Hydrodynamic Control and the Effect of Additives. J. Phys. Chem. C 2011, 115, 10147–10154. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiao, F.; Zhang, L.; Dong, Z.; Namioka, T.; Yamada, N.; Ninomiya, Y. Study on the species of heavy metals in MSW incineration fly ash and their leaching behavior. Fuel Process. Technol. 2016, 152, 108–115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Funatsuki, A.; Takaoka, M.; Oshita, K.; Takeda, N. Methods of determining lead speciation in fly ash by X-ray absorption fine-structure spectroscopy and a sequential extraction procedure. Anal. Sci. 2012, 28, 481–490. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, Y.; Cetin, B.; Likos, W.J.; Edil, T.B. Impacts of pH on leaching potential of elements from MSW incineration fly ash. Fuel 2016, 184, 815–825. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
| wt% | Bulk Fly Ash | Res.L/S 2 | Res.L/S 5 | Res.L/S 10 | Res.L/S 20 | Res.L/S 50 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Halite | 12 | 6 | 4 | |||
| Sylvite | 8 | 2 | ||||
| Calcite | 6 | 6 | 6 | 7 | 8 | 7 |
| Syngenite | 7 | 5 | 2 | |||
| Anhydrite | 10 | 12 | 13 | 14 | 15 | 14 |
| Quartz | 2 | 2 | 4 | 6 | 5 | 6 |
| Bassanite | 8 | |||||
| Gypsum | 11 | 12 | 10 | 12 | ||
| Gehlenite | 4 | 5 | 6 | 6 | 6 | 6 |
| Amorphous | 51 | 54 | 54 | 55 | 56 | 55 |
| 1 | 2 | 3 | 4 | 5 | 6 | 7 | Not Reactive [40] | Non Hazardous [40] | Hazardous | Reuse [41] | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| E.Cond. (μs/cm) | 1650 | 1037 | 1858 | 1500 | 1340 | 1400 | 3160 | ||||
| pH | 9.6 | 9.6 | 9.7 | 9.2 | 9.2 | 9.1 | 9.4 | 5.5–12 | |||
| Na (mg/L) | 36 | 15 | 45 | 25 | 20 | 41 | 167 | ||||
| K(mg/L) | 37 | 31 | 58 | 15 | 9 | 31 | 159 | ||||
| Ca (mg/L) | 440 | 240 | 409 | 329 | 311 | 273 | 365 | ||||
| Mg (mg/L) | 0.3 | 0.2 | 0.3 | 0.3 | 0.2 | 0.6 | 7 | ||||
| Chloride (mg/L) | 51 | 43 | 100 | 83 | 73 | 125 | 500 | 80 | 2500 | 2500 | 100 |
| Bromides (mg/L) | 0.5 | n.d. | 3.4 | 2.8 | n.d. | 1.1 | n.d. | ||||
| Fluorides (mg/L) | n.d. | 1.1 | 1.7 | 2 | 1.2 | 0.5 | n.d. | 1 | 15 | 50 | 1.5 |
| Sulfate (mg/L) | 574 | 431 | 860 | 662 | 578 | 475 | 920 | 100 | 5000 | 5000 | 250 |
| NO3− (mg/L) | 0.4 | n.d. | n.d. | 0.8 | n.d. | 1.3 | n.d. | 50 | |||
| Cr (mg/L) | 0.18 | 0.10 | 0.08 | 0.03 | 0.06 | 0.13 | 0.25 | 0.05 | 1 | 7 | 0.05 |
| Ni (mg/L) | 0.09 | 0.08 | 0.02 | n.d. | 0.05 | 0.06 | 0.11 | 0.04 | 1 | 4 | 0.01 |
| Cu (mg/L) | 0.04 | 0.05 | n.d. | n.d. | n.d. | n.d. | n.d. | 0.2 | 5 | 10 | 0.05 |
| Zn (mg/L) | 0.1 | 0.2 | n.d. | n.d. | 0.005 | 0.05 | 0.04 | 4 | 5 | 20 | 3 |
| Cd (mg/L) | 0.02 | 0.02 | n.d. | n.d. | n.d. | n.d. | n.d. | 0.004 | 0.1 | 0.5 | 0.005 |
| Ba (mg/L) | 0.12 | 0.12 | 0.04 | 0.08 | 0.06 | 0.11 | 0.1 | 2 | 10 | 30 | 1 |
| Pb (mg/L) | 0.04 | 0.05 | n.d. | n.d. | n.d. | 0.005 | n.d. | 0.05 | 1 | 5 | 0.05 |
| Temperature (°C) | R2 (R) | R2 (D) | |
|---|---|---|---|
| Σheavy metals | 25 | 0.93 | 0.93 |
| 80 | 0.91 | 0.93 | |
| Σmajor ions | 25 | 0.91 | 0.93 |
| 80 | 0.92 | 0.94 |
| Cs (mg/L) | k (L mg−1 min−1) | R2 | |
|---|---|---|---|
| Σheavy metals | 35.71 | 3.2 × 103 | 0.9841 |
| 111.11 | 7.4 × 105 | 0.9982 | |
| Σmajor ions | 40,000 | 5.3 × 1013 | 0.9999 |
| 42,478 | 7.2 × 1013 | 0.9999 |
| lnk | 1/T (K−1) | Ea (KJ/mol) | |
|---|---|---|---|
| Σheavy metals | 8.075 | 3.2 × 10−3 | 1.25 |
| 13.52 | 2.8 × 10−3 | ||
| Σmajor ions | 31.6 | 3.2 × 10−3 | 0.104 |
| 31.9 | 2.8 × 10−3 |
| wt% | 5-Step at 25 °C | 12-Step at 25 °C | 5-Step at 80 °C | 12-Step at 80 °C | 30-Step |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Calcite | 8 | 7 | 9 | 8 | 6 |
| Anhydrite | 15 | 14 | 17 | 16 | 13 |
| Quartz | 8 | 10 | 7 | 10 | 10 |
| Gehlenite | 7 | 8 | 8 | 7 | 9 |
| Amorphous | 62 | 61 | 60 | 59 | 62 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Caviglia, C.; Destefanis, E.; Pastero, L.; Bernasconi, D.; Bonadiman, C.; Pavese, A. MSWI Fly Ash Multiple Washing: Kinetics of Dissolution in Water, as Function of Time, Temperature and Dilution. Minerals 2022, 12, 742. https://doi.org/10.3390/min12060742
Caviglia C, Destefanis E, Pastero L, Bernasconi D, Bonadiman C, Pavese A. MSWI Fly Ash Multiple Washing: Kinetics of Dissolution in Water, as Function of Time, Temperature and Dilution. Minerals. 2022; 12(6):742. https://doi.org/10.3390/min12060742
Chicago/Turabian StyleCaviglia, Caterina, Enrico Destefanis, Linda Pastero, Davide Bernasconi, Costanza Bonadiman, and Alessandro Pavese. 2022. "MSWI Fly Ash Multiple Washing: Kinetics of Dissolution in Water, as Function of Time, Temperature and Dilution" Minerals 12, no. 6: 742. https://doi.org/10.3390/min12060742
APA StyleCaviglia, C., Destefanis, E., Pastero, L., Bernasconi, D., Bonadiman, C., & Pavese, A. (2022). MSWI Fly Ash Multiple Washing: Kinetics of Dissolution in Water, as Function of Time, Temperature and Dilution. Minerals, 12(6), 742. https://doi.org/10.3390/min12060742






