Fluorine Controls Mineral Assemblages of Alkaline Metasomatites
Abstract
:1. Introduction
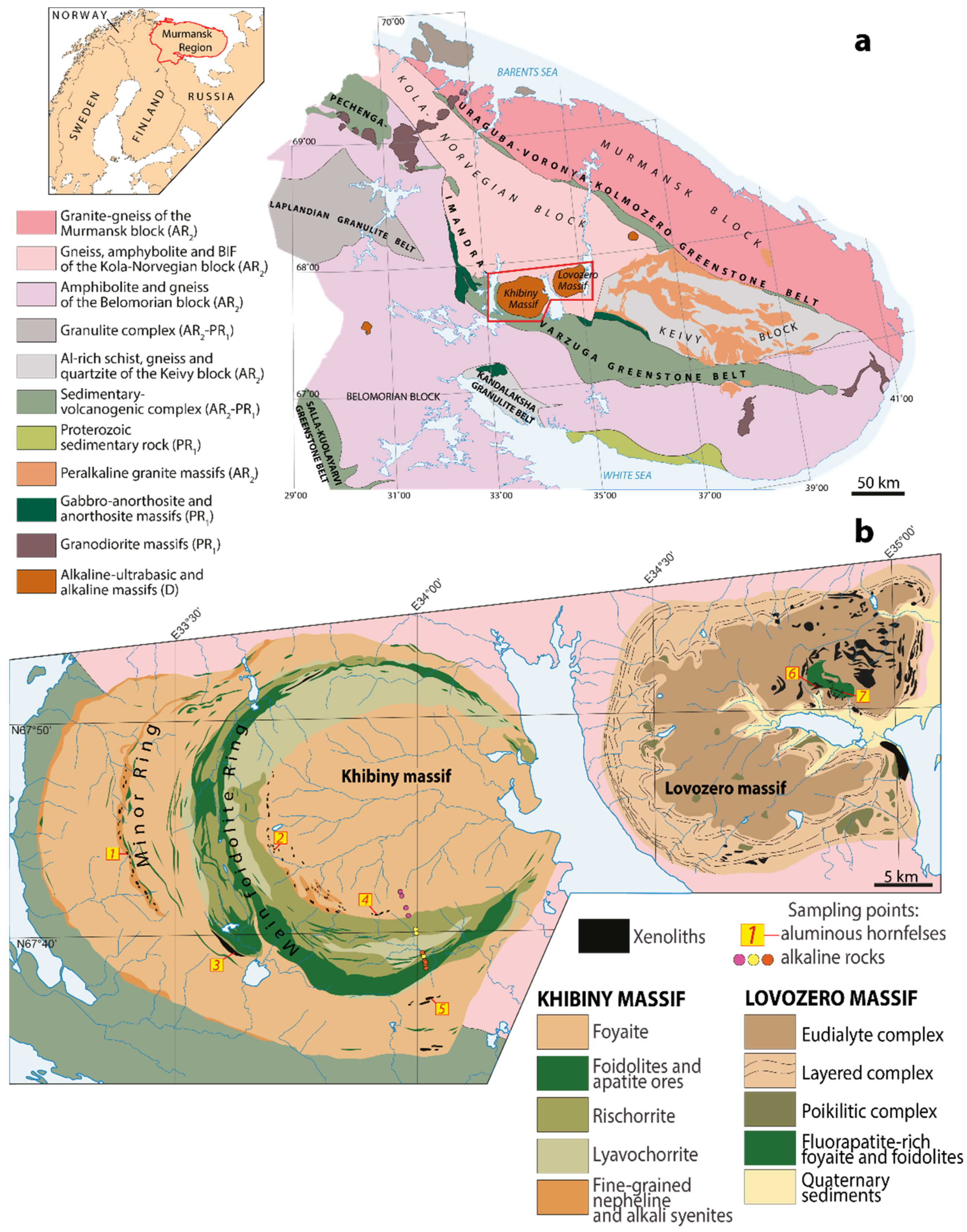
2. Geological Background and Previous Research
- foyaite is a massive, less often weakly trachytoid, leucocratic nepheline syenite;
- rischorrite is a leucocratic nepheline syenite in which the nepheline crystals are poikilitically enclosed in microcline perthite;
- lyavochorrite is a leucocratic nepheline syenite in which only part of the feldspar crystals is poikilitic;
- lujavrite is a trachytoid (i.e., with subparallel feldspar laths) meso- or melanocratic nepheline syenite.

3. Materials and Methods
4. Results
4.1. Petrography and Mineralogy of the Aluminous Hornfelses
4.2. Rock Chemistry
5. Discussion
6. Conclusions
- Aluminous hornfelses, previously found in the central parts of the Khibiny and Lovozero massifs, were formed as a result of the influence on the protolith of fluids expelled from crystallizing foidolites and containing, in addition to alkalis, aluminum in the form of Na-Al-OH-F complexes. Thus, it is fluorine that controls the mobility of aluminum in the fluid and, consequently, the mineral associations of alkaline metasomatites.
- The protolith of aluminous hornfelses cannot be unambiguously identified due to the high intensity of metasomatic alterations and the relatively small size of xenoliths. However, it can be argued that the protolith was extremely heterogeneous in terms of mineral and chemical composition.
- The gain of alkalis and aluminum to rocks of protolith was the reason for the intense crystallization of (K,Na)-feldspar. As a result, a strong SiO2 deficiency was formed, and Si-poor silicates (e.g., fayalite, Al2SiO5 polymorphs) and/or oxides (e.g., corundum, hercynite) crystallized.
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Morogan, V. Ijolite versus carbonatite as sources of fenitization. Terra Nova 1994, 6, 166–176. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kramm, U.; Sindern, S. Volume characteristics and element transfer of fenite aureoles: A case study from the Iivaara Alkaline Complex, Finland. Lithos 2000, 51, 75–93. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kresten, P.; Morogan, V. Fenitization at the Fen Complex, Southern Norway. Lithos 1986, 19, 27–42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Morogan, V.; Woolley, A.R. Fenitization at the Alno Carbonatite Complex, Sweden; Distribution, mineralogy and genesis. Contrib. Mineral. Petrol. 1988, 100, 169–182. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Elliott, H.A.L.; Wall, F.; Chakhmouradian, A.R.; Siegfried, P.R.; Dahlgren, S.; Weatherley, S.; Finch, A.A.; Marks, M.A.W.; Dowman, E.; Deady, E. Fenites associated with carbonatite complexes: A review. Ore Geol. Rev. 2018, 93, 38–59. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brögger, W.G. Die eruptivegestein des kristianiagebietes, IV. Das fengebiet intelemark. Norvegen. Naturv. Klasse 1921, 9, 150–167. [Google Scholar]
- Cooper, A.F.; Palin, J.M.; Collins, A.K. Fenitization of metabasic rocks by ferrocarbonatites at Haast River, New Zealand. Lithos 2016, 244, 109–121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Le Bas, M.J. Nephelinites and carbonatites. Geol. Soc. Spec. Publ. 1987, 30, 53–83. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Robins, B.; Tysseland, M. Fenitization of some mafic igneous rocks in the Seiland province, northen Norway. Norsk Geologisk Tidsskrift 1979, 59, 1–23. [Google Scholar]
- Viladkar, S.G. Mineralogy and geochemistry of fenitized nephelinites of the Amba Dongar Complex, Gujarat. J. Geol. Soc. India 2015, 85, 87–97. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kostyleva-Labuntsova, E.E.; Borutskii, B.E.; Sokolova, M.N.; Shlykova, Z.V. Mineralogy of the Khibiny Massif: Magmatism and Postmagmatic Transformations; Nauka: Moscow, Russia, 1978. [Google Scholar]
- Shlykova, Z.V. Mineralogy of Contact Rocks of the Khibiny Massif; Nauka: Moscow, Russia, 1986. [Google Scholar]
- Arzamastsev, A.A.; Arzamastseva, L.V.; Zaraiskii, G.P. Contact Interaction of agpaitic magmas with basement gneisses: An example of the Khibina and Lovozero Massifs. Petrology 2011, 19, 109–133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gorstka, V.N. Contact Zone of the Khibiny Alkaline Massif; Nauka: Leningrad, Russia, 1971. [Google Scholar]
- Fersman, A.E. Minerals of the Khibina and Lovozero Tundras; Izdatel’stvo AN SSSR: Moscow-Leningrad, Russia, 1937. [Google Scholar]
- Zak, S.I.; Kamenev, E.A.; Minakov, F.V.; Armand, A.L.; Mikheichev, A.S.; Peresilie, I.A. Khibiny Alkaline Massif; Nauka: Leningrad, Russia, 1972. [Google Scholar]
- Gerasimovsky, V.I.; Volkov, V.P.; Kogarko, L.N.; Polyakov, A.I.; Saprykina, T.V.; Balashov, Y.A. Geochemistry of the Lovozero Alkaline Massif; Nauka: Moscow, Russia, 1966. [Google Scholar]
- Yakovleva, O.S.; Pekov, I.V.; Bryzgalov, I.A.; Men’shikov, Y.P. Chalcogenide mineralization in the alumina-rich fenites of the Khibiny Alkaline Complex (Kola Peninsula, Russia). New Data Miner. 2010, 45, 33–49. [Google Scholar]
- Arzamastsev, A.A.; Arzamastseva, L.V.; Travin, A.V.; Belyatsky, B.V.; Shamatrina, A.M.; Antonov, A.V.; Larionov, A.N.; Rodionov, N.V.; Sergeev, S.A. Duration of formation of magmatic system of polyphase paleozoic alkaline complexes of the central Kola: U–Pb, Rb–Sr, Ar–Ar Data. Dokl. Earth Sci. 2007, 413, 666–670. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kramm, U.; Kogarko, L.N. Nd and Sr isotope signatures of the Khibina and Lovozero Agpaitic Centres, Kola Alkaline Province, Russia. Lithos 1994, 32, 225–242. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mitchell, R.H.; Wu, F.Y.; Yang, Y.H. In Situ U-Pb, Sr and Nd isotopic analysis of loparite by LA-(MC)-ICP-MS. Chem. Geol. 2011, 280, 191–199. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, F.Y.; Yang, Y.H.; Marks, M.A.W.; Liu, Z.C.; Zhou, Q.; Ge, W.C.; Yang, J.S.; Zhao, Z.F.; Mitchell, R.H.; Markl, G. In Situ U-Pb, Sr, Nd and Hf isotopic analysis of eudialyte by LA-(MC)-ICP-MS. Chem. Geol. 2010, 273, 8–34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yakovenchuk, V.N.; Ivanyuk, G.Y.; Pakhomovsky, Y.A.; Men’shikov, Y.P. Khibiny; Laplandia Minerals: Apatity, Russia, 2005. [Google Scholar]
- Ivanyuk, G.Y.; Yakovenchuk, V.N.; Pakhomovsky, Y.A.; Kalashnikov, A.O.; Mikhailova, J.A.; Goryainov, P.M. Self-organization of the Khibiny Alkaline Massif (Kola Peninsula, Russia). In Earth Sciences; Dar, I.A., Ed.; InTech: Rijeka, Croatia, 2012; pp. 131–156. [Google Scholar]
- LeMaitre, R.W.; Streckeisen, A.; Zanettin, B.; Le Bas, M.J.; Bonin, B.; Bateman, P.; Bellieni, G.; Dudek, A.; Efremova, S.; Keller, J.; et al. Igneous Rocks. A Classification and Glossary of Terms. Recommendations of the International Union of Geological Sciences Subcommission on the Systematics of Igneous Rocks; LeMaitre, R.W., Ed.; Cambridge University Press: Cambridge, UK, 2005; ISBN 0 521 66215 X. [Google Scholar]
- Balagansky, V.V.; Basalaev, A.A.; Belyaev, O.A.; Pozhilenko, V.I.; Radchenko, A.T.; Radchenko, M.K. Geological Map of Kola Region 1:500,000; GI KSC RAS: Apatity, Russia, 1996. [Google Scholar]
- Snyatkova, O.L.; Mikhnyak, N.K.; Markitakhina, T.M.; Prinyagin, N.I.; Chapin, V.A.; Zhelezova, N.N.; Durakova, A.B.; Evstaf’yev, A.S.; Podurushin, V.F.; Kalinkin, M.M. Report on Results of Supplement Geological Investigation and Geochemical Exploration of Rare Metals and Apatite within Khibiny Massif and Its Surroundings, Scale 1:50,000; GI KSC RAS: Apatity, Russia, 1983. [Google Scholar]
- Bussen, I.V.; Sakharov, A.S. Petrology of the Lovozero Alkaline Massif; Nauka: Leningrad, Russia, 1972. [Google Scholar]
- Shablinsky, G.N. On problem of deep structure of the Khibiny and Lovozero Plutons. Tr. Leningr. Obs. Estestvoispyt. 1963, 74, 41–43. [Google Scholar]
- Arzamastsev, A.A. Unique Paleozoic Intrusions of the Kola Peninsula; GI KSC RAS: Apatity, Russia, 1994. [Google Scholar]
- Tikhonenkova, R.I.; Osokin, E.D.; Gonzeev, A.A. Rare-Metal Metasomatites of Alkaline Massifs; Borodin, L.S., Ed.; Nauka: Moscow, Russia, 1967. [Google Scholar]
- Korchak, Y.A.; Men’shikov, Y.P.; Pakhomovskii, Y.A.; Yakovenchuk, V.N.; Ivanyuk, G.Y. Trap formation of the Kola Peninsula. Petrology 2011, 19, 87–101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eliseev, N.A. Devonian effusive rocks of the Lovozero Tundra. ZVMO 1946, 75, 113. [Google Scholar]
- Krishtofovich, A.N. Upper devonian plants from the northeastern part of the Lovozero tundra of the Kola Peninsula. Izv. AN SSSR 1937, 4, 693–699. [Google Scholar]
- Tikhonenkova, R.P. New data on the composition and age of the lovozero formation in the Kola Region. Rep. Acad. Sci. USSR 1972, 203, 903–906. [Google Scholar]
- Men’shikov, Y.P. Corundum mineralization in the Khibina Alkaline Complex. Dokl. Akad. Nauk SSSR 1978, 243, 1247–1249. [Google Scholar]
- Kupletsky, B.M. Kukisvumchorr and adjacent massifs in the central part of the Khibina Tindra on the basis of mapping in the 1929 and 1930s. Proc. SOPS (“Sovet po Proizvoditel’nym Silam’’) 1932, 2, 5–62. [Google Scholar]
- Yakovleva, O.S.; Pekov, I.V.; Horváth, L.; Bryzgalov, I.A.; Yapaskurt, V.O.; Guseva, E.V. Mineralogy, geochemistry, and genesis of high-alumina fenites of the mont saint-hilaire Alkaline Pluton, Québec, Canada. Geol. Ore Depos. 2010, 52, 725–735. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barkov, A.Y.; Martin, R.F.; Poirier, G.; Men’shikov, Y.P. Zoned Tungstenoan Molibdenite from a fenitized magaxenolith in the Khibina Alkaline Complex, Kola Peninsula, Russia. Can. Mineral. 2000, 38, 1377–1385. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lafuente, B.; Downs, R.T.; Yang, H.; Stone, N. The power of databases: The RRUFF project. In Highlights in Mineralogical Crystallography; De Gruyter: Berlin, Germany, 2015; pp. 1–30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Warr, L.N. IMA-CNMNC approved mineral symbols. Mineral. Mag. 2021, 85, 291–320. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ivanyuk, G.Y.; Goryainov, P.M.; Pakhomovsky, Y.A.; Konopleva, N.G.; Yakovanchuk, V.N.; Bazai, A.V.; Kalashnikov, A.O. Self-Organization of Ore Complexes; GEOKART-GEOS: Moskow, Russia, 2009; ISBN 978-5-89118-458-9. [Google Scholar]
- Rieder, M.; Cavazzini, G.; Guggenheim, S.; Koval’, P.V.; Müller, G.; Neiva, A.M.R.; Radoslovich, E.W.; Robert, J.-L.; Sassi, F.P.; Wones, D.R. Nomenclature of the Micas. Can. Mineral. 1998, 36, 41–48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arzamastsev, A.A.; Bea, F.; Arzamastseva, L.V.; Montero, P. Trace Elements in Minerals of the Khibiny Massif as indicators of mineral formation evolution: Results of LA-ICP-MS study. Geochem. Int. 2005, 43, 80–95. [Google Scholar]
- Sun, S.S.; McDonough, W.F. Chemical and Isotopic Systematics of Oceanic Basalts: Implications for mantle composition and processes. Geol. Soc. Spec. Publ. 1989, 42, 313–345. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shulters, J.C.; Bohlen, S.R. The stability of hercynite and hercynite-gahnite spinels in corundum-or quartz-bearing assemblages. J. Petrol. 1989, 30, 1017–1031. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pitra, P.; de Waal, S.A. High-temperature, low-pressure metamorphism and development of prograde symplectites, marble hall fragment, Bushveld Complex (South Africa). J. Metamorph. Geol. 2001, 19, 311–325. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pattison, D.R.M.; Spear, F.S.; Debuhr, C.L.; Cheney, J.T.; Guidotti, C.V. Thermodynamic modelling of the reaction muscovite+cordierite = Al2SiO5 + biotite + quartz + H2O: Constraints from natural assemblages and implications for the metapelitic petrogenetic grid. J. Metamorph. Geol. 2002, 20, 99–118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rock, N.M.S. Fenitisation around the Monchique Alkaline Complex, Portugal. Lithos 1976, 9, 263–279. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Galakhov, A.V. Petrology of the Khibiny Alkaline Massif; Nauka: Leningrad, Russia, 1975. [Google Scholar]
- Tikhonenkov, I.P. Nepheline Syenites and Pegmatites of the Northeastern Part of the Khibiny Massif and the Role of Postmagmatic Events in Their Formation; USSR Academy of Sciences: Moskow, Russia, 1963. [Google Scholar]
- Tagirov, B.; Schott, J.; Harrichourry, J.-C.; Salvi, S. Experimental study of aluminum speciation in fluoride-rich supercritical fluids. Geochim. Cosmochim. Acta 2002, 66, 2013–2024. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Berndt, M.E.; Seyfried, W.E. Calcium and sodium exchange during hydrothermal alteration of calcic plagioclase at 400 °C and 400 bars. Geochim. Cosmochim. Acta 1993, 57, 4445–4451. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Migdisov, A.A.; Williams-Jones, A.E. Hydrothermal transport and deposition of the rare earth elements by fluorine-bearing aqueous liquids. Miner. Depos. 2014, 49, 987–997. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Anenburg, M.; Mavrogenes, J.A.; Frigo, C.; Wall, F. Rare earth element mobility in and around carbonatites controlled by sodium, potassium, and silica. Sci. Adv. 2020, 6, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Migdisov, A.; Williams-Jones, A.E.; Brugger, J.; Caporuscio, F.A. Hydrothermal transport, deposition, and fractionation of the REE: Experimental data and thermodynamic calculations. Chem. Geol. 2016, 439, 13–42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Louvel, M.; Etschmann, B.; Guan, Q.; Testemale, D.; Brugger, J. Carbonate complexation enhances hydrothermal transport of rare earth elements in alkaline fluids. Nat. Commun. 2022, 13, 1456. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Preston, R.F.; Stevens, G.; McCarthy, T.S. Fluid compositions in equilibrium with silica-undersaturated magmas in the system Na2O-Al2O3-SiO2-H2O: Clues to the composition of fenitizing fluids. Contrib. Mineral. Petrol. 2003, 144, 559–569. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wall, F.; Zaitsev, A.N. Phoscorites and Carbonatites from Mantle to Mine: The Key Example of the Kola Alkaline Province; Wall, F., Zaitsev, A.N., Eds.; The Mineralogical Society of Great Britain and Ireland: Twickenham, UK, 2004; ISBN 0-903056-22-4. [Google Scholar]
- Rimskaya-Korsakova, O.M.; Krasnova, N.I. Geology of Deposits of the Kovdor Massif; Saint-Peterburg State University: Saint-Peterburg, Russia, 2002; ISBN 5-288-02859-1. [Google Scholar]
- Frost, B.R. On the stability of sulfides, oxides, and native metals in serpentinite. J. Petrol. 1985, 26, 31–63. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sleep, N.H.; Meibom, A.; Fridriksson, T.; Coleman, R.G.; Bird, D.K. H2-rich fluids from serpentinization: Geochemical and biotic implications. Proc. Nat. Acad. Sci. USA 2004, 101, 12818–12823. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Klein, F.; Bach, W. Fe-Ni-Co-O-S phase relations in peridotite-seawater interactions. J. Petrol. 2009, 50, 37–59. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Frost, R.B.; Beard, J.S. On silica activity and serpentinization. J. Petrol. 2007, 48, 1351–1368. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]










| Massif | Sampling Point | Samples | Short Geological Description |
|---|---|---|---|
| Khibiny | 1 | KH-61-2, KH-61-3, KH-61-4, KH-61-6, KH-61-9, KH-61-11, KH-61-13, KH-61-15, KH-31-1, KH-31-2, KH-32-2, KH-32-3, KH-33-1 | Numerous small, rounded xenoliths located at the contact of foyaite and foidolites. The sizes of individual xenoliths are from 10 cm × 20 cm to 1 m × 3 m. |
| Khibiny | 2 | KCH-05-11, KCH-05-13, KCH-05-15, KCH-05-21, KCH-05-24, KCH-05-31, KC-4, M-01-1-10, M-01-2-12, M-01-2-15, M-01-26, M-01-27, M-01-2-8, M-01-2-9, M-01-3, M-01-2, M-01-2-1, M-01-2-4 | Numerous small xenoliths located near the contact of foyaite and rischorrite. The size of individual xenoliths is on average 2 m × 3 m. |
| Khibiny | 3 | KH-16/86, KH-17/86, KH-18/86 | Samples from a borehole. Very large xenolith (600 m × 3000 m × 6000 m) located at the contact of foyaite and rischorrite [12,16]. |
| Khibiny | 4 | from E-97-1 to E-97-45 | Large (120 m × 40 m) xenolith located near the contact of foyaite and rischorrite. |
| Khibiny | 5 | KH-110, KH-111 | Large (100 m × 40 m) xenolith in foyaite. |
| Lovozero | 6, 7 | LV-117, LV-119, LV-119A, LV-120, LV-121, LV-121A, LV-122, LV-132, LV-149/2, LV-150/2, LV-160/1, LV-160/4, LV-01-45 | Several xenoliths located among fluorapatite-enriched foyaite and foidolites. The sizes of individual xenoliths are from 0.5 m × 1 m to 2 m × 5 m. |
| Abbreviation [41] | Mineral | Formula * |
|---|---|---|
| Ab | albite | Na(AlSi3O8) |
| Afs | alkali feldspar | (K,Na)AlSi3O8 |
| Alm | almandine | Fe2+3Al2(SiO4)3 |
| And | andalusite | Al2SiO5 |
| Ann | annite | KFe2+3(AlSi3O10)(OH)2 |
| Arf | arfvedsonite | NaNa2(Fe2+4Fe3+)Si8O22(OH)2 |
| Ast | astrophyllite | K2NaFe2+7Ti2(Si4O12)2O2(OH)4F |
| Crd | cordierite | Mg2Al4Si5O18 |
| Crn | corundum | Al2O3 |
| Fa | fayalite | Fe2+2(SiO4) |
| Fap | fluorapatite | Ca5(PO4)3F |
| Flr | fluorite | CaF2 |
| Hc | hercynite | Fe2+Al2O4 |
| Ilm | ilmenite | Fe2+Ti4+O3 |
| Mag | magnetite | Fe2+Fe3+2O4 |
| Mnz-Ce | monazite-(Ce) | Ce(PO4) |
| Ms | muscovite | KAl2(Si3Al)O10(OH)2 |
| Nph | nepheline | Na3K(Al4Si4O16) |
| Pcl | pyrochlore-group mineral | A2–m B2 X6–w Y1–n A = Na, Ca, Ag, Mn, Sr, Ba, Fe, Pb, Sn, Sb, Bi, Y, Ce, Sc, U, Th, □, or H2O; B = Ta, Nb, Ti, Sb, W; X = O, OH, F; Y = OH, F, O, □, H2O, K, Cs, Rb. |
| Phl | phlogopite | KMg3(AlSi3O10)(OH)2 |
| Pyh | pyrrhotite | Fe7S8 |
| Qz | quartz | SiO2 |
| Rct | richterite | Na(NaCa)Mg5Si8O22(OH)2 |
| Sil | sillimanite | Al2SiO5 |
| Skn | sekaninaite | Fe2+2Al4Si5O18 |
| Sps | spessartine | Mn2+3Al2(SiO4)3 |
| Ttn | titanite | CaTi(SiO4)O |
| Uspl | ulvöspinel | Fe2+2TiO4 |
| Zrn | zircon | Zr(SiO4) |
| Hornfels Minerals | Fenite Minerals | ||
|---|---|---|---|
| Al-Si minerals (high Si association) | ubiquitous minerals | Al-Fe minerals (low Si association) | |
| muscovite andalusite sillimanite quartz | (K,Na)-fieldspar albite (Ab51-98An2-48Or0-1) sekaninaite-cordierite annite-phlogopite corundum almandine-spessartine | hercynite fayalite | nepheline albite (Ab99-100An0-1) alkali amphiboles astrophyllite titanite |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Mikhailova, J.A.; Pakhomovsky, Y.A.; Konopleva, N.G.; Kalashnikov, A.O.; Yakovenchuk, V.N. Fluorine Controls Mineral Assemblages of Alkaline Metasomatites. Minerals 2022, 12, 1076. https://doi.org/10.3390/min12091076
Mikhailova JA, Pakhomovsky YA, Konopleva NG, Kalashnikov AO, Yakovenchuk VN. Fluorine Controls Mineral Assemblages of Alkaline Metasomatites. Minerals. 2022; 12(9):1076. https://doi.org/10.3390/min12091076
Chicago/Turabian StyleMikhailova, Julia A., Yakov A. Pakhomovsky, Natalia G. Konopleva, Andrey O. Kalashnikov, and Victor N. Yakovenchuk. 2022. "Fluorine Controls Mineral Assemblages of Alkaline Metasomatites" Minerals 12, no. 9: 1076. https://doi.org/10.3390/min12091076
APA StyleMikhailova, J. A., Pakhomovsky, Y. A., Konopleva, N. G., Kalashnikov, A. O., & Yakovenchuk, V. N. (2022). Fluorine Controls Mineral Assemblages of Alkaline Metasomatites. Minerals, 12(9), 1076. https://doi.org/10.3390/min12091076







