Rock Magnetic Results from the Early Ordovician Limestone Rocks in the Northern Qaidam Block, Tibetan Plateau
Abstract
1. Introduction

2. Geological Background and Sampling
3. Rock Magnetism
3.1. Isothermal Remanent Magnetization (IRM) Experiment
3.2. The Stepwise Thermal Demagnetization of the Three-Axis IRM
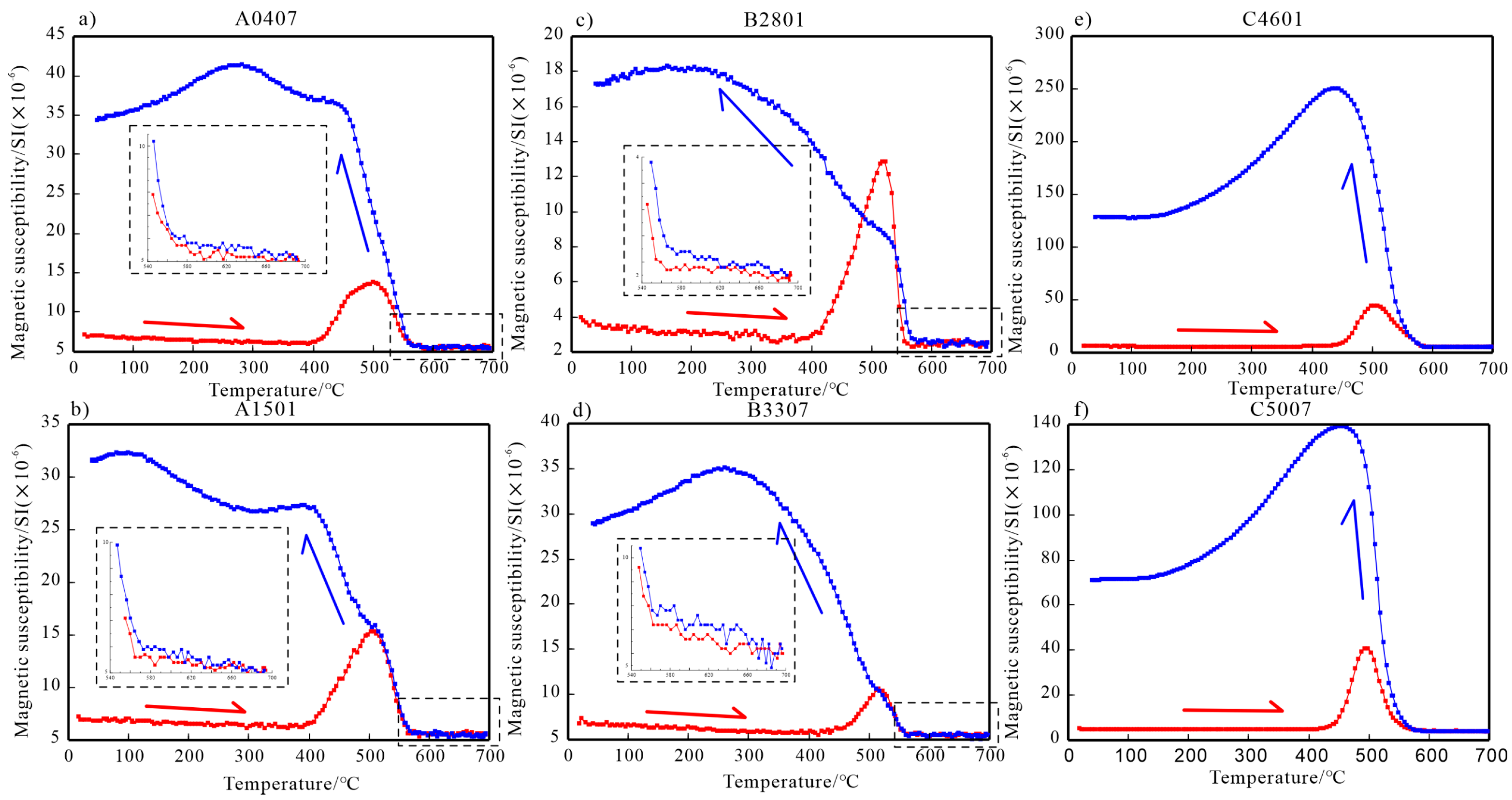
3.3. Magnetic Susceptibility Versus Temperature (k-T) Experiment
3.4. Low-Temperature Magnetic Properties
4. Petrology
4.1. Optical Microscope Observation
4.2. SEM (Scanning Electron Microscope) and EDS (Energy Dispersive Spectrometer)
5. Demagnetization Results
6. Discussion
6.1. The Magnetic Mineral Assemblage in Limestone Samples of the Duoquanshan Formation
6.2. Mechanism of the Remagnetization
7. Conclusions
- Rock magnetic and petrological studies were conducted on the early Ordovician limestone samples from the northern Qaidam block. The results show that the predominant magnetic carrier of the Dameigou section is magnetite and hematite, while the Shihuigou and Olongbuluke sections are goethite, pyrrhotite, hematite, and magnetite.
- The difference in demagnetization behaviors was exhibited by the samples from three sections. The samples from the Dameigou section exhibited two components (low- and high-temperature components), while the Shihuigou and Olongbuluke sections showed three components (a new medium-temperature component was detected). The medium-temperature component carried by the pyrrhotite may have been remagnetized by orogenic fluid and/or magma activity.
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Ren, J.S.; Xiao, L.W. Lifting the mysterious veil of the tectonics of the Qinghai-Tibet Plateau by 1:250000 geological mapping. Geol. Bull. China 2004, 23, 1–11. [Google Scholar]
- Allégre, C.J.; Courtillot, V.; Tapponnier, P.; Hirn, A.; Mattauer, M.; Coulon, C.; Jaeger, J.J.; Achache, J.; Schärer, U.; Marcoux, J.; et al. Structure and evolution of the Himalaya–Tibet orogenic belt. Nature 1984, 307, 17–22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dewey, J.F. Extensional collapse of orogens. Tectonics 1988, 7, 1123–1139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yin, A.; Harrison, T.M. Geologic Evolution of the Himalayan-Tibetan Orogen. Annu. Rev. Earth Planet. Sci. 2000, 28, 211–280. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pan, G.; Wang, L.; Li, R.; Yuan, S.; Ji, W.; Yin, F.; Zhang, W.; Wang, B. Tectonic evolution of the Qinghai-Tibet Plateau. J. Asian Earth Sci. 2012, 53, 3–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ding, L.; Li, Z.Y.; Song, P.P. Core Fragments of Tibetan Plateau from Gondwanaland United in Northern Hemisphere. Bull. Chin. Acad. Sci. 2017, 32, 945–950. [Google Scholar]
- Song, S.G.; Zhang, L.F.; Niu, Y.L.; Su, L.; Song, B.; Liu, D.N. Evolution from Oceanic Subduction to Continental Collision: A Case Study from the Northern Tibetan Plateau Based on Geochemical and Geochronological Data. J. Petrol. 2006, 47, 435–455. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, S.; Niu, Y.; Su, L.; Zhang, C.; Zhang, L. Continental orogenesis from ocean subduction, continent collision/subduction, to orogen collapse, and orogen recycling: The example of the North Qaidam UHPM belt, NW China. Earth-Sci. Rev. 2014, 129, 59–84. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, Z.F.; Liu, Z.B.; Chen, Q. Melting of subducted continental crust: Geochemical evidence from Mesozoic granitoids in the Dabie-Sulu orogenic belt, east-central China. Asian Earth Sci. 2017, 145, 260–277. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dong, Y.; He, D.; Sun, S.; Liu, X.; Zhou, X.; Zhang, F.; Zhao, Y.; Cheng, B.; Zhao, G.C.; Li, J. Subduction and accretionary tectonics of the East Kunlun orogen, western segment of the Central China Orogenic System. Earth-Sci. Rev. 2018, 186, 231–261. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Q.Y.; Dong, Y.J.; Pan, Y.M.; Liao, F.X.; Guo, X.W. Early Paleozoic Granulite-Facies Metamorphism and Magmatism in the Northern Wulan Terrane of the Quanji Massif: Implications for the Evolution of the Proto-Tethys Ocean in Northwestern China. Earth Sci. 2018, 29, 1081–1101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fu, C.L.; Yan, Z.; Xiao, W.J.; Wang, B.Z.; Niu, M.L.; Li, X.C.; Yu, L.J. Identification and geological significance of the Early Paleozoic Tianjunnanshan remnant ocean basin in the Zongwulong belt, Ne Tibetan Plateau. Acta Petrol. Sin. 2021, 37, 2401–2418. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, C.; Bader, T.; Zhang, L.F.; Roermund, H.V. The multi-stage tectonic evolution of the Xitieshan terrane, North Qaidam orogen, western China: From Grenville-age orogeny to early-Paleozoic ultrahigh-pressure metamorphism. Gondwana Res. 2017, 41, 290–300. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zuza, A.V.; Wu, C.; Reith, R.C.; Yin, A.; Li, J.H.; Zhang, J.Y.; Zhang, Y.X.; Wu, L.; Liu, W.C. Tectonic evolution of the Qilian Shan: An early Paleozoic orogen reactivated in the Cenozoic. GSA Bull. 2018, 130, 881–925. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, S.; Chung, S.L.; Hou, Z.Q.; Chew, D.; Wang, T.; Wang, B.D.; Wang, Y.B. Early Mesozoic Magmatism Within the Tibetan Plateau: Implications for the Paleo-Tethyan Tectonic Evolution and Continental Amalgamation. Tectonics 2019, 38, 3505–3543. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wan, B.; Chu, Y.; Chen, L.; Liang, X.F.; Zhang, Z.Y.; Ao, S.J.; Talebian, M. Paleo-Tethys subduction induced slab-drag opening the Neo-Tethys: Evidence from an Iranian segment of Gondwana. Earth-Sci. Rev. 2021, 221, 103788. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, B.; Yan, Y.; Piper, J.D.; Zhang, D.; Yi, Z.; Yu, S.; Zhou, T. Paleomagnetic constraints on the paleogeography of the East Asian blocks during Late Paleozoic and Early Mesozoic times. Earth-Sci. Rev. 2018, 186, 8–36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Y.; Gilder, S.; Halim, N.; Cogné, J.P.; Courtillot, V. New paleomagnetic constraints on central Asian kinematics: Displacement along the Altyn Tagh fault and rotation of the Qaidam Basin. Tectonics 2002, 21, 6-1–6-19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, Z.M.; Yang, Z.Y.; Pei, J.L.; Yang, T.S.; Wang, X.S. New Early Cretaceous paleomagnetic data from volcanic and red beds of the eastern Qaidam Block and its implications for tectonics of Central Asia. Earth Planet. Sci. Lett. 2006, 243, 268–281. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dupont-Nivet, G.; Butler, R.F.; Yin, A.; Chen, X.H. Paleomagnetism indicates no Neogene rotation of the Qaidam Basin in northern Tibet during Indo-Asian collision. Geology 2002, 30, 263–266. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, H.X.; Yu, H.M.; Li, P.W. Palaeomagnetic study of Chaidam palte and its evolution. Chang. Univ. Earth Sci. 1992, 22, 420–426. [Google Scholar]
- Wu, H.N.; Liu, C.Y.; Zhang, X.H.; Ren, Z.L. Discuss the tectonic evolution of Qaidam Block by paleomagnetic evidence. Sci. China. Ser. D Earth Sci. 1997, 27, 9–14. [Google Scholar]
- Yan, Z.; Fu, C.; Aitchison, J.C.; Buckman, S.; Niu, M.; Cao, B.; Sun, Y.; Guo, X.; Wang, Z.Q.; Zhou, R. Retro-foreland basin development in response to Proto-Tethyan Ocean closure, NE Tibet Plateau. Tectonics 2019, 38, 4229–4248. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qinghai Bureau of Geology and Mineral Resources (BGMR). Regional Geological Investigation of the Tuosuhu Area; Unpublished scientific report as a part of the Regional Geology of Qinghai Province; Geological Publishing House: Beijing, China, 1978; pp. 1–124. [Google Scholar]
- Qinghai Bureau of Geology and Mineral Resources (BGMR). Regional Geological Investigation of the Huaitoutala Area; Unpublished scientific report as a part of the Regional Geology of Qinghai Province; Geological Publishing House: Beijing, China, 1980; pp. 1–127. [Google Scholar]
- Cao, Y.; Sun, Z.M.; Pei, J.L.; Li, H.B.; Xu, W.; Zhang, L. Paleomagnetic constraints on the Early Ordovician paleogeographical position of the Qaidam Block. Acta Geol. Sin. 2021, 95, 1448–1458. [Google Scholar]
- Cheng, F.; Jolivet, M.; Hallot, E.; Zhang, D.; Zhang, C.; Guo, Z. Tectono-magmatic rejuvenation of the Qaidam craton, northern Tibet. Gondwana Res. 2017, 49, 248–263. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dai, K.; Liu, C.L.; Xiao, D.Q.; Ma, Y.S.; Peng, Y.; Zhang, X.; Zheng, C.; Zhang, Y.F.; Sun, J.P. The tectonic deformation and evolution of the Olongbluke area in Eastern Qaidam Basin. Earth Sci. Front. 2016, 23, 033–044. [Google Scholar]
- Qian, T.; Wang, Z.X.; Liu, Y.Q.; Liu, S.F.; Gao, W.L.; Li, W.P.; Hu, J.J.; Li, L.L. Provenance analysis of the Jurassic northern Qaidam Basin: Stratigraphic succession and LA-ICP-MS geochronology. Sci. Sin. Terrae 2018, 48, 224–242. [Google Scholar]
- Qian, T.; Wang, Z.; Wang, Y.; Liu, S.; Gao, W.; Li, W. Jurassic evolution of the Qaidam Basin in western China: Constrained by stratigraphic succession, detrital zircon U-Pb geochronology and Hf isotope analysis. GSA Bull. 2021, 133, 2291–2318. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qian, T.; Li, W.P.; Gao, W.L.; Jiang, W. A preliminary study on post-orogenesis of the North Qaidam tectonic belt during the Early Paleozoic by provenance analysis of the Devonian sediments. Acta Geol. Sin. 2021, 95, 1–17. [Google Scholar]
- Sun, J.; Dong, Y.; Ma, L.; Peng, Y.; Chen, S.; Du, J.; Jiang, W. Late Paleoproterozoic tectonic evolution of the Olongbuluke Terrane, northern Qaidam, China: Constraints from stratigraphy and detrital zircon geochronology. Precambrian Res. 2019, 331, 105349. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, J.; Dong, Y.; Jiang, W.; Ma, L.; Chen, S.; Du, J.; Peng, Y. Reconstructing the Olongbuluke Terrane (northern Tibet) in the end-Neoproterozoic to Ordovician Indian margin of Gondwana. Precambrian Res. 2020, 348, 105865. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, J.P.; Dong, Y.P.; Ma, L.C.; Chen, S.Y.; Jiang, W. Devonian to Triassic tectonic evolution and basin transition in the East Kunlun-Qaidam area, northern Tibetan Plateau: Constraints from stratigraphy and detrital zircon U-Pb geochronology. GSA Bull. 2022, 134, 1967–1993. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, S.; Bi, M.; Sun, J.; Zhang, Y.; Zhuang, Y.; Liu, J.; Wang, F.; Ma, S. Mixed sedimentary characteristics and controlling factors of Upper Paleozoic Group in Northern Qaidam Basin. Geol. Bull. China 2016, 35, 282–292. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, T.; Zhou, Y.N.; He, W.D.; He, L.; Cheng, X.; Deng, X.H.; Zhang, D.M.; Wei, B.T.; Jiang, N.; Wu, H.N. Provenance change in Carboniferous-early Permian sedimentary successions in the North Qaidam tectonic belt, northern Tibetan Plateau: Implications for the Kunlun oceanic plate subduction process. J. Asian Earth Sci. 2022, 240, 105434. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiao, A.C.; Yu, L.; Xiong, G.Y.; Zhang, J.Y.; Zhang, Y.S.; Wu, L.; Zhao, H.F.; Qin, S.H. Triassic retroarc foreland basin in southern Qilian area: Evidence from sedimentary filling and tectonics. Acta Petrol. Sin. 2021, 37, 2385–2400. [Google Scholar]
- Ma, S.; Chen, S.Y.; Jia, B.B.; Sun, J.P.; Wang, F.; Zeng, H.Y. Sedimentary characteristics and controlling factors of the Early Ordovician platform-slope-basin in the northern margin of the Qaidam Basin. Earth Sci. Front. 2018, 25, 185–197. [Google Scholar]
- Chen, Q.; Li, H.P.; Dong, Y.P.; Feng, Q.; He, D.F.; Chen, H. Redefinition of the Cambrian-Ordovician strata in the Olongbuluck area, northern margin of the Qaidam basin. Geol. Explor. 2013, 49, 825–835. [Google Scholar]
- Lai, C.G. Cephalopoda of the Duoquanshan Formation from Shihuigou, Ulan, Qinghai Province. Bull. Inst. Geol. Chin. Acad. Geol. Sci. 1985, 2, 109–117. [Google Scholar]
- Zhao, G.Z. Study of the Lower Ordovician in the northeastern margin of the Qaidam Basin, Qinghai Province. Qinghai Geol. 1986, 2, 1–11. [Google Scholar]
- Zhu, G.K. Paleomagnetism—Fundamentals, Principles, Methods, Results, and Applications; Beijing China Science Publishing & Media Ltd. (CSPM): Beijing, China, 2005; pp. 1–256. [Google Scholar]
- Kruiver, P.P.; Dekkers, M.J.; Heslop, D. Quantification of magnetic coercivity components by the analysis of acquisition curves of isothermal remanent magnetization. Earth Planet. Sci. Lett. 2001, 189, 269–276. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stockhausen, H. Some new aspects for the modelling of isothermal remanent magnetization acquisition curves by cumulative log Gaussian functions. Geophys. Res. Lett. 1998, 25, 2217–2220. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ao, H.; Deng, C.L. Review in the identification of magnetic minerals. Prog. Geophys. 2007, 22, 432–442. [Google Scholar]
- Lowrie, W. Identification of ferromagnetic minerals in a rock by coercivity and unblocking temperature properties. Geophys. Res. Lett. 1990, 17, 159–162. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yan, Y.; Duan, L.; Liang, S.; Wang, J.; Huang, B.; Zheng, W.; Zhang, P. Paleomagnetic Constraint on the Carboniferous Paleoposition of Indochina and Its Implications for the Evolution of Eastern Paleo-Tethys Ocean. Tectonics 2020, 39, e2020TC006168. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dekkers, M.J.; Mattéi, J.L.; Fillion, G.; Rochette, P. Grain-size dependence of the magnetic behavior of pyrrhotite during its low-temperature transition at 34 K. Geophys. Res. Lett. 1989, 16, 855–858. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hrouda, F. A technique for the measurement of thermal changes of magnetic susceptibility of weakly magnetic rocks by the CS-2 apparatus and KLY-2 Kappabridge. Geophys. J. Int. 1994, 118, 604–612. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- VanVelzen, A.J.; Dekkers, M.J. The incorporation of thermal methods in mineral magnetism of loess-paleosol sequence: A brief overview. Chin. Sci. Bull. 1999, 44, 53–63. [Google Scholar]
- Aubourg, C.; Pozzi, J.P.; Kars, M. Burial, claystones remagnetization and some consequences for magnetostratigraphy. Geol. Soc. Lond. Spec. Publ. 2012, 371, 181–188. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zegers, T.E.; Dekkers, M.J.; Bailly, S. Late Carboniferous to Permian remagnetization of Devonian limestones in the Ardennes: Role of temperature, fluids, and deformation. J. Geophys. Res. Solid Earth 2003, 108, 2357. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, W.; Lippert, P.C.; Jackson, M.J.; Dekkers, M.J.; Zhang, Y.; Li, J.; Guo, Z.; Kapp, P.; van Hinsbergen, D.J.J. Remagnetization of the Paleogene Tibetan Himalayan carbonate rocks in the Gamba area: Implications for reconstructing the lower plate in the India-Asia collision. J. Geophys. Res. Solid Earth 2017, 122, 808–825. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, W.; Lippert, P.C.; Jackson, M.J.; Dekkers, M.J.; Zhang, Y.; Li, J.; Guo, Z.; Kapp, P.; van Hinsbergen, D.J.J. Reply to comment by Z. Yi et al. on “Remagnetization of the Paleogene Tibetan Himalayan carbonate rocks in the Gamba area: Implications for reconstructing the lower plate in the India-Asia collision”. J. Geophys. Res. Solid Earth 2017, 122, 4859–4863. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roberts, A.P.; Florindo, F.; Larrasoaña, J.C.; O’Regan, M.A.; Zhao, X. Complex polarity pattern at the former Plio–Pleistocene global stratotype section at Vrica (Italy): Remagnetization by magnetic iron sulphides. Earth Planet. Sci. Lett. 2010, 292, 98–111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dunlop, D.J.; Özdemir, Ö.; Schmidt, P.W. Paleomagnetism and paleothermometry of the Sydney Basin 2. Origin of anomalously high unblocking temperatures. J. Geophys. Res. Solid Earth 1997, 102, 27285–27295. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Morin, J. Magnetic Susceptibility of αFe2O3 and αFe2O3 with Added Titanium. Phys. Rev. 1950, 78, 819. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moskowitz, B.M.; Frankel, R.B.; Walton, S.A.; Dickson, D.P.; Wong, K.K.W.; Douglas, T.; Mann, S. Determination of the preexponential frequency factor for superparamagnetic maghemite particles in magnetoferritin. J. Geophys. Res. Solid Earth 1997, 102, 22671–22680. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Verwey, E. Electronic Conduction of Magnetite (Fe3O4) and its Transition Point at Low Temperatures. Nature 1939, 144, 327–328. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guyodo, Y.; Mostrom, A.; Lee Penn, R.; Banerjee, S.K. From nanodots to nanorods: Oriented aggregation and magnetic evolution of nanocrystalline goethite. Geophys. Res. Lett. 2003, 30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, W.T.; Jackson, M.J.; Dekkers, M.J.; Zhang, Y.; Zhang, B.; Guo, Z.; Dupont-Nivet, G. Challenges in isolating primary remanent magnetization from Tethyan carbonate rocks on the Tibetan Plateau: Insight from remagnetized Upper Triassic limestones in the eastern Qiangtang block. Earth Planet. Sci. Lett. 2019, 523, 115695. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yan, Y.; Huang, B.; Zhang, D.; Charusiri, P.; Veeravinantanakul, A. Paleomagnetic Study on the Permian Rocks of the Indochina Block and Its Implications for Paleogeographic Configuration and Northward Drifting of Cathaysialand in the Paleo-Tethys. J. Geophys. Res. Solid Earth 2018, 123, 4523–4538. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Enkin, R.J. Formation ET Déformation de L’Asie Depuis la Fin de Lère Primaire: Les Apports de L’éTude Paléomagnétique Des Formations Secondaires de Chine du Sud. Ph.D. Thesis, Univ de Paris, Paris, France, July 1990. [Google Scholar]
- Yang, Z.Y. Indosinian remagnetization of Permian limestone from the Khorat basin, Thailand. Acta Geophys. Sin. 1996, 39, 173–181. [Google Scholar]
- Yang, Z.Y.; Ma, X.H.; Sun, Z.M.; Huang, B.C. Remagnetization of the Early Paleozoic rocks from the southern part of the Huabei basin I—Paleomagnetic result and its implications. Sci. China (Ser. D) 1998, 41, 20–27. [Google Scholar]
- Yang, Z.Y.; Ma, X.H.; Sun, Z.M.; Huang, B.C. Remagnetization of the Early Paleozoic rocks from the southern part of the Huabei basin II—Rock magnetic results. Sci. China (Ser. D) 1998, 41, 28–35. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, C.Y.; Li, S.H.; Deng, C.L.; Zhu, R.X. On the mechanism of remagnetization of Ordovician carbonates from the Yangtze Block, southwestern China. Chin. Geophys. 2013, 56, 579–591. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Cao, Y.; Sun, Z.M.; Li, H.B.; Ye, X.Z.; Pan, J.W.; Zhang, L.; Liu, D.L.; Liu, C.G. Paleomagnetic Study of the Late Triassic limestones in the western portion of the Qiangtang Block and its tectonic implications. Acta Geol. Sin. 2019, 93, 2463–2476. [Google Scholar]
- Dunlop, D.J.; Özdemir, Ö.; Clark, D.A.; Schmidt, P.W. Time-temperature relations for the remagnetization of pyrrhotite (Fe7S8) and their use in estimating paleotemperatures. Earth Planet. Sci. Lett. 2000, 176, 107–116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, H.L.; Ma, X.H.; Sun, Z.M.; Chen, K.Q. Magnetic minerals in carbonate rocks and their role in palaeogeographic study. J. Palaeogeogr. 2000, 2, 75–82. [Google Scholar]
- Sun, L.S.; Huang, B.C. New paleomagnetic result for Ordovician rocks from the Tarim Block, Northwest China and its tectonic implications. Chin. J. Geophys. 2009, 52, 1836–1848. [Google Scholar]
- Shi, C.D.; Zhu, R.X. Applications of research of iron sulphides in paleomagnetism and environmental magnetism. Prog. Geophys. 2000, 15, 91–97. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Menard, G.; Rochette, P. Utilisation de re aimantation postme´tamorphique pour une e´tude del’e´volution tectonique et thermique tardive dans lesAlpes occidentales (France). Bull. Socie Ologique Fr. 1992, 163, 381–392. [Google Scholar]
- Appel, E.; Müller, R.; Widder, R.W. Palaeomagnetic results from the Tibetan Sedimentary Series of the Manang area (north central Nepal). Geophys. J. Int. 1991, 104, 255–266. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, X.; Xu, R.; Zheng, Y.Y.; Gao, S.B.; Cai, P.J.; Yu, J.Z.; Wang, Q.M. The geodynamic setting of Dulan eclogite-type rutile deposits in the North Qaidam orogen, western China. Ore Geol. Rev. 2019, 110, 102936. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Metcalfe, I. Multiple Tethyan ocean basins and orogenic belts in Asia. Gondwana Res. 2021, 100, 87–130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Niu, M.L.; Cai, Q.R.; Li, X.C.; Yakymchuk, C.; Wu, Q.; Yuan, X.Y.; Sun, Y. Early Paleozoic tectonic transition from oceanic to continental subduction in the North Qaidam tectonic belt: Constraints from geochronology and geochemistry of syncollisional magmatic rocks. Gondwana Res. 2021, 91, 58–80. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jackson, M.; Swanson-Hysell, N.L. Rock magnetism of remagnetized carbonate rocks: Another look. Geol. Soc. Lond. Spec. Publ. 2012, 371, 229–251. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oliver, J. Fluids expelled tectonically from orogenic belts: Their role in hydrocarbon migration and other geologic phenomena. Geology 1986, 14, 99–102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]









Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Deng, X.; Zhou, Y.; Wang, T.; Cheng, X.; Wei, B.; Jiang, N.; Zhang, D.; Li, T.; Lan, S.; Xing, L.; et al. Rock Magnetic Results from the Early Ordovician Limestone Rocks in the Northern Qaidam Block, Tibetan Plateau. Minerals 2023, 13, 65. https://doi.org/10.3390/min13010065
Deng X, Zhou Y, Wang T, Cheng X, Wei B, Jiang N, Zhang D, Li T, Lan S, Xing L, et al. Rock Magnetic Results from the Early Ordovician Limestone Rocks in the Northern Qaidam Block, Tibetan Plateau. Minerals. 2023; 13(1):65. https://doi.org/10.3390/min13010065
Chicago/Turabian StyleDeng, Xiaohong, Yanan Zhou, Teng Wang, Xin Cheng, Bitian Wei, Nan Jiang, Dongmeng Zhang, Teng Li, Shuqi Lan, Longyun Xing, and et al. 2023. "Rock Magnetic Results from the Early Ordovician Limestone Rocks in the Northern Qaidam Block, Tibetan Plateau" Minerals 13, no. 1: 65. https://doi.org/10.3390/min13010065
APA StyleDeng, X., Zhou, Y., Wang, T., Cheng, X., Wei, B., Jiang, N., Zhang, D., Li, T., Lan, S., Xing, L., & Wu, H. (2023). Rock Magnetic Results from the Early Ordovician Limestone Rocks in the Northern Qaidam Block, Tibetan Plateau. Minerals, 13(1), 65. https://doi.org/10.3390/min13010065




