Automated Mineralogy and Diagnostic Leaching Studies on Bulk Sulfide Flotation Concentrate of a Refractory Gold Ore
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Materials and Sample Preparation
2.2. Methods
2.2.1. Cyanide Leaching Tests
2.2.2. Flotation Tests
2.2.3. Automated Mineralogy Analysis
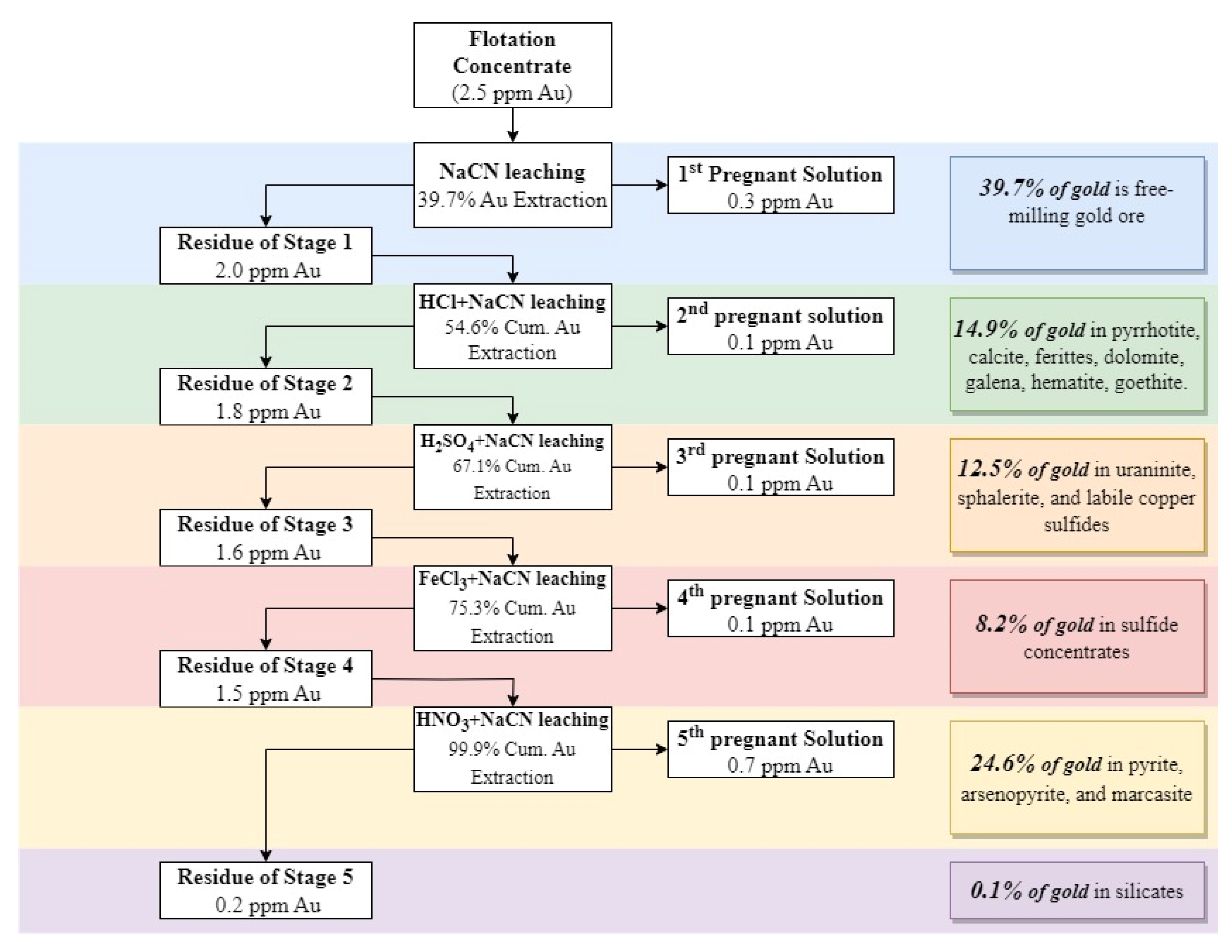
2.2.4. Diagnostic Leaching Tests
3. Results and Discussions
3.1. Feed Properties
3.2. Cyanide Leaching and Flotation
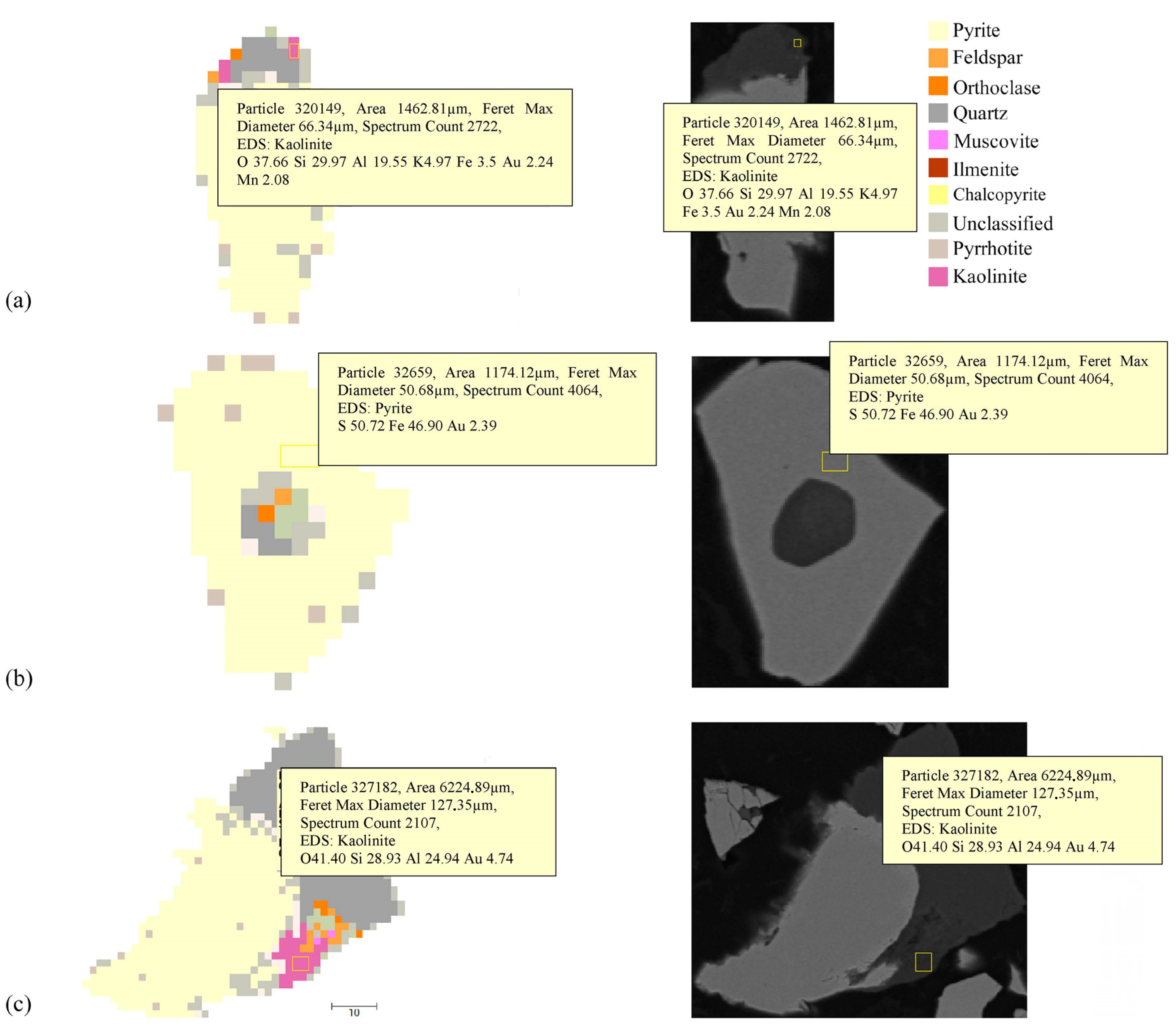
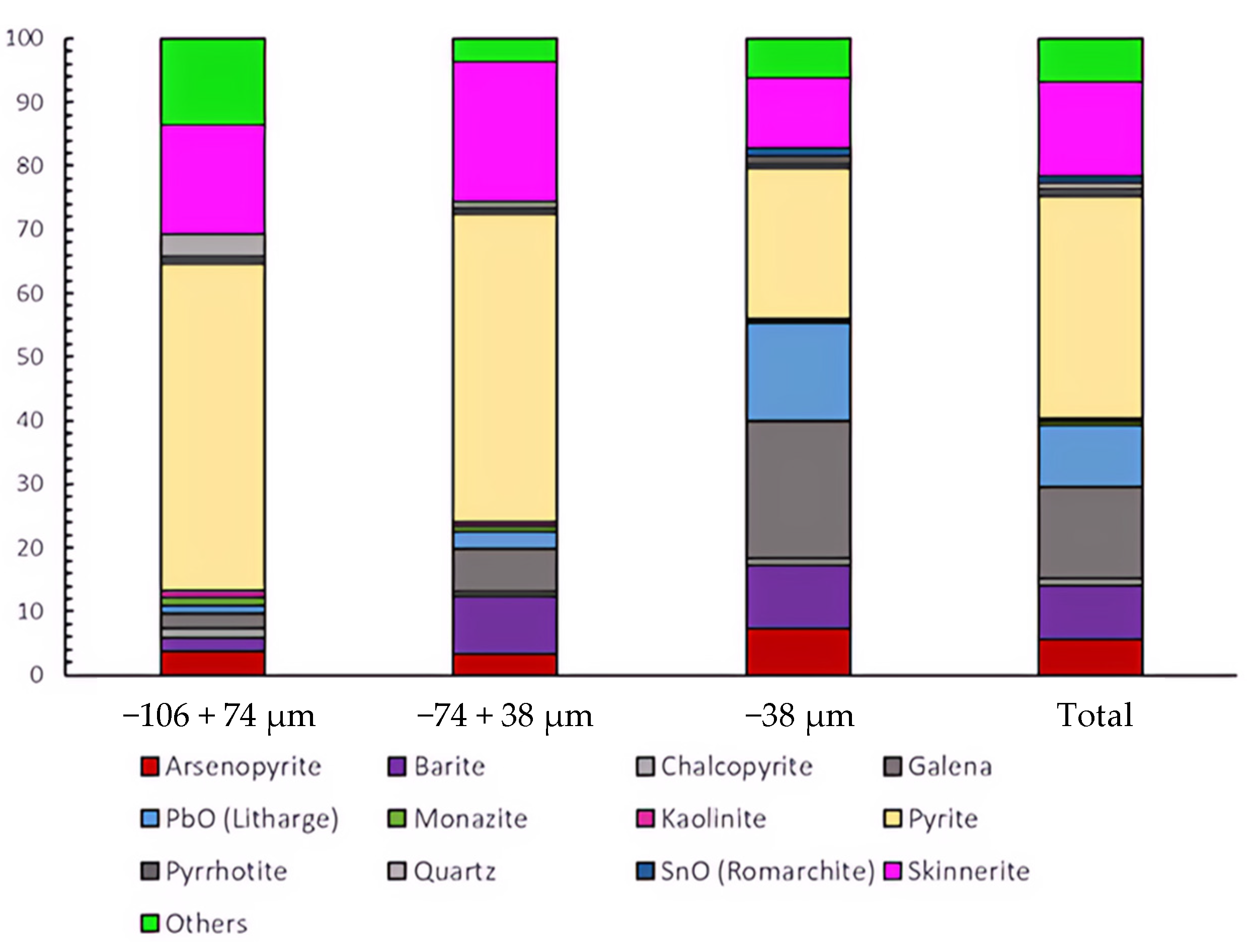
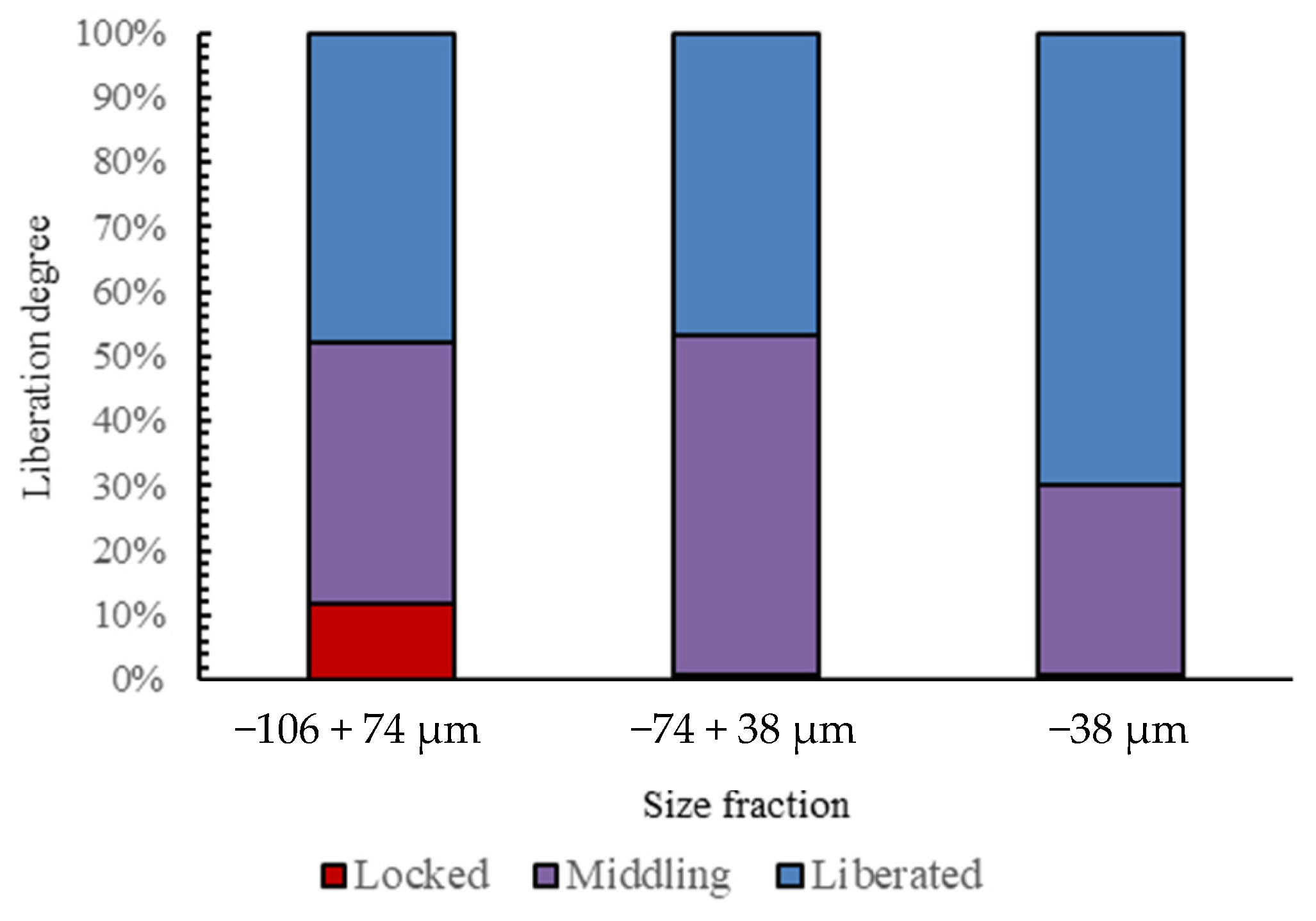
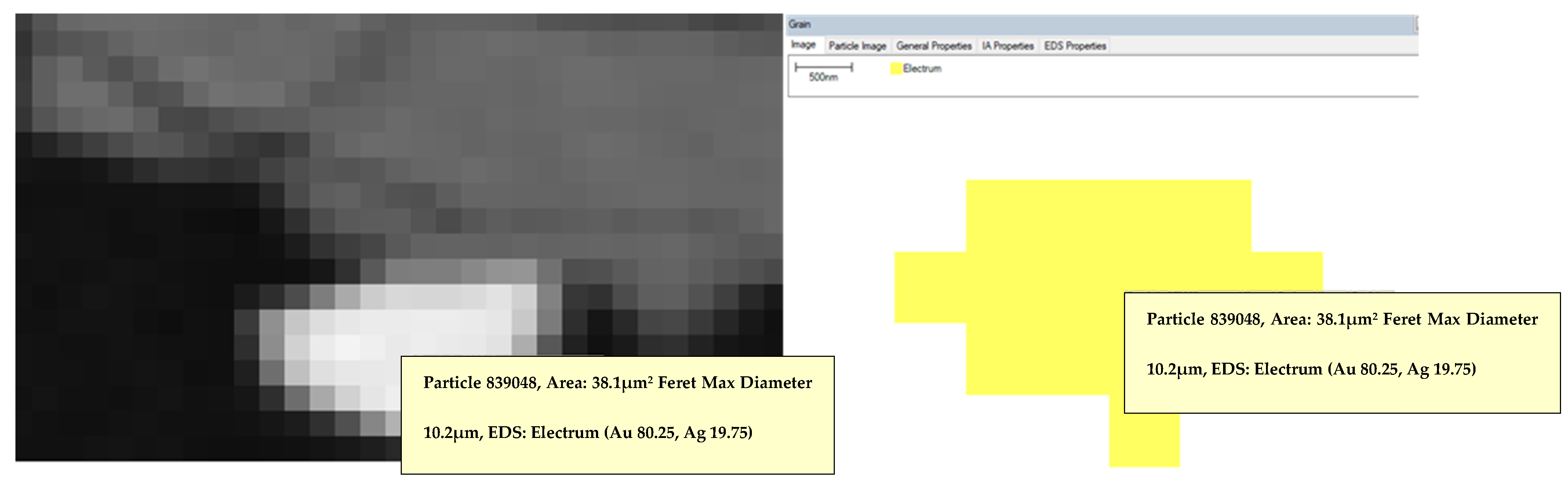
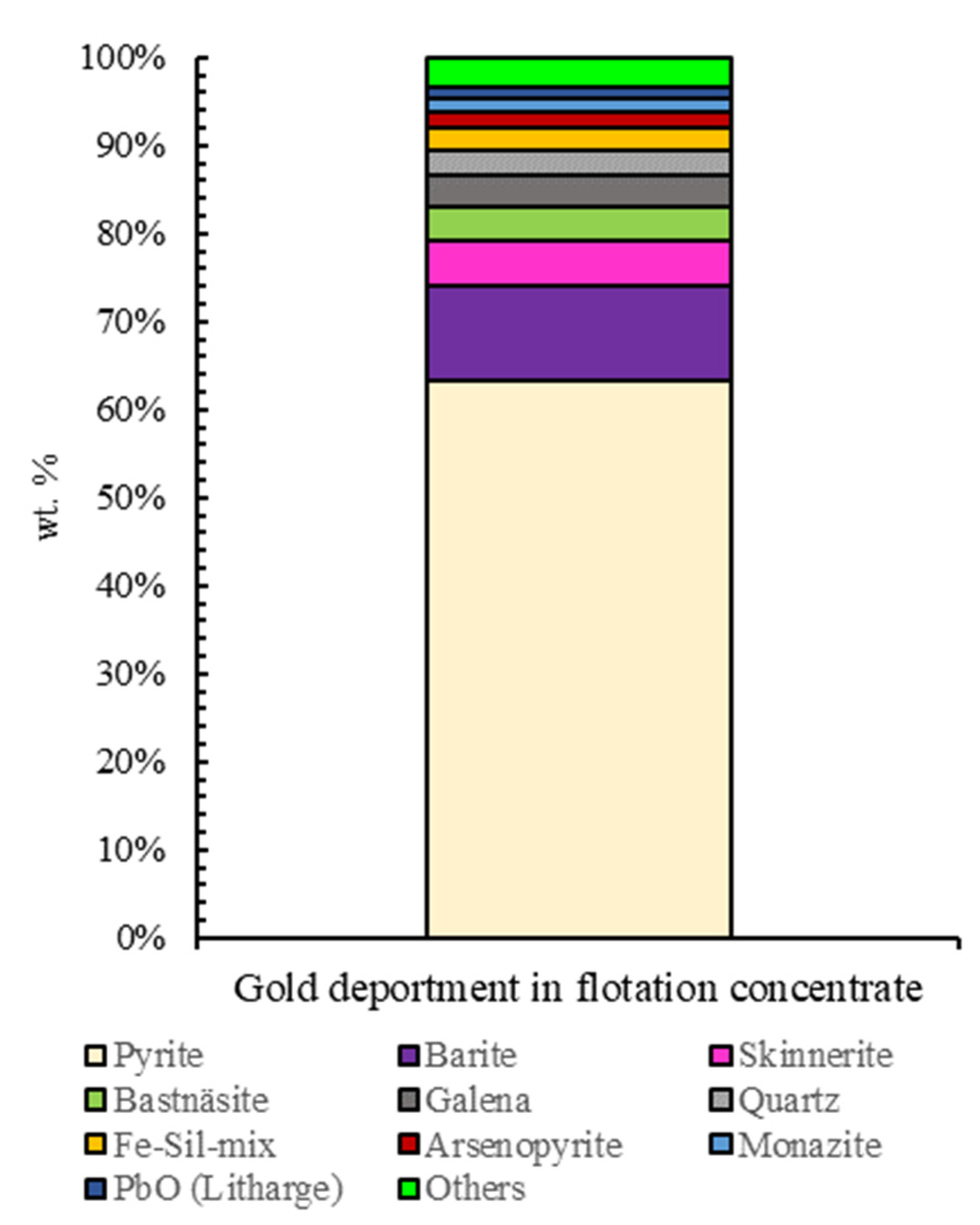
3.3. Automated Mineralogy (AM)
3.4. Diagnostic Leaching
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Lakshmanan, V.I.; Gorain, B. Innovations and Breakthroughs in the Gold and Silver Industries; Springer: Cham, Switzerland, 2019; p. 288. ISBN 978-3-030-32551-0. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hassanzadeh, A.; Safari, M.; Hoang, D.H.; Khoshdast, H.; Albijanic, B.; Kowalczuk, P. Technological assessments on recent developments in fine and coarse particle flotation systems. Miner. Eng. 2022, 180, 107509. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Afenya, P. Treatment of carbonaceous refractory gold ores. Miner. Eng. 1991, 4, 1043–1055. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Akçıl, A.; Çiftçi, H. Pretreatments Applied to Refractory Gold Ores. Sci. Min. J. 2009, 48, 17–30. [Google Scholar]
- Asamoah, R.; Amankwah, R.; Addai-Mensah, J. Cyanidation of refractory gold ores: A review. In Proceedings of the 3rd UMaT Biennial International Mining and Mineral Conference, Tarkwa, Ghana, 30 July 2014. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yüce, A.E. Cevher Hazırlama el Kitabı, 1st ed.; Önal, G., Ateşok, G., Perek, K., Eds.; Yurt Madenciliğini Geliştirme Vakfı: Istanbul, Turkey, 2014; pp. 425–450. [Google Scholar]
- Marsden, J.; House, I. The Chemistry of Gold Extraction, 2nd ed.; SME: Denver, CO, USA, 2006; pp. 19–68. [Google Scholar]
- La Brooy, S.R.; Linge, H.G.; Walker, G.S. Review of gold extraction from ores. Miner. Eng. 1994, 7, 1213–1241. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Komnitsas, C.; Pooley, F. Mineralogical characteristics and treatment of refractory gold ores. Miner. Eng. 1989, 2, 449–457. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, T.; Cabri, L.; Dutrizac, J. Characterizing gold in refractory sulfide gold ores and residues. JOM 2002, 54, 20–22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reich, M.; Kesler, S.E.; Utsunomiya, S.; Palenik, C.S.; Chryssoulis, S.L.; Ewing, R.C. Solubility of gold in arsenian pyrite. Geochim. Cosmochim. Acta 2005, 69, 2781–2796. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yannopoulos, J.C. (Ed.) Treatment of Refractory Gold Ores. In The Extractive Metallurgy of Gold, 1st ed.; Springer: New York, NY, USA, 1991; pp. 79–110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Butcher, A.R.; Helms, T.A.; Gottlieb, P.; Bateman, R.; Ellis, S.; Johnson, N.W. Advances in the quantification of gold deportment by QEMSCAN. In Proceedings of the Seventh Mill Operators Conference, Kalgoorlie, Australia, 12–14 October 2000. [Google Scholar]
- Baum, W.; Lotter, N.O.; Whittaker, P.J. Process Mineralogy–A New Generation for Ore Characterization and Plant Optimization. In Proceedings of the SME Annual Meeting, Denver, CO, USA, 23–25 February 2004; pp. 23–25. [Google Scholar]
- Fandrich, R.; Gladys, O. Modern SEM based quantitative mineralogy. Acta Microsc. 2007, 16, 44–45. [Google Scholar]
- Malvik, T. History and growth of modern process mineralogy. Mineralproduksjon 2014, 5, A1–A19. [Google Scholar]
- Zhou, J.; Gu, Y. Geometallurgical characterization and automated mineralogy of gold ores. In Gold Ore Processing; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2016; pp. 95–111. [Google Scholar]
- Fernandes, I.B.; Rudolph, M.; Hassanzadeh, A.; Bachmann, K.; Meskers, C.; Peuker, U.; Reuter, M.A. The Quantification of entropy for multicomponent systems: Application to microwave-assisted comminution. Miner. Eng. 2021, 170, 107016. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gu, Y. Automated scanning electron microscope based mineral liberation analysis: An introduction to JKMRC/FEI mineral liberation analyser. J. Miner. Mater. Charact. Eng. 2003, 2, 33–41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Graham, S.D.; Brough, C.; Cropp, A. An introduction to ZEISS mineralogic mining and the correlation of light microscopy with automated mineralogy: A case study using BMS and PGM analysis of samples from a PGE-bearing chromite prospect. In Proceedings of the Precious Metals ‘15, Falmouth, UK, 11–12 May 2015. volume 11. [Google Scholar]
- Becker, M. The contribution of applied mineralogy to sustainability in the mine life cycle. Miner. Eng. 2023, 199, 108121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Coetzee, L.L.; Theron, S.J.; Martin, G.J.; Van der Merwe, J.D.; Stanek, T.A. Modern gold deportments and its application to industry. Miner. Eng. 2011, 24, 565–575. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Petruk, W. Applied Mineralogy in the Mining Industry; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2000. [Google Scholar]
- Chryssoulis, S.L.; Cabri, L.J. Significance of Gold Mineralogical Balances in Mineral Processing. Trans. Inst. Min. Metall. Sect. A Min. Technol. 1990, 99, C1–C10. [Google Scholar]
- Nazari, A.M.; Ghahreman, A.; Bell, S. A comparative study of gold refractoriness by the application of QEMSCAN and diagnostic leach process. Int. J. Miner. Process. 2017, 169, 35–46. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Goodall, W.R.; Scales, P.J.; Ryan, C.G. Applications of PIXE and diagnostic leaching in the characterisation of complex gold ores. Miner. Eng. 2005, 18, 1010–1019. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lorenzen, L.; Tumilty, J. Diagnostic Leaching as an analytical tool for evaluating the effect of reagents on the performance of a gold plant. Miner. Eng. 1992, 5, 503–512. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lorenzen, L. Some guidelines to the design of a diagnostic leaching experiment. Miner. Eng. 1995, 8, 247–256. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Celep, O.; Alp, I.; Deveci, H.; Vicil, M. Characterization of refractory behaviour of complex gold/silver ore by diagnostic leaching. Trans. Nonferrous Met. Soc. China 2009, 19, 707–713. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lorenzen, L.; Van Deventer, J. The mechanism of leaching of gold from refractory ores. Miner. Eng. 1992, 5, 1377–1387. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tumilty, J.; Sweeney, A.; Lorenzen, L. Diagnostic leaching in the development of flowsheets for new ore deposits. In Proceedings of the Metallurgical Society of the Canadian Institute of Mining and Metallurgy; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 1987; pp. 157–167. [Google Scholar]
- Celep, O.; Yazici, E.Y.; Altinkaya, P.; Deveci, H. Characterization of a refractory arsenical silver ore by mineral liberation analysis (MLA) and diagnostic leaching. Hydrometallurgy 2019, 189, 105106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Goodall, W.R.; Scales, P.J.; Butcher, A.R. The Use of QEMSCAN and diagnostic leaching in the characterisation of visible gold in complex ores. Miner. Eng. 2005, 18, 877–886. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Teague, A.; Swaminathan, C.; Van Deventer, J. The behaviour of gold bearing minerals during froth flotation as determined by diagnostic leaching. Miner. Eng. 1998, 11, 523–533. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Henley, K.; Clarke, N.; Sauter, P. Evaluation of a diagnostic leaching technique for gold in native gold and gold-silver tellurides. Miner. Eng. 2001, 14, 1–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Celep, O.; Alp, I.; Deveci, H. Application of diagnostic leaching technique for refractory gold ores. DPÜ. Fen Bilim. Enstitüsü 2008, 16, 81–90. [Google Scholar]
- Bidari, E.; Aazami, M.; Aghazadeh, V. Process Mineralogical Study of the Arsenical Zone from a Carlin-type Gold Deposit. Min. Metall. Explor. 2020, 37, 1307–1315. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stephen, R.S.; Anuar WN, S.; Ismail, S.; Jabit, N.A. Characterisation and diagnostic leaching of gold-bearing mineral ore, East Coast Peninsular Malaysia. Malays. J. Microsc. 2021, 17, 139–153. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, J.; Wang, W.; Dong, K.; Fu, Y.; Xie, F. Research on leaching of carbonaceous gold ore with copper-ammonia-thiosulfate solutions. Miner. Eng. 2019, 137, 232–240. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eric, O.J. Diagnostic Leaching for Refractory Gold Ores. Available online: https://www.srk.com/en/publications/diagnostic-leaching-for-refractory-gold-ores (accessed on 1 March 2019).
- Acarkan, N.; Bulut, G.; Gül, A.; Kangal, O.; Karakaş, F.; Kökkılıç, O.; Önal, G. The effect of collector’s type on gold and silver flotation in a complex ore. Sep. Sci. Technol. 2010, 46, 283–289. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dunne, R. Flotation of gold and gold-bearing ores. In Gold Ore Processing; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2016; pp. 315–338. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Forrest, K.; Yan, D.; Dunne, R. Optimisation of gold recovery by selective gold flotation for copper-gold-pyrite ores. Miner. Eng. 2001, 14, 227–241. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, M.; Sun, Y.; Duan, H.; Xie, D.; Chen, Z.; Wang, J.; Wang, C. A working condition recognition method based on multivariable trend analysis for gold-antimony rougher flotation. Miner. Eng. 2020, 156, 106493. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Teague, A.; Van Deventer, J.; Swaminathan, C. A conceptual model for gold flotation. Miner. Eng. 1999, 12, 1001–1019. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- O’Connor, C.; Dunne, R. The flotation of gold bearing ores—A review. Miner. Eng. 1994, 7, 839–849. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Røisi, I.; Aasly, K. The effect of graphite filler in sample preparation for automated mineralogy—A preliminary study. Mineralproduksjon 2018, 8, A1–A23. [Google Scholar]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions, and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions, or products referred to in the content. |


| Reagent | Removed Material |
|---|---|
| Sodium cyanide | Gold |
| Sodium carbonate | Gypsum and arsenates |
| Hydrochloric acid | Pyrrhotite, calcite, dolomite, galena, and goethite |
| Hydrochloric acid/Tin(II) chloride | Hematite, calcine, and ferrites |
| Sulfuric acid | Uraninite, sphalerite, unstable copper sulfides, unstable base metal sulfides, and unstable pyrite |
| Iron(III) chloride | Sphalerite, galena, unstable sulfides, and tetrahedrite |
| Nitric acid | Pyrite, arsenopyrite, and marcasite |
| Oxalic acid | Oxide coatings |
| Hydrofluoric acid | Silicates |
| Acetonitrile elution | Loaded carbons |
| Material | Method | Reference |
|---|---|---|
| Refractory gold ore | QEMSCAN and diagnostic leaching | [25] |
| Complex gold ore | PIXE and diagnostic leaching | [26] |
| Flotation tailing | Diagnostic leaching | [27] |
| Roasted calcine sample | Diagnostic leaching | [27] |
| Refractory arsenic–silver ore | MLA and diagnostic leaching | [32] |
| Refractory gold–silver ore | Diagnostic leaching | [29] |
| Refractory gold ore | Diagnostic leaching | [30] |
| Complex gold ore | QEMSCAN and diagnostic leaching | [33] |
| Flotation concentrate | Diagnostic leaching | [34] |
| Refractory gold–silver ore | Diagnostic leaching | [36] |
| Refractory arsenic–gold ore | X-ray spectrometer (EDS), electron probe microanalysis (EPMA), and diagnostic leaching | [37] |
| Refractory gold ore | Diagnostic leaching | [38] |
| Carbonaceous gold ore | Diagnostic leaching | [39] |
| Stage | Feed Product | Solid Ratio (%, w/w) | Leaching Time (h) | Reagent | Temperature (°C) | pH | DO |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1st stage | Flotationconcentrate | 45 | 48 | NaCN 5 kg/t | 25 | 11.5–12.0 | 20–30 |
| 2nd stage | Residue of the previous leaching | 33 | 24 | HCl %12 v/v | 70 | - | |
| Residue of the previous leaching | 45 | 48 | NaCN 1 kg/t | 25 | 11.5–12.0 | 20–30 | |
| 3rd stage | Residue of the previous leaching | 33 | 24 | H2SO4 %48 v/v | 80 | - | |
| Residue of the previous leaching | 45 | 48 | NaCN 1 kg/t | 25 | 11.5–12.0 | 20–30 | |
| 4th stage | Residue of the previous leaching | 33 | 24 | FeCl3 100 mg/L, 2 M HCl | 95 | - | |
| Residue of the previous leaching | 45 | 48 | NaCN 1 kg/t | 25 | 11.5–12.0 | 20–30 | |
| 5th stage | Residue of the previous leaching | 33 | 24 | HNO3 %55 v/v | 90 | - | |
| Residue of the previous leaching | 45 | 48 | NaCN 1 kg/t | 25 | 11.5–12.0 | 20–30 |
| Method | Element | Unit | Content | Element | Unit | Content |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| ICP-OES | Au | g/t | 0.7 | Fe | wt% | 3.4 |
| Ag | g/t | 1.2 | S | wt% | 2.5 | |
| Cu | g/t | 73.1 | C | wt% | 0.4 | |
| As | g/t | 449.8 | Ni | g/t | 93.1 | |
| Pb | g/t | 94.5 | Zn | g/t | 95.1 | |
| Mo | g/t | 13.0 | Cr | g/t | 28.3 | |
| Sn | g/t | <10 | Sb | g/t | 21.6 | |
| XRF | Al2O3 | wt% | 10.8 | SiO2 | wt% | 73.7 |
| K2O | wt% | 2.1 | SO3 | wt% | 2.5 | |
| CO2 | wt% | 4.8 | MgO | wt% | 0.8 | |
| TiO2 | wt% | 0.4 | Na2O | wt% | 0.2 |
| Leaching Size, d80 (µm) | Leaching Time (h) | Au Recovery (%) | NaCN Consumption (kg/t) |
|---|---|---|---|
| 45 | 2 | 32.2 | 0.28 |
| 8 | 35.5 | 0.69 | |
| 24 | 37.0 | 0.82 | |
| 48 | 38.6 | 0.90 | |
| 72 | 39.0 | 0.98 | |
| 73 | 2 | 35.8 | 0.37 |
| 8 | 35.8 | 0.56 | |
| 24 | 39.2 | 0.75 | |
| 48 | 39.2 | 0.86 | |
| 72 | 39.7 | 0.97 | |
| 106 | 2 | 29.8 | 0.38 |
| 8 | 33.4 | 0.49 | |
| 24 | 33.4 | 0.54 | |
| 48 | 36.8 | 0.62 | |
| 72 | 36.8 | 0.69 |
| Product | Mass (wt%) | Au Content (ppm) | Au Recovery (wt%) |
|---|---|---|---|
| Concentrate | 15.9 | 2.5 | 59.7 |
| Tailing | 84.1 | 0.3 | 40.3 |
| Total | 100.0 | 0.7 | 100.0 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Guner, M.K.; Bulut, G.; Hassanzadeh, A.; Lode, S.; Aasly, K. Automated Mineralogy and Diagnostic Leaching Studies on Bulk Sulfide Flotation Concentrate of a Refractory Gold Ore. Minerals 2023, 13, 1243. https://doi.org/10.3390/min13101243
Guner MK, Bulut G, Hassanzadeh A, Lode S, Aasly K. Automated Mineralogy and Diagnostic Leaching Studies on Bulk Sulfide Flotation Concentrate of a Refractory Gold Ore. Minerals. 2023; 13(10):1243. https://doi.org/10.3390/min13101243
Chicago/Turabian StyleGuner, Mustafa K., Gülay Bulut, Ahmad Hassanzadeh, Stefanie Lode, and Kurt Aasly. 2023. "Automated Mineralogy and Diagnostic Leaching Studies on Bulk Sulfide Flotation Concentrate of a Refractory Gold Ore" Minerals 13, no. 10: 1243. https://doi.org/10.3390/min13101243
APA StyleGuner, M. K., Bulut, G., Hassanzadeh, A., Lode, S., & Aasly, K. (2023). Automated Mineralogy and Diagnostic Leaching Studies on Bulk Sulfide Flotation Concentrate of a Refractory Gold Ore. Minerals, 13(10), 1243. https://doi.org/10.3390/min13101243









