Study on the Reverse Flotation Separation of Smithsonite from Dolomite Using the Saponified 2-(4,4-Dimethylpentan-2-yl)-5,7,7-trimethyloctanoic Acid as a Collector
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Minerals and Reagents
2.2. Micro-Flotation Tests
2.3. Zeta Potential Measurement
2.4. ATR-FTIR Spectroscopy
2.5. Depth-Profiling XPS Analysis
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Micro-Flotation Results
3.1.1. Micro-Flotation Tests on Single Minerals
3.1.2. Micro-Flotation Tests on Artificially Mixed Minerals
3.2. Zeta Potential Measurement Results
3.3. ATR-FTIR Spectra Analysis
3.4. XPS Depth Profile Analysis
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- U.S. Geological Survey. Mineral Commodity Summaries 2023; U.S. Geological Survey: Reston, VA, USA, 2023; 210p. [CrossRef]
- Feng, D.; Bai, L.; Xie, H.; Tong, X. Study on Separation of Low-Grade Zinc Oxide Ore with Sulfurizationamination Flotation. Physicochem. Probl. Miner. Process. 2019, 55, 1082–1090. [Google Scholar]
- Araújo, A.C.A.; Lima, R.M.F. Influence of Cations Ca2+, Mg2+ and Zn2+ on the Flotation and Surface Charge of Smithsonite and Dolomite with Sodium Oleate and Sodium Silicate. Int. J. Miner. Process. 2017, 167, 35–41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ejtemaei, M.; Irannajad, M.; Gharabaghi, M. Influence of Important Factors on Flotation of Zinc Oxide Mineral Using Cationic, Anionic and Mixed (Cationic/Anionic) Collectors. Miner. Eng. 2011, 24, 1402–1408. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Irannajad, M.; Ejtemaei, M.; Gharabaghi, M. The Effect of Reagents on Selective Flotation of Smithsonite-Calcite-Quartz. Miner. Eng. 2009, 22, 766–771. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, L.; Hu, G.; Sun, W.; Khoso, S.A.; Liu, R.; Zhang, X. Selective Flotation of Smithsonite from Dolomite by Using Novel Mixed Collector System. Trans. Nonferrous Met. Soc. China 2019, 29, 1082–1089. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luo, B.; Liu, J.; Liu, Q.; Song, C.; Yu, L.; Li, S.; Lai, H. A Mechanism for the Adsorption of 2-(Hexadecanoylamino)Acetic Acid by Smithsonite: Surface Spectroscopy and Microflotation Experiments. Minerals 2019, 9, 15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dhar, P.; Thornhill, M.; Kota, H.R. An Overview of Calcite Recovery by Flotation. Mater. Circ. Econ. 2020, 2, 9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luo, Y.; Zhang, G.; Li, C.; Mai, Q.; Liu, H.; Zhou, H.; Shi, Q. Flotation Separation of Smithsonite from Calcite Using a New Depressant Fenugreek Gum. Colloids Surf. A Physicochem. Eng. Asp. 2019, 582, 123794. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, H.; Yang, Z.; Zhang, Y.; Xie, F.; Luo, X. Flotation Separation of Smithsonite from Calcite by Using Flaxseed Gum as Depressant. Miner. Eng. 2021, 167, 106904. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, D.; Li, B.; Feng, D.; Xie, X.; Mo, F.; Tong, X.; Song, Q. Flotation Separation of Smithsonite from Calcite with Guar Gum as Depressant. Colloids Surf. A Physicochem. Eng. Asp. 2022, 650, 129562. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, H.; Niu, F.; Zhang, J. Investigation on the Flotation Separation of Smithsonite from Calcite Using Calcium Lignosulphonate as Depressant. Colloids Surf. A Physicochem. Eng. Asp. 2021, 630, 127571. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, C.; Wang, X.; Yang, S.; Ren, Z.; Li, C.; Hu, Z. Utilization of Polyepoxysuccinic Acid as a Green Depressant for the Flotation Separation of Smithsonite from Calcite. Miner. Eng. 2021, 168, 106933. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zeng, Y.; Yao, X.; Liu, G.; He, G.; Yu, X.; He, G.; Huang, Z.; Zhang, R.; Cheng, C. Flotation Behavior and Mechanism of Phenylpropenyl Hydroxamic Acid for the Separation of Smithsonite and Calcite. J. Mol. Liq. 2021, 339, 116893. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Y.; Guo, X.; Chen, Y. Using Phytic Acid as a Depressant for the Selective Flotation Separation of Smithsonite from Calcite. Sep. Purif. Technol. 2022, 302, 122104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, C.; Zhang, W.; Song, S.; Li, H.; Liu, Y. Flotation Separation of Smithsonite from Calcite Using 2-Phosphonobutane-1,2,4-Tricarboxylic Acid as a Depressant. Powder Technol. 2019, 352, 11–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, L.; Shen, L.; Sun, W.; Zhang, X.; Zhang, Y.; Wang, Y. Selective Flotation Separation of Smithsonite from Dolomite by Using Sodium Hexametaphosphate as a Depressant. Colloids Surf. A Physicochem. Eng. Asp. 2022, 651, 129621. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, L.; Lyu, W.; Zhou, W.; Zhang, H. The Role of Sodium Phytate in the Flotation Separation of Smithsonite from Calcite. Miner. Eng. 2022, 187, 107775. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feng, Q.; Wen, S.; Bai, X.; Chang, W.; Cui, C.; Zhao, W. Surface Modification of Smithsonite with Ammonia to Enhance the Formation of Sulfidization Products and Its Response to Flotation. Miner. Eng. 2019, 137, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feng, Q.; Zhao, W.; Wen, S. Ammonia Modification for Enhancing Adsorption of Sulfide Species onto Malachite Surfaces and Implications for Flotation. J. Alloys Compd. 2018, 744, 301–309. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, M.; Zhang, G.; Chen, Y.; Zhao, L. Effect of Surface Oxidization on Quartz Slime Coating in the Sulfidization-Amine Flotation of Smithsonite. Miner. Eng. 2022, 188, 107847. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wei, Q.; Dong, L.; Qin, W.; Jiao, F.; Qi, Z.; Feng, C.; Sun, D.; Wang, L.; Xiao, S. Efficient Flotation Recovery of Lead and Zinc from Refractory Lead-Zinc Ores under Low Alkaline Conditions. Geochemistry 2021, 81, 125769. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, D.; Ma, W.; Wen, S.; Deng, J.; Bai, S. Enhancing the Sulfidation of Smithsonite by Superficial Dissolution with a Novel Complexing Agent. Miner. Eng. 2017, 114, 1–7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ejtemaei, M.; Gharabaghi, M.; Irannajad, M. A Review of Zinc Oxide Mineral Beneficiation Using Flotation Method. Adv. Colloid Interface Sci. 2014, 206, 68–78. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, Z.; Wang, L.; Ni, X.; Liao, Y.; Liang, Z. Zinc Recovery from Wulagen Sulfide Flotation Plant Tail by Applying Ether Amine Organic Collectors. Molecules 2021, 26, 5365. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhou, Q. Selective Flotation between Smithsonite and Calcite. Ph.D. Thesis, Central South University, Changsha, China, 2010. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, Y. Recovery Valuable Metals from Processing Gangue Minerals. Ph.D. Thesis, Autonomous University of San Luis Potosí, San Luis Potosí, Mexico, 2022. [Google Scholar]
- Dehaine, Q.; Filippov, L.O.; Filippova, I.V.; Tijsseling, L.T.; Glass, H.J. Novel Approach for Processing Complex Carbonate-Rich Copper-Cobalt Mixed Ores via Reverse Flotation. Miner. Eng. 2021, 161, 106710. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Q.; Liu, R.; Cao, X.; Sun, W.; Yang, Y. Relationship between Structure and Property of Collecting Agent for Fatty Acids Scheelite. Nonferrous Met. Sci. Eng. 2013, 4, 85–90. [Google Scholar]
- Sheng, Q.; Yin, W.; Yang, B.; Sun, H.; Yao, J. Efficiently Separating Malachite from Talc Using New Collector Famciclovir via Reverse Flotation. Miner. Eng. 2021, 174, 107243. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, G.; Kazarian, S.G. Recent Advances and Applications to Cultural Heritage Using ATR-FTIR Spectroscopy and ATR-FTIR Spectroscopic Imaging. Analyst 2022, 147, 1777–1797. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fuerstenau, D.W.; Pradip. Zeta Potentials in the Flotation of Oxide and Silicate Minerals. Adv. Colloid Interface Sci. 2005, 114–115, 9–26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, X.; Liu, W.; Wang, L.; Liu, W.; Sun, W.; Zhang, N. A novel depressant N, N-bis (phosphonomethyl) glycine for magnesite-dolomite separation and its mechanism. Miner. Eng. 2023, 202, 108281. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, J.; Xiao, Z.; Zhang, H. Selective Flotation Behavior of Dolomite from Fluorapatite Using Hydroxy Ethylene Diphosphonic Acid as High-Efficiency Depressant. Minerals 2022, 12, 1633. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, Q.; Feng, Q.; Zhang, G.; Deng, H. Electrokinetic properties of smithsonite and its floatability with anionic collector. Colloids Surf. A Physicochem. Eng. Asp. 2012, 410, 178–183. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zou, H.; Cao, Q.; Liu, D.; Yu, X.; Lai, H. Surface Features of Fluorapatite and Dolomite in the Reverse Flotation Process Using Sulfuric Acid as a Depressor. Minerals 2019, 9, 33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, X.; Zhang, R.; Zeng, Y.; Cheng, C.; Huang, Z.; Wang, J.; He, G.; Wang, H. The Effect and Mechanism of Cinnamic Hydroxamic Acid as a Collector in Flotation Separation of Malachite and Calcite. Miner. Eng. 2021, 164, 106847. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cui, Y.; Jiao, F.; Wei, Q.; Wang, X.; Dong, L. Flotation Separation of Fluorite from Calcite Using Sulfonated Lignite as Depressant. Sep. Purif. Technol. 2020, 242, 116698. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, M.; Li, H.; Jiang, T.; Liu, Q. Flotation of Coarse and Fine Pyrochlore Using Octyl Hydroxamic Acid and Sodium Oleate. Miner. Eng. 2019, 132, 191–201. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ebajo, V.D.; Santos, C.R.L.; Alea, G.V.; Lin, Y.A.; Chen, C.H. Regenerable Acidity of Graphene Oxide in Promoting Multicomponent Organic Synthesis. Sci. Rep. 2019, 9, 15579. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dolgov, A.; Lopaev, D.; Lee, C.J.; Zoethout, E.; Medvedev, V.; Yakushev, O.; Bijkerk, F. Characterization of Carbon Contamination under Ion and Hot Atom Bombardment in a Tin-Plasma Extreme Ultraviolet Light Source. Appl. Surf. Sci. 2015, 353, 708–713. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, K.; Zhang, J.; Ma, X.; Ma, Y.; Kan, C.; Ma, H.; Li, Y.; Yuan, Y.; Liu, C. β-Tricalcium Phosphate/Poly(Glycerol Sebacate) Scaffolds with Robust Mechanical Property for Bone Tissue Engineering. Mater. Sci. Eng. C 2015, 56, 37–47. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xing, X.; Wang, B.; Liu, H.; Luo, S.; Wang, S.; Wei, J.; Xu, W.; Yu, Q. The Mechanism of Silane-Grafted Sodium Polyacrylate on the Toughening of Slag-Based Geopolymer: An Insight from Macroscopic–Microscopic Mechanical Properties. J. Mater. Sci. 2023, 58, 8757–8778. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, B.; Wang, D.; Cao, S.; Yin, W.; Xue, J.; Zhu, Z.; Fu, Y.; Yao, J. Selective Adsorption of a High-Performance Depressant onto Dolomite Causing Effective Flotation Separation of Magnesite from Dolomite. J. Colloid Interface Sci. 2020, 578, 290–303. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Li, L.; Dai, P.; Yan, L.; Cao, L.; Gu, X.; Zhao, X. Missing-Node Directed Synthesis of Hierarchical Pores on a Zirconium Metal-Organic Framework with Tunable Porosity and Enhanced Surface Acidity: Via a Microdroplet Flow Reaction. J. Mater. Chem. A 2017, 5, 22372–22379. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, J.P.H.; Zhou, X.; Pang, Y.; Zhu, L.; Vovk, E.I.; Cong, L.; Van Bavel, A.P.; Li, S.; Yang, Y. Understanding of Binding Energy Calibration in XPS of Lanthanum Oxide by: In Situ Treatment. Phys. Chem. Chem. Phys. 2019, 21, 22351–22358. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pang, Y.; Zhou, X.; Vovk, E.I.; Guan, C.; Li, S.; van Bavel, A.P.; Yang, Y. Understanding Lanthanum Oxide Surface Structure by DFT Simulation of Oxygen 1s Calibrated Binding Energy in XPS after in Situ Treatment. Appl. Surf. Sci. 2021, 548, 149214. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, X.; Wang, X.; Fang, D. A Review on C1s XPS-Spectra for Some Kinds of Carbon Materials. Fuller. Nanotub. Carbon Nanostruct. 2020, 28, 1048–1058. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, C.; Bai, S.; Ding, Z.; Yu, P.; Wen, S. Visual MINTEQ Model, ToF–SIMS, and XPS Study of Smithsonite Surface Sulfidation Behavior: Zinc Sulfide Precipitation Adsorption. J. Taiwan Inst. Chem. Eng. 2019, 96, 53–62. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Araújo, M.P.; Soares, O.S.G.P.; Fernandes, A.J.S.; Pereira, M.F.R.; Freire, C. Tuning the Surface Chemistry of Graphene Flakes: New Strategies for Selective Oxidation. RSC Adv. 2017, 7, 14290–14301. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]


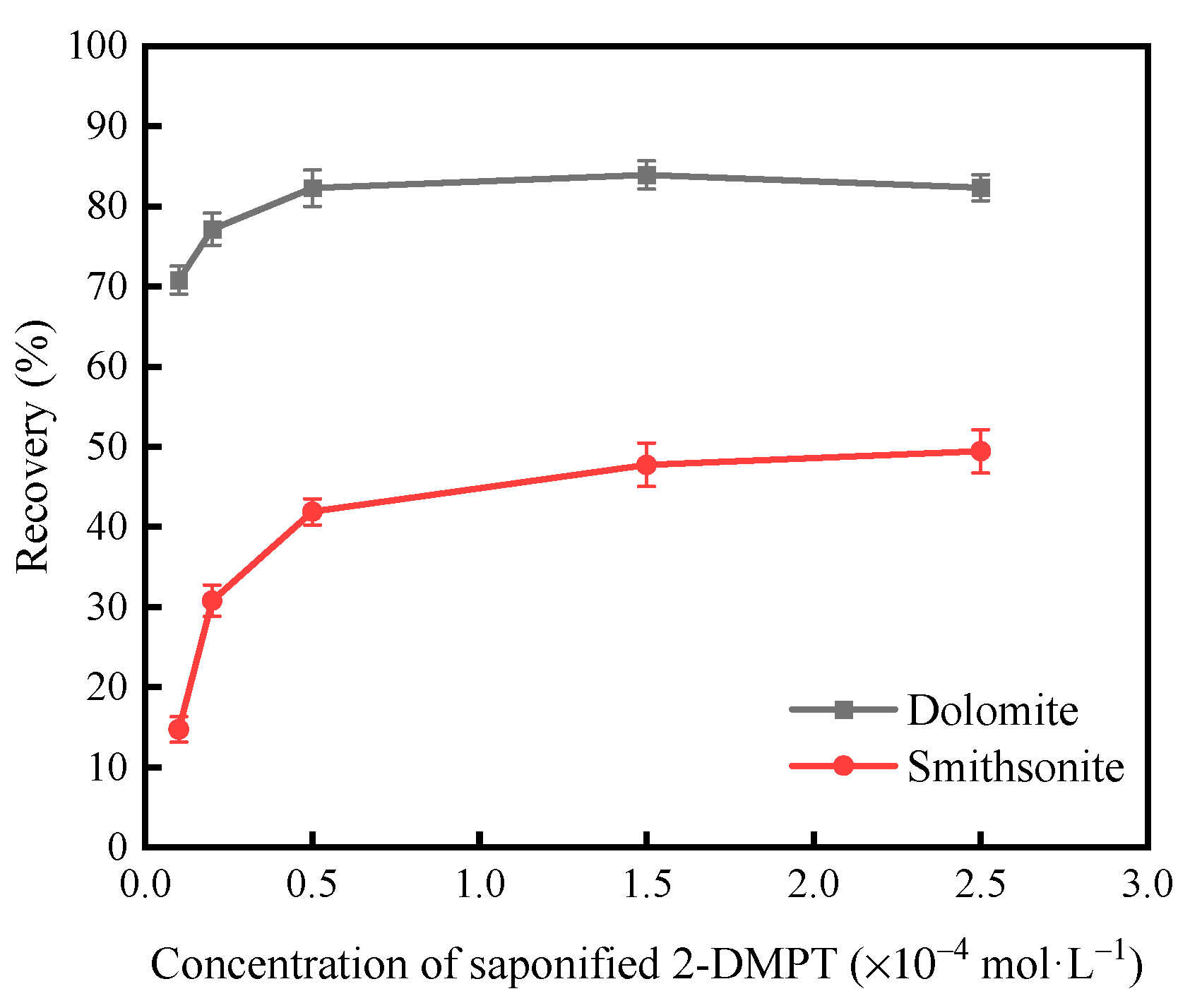

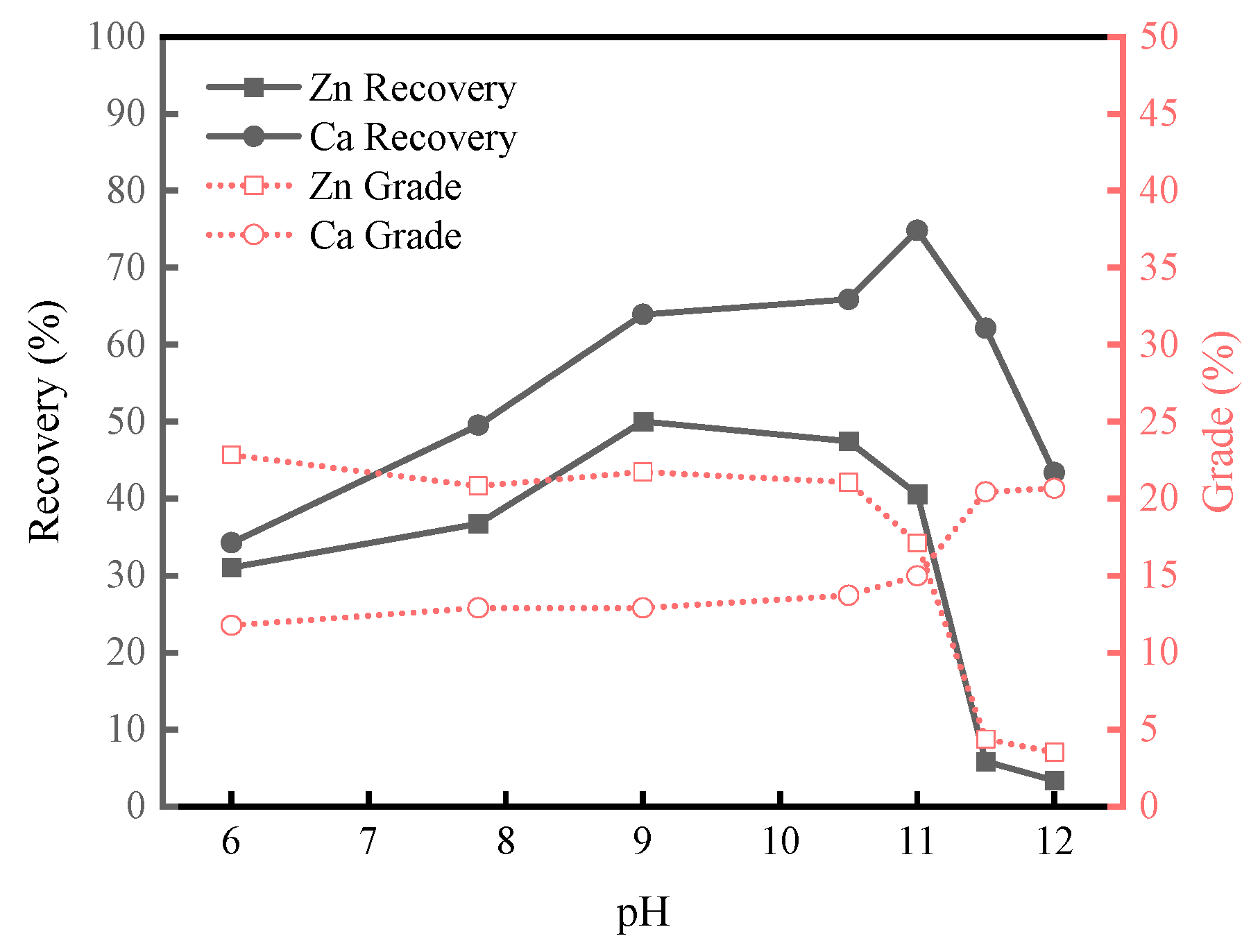
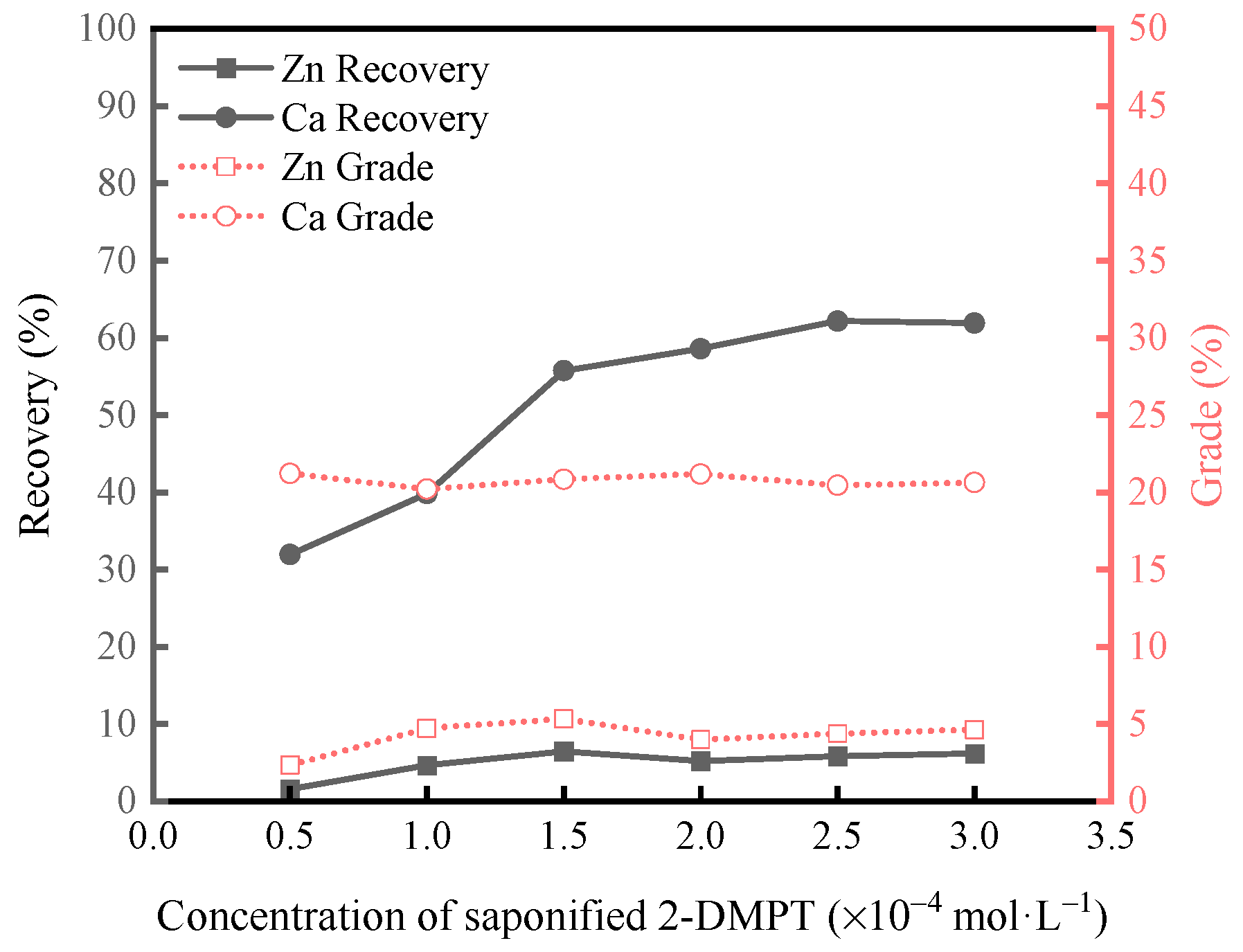

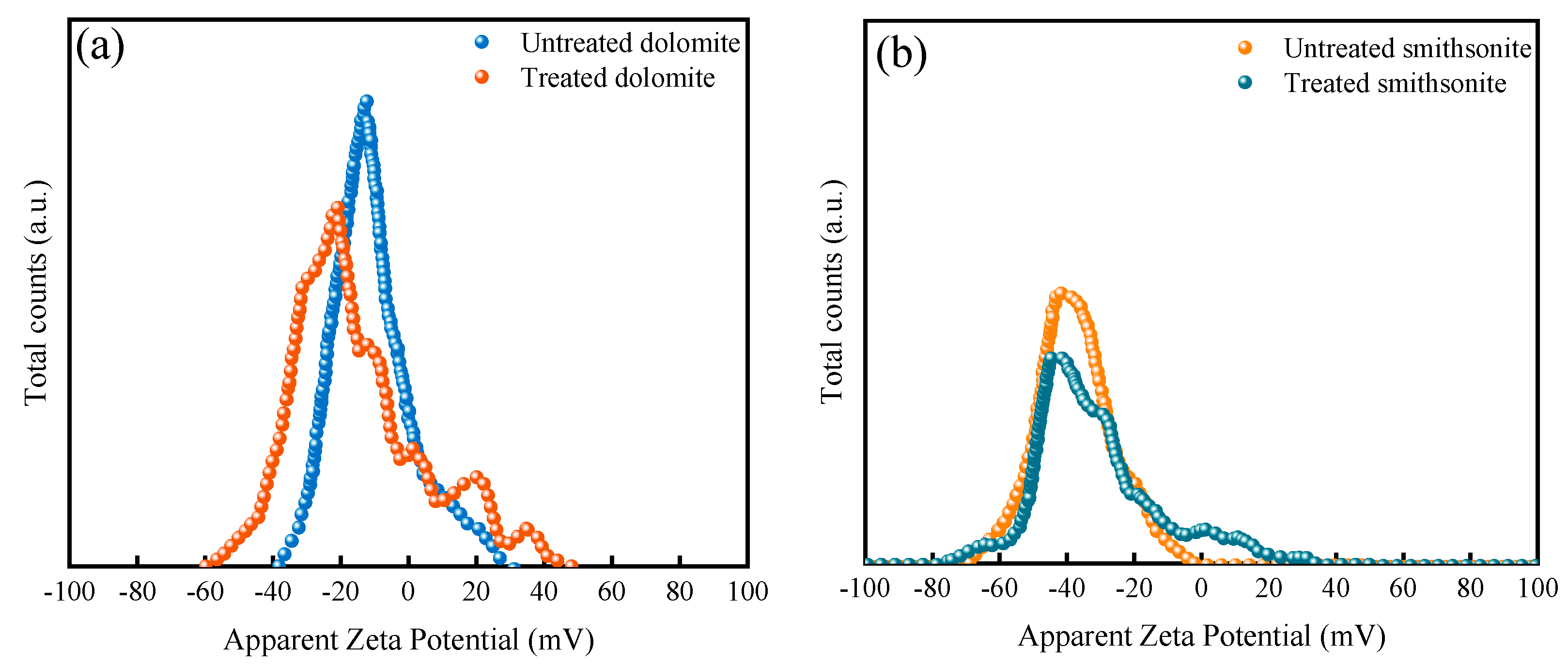
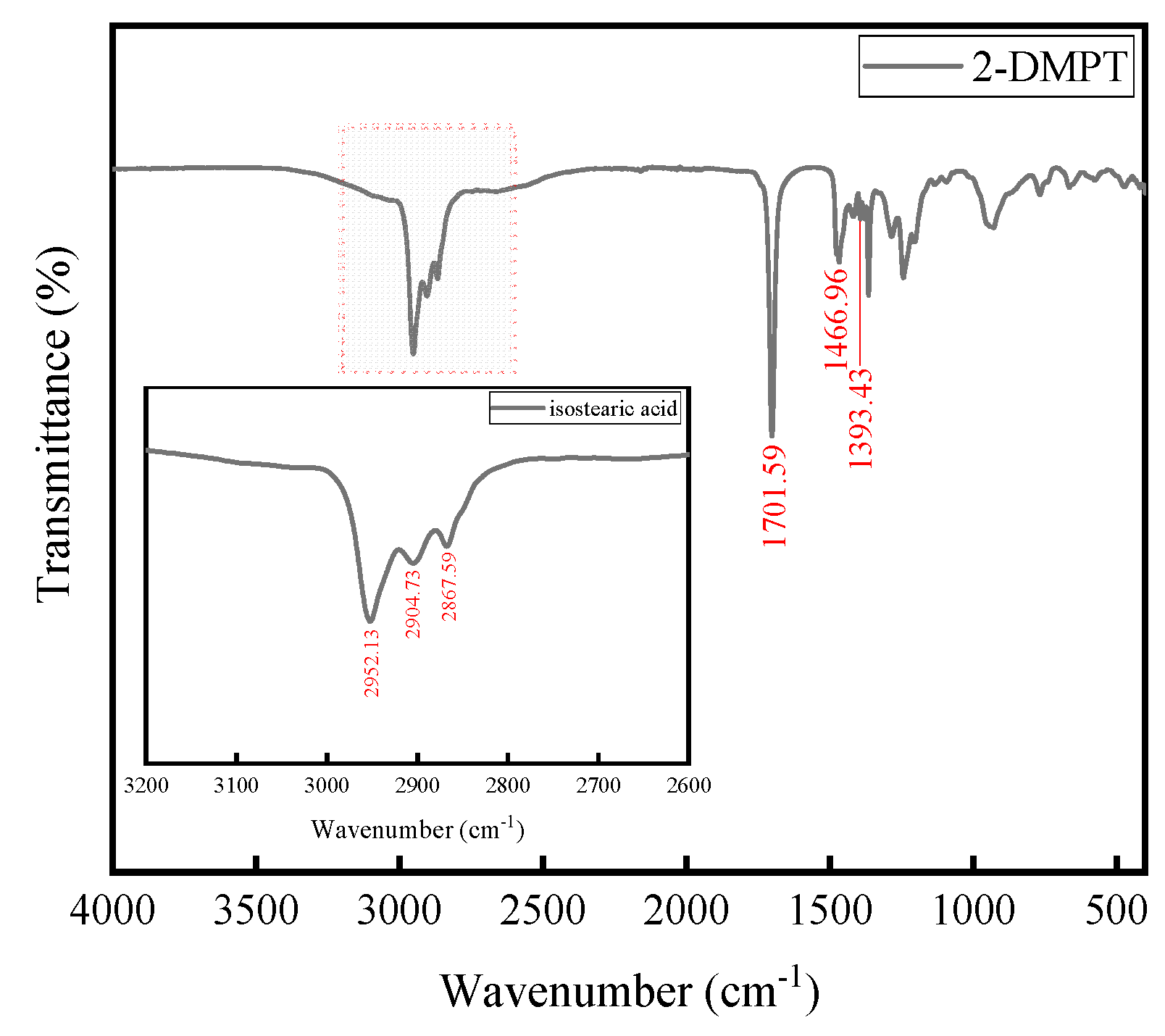
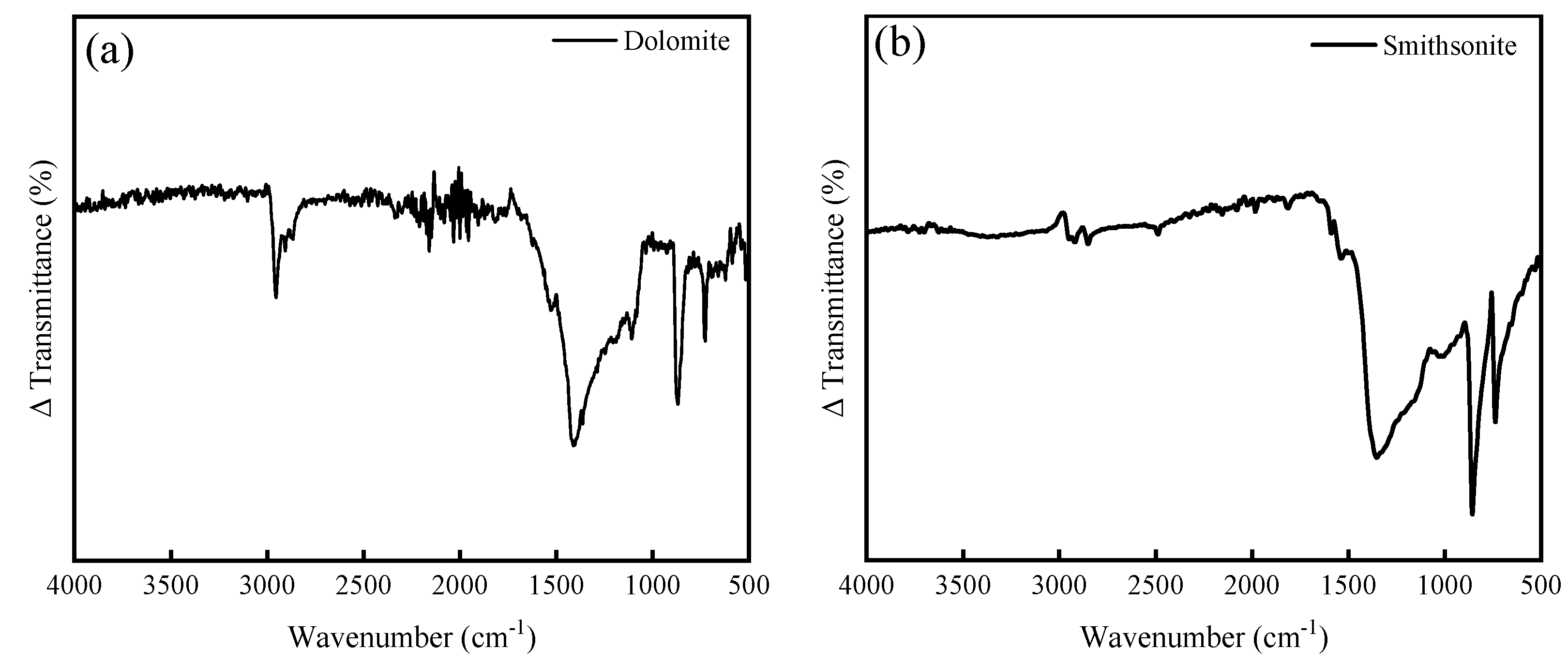

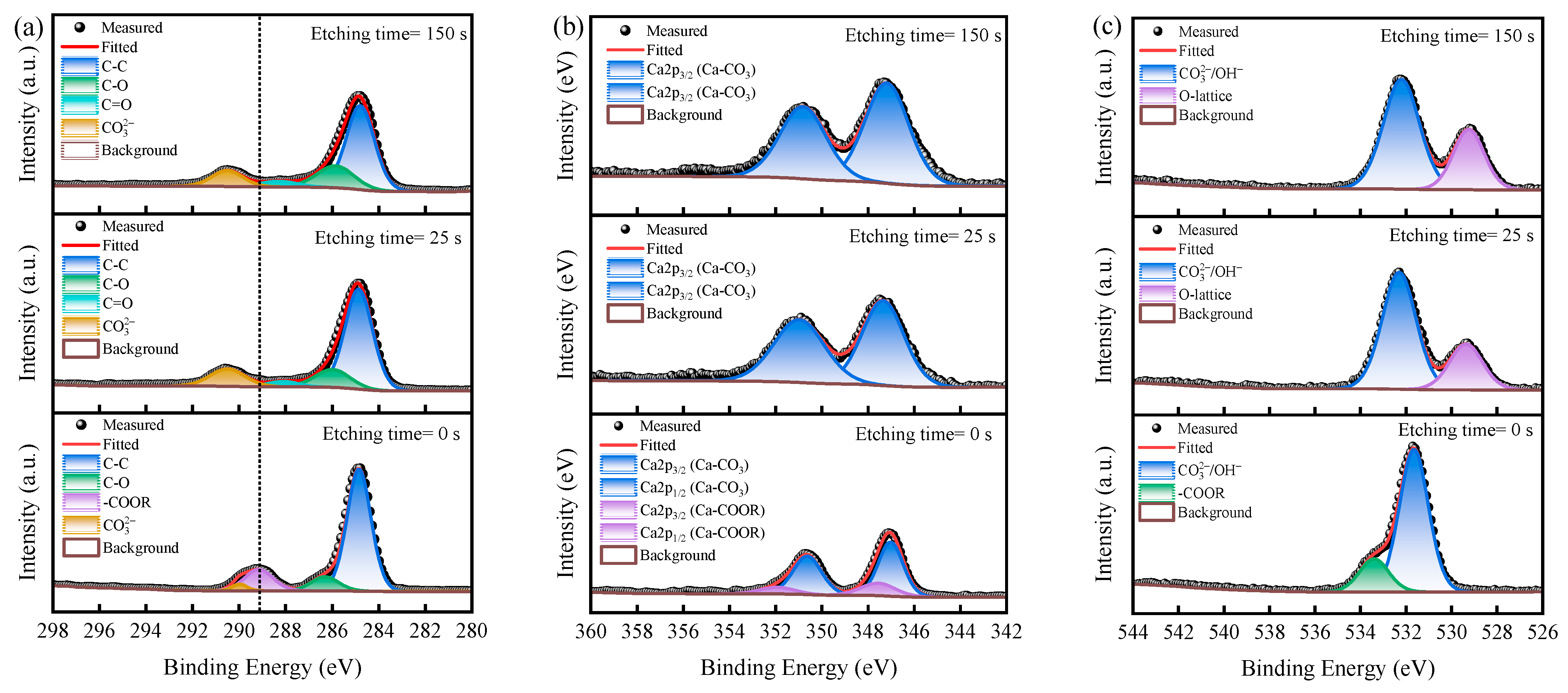
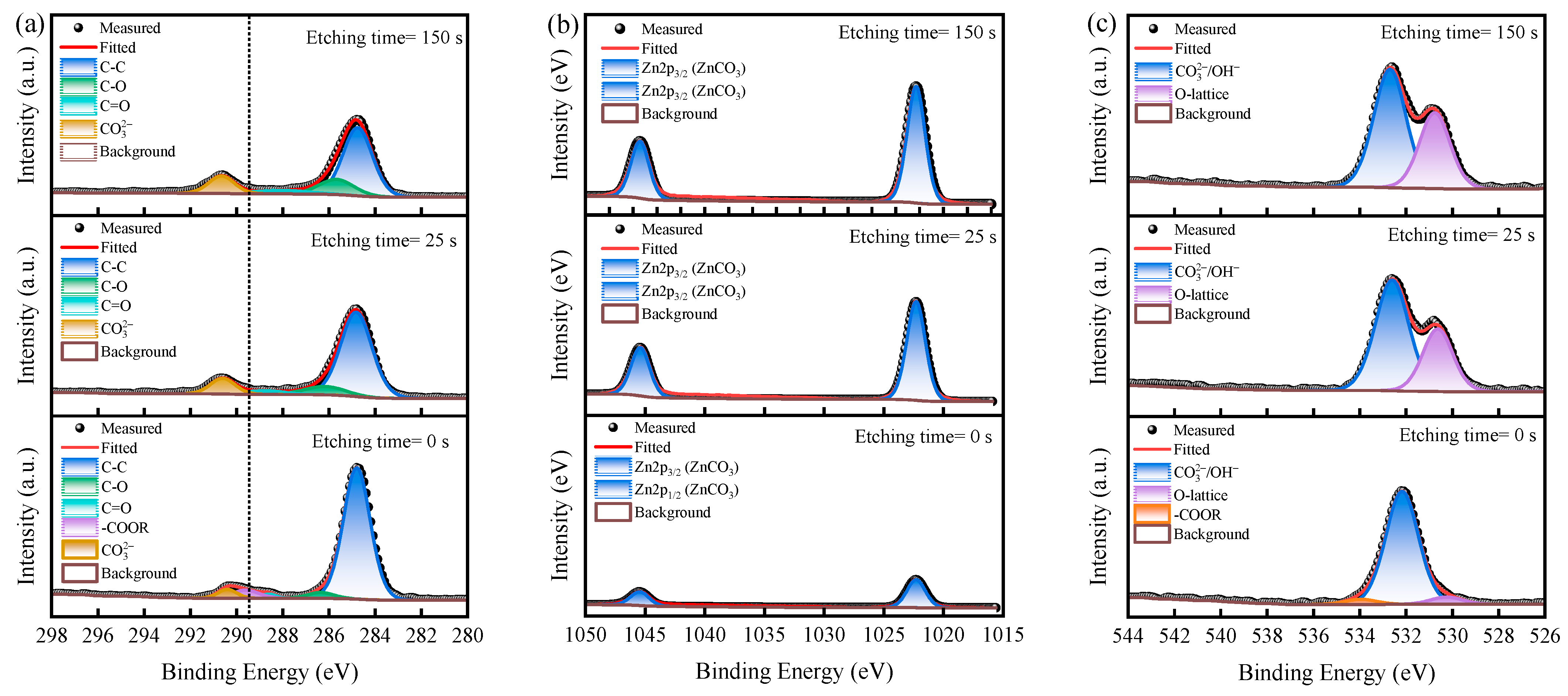
| Sample | CaCO3 | MgCO3 | SiO2 | Al2O3 | TFe | ZnCO3 | Others |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Dolomite | 53.73 | 44.63 | 0.41 | 0.04 | 0.05 | / | 1.14 |
| Smithsonite | / | / | 0.11 | 0.01 | 0.42 | 95.52 | 3.94 |
| Sample | Space Group | Lattice Parameters (Å) | Volume (Å3) | R-Factors | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| a = b | c | Rwp (%) | Rwp (%) | Chi2 | |||
| Dolomite | R3c | 4.8072 | 16.0099 | 320.413 | 13.4 | 18.4 | 2.42 |
| Smithsonite | R3c | 4.6643 | 15.1037 | 284.574 | 10.9 | 13.9 | 2.91 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Zhang, X.; Zhu, Y.; Zhao, Z.; Wang, P. Study on the Reverse Flotation Separation of Smithsonite from Dolomite Using the Saponified 2-(4,4-Dimethylpentan-2-yl)-5,7,7-trimethyloctanoic Acid as a Collector. Minerals 2023, 13, 1322. https://doi.org/10.3390/min13101322
Zhang X, Zhu Y, Zhao Z, Wang P. Study on the Reverse Flotation Separation of Smithsonite from Dolomite Using the Saponified 2-(4,4-Dimethylpentan-2-yl)-5,7,7-trimethyloctanoic Acid as a Collector. Minerals. 2023; 13(10):1322. https://doi.org/10.3390/min13101322
Chicago/Turabian StyleZhang, Xiaoliang, Yangge Zhu, Zhiqiang Zhao, and Peilong Wang. 2023. "Study on the Reverse Flotation Separation of Smithsonite from Dolomite Using the Saponified 2-(4,4-Dimethylpentan-2-yl)-5,7,7-trimethyloctanoic Acid as a Collector" Minerals 13, no. 10: 1322. https://doi.org/10.3390/min13101322
APA StyleZhang, X., Zhu, Y., Zhao, Z., & Wang, P. (2023). Study on the Reverse Flotation Separation of Smithsonite from Dolomite Using the Saponified 2-(4,4-Dimethylpentan-2-yl)-5,7,7-trimethyloctanoic Acid as a Collector. Minerals, 13(10), 1322. https://doi.org/10.3390/min13101322





