Abstract
Feldspar, which is one of the main inputs of the ceramic and glass industries, has widespread sources in Turkey and thus forms a large component of the country’s mineral exportation. In addition to this, potassium feldspars are one of the raw materials suitable for the production of potash, which is a vital component of the agricultural industry. In our work, the chlorination technique was used to produce potassium chloride (KCl) from potassium feldspar ore of the Kırşehir-Buzlukdağı region. The aim of this study was to determine the most suitable and economical additive for producing KCl from potassium feldspar ore with high efficiency. The calcination process was used to decompose potassium feldspar and form potassium chloride using different kinds of salts, such as CaCl2, NaCl, and CaSO4, followed by the water-leaching process. While 93.4% K dissolution efficiency was achieved in the tests performed with CaCl2, the same dissolution efficiency (93.7%) was obtained in the experiments with a CaCl2-NaCl mixture by using less CaCl2. Furthermore, the CaSO4-NaCl mixture achieved the highest dissolution efficiency. The recovery of KCl from feldspar, by assaying its 7.21% K2O, was carried out using a 1:1.25:1.5 ratio of feldspar:CaSO4:NaCl at 1000 °C for 60 min, followed by leaching, to obtain KCl with 96.1% potassium dissolution.
1. Introduction
Potash, often known as KCl, is a general name for potassium compounds. Ninety percent of potash usage is attributed to fertilizer production, which is an essential component of agriculture. Potassium chloride (KCl) stands as the predominant source of potassium employed in global agriculture, as approximately 96% of the world’s potash production is used in fertilizers. The remaining 4% is supplied by potassium sulfate (K2SO4), potassium nitrate (KNO3), and potassium-magnesium salts. The potassium content in KCl fertilizers is often quantified in terms of its oxide equivalent (K2O), and commercial KCl fertilizers typically exhibit a potassium oxide (K2O) content ranging between 60% and 62%, rendering them a very potassium-rich option among the various potassium fertilizers [1]. Potash fertilizers are used because they are useful in assisting with water retention, nutritional value, crop food resistance, and flavor [2]. Excess calcium and magnesium in the soil prevents potassium uptake. In order for potassium to have sufficient efficiency of use in a plant, there must be enough nitrogen present as well. Low potassium makes the plant tasteless, the fruits of the plant that cannot get enough potassium are shapeless, fruit quality decreases, and damage increases in winter frost events. Among various fruit species, potassium deficiency is very commonly found in peaches. The majority of important potash deposits are in Canada, Germany, France, Spain, and Russia, with Canada dominating in reserves and production [3]. Depending on the deposit, potash can be obtained using conventional mining methods, solution mining methods, or from lakes [4]. However, with its rising demand and limited resources, different methods of producing potash are being investigated. Potassium feldspar and nepheline syenite are the most effective minerals for producing potash. Several studies have been conducted to produce potash from potassium feldspar using various additives (Table 1).

Table 1.
Selected studies that have produced potash from K-feldspar utilizing different kinds of additives.
Feldspar is abundant in the Earth’s crust and is mainly utilized in the glass and ceramic industries. Feldspar is defined by its K2O content. If the K2O content is over 10%, it is called potassium feldspar. Turkey is the leading country in feldspar production in the world. Besides Turkey, China, Italy, India, and Thailand are other countries that have a share in feldspar production [17]. Feldspar can be used to produce potash, especially KCl, via the chlorination process. Feldspar constitutes a three-dimensional-lattice network of interconnected tetrahedrons containing oxygen (O), aluminum (Al), and silicon (Si) atoms. Each aluminum atom within this structure forms bonds with four oxygen atoms arranged in a tetrahedral configuration. To maintain electrical neutrality within this mineral, positively charged ions, such as potassium (K), sodium (Na), and calcium (Ca), are incorporated into the lattice. In the context of extracting potassium from feldspar using inorganic acids, the efficiency of leaching is relatively modest. To liberate potassium from this lattice, it is imperative to disrupt the crystal structure of feldspar. Both sodium chloride (NaCl) and calcium chloride (CaCl2) have the capacity to engage with feldspar at elevated temperatures, thereby facilitating the conversion of potassium into its soluble form [18]. The roast-leaching method is a commonly used approach for potassium extraction from complex minerals. It involves two steps: roasting the mineral with a chloride-containing additive at a specific temperature and then leaching the roasted material. The free energy–temperature diagram of the metal–chloride system demonstrates that the standard free energy change for producing KCl is smaller at 900 °C than for other achievable metal chlorides. The choice of additive is critical for facilitating the formation of water-soluble potassium chloride (KCl). Maintaining the roasting temperature above the additive’s melting point is crucial to achieving high extraction efficiency, typically 80%–95%. This method is preferred for its simplicity and efficiency in recovering potassium from challenging mineral sources [19]. K+ and Ca2+ ions can exchange within a crystal matrix due to their similar electronic properties, which are more favorable than those of Na+ ions. The larger size of Ca2+ makes it a better substitute for K+ in the crystal lattice than Na+. In feldspar, K+ balances charges, releasing two potassium ions for every Ca2+ during extraction. Meanwhile, NaCl creates a water-soluble sodium silicate, which increases the solution’s viscosity and hinders the crystal structure’s breakdown when compared to CaCl2. Therefore, Ca2+ is a superior replacement due to its higher charge and larger size, resulting in a higher cation exchange factor for CaCl2 over that of NaCl. The formation and release of KCl are also influenced by electronegativity differences and lattice energy values [18]. Ciceri et al. [20] presented a review including a list of patents for potash production from K-feldspar. There have been laboratory-scale studies with K-feldspar, but no industrial-scale studies have yet been conducted.
The objective of this research was to find the most cost-effective approach to producing KCl from potassium feldspar through the use of various types of additives. The aim was to extract potassium from feldspar using a roasting process, followed by water leaching, utilizing various types of salts, such as CaCl2, NaCl, and CaSO4. Experiments were carried out with a CaCl2 additive that gave the best performance based on the literature on KCl production from feldspar. However, due to the high cost of CaCl2, NaCl salt was used as the chlorine source in order to both reduce the ratio of CaCl2 salt and find additives with similar performance. CaSO4 salt was used to prevent the sodium ion from being released during the roasting process and also from reacting with the chlorine ion again.
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Materials and Characterization
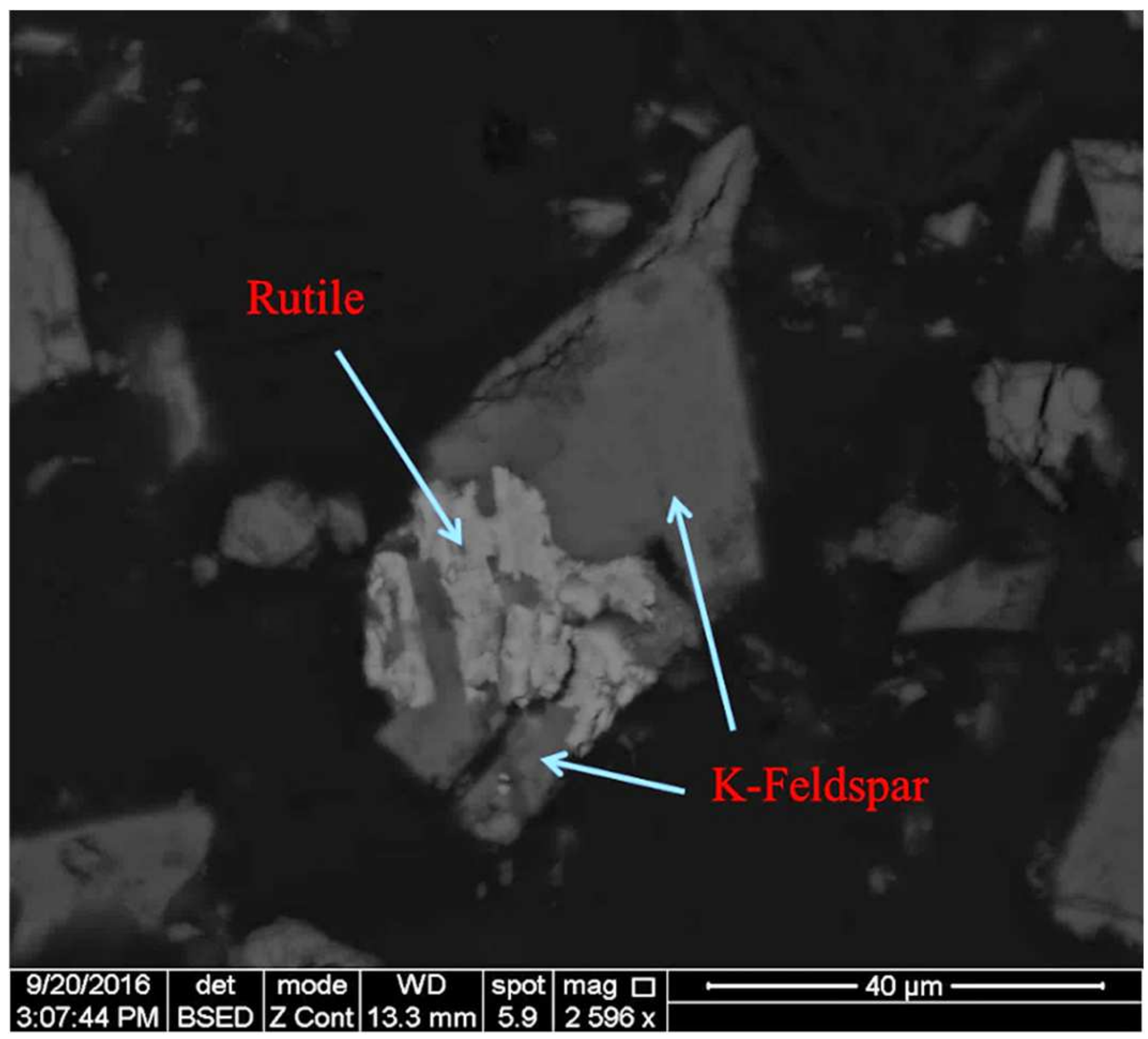
Feldspar ore, obtained from the Kırşehir-Buzlukdağı region of Turkey, was used in this experiment’s studies. The feldspar ore was crushed to less than 2 mm using a roll crusher. A representative sample was taken from the crushed sample for characterization. A 106-micron particle size was chosen based on previous studies conducted with the same sample. Afterward, the sample was ground to less than 106 microns with a ceramic mill. The ceramic mill was chosen for the grinding step to avoid contaminants. The grinding process used a 60% solid ratio with a 40% ball charge. The feldspar sample with a size of less than 106 microns was used in all of the experiments. In order to determine the chemical composition of the ore, the Varian brand inductively coupled plasma (ICP) from Activation Laboratories Ltd. (Hamilton, ON, Canada) was used for analyses (Table 2). Analyses were carried out in Actlabs, which is accredited according to international quality standards through the Standards Council of Canada (SCC), the Canadian Laboratory Accreditation Association (CALA), Health Canada, the Food and Drug Administration (FDA), and the Ontario Ministry of Agriculture and Food (OMAFRA). Additionally, Actlabs is accredited and/or certified to ISO/IEC17025:2017, ISO 9001:2015, Health Canada Licensed, FDA Registered and Inspected, OMAFRA, and GMP/GLP Compliant standards [21]. According to chemical analyses, the feldspar ore contained 7.21% K2O and 4.9% Na2O within its structure. The BSE (Back-Scattered Electron) images of samples are given in Figure 1. A significant quantity of K-feldspar was present with rutile, which was present as an accessory mineral, according to the image analysis produced with SEM using the XFlash 5010 SDD (Bruker, Billerica, MA, USA) device.

Table 2.
Chemical analyses of the ore.
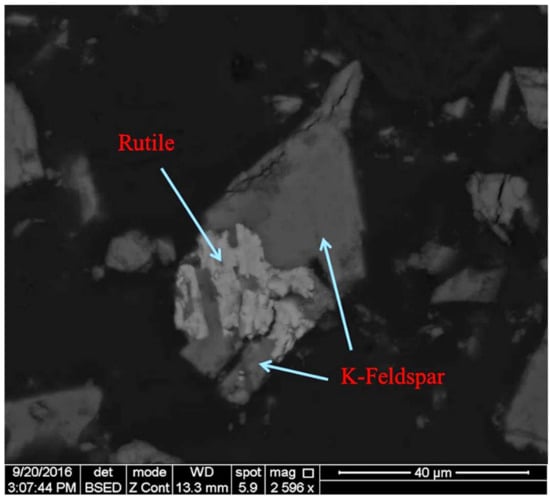

Figure 1.
Imaging analysis of the ore.
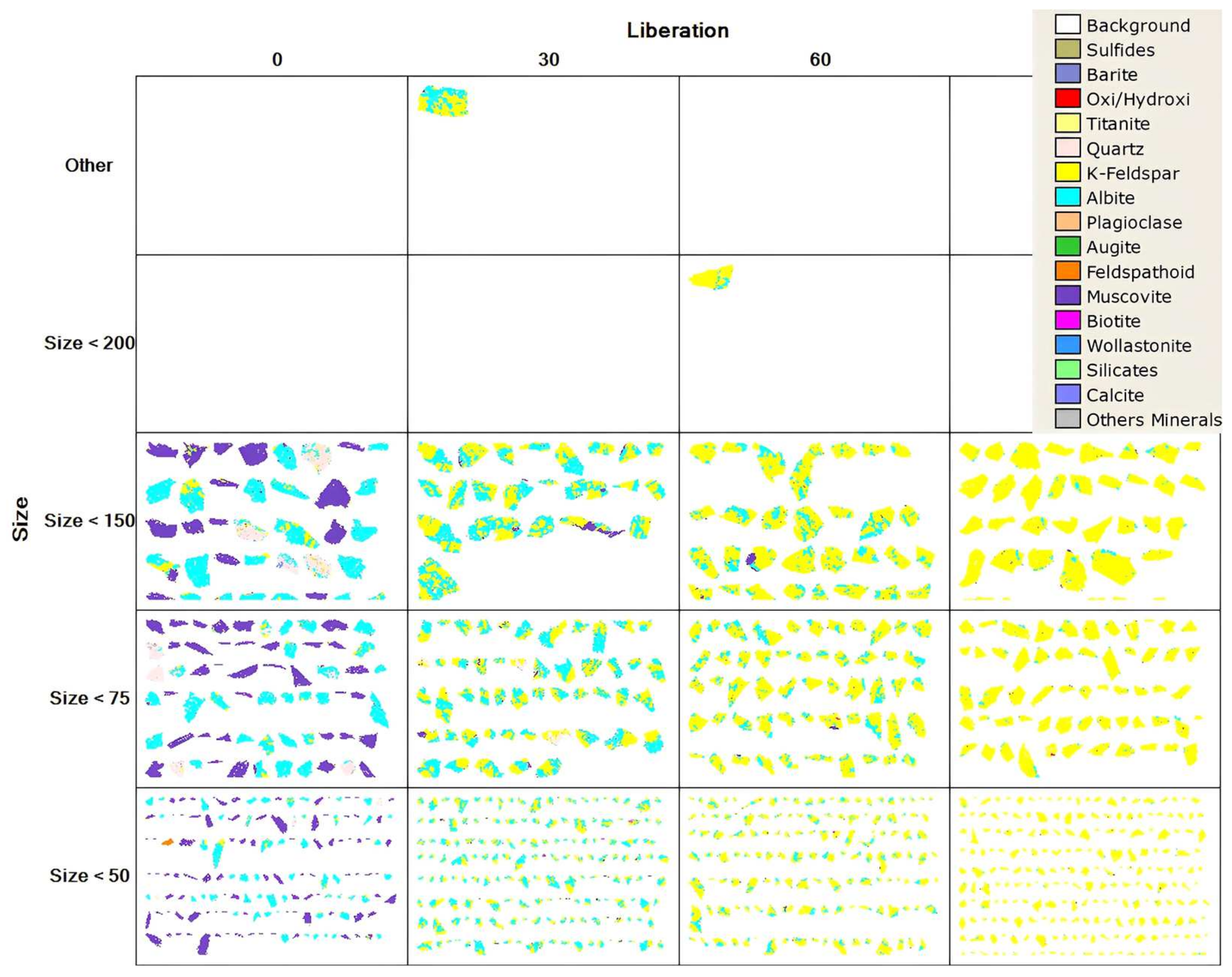
Modal mineralogy and mineral liberation analyses were performed using the MLA 650F (FEI, Brisbane, QLD, Australia) device, and the results are given in Table 3 and Figure 2, respectively. According to the modal mineralogy analyses, the ore contained 39.96% potassium feldspar (KAlSi3O8) and 27.08% muscovite (KAl3Si3O10(OH)2) as a potassium source and also contained a significant amount of albite (NaAlSi3O8). The MLA (Mineral Liberation Analysis) showed that, at under 200 microns, 90% of K-feldspar was liberated.

Table 3.
Modal mineralogy analyses of ore.
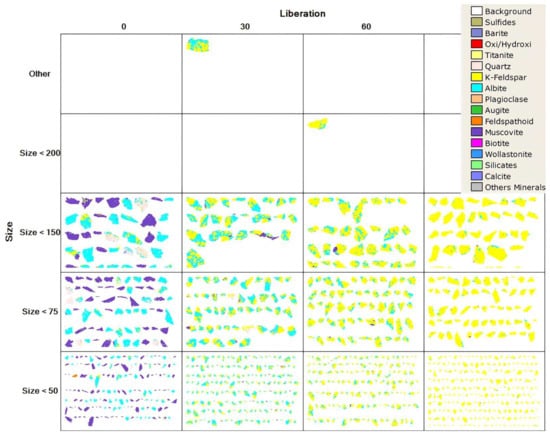
Figure 2.
MLA of the ore.
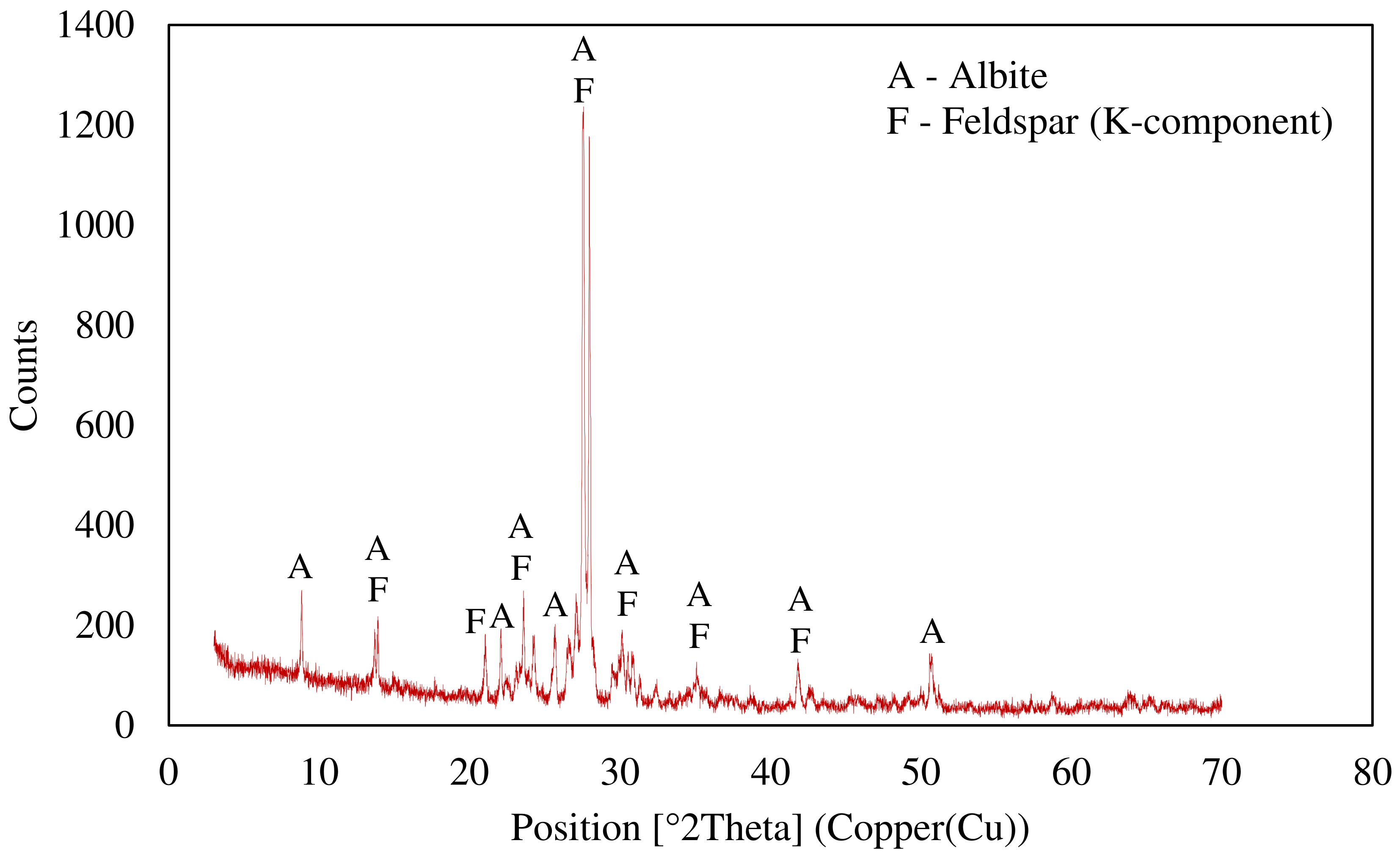
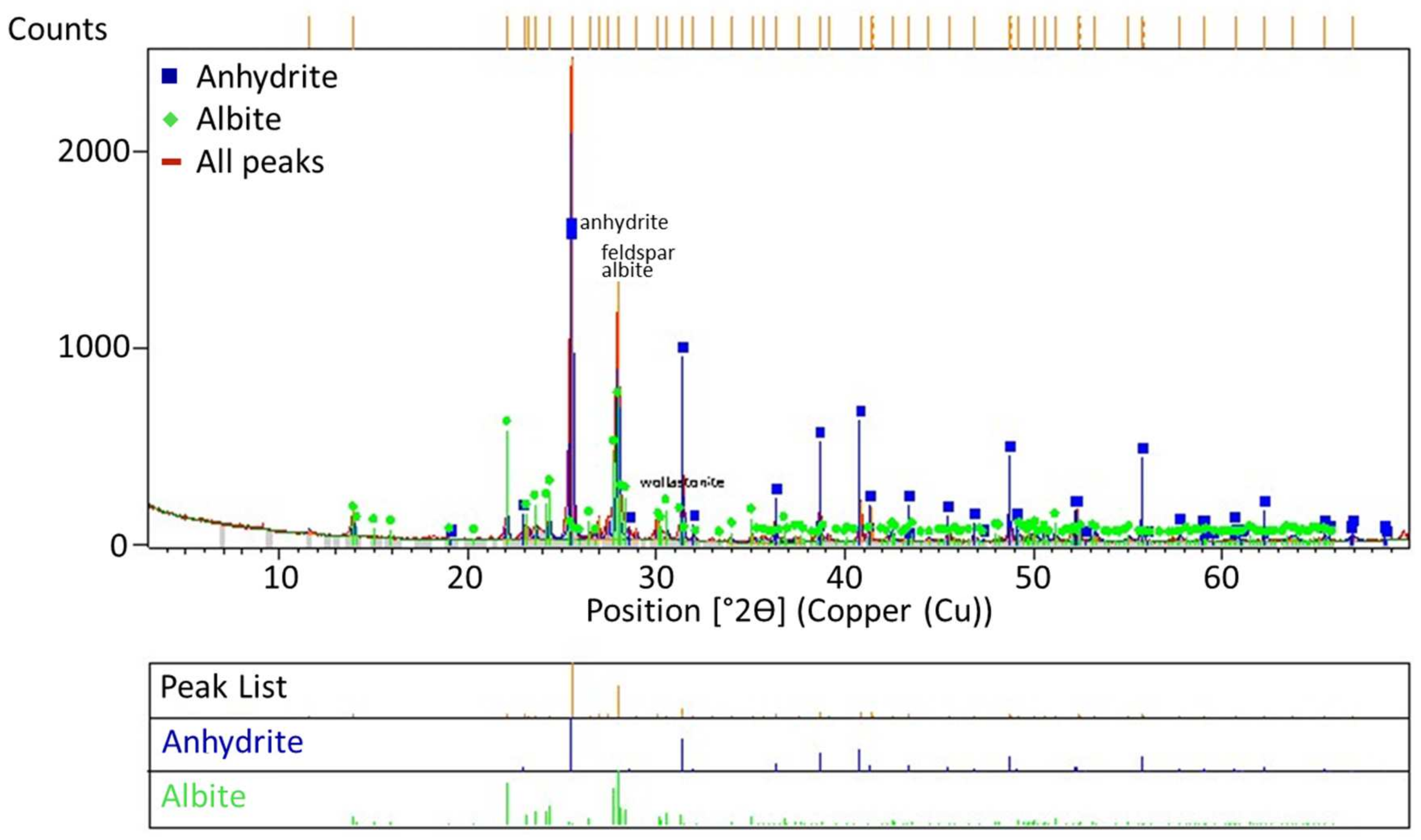
An X-ray diffraction (XRD) analysis was conducted with a copper X-ray-sourced Panalytical X’Pert Pro diffractometer (UK), using PDF4/Minerals ICDD software for mineral characterization. The XRD pattern of the ore is given in Figure 3 and the results display that the ore was mainly composed of K-feldspar and albite.
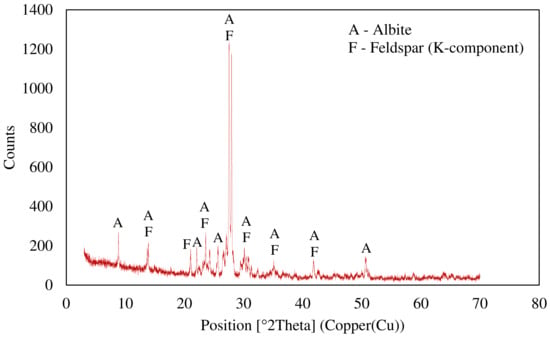
Figure 3.
X-ray diffraction pattern of the ore.
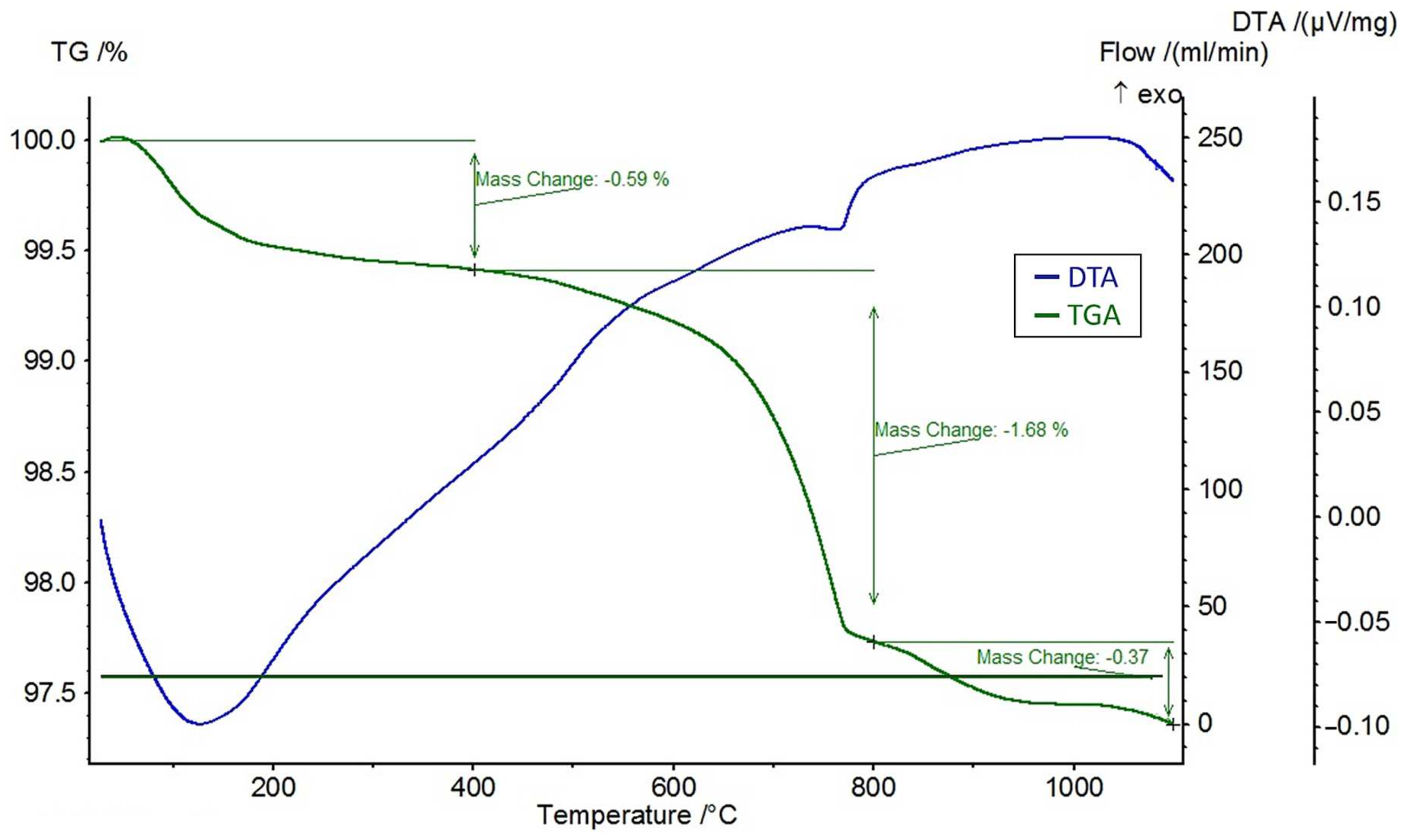
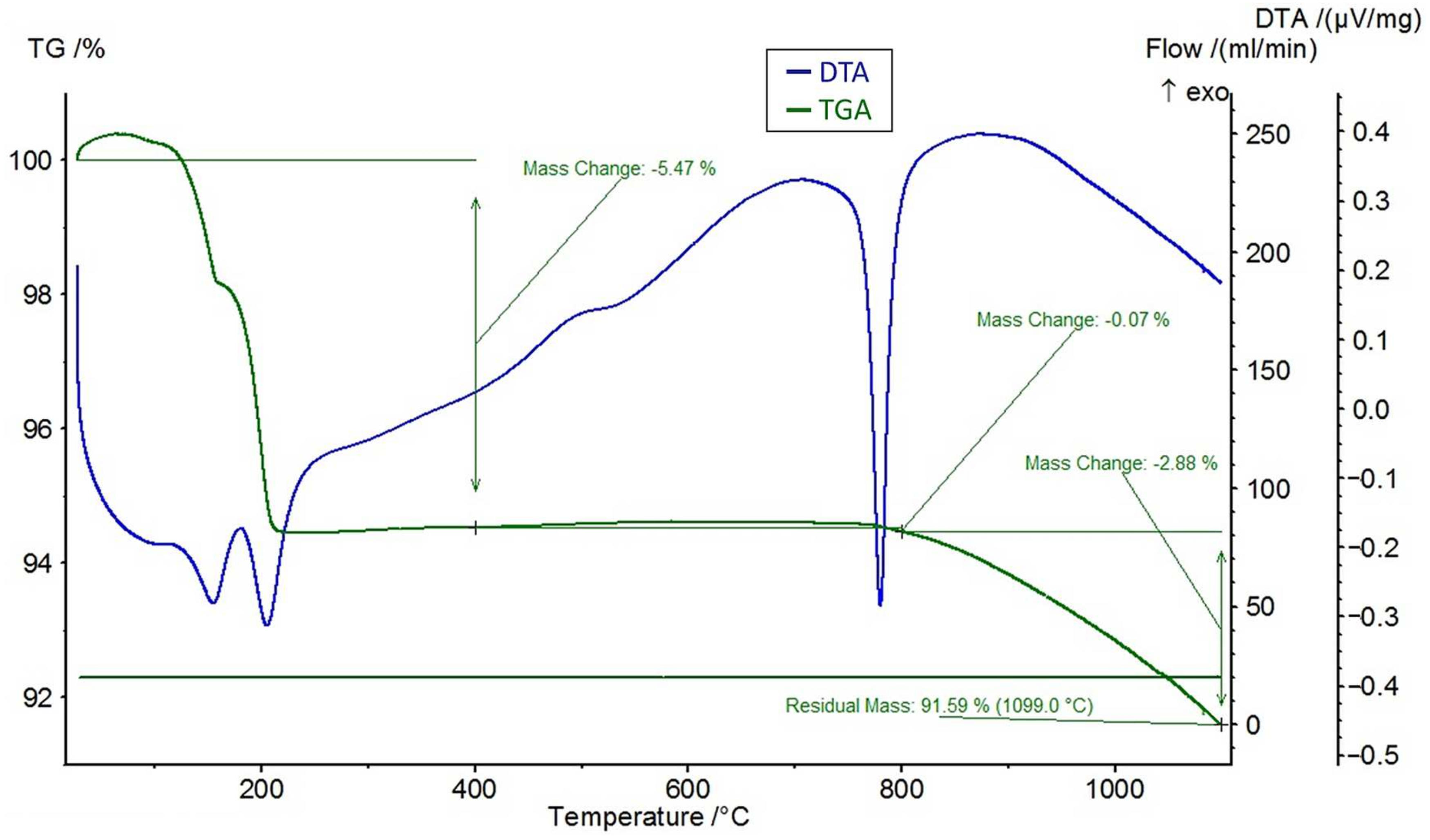
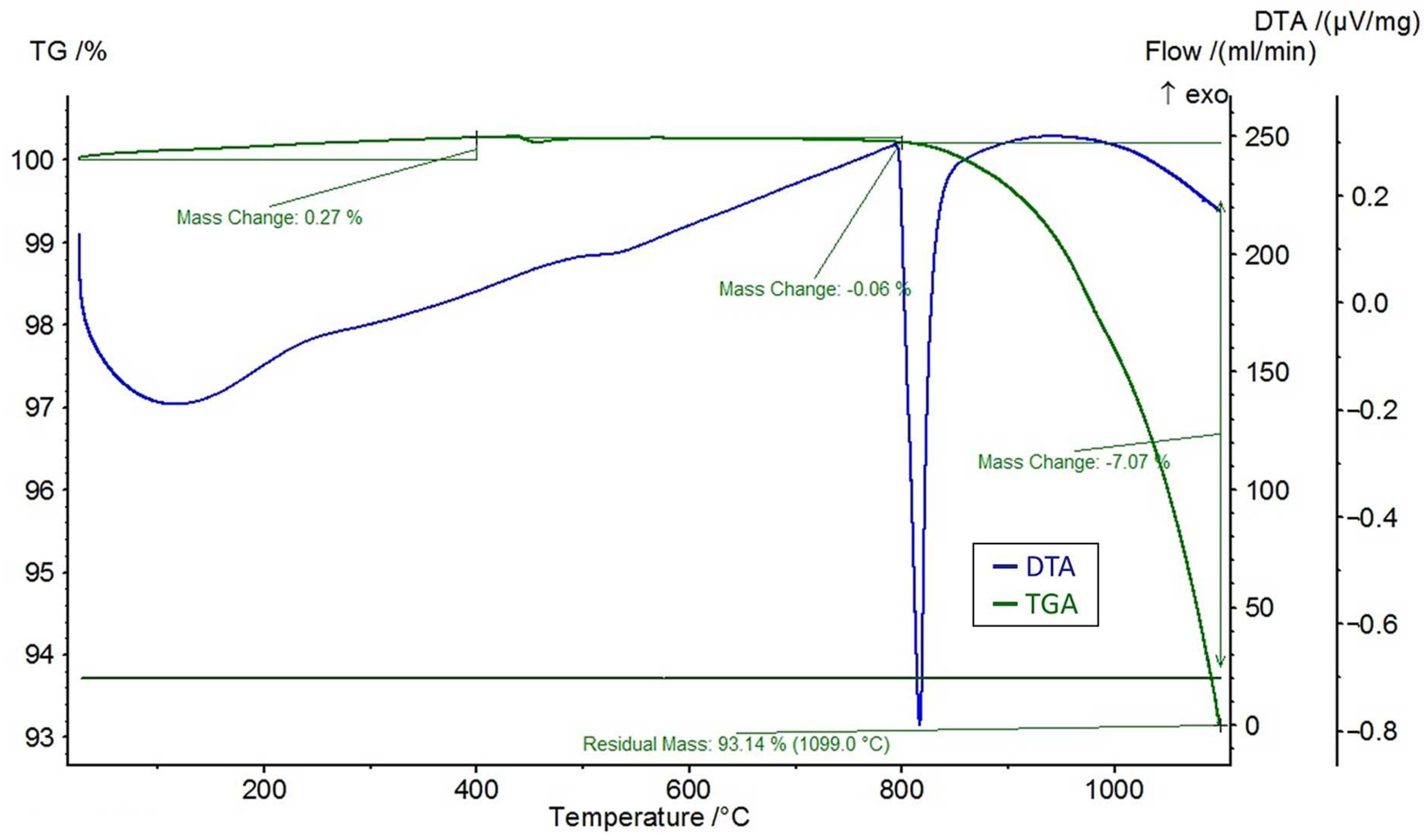
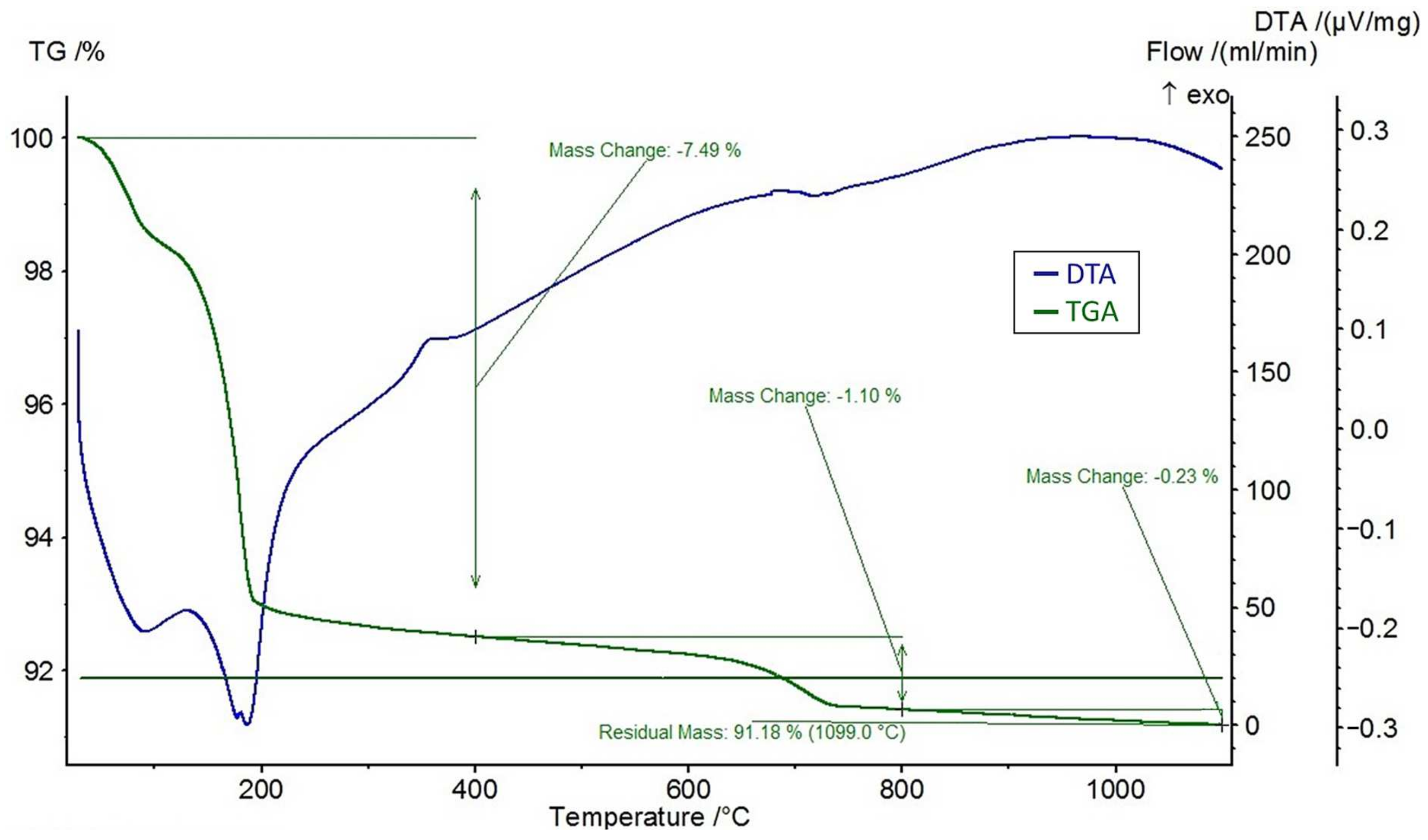
A differential thermal analysis (DTA) and a thermogravimetric analysis (TGA) were performed on the feldspar ore and the additives of CaCl2, NaCl, and CaSO4 using the STA 449 F3 Jupiter® thermal analyzer (NETZSCH, Selb, Germany). The DTA and TGA curves of feldspar ore and additives (CaCl2, NaCl, CaSO4) are given in Figure 4, Figure 5, Figure 6, and Figure 7, respectively. Conforming to the TGA results of the ore, a mass loss of 0.59% was observed between 100 and 400 °C and 1.68% between 400 and 800 °C. The mass loss experienced was due to the presence of small amounts of moisture and carbon dioxide contents within the sample. In conformity with the DTA results, moisture loss occurred at 100 °C, and decomposition occurred at around 780 °C in the ore. According to the results of the TGA analysis of the additives, a mass loss of 5.47% was observed between 100 and 400 °C and 2.88% after 800 °C for CaCl2, while there was a slight change between 400 and 800 °C. Evidently, CaCl2 is a substance that easily absorbs moisture from the air, and the mass change between 100 and 400 °C was caused by such water absorption. For NaCl, a mass loss of 7.07% occurred after 800 °C with slight changes before 800 °C. For CaSO4, a mass loss of 7.49% was observed between 100 and 400 °C and 1.1% between 400 and 800 °C. Based on the DTA analysis results, decomposition happened at around 780, 820, and 190 °C in the CaCl2, NaCl, and CaSO4 samples, respectively.
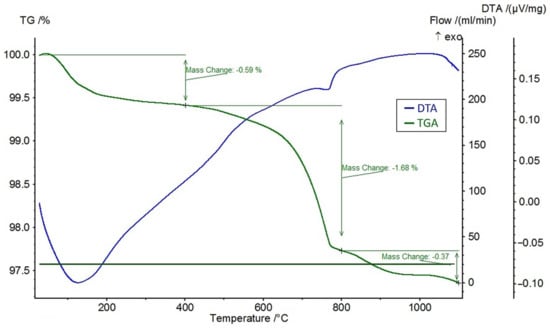
Figure 4.
DTA and TGA curves of the ore.
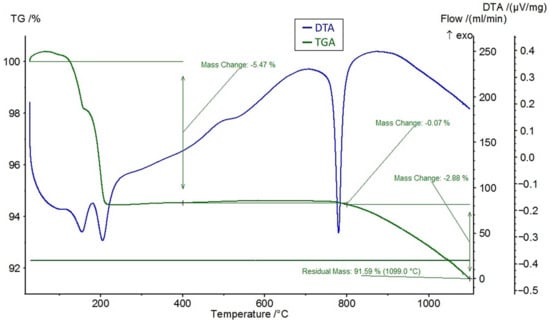
Figure 5.
DTA and TGA curves of CaCl2.
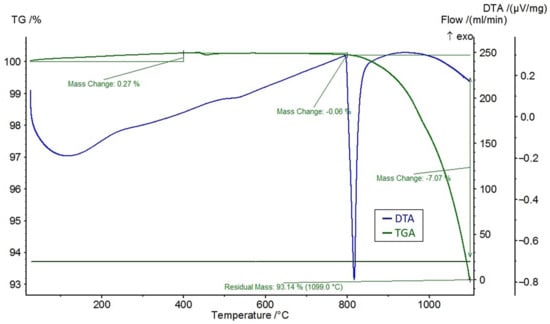
Figure 6.
DTA and TGA curves of NaCl.
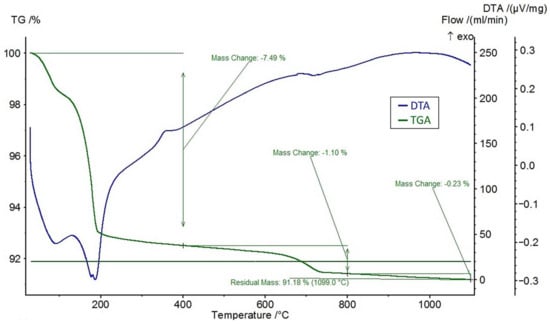
Figure 7.
DTA and TGA curves of CaSO4.
2.2. Beneficiation Methods
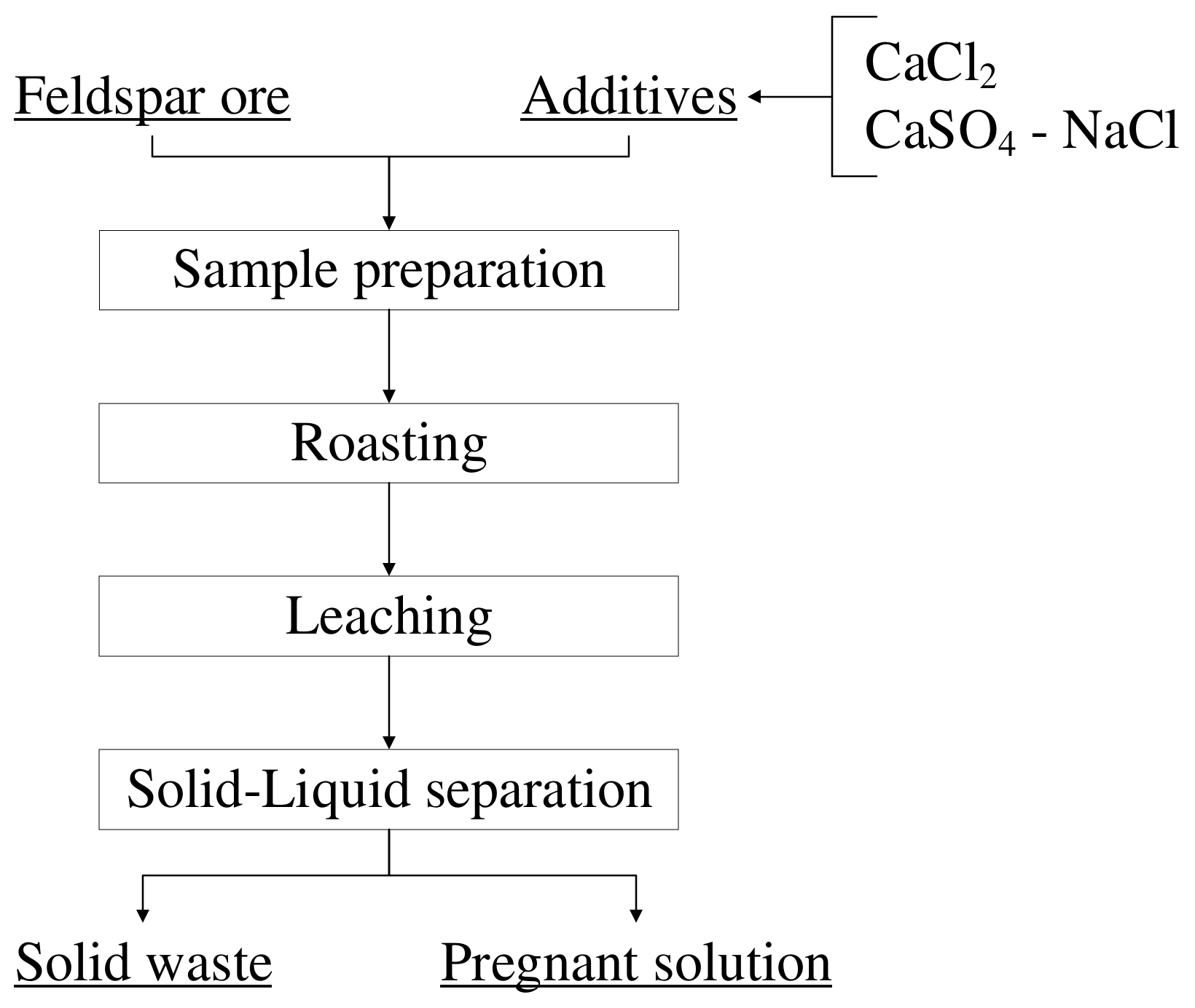
For the enrichment processes, a −106-micron-sized feldspar sample was subjected to roasting with various additives at certain ratios before leaching experiments. During the roasting processes, the PLF 130/6 model furnace (Protherm, Skalica, Slovakia) was used for experiments at temperatures up to 1000 °C, while the P 320 model furnace (Nabertherm, Lilienthal, Germany) was used for those at temperatures above 1000 °C. Experiments were carried out with mixtures of feldspar-CaCl2 and feldspar-CaSO4-NaCl at different ratios and roasting temperatures, while the roasting time was kept constant at 1 h. The leaching experiments were accomplished at a 10% solid ratio at 60 °C and a stirring speed of 500 RPM for 2 h, and the conditions were kept constant for all the experiments. The pulp obtained after leaching was separated from the solid with the help of a vacuum filter. For the filtration process, Sartorius brand blue labeled 391 coded filter paper was used. The pregnant solution and solid waste obtained from the leaching processes were sent for analysis using the AA240FS model atomic absorption device (Varian, Palo Alto, CA, USA). The basic flowsheet of the experiments is given in Figure 8.
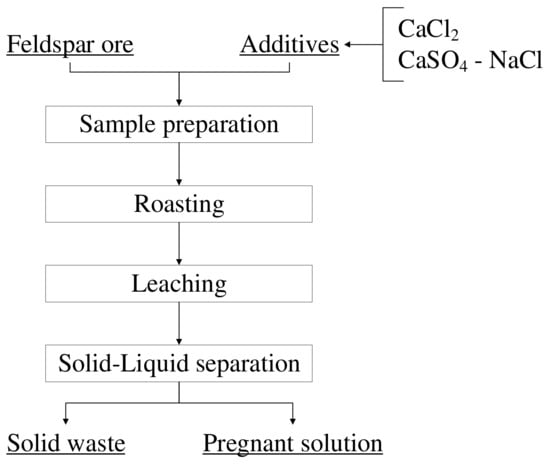
Figure 8.
Basic flowsheet of the experiments.
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Feldspar-CaCl2 Experiments
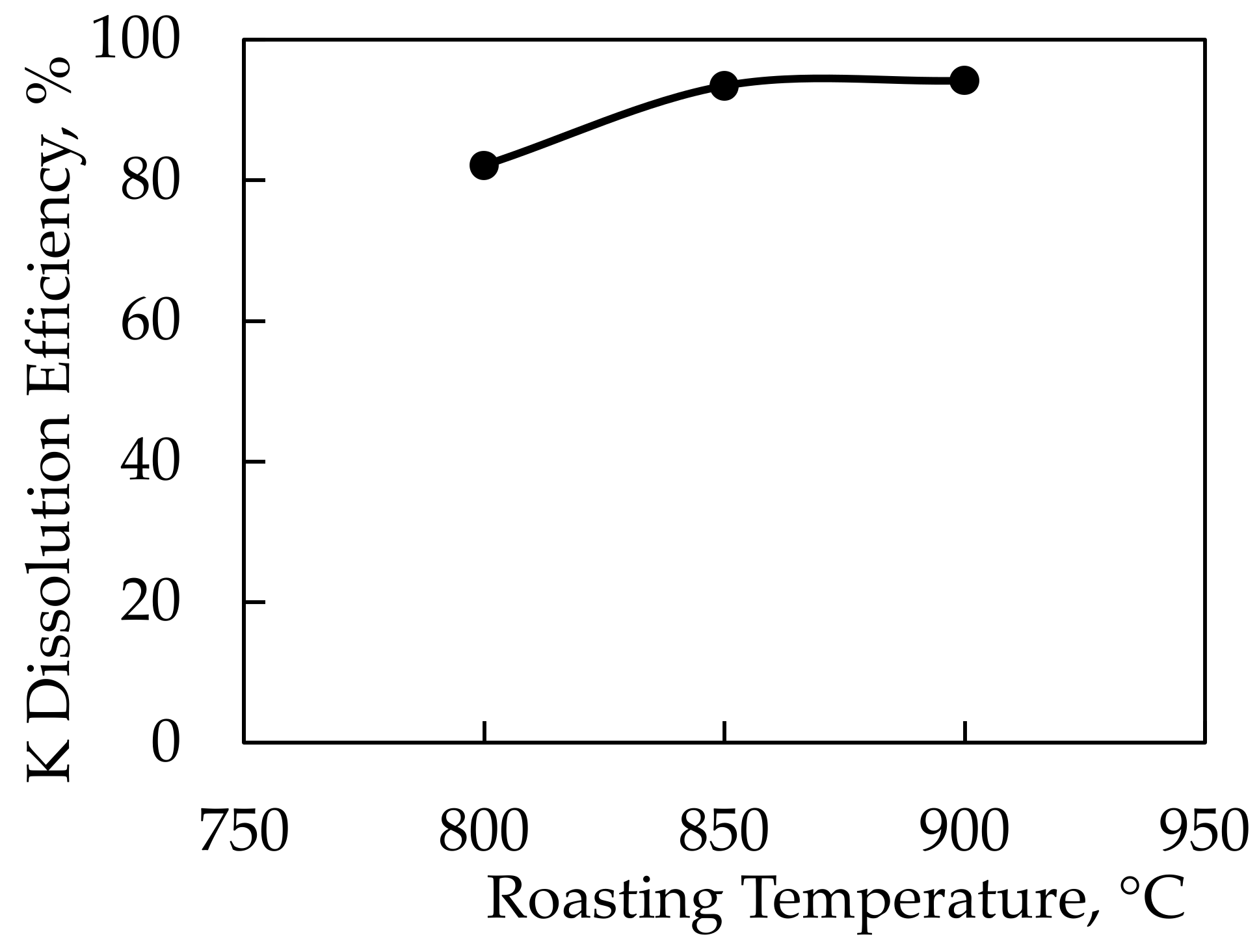
In the potassium extraction experiments performed using CaCl2 salt, the feldspar:CaCl2 ratio was determined to be 1:1.5 by wt. based on the previous work conducted by Serdengeçti et al. [8]. In the roasting experiments, the roasting time was determined to be 60 min for a range of 800–850–900 °C roasting temperatures. The lowest roasting temperature used in the tests was 800 °C since the decomposition points, according to the DTA-TGA analysis of the feldspar sample and CaCl2, were around 780 °C. After the roasting process, leaching experiments were performed on all roasted samples. The leaching parameters were kept constant at a 10% solid ratio at 60 °C and a stirring speed of 500 RPM for 2 h. Figure 9 displays the results of the leaching studies carried out on roasted samples as a function of roasting temperature. Figure 10 shows the results of an X-ray diffractometer analysis of the solid waste obtained during leaching.
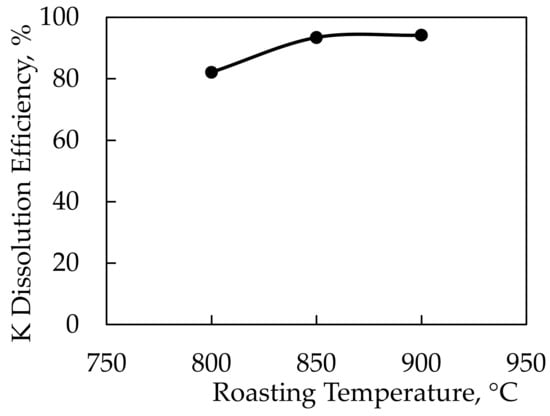
Figure 9.
Dissolution efficiency of K-feldspar against roasting temperatures using CaCl2 additive.
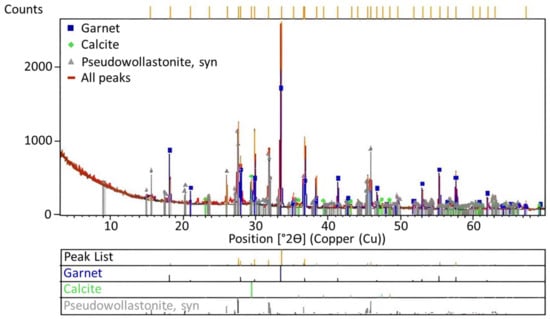
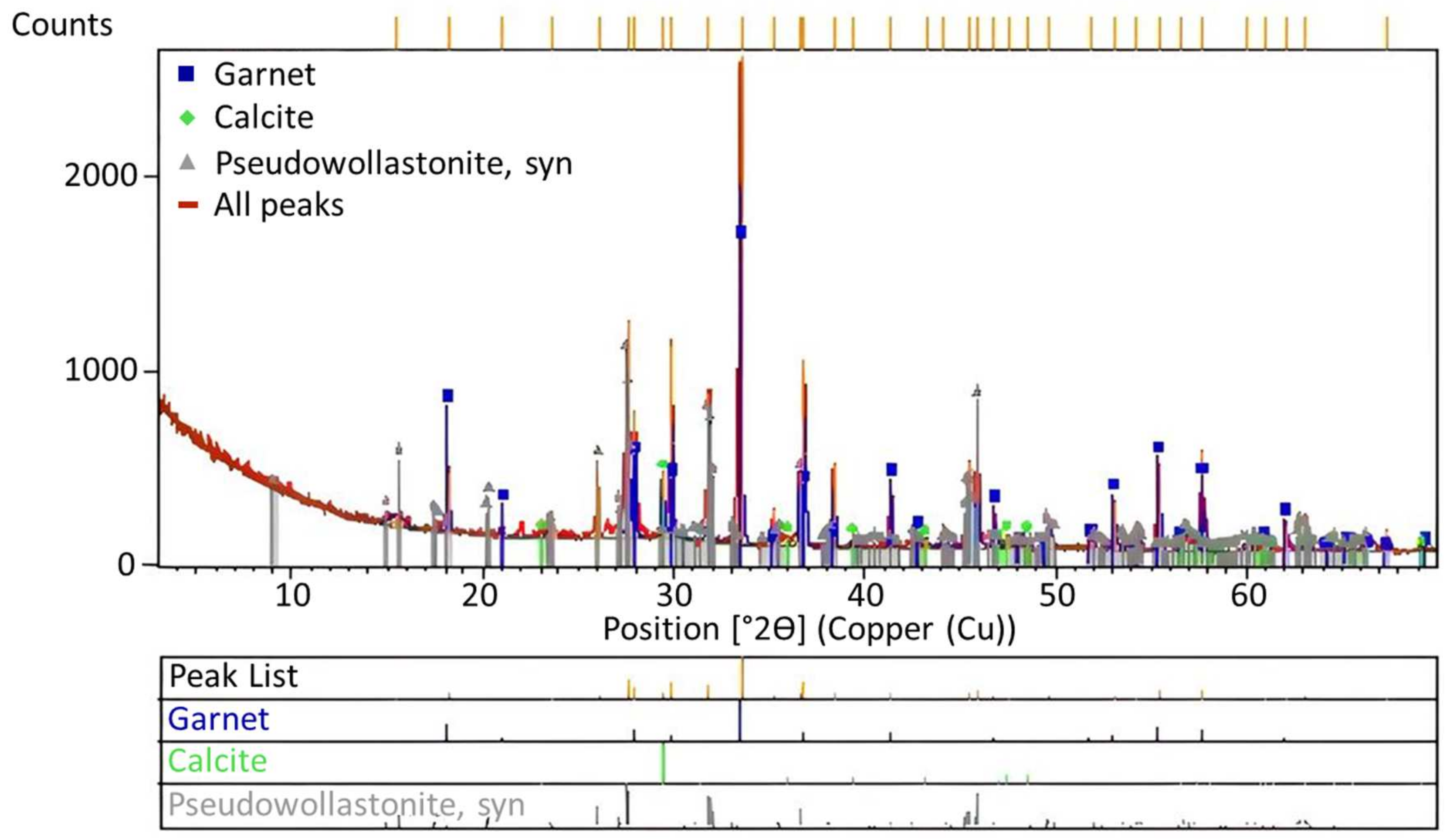
Figure 10.
XRD analysis results of the solid waste obtained during leaching experiments.
Potassium dissolution efficiencies of 93.4% and 94.2% were achieved in experiments conducted at 850 and 900 °C roasting temperatures, respectively. Since there was no significant difference in efficiencies, a roasting temperature of 850 °C was chosen as ideal. Thus, the optimal efficiency was achieved with a −106-micron particle size, 850 °C roasting temperature, and 1:1.5 feldspar:CaCl2 ratio. A comparison of findings from this study with those of the literature showed that potassium could be extracted at the same roasting temperatures with similar efficiencies [5,6,7,9,22].
According to the study of Jena et al. [11], due to the presence of high amounts of Ca2+ ions above the melting temperature during roasting, calcium substitutes potassium, leading to anorthite formation, while potassium is converted to the KCl form. While calcium and potassium, which have similar electronic configurations, are in their most stable forms, the Ca2+ ion can be replaced by the K+ ion. However, this process can only occur when only potassium feldspar is present in the environment. The XRD curve given in Figure 8 reveals that garnet, calcite, and wollastonite formations appeared in the waste solid after KCl was taken into a solution through leaching after roasting. Instead of anorthite, the high quantities of albite and muscovite minerals in the ore resulted in the formation of these minerals.
3.2. Feldspar-CaCl2-NaCl Experiments
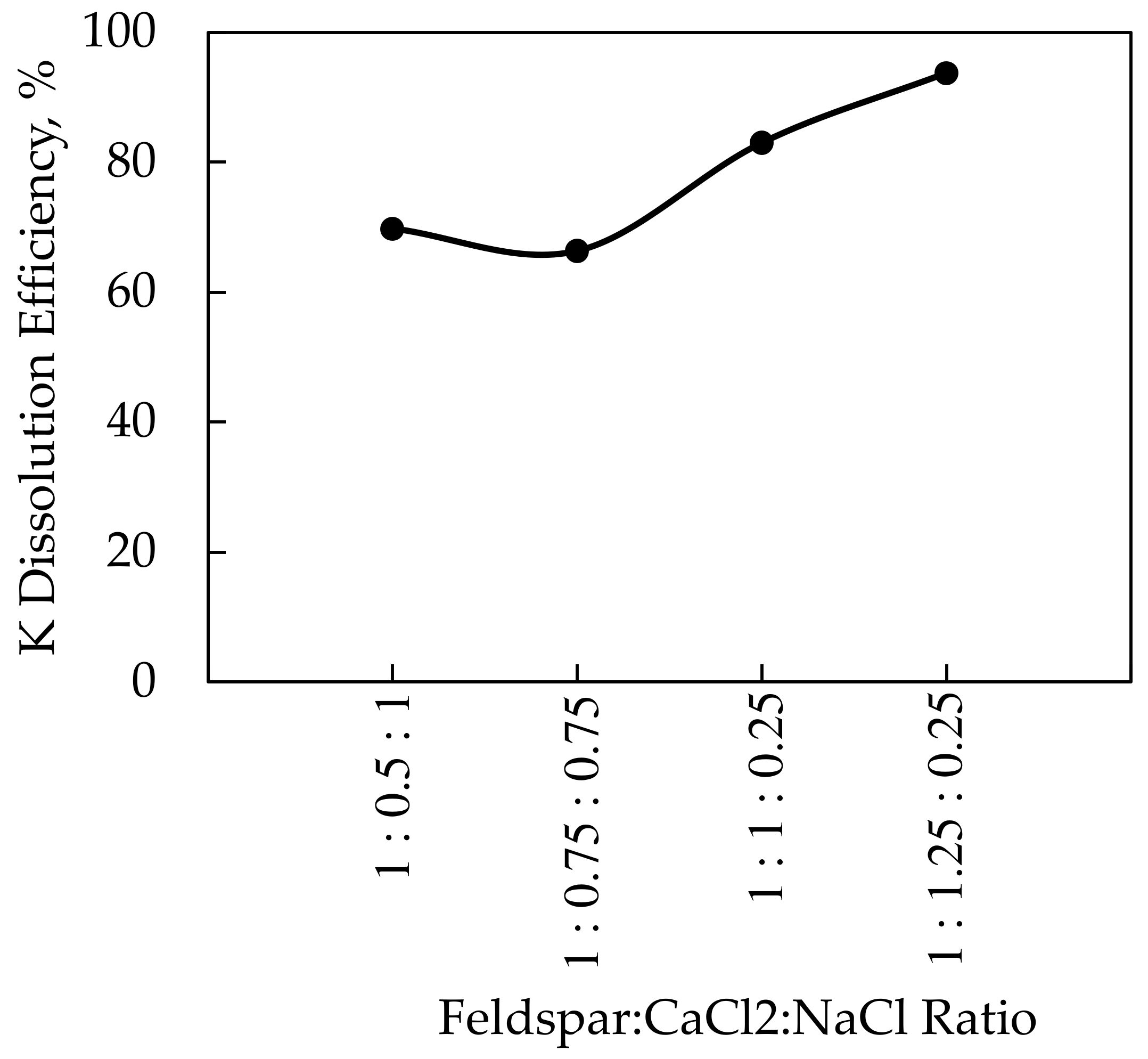
Since CaCl2 is a costly additive, different additives were examined for the dissolution of potassium from potassium feldspar with high efficiency. CaCl2 was mixed with NaCl as an additive in these experiments to minimize the CaCl2 amount. Within the scope of the research, the roasting temperature of 850 °C, which was the optimal temperature for CaCl2, and the roasting period of 60 min were held constant while the feldspar:CaCl2:NaCl ratio varied. A roasting temperature of 850 °C was acceptable for the CaCl2-NaCl mixture because the decomposition points of the additives were below 850 °C according to the DTA-TGA analyses. These experiments were carried out at feldspar:CaCl2:NaCl ratios of 1:1.25:0.25; 1:1:0.25; 1:0.75:0.75, and 1:0.5:1. The results of the experiments and the XRD analyses of the solid wastes obtained after leaching are given in Figure 11 and Figure 12, respectively.
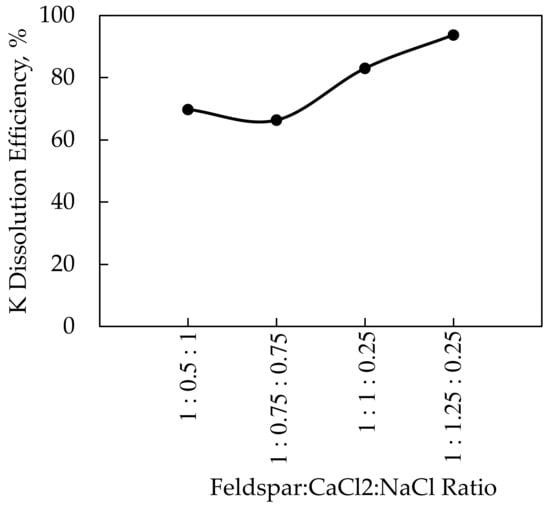
Figure 11.
K dissolution of feldspar versus the additive ratio using CaCl2-NaCl mixture.
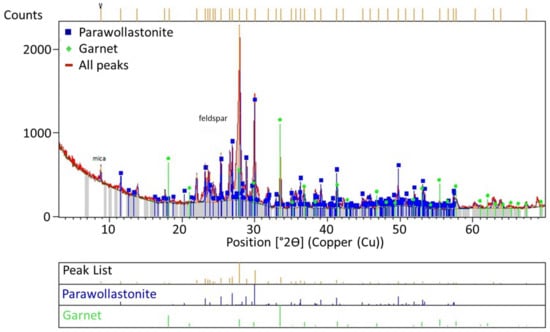
Figure 12.
XRD analysis of the solid waste obtained upon leaching at feldspar:CaCl2:NaCl ratios of 1:1.25:0.25.
The highest efficiency of 93.7% at the 850 °C roasting temperature was reached with a 1:1.25:0.25 ratio in the CaCl2-NaCl mixture experiments. The potassium dissolution efficiency of 93.4% was obtained as a result of the experiments performed at 850 °C roasting temperature using only CaCl2. Based on the data, it is clear that using less CaCl2 resulted in the same potassium dissolution efficiency at the same roasting temperature and time. According to the studies in the literature [7,13], an efficiency of 90%–96% was achieved as a consequence of processes carried out at the 800–850 °C roasting temperature range using CaCl2 and NaCl. The primary difference between the experimental conditions is that, while the CaCl2/NaCl ratio in the literature is around 2, the CaCl2/NaCl ratio in this study was maintained at 5. The difference in NaCl amount was attributed to the higher K2O contents of 10.50% [7] and 14.81% [13] in the literature’s studies.
3.3. Feldspar-CaSO4-NaCl Experiments
Since CaCl2 is a costly additive, different additives were examined for the dissolution ability of potassium from potassium feldspar with high efficiency. High yields could not be obtained using only NaCl salt. Therefore, studies were carried out using NaCl salt mixed with CaSO4. The expected reaction to occur was as follows [11]:
CaSO4 + 2NaCl = CaCl2 + Na2SO4
2KAlSi3O8 + CaCl2 = 2KCl + CaAl2Si2O8+ 4SiO2
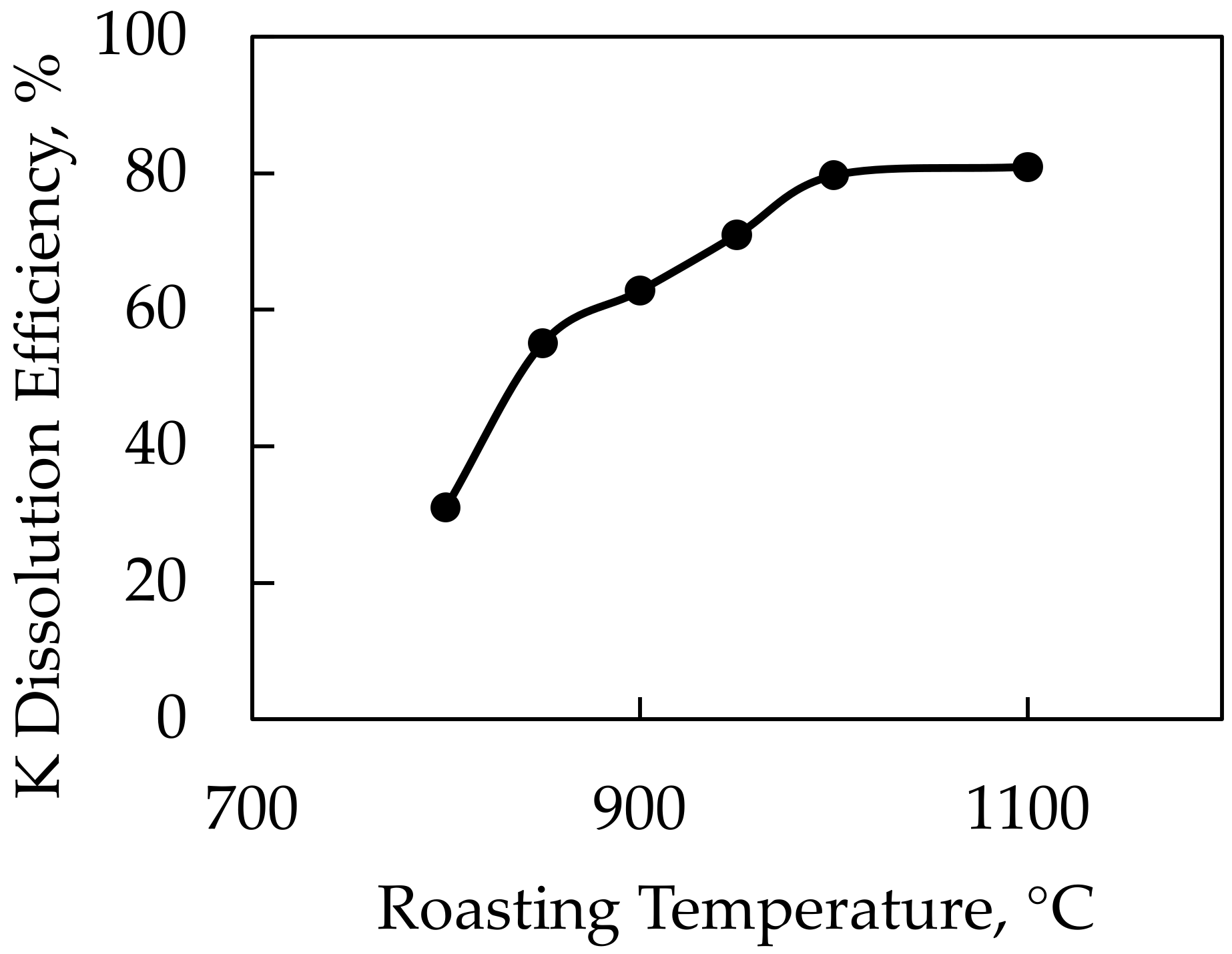
In this study, it was expected that CaSO4 decomposed at very low temperatures and Ca ions were replaced with K ions at the temperature of 780 °C, which was the decomposition temperature of the feldspar sample. After reaching the temperature of 820 °C, which is the decomposition temperature for NaCl, Na ions are replaced with K ions, leading to the formation of KCl. Pure gypsum was used as a source of CaSO4 in the experiments. The feldspar:Gypsum:NaCl ratio was held constant during the experiments at 1:1.25:0.25 and we used roasting temperatures of 800–850–900–950–1000–1100 °C. According to the results of the DTA-TGA analysis, NaCl decomposed at 820 °C and CaSO4 decomposed at 190 °C. In the experiments conducted with the CaSO4-NaCl mixture, the lowest roasting temperature was recorded as 800 °C, which was close to the decomposition temperature of the NaCl additive, but higher yields were not expected at this temperature. The results of the roasting temperature experiments are given in Figure 13.
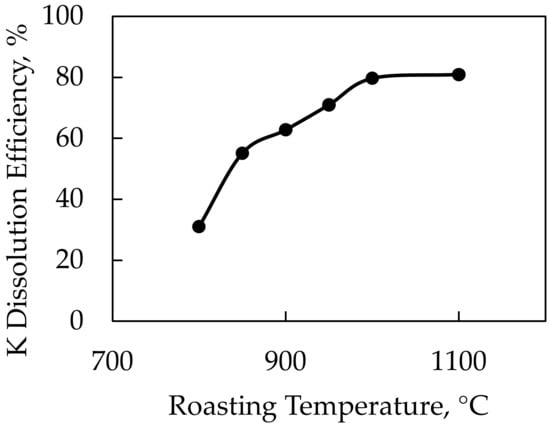
Figure 13.
K dissolution efficiency of K-feldspar against roasting temperatures using CaSO4-NaCl mixture as an additive.
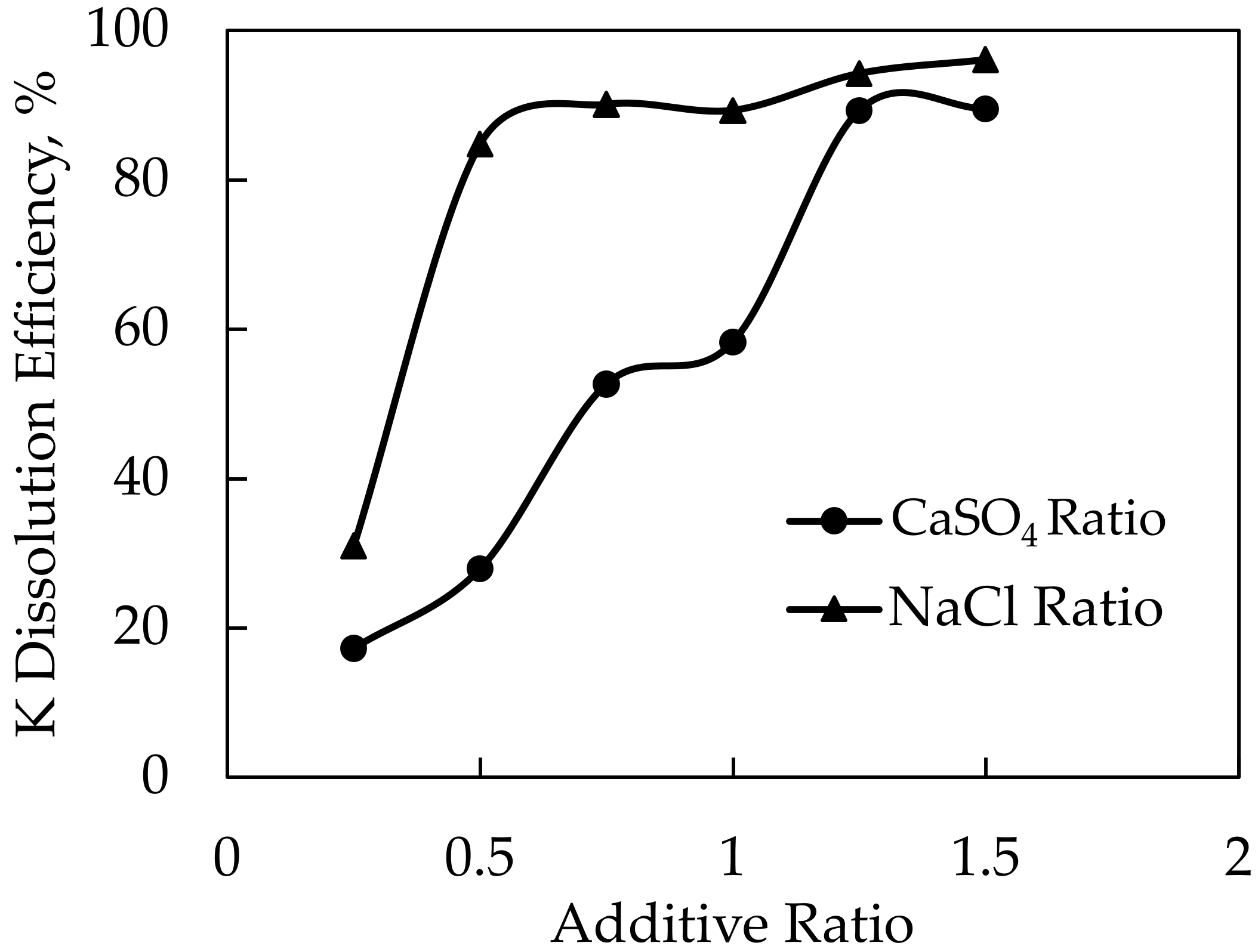
Potassium dissolution efficiencies of 79.7% and 80.9% were achieved in experiments conducted at 1000 and 1100 °C roasting temperatures, respectively. The yield began to stabilize after the roasting temperature of 1000 °C. As a result, after settling at 1000 °C as the ideal roasting temperature, experiments were carried out by changing the CaSO4 and NaCl ratios. In this context, the feldspar and NaCl ratios were held constant, and experiments were performed at 1:0.25:1, 1:0.5:1, 1:0.75:1, 1:1:1, 1:1.25:1, and 1:1.5:1 ratios of feldspar:CaSO4:NaCl. After conducting these experiments, the optimal CaSO4 ratio was determined. The feldspar and CaSO4 ratios were then held constant while experiments were carried out at 1:1.25:0.25, 1:1.25:0.5, 1:1.25:0.75, 1:1.25:1, 1:1.25:1.25, and 1:1.25:1.5 ratios of feldspar:CaSO4:NaCl. The results of these experiments and the XRD analysis of the solid wastes obtained after leaching are given in Figure 14 and Figure 15, respectively.
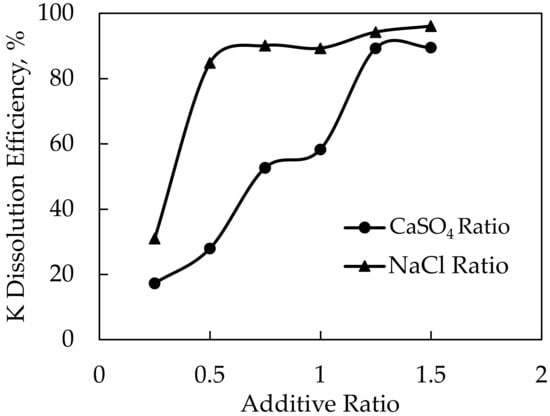
Figure 14.
Dependence of K dissolution on additive ratio upon using CaSO4-NaCl mixture as an additive.
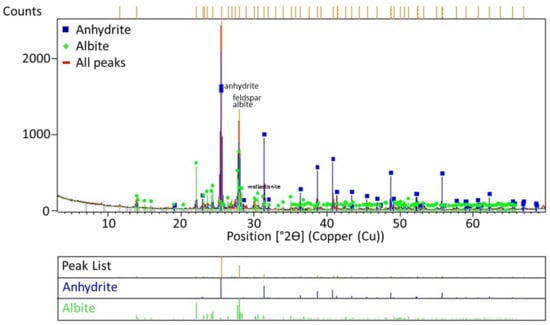
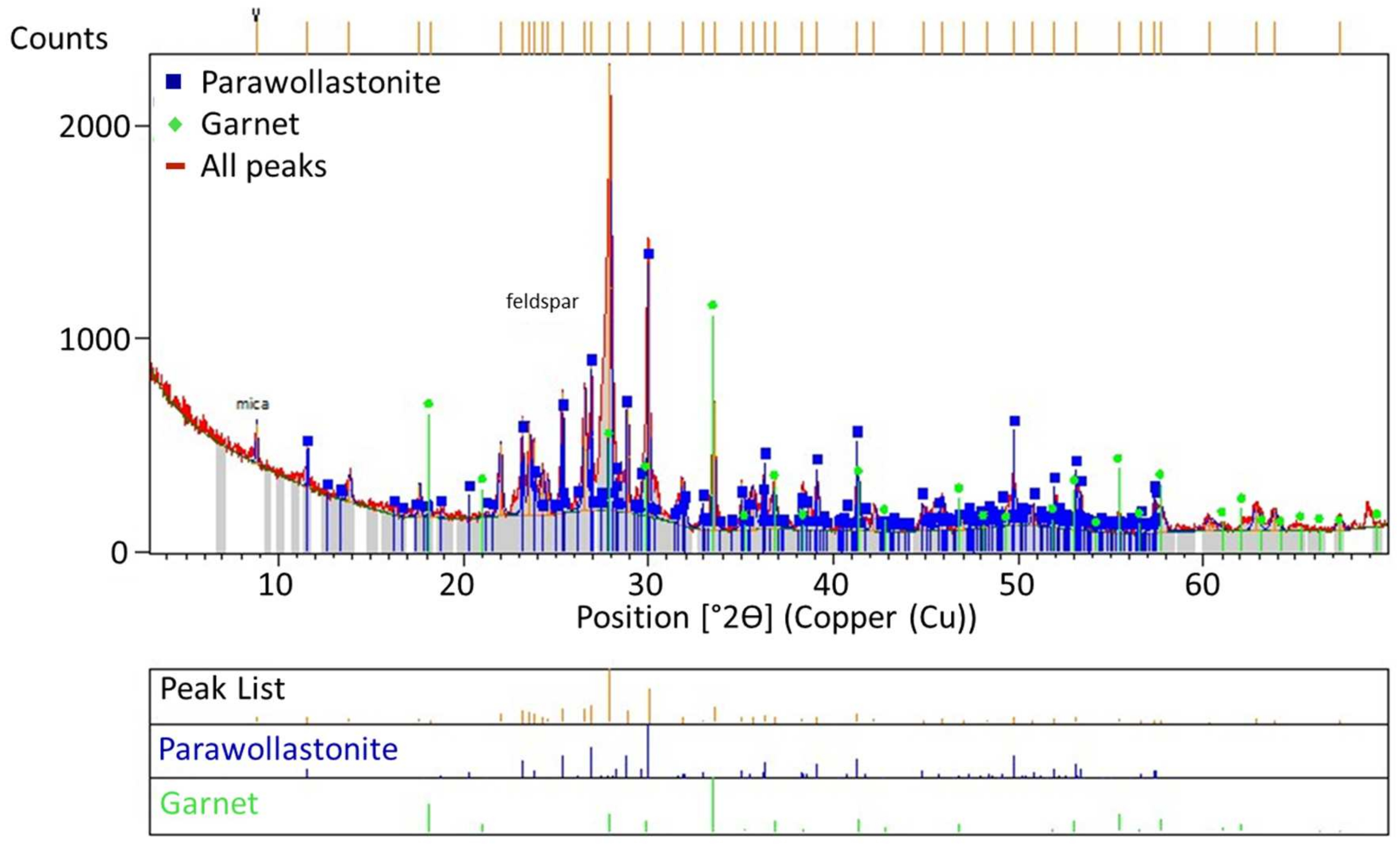
Figure 15.
XRD analysis results of the solid waste obtained during leaching at feldspar:CaSO4:NaCl ratios of 1:1.25:1.5.
The experiments with different CaSO4 ratios resulted in 89.3% and 89.5% efficiencies at 1.25 and 1.5 CaSO4 ratios, respectively. The ratio of 1.25 CaSO4 was determined to be optimal since there was no significant increase in potassium dissolution efficiency above the 1.25 CaSO4 ratio. After the CaSO4 ratio was determined, the highest dissolution efficiency obtained was 96.1% at the ratio of 1:1.25:1.5 feldspar:CaSO4:NaCl within the scope of the experiments performed by changing the NaCl ratios. CaSO4 was used to prevent the reaction of Na ions with Cl ions after the decomposition and to increase the probability of KCl formation. Therefore, a higher extraction efficiency was achieved with the CaSO4-NaCl mixture. Although there are not many studies in the literature with the mixture of CaSO4 and NaCl, in the study by Jena et al. [11], the dissolution of potassium was carried out at 900 °C and a 1:1:1 ratio with 92.8% efficiency by using phosphogypsum and NaCl, which has a similar structure to CaSO4.
4. Conclusions
In this study, different kinds of salts were used as additives in order to extract potassium from potassium feldspar to produce KCl for use as fertilizer. In this context, CaCl2, NaCl, and CaSO4 salts were studied to clarify if it was possible to extract potassium with high efficiency by using these inorganic salts. The main purpose here was to obtain KCl from potassium feldspar with less production cost. The maximum efficiency was obtained using CaCl2 as an additive, with 93.4% potassium dissolution at an 850 °C roasting temperature for 60 min at the feldspar:CaCl2 ratio of 1:1.5. The maximum potassium dissolution efficiency of 93.7% at the 850 °C roasting temperature for 60 min was obtained at a feldspar:CaCl2:NaCl ratio of 1:1.25:0.25. Finally, the maximum efficiency obtained after using the CaSO4-NaCl mixture was 96.1%, at a 1000 °C roasting temperature for 60 min with a feldspar:CaSO4:NaCl ratio of 1:1.25:1.5. It was observed that the difference in efficiencies between the mixtures of CaCl2-NaCl and CaSO4-NaCl was not significant. However, the CaSO4-NaCl mixture is more feasible considering the additive cost. It is possible to produce KCl more economically by using the CaSO4-NaCl mixture as an additive, which is cheaper than CaCl2. However, the cost-effectiveness also depends on the present economic situation because a higher roasting temperature (1000 °C) is needed in the process of KCl production with the CaSO4-NaCl mixture.
Author Contributions
All researchers conceived of and designed the experiments; T.T. performed the experiments and analyzed the data; T.T. and M.O.K. contributed to writing the paper. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This research was funded by the Istanbul Technical University Circulating Capital Enterprise R&D, Project ID: 42017, and the Scientific and Technological Research Council of Turkey, Project ID: 218M107.
Data Availability Statement
The data presented in this study is contained within the article.
Acknowledgments
The authors would like to express their sincere thanks and appreciation to the Istanbul Technical University Circulating Capital Enterprise R&D, the Scientific and Technological Research Council of Turkey for financial support, and BS Invest Co. for kindly providing the feldspar samples.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
References
- Prakash, S.; Verma, J.P. Global perspective of potash for fertilizer production. In Potassium Solubilizing Microorganisms for Sustainable Agriculture; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2016; pp. 327–331. [Google Scholar]
- Al Rawashdeh, R.; Xavier-Oliveira, E.; Maxwell, P. The potash market and its future prospects. Resour. Policy 2016, 47, 154–163. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bulatovic, A.M. Beneficiation of Potash Ore. In Handbook of Flotation Reagents: Chemistry, Theory and Practice, Volume 3: Flotation of Industrial Minerals; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2015; Volume 36, pp. 153–162. [Google Scholar]
- Prud’homme, M. Potash. Canadian Encyclopedia. 2015. Available online: https://www.thecanadianencyclopedia.ca/en/article/potash (accessed on 9 August 2023).
- Yuan, B.; Li, C.; Liang, B.; Lü, L.; Yue, H.; Sheng, H.; Ye, L.; Xie, H. Extraction of potassium from K-feldspar via the CaCl2 calcination route. Chin. J. Chem. Eng. 2015, 23, 1557–1564. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Samantray, J.; Anand, A.; Dash, B.; Ghosh, M.K.; Behera, A.K. Production of potassium chloride from K-Feldspar through roast–leach-solvent extraction route. Trans. Indian Inst. Met. 2019, 72, 2613–2622. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Haseli, P.; Majewski, P.; Christo, F.; Raven, M.; Klose, S.; Bruno, F. Experimental kinetic analysis of potassium extraction from ultrapotassic syenite using NaCl–CaCl2salt mixture. ACS Omega 2020, 5, 16421–16429. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Serdengeçti, M.T.; Baştürkcü, H.; Burat, F.; Kangal, M.O. The correlation of roasting conditions in selective potassium extraction from K-feldspar ore. Minerals 2019, 9, 109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tanvar, H.; ve Dhawan, N. Recovery of potash values from feldspar. Sep. Sci. Technol. 2020, 55, 1398–1406. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Samantray, J.; Anand, A.; Dash, B.; Ghosh, M.K.; Behera, A.K. Sustainable Process for the Extraction of Potassium from Feldspar Using Eggshell Powder. ACS Omega 2020, 5, 14990–14998. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jena, S.K.; Misra, P.K.; Das, B. Studies on extraction of potassium from feldspar by roast-leach method using phosphogypsum and sodium chloride. Miner. Process. Extr. Metall. Rev. 2016, 37, 323–332. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Orosco, P.; Barrios, O.; Ojeda, M. Extraction of potassium from microcline by chlorination. Minerals 2019, 9, 295. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, H.; Sun, D.S.; Bao, H. The Extraction of Potassium from Feldspar by Molten Salt Leaching Method with Composite Additives. Adv. Mater. Res. 2012, 524, 1136–1139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Asselin, E.; Li, Z. Laboratory and pilot scale studies of potassium extraction from K-feldspar decomposition with CaCl2 and CaCO3. J. Chem. Eng. Jpn. 2018, 49, 111–119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhong, Y.; Gao, J.; Chen, P.; Guo, Z. Recovery of potassium from K-feldspar by thermal decomposition with flue gas desulfurization gypsum and CaCO3: Analysis of mechanism and kinetics. Energy Fuels 2017, 31, 699–707. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Orosco, P.; del Carmen Ruiz, M. Potassium chloride production by microcline chlorination. Thermochim. Acta 2015, 613, 108–112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ghalayini, Z.T. Feldspar and Nepheline Syenite. U.S. Geological Survey, Mineral Commodity Summaries. 2020. Available online: https://pubs.usgs.gov/periodicals/mcs2020/mcs2020-feldspar.pdf (accessed on 23 August 2023).
- Jena, S.K.; Dash, N.; Samal, A.K.; Misra, P.K. Competency of chlorination roasting coupled water leaching process for potash recovery from K-feldspar: Mechanism and kinetics aspects. Korean J. Chem. Eng. 2019, 36, 2060–2073. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jena, S.K. A review on potash recovery from different rock and mineral sources. Min. Metall. Explor. 2021, 38, 47–68. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ciceri, D.; Manning, D.A.; Allanore, A. Historical and technical developments of potassium resources. Sci. Total Environ. 2015, 502, 597. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Available online: https://actlabs.com/our-advantage/quality/accreditation/ (accessed on 11 October 2023).
- Alyosif, B.; Uysal, T.; Aydemir, M.K.; Erdemoğlu, M. Contribution of mechanical activation for obtaining potassium chloride from microcline. Min. Metall. Explor. 2023, 40, 1311–1319. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).