Abstract
The work presents the latest scientific research on the far infrared spectrum of the natural mineral villiaumite (chemical formula NaF). The three samples of villiaumite examined came from the Khibiny Mountains in the Kola Peninsula (Russia) and from Mon Saint Hilaire in Quebec (Canada). The tested villiaumite samples began to change color very slowly after being heated above 300 °C in a muffle furnace. Subsequent color changes required heating at increasingly higher temperatures for approximately 48–72 h. Samples of the reddish mineral villiaumite turned orange, pink and finally colorless (at approximately at 430 °C). Because the color of villiaumite changes under the influence of temperature, far infrared spectra were measured for the samples at room temperature and for the sample heated to 100, 200, 300, 400 and 500 °C. Additionally, using density functional theory (DFT/B3LYP/6-31+g*), the spectrum of NaF (125-atom model of crystal structure) was simulated for the first time and compared with the experimental spectrum of pure sodium fluoride (a chemical reagent) and the mineral villiaumite.
1. Introduction
Villiaumite (NaF) is a rare mineral. The most well-known places where it occurs are as follows: Guinea—Los Islands, where it was first discovered by Maxime Villiaume; Russia—Khibiny and Lovozero massive, Kola Peninsula; Canada—Mon Saint Hilaire in Quebec; Kenya—Magadi Lake; Namibia—Aris; Greenland—Kvanefjeld; Brazil—Minas Gerais; and USA—Point of Rocks, New Mexico, and Porphyry Mountain, Colorado [1]. The thermally unstable color of villiaumite, which includes various shades of red and pink, is not caused by impurities [2] but comes from metal Na nanoparticles (2.5–3 nm in diameter) [3]. Despite its impressive appearance, it is practically not used in the jewelry industry due to its high solubility in water [4] and its toxicity [5].
Although villiaumite is quite a rare mineral, fluorine in general is an element that is quite common on Earth. It is ranked as the 13th most common element in the Earth’s crust [6]. The occurrence of fluoride in the human environment is increasing because it is widely used in medicine, dentistry and industry. The importance of fluorine compounds for the economy is very great, as is confirmed by the fact that fluorite (CaF2, also called fluorspar) is on the EU list of critical raw materials [7].
Sodium fluoride is directly used to produce advanced materials. One of them is ZBLAN glass, whose name comes from the first letters of the element symbols of its chemical formula: ZrF4-BaF2-LaF3-AlF3-NaF [8]. Typically, its composition is 53% ZrF4, 20% BaF2, 4% LaF3, 3% AlF3 and 20% NaF, but under the name ZBLAN, it covers the entire spectrum of fluoride glass. ZBLAN glass has a wide range of light transmittance of various wavelengths (300 nm (UV) to 7 μm (infrared)) and a low refractive index of ~1.5 for the sodium D line. ZBLAN glass is used, among others, for the production of optical fiber and high-power beam-pumping diodes, as well as in beam-splicing techniques and heat dissipation technologies [9]. Sodium fluoride is also a key component of various other types of glass [10,11]. Another important fluoride glass is photothermofraction glass (PTR), which is a photosensitive, multi-component silicate glass [12]. PTR glass is well known as a holographic medium for producing holographic Bragg gratings and diffractive optical elements [13,14]. NaF is also used in photovoltaics (solar cells) [15,16,17].
The literature shows that polymer materials modified by the addition of NaF (and other metal salts) are useful in the production and development of advanced high-energy electrochemical devices such as rechargeable batteries, fuel cells, electrochromic displays, sensors and solar cells [18]. The incorporation of NaF into a polymer structure increases its conductivity (by several orders of magnitude) and changes its optical properties [19,20].
Fluorine plays an important role in geochemical and biogeochemical systems on Earth, and its natural occurrence affects the environment and human health [21,22]. Currently, two different opinions can be found in the literature on the impact of fluoride on the human body. Some claim that fluoride is an essential component of the human body and moderate consumption has a beneficial effect on human health [23,24,25]. Fluoride is an effective agent in the prevention of dental caries [26] and positively affects the height and weight of children [27]. On the other hand, there are many articles warning against fluoride, as overexposure can lead to fluorosis and have a neurotoxic effect that reduces intelligence in children [28,29]. Due to the increasing presence of fluoride in the human environment, all these studies are necessary and lead to a better understanding of the impact of fluorine on the human body.
Interest in the experimental and theoretical vibrational spectra of halides, including sodium fluoride is nothing new. The Raman spectrum of NaF sample has been measured at two wavelengths at 532 and at 785 nm [30]. Muntianu et al. presented a high-resolution infrared emission spectrum (rotation–vibration spectrum) of the NaF gas phase [31]. Ismail et al. obtained the IR absorption spectra of sodium fluoride isolated in a matrix of solid argon [32]. However, to our knowledge, the far infrared vibrational spectrum of the natural mineral villiaumite has not yet been presented in the literature.
The aim of this work was to use far infrared spectroscopy to fill the gap in the characterization of villiaumite in an innovative way. Due to the change in the color of the mineral from red to colorless when heated [2,3,33], the far infrared spectra were also measured for samples in the temperature range of 20–500 °C. Additionally, the IR spectrum was calculated for the sodium fluoride structure model (125 atoms) using density functional theory (DFT). The theoretical results were compared with experimental data. The theoretical spectroscopic parameters of the NaF ground state have previously been calculated by Garcia-Cuesta et al. using the interaction of a multireference configuration and second-order perturbation theory [34]. However, to our knowledge, the current work is the first to attempt to calculate the infrared spectrum of a crystal lattice model of NaF salt as we did in this work.
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Samples
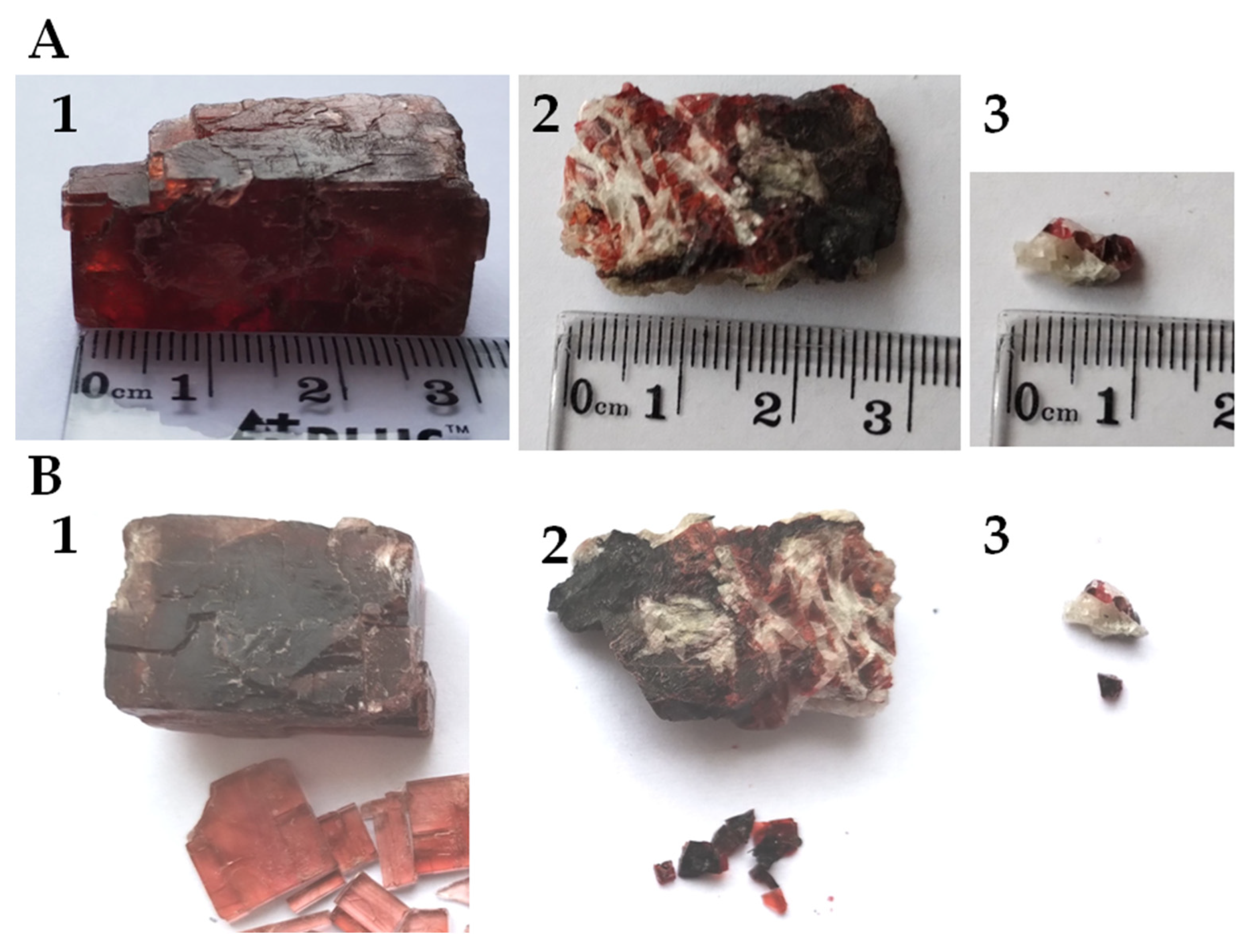
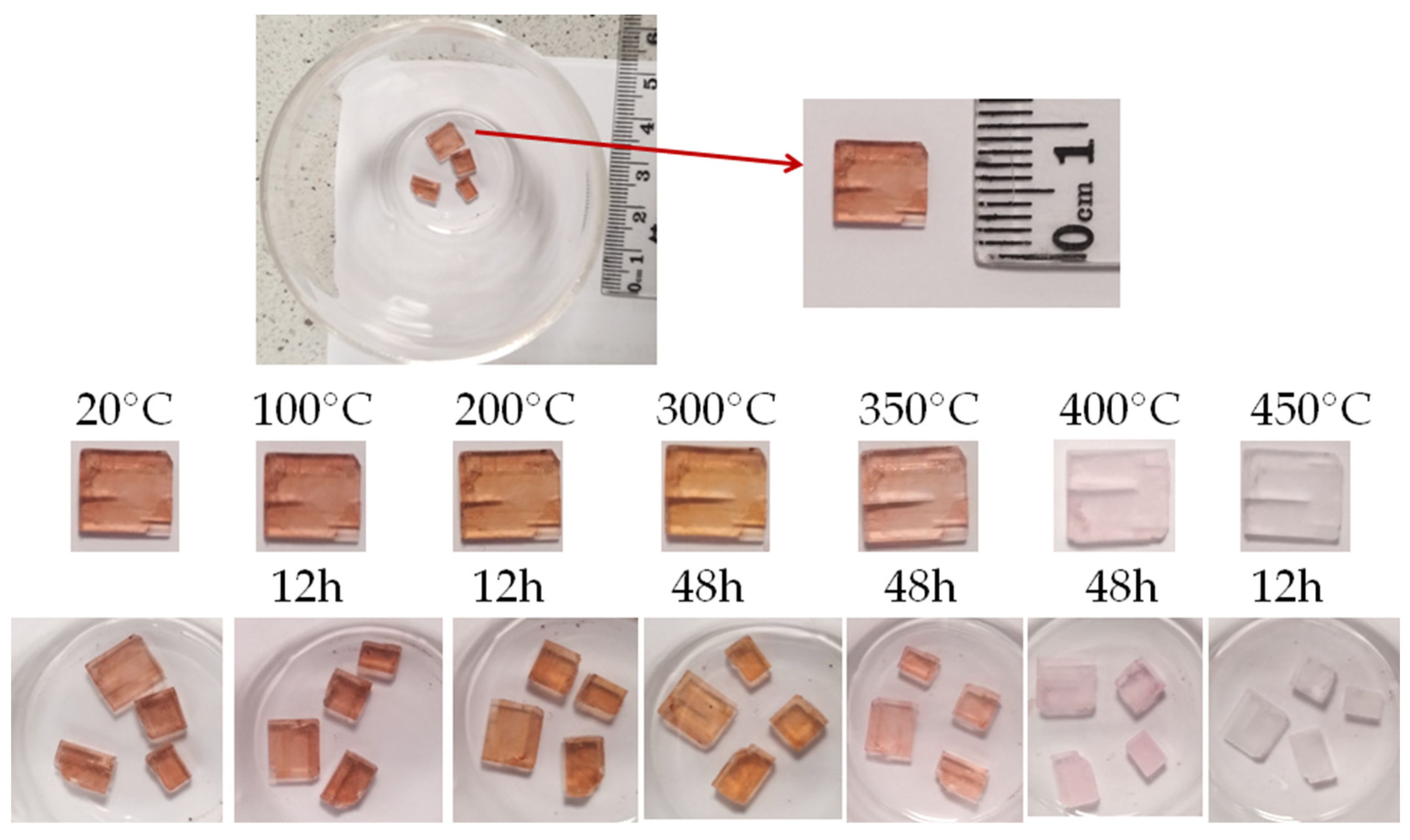
Photographs of the examined minerals are presented in Figure 1A. Two samples (1–2) of villiaumite originated from the Khibiny Mountains in the Kola Peninsula (Russia) the third sample (3) is from Mon Saint Hilaire in Quebec (Canada). As is seen in Figure 1, two of the villiaumite specimens coexist with white natrolite (Na2Al2Si3O10·2H2O). The crystals of villiaumite are red in color, with varying saturation: carmine, scarlet red or slightly pinkish. Figure 1B shows that the mineral samples examined in this work differ in color. In addition to the natural mineral samples, the research also used sodium fluoride (NaF—analytical grade, 99%) as a chemical reagent. Anhydrous salt of NaF was purchased from Warchem, Poland.

Figure 1.
Photographs of the three tested samples of villiaumite (1 and 2—mineral specimens from the Kola Peninsula (Russia); 3—specimen from Quebec (Canada)). (A) Photographs with scale. (B) Photographs of broken mineral samples.
2.2. Far Infrared Spectroscopy
The measurements of the far infrared absorption spectra were taken on a Bruker VERTEX 70v FT-IR spectrometer. The spectra of each of the three samples of villiaumite (Figure 1) were recorded in room conditions in a spectral range of 600–50 cm−1. This wavenumber range is the domain of far infrared spectroscopy. The spectra were measured in triplicate (the spectrum of each sample was measured three times) with 32 scans at a resolution of 2 cm−1. All samples were suspended in Apiezon grease and placed on a polyethylene window. Due to the change in color of villiaumite upon heating, measurements were also taken of the far infrared spectra of samples of these minerals heated to given temperatures. These samples were measured in the temperature range of 20–500 °C (at 20, 100, 200, 300, 400 and 500 °C).
2.3. XRD Measurements
The XRD pattern of powdered villiaumite was obtained at room temperature using an XPert Pro MPD X-ray diffractometer by PANalytical with CuKα radiation (λ = 1.54060 Å) in the range of 5–90 °2θ with a step size of 0.02 °2θ, at a voltage of 45 kV and a current of 30 mA. The qualitative analyses were performed using X’Pert High Score Plus software [35]. The structural parameters (including lattice parameters) were determined from the Rietveld refinements using Maud software [36].
2.4. DFT Calculations
In this work, calculations were performed at the DFT level, with the B3LYP functional [37,38] and 6-31+g* basis set [39], with the Gaussian’16 program [40]. The sodium fluoride crystal model that was adopted as the input structure for the calculations was a system of 125 atoms. The geometry of the model was taken from crystallographic data [41,42]. The assumed structure was fully optimized with a 90° restriction for all angles. No imaginary frequencies were determined. In our previous study on LiCl, NaCl, KCl, LiBr and LiF, calculations using a 125-atom model for very similar chemical compounds to those mentioned, gave reliable results [43,44]. The theoretical IR spectrum of the structure of sodium fluoride was derived by representing each band as a Lorentzian-shaped curve. Half-bandwidths of 60 cm−1 were used to take temperature broadening into account.
3. Results
3.1. Far Infrared Spectrum of Villiaumite
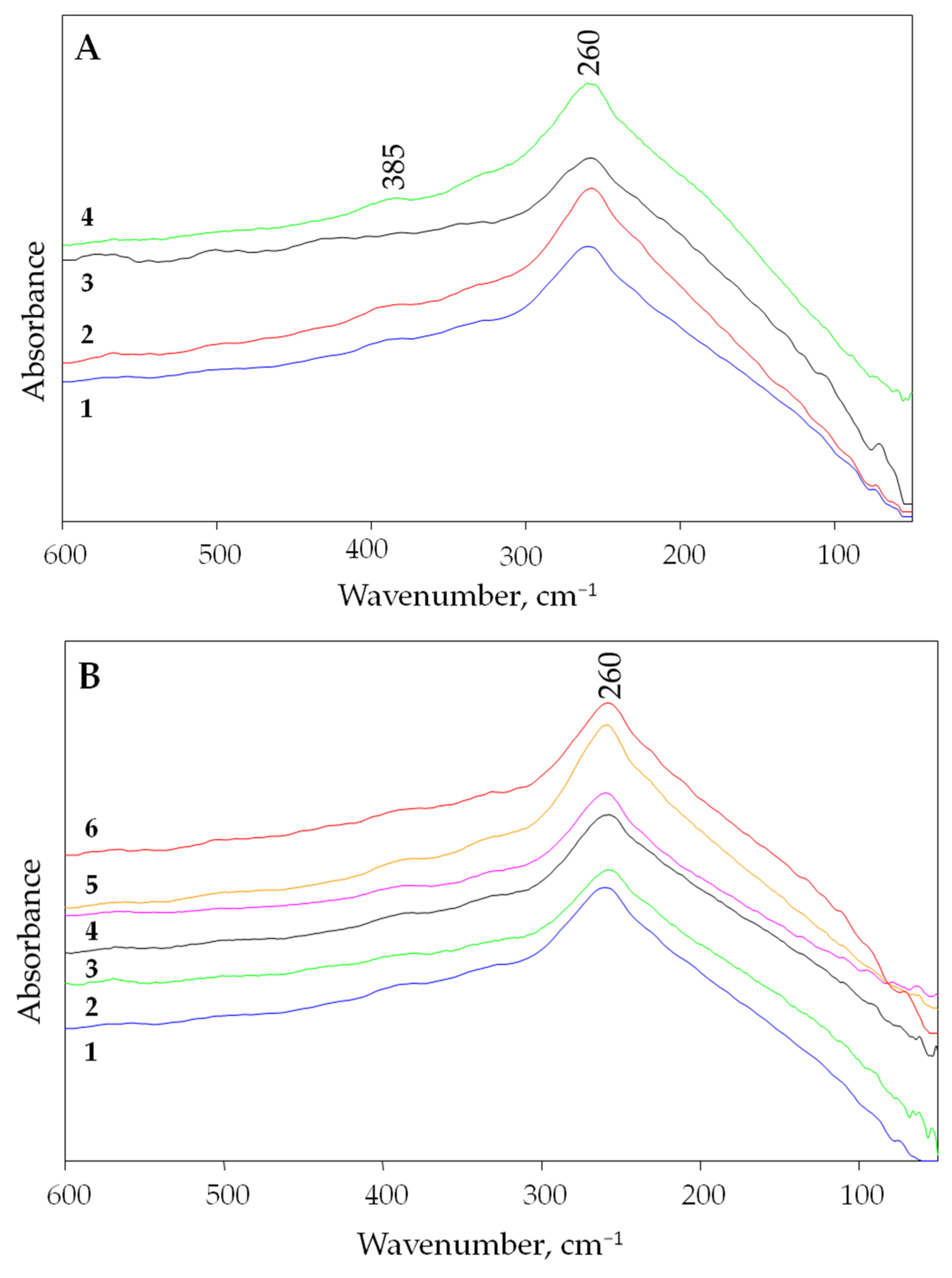
The experimental far infrared spectra (measured at room temperature) of three different villiaumite samples are presented in Figure 2A. Additionally, Figure 2A shows the spectrum of the pure chemical reagent NaF, which is a white powder (green line). Due to the disappearance of the red color of villiaumite upon heating (see Figure 3), far infrared spectra were also measured for villiaumite samples heated to temperatures of 100, 200, 300, 400 and 500 °C (Figure 2B).
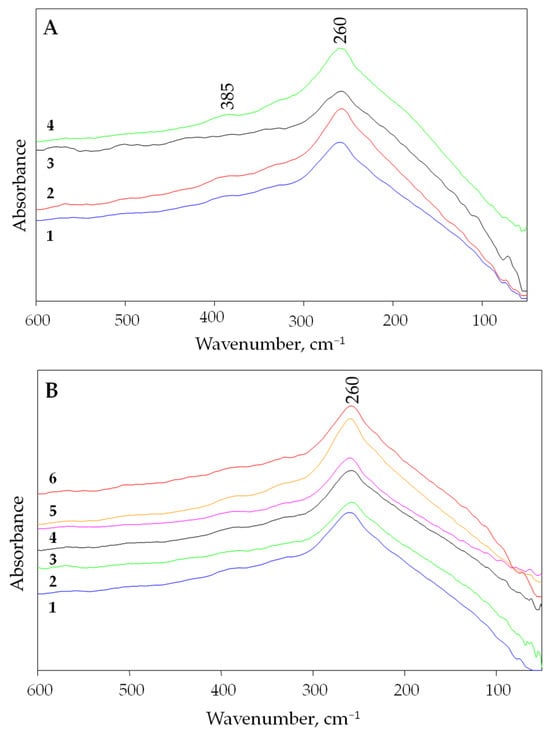
Figure 2.
The experimental far infrared spectra of NaF in the range of 600–50 cm−1. (A) Measurements at 20 °C: 1—villiaumite, sample 1; 2—villiaumite, sample 2; 3—villiaumite, sample 3; 4—chemical reagent NaF. (B) Measurements for villiaumite (sample 1): 1—20 °C; 2—100 °C; 3—200 °C; 4—300 °C; 5—400 °C; 6—500 °C.
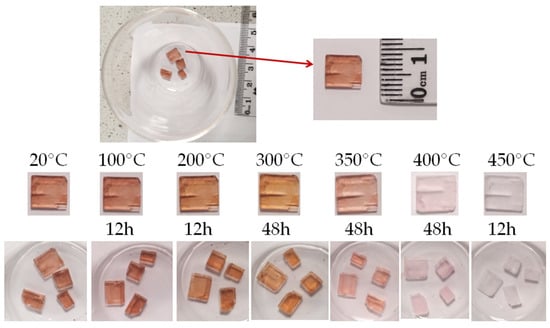
Figure 3.
Color change of villiaumite crystal after heating (a piece of sample 1 from Figure 1).
Our observations of color changes (Figure 3) of all villiaumite samples with increasing temperature are not fully consistent with the data in the literature. The “mindat.org” database [45] and Manutchehr-Danai [33] inform that villiaumite becomes colorless when heated to 300 °C. Sørensen [2] wrote that the gorgeous red color of villiaumite fades away upon heating it to 300 °C. By heating all the tested villiaumite samples, we observed that the color change actually starts at 300 °C, but the change is small. Minerals heated for two days at 300 °C become more orange (Figure 3). When heated for an additional two days at 400 °C, the tested samples still had a slightly pink color. Only after three days at 430 °C or several hours of heating at 450 °C did all crystals become colorless. Perhaps Calas et al. [3] had a similar experience, because they wrote in their article: “The tested samples have an intense red color that disappears within a few minutes at 500 °C and after 2 h at 400 °C”.
Even though the crystals became colorless, no changes in the far infrared spectra were observed, except for a small broadening of the band. This can be seen in Figure 2B, which shows the spectra of villiaumite (sample 1) at 20, 100, 200, 300, 400 and 500 °C. As can be seen in Figure 2B, all spectra sets are dominated by a broad band with the absorption maximum at 260 cm−1. Lower intensity bands are also found at the higher wavenumbers in the spectra. Comparing the presented far infrared spectrum of NaF with the spectrum of LiF [44], one can see a shift towards lower frequencies of about 93 cm−1 for the most intense band (for LiF, the most intense band is observed at 353 cm−1). This result is consistent with theory, which indicates that the greater the mass of the metal, the more the metal–halogen vibrations shift to lower frequencies [46]. We observed the same relationship for a series of chlorides. The most intense bands for LiCl, NaCl and KCl, were observed at 200, 175 and 145 cm−1, respectively [43,44].
3.2. XRD Measurements
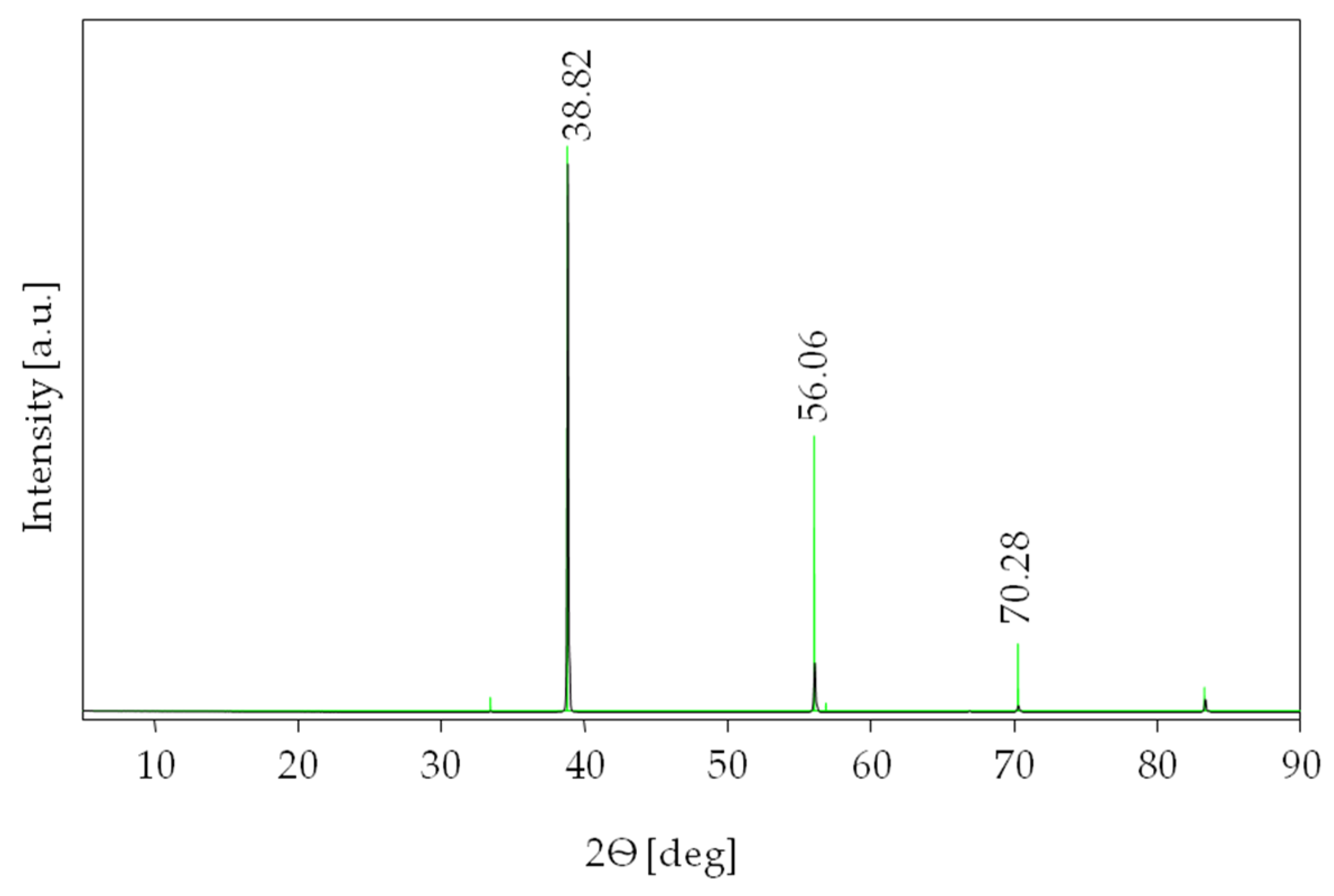
The villiaumite was identified by comparing the experimental XRD patterns of the powder with data contained in the Inorganic Crystal Structure Database (ICSD). Figure 4 presents the XRD pattern of the tested sample 1 (Figure 1) over an angular range of 5 to 90° 2θ. All the diffraction lines were found to belong to villiaumite (reference code of card: 04-007-4473) with a cubic crystal system and space-group symmetry [41]. For clarity, in Figure 2, the ICSD standard of NaF has been superimposed as a green line. Additionally, the diffraction data for our experimental measurement and literature data (reference code of card: 04-007-4473) are listed in Table 1. The X-ray diffraction pattern shows that other phases do not exist in the investigated sample of villiaumite.
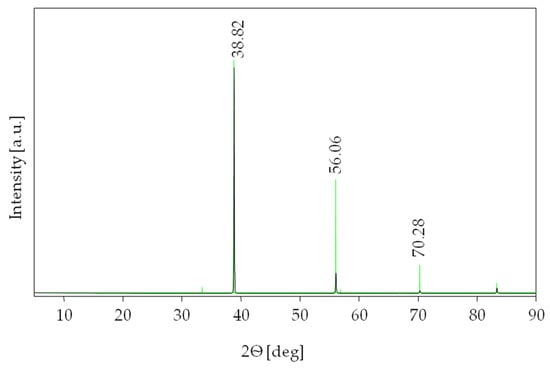
Figure 4.
XRD pattern of the villiaumite (sample 1, Figure 1) (black) and the ICSD standard of NaF (green).

Table 1.
List of selected X-ray diffraction data for NaF, the ICSD standard [41] (green) and our experimental measurement (black).
3.3. DFT Calculations
3.3.1. Geometry
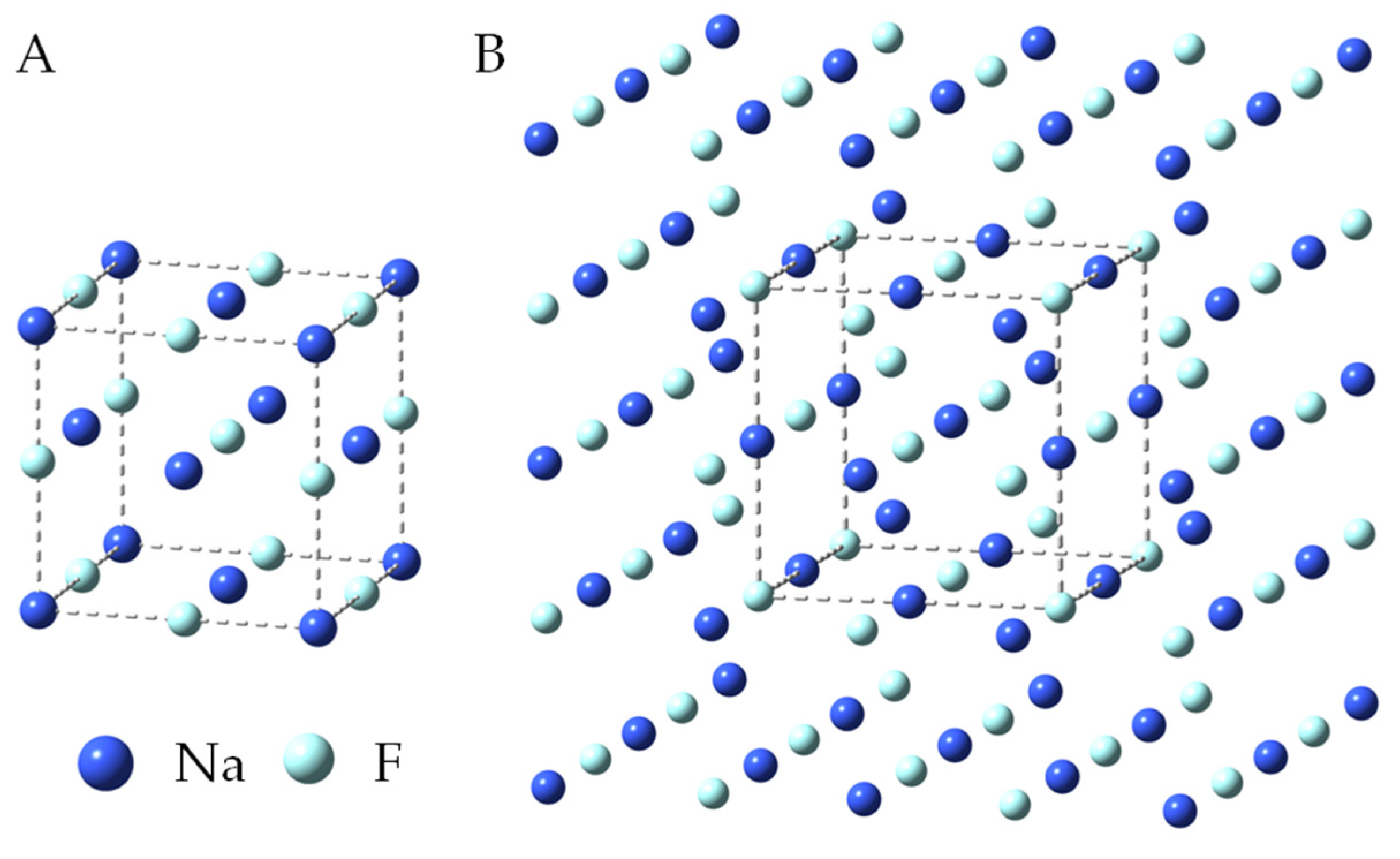
The infrared frequency calculations were preceded by the optimization of the geometry of the model structure of the sodium fluoride crystal. Figure 5A shows the NaF unit cell, which contains 27 atoms (3 × 3 × 3). Our model of a crystal lattice of NaF salt was built by adding one more layer of atoms to each of the walls of a unit cell. In order to preserve the symmetry of the unit cell and, at the same time, make each of the 27 atoms of this unit cell have 6-fold coordination, a model containing 125 atoms (5 × 5 × 5) (Figure 5B) had to be used for DFT calculations. In such a model, none of the atoms of the unit cell (Figure 5A) are located at the edge of the crystal. Geometric parameters (interatomic distances and angles) for the 125-atom crystal model of sodium fluoride were taken from crystallographic studies [41,42]. According to our previous work, we rigidly assumed in the calculations that all angles were 90°. Freezing the angles in the structure makes the obtained computational parameters more consistent with the experimental results [41,42,47,48,49,50,51,52,53,54]. During the optimization of geometry, there was no change in the symmetry of the assumed model of the NaF crystal, and the final structure also had Oh symmetry.
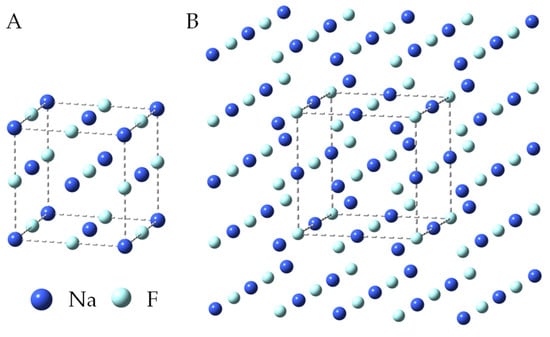
Figure 5.
Unit cell of sodium fluoride (A) and geometry of the optimized 125-atom model of NaF crystal (DFT/B3LYP/6-31+g*) (B).
Table 2 lists the experimental and calculated geometrical parameters for the NaF unit cells. The theoretical values derived for the lattice parameter and the cubic structure are equal to a = 4.600 Å and α = 90.0°, respectively. These results correspond well with the experimental data presented in the literature [41,42,47,48,49,50,51,52,53,54]. This means that the assumed model of the NaF crystal well reflects the actual structure of this salt. The angle value is unchanged for all experimental measurements and is 90.0°. As listed in Table 2, the interatomic distance varies in the range of 3.614–3.78 Å. Thus, the obtained calculated value is slightly lower than the experimentally measured values for NaF compound.

Table 2.
List of experimental and calculated (DFT/B3LYP/6-31+g*) lattice parameters for NaF at room temperature and atmospheric pressure (# temperature 302.6 K, ## temperature 300 K).
3.3.2. Calculated Infrared Frequency of NaF
The IR frequencies for the adopted NaF crystal model were calculated at the same level of theory (DFT/B3LYP/6-31+g*). The frequency and intensity of active T1u IR vibrations are listed in Table 3. The symbol T1u means that these are normal vibrations that are three times degenerate (T), symmetrical about an axis other than the axis of the greatest multiplicity (1) and antisymmetric about the center of symmetry (u). It should be emphasized that in the Oh point group, only vibrations with T1u symmetry are active in the infrared. As listed in Table 3, the infrared absorption of NaF appears in a small wavenumber range of 74.41–411.69 cm−1. The absorption band intensities are relatively small or even negligible, except for two of them positioned at 255.05 and 411.69 cm−1.

Table 3.
Calculated IR frequency and intensity of T1u vibrational modes for the 125-atom model of NaF (DFT/B3LYP/6-31+g*, values not scaled).
3.3.3. Comparison of Calculated and Experimental Spectra of NaF
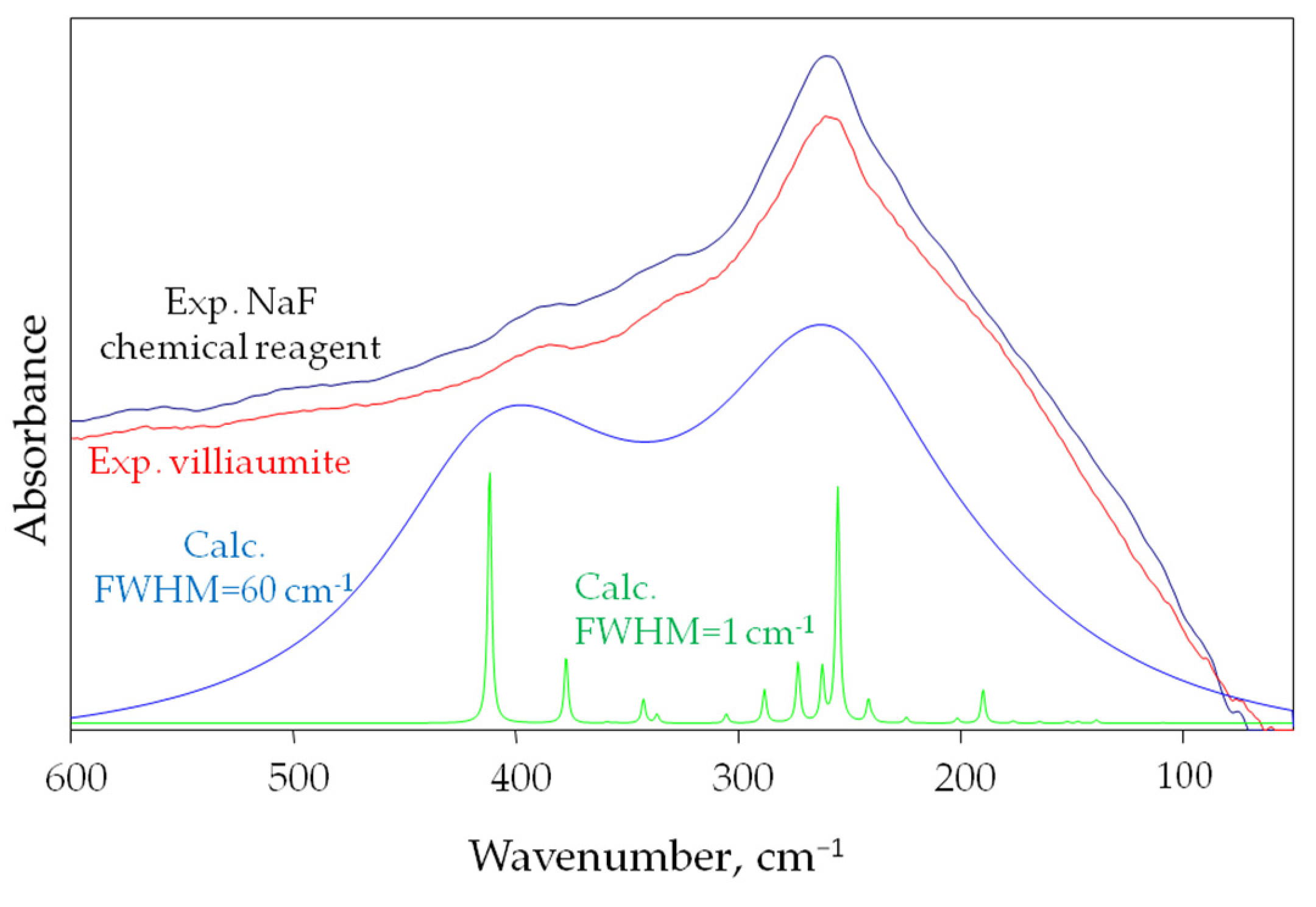
Figure 6 shows the calculated infrared spectra for the 125-atom NaF salt model, the experimental spectra of villiaumite, and the NaF chemical reagent in the spectral range 600–50 cm−1 is shown in Figure 6.
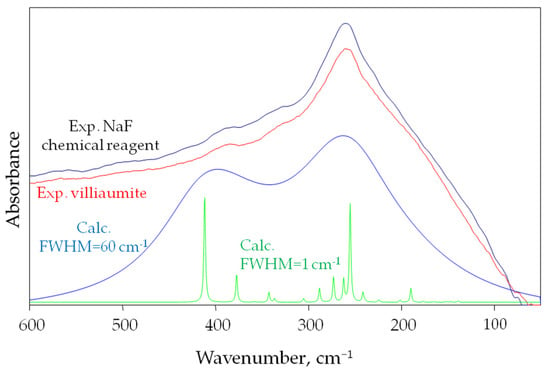
Figure 6.
Both theoretical spectrum in the far infrared, with half-bandwidths 1 and 60 cm−1, for the 125-atom model of NaF salt model and two experimental spectra (villiaumite and chemical reagent NaF) in the spectral far infrared domain range of 600–50 cm−1.
Figure 6 shows computational spectra with two different half widths of 1 and 60 cm−1. The experimental spectrum shows that the absorption bands of sodium fluoride are very wide. Therefore, the computational spectrum in which FWHM (full width at half maximum) equals 60 cm−1 reflects the experimental spectrum much better. Figure 6 clearly shows that the calculated infrared absorption range for sodium fluoride is within the experimental range. As can be seen in Figure 6, the most intense band in the experimental spectrum (260 cm−1) is also the most intense in the computational spectrum (255.05 cm−1). Nevertheless, the second strong computational band with a maximum at 411.69 cm−1 is not as intense in the experimental spectrum (385 cm−1). The differences seen in the vibrational spectra may result from discrepancies between experimental and calculated structural parameters, as well as from the limitation of DFT approximation.
4. Conclusions
In this work, three samples of villiaumite (from the Khibiny Mountains in the Kola Peninsula (Russia) and from Mon Saint Hilaire in Quebec (Canada)) were investigated using far infrared spectroscopy and DFT calculation.
- The far infrared spectra of the natural mineral villiaumite (NaF) were measured. The maximum infrared absorption of villiaumite was observed at about 260 cm−1.
- The tested villiaumite samples began to change color very slowly after being heated above 300 °C. When heated, the samples of the reddish mineral villiaumite turn orange, pink and finally colorless at appropriate temperatures. The tested samples remained colorless after 3 days of heating at 430 °C. This observation is not consistent with previously reported data in the literature and probably requires confirmation by other researchers.
- Because the color of villiaumite changes from red to colorless under the influence of temperature, far infrared spectra were measured for samples at room temperature (red) and at 100, 200, 300, 400 and 500 °C (colorless). It was observed that the spectra of sodium fluoride are independent of its color. Red villiaumite and orange, pink and colorless villiaumite (after heating the red sample) and white chemical reagent (NaF) have almost identical far infrared spectra.
- The calculation (DFT/B3LYP/6-31+g*) for the 125-atom model of the crystal structure of NaF provided results that very good reflect the geometric parameters of the NaF unit cell and the range of absorption of the sample in infrared light.
Author Contributions
Conceptualization, K.C.-L.; methodology, K.C.-L., E.S. and K.K.Z.; software, K.C.-L., E.S. and K.K.Z.; validation, K.C.-L., E.S. and K.K.Z.; formal analysis, K.C.-L., E.S. and K.K.Z.; investigation, K.C.-L., E.S. and K.K.Z.; resources, K.C.-L., E.S. and K.K.Z.; data curation, K.C.-L., E.S. and K.K.Z.; writing—original draft preparation, K.C.-L.; writing—review and editing, K.C.-L., E.S. and K.K.Z.; visualization, K.C.-L.; supervision, K.C.-L.; project administration, K.C.-L.; funding acquisition, K.C.-L., E.S. and K.K.Z. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This research was partly funded by AGH University of Science and Technology in Krakow, The Faculty of Drilling, Oil and Gas (No. 16.16.190.779). Research project partly supported by the program “Excellence Initiative-Research University” for the AGH University of Science and Technology.
Data Availability Statement
The data presented in this study are available on request from the corresponding author.
Acknowledgments
Academic Computer Centre Cyfronet AGH (Krakow, Poland) is acknowledged for computing time. This research was supported in part by PL-Grid Infrastructure.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest. The funders had no role in the design of the study; in the collection, analyses, or interpretation of data; in the writing of the manuscript; or in the decision to publish the results.
References
- Anthony, J.W.; Bideaux, R.A.; Bladh, K.W.; Nichols, M.C. Handbook of Mineralogy; Mineral Data Publishing: Tucson, AZ, USA, 1990. [Google Scholar]
- Sørensen, E. On the adsorption of some anionic collectors on fluoride minerals. J. Colloid Interface Sci. 1973, 45, 601–607. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Calas, G.; Galoisy, L.; Geisler, A. Sodium nanoparticles in alkali halide minerals: Why is villiaumite red and halite blue? Am. Mineral. 2021, 106, 838–842. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reynolds, J.G.; Belsher, J.D. A review of sodium fluoride solubility in water. J. Chem. Eng. Data 2017, 62, 1743–1748. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Johnston, N.R.; Strobel, S.A. Principles of fluoride toxicity and the cellular response: A review. Arch. Toxicol. 2020, 94, 1051–1069. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- García, M.G.; Borgnino, L. Fluoride in the context of the environment. In Fluorine Chemistry, Analysis, Functions and Effects; Preedy, V., Ed.; Royal Society of Chemistry: Cambridge, UK, 2015; pp. 3–21. [Google Scholar]
- Grohol, M.; Veeh, C. Study on the Critical Raw Materials for the EU 2023—Final Report. Directorate-General for Internal Market, Industry, Entrepreneurship and SMEs; European Commission: Brussels, Belgium, 2023. [Google Scholar]
- Poulain, M.; Poulain, M.; Lucas, J. Verres fluores au tetrafluorure de zirconium proprietes optiques d’un verre dope au Nd3+. Mat. Res. Bull. 1975, 10, 243–246. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, X.; Peyghambarian, N. High-power ZBLAN glass fiber lasers: Review and prospect. Adv. OptoElectron. 2010, 2010, 501956. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marinov, M.; Kozhukharov, V.; Vasilev, S. Glass formation and properties in the Ba(PO3)2-AIF3-NaF system. J. Mater. Sci. Lett. 1986, 5, 1129–1130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahammed, S.; Chandra Sekhar, K.; Narasimha Chary, M.; Shareefuddin, M. The role of sodium fluoride on CdO-B2O3 glasses doped with chromium ions. Appl. Phys. A 2019, 125, 882. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lumeau, J.; Glebova, L.; Glebov, L.B. Influence of UV-exposure on the crystallization and optical properties of photo-thermo-refractive glass. J. Noncryst. Solids 2008, 354, 425–430. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fokin, V.M.; Guilherme, P.; Souza, G.P.; Zanotto, E.D. Sodium fluoride solubility and crystallization in photo-thermo-refractive glass. J. Am. Ceram. Soc. 2010, 93, 716–721. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tustison, R.W. Fluorinated silicate glass for conventional and holographic optical elements. In Window and Dome Technologies and Materials X; Glebov, L., Ed.; Proceedings of SPIE; SPIE: Bellingham, WA, USA, 2007; Volume 6545, p. 654507. [Google Scholar]
- Sadegh, F.; Akman, E.; Prochowicz, D.; Tavakoli, M.M.; Yadav, P.; Akin, S. Facile NaF treatment achieves 20% efficient ETL-free perovskite solar cells. ACS Appl. Mater. Inter. 2022, 14, 38631–38641. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Takahiro, M.; Shin, T.; Tatsuo, F. Improving the photovoltanic performance of co-evaporated Cu2ZnSnS4 thin-film solar cells by incorporation of sodium from NaF layers. Prog. Photovolt. Res. Appl. 2016, 24, 1009–1015. [Google Scholar]
- Ehira, H.; Jimbo, K.; Katagiri, H. Impact of Na-addition effect into CZTS thin film solar cells. AIP Conf. Proc. 2016, 1865, 050004. [Google Scholar]
- Irfan, M.; Banu, S.R.; Manjunath, A.; Mahesh, S.S. Electrical and structural characterization of NaF doped PVA-PEG solid polymer blend electrolyte films. AIP Conf. Proc. 2019, 2115, 030594. [Google Scholar]
- Comparative Studies on Plasticized and Unplasticized Polyacrylonitrile (PAN) Polymer Electrolytes Containing Lithium and Sodium Salts. Available online: www.researchgate.net/publication/252932759_Comparative_Studies_on_Plasticized_and_Unplasticized_Polyacrylonitrile_PAN_Polymer_Electrolytes_Containing_Lithium_and_Sodium_Salts (accessed on 15 September 2023).
- Irfan, M.; Manjunath, A.; Mahesh, S.S. Study on the optical properties of polyvinyl alcohol doped sodium fluoride polymer electrolyte films. AIP Conf. Proc. 2020, 2220, 080063. [Google Scholar]
- Koga, K.T.; Rose-Koga, E.F. Fluorine in the Earth and the solar system, where does it come from and can it be found? C. R. Chim. 2018, 21, 749–756. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Allibone, R.; Cronin, S.J.; Charley, D.T.; Neall, V.E.; Stewart, R.B.; Oppenheimer, C. Dental fluorosis linked to degassing of Ambrym volcano, Vanuatu: A novel exposure pathway. Environ. Geochem. Health. 2012, 34, 155–170. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lubojanski, A.; Piesiak-Panczyszyn, D.; Zakrzewski, W.; Dobrzynski, W.; Szymonowicz, M.; Rybak, Z.; Mielan, B.; Wiglusz, R.J.; Watras, A.; Dobrzynski, M. The safety of fluoride compounds and their effect on the human body—A narrative review. Materials 2023, 16, 1242. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.; Zheng, N.; Liu, H.; Cao, X.; Teng, Y.; Zhai, Y. Distribution, formation and human health risk of fluorine in groundwater in Songnen plain, NE China. Water 2021, 13, 3236. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dar, M.A.; Sankar, K.; Dar, I.A. Fluorine contamination in groundwater: A major challenge. Environ. Monit. Assess. 2011, 173, 955–968. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martinez-Mier, E.A. Fluoride: Its metabolism, toxicity, and role in dental health. J. Evid. Based Complement. Altern. Med. 2012, 17, 28–32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bergmann, R. Fluorid in der Ernährung des Menschen. Biologische Bedeutung für den Wachsenden Organismus; Habilitationsschrift Medical Faculty, Free University Berlin: Berlin, Germany, 1994. [Google Scholar]
- Guth, S.; Hüser, S.; Roth, A.; Degen, G.; Diel, P.; Edlund, K.; Eisenbrand, G.; Engel, K.H.; Epe, B.; Grune, T.; et al. Toxicity of fluoride: Critical evaluation of evidence for human developmental neurotoxicity in epidemiological studies, animal experiments and in vitro analyses. Arch. Toxicol. 2020, 94, 1375–1415. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Grandjean, P.; Landrigan, P.J. Neurobehavioural effects of developmental toxicity. Lancet Neurol. 2014, 13, 330–338. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- The mineral list on the Rruff Project website. Available online: https://rruff.info/Villiaumite (accessed on 8 November 2023).
- Muntianu, A.; Guo, B.; Bernath, P.F. High-resolution infrared emission spectrum of NaF. J. Mol. Spectr. 1996, 176, 274–279. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ismail, Z.K.; Hauge, R.H.; Margrave, J.L. Infrared spectra of sodium and potassium fluorides by matrix isolation. J. Inorg. Nucl. Chem. 1973, 35, 3201–3206. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Manutchehr-Danai, M. Villiaumite. In Dictionary of Gems and Gemology; Manutchehr-Danai, M., Ed.; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2009. [Google Scholar]
- García-Cuesta, I.; Serrano-Andrés, L.; Sánchez de Merás, A.; Nebot-Gil, I. Theoretical spectroscopic parameters of the alkali monofluorides LiF, NaF and KF. Chem. Phys. Lett. 1992, 199, 535–544. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Degen, T.; Sadki, M.; Bron, E.; König, U.; Né-nert, G. The HighScore suite. Powder Diffr. 2014, 29, 13–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lutterotti, L.; Matthies, S.; Wenk, H.R. MAUD (Material analysis using diffraction): A user friendly Java program for Rietveld texture analysis and more. In Proceedings of the Twelfth International Conference on Textures of Materials (ICOTOM-12), Montreal, QC, Canada, 9–13 August 1999. [Google Scholar]
- Becke, A.D. Density-functional exchange-energy approximation with correct asymptotic behavior. Phys. Rev. A 1988, 38, 3098–3100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, C.; Yang, W.; Parr, R.G. Development of the Colle-Salvetti correlation-energy formula into a functional of the electron density. Phys. Rev. B 1988, 37, 785–798. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Francl, M.M.; Pietro, W.J.; Hehre, W.J.; Binkley, J.S.; DeFrees, D.J.; Pople, J.A.; Gordon, M.S. Self-consistent molecular orbital methods. 23. A polarization-type basis set for 2nd-row elements. J. Chem. Phys. 1982, 77, 3654–3665. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Frisch, M.J.; Trucks, G.W.; Schlegel, H.B.; Scuseria, G.E.; Robb, M.A.; Cheeseman, J.R.; Scalmani, G.; Barone, V.; Petersson, G.A.; Nakatsuji, H.; et al. Wallingford CT, 2016. Program Gaussian 16, Revision C.01. Available online: https://www.scirp.org/reference/referencespapers?referenceid=2418053 (accessed on 8 November 2023).
- Srivastava, K.K.; Merchant, H.D. Thermal expansion of alkali halides above 300 K. J. Phys. Chem. Solids 1973, 34, 2069–2073. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deshpande, V.T. Thermal expansion of sodium fluoride and sodium bromide. Acta Crystallogr. 1961, 14, 794. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chruszcz-Lipska, K.; Zelek-Pogudz, S.; Solecka, U.; Solecki, M.L.; Szostak, E.; Zborowski, K.K.; Zając, M. Use of the far infrared spectroscopy for NaCl and KCl minerals characterization—A case study of halides from Kłodawa in Poland. Mineral 2022, 12, 1561. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chruszcz-Lipska, K.; Szostak, E.; Zborowski, K.K.; Knapik, E. Study of the structure and infrared spectra of LiF, LiCl and LiBr using density functional theory (DFT). Materials 2023, 16, 5353. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mindat.Org Non-Commercial Interactive Online Database of Minerals. Available online: https://www.mindat.org/min-4181.html (accessed on 8 November 2023).
- Ferraro, J.R. Metal halide vibrations. In Low-Frequency Vibration of Inorganic and Coordination Compounds; Ferraro, J.R., Ed.; Springer: New York, NY, USA, 1971; pp. 111–189. [Google Scholar]
- Debye, P.; Scherrer, P. Crystal structure of lithium halides. Phys. Zeitschrif 1918, 19, 474–483. [Google Scholar]
- Hull, A.W. Chemical analysis by X-rays. Trans. Am. Inst. Electr. Eng. 1919, 38, 1445–1466. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bragg, W.L. Crystal structure. Nature 1920, 105, 646–648. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barth, T.; Lunde, G. Über das Mineral Villiaumit. Zentralblatt Fuer Mineral. Geol. Palaeontol. 1927, 1927, 57–66. [Google Scholar]
- Finch, G.J.; Fordham, S. The effect of crystal-size on lattice-dimensions. Proc. Phys. Soc. 1936, 48, 85–94. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Streltsov, V.A.; Tsirelson, V.G.; Ozerov, R.P.; Golovanov, O.A. Electronic and thermal parameters of ions in CaF2: Regularized least squares treatment. Kristallografiya 1988, 33, 90–97. [Google Scholar]
- Srinivasa, R.B.; Sanyal, S.P. Structural and elastic properties of sodium halides at high pressure. Phys. Rev. B Condens. Matter Mater. Phys. 1990, 42, 1810–1816. [Google Scholar]
- Shirako, Y.; Shi, Y.G.; Aimi, A.; Mori, D.; Kojitani, H.; Yamaura, K.; Inaguma, Y.; Akaogi, M. High-pressure stability relations, crystal structures, and physical properties of perovskite and post-perovskite of NaNiF3. J. Solid State Chem. 2012, 191, 167–174. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).