Waste Corn Straw as a Green Reductant for Hematite Reduction Roasting: Phase Transformation, Microstructure Evolution and Process Mechanism
Abstract
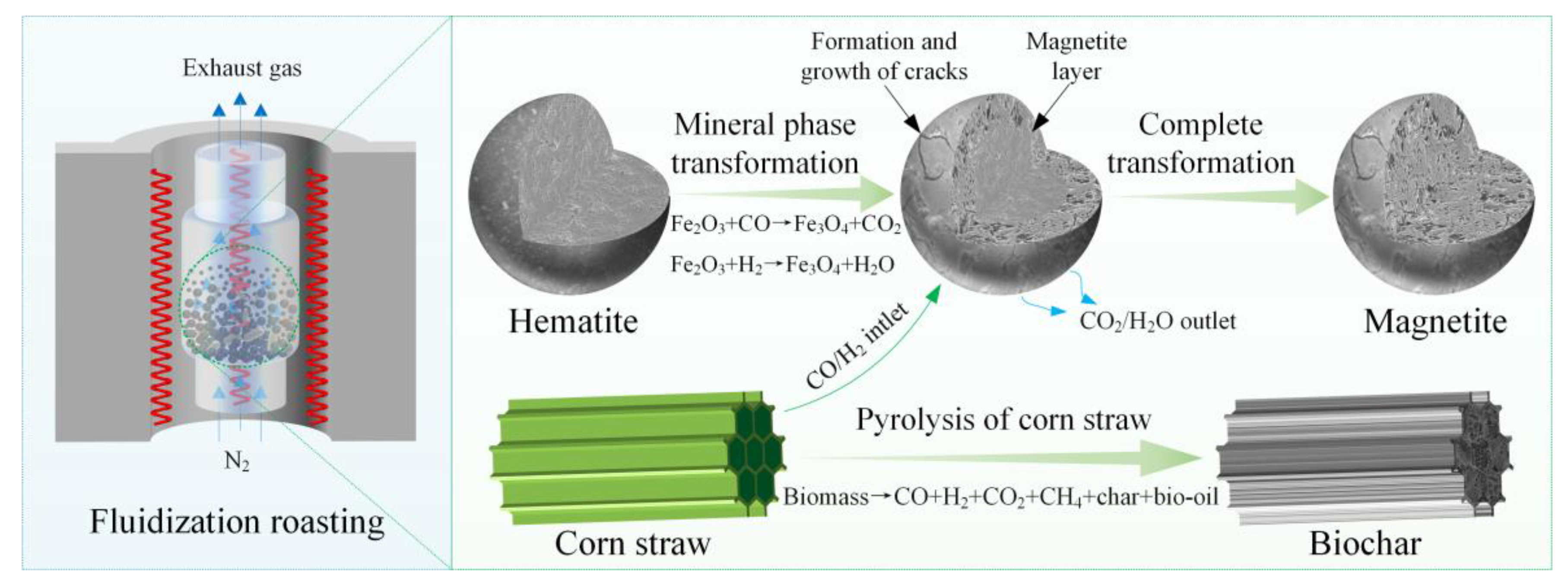
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
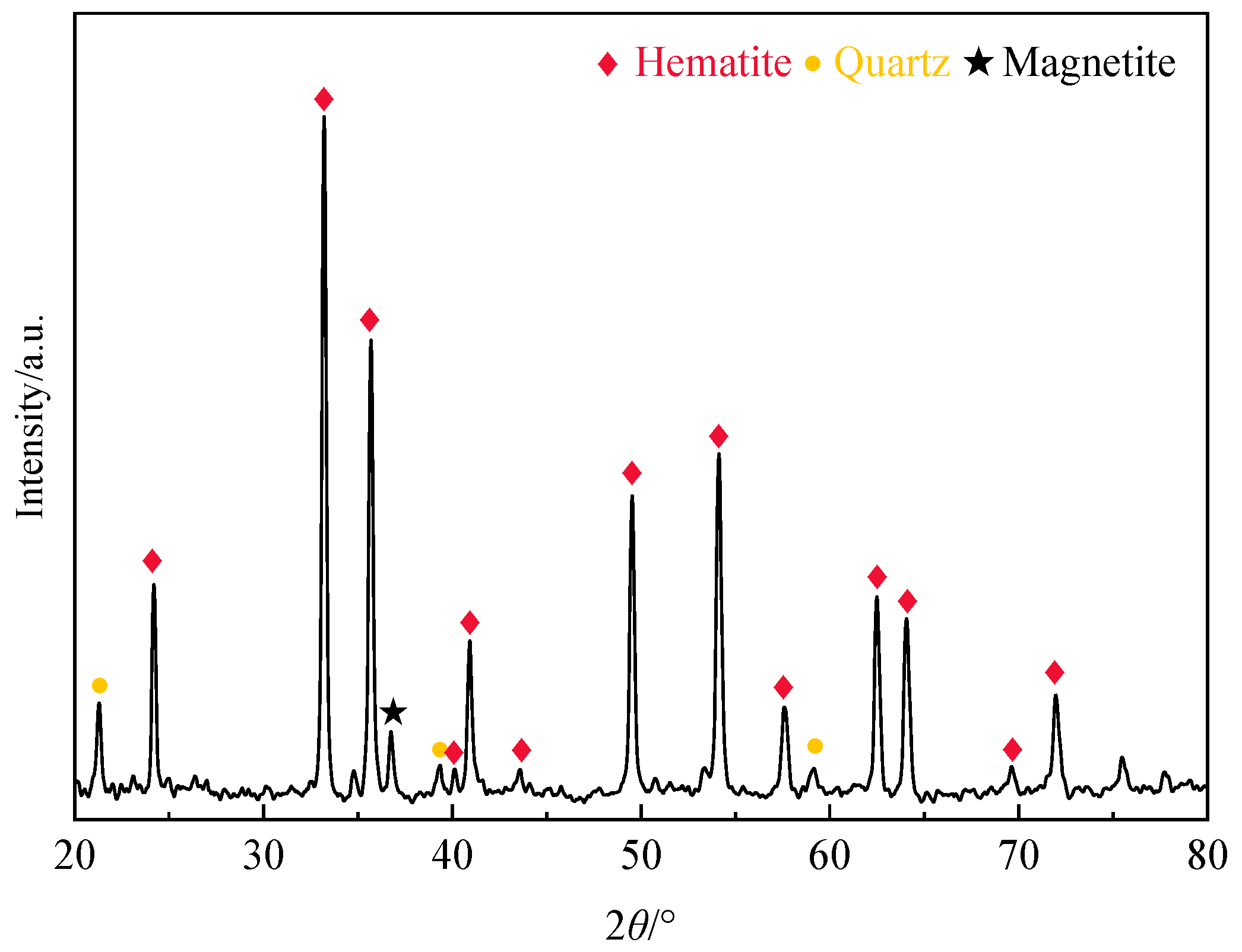
2.1. Materials
2.2. Methods and Equipment
2.2.1. Experimental Apparatus and Procedure
2.2.2. Characterization Methods
3. Results and Discussion
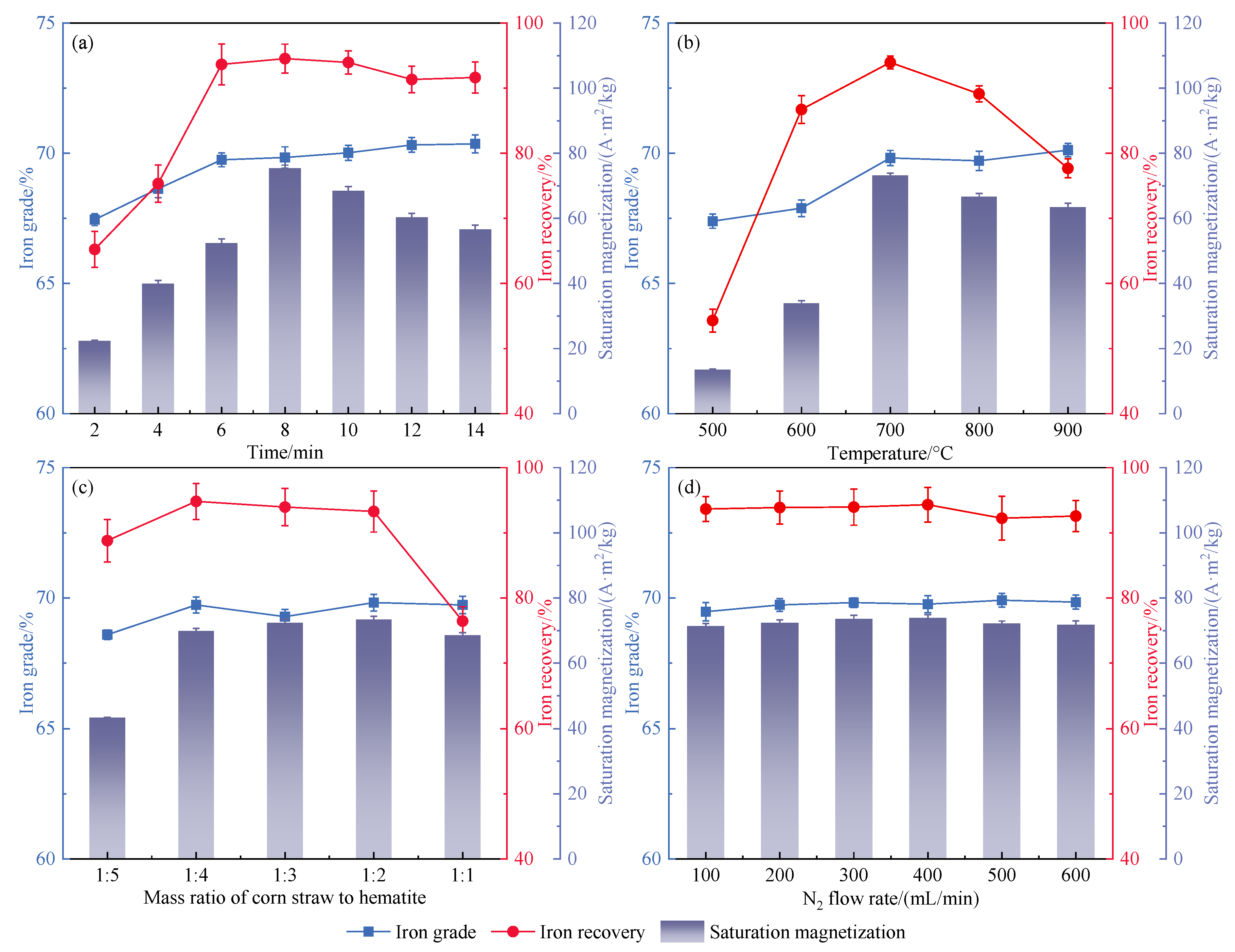
3.1. Effect of Roasting Conditions
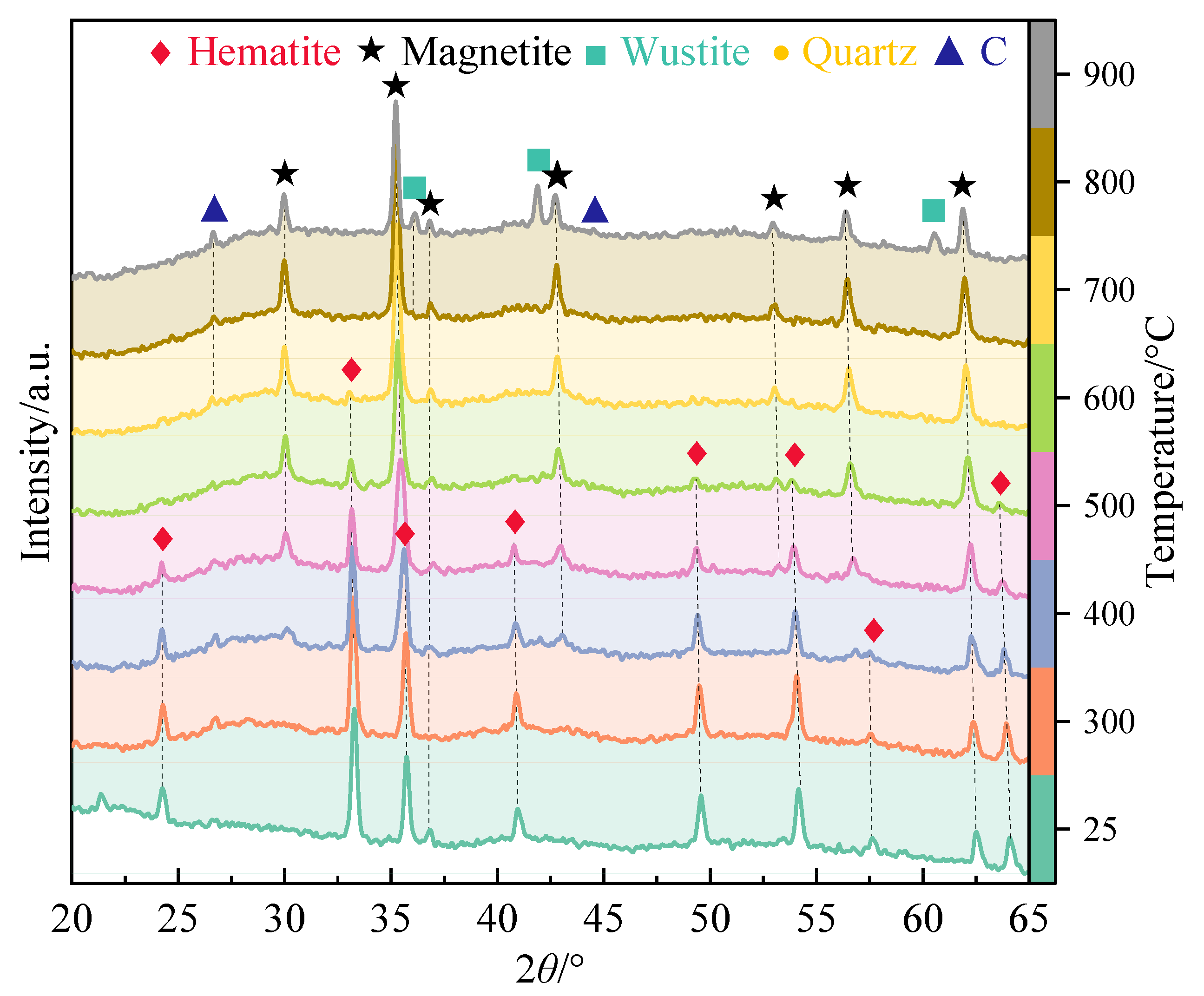
3.2. Phase Transformation
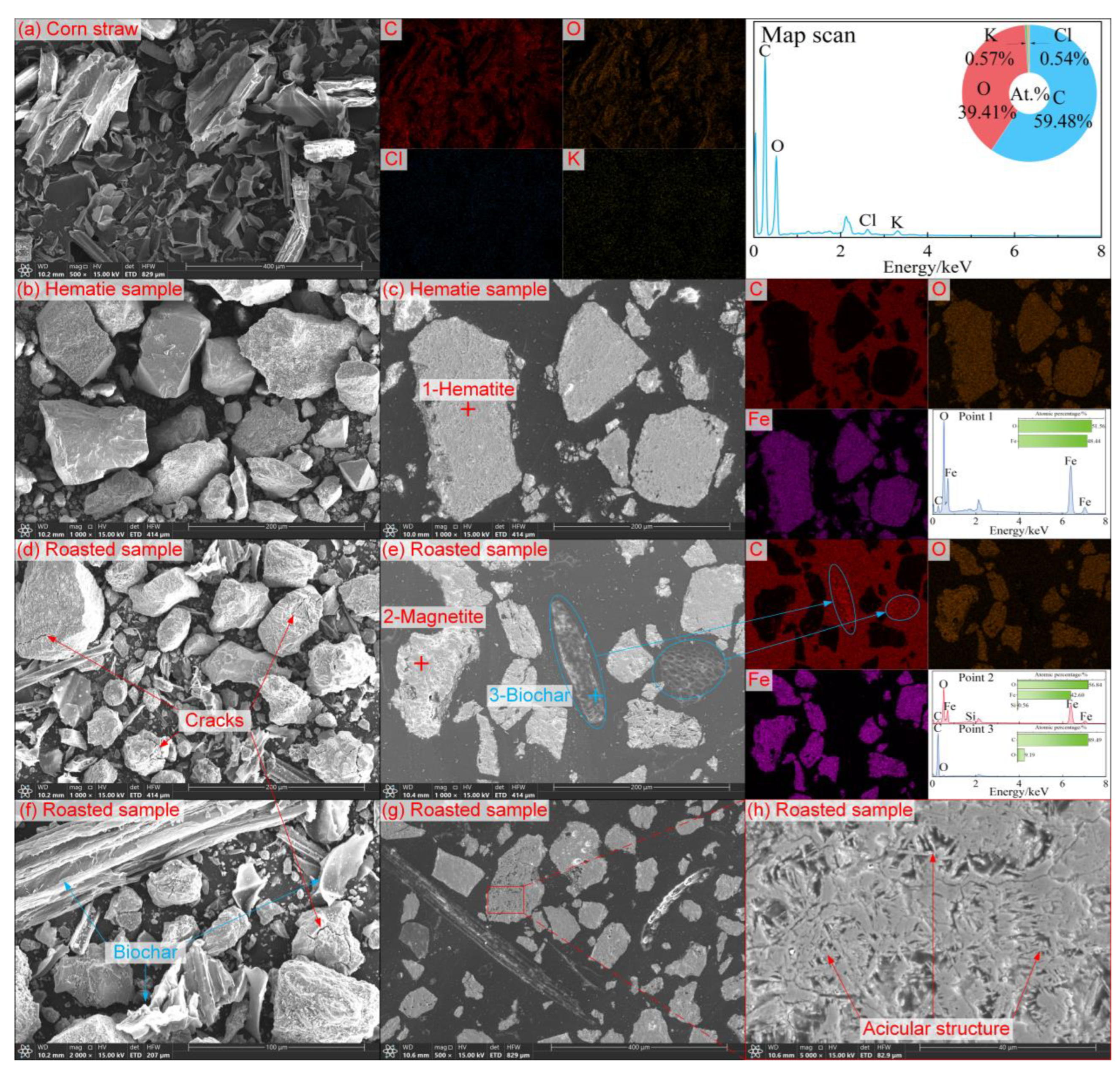
3.3. Microstructure Evolution
3.4. Process Mechanism, Environmental Benefits and Feasibility
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Yu, J.; Xu, R.; Zhang, J.; Zheng, A. A review on reduction technology of air pollutant in current China’s iron and steel industry. J. Clean. Prod. 2023, 414, 137659. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Q.; Sun, Y.; Han, Y.; Li, Y.; Gao, P. Review on coal-based reduction and magnetic separation for refractory iron-bearing resources. Int. J. Miner. Met. Mater. 2022, 29, 2087–2105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, H.; Zhang, P.; Zhou, F.; Lu, M. Application of multi-stage dynamic magnetizing roasting technology on the utilization of cryptocrystalline oolitic hematite: A review. Int. J. Min. Sci. Technol. 2022, 32, 865–876. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roy, S.K.; Nayak, D.; Rath, S.S. A review on the enrichment of iron values of low-grade Iron ore resources using reduction roasting-magnetic separation. Powder Technol. 2020, 367, 796–808. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, K.; Chen, X.; Guo, W.; Luo, H.; Gong, Z.; Li, B.; Wu, W. Effects of biomass reducing agent on magnetic properties and phase transformation of Baotou low-grade limonite during magnetizing-roasting. PLoS ONE 2017, 12, e0186274. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wu, S.; Sun, T.; Kou, J.; Xu, H. A new iron recovery and dephosphorization approach from high-phosphorus oolitic iron ore via oxidation roasting-gas-based reduction and magnetic separation process. Powder Technol. 2023, 413, 118043. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nayak, D.; Dash, N.; Ray, N.; Rath, S.S. Utilization of waste coconut shells in the reduction roasting of overburden from iron ore mines. Powder Technol. 2019, 353, 450–458. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- You, J.; Zhang, S.; Wu, S.; Yan, L.; Huang, W.; Rao, M. Preparation of Reduced Iron Powder from High-Phosphorus Iron Ore: A Pilot-Scale Rotary-Kiln Investigation. Miner. Process. Extr. Metall. Rev. 2023, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, H.; Zhang, M.; Zou, Z.; Yan, D. Fluidized magnetization roasting utilization of refractory siderite-containing iron ore with low gas reduction potential. Adv. Powder Technol. 2023, 34, 103994. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, S.; Sun, T.; Kou, J. A novel and clean utilization of converter sludge by co-reduction roasting with high-phosphorus iron ore to produce powdery reduced iron. J. Clean. Prod. 2022, 363, 132362. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Altiner, M. Roasting of a low-grade goethite ore using horse residue and its beneficiation by magnetic separation. Min. Metall. Explor. 2020, 37, 1357–1365. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Q.; Sun, Y.; Han, Y.; Li, Y.; Gao, P. Reaction behavior and non-isothermal kinetics of suspension magnetization roasting of limonite and siderite. Int. J. Miner. Met. Mater. 2023, 30, 824–833. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cao, Y.; Sun, Y.; Gao, P.; Han, Y.; Li, Y. Mechanism for suspension magnetization roasting of iron ore using straw-type biomass reductant. Int. J. Min. Sci. Technol. 2021, 31, 1075–1083. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Li, D.; Liu, X.; Zhang, W.; Li, Z.; Li, Y.; Ren, Y.; Li, H. Mechanism of magnetizing the Bayer red mud and meanwhile improving the cementitious activity of its tailings by using biomass. J. Clean. Prod. 2021, 287, 125016. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deng, J.; Ning, X.-A.; Shen, J.; Ou, W.; Chen, J.; Qiu, G.; Wang, Y.; He, Y. Biomass waste as a clean reductant for iron recovery of iron tailings by magnetization roasting. J. Environ. Manag. 2022, 317, 115435. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Qiu, G.; Ning, X.; Shen, J.; Wang, Y.; Zhang, D.; Deng, J. Recovery of iron from iron tailings by suspension magnetization roasting with biomass-derived pyrolytic gas. Waste Manag. 2023, 156, 255–263. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sahu, S.N.; Meikap, B.; Biswal, S.K. Magnetization roasting of waste iron ore beneficiation plant tailings using sawdust biomass; A novel approach to produce metallurgical grade pellets. J. Clean. Prod. 2022, 343, 130894. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, K.; Ge, Y.; Guo, W.; Li, N.; Wang, Z.; Luo, H.; Hu, Q.; Li, B.; Wu, W.; Shang, S. Phase transition and magnetic properties of low-grade limonite during reductive roasting. Vacuum 2019, 167, 163–174. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jaiswal, R.K.; Soren, S.; Jha, G. A novel approach of utilizing the waste biomass in the magnetizing roasting for recovery of iron from goethitic iron ore. Environ. Technol. Innov. 2023, 31, 103184. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sahu, S.N.; Meikap, B.; Biswal, S.K. Reduction in fossil fuel consumption by exploiting separation of refractory grade oolitic iron ores using black plum leaf litter via magnetization roasting & pelletization; a small step toward decarbonization & sustainability. Sep. Purif. Technol. 2023, 311, 123327. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fang, H.; Zhou, X.; Gao, L.; Yan, H.; Wang, Y.; Ji, H. Characteristic and kinetic study of the hot air-drying process of artificial limonite pellets. J. Taiwan Inst. Chem. Eng. 2023, 147, 104925. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Q.; Sun, Y.; Wang, S.; Han, Y.; Li, Y.; Gao, P. Partial magnetization of siderite via fluidization roasting for efficient recovery of iron: Phase transition, microstructure evolution and kinetics. Adv. Powder Technol. 2023, 34, 104194. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yuan, X.; Luo, F.; Liu, S.; Zhang, M.; Zhou, D. Comparative Study on the Kinetics of the Isothermal Reduction of Iron Ore Composite Pellets Using Coke, Charcoal, and Biomass as Reducing Agents. Metals 2021, 11, 340. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, X.; Zhang, H.; Li, S.; Li, D.; Huang, D. Research on reduction of Fe2O3 by biomass sawdust. J. Shanghai Jiaotong Univ. (Sci.) 2017, 22, 280–285. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Q.; Sun, Y.; Wang, S.; Han, Y.; Li, W.; Li, Y. Whether magnetization roasting requires complete phase reconstruction of iron minerals: A study of phase transition and microstructure evolution. Powder Technol. 2022, 411, 117934. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sahoo, A.; Kumar, S.; Kumar, J.; Bhaskar, T. A detailed assessment of pyrolysis kinetics of invasive lignocellulosic biomasses (Prosopis juliflora and Lantana camara) by thermogravimetric analysis. Bioresour. Technol. 2021, 319, 124060. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, X.; Wang, Z.; Can, M.; Bai, H.; Ta, N. Analysis of yield and current comprehensive utilization of crop straws in China. J. China Agric. Univ. 2021, 26, 30–41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shang, X.; Song, S.; Yang, J. Comparative Environmental Evaluation of Straw Resources by LCA in China. Adv. Mater. Sci. Eng. 2020, 2020, 4781805. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]


| Preliminary Analysis | Elemental Analysis | Biomass Constituent | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Moisture ad | 5.57 | C | 41.82 | Cellulose | 40.91 |
| Ash ad | 1.37 | H | 5.60 | Hemicellulose | 28.57 |
| Volatile ad | 77.52 | O | 48.60 | Lignin | 5.48 |
| Fixed carbon ad | 15.54 | N | 1.25 | Others | 24.92 |
| – | – | P | 0.034 | – | – |
| – | – | S | 0.07 | – | – |
| Component | TFe | FeO | SiO2 | Al2O3 | CaO | MgO | Mn | TiO2 | S | P |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Content/% | 67.34 | 0.88 | 0.80 | 0.38 | 0.05 | 0.24 | 0.13 | 0.047 | <0.01 | 0.04 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Zhang, Q.; Sun, Y.; Jin, G.; Cao, Y.; Han, Y. Waste Corn Straw as a Green Reductant for Hematite Reduction Roasting: Phase Transformation, Microstructure Evolution and Process Mechanism. Minerals 2023, 13, 1541. https://doi.org/10.3390/min13121541
Zhang Q, Sun Y, Jin G, Cao Y, Han Y. Waste Corn Straw as a Green Reductant for Hematite Reduction Roasting: Phase Transformation, Microstructure Evolution and Process Mechanism. Minerals. 2023; 13(12):1541. https://doi.org/10.3390/min13121541
Chicago/Turabian StyleZhang, Qiang, Yongsheng Sun, Guojie Jin, Yue Cao, and Yuexin Han. 2023. "Waste Corn Straw as a Green Reductant for Hematite Reduction Roasting: Phase Transformation, Microstructure Evolution and Process Mechanism" Minerals 13, no. 12: 1541. https://doi.org/10.3390/min13121541
APA StyleZhang, Q., Sun, Y., Jin, G., Cao, Y., & Han, Y. (2023). Waste Corn Straw as a Green Reductant for Hematite Reduction Roasting: Phase Transformation, Microstructure Evolution and Process Mechanism. Minerals, 13(12), 1541. https://doi.org/10.3390/min13121541





