Abstract
The Dongxiang tungsten–copper deposit is a large W–Cu deposit located in the northeast of Jiangxi province in south China. Previous studies have mainly considered the geochemical and isotopic attributes of the ore deposit, but information is still lacking on the genesis and setting of Dongxiang W–Cu mineralization-related intrusive rocks. This paper presents systematic elements and Sr–Nd–Hf isotopic data of the Dongxiang granodiorite porphyry. The Dongxiang granodiorite porphyry is intermediate–acidic in composition, with SiO2 contents of 60.00–75.16 wt.%, Al2O3 contents of 10.15–18.53 wt.%, an K2O contents of 2.95–4.28 wt.%. The REEs content ranges from 64.2 to 198.1 ppm, with LREE/HREE ratios of 7.67–17.47. It is characterized by adakitic geochemical affinities with high Sr/Y and (La/Yb)N ratios but low Y and Yb contents. A slight Eu anomaly, extreme depletion in Y and Yb, relatively low MgO content, and relatively high 207Pb/204Pb ratios together indicate that the Dongxiang granodiorite porphyry was likely derived from partial melting of the thickened lower continental crust. Based on zircon εHf(t) values (−11.8–−4.5), two-stage Hf model ages (1.33–1.94 Ga), and the regional geological setting, it can be inferred that Dongxiang granodiorite porphyry magma is mainly derived from Neoproterozoic juvenile crust with the involvement of Paleoproterozoic ancient crust.
1. Introduction
Southeast (SE) China is well-known for its extensive development of Mesozoic igneous rocks (Figure 1a) [1,2]. Due to the large-scale Cu-Au-Pb-Zn-W-Sn polymetallic mineralization and the important tectonic features of this area, its igneous rocks have been studied in great depth [2,3,4,5,6]. The Dexing–Dongxiang district in eastern Jiangnan Orogen (northeast Jiangxi province) and the middle–lower reaches of the Yangtze river valley metallogenic belt (MLYB; Figure 1a) are the two most important metallogenic districts, and both have been studied extensively [7,8]. The Dongxiang W–Cu deposit (E 116°36′34″–116°39′41″, N 28°17′15″–28°17′55″) is located 100 km southwest of the Dexing and Yinshan deposits in the northeast of Jiangxi province. By means of a geological survey, the Dongxiang W–Cu deposit was discovered in the 1950s by the 912 Geological Team of the Jiangxi Bureau of Geology and Mineral Resources. The deposit contains 19,000 t of W with an average grade of 0.65 wt.% W, 0.166 Mt of Cu metal with an average grade of 1.1 wt.% Cu, 1.09 Mt of iron with an average grade of 46 wt.% Fe, and 3.59 Mt of sulfur metal with an average grade of 22 wt.% S [9].
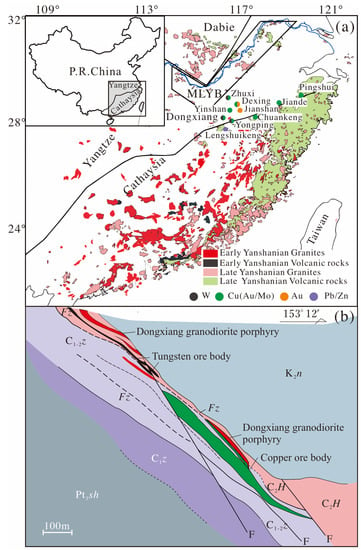
Figure 1.
(a) Sketch map of the late Mesozoic volcanic-intrusive complex belt in southeast China (adapted from Wang et al., 2012 [10]); (b) cross-section through the ore bodies (prospecting line 67) of the Dongxiang deposit (adapted from Cai et al., 2016) [11]. Pt3sh—Shuangqiaoshan Group; C1z—Zhongpeng Formation; C1-2z—Zishan Formation; C2H—Hutian Group; K2n—Nanxiong Formation; Fz—fracture zone.
This deposit has been previously studied by researchers [11,12,13,14,15,16,17] who have considered such matters as fluid inclusions and H–O–S–Pb isotopes [11], zircon U-Pb dating and Rb–Sr dating [12], mine structural geology [16], sedimentary rocks [14] and volcanic rocks [17] in ore-bearing strata, and prospecting exploration [9,18]. The deposit is of the Manto type which is associated with Jurassic magmatic hydrothermal activities [11]. However, the ore-related granodiorite porphyry that is closely related to W–Cu mineralization is still poorly understood. In this study, we selected Dongxiang intrusive rocks that were closely related to W–Cu mineralization, carried out detailed geochemical and Sr–Nd–Hf isotope analysis, and discussed the origin of the intrusive rocks in the Dongxiang deposit.
2. Geological Setting
South China consists of the Yangtze block in the northwest and the Cathaysia block in the southeast, separated by the Qinzhou–Hangzhou belt, whose eastern part is well-known as the Jiangshan–Shaoxing fault zone (Figure 1a) or shear zone [1,19,20].
Between the two blocks, the Jiangnan Orogen belt extends 1500 km along the southeastern margin of the Yangtze block, and represents both Neoproterozoic subduction and convergence between the Yangtze and Cathaysia blocks [1,6,20,21]. It is also an important polymetallic metallogenic region which is especially noted as one of the major W–Cu resources of the world [22]. The eastern part of the Jiangnan Orogen is located in the eastern part of the Yangtze block, north of the Jiangshan–Shaoxing fault zone, and is cut off by the northeast Jiangxi deep fault in the southeast. The ophiolite complex (ca. 1000 Ma) is distributed along the line of this fault and represents a subordinate Neoproterozoic suture zone between the Yangtze block and the oceanic island arc [23,24].
The northeast Jiangxi region of the Qinzhou–Hangzhou belt is one of the most important polymetallic deposits in China, and many large- and superlarge-size Cu (Au) polymetallic deposits have been discovered, such as the Dexing Cu–Au deposit, the Yongpin Cu deposit, and the Yinshan Cu–Pb–Zn polymetallic deposit [1,6,11,25,26,27,28,29,30]. Recently, W–Sn deposits have also been discovered, such as the Dahutang, Zhuxi, Yangchuliang, Xianglushan, and Pengshan deposits, whose identified resources total nearly 4 Mt. WO3, 0.75 Mt. Cu and 0.3 Mt. Sn [22]. In this belt, magmatic activities were frequent and intensive from the Jurassic to Cretaceous periods, especially during the mid–late Jurassic.
3. Dongxiang Deposit and Intrusive Rocks
The Dongxiang W–Cu deposit is located at the junction of the northeast Jiangxi deep fault and the Pinxiang–Guangfeng deep fault. The stratigraphy sequence in the ore district comprises the Neoproterozoic Shuangqiaoshan Group, the Upper Devonian–Lower Carboniferous Zhongpeng Formation, the Upper–Lower Carboniferous Zishan Formation, the Upper Carboniferous Hutian Group, and Cretaceous sedimentary rocks (Figure 1b). Neoproterozoic rocks, occurring in the northwestern parts of this area, consist of phyllite-based epimetamorphic rocks. The Upper Devonian–Lower Carboniferous Zhongpeng Formation unconformity covers the Neoproterozoic rocks, mainly composed of clasolite and shale, which are exposed in the middle area of the deposit. The Upper–Lower Carboniferous Zishan Formations are composed of gray quartz sandstone, sandstone, shale, and conglomerate, intercalated with marl. The Upper Carboniferous Hutian Group is composed of marine carbonate rocks. Cretaceous sedimentary rocks consist of silicious clasolite conglomerate, and sandstone with thick-layered siltstone, both of which occur in the southeastern area of the deposit [11,12,31].
The ore bodies occur in the sandstone and shale of the upper section of the Zishan Formation as stratiform-to-substratiform lenses and veins. Ore minerals include wolframite, chalcopyrite, pyrite, bornite, and chalcocite. The ore bodies and intrusive rocks are all restricted by NE-NEE faults, indicating that the intrusive rocks and faults are closely related to mineralization. Wall rocks locally exhibit phyllic alteration, within more widespread alteration minerals that include quartz, sericite, pyrite, and chlorite [11,12,31].
The main intrusions are granodiorite porphyries and quartz porphyry dikes in the Dongxiang area. The granodiorite porphyry in this area extends underground from southwest to northeast and is controlled by NE faults but cut by NNE or NWW faults. Unlike concealed granodiorite porphyry, the quartz porphyry is exposed on the surface. It contains large quartz phenocrysts and plagioclase with accessory zircon, apatite, and titanite. The quartz porphyry exhibits weathering processes and most of the plagioclase has been altered to kaolin. However, there is no evidence that quartz porphyries are related to metal mineralization. Therefore, in this study, only the granodiorite porphyry is analyzed, tested and discussed.
4. Samples and Analytical Methods
The samples for analysis were collected from the drill cores ZK6702 and ZK6701. The samples were initially observed by optical microscopy. The least-altered samples were selected for the geochemical and Sr–Nd isotopes analyses. They exhibited porphyritic textures and were mainly composed of 10%–30% quartz, 50%–60% plagioclase, and 5%–10% biotite. Phenocrysts are basically euhedral or subhedral, with a grain size of 0.2–4 mm. Quartz is frequently characterized by a melting corrosion structure. The matrix displays a fine microcrystalline texture, consisting of quartz, biotite, amphibole, and plagioclase with accessory zircon, apatite, and titanite (Figure 2). The alteration mainly involves silicification, sericitization, and pyritization. The mineralization-related alterations are mainly intensive silication and sericitization.
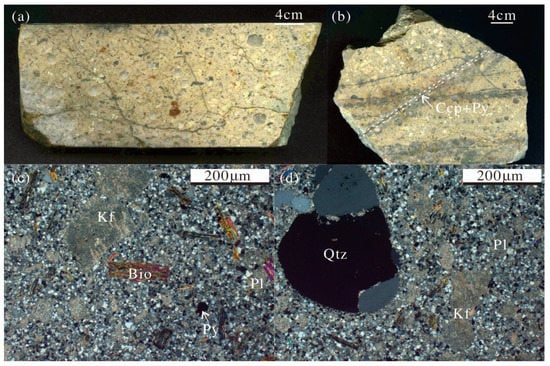
Figure 2.
Pictures and photomicrographs of the Dongxiang granodiorite porphyry. (a,b) Hand specimens of Dongxiang granodiorite porphyry samples ZK6701 and DT026; (c,d) photomicrographs showing the mineralogy of the two sample porphyries from the area. Abbreviations: Pl—plagioclase; Kf—alkaline feldspar; Bio—biotite; Qtz—quartz.
To carry out a whole-rock analysis of major and trace elements, eleven samples were collected from the granodioritic porphyries. Among these, the five samples with the least alteration were used for Sm–Nd and Rb–Sr isotope analysis, and two samples were used for a combined study involving CL imaging and the Lu–Hf isotope.
The major-element content of the samples was determined at the MiDeR, Nanjing University by ICP-OES. Trace elements were analyzed by Finnigan Element II ICP-MS at MiDeR, Nanjing University. The precision was higher than 5% for all the major elements, and higher than 10% for the trace elements [32].
The isotopic compositions of Sr and Nd were measured using Triton Ti thermal ionization mass spectrometry (TIMS) equipment at Nanjing University [33]. 87Sr/86Sr and 143Nd/144Nd ratios were recorded as measured and normalized to a 86Sr/88Sr value of 0.1194 for Sr and to a 146Nd/144Nd value of 0.7219 for Nd. During the analysis, measurements resulted in a 143Nd/144Nd ratio of 0.511842 ± 4 (2σ, n = 5) for the La Jolla standard and a 87Sr/86Sr ratio of 0.710260 ± 10 (2σ, n = 30) for the NBS-987 Sr standard. The total analytical blanks were 5 × 10−11 g for Sm and Nd and (2-5) × 10−10 g for Rb and Sr.
An in situ analysis of the zircon Hf isotope was carried out using a New Wave UP213 laser-ablation microprobe, attached to a Neptune Multi-Collector ICP-MS at the Institute of Mineral Resources, Chinese Academy of Geological Sciences (CAGS) [34]. In this study, a stationary spot was used for analysis, with a beam diameter of 40 μm or 55 μm depending on the size of ablated domains. For routine analysis, zircon GJ1 and Plesovice were used as reference standards, and the weighted average 176Lu/177Hf ratios were 0.282001 ± 0.000006 (2σ, n = 33) and 0.282476 ± 0.000009 (2σ, n = 8), respectively. Using the solution analysis method, these values are not distinguishable from the weighted average 176Hf/177Hf ratios of 0.282000 ± 0.000005 (2σ) and 0.282482 ± 0.000008 (2σ) [35,36]. We calculated the εHf(t) values [37] and two-stage “crustal” model Hf ages for their source materials, assuming a 176Lu/177Hf ratio of 0.015 for average continental crust [38]. The data were processed using the software package GLITTER (v 4.4) and program ISOPLOT (v 3.0) [39], and common lead correction was carried out using the EXCEL program of ComPbCorr#151 [40].
5. Results
5.1. Major Elements
Dongxiang intrusive rocks are of intermediate–acidic composition, with a SiO2 content of 60.00–75.16 wt.% (Table 1), Al2O3 content of 10.15–18.53 wt.%, and K2O content of 2.95–4.28 wt.%. They are calc-alkaline, and the data are mainly concentrated around the calc-alkaline series, usually with relatively low MgO content (0.32–0.67 wt.%). In the TAS diagram (Figure 3), most of the test results are plotted in the granodiorite–granite region.

Table 1.
Test data for major and trace elements of Dongxiang granodiorite porphyry.
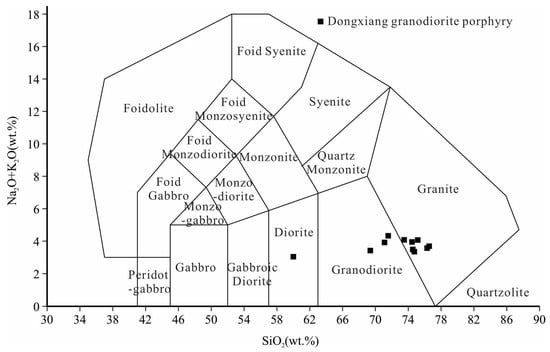
Figure 3.
Total alkali vs. silica (TAS) diagram (adapted from Winchester and Floyd, 1977) for the Dongxiang granodiorite porphyry [41].
5.2. Trace Elements
The Dongxiang intrusive rocks exhibit enrichment of LREE relative to HREE with (La/Yb)N ratios ranging from 7.2 to 25.7. The REE ranges from 64.2 to 198.1 ppm with an average of 108 ppm, with LREE/HREE ratios of 7.67–17.47. On primitive mantle-normalized trace element diagrams, they show enrichments of large ion lithophile elements (LILEs), but depletions of Nb and Ti (Figure 4). They exhibit a narrow range of Eu/Eu* (Eu/Eu* = 2EuN/(SmN + GdN)) ratios, and insignificant negative Eu anomalies with an average ratio of 0.75.
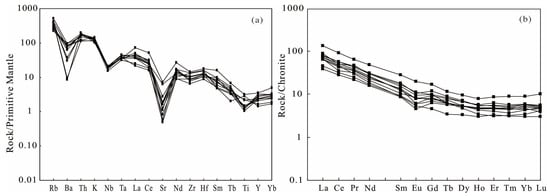
Figure 4.
(a) Normalized trace element patterns for the Dongxiang granodiorite porphyry; (b) REE patterns for the Dongxiang granodiorite porphyry. Chondrite and primitive mantle data are from Boynton,1984, respectively [42].
5.3. Sr-Nd-Hf Isotopes
The whole-rock Sr and Nd isotopic data for Dongxiang granodiorite porphyry are shown in Table 2. The Nd isotope composition of Dongxiang intrusive rocks is relatively homogeneous, with εNd (t = 164 Ma) levels ranging from −6.6 to −7.5, and two-stage Nd model ages of 1.57 to 1.68 Ga. These samples have variable (87Sr/86Sr)i ratios of 0.706675–0.715872. The εNd(t) vs. (87Sr/86Sr)i diagram shows no anticipated inverse (87Sr/86Sr)i vs. εNd(t) correlation (Figure 5b), possibly the result of post-emplacement mobilization of Rb and Sr [43,44,45].

Table 2.
Sr–Nd isotope data of the Dongxiang granodiorite porphyry.
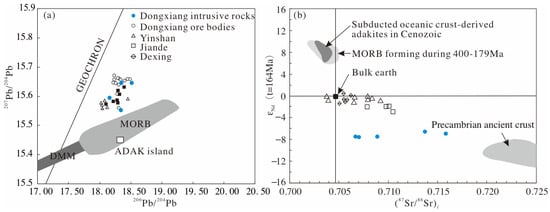
Figure 5.
(a) 207Pb/204Pb vs. 206Pb/204Pb diagram and (b) εNd(t) vs. (87Sr/86Sr)i diagram (data from Cai et al., 2017), with (a) showing isotopic signatures for the Dongxiang intrusive rocks [12,21,23,46,47,48]. Data sources are as follows: data of Cenozoic subducted oceanic crust-derived adakites, 400–179 Ma MORB and Dexing adakitic rocks are from Wang et al., 2006 [21]; data of adakites and oceanic slab, Adak Island are from Kay and Hubbard, 1978 [46]; DMM data representing one type of mantle end-members are from Zindler and Hart, 1986 [47]; data of Precambrian ancient crust are from Qi et al., 2007 [48]. Additional data are from Wang et al., 2008 [23].
Zircon U–Pb dating has been used in previous research on the Dongxiang intrusive rocks [12]. In this study, Lu–Hf isotope analysis was also carried out on zircons with the same domain position or a similar structure (Figure 6a). Initial 176Hf/177Hf ratios and εHf(t) values were calculated at the time of zircon growth from the magmas. The results indicated that Dongxiang intrusive rocks have negative initial εHf values (age corrected using U–Pb age for individual grains), with a weighted mean of −11.8–−4.5. In addition, the Hf model ages of zircons from Dongxiang intrusive rocks were 1.01–1.33 Ga, with a two-stage model age of 1.33–1.94 Ga.
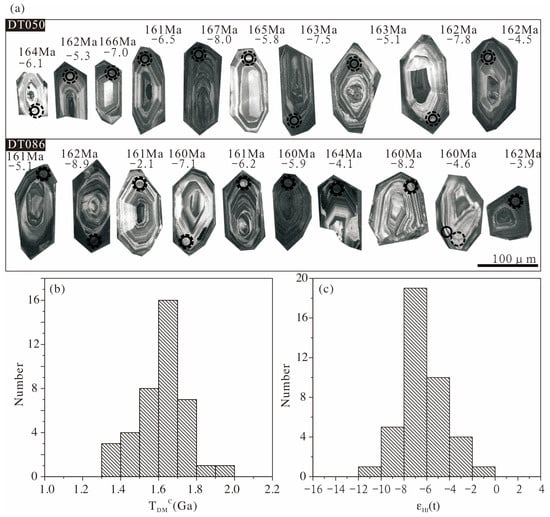
Figure 6.
(a) CL images of zircons from Dongxiang granodiorite porphyries (DT050 and DT086) [12]. Smaller circles indicate the spots of U-Pb dating, using data from Cai et al., 2017, whereas the bigger dashed circles indicate the spots of Hf isotopes analyses. Ages and εHf(t) values are shown for each spot (age data are from Cai et al., 2017) [12]. (b) Histogram of two-stage model ages (TDMC) for zircons from the Dongxiang intrusive rocks. (c) Histogram of εHf(t) values for zircons from the Dongxiang intrusive rocks.
6. Discussions
6.1. Alteration Effects
Petrological observations show that the Dongxiang intrusive rocks exhibit different degrees of magmatic hydrothermal alteration. These alterations show a transformation from Ca- and Na-rich plagioclase and alkaline feldspar to K-rich sericite, calcite, and clay. The Sr content decreases with the reduction of Ca content in the plagioclase. These data are consistent with previous results indicating Ca, Na, and the LILEs (e.g., Sr, Ba, Pb, Rb) are generally mobile [21,49]. In contrast, during the most intense hydrothermal alteration, some major elements, such as Al, P, and the HFSEs, are essentially immobile [21,49]. As sericite can take up all of the available REE, whole-rock REE abundance was not affected during serictic alteration in this study [50].
Although Table 1 shows that the LOI varies from 2% to 5%, the ratios of MgO, TiO2, Nb, Zr, La, and (87Sr/86Sr)i of the intrusive rocks do not change significantly with higher LOI values, and neither do their La/Sm and La/Yb values, indicating that these data were not significantly affected by alteration (Figure 7). The LOI versus εNd(t) diagram (Figure 7i) also shows minimal variation in the εNd(t) values of the Dongxiang intrusive rocks as the LOI increases, indicating that the 143Nd/144Nd ratios of rocks are rarely affected by hydrothermal alteration. Therefore, for discussion purposes, for samples of igneous rocks with large alterations, only certain major elements (e.g., TiO2, MgO), HFSEs (e.g., Zr, Nb, Ta, Hf), REEs, and isotopic compositions (Nd, Pb) that are not significantly affected by alterations were considered.
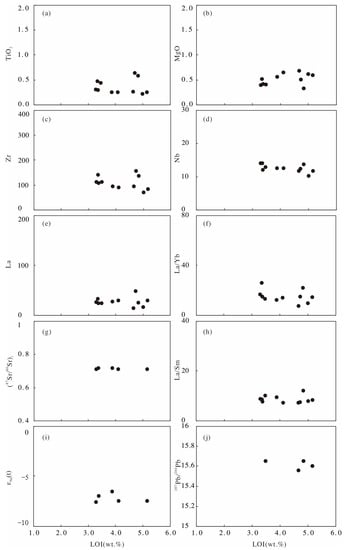
Figure 7.
Loss on ignition (LOI) versus TiO2 (a), MgO (b), Zr (c), Nb (d), La (e), La/Yb (f), (87Sr/86Sr)i (g), La/Sm (h), εNd(t) (i), and 207Pb/204Pb (j) for the Dongxiang granodiorite porphyry.
6.2. Genesis of the Dongxiang Intrusive Rocks
The intrusive rocks in the Dongxiang deposit have relatively high Sr content (10–145 ppm), and ratios of Sr/Y (1.0–13.6) and La/Yb (7.2–25.7), as well as low Y (<12.8 ppm) and Yb (<2.2 ppm) content. In addition, chondrite-normalized REE patterns show that these rocks are enriched with light REEs (LREEs), and depleted in heavy REEs (HREEs), with a slight Eu anomaly (Figure 5). Moreover, the data of Dongxiang intrusive rocks can be plotted in the adakite region on a (La/Yb)N versus YbN diagram (Figure 8). This indicates that the Dongxiang ore-related granodiorite porphyry has adakite affinities, in common with other igneous rocks in the Dexing, Yinshan, and Jiande regions [10,26]. Previous research has found that many typical adakites are formed by slab melting in subduction zones [6,51,52]. Similar models have been proposed to explain the origin of the Mesozoic adakitic rocks in the Dexing area and in the Yangtze river valley metallogenic belts in southeastern China [6,10,26,53,54]. In intracontinental settings, partial melting of thickened or delaminated lower continental crust has been proposed as a possible mechanism for the formation of adakitic rocks [55,56,57,58]. Alternatively, the origin of adakitic rocks may be a consequence of the fractional crystallization process of basaltic magmas [59].
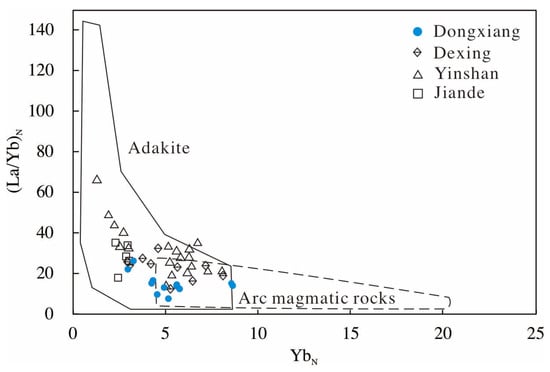
Figure 8.
(La/Yb)N vs. YbN for the Dongxiang intrusive rocks (adapted from Defant and Drummond, 1990) [52].
There are two explanations for the crystallization process and melting. The first draws attention to the phenomenon that removal of plagioclase and amphibole under low pressure produces patterns that are concave-upwards between MREE and HREE, resulting in a higher Dy/Yb ratio and increased SiO2 content [59]. The alternative explanation involves high-pressure crystallization with garnet as a residual phase in the deep magma chamber [59].
Figure 9 clearly shows the partial melting trend in plots of Zr/Nb versus Zr and Y versus Ce. In addition, samples from the Dongxiang intrusive rocks showed no concave-upwards REE patterns between MREEs and HREEs (Figure 4) and the Dy/Yb ratio did not decrease significantly with an increase in SiO2 (Figure 9c). Therefore, the geochemical characteristics of the Dongxiang intrusive rocks indicate that their adakitic features are unlikely to have been generated by fractional crystallization under low pressure.
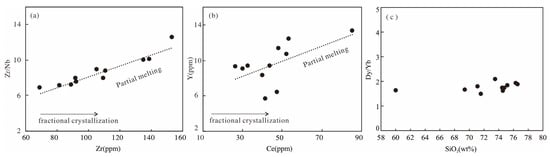
Figure 9.
(a) Zr/Nb vs. Zr diagram; (b) Y vs. Ce diagram; (c) Dy/Yb vs. SiO2 diagram.
6.2.1. Partial Melting of the Subducted Oceanic Slab and the Delaminated Lower Continental Crust
Adakite was originally thought to be produced by partial melting of the subducting oceanic plate [51,52]. Adakitic rocks from Dongxiang have higher 207Pb/204Pb ratios than MORB and adakites that are derived from slab melting [46], suggesting that the Dongxiang intrusive rocks have radiogenic 207Pb which differs from that of the adakitic rocks originating from the subducted oceanic crust (Figure 6a). Dongxiang samples show notably higher (87Sr/86Sr)i values, and lower εNd(t) values (Figure 6b) than study samples of MORB and adakites that are derived from slab melting [60], indicating a source other than the oceanic crust. Furthermore, no definite Mesozoic basaltic arc magmatism has been found in the intracontinental region of southeast China. Therefore, the partial melting of the subducted oceanic plate cannot be considered a reasonable mechanism to explain the adakitic character of the Dongxiang intrusion.
Partial melting of the delaminated lower continental crust has also been proposed as a genetic mechanism for adakitic rocks in southeastern China [57]. Partial melting occurs when the delaminated lower crust is heated by the surrounding hot mantle, and pristine melt is created. During the emplacement of pristine melt through mantle rocks into the upper crust, significant chemical interactions occur between mantle rocks and the melts. Thus, adakite magmas that are produced in this model show higher MgO, Cr, and Ni contents, indicating a significant involvement of mantle components [57]. However, the Dongxiang intrusive rocks have lower MgO content, in comparison with the adakitic rocks that are formed by partial melting of the delaminated lower crust (Figure 10), and this indicates that they were not hybridized by the mantle material. Therefore, the model is not suitable for assessment of the Dongxiang intrusive rocks genesis.
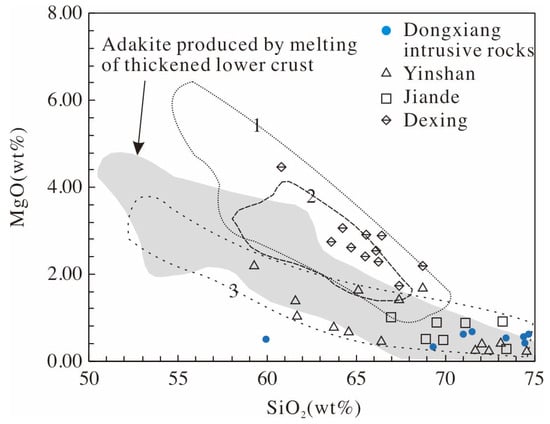
Figure 10.
MgO vs. SiO2 diagram for the Dongxiang intrusive rocks, showing (1) adakite that is produced by melting of subducted oceanic slab; (2) Delaminated lower crust-derived adakitic rocks; (3) metabasaltic and eclogitic melts (1.0–4.0 GPa) [55]. Data were obtained from Zhao and Zhou, 2008.
6.2.2. Partial Melting of the Thickened Juvenile Continental Crust
Direct partial melting of the thickened lower continental crust has also been proposed to explain the production of adakitic magmas [55,56]. This model is consistent with the elemental characteristics of the Dongxiang intrusive rocks, such as high SiO2 and K2O (Figure 5). In a previous study, U–Pb dating data of the Dongxiang intrusive rocks revealed a relatively high radiogenic 207Pb/204Pb [12] ratio, indicating that Dongxiang adakitic rocks were derived from continental crustal materials (Figure 6a). The low εNd(t) and high (87Sr/86Sr)i values of the Dongxiang intrusive rocks are similar to those of adakitic porphyries from the melting of the lower continental crust [61], indicating that these intrusive rocks were probably generated by partial melting from the continental crust rather than the oceanic crust. The εNd vs. (87Sr/86Sr)i diagram (Figure 6b) shows that all of the samples are plotted below the average Nd isotopic bulk earth line, suggesting that they originated from the juvenile continental crust [62,63]. Two-stage models of Nd and Hf isotope ages also support a continental crustal origin, and the ages of these two isotopes are significantly older than their emplacement ages. In addition, their relatively low MgO levels are similar to those that were found in experimental melts of metabasalts and eclogites at 1.0–4.0 GPa [64], and in adakitic rocks that were generated by partial melting of the lower continental crust [55] (Figure 10). The low MgO content suggests that these adakitic magmas were directly derived from the lower continental crust without any interaction between the adakitic melts and the mantle source [65]. According to the history of regional evolution, such reworking (i.e., re-melting and emplacement) is also thought to have occurred along the Jiangnan Orogen, with the growth of the juvenile crust resulting from arc magmatism at 1.0–0.9 Ga. [66]. The reworking of arc crust by syncollisional and postcollisional magmatism (870–800 Ma) led to a bulk crust composition more similar to a continental crust composition [66,67]. A continental origin of the Dongxiang adakitic rocks is, therefore, consistent with regional reworking of the Neoproterozoic juvenile crust, and supports the assumption of partial melting of the thickened continental crust.
High levels of elements such as Th, U, and LREEs, along with a marked depletion in Nb, Ta, and Ti, represent findings similar to those that were obtained from rocks that were generated from the arc-like magma source [68], and show that Dongxiang intrusive rocks also exhibit arc geochemical affinities. However, according to previous studies, during the Jurassic, southern China was in an intracontinental tectonic setting [3,20,43,69]. Therefore, the intrusive rocks with typical arc-like magmatic characteristics, may be inherited from the juvenile crust in this region, as has been suggested for Yinshan and Jiande igneous rocks, produced during the Neoproterozoic oceanic subduction between the Yangtze and Cathaysia blocks [6,10,25,70,71].
The Neoproterozoic juvenile lithosphere in the eastern part of the Jiangnan orogenic belt has been widely identified, and includes the sedimentary rocks of the Shuangqiaoshan Group, the Shuangxiwu arc volcanic rocks, and the Tieshajie arc volcanic rocks [70,72]. The Dongxiang intrusive rocks can be almost perfectly plotted in the Neoproterozoic band of crustal evolution of the eastern Jiangnan Orogen (Figure 11), indicating that these rocks were mainly generated by melting of the Neoproterozoic juvenile crust. However, the Dongxiang intrusive rocks have lower εHf(t) (Figure 11) and εNb(t) (Figure 6b) values than the Dexing igneous rocks, indicating that an older crustal endmember is required. The Paleoproterozoic crust (such as the Zhoutan Group) is distributed in the northwest margin of the Cathaysia Block near the Dongxiang deposit. Moreover, there are both Neoproterozoic juvenile crustal materials and Paleoproterozoic ancient crustal materials in the regional basement rocks of the Zhoutan Group [28,73]. The evidence suggests that the underlying juvenile and ancient crustal materials may be the source of the Dongxiang granodiorite porphyries.
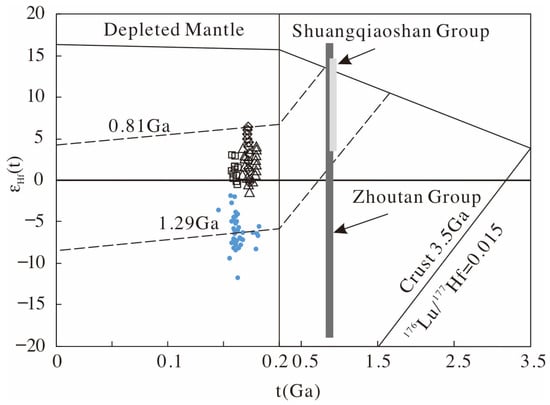
Figure 11.
εHf(t) vs. U-Pb ages diagram for the Dongxiang intrusive rocks [21,38,70]. The dashed lines of crustal extraction were calculated using an 176Lu/177Hf ratio of 0.015 as an average for the continental crust using data from Griffin et al., 2002 [38]. The data of the Shuangqiaoshan Group and Zhoutan Group are from Li et al., 2009 [70]. The data of Dexing, Yinshan and Jiande are from Wang et al., 2006 [21]. Symbols are the same as in Figure 10.
7. Conclusions
- (1)
- The geochemical characteristics of Dongxiang granodiorite porphyry indicate that the Dongxiang intrusive rocks have arc-like geochemical characteristics and the granodiorite porphyry has adakite affinities, in common with other igneous rocks in the Dexing, Yinshan, and Jiande regions.
- (2)
- The Dongxiang granodiorite porphyry was probably generated by the partial melting of the thickened juvenile continental crust and ancient crustal materials, during the Middle Jurassic.
Author Contributions
Methodology, P.N. and G.W.; formal analysis, Y.C. and G.W.; investigation, Y.C., P.N., G.W. and H.C.; writing—original draft preparation, Y.C.; writing—review and editing, Y.C., G.W. and H.C.; supervision, P.N.; project administration, Y.C. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This research was funded by a Key Project of National Nature Science Foundation of China, grant number 41830426, Research Foundation for High-Level Personnel of Jinling Institute of Technology, grant number JIT-b-202207, The Ministry of Science and Technology of The People’s Republic of China, grant number 2016YFC0600206, and Natural Science Foundation of Jiangsu Province, China, grant number BK20191132.
Data Availability Statement
The data presented in this study are available in this article.
Acknowledgments
The authors thank Xiuchang Zhang and Xueyun Le from Dongtong Mining Ltd. of Jiangxi Copper Corporation, Qiuyun Yuan and Hui Zeng from Nanjing Hongchuang Geological Exploration Technology Service Co. LTD We thank all the reviewers and the editor for their constructive comments that greatly improved the paper.
Conflicts of Interest
The funders had no role in the design of the study; in the collection, analyses, or interpretation of data; in the writing of the manuscript; or in the decision to publish the results.
References
- Ni, P.; Wang, G. Multiple episodes of Cu-Au mineralization in the northeastern section of the Qin-Hang metallogenic belt induced by reworking of continental crust. Acta Petrol. Sin. 2017, 33, 3373–3394. [Google Scholar]
- Ni, P.; Wang, G.; Li, W.; Chi, Z.; Li, S.; Gao, Y. A review of the Yanshanian ore-related felsic magmatism and tectonic settings in the Nanling W-Sn and Wuyi Au-Cu metallogenic belts, Cathaysia Block, South China. Ore Geol. Rev. 2021, 133, 104088. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Z.; Li, X. Formation of the 1300-km-wide intracontinental orogen and postorogenic magmatic province in Mesozoic South China: A flat-slab subduction model. Geology 2007, 35, 179–182. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, J.; Jahn, B. Crustal evolution of southeastern China: Nd and Sr isotopic evidence. Tectonophysics 1998, 284, 101–133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, X.; Li, W. Origin of Late Mesozoic igneous rocks in Southeastern China: Implications for lithosphere subduction and underplating of mafic magmas. Tectonophysics 2000, 326, 269–287. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, G.; Ni, P.; Yao, J.; Wang, X.; Zhao, K.; Zhu, R.; Xu, Y.; Pan, J.; Li, L.; Zhang, Y. The link between subduction-modified lithosphere and the giant Dexing porphyry copper deposit, South China: Constraints from high-Mg adakitic rocks. Ore Geol. Rev. 2015, 67, 109–126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chang, Y.F.; Liu, X.P.; Wu, Y.C. The Cu, Fe Metallogenic Belt in the Middle-Lower Reaches of Yangtze River; Geological Publish House: Beijing, China, 1991; pp. 1–379. [Google Scholar]
- Pan, Y.; Dong, P. The Lower Changjiang (Yangzi/Yangtze River) metallogenic belt, east central China: Intrusion-and wall rock-hosted Cu-Fe-Au, Mo, Zn, Pb, Ag deposits. Ore Geol. Rev. 1999, 15, 177–242. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- JGEB. The Geological Reports of Tungsten Reserves and Copper Census in Fenglin Deposit of Dongxiang, Jiangxi Province; Jiangxi Geological Exploration Bureau: Jiangxi, China, 1983; pp. 1–55.
- Wang, G.; Ni, P.; Zhao, K.; Wang, X.; Liu, J.; Jiang, S.; Chen, H. Petrogenesis of the Middle Jurassic Yinshan volcanic-intrusive complex, SE China: Implications for tectonic evolution and Cu-Au mineralization. Lithos 2012, 150, 135–154. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cai, Y.; Ni, P.; Wang, G.; Pan, J.; Zhu, X.; Chen, H.; Ding, J. Fluid inclusion and H-O-S-Pb isotopic evidence for the Dongxiang Manto-type copper deposit, South China. J. Geochem. Explor. 2016, 171, 71–82. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cai, Y.; Ni, P.; Wang, G.; Chen, H.; Zhang, J. Determination of the diagenetic age and metallogenic age and their significance in Dongxiang copper deposit, North-east of Jiangxi Province, China. Earth Sci. 2017, 42, 1495–1507. [Google Scholar]
- Tian, M.; Di, Y.; Yang, Q.; Yang, M.; Wang, S.; Wang, S. Geochemical Characteristics and Tectonic Background of Trachydacite in the Rough Surface of North Wuyi Dongxiang Volcanic Basin. Adv. Geosci. 2020, 4, 312–328. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, Y.T. The Origin and Geochemical Characteristics of Sedimentary Silicalites in Dongxiang mine, Jiangxi Province. Actased Imentologica Sin. 1997, 15, 110–114. [Google Scholar]
- Xue, J.Y.; Sun, T.; Zhang, W.L.; Cheng, W. Some microstructures of copper sulfides in Dongxiang copper mine, Jiangxi Province, and their Geological Implications. Geol. J. China Univ. 2000, 6, 149–155. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, G.L. Peel fault system of Dongxiang copper deposit and its ore-controlling significance. Miner. Resour. Geol. 2001, 15, 157–161. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, Z.L.; Huang, X.C. On the Occurrence of Carboniferous volcanics of the Fenglin district, Dongxiang, Jiangxi. J. Jiangxi Norm. Univ. Nat. Sci. Ed. 1979, 1, 41–50. [Google Scholar]
- CSU. Dongxiang Copper Mine Rich Ore Body Prediction Research and Periphery Prospecting; Central South University: Chang Sha, Hunan, 1997; pp. 1–120. [Google Scholar]
- Sun, W.; Yang, X.; Fan, W.; Wu, F. Mesozoic large scale magmatism and mineralization in South China: Preface. Lithos 2012, 150, 1–5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, B.X.; Sun, T.; Shen, W.; Shu, L.; Niu, Y. Petrogenesis of Mesozoic granitoids and volcanic rocks in South China: A response to tectonic evolution. Episodes 2006, 29, 26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, Q.; Xu, J.; Jian, P.; Bao, Z.; Zhao, Z.; Li, C.; Xiong, X.; Ma, J. Petrogenesis of adakitic porphyries in an extensional tectonic setting, Dexing, South China: Implications for the genesis of porphyry copper mineralization. J. Pet. 2006, 47, 119–144. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feng, C.; Wang, H.; Xiang, X.; Zhang, M. Late Mesozoic granite-related W–Sn mineralization in the northern Jiangxi region, SE China: A review. J. Geochem. Explor. 2018, 195, 31–48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.; Zhao, G.; Zhou, J.; Liu, Y.; Hu, J. Geochronology and Hf isotopes of zircon from volcanic rocks of the Shuangqiaoshan Group, South China: Implications for the Neoproterozoic tectonic evolution of the eastern Jiangnan orogen. Gondwana Res. 2008, 14, 355–367. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, X.; Zhao, J.; McCulloch, M.T.; Zhou, G.; Xing, F. Geochemical and Sm/Nd isotopic study of Neoproterozoic ophiolites from southeastern China: Petrogenesis and tectonic implications. Precambrian Res. 1997, 81, 129–144. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, H.; Ni, P.; Wang, G.; Chen, R.; Lü, Z.; Pang, Z.; Geng, L.; Zhang, B.; Yuan, H. Petrogenesis of Ore-Related Granodiorite Porphyry in the Jiande Copper Deposit, SE China: Implications for the Tectonic Setting and Mineralization. Resour. Geol. 2017, 67, 117–138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, H.; Ni, P.; Wang, R.; Wang, G.; Zhao, K.; Ding, J.; Zhao, C.; Cai, Y.; Xu, Y. A combined fluid inclusion and S-Pb isotope study of the Neoproterozoic Pingshui volcanogenic massive sulfide Cu-Zn deposit, Southeast China. Ore Geol. Rev. 2015, 66, 388–402. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ni, P.; Wang, G.; Chen, H.; Xu, Y.; Guan, S.; Pan, J.; Li, L. An Early Paleozoic orogenic gold belt along the Jiang—Shao Fault, south China: Evidence from fluid inclusions and Rb–Sr dating of quartz in the Huangshan and Pingshui deposits. J. Asian Earth Sci. 2015, 103, 87–102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, G.; Ni, P.; Wang, R.; Zhao, K.; Chen, H.; Ding, J.; Zhao, C.; Cai, Y. Geological, fluid inclusion and isotopic studies of the Yinshan Cu–Au–Pb–Zn–Ag deposit, South China: Implications for ore genesis and exploration. J. Asian Earth Sci. 2013, 74, 343–360. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, X.; Ni, P.; Wang, G.; Cai, Y.; Chen, H.; Pan, J. Fluid inclusion, H-O isotope and Pb-Pb age constraints on the genesis of the Yongping copper deposit, South China. J. Geochem. Explor. 2016, 171, 55–70. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, X.; Ni, P.; Wang, G.; Jiang, Y.; Jiang, D.; Li, S.; Fan, M. Petrogenesis and oxidation state of granodiorite porphyry in the Jurassic Chuankeng skarn Cu deposit, South China: Implications for the Cu fertility and mineralization potential. J. Asian Earth Sci. 2020, 191, 104184. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cai, Y.; Ni, P.; Shen, K.; Zhu, X.; Huang, S.; Zhang, X.; Xu, J. Study on the fluid inclusion from Dongxiang copper deposit, Jiangxi Province. Acta Petrol. Sin. 2011, 27, 1375–1386. [Google Scholar]
- Gao, J.; Lu, J.; Lai, M.; Lin, Y.; Pu, W. Analysis of trace elements in rock samples using HR-ICPMS. J. Nanjing Univ. Nat. Sci. Ed. 2003, 39, 844–850. [Google Scholar]
- Pu, W.; Gao, J.; Zhao, K.; Ling, H.; Jiang, S. Separation Method of Rb-Sr, Sm-Nd Using DCTA and HIBA. J. Nanjing Univ. Nat. Sci. 2005, 1, 445–450. [Google Scholar]
- Hou, K. Laser ablation-MC-ICP-MS technique for Hf isotope microanalysis of zircon and its geological applications. Acta Petrol. Sin. 2007, 23, 2595–2604. [Google Scholar]
- Morel, M.; Nebel, O.; Nebel-Jacobsen, Y.J.; Miller, J.S.; Vroon, P.Z. Hafnium isotope characterization of the GJ-1 zircon reference material by solution and laser-ablation MC-ICPMS. Chem. Geol. 2008, 255, 231–235. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sláma, J.; Košler, J.; Condon, D.J.; Crowley, J.L.; Gerdes, A.; Hanchar, J.M.; Horstwood, M.S.; Morris, G.A.; Nasdala, L.; Norberg, N. Plešovice zircon—A new natural reference material for U–Pb and Hf isotopic microanalysis. Chem. Geol. 2008, 249, 1–35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Blichert-Toft, J.; Albarède, F. The Lu-Hf isotope geochemistry of chondrites and the evolution of the mantle-crust system. Earth Planet Sci. Lett. 1997, 148, 243–258. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Griffin, W.L.; Wang, X.; Jackson, S.E.; Pearson, N.J.; O’Reilly, S.Y.; Xu, X.; Zhou, X. Zircon chemistry and magma mixing, SE China: In-situ analysis of Hf isotopes, Tonglu and Pingtan igneous complexes. Lithos 2002, 61, 237–269. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ludwig, K.R. User’s Manual for Isoplot 3.00: A Geochronological Toolkit for Microsoft Excel; Berkeley Geochronology Center: Berkeley, CA, USA, 2003; pp. 1–60. [Google Scholar]
- Andersen, T. Correction of common lead in U-Pb analyses that do not report 204Pb. Chem. Geol. 2002, 192, 59–79. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Winchester, J.A.; Floyd, P.A. Geochemical discrimination of different magma series and their differentiation products using immobile elements. Chem. Geol. 1977, 20, 325–343. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boynton, W.V. Cosmochemistry of the earth elements: Meteorite studies. Rare Earth Elem. Geochem. Dev. Geochem. 1984, 2, 89–92. [Google Scholar]
- He, Z.; Xu, X.; Niu, Y. Petrogenesis and tectonic significance of a Mesozoic granite–syenite–gabbro association from inland South China. Lithos 2010, 119, 621–641. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, X.; Chen, Z.; Liu, D.; Li, W. Jurassic gabbro-granite-syenite suites from Southern Jiangxi Province, SE China: Age, origin, and tectonic significance. Int. Geol. Rev. 2003, 45, 898–921. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Curtis, M.L.; Leat, P.T.; Riley, T.R.; Storey, B.C.; Millar, I.L.; Randall, D.E. Middle Cambrian rift-related volcanism in the Ellsworth Mountains, Antarctica: Tectonic implications for the palaeo-Pacific margin of Gondwana. Tectonophysics 1999, 304, 275–299. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kay, R.W.; Hubbard, N.J. Trace elements in ocean ridge basalts. Earth Planet Sci. Lett. 1978, 38, 95–116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zindler, A.; Hart, S. Chemical geodynamics. Annu. Rev. Earth Planet Sci. 1986, 14, 493–571. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qi, C.S.; Deng, X.G.; Li, W.X.; Li, X.H.; Yang, Y.H.; Xie, L.W. Origin of the Darongshan-Shiwandashan S-type granitoid belt from southeastern Guangxi: Geochemical and Sr-Nd-Hf isotopic constraints. Acta Petrol. Sin. 2007, 23, 403–412. [Google Scholar]
- Smith, R.E.; Smith, S.E. Comments on the use of Ti, Zr, Y, Sr, K, P and Nb in classification of basaltic magmas. Earth Planet Sci. Lett. 1976, 32, 114–120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alderton, D.; Pearce, J.A.; Potts, P.J. Rare earth element mobility during granite alteration: Evidence from southwest England. Earth Planet Sci. Lett. 1980, 49, 149–165. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kay, R.W.; Kay, S.M. Delamination and delamination magmatism. Tectonophysics 1993, 219, 177–189. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Defant, M.J.; Drummond, M.S. Derivation of some modern arc magmas by melting of young subducted lithosphere. Nature 1990, 347, 662–665. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, F.; Ling, M.; Ding, X.; Hu, Y.; Zhou, J.; Yang, X.; Liang, H.; Fan, W.; Sun, W. Mesozoic large magmatic events and mineralization in SE China: Oblique subduction of the Pacific plate. Int. Geol. Rev. 2011, 53, 704–726. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ling, M.; Wang, F.; Ding, X.; Hu, Y.; Zhou, J.; Zartman, R.E.; Yang, X.; Sun, W. Cretaceous ridge subduction along the lower Yangtze River belt, eastern China. Econ. Geol. 2009, 104, 303–321. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, J.; Zhou, M. Neoproterozoic adakitic plutons in the northern margin of the Yangtze Block, China: Partial melting of a thickened lower crust and implications for secular crustal evolution. Lithos 2008, 104, 231–248. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Petford, N.; Atherton, M. Na-rich partial melts from newly underplated basaltic crust: The Cordillera Blanca Batholith, Peru. J. Pet. 1996, 37, 1491–1521. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, J.; Shinjo, R.; Defant, M.J.; Wang, Q.; Rapp, R.P. Origin of Mesozoic adakitic intrusive rocks in the Ningzhen area of east China: Partial melting of delaminated lower continental crust? Geology 2002, 30, 1111–1114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chung, S.; Liu, D.; Ji, J.; Chu, M.; Lee, H.; Wen, D.; Lo, C.; Lee, T.; Qian, Q.; Zhang, Q. Adakites from continental collision zones: Melting of thickened lower crust beneath southern Tibet. Geology 2003, 31, 1021–1024. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Macpherson, C.G.; Dreher, S.T.; Thirlwall, M.F. Adakites without slab melting: High pressure differentiation of island arc magma, Mindanao, the Philippines. Earth Planet Sci. Lett. 2006, 243, 581–593. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jahn, B. Mesozoic thermal events in southeast China. Nature 1974, 248, 480–483. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.; Zhou, J.; Qiu, J.; Zhang, W.; Liu, X.; Zhang, G. LA-ICP-MS U-Pb zircon geochronology of the Neoproterozoic igneous rocks from Northern Guangxi, South China: Implications for tectonic evolution. Precambrian Res. 2006, 145, 111–130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McCulloch, M.T.; Chappell, B.W. Nd isotopic characteristics of S-and I-type granites. Earth Planet Sci. Lett. 1982, 58, 51–64. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, F.; Yang, Y.; Xie, L.; Yang, J.; Xu, P. Hf isotopic compositions of the standard zircons and baddeleyites used in U–Pb geochronology. Chem. Geol. 2006, 234, 105–126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rapp, R.P.; Shimizu, N.; Norman, M.D.; Applegate, G.S. Reaction between slab-derived melts and peridotite in the mantle wedge: Experimental constraints at 3.8 GPa. Chem. Geol. 1999, 160, 335–356. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Atherton, M.P.; Petford, N. Generation of sodium-rich magmas from newly underplated basaltic crust. Nature 1993, 362, 144–146. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, R.; Zheng, Y.; Wu, Y.; Zhao, Z.; Zhang, S.; Liu, X.; Wu, F. Reworking of juvenile crust: Element and isotope evidence from Neoproterozoic granodiorite in South China. Precambrian Res. 2006, 146, 179–212. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, Y.; Wu, R.; Wu, Y.; Zhang, S.; Yuan, H.; Wu, F. Rift melting of juvenile arc-derived crust: Geochemical evidence from Neoproterozoic volcanic and granitic rocks in the Jiangnan Orogen, South China. Precambrian Res. 2008, 163, 351–383. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kelemen, P.B.; Hanghøj, K.; Greene, A.R. One view of the geochemistry of subduction-related magmatic arcs, with an emphasis on primitive andesite and lower crust. Treatise Geochem. 2003, 3, 659. [Google Scholar]
- Chen, P.; Hua, R.; Zhang, B.; Lu, J.; Fan, C. Early Yanshanian post-orogenic granitoids in the Nanling region. Sci. China Ser. D Earth Sci. 2002, 45, 755–768. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, X.; Li, W.; Li, Z.; Lo, C.; Wang, J.; Ye, M.; Yang, Y. Amalgamation between the Yangtze and Cathaysia Blocks in South China: Constraints from SHRIMP U-Pb zircon ages, geochemistry and Nd-Hf isotopes of the Shuangxiwu volcanic rocks. Precambrian Res. 2009, 174, 117–128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.; Zhou, J.; Griffin, W.A.; Wang, R.; Qiu, J.; O’Reilly, S.Y.; Xu, X.; Liu, X.; Zhang, G. Detrital zircon geochronology of Precambrian basement sequences in the Jiangnan orogen: Dating the assembly of the Yangtze and Cathaysia Blocks. Precambrian Res. 2007, 159, 117–131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, D.; Wu, G.; Luo, P.; Huang, H. SHRIMP U-Pb zircon geochronology of the Tieshajie Group in the Cathaysia Block-China: Implications for Neoproterozoic tectonic significance. Geochim. Cosmochim. Acta Suppl. 2009, 73, A1503. [Google Scholar]
- Li, H.; Zhang, H.; Ling, M.; Wang, F.; Ding, X.; Zhou, J.; Yang, X.; Tu, X.; Sun, W. Geochemical and zircon U–Pb study of the Huangmeijian A-type granite: Implications for geological evolution of the Lower Yangtze River belt. Int. Geol. Rev. 2011, 53, 499–525. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).