Petrogenesis of Early Triassic Felsic Volcanic Rocks in the East Kunlun Orogen, Northern Tibet: Implications for the Paleo-Tethyan Tectonic and Crustal Evolution
Abstract
:1. Introduction
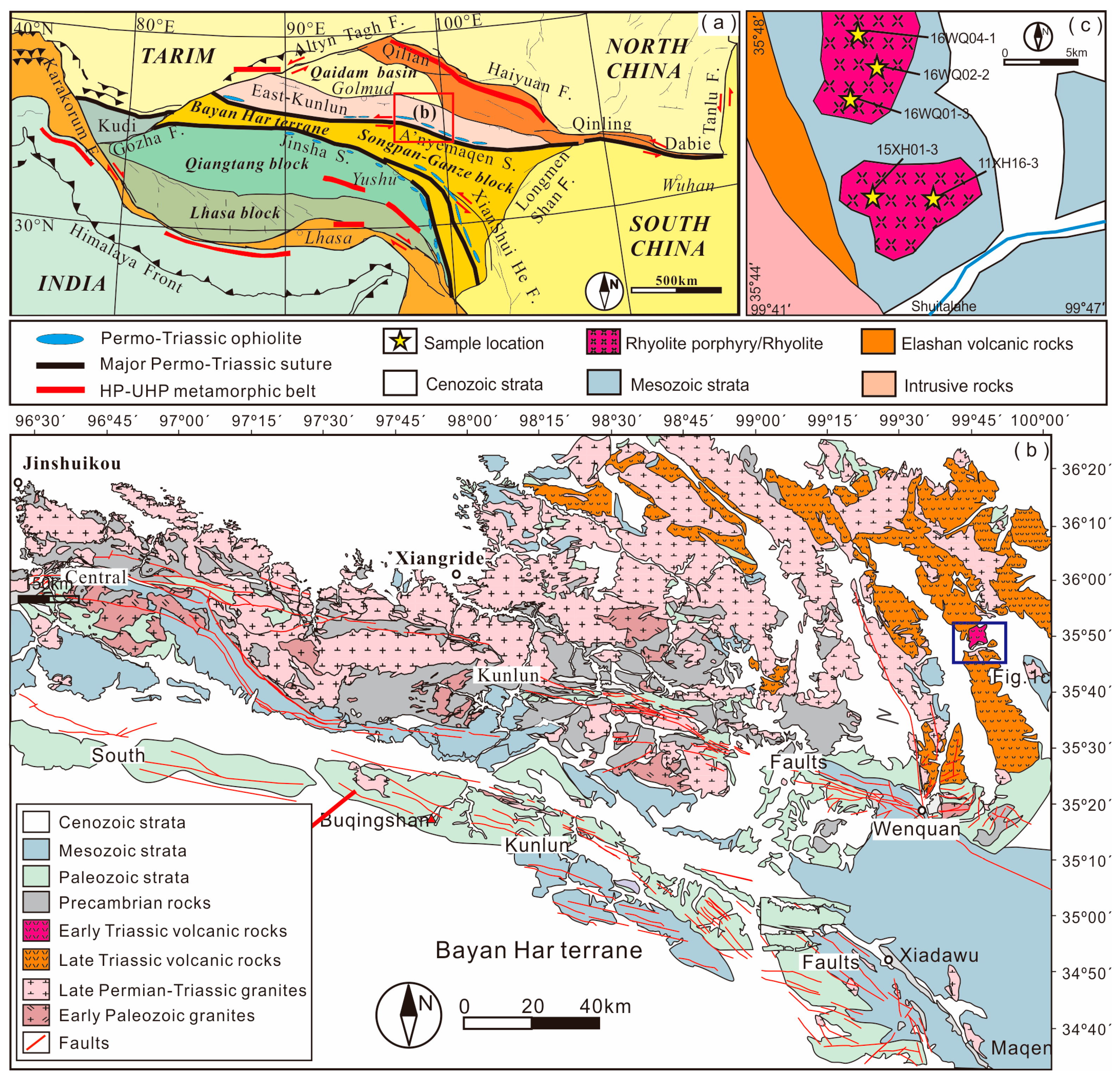
2. Regional Geologic Background
3. Sampling and Petrography
4. Analytical Methods
4.1. LA-ICP-MS Zircon U-Pb Dating
4.2. Whole-Rock Major and Trace Element Analyses
4.3. Zircon Lu-Hf Isotope Analyses
5. Results
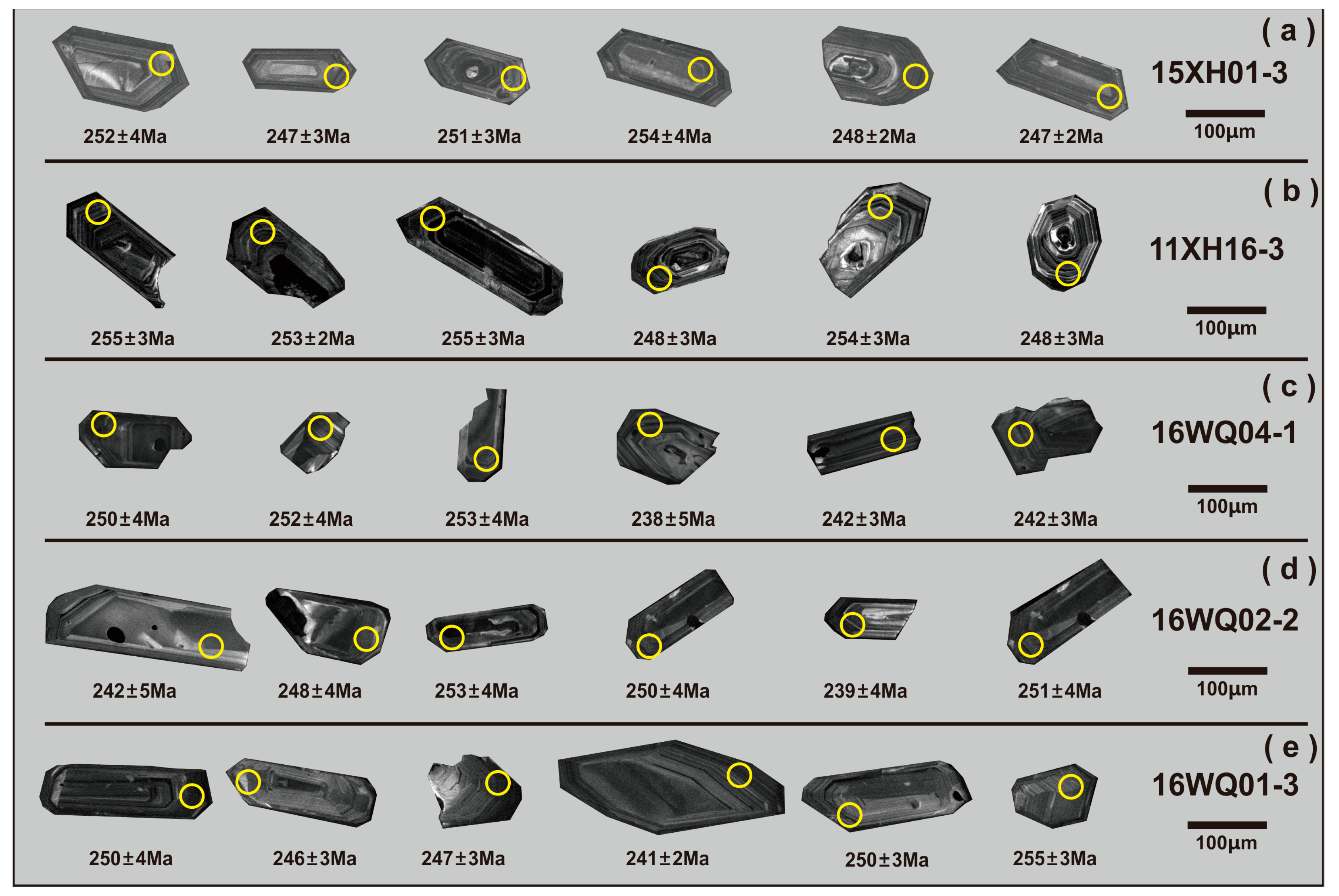
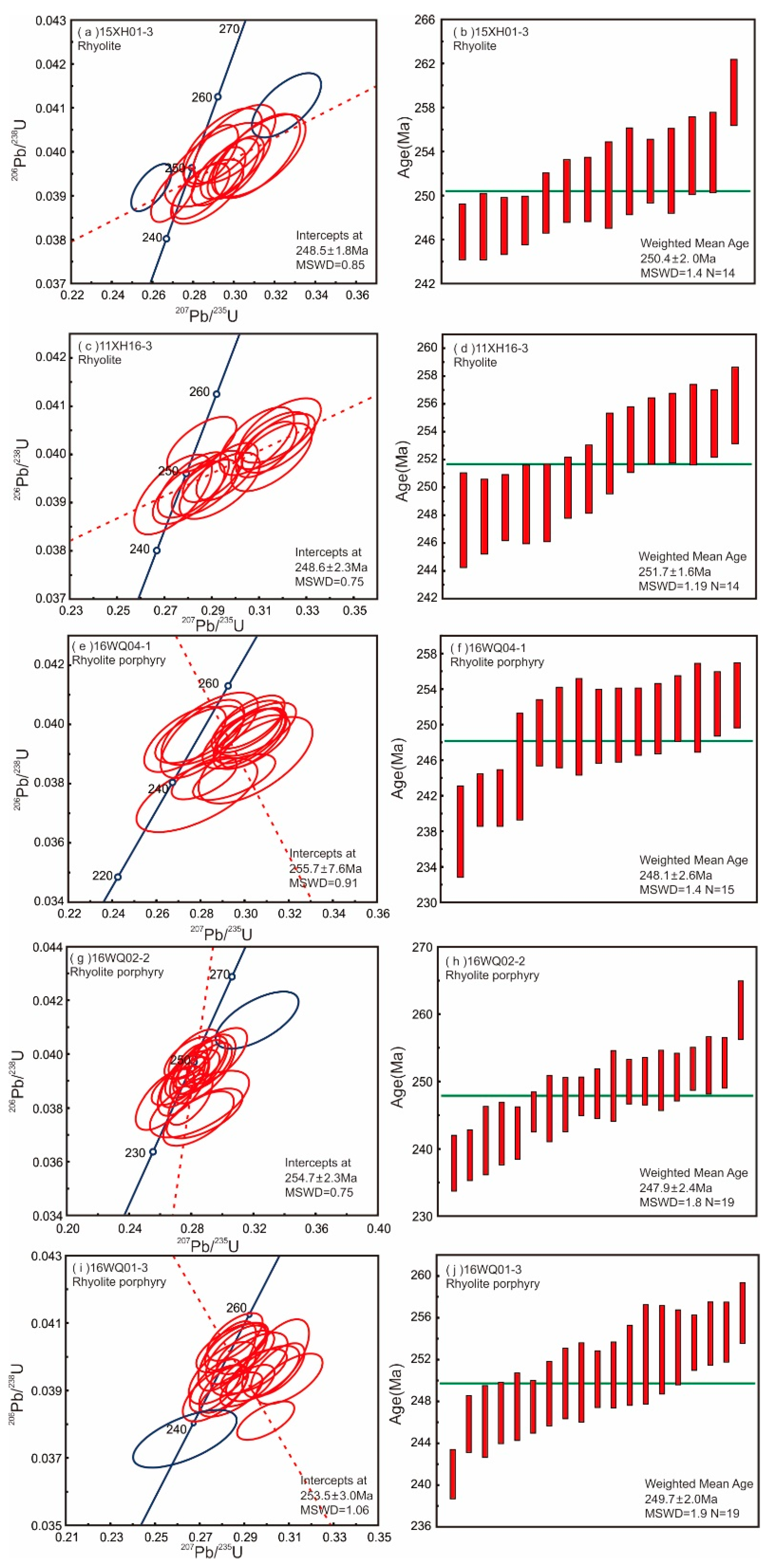
5.1. Zircon U–Pb Ages and Trace Elements
5.1.1. Zircon U–Pb Ages
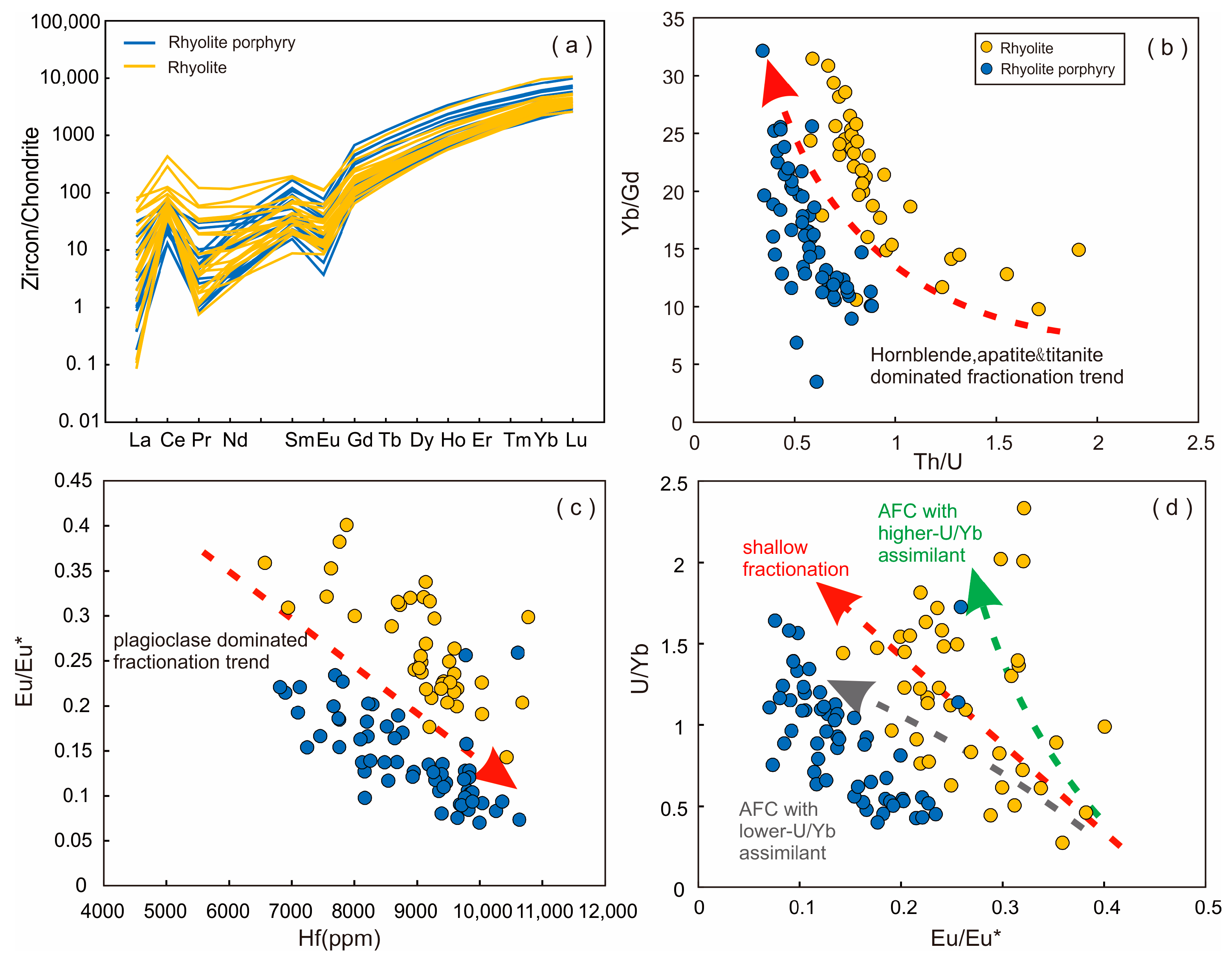
5.1.2. Zircon Trace Elements
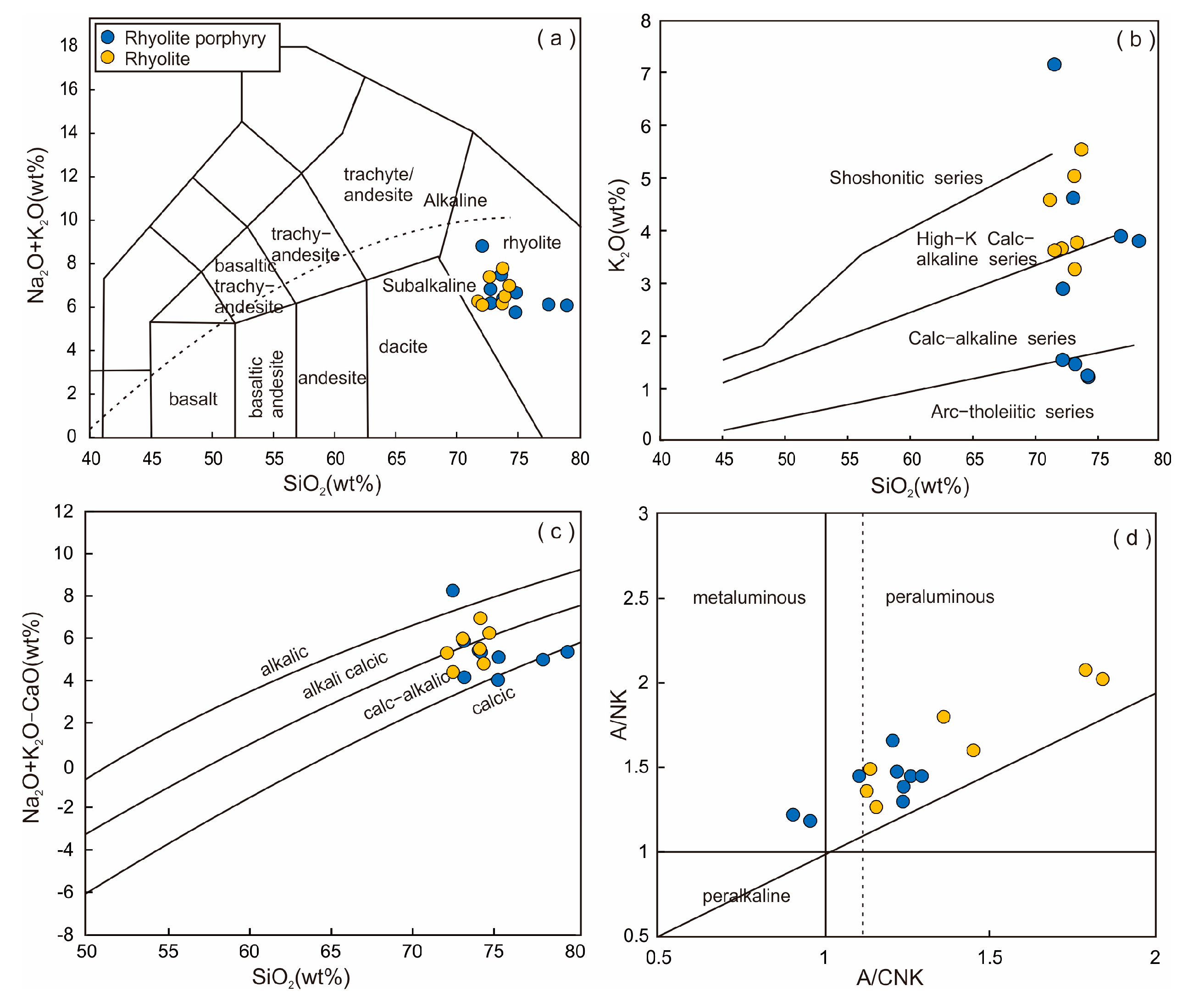
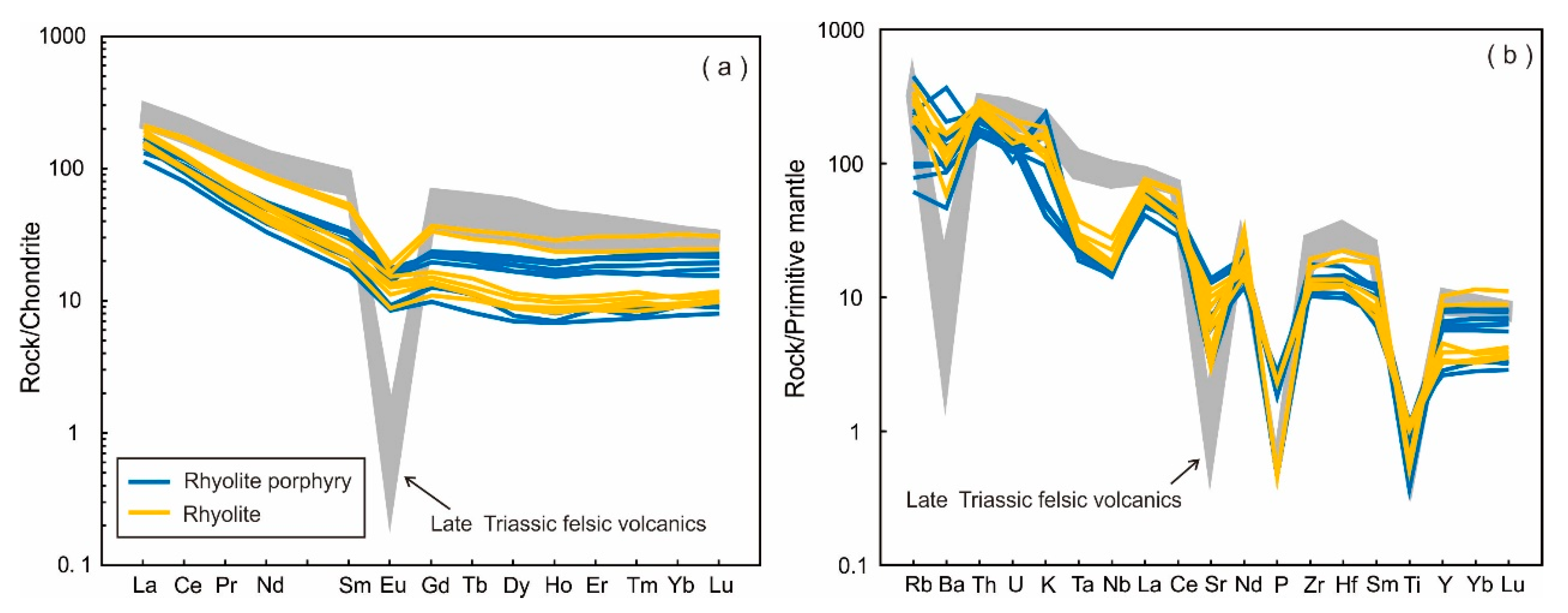
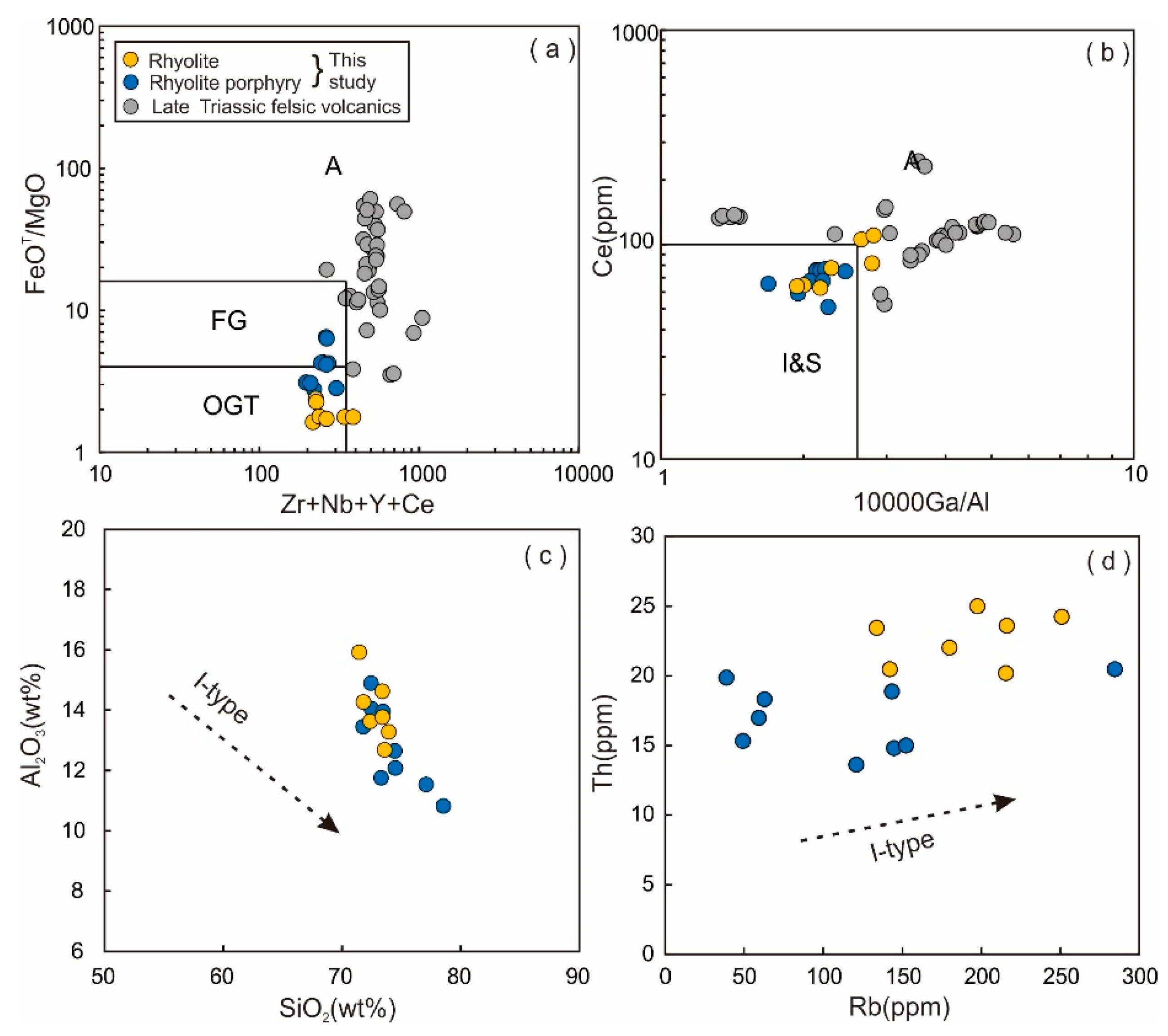
5.2. Whole-Rock Geochemistry
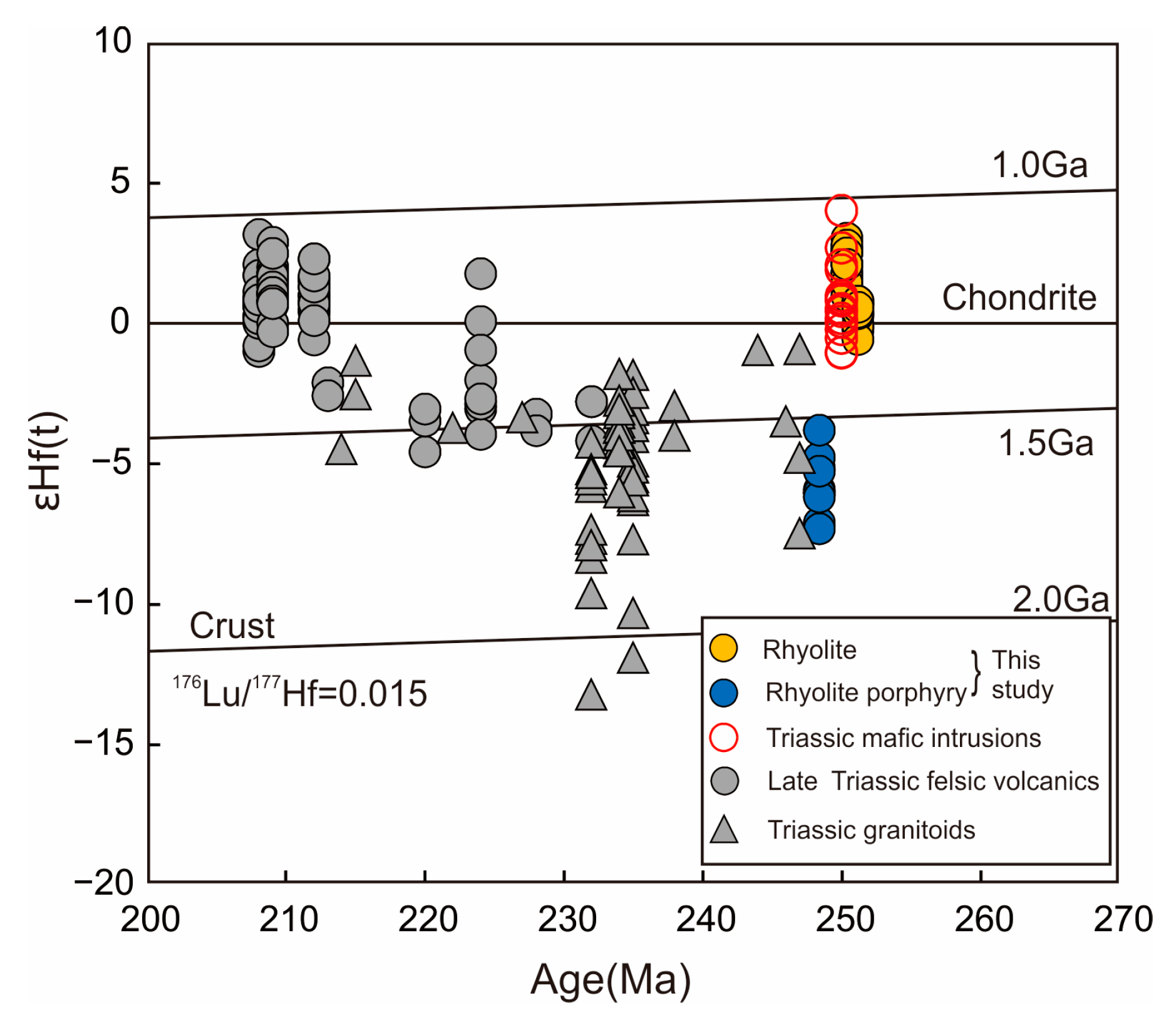
5.3. Zircon Lu-Hf Isotope
6. Discussion
6.1. Petrogenetic Type of the Felsic Volcanic Rocks
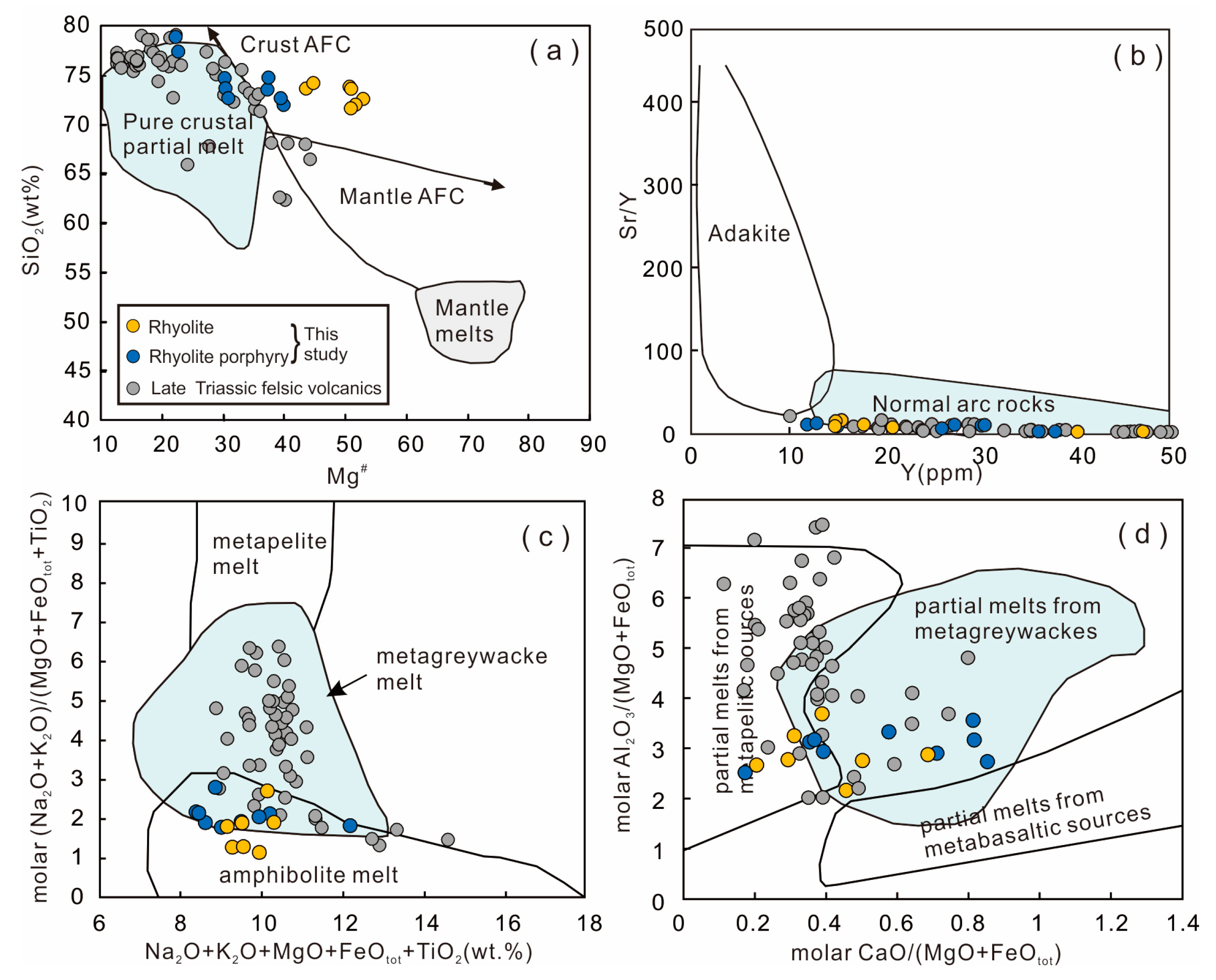
6.2. Origin of the Felsic Volcanic Rocks
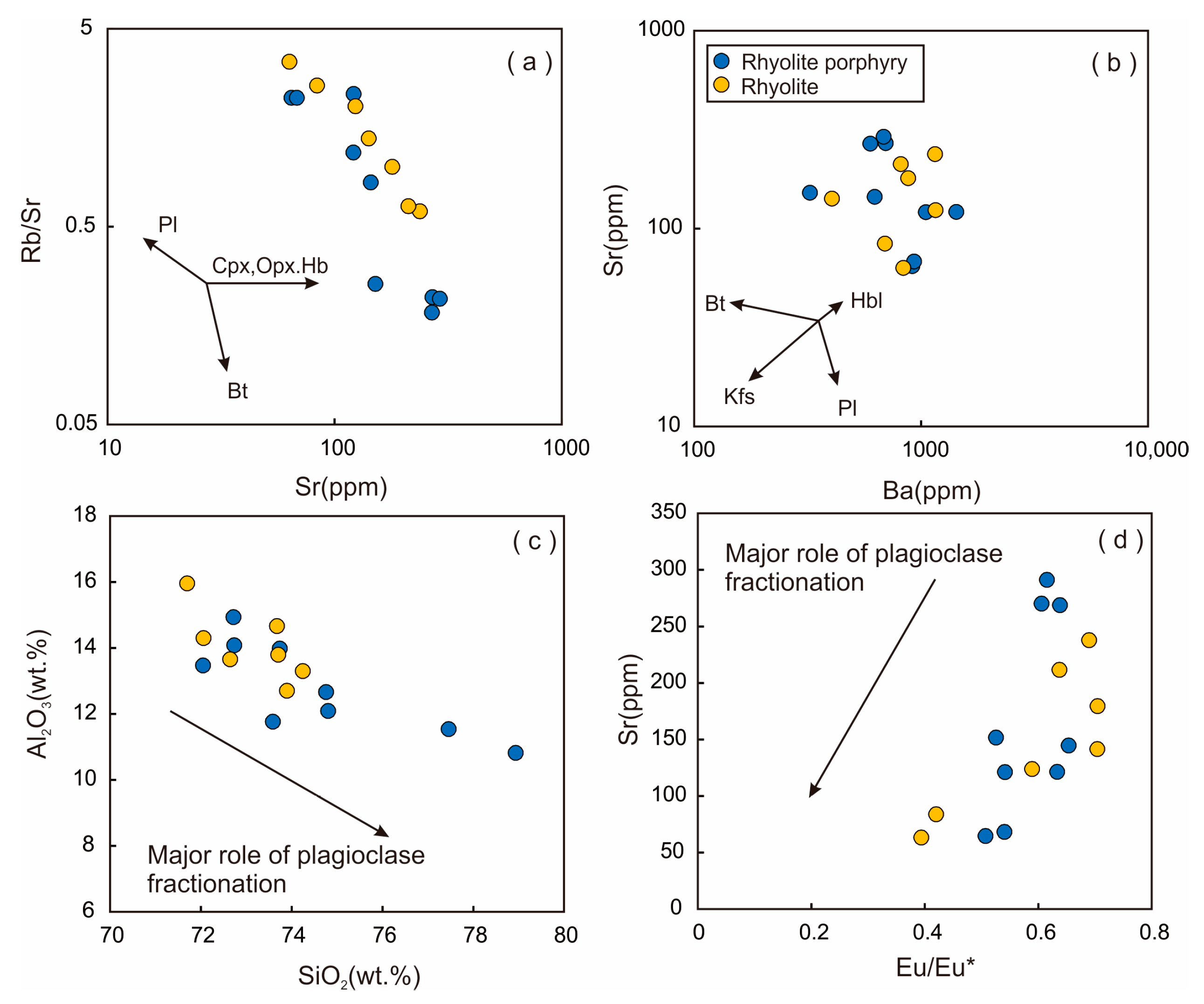
6.3. Fractional Crystallization
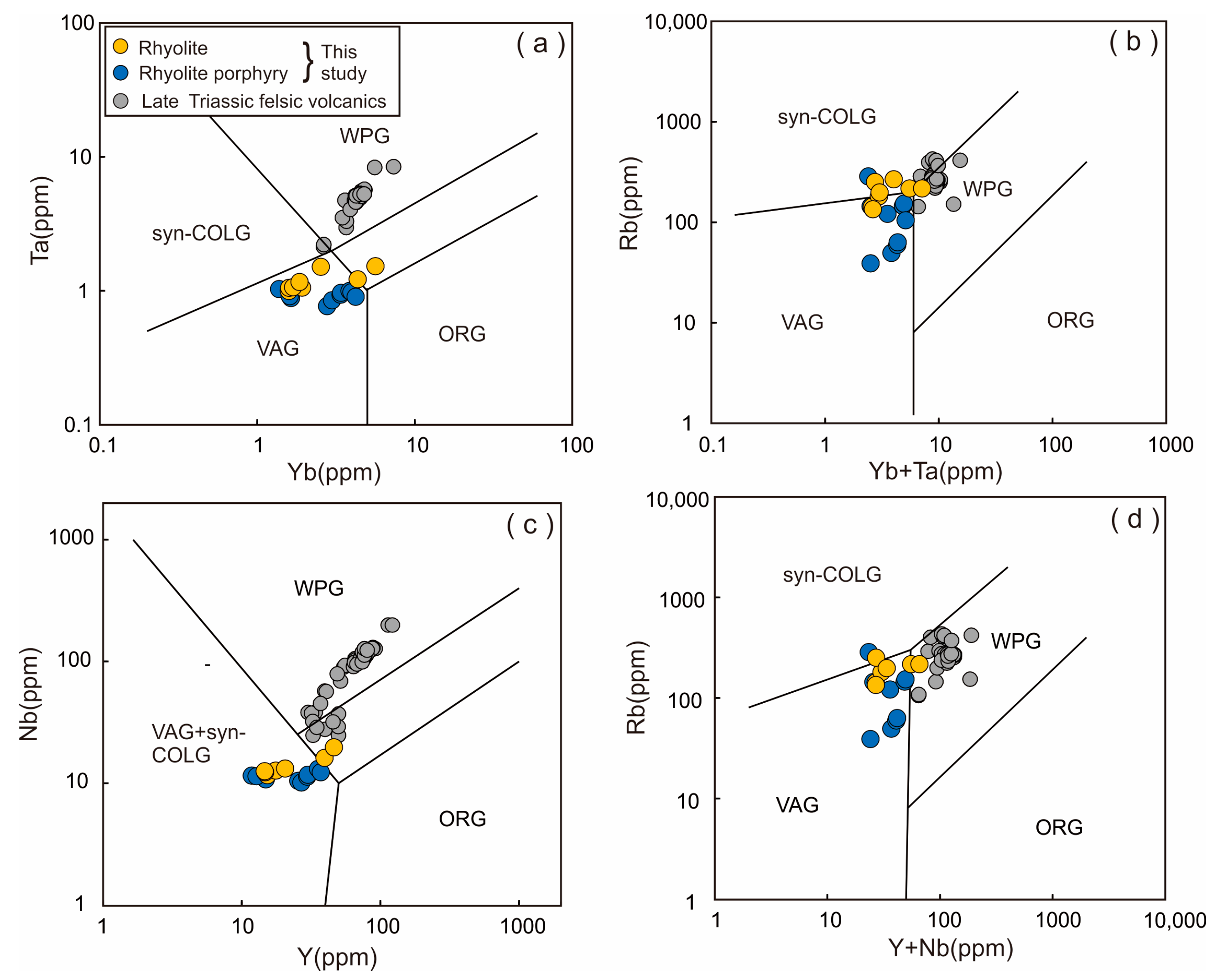
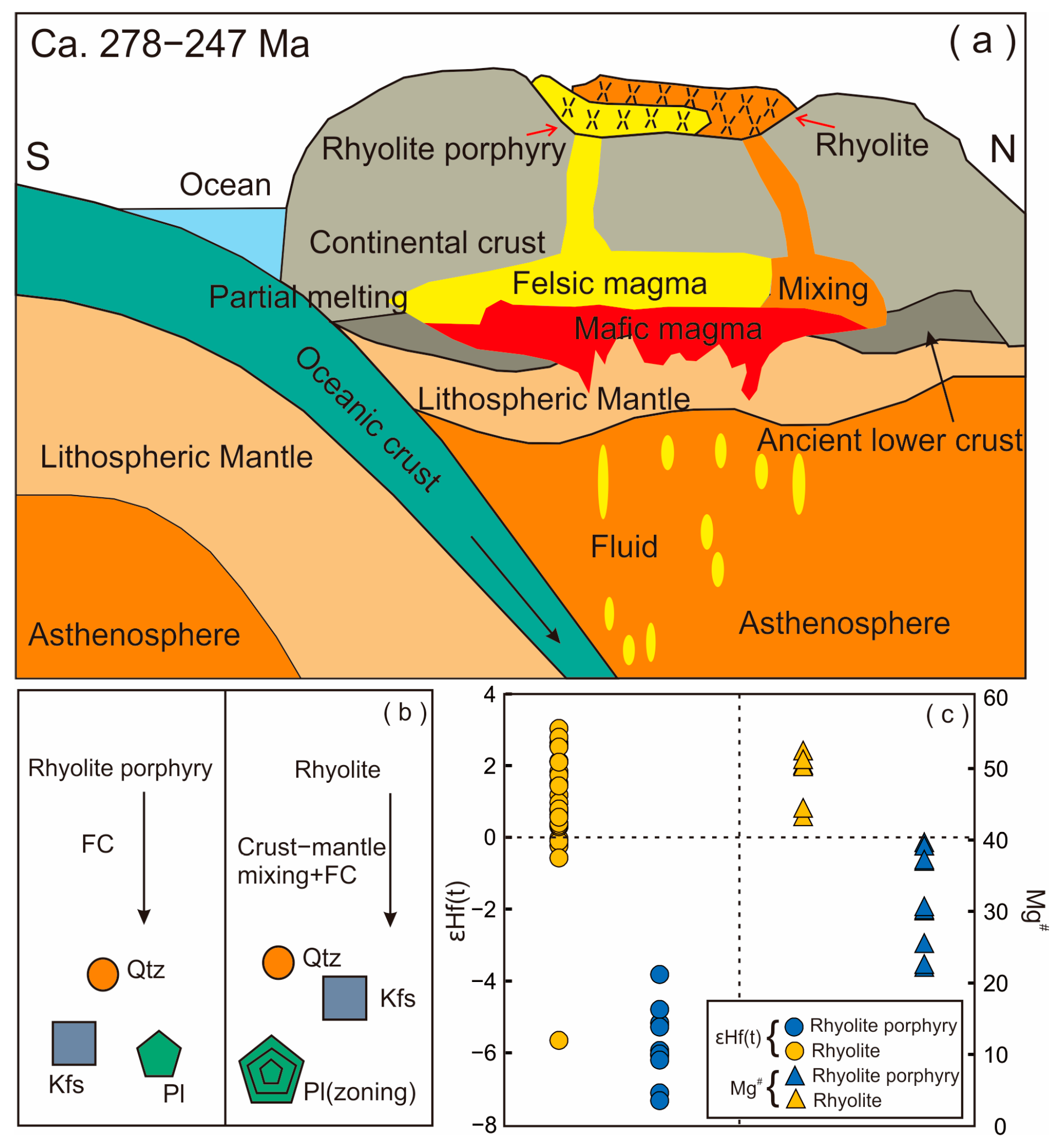
6.4. Geodynamic Implications
7. Conclusions
- The studied rhyolite and rhyolite porphyry in the Hongshuichuan Formation from the East Kunlun orogenic belt, North Tibet, are synchronously formed in Early Triassic (ca. 251–247 Ma).
- Elemental and isotopic geochemistry studies indicate that the rhyolite porphyry and rhyolite have typical lower crust-derived characteristics, and they are generated by partial melting of Mesoproterozoic metagreywacke sources with a certain amount of mantle-derived mafic magmas involved in the origin of the high Mg# rhyolite.
- The studied ca. 250 Ma felsic volcanic rocks were formed during the northward subduction of the East Kunlun Paleo-Tethyan oceanic slab. This study suggests that the reworking of ancient continental crust and crust–mantle magma mixing are important mechanisms for the evolution of the orogenic continental crust.
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Chen, G.C.; Pei, X.Z.; Li, R.; Li, Z.C.; Pei, L.; Liu, C.J.; Chen, Y.X.; Wang, M. Late Paleozoic-Early Mesozoic tectonic-magmatic evolution and mineralization in the eastern section of the East Kunlun Orogenic Belt. Acta Geol. Sin. (Engl. Ed.) 2019, 93, 158–159. [Google Scholar]
- Dong, Y.P.; He, D.F.; Sun, S.S.; Liu, X.M.; Zhou, X.H.; Zhang, F.F.; Yang, Z.; Cheng, B.; Zhao, G.C.; Li, J.H. Subduction and accretionary tectonics of the East Kunlun orogen, western segment of the Central China Orogenic System. Earth Sci. Rev. 2018, 186, 231–261. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, R.B.; Pei, X.Z.; Li, Z.C.; Liu, Z.Q.; Chen, G.C.; Chen, Y.X.; Wei, F.H.; Gao, J.M.; Liu, C.J.; Pei, L. Geological characteristics of Late Paleozoic-Mesozoic unconformities and their response to some significant tectonic events in eastern part of Eastern Kunlun. Earth Sci. Front. 2012, 19, 244–254, (In Chinese with English Abstract). [Google Scholar]
- Shao, F.L.; Niu, Y.L.; Regelous, M.; Zhu, D.C. Petrogenesis of peralkaline rhyolites in an intra-plate setting: Glass House Mountains, southeast Queensland, Australia. Lithos 2015, 216, 196–210. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tian, W.; Campbell, I.H.; Allen, C.M.; Guan, P.; Pan, W.Q.; Chen, M.M.; Yu, H.J.; Zhu, W.P. The Tarim picrite–basalt–rhyolite suite, a Permian flood basalt from northwest China with contrasting rhyolites produced by fractional crystallization and anatexis. Contrib. Mineral. Petrol. 2010, 160, 407–425. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ratajeski, K.; Glazner, A.F.; Miller, B.V. Geology and geochemistry of mafic to felsic plutonic rocks in the Cretaceous intrusive suite of Yosemite Valley, California. Geol. Soc. Am. Bull. 2001, 113, 1486–1502. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Takanashi, K.; Shuto, K.; Sato, M. Origin of Late Paleogene to Neogene basalts and associated coeval felsic volcanic rocks in Southwest Hokkaido, northern NE Japan arc: Constraints from Sr and Nd isotopes and major- and trace-element chemistry. Lithos 2011, 125, 368–392. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, S.Y.; Ren, Y.S.; Hou, H.N.; Li, J.M.; Hao, Y.J.; Shang, Q.Q. Petrogenesis, tectonic setting, and metallogenic significance of the Middle Permian volcanic rock system of the Miaoling Formation, Yanbian area, NE China: Constraints from geochronology, geochemistry, and Sr–Nd–Hf isotopes. Geochemistry 2022, 82, 125902. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gogoi, B.; Saikia, A.; Ahmad, M. Field evidence, mineral chemical and geochemical constraints on mafic-felsic magma interactions in a vertically zoned magma chamber from the Chotanagpur Granite Gneiss Complex of Eastern India. Geochemistry 2018, 78, 78–102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gogoi, B.; Chauhan, H.; Saikia, A. Understanding mafic-felsic magma interactions in a subvolcanic magma chamber using rapakivi feldspar: A case study from the Bathani volcano-sedimentary sequence, eastern India. Geochemistry 2021, 81, 125730. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yan, H.; Niu, Y.L.; Li, J.Y.; Lei, Y.; Kong, J.J.; Chen, S.; Zhang, Y.; Zhang, G.R. Petrogenesis and tectonic significance of the late Triassic mafic dikes and felsic volcanic rocks in the East Kunlun Orogenic Belt, Northern Tibet Plateau. Lithos 2016, 245, 205–222. [Google Scholar]
- Yang, J.H.; Wu, F.Y.; Wilde, S.A.; Chen, F.K.; Liu, X.M.; Xie, L.W. Petrogenesis of an alkali syenite–granite–rhyolite suite in the Yanshan fold and thrust belt, Eastern North China Craton: Geochronological, geochemical and Nd–Sr–Hf isotopic evidence for lithospheric thinning. J. Petrol. 2008, 49, 315–351. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Huang, H.; Niu, Y.; Nowell, G.; Zhao, Z.; Yu, X.; Zhu, D.C. Geochemical Constraints on the Petrogenesis of Granitoids in the East Kunlun Orogenic Belt, Northern Tibetan Plateau: Implications for Continental Crust Growth through Syn-Collisional Felsic Magmatism. Chem. Geol. 2014, 370, 1–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiong, F.H.; Ma, C.Q.; Zhang, J.Y.; Liu, B.; Jiang, H.A. Reworking of old continental lithosphere: An important crustal evolution mechanism in orogenic belts, as evidenced by Triassic I-type granitoids in the East Kunlun orogen, Northern Tibetan Plateau. J. Geol. Soc. 2014, 171, 847–863. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, X.W.; Huang, X.F.; Luo, M.F.; Dong, G.C.; Mo, X.X. Petrogenesis and geodynamic implications of the Mid-Triassic lavas from East Kunlun, northern Tibetan Plateau. J. Asian Earth Sci. 2015, 105, 32–47. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, Y.X.; Wang, L.X.; Ma, C.Q.; He, Z.X.; Deng, X.; Tian, Y. Petrogenesis and tectonic implication of the Late Triassic A1-type alkaline volcanics from the Xiangride area, eastern segment of the East Kunlun Orogen (China). Lithos 2022, 412–413, 106595. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shao, F.L.; Niu, Y.L.; Kong, J.J.; Liu, Y.; Wang, G.D.; Zhang, Y. Petrogenesis and tectonic implications of the Triassic rhyolites in the East Kunlun Orogenic Belt, northern Tibetan Plateau. Geosci. Front. 2021, 12, 101243. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiong, F.H.; Ma, C.Q.; Jiang, H.A.; Liu, B.; Huang, J. Geochronology and geochemistry of Middle Devonian mafic dykes in the East Kunlun orogenic belt, Northern Tibet Plateau: Implications for the transition from Prototethys to Paleotethys orogeny. Geochemistry 2014, 74, 225–235. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, G.C.; Pei, X.Z.; Li, R.B.; Li, Z.C.; Chen, Y.X.; Liu, C.J.; Pei, L. Multiple Sources of Indosinian Granites and Constraints on the Tectonic Evolution of the Paleo-Tethys Ocean in East Kunlun Orogen. Minerals 2022, 12, 1604. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xia, R.; Wang, C.M.; Qing, M.; Li, W.L.; Carranza, E.J.M.; Guo, X.D.; Ge, L.S.; Zeng, G.Z. Zircon U-Pb dating, geochemistry and Sr–Nd–Pb–Hf–O isotopes for the Nan’getan granodiorites and mafic microgranular enclaves in the East Kunlun Orogen: Record of closure of the Paleo-Tethys. Lithos 2015, 234–235, 47–60. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shao, F.L.; Niu, Y.L.; Liu, Y.; Chen, S.; Kong, J.J.; Duan, M. Petrogenesis of Triassic granitoids in the East Kunlun Orogenic Belt, northern Tibetan Plateau and their tectonic implications. Lithos 2017, 282, 33–44. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Ren, H.D.; Wang, T.; Zhang, L.; Wang, X.X.; Huang, H.; Feng, C.Y.; Teschner, C.; Song, P. Ages, sources and tectonic settings of the triassic igneous rocks in the easternmost Segment of the East Kunlun Orogen, Central China. Acta Geol. Sin. (Engl. Ed.) 2016, 90, 641–668. [Google Scholar]
- Roger, F.; Jolivet, M.; Malavieille, J. Tectonic evolution of the Triassic fold belts of Tibet. Compt. Rendus Geosci. 2008, 340, 180–189. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, C.F.; Yang, J.S.; Feng, B.G.; Zhu, Z.Z.; Zhao, M.; Chai, Y.C.; Shi, X.D.; Wang, H.D.; Hu, J.Q. Opening–closing tectonics of Kunlun Mountains. Ser. Geol. Mem. 1992, 5, 1–224, (In Chinese with English Abstract). [Google Scholar]
- Liu, B.; Ma, C.Q.; Zhang, J.Y.; Xiong, F.H.; Huang, J.; Jiang, H.A. 40Ar–39Ar age and geochemistry of subduction-related mafic dikes in northern Tibet, China: Petrogenesis and tectonic implications. Int. Geol. Rev. 2014, 56, 57–73. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mo, X.X.; Luo, Z.H.; Deng, J.F.; Yu, X.H.; Liu, C.D.; Chen, H.W.; Yuan, W.M.; Liu, Y.H. Granitoids and crustal growth in the East-Kunlun Orogenic Belt. Geol. J. China Univ. 2007, 13, 403–414, (In Chinese with English Abstract). [Google Scholar]
- Ren, J.H.; Liu, Y.Q.; Zhou, D.W.; Feng, Q.; Zhang, K.; Dong, Z.L.; Qin, P.L. Geochemical characteristics and LA-ICP-MS zircon U–Pb dating of basic dykes in the Xiaomiao area, East Kunlun. J. Jilin Univ. (Earth Sci. Ed.) 2010, 40, 859–868, (In Chinese with English Abstract). [Google Scholar]
- Ludwig, K.R. User’s Manual for Isoplot/ex Version 3.00: A Geochronological Toolkit for Microsoft Excel; Special Publication; Berkeley Geochronology Center: Berkeley, CA, USA, 2003. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, Y.; Gao, S.; Hu, Z.; Gao, C.; Zong, K.; Wang, D. Continental and oceanic crust recycling-induced melt–peridotite interactions in the Trans-North China Orogen: U–Pb dating, Hf isotopes and trace elements in zircons from mantle xenoliths. J. Petrol. 2010, 51, 537–571. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, Q.; Zheng, J.; Griffin, W.L.; Zhang, M.; Tang, H.; Su, Y.; Ping, X. Triassic “adakitic” rocks in an extensional setting (North China): Melts from the cratonic lower crust. Lithos 2012, 149, 159–173. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.; Hu, Z.; Gao, S.; Günther, D.; Xu, J.; Gao, C. In Situ Analysis of Major and Trace Elements of Anhydrous Minerals by La-Icp-Ms without Applying an Internal Standard. Chem. Geol. 2008, 257, 34–43. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, Z.; Liu, Y.; Gao, S.; Liu, W.; Zhang, W.; Tong, X.; Lin, L.; Zong, K.; Li, M.; Chen, H.; et al. Improved in situ Hf isotope ratio analysis of zircon using newly designed X skimmer cone and jet sample cone in combination with the addition of nitrogen by laser ablation multiple collector ICP-MS. J. Anal. At. Spectrom. 2012, 27, 1391–1399. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Belousova, E.A.; Griffin, W.L.; O’Reilly, S.Y. Zircon crystal morphology, trace element signatures and Hf isotope composition as a tool for petrogenetic modelling: Examples from Eastern Australian granitoids. J. Petrol. 2006, 47, 329–353. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Zhu, Y.X.; Wang, L.X.; Ma, C.Q.; Wiedenbeck, M.; Wang, W. The Neoproterozoic alkaline rocks from Fangcheng area, East Qinling (China) and their implications for regional Nb mineralization and tectonic evolution. Precambrian Res. 2020, 350, 105852. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Middlemost, E.A.K. Naming materials in the magma/igneous rock system. Earth-Sci. Rev. 1994, 37, 215–224. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peccerillo, A.; Taylor, S.R. Geochemistry of Eocene calc-alkaline volcanic rocks from the Kastamonu area, northern Turkey. Contrib. Mineral. Petrol. 1976, 58, 63–81. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Frost, C.D.; Frost, B.R. On ferroan (A-type) granitoids: Their compositional variability and modes of origin. J. Petrol. 2010, 52, 39–53. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Sun, S.S.; McDonough, W.F. Chemical and isotopic systematics of oceanic basalts:implications for mantle composition and processes. In Magmatism in the Ocean Basins; Saunders, A.D., Norry, M.J., Eds.; Special Publications; Geological Society: London, UK, 1989; Volume 42, pp. 313–345. [Google Scholar]
- Taylor, S.R.; McLennan, S.M. The Continental Crust: Its Composition and Evolution; Oxford Press: Blackwell, UK, 1985; pp. 1–312. [Google Scholar]
- Ding, S.; Huang, H.; Niu, Y.L.; Zhao, Z.D.; Yu, X.H.; Mo, X.X. Geochemistry, geochronology and petrogenesis of East Kunlun high Nb-Ta rhyolites. Acta Petrol. Sin. 2011, 27, 3603–3614, (In Chinese with English Abstract). [Google Scholar]
- Wei, X.; Sun, F.Y.; Zhang, Y.T.; Fan, X.Z.; Wang, Y.C.; Li, L. Mafic–intermediate igneous rocks in the East Kunlun Orogenic Belt, northwestern China: Petrogenesis and implications for regional geodynamic evolution during the Triassic. Lithos 2019, 346–347, 105159. [Google Scholar]
- Kamaunji, V.D.; Wang, L.X.; Ma, C.Q.; Liu, J.; Zhu, Y.X. Petrogenesis and tectonic implication of the Permian-Triassic syenogranites from the eastern segment of the East Kunlun Orogen, China. Lithos 2020, 25, 105932. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kong, J.J.; Niu, Y.L.; Hu, Y.; Zhang, Y.; Shao, F.L. Petrogenesis of the Triassic granitoids from the East Kunlun Orogenic Belt, NW China: Implications for continental crust growth from syn-collisional to post-collisional setting. Lithos 2020, 364–365, 105513. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yan, D.D.; Xiong, F.H.; Ma, C.Q.; Hou, M.C.; Zhao, H. Petrogenesis of Middle Triassic intermediate-mafic igneous rocks in East Kunlun, Northern Tibet: Implications for the crust growth and Paleo-Tethyan orogeny. Geosyst. Geoenviron. 2022, 100096. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, Z.T.; Xu, X.S. Petrogenesis of high-maficity S-type granites: Insight from the early Paleozoic Jinxi granite, South China. Lithos 2022, 106597, 412–413. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Whalen, J.B.; Currie, K.L.; Chappell, B.W. A-type granites; geochemical characteristics, discrimination and petrogenesis. Contrib. Mineral. Petrol. 1987, 95, 407–419. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, S.W.; Li, J.H.; Yuan, F.; Li, L.M.; Deng, Y.F.; Jowitt, S.M.; Jiang, R.; Li, Z.W.; Yuan, F.; Li, Y.; et al. Geochemistry and geochronology of I–type granites of the Feidong Complex, eastern China: Implications for the Paleoproterozoic tectonic evolution of the Yangtze Craton. Precambrian Res. 2022, 382, 106884. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, X.Y.; Luo, J.C.; Guo, J.; Wu, K.; Zhang, Z.K.; Sun, W.D.; Xia, X.P. Geochemistry of I- and A-type granites of the Qingyang–Jiuhuashan complex, eastern China: Insights into early cretaceous multistage magmatism. Lithos 2018, 316–317, 278–294. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yokoyama, T.; Okumura, S.; Nakashima, S. Hydration of rhyolitic glass during weathering as characterized by IR microspectroscopy. Geochim. Cosmochim. Acta 2008, 72, 117–125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shellnutt, G.J.; Wang, C.Y.; Zhou, M.F.; Yang, Y. Zircon Lu–Hf isotopic compositions of metaluminous and peralkaline A-type granitic plutons of the Emeishan large igneous province (SW China): Constraints on the mantle source. J. Asian Earth Sci. 2009, 35, 45–55. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Green, T.H. Significance of Nb/Ta as an indicator of geochemical processes in the crust-mantle system. Chem. Geol. 1995, 120, 347–359. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Weaver, B.L. The origin of ocean island basalt end member compositions: Trace element and isotopic constrains. Earth Planet. Sci. Lett. 1991, 104, 381–397. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Patiňo Douce, A.E.; Johnston, A.D. Phase equilibria and melt productivity in the pelitic system: Implications for the origin of peraluminous granitoids and aluminous granulites. Contrib. Mineral. Petrol. 1991, 107, 202–218. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rapp, R.P.; Watson, E.B. Dehydration melting of metabasalt at 8–32 kbar: Implications for continental growth and crust–mantle recycling. J. Petrol. 1995, 36, 891–931. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Castillo, P.R. Origin of the adakite high-Nb basalt association and its implications for postsubduction magmatism in Baja California, Mexico. Geol. Soc. Am. Bull. 2008, 120, 451–462. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vielzeuf, D.; Holloway, J.R. Experimental determination of the fluid-absent melting relations in the pelitic system. Contrib. Mineral. Petrol. 1988, 98, 257–276. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rapp, R.P.; Watson, E.B.; Miller, C.F. Partial melting of amphibolite/eclogite and the origin of Archean trondhjemites and tonalites. Precambrian Res. 1991, 51, 1–25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gardien, V.; Thompson, A.B.; Grujic, D.; Ulmer, P. Experimental melting of biotite + plagioclase + quartz ± muscovite assemblages and implications for crustal melting. J. Geophys. Res. 1995, 100, 15581–15591. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Patiño Douce, A.E.; Beard, J.S. Effects of P, f(O2) and Mg/Fe ratio on dehydration melting of model metagreywackes. J. Petrol. 1996, 37, 999–1024. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Skjerlie, K.P.; Johnston, A.D. Vapour-absent melting from 10 to 20 kbar of crustal rocks that contain multiple hydrous phases: Implications for anatexis in the deep to very deep continental crust and active continental margins. J. Petrol. 1996, 37, 661–691. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Patiño Douce, A.E. Generation of metaluminous A-type granites by low-pressure melting of calc-alkaline granitoids. Geology 1997, 25, 743–746. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stevens, G.; Clemens, J.D.; Droop, G.T.R. Melt production during granulite-facies anatexis: Experimental data from ‘primitive’ metasedimentary protoliths. Contrib. Mineral. Petrol. 1997, 128, 352–370. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Druitt, T.H.; Costa, F.; Deloule, E.; Dungan, M.; Scaillet, B. Decadal to monthly timescales of magma transfer and reservoir growth at a caldera volcano. Nature 2012, 482, 77–80. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Xiong, F.H.; Ma, C.Q.; Chen, B.; Ducea, M.N.; Hou, M.C.; Ni, S.J. Intermediate-mafic Dikes in the East Kunlun Orogen, Northern Tibetan Plateau: A Window into Paleo-arc Magma Feeding System. Lithos 2019, 340–341, 152–165. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gualda, G.A.R.; Ghiorso, M.S. Low-pressure origin of high-silica rhyolites and granites. J. Geol. 2013, 121, 537–545. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vasyukova, O.; Williams-Jones, A. Partial melting, fractional crystallisation, liquid immiscibility and hydrothermal mobilisation—A ‘recipe’ for the formation of economic A-type granite-hosted HFSE deposits. Lithos 2019, 356–357, 105300. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Villiger, S.; Müntener, O.; Ulmer, P. Crystallization pressures of mid-ocean ridge basalts derived from major element variations of glasses from equilibrium and fractional crystallization experiments. J. Geophys. Res. Solid Earth 2007, 112, B01202. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, R.G.; Dilles, J.H.; Tosdal, R.M.; Wooden, J.L.; Mazdab, F.K. Magmatic evolution of granodiorite intrusions at the El Salvador porphyry copper deposit, Chile, based on trace element composition and U/Pb age of zircons. Econ. Geol. 2017, 112, 245–273. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, L.; Sun, Y.; Pei, X.; Gao, M.; Feng, T.; Zhang, Z.; Chen, W. Northernmost paleo-tethyan oceanic basin in Tibet: Geochronological evidence from 40Ar/39Ar age dating of Dur’ngoi ophiolite. Chin. Sci. Bull. 2001, 46, 1203–1205. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bian, Q.T.; Li, D.H.; Pospelov, I.; Yin, L.M.; Li, H.S.; Zhao, D.S.; Chang, C.F.; Luo, X.Q.; Gao, S.L.; Astrakhantsev, O.; et al. Age, geochemistry and tectonic setting of Buqingshan ophiolites, North Qinghai-Tibet Plateau, China. J. Asian Earth Sci. 2004, 23, 577–596. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, J.S.; Shi, R.D.; Wu, C.L.; Wang, X.B.; Robinson, P. Dur’ngoi ophiolite in East Kunlun, Northeast Tibetan plateau: Evidence for paleo-Tethyan suture in Northwest China. J. Earth Sci. 2009, 20, 303–331. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Z.Q.; Pei, X.Z.; Li, R.B.; Li, Z.C.; Zhang, X.F.; Liu, Z.G.; Chen, G.H.; Chen, Y.X.; Ding, S.P.; Guo, J.F. LA-ICP-MS Zircon U-Pb Geochronology of the Two Suites of Ophiolites at the Buqiangshan Area of the A’nyemaqen Orogenic Belt in the Southern Margin of East Kunlun and its tectonic implication. Acta Geol. Sin. 2011, 85, 185–194. [Google Scholar]
- Li, R.B.; Pei, X.Z.; Li, Z.C.; Pei, L.; Chen, G.H.; Liu, Z.Q.; Chen, Y.X.; Liu, C.J.; Wang, M.; Zhang, M. Paleo-Tethyan Ocean Evolution and Indosinian Orogenesis in the East Kunlun Orogen, Northern Tibetan Plateau. Minerals 2022, 12, 1590. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiong, F.H.; Ma, C.Q.; Zhang, J.Y.; Liu, B. The origin of mafic microgranular enclaves and their host granodiorites from East Kunlun, Northern qinghai–Tibet Plateau: Implications for magma mixing during subduction of Paleo-Tethyan lithosphere. Miner. Petrol. 2012, 104, 211–224. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martin, H. Adakitic magmas: Modern analogues of Archaean granitoids. Lithos 1999, 46, 411–429. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, R.B.; Pei, X.Z.; Pei, L.; Li, Z.C.; Chen, G.C.; Chen, Y.X.; Liu, C.J.; Wang, M. The Early Triassic Andean-type Halagatu granitoids pluton in the East Kunlun orogen, northern Tibet Plateau: Response to the northward subduction of the Paleo-Tethys Ocean. Gondwana Res. 2018, 62, 212–226. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pearce, J.A.; Harris, N.; Tindle, A.G. Trace element discrimination diagrams for the tectonic interpretation of granitic rocks. J. Petrol. 1984, 25, 956–983. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Yan, Z.; Bian, Q.T.; Korchagin, O.A.; Pospelov, I.I.; Li, J.L.; Wang, Z.Q. Provenance of Early Triassic Hongshuichuan formation in the southern margin of the East Kunlun Mountains: Constrains from detrial framework, heavy mineral analysis and geochem istry. Acta Petrol. Sin. 2008, 24, 1068–1078, (In Chinese with English Abstract). [Google Scholar]
- Yue, Y.G.; Dong, Y.P.; Sun, S.S.; He, D.F. Mafic-ultramafic rocks in the Buqingshan Complex of the East Kunlun Orogen, northern Tibetan Plateau: Remnants of the Paleo-Tethys Ocean. Int. Geol. Rev. 2022, 64, 3149–3170. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fan, X.Z.; Sun, F.Y.; Xu, C.H.; Wu, Q.Q.; Yu, L.; Wang, L.; Yan, C.; Bakht, S. Volcanic rocks of the Elashan Formation in the Dulan-Xiangride Basin, East Kunlun Orogenic Belt, NW China: Petrogenesis and implications for Late Triassic geodynamic evolution. Int. Geol. Rev. 2021, 64, 1270–1293. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Yan, D.; Chu, Z.; Liu, Z.; Wang, W.; Xiong, F. Petrogenesis of Early Triassic Felsic Volcanic Rocks in the East Kunlun Orogen, Northern Tibet: Implications for the Paleo-Tethyan Tectonic and Crustal Evolution. Minerals 2023, 13, 607. https://doi.org/10.3390/min13050607
Yan D, Chu Z, Liu Z, Wang W, Xiong F. Petrogenesis of Early Triassic Felsic Volcanic Rocks in the East Kunlun Orogen, Northern Tibet: Implications for the Paleo-Tethyan Tectonic and Crustal Evolution. Minerals. 2023; 13(5):607. https://doi.org/10.3390/min13050607
Chicago/Turabian StyleYan, Dongdong, Zhiqiang Chu, Zhongyuan Liu, Wei Wang, and Fuhao Xiong. 2023. "Petrogenesis of Early Triassic Felsic Volcanic Rocks in the East Kunlun Orogen, Northern Tibet: Implications for the Paleo-Tethyan Tectonic and Crustal Evolution" Minerals 13, no. 5: 607. https://doi.org/10.3390/min13050607
APA StyleYan, D., Chu, Z., Liu, Z., Wang, W., & Xiong, F. (2023). Petrogenesis of Early Triassic Felsic Volcanic Rocks in the East Kunlun Orogen, Northern Tibet: Implications for the Paleo-Tethyan Tectonic and Crustal Evolution. Minerals, 13(5), 607. https://doi.org/10.3390/min13050607






