The Perturbation of the Guadalupian Marine Environment Triggered by Early-Stage Eruption of the Emeishan Large Igneous Province: Rare Earth Element and Sr-Nd Isotope Evidence from Zunyi Manganese Deposit, South China
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Geological Setting
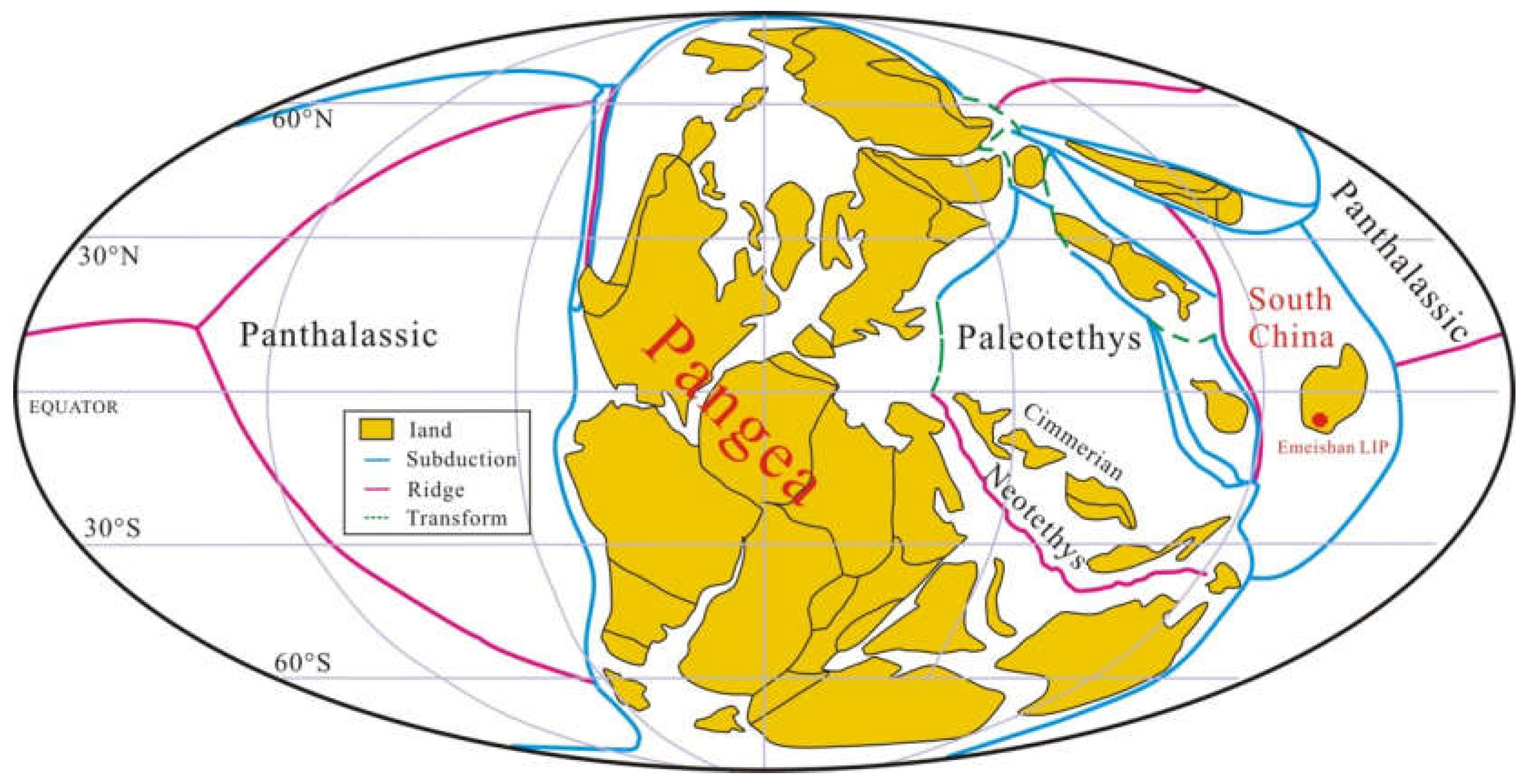
2.1. Emeishan Large Igneous Province
2.2. Deposit Description
3. Materials and Methods
4. Results
4.1. Major and Trace Elements
4.2. Sr-Nd Isotopes
5. Discussion
5.1. Depositional Controls on REY in the Zunyi Mn Deposit
5.1.1. Syn-Depositional Detrital Contamination
5.1.2. Post-Depositional Alteration
5.1.3. Scavenged by Mn Oxyhydroxides from Ambient Seawater
5.2. Middle–Late Permian Seawater in South China
5.2.1. Sr Isotopes in the Middle–Late Permian Seawater
5.2.2. A Hydrothermal Input?
5.2.3. Nd Isotopes in the Middle–Late Permian Seawater
5.2.4. Nd Isotopes in the Zunyi Mn Deposit
6. Potential Link between the Guadalupian Marine Environmental Perturbation and the Early Stage of the ELIP
7. Conclusions
- The clastic Mn ore has been contaminated by mafic aluminosilicates, whereas the massive and oolitic Mn ores, as well as associated siliceous limestones, have not been altered and thus have preserved their pristine signature as chemical sediments.
- The REYSN patterns of the massive and oolitic Mn ores and siliceous limestones are consistent with modern seawater-like patterns, further demonstrating that these samples recorded the geochemical signatures of the end-Guadalupian seawater in South China.
- The εNd(t) values for the massive and oolitic Mn ores and the siliceous limestones (−2.4 to −3.2) are relatively high, lying at the high end of the range of global end-Guadalupian seawater values.
- These high εNd(t) values result from the input of mantle-derived Nd into seawater by the hydrolysis of contemporaneous subaqueous mafic volcaniclastic materials from the early-stage eruption of the ELIP, which resulted in the chemical property change of contemporaneous seawater in South China.
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Ali, J.R.; Thompson, G.M.; Zhou, M.F.; Song, X. Emeishan large igneous province, SW China. Lithos 2005, 79, 475–489. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, H.; Du, Y.S.; Yang, J.H.; Zhou, L.; Hu, L.S.; Huang, H.W.; Huang, Z.Q. Origin of Permian basalts and clastic rocks in Napo, Southwest China: Implications for the erosion and eruption of the Emeishan large igneous province. Lithos 2014, 208–209, 324–338. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shellnutt, J.G. The Emeishan large igneous province: A synthesis. Geosci. Front. 2014, 5, 369–394. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Xu, Y.G.; Chung, S.L.; Shao, H.; He, B. Silicic magmas from the Emeishan large igneous province, Southwest China: Petrogenesis and their link with the endGuadalupian biological crisis. Lithos 2010, 119, 47–60. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, M.F.; Zhao, J.H.; Qi, L.; Su, W.; Hu, R. Zircon U-Pb geochronology and elemental and Sr-Nd isotope geochemistry of Permian mafic rocks in the Funing area, SW China. Contrib. Mineral. Petrol. 2006, 151, 1–19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, B.; Guo, Z.J.; Zhang, S.N.; Ukstins, I.; Du, W.; Liu, R.C. What triggered the early-stage eruption of the Emeishan large igneous province? Geol. Soc. Am. Bull. 2019, 131, 1837–1856. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bond, D.P.G.; Hilton, J.; Wignall, P.B.; Ali, J.R.; Stevens, L.G.; Sun, Y.D.; Lai, X.L. The Middle Permian (Capitanian) mass extinction on land and in the oceans. Earth Sci. Rev. 2010, 109, 100–116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, J.H.; Cawood, P.A.; Du, Y.S. Voluminous silicic eruptions during late Permian Emeishan igneous province and link to climate cooling. Earth Planet. Sci. Lett. 2015, 432, 166–175. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Zhao, L.X.; Dai, S.F.; Graham, I.T.; Li, X.; Zhang, B.B. New insights into the lowest Xuanwei Formation in eastern Yunnan Province, SW China: Implications for Emeishan large igneous province felsic tuff deposition and the cause of the endGuadalupian mass extinction. Lithos 2016, 264, 375–391. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lai, X.L.; Wang, W.; Wignall, P.B.; Bond, D.; Jiang, H.S.; Ali, J.R.; John, E.H.; Sun, Y.D. Palaeoenvironmental change during the end-Guadalupian (Permian) mass extinction in Sichuan, China. Palaeogeogr. Palaeoclimatol. Palaeoecol. 2008, 269, 78–93. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wignall, P.B.; Sun, Y.D.; Bond, D.P.G.; Izon, G.; Newton, R.J.; Védrine, S.; Widdowson, M.; Ali, J.R.; Lai, X.L.; Jiang, H.S.; et al. Volcanism, mass extinction, and carbon isotope fluctuations in the Middle Permian of China. Science 2009, 324, 1179–1182. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ogg, J.G.; Ogg, G.; Gradstein, F.M. The Concise Geologic Time Scale; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2016; pp. 123–124. [Google Scholar]
- Yan, H.; Pi, D.H.; Jiang, S.Y.; Hao, W.D.; Mänd, K.; Robbins, L.J.; Li, L.; Konhauser, K.O. New constraints on the onset age of the Emeishan LIP volcanism and implications for the Guadalupian mass extinction. Lithos 2020, 360–361, 105441. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jerram, D.A.; Widdowson, M.; Wignall, P.B.; Sun, Y.D.; Lai, X.L.; Bond, D.P.; Torsvik, T.H. Submarine palaeoenvironments during Emeishan flood basalt volcanism, SW China: Implications for plume-lithosphere interaction during the Capitanian, Middle Permian (‘end Guadalupian’) extinction event. Palaeogeogr. Palaeoclimatol. Palaeoecol. 2016, 441, 65–73. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wignall, P.B.; Védrine, S.; Bond, D.; Wang, W.; Lai, X.L.; Ali, J.R.; Jiang, H.S. Facies analysis and sea-level change at the Guadalupian–Lopingian Global Stratotype (Laibin, South China), and its bearing on the end-Guadalupian mass extinction. J. Geol. Soc. Lond. 2009, 166, 655–666. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bagherpour, B.; Bucher, H.; Schneebeli-Hermann, E.; Vennemann, T.; Chiaradia, M.; Shen, S.Z. Early late Permian coupled carbon and strontium isotope chemostratigraphy from South China: Extended Emeishan volcanism? Gondwana Res. 2018, 58, 58–70. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, H.; Hou, M.C.; Qing, H.R.; Zhou, L.; Yang, J.H.; Du, Y.S.; Tian, J.C.; Ni, S.J.; Xiong, F.H. The contribution of the Emeishan large igneous province to the strontium isotope evolution of the Capitanian seawater. Int. Geol. Rev. 2019, 61, 1927–1939. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bau, M. Effects of syn- and post-depositional processes on the rare-earth element distribution in Precambrian iron-formations. Eur. J. Mineral. 1993, 5, 257–267. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bau, M.; Dulski, P. Distribution of yttrium and rare-earth elements in the Penge and Kuruman iron-formations, Transvaal supergroup, South Africa. Precambrian Res. 1996, 79, 37–55. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bau, M.; Schmidt, K.; Koschinsky, A.; Hein, J.; Kuhn, T.; Usui, A. Discriminating between different genetic types of marine ferro-manganese crusts and nodules based on rare earth elements and yttrium. Chem. Geol. 2014, 381, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stille, P.; Clauer, N.; Abrecht, J. Nd isotopic composition of Jurassic Tethys seawater and the genesis of Alpine Mn-deposits: Evidence from Sr–Nd isotope data. Geochim. Cosmochim. Acta 1989, 53, 1095–1099. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Konhauser, K.O.; Planavsky, N.J.; Hardisty, D.S.; Robbins, L.J.; Warchola, T.J.; Haugaard, R.; Lalonde, S.V.; Partin, C.A.; Oonk, P.B.H.; Tsikos, H.; et al. Iron formations: A global record of Neoarchaean to Palaeo-proterozoic environmental history. Earth Sci. Rev. 2017, 172, 140–177. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Bau, M.; Moller, P.; Dulski, P. Yttrium and lanthanides in eastern Mediterranean seawater and their fractionation during redox-cycling. Mar. Chem. 1997, 56, 123–131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bau, M.; Hohndorf, A.; Dulski, P.; Beukes, N.J. Sources of rare-earth elements and iron in paleoproterozoic iron-formations from the Transvaal supergroup, South Africa: Evidence from neodymium isotopes. J. Geol. 1997, 105, 121–129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kamber, B.S.; Webb, G.E. The geochemistry of late Archaean microbial carbonate: Implications for ocean chemistry and continental erosion history. Geochim. Cosmochim. Acta 2001, 65, 2509–2525. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alexander, B.; Bau, M.; Andersson, P.; Dulski, P. Continentally-derived solutes in shallow Archean seawater: Rare earth element and Nd isotope evidence in iron formation from the 2.9 Ga Pongola supergroup. Geochim. Cosmochim. Acta 2008, 72, 378–394. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alexander, B.; Bau, M.; Andersson, P. Neodymium isotopes in Archean seawater and implications for the marine Nd cycle in Earth’s early oceans. Earth Planet. Sci. Lett. 2009, 283, 144–155. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Viehmann, S.; Hoffmann, J.E.; Münker, C.; Bau, M. Decoupled Hf-Nd isotopes in Neoarchean seawater reveal weathering of emerged continents. Geology 2014, 42, 115–118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Blaser, P.; Lippold, J.; Gutjahr, M.; Frank, N.; Link, J.M.; Frank, M. Extracting foraminiferal seawater Nd isotope signatures from bulk deep sea sediment by chemical leaching. Chem. Geol. 2016, 439, 189–204. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, J.B.; Yang, R.D.; Xu, H.; Zhang, X.; Feng, K.N.; Zheng, L.L. Genesis of Permian sedimentary manganese deposits in Zunyi, Guizhou Province, SW China: Constraints from geology and elemental geochemistry. J. Geochem. Explor. 2018, 192, 142–154. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, H.; Gao, J.B.; Yang, R.D.; Feng, K.N.; Wang, L.B.; Chen, J. Metallogenic mechanism of large manganese deposits from Permian manganese ore belt in western South ChinaBlock: New mineralogical and geochemical evidence. Ore Geol. Rev. 2021, 132, 103993. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yan, H.; Pi, D.H.; Jiang, S.Y.; Mao, J.W.; Xu, L.G.; Yang, X.Q.; Hao, W.D.; Mänd, K.; Li, L.; Konhauser, K.O.; et al. Mineral paragenesis in Paleozoic manganese ore deposits: Depositional versus post-depositional formation processes. Geochim. Cosmochim. Acta 2022, 325, 65–86. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, W.C.; Polgari, M.; Du, Y.S. Microbial metallogenesis of Cryogenian manganese ore deposits in South China. Precambr. Res. 2019, 322, 122–135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Domeier, M.; Torsvik, T.H. 2014, Plate tectonics in the late Paleozoic. Geosci. Front. 2014, 5, 303–350. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Editing Committee of Stratigraphy (ECS). Permian in China; Geological Publishing House: Beijing, China, 2000; p. 149, (In Chinese with English abstract). [Google Scholar]
- He, B.; Xu, Y.G.; Huang, X.L.; Luo, Z.Y.; Shi, Y.R.; Yang, Q.J.; Yu, S.Y. Age and duration of the Emeishan flood volcanism, SW China: Geochemistry and SHRIMP zircon U-Pb dating of silicic ignimbrites, post-volcanic Xuanwei Formation and clay tuff at the Chaotian section. Earth Planet. Sci. Lett. 2007, 255, 306–323. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, Y.D.; Lai, X.L.; Wignall, P.B.; Widdowson, M.; Ali, J.R.; Jiang, H.S.; Wang, W.; Yan, C.B.; Bond, D.P.; Védrine, S. Dating the onset and nature of the middle Permian Emeishan large igneous province eruptions in SW China using conodont biostratigraphy and its bearing on mantle plume uplift models. Lithos 2010, 119, 20–33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- He, B.; Xu, Y.G.; Chung, S.L.; Xiao, L.; Wang, Y. Sedimentary evidence for a rapid, kilometer-scale crustal doming prior to the eruption of the Emeishan flood basalts. Earth Planet. Sci. Lett. 2003, 213, 391–405. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saitoh, M.; Isozaki, Y.; Yao, J.X.; Ji, Z.S.; Ueno, Y.; Yoshida, N. The appearance of an oxygen-depleted condition on the Capitanian disphotic slope/basin in South China: Middle-Upper Permian stratigraphy at Chaotian in northern Sichuan. Glob. Planet. Change 2013, 105, 180–192. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pu, W.; Gao, J.F.; Zhao, K.D.; Ling, H.F.; Jiang, S.Y. Separation method of Rb-Sr, Sm-Nd using DCTA and HIBA. J. Nanjing University (Nat. Sci.) 2005, 41, 445–450, (In Chinese with English abstract). [Google Scholar]
- Tanaka, T.; Togashi, S.; Kamioka, H.; Amakawa, H.; Kagami, H.; Hamamoto, T.; Yuhara, M.; Orihashi, Y.; Yoneda, S.; Shimizu, H.; et al. JNdi-1: A neodymium isotopic reference in consistency with LaJolla neodymium. Chem. Geol. 2000, 168, 279–281. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bau, M.; Dulski, P. Comparing yttrium and rare earths in hydrothermal fluids from the Mid-Atlantic Ridge: Implications for Y and REE behaviour during near-vent mixing and for the Y/Ho ratio of Proterozoic seawater. Chem. Geol. 1999, 155, 77–90. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Douville, E.; Bienvenu, P.; Charlou, J.L.; Donval, J.P.; Fouquet, Y.; Appriou, P.; Gamo, T. Yttrium and rare earth elements in fluids from various deep-sea hydrothermal systems. Geochim. Cosmochim. Acta 1999, 63, 627–643. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, C.Q.; Ehlers, C.; Xu, C.H.; Li, Z.C.; Yang, K.G. The roots of the Dabieshan ultrahigh-pressure metamorphic terrain: Constraints from geochemistry and Nd–Sr isotope systematics. Precambrian Res. 2000, 102, 279–301. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, C.Y.; Zhou, M.F.; Qi, L. Permian flood basalts and mafic intrusions in the Jinping (SW China)–Song Da (northern Vietnam) district: Mantle sources, crustal contamination and sulfide segregation. Chem. Geol. 2007, 243, 317–343. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Morford, J.L.; Emerson, S. The geochemistry of redox sensitive trace metals in sediments. Geochim Cosmochim Acta. 1999, 63, 1735–1750. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bau, M. Scavenging of dissolved yttrium and rare earths by precipitating iron oxyhydroxide: Experimental evidence for Ce oxidation, Y–Ho fractionation, and lanthanide tetrad effect. Geochim. Cosmochim. Acta 1999, 63, 67–77. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pi, D.H.; Liu, C.Q.; Shields-Zhou, G.A.; Jiang, S.Y. Trace and rare earth element geochemistry of black shale and kerogen in the early Cambrian Niutitang Formation in Guizhou province, South China: Constraints for redox environments and origin of metal enrichments. Precambr. Res. 2013, 225, 218–229. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shields, G.; Stille, P. Diagenetic constraints on the use of cerium anomalies as palaeoseawater redox proxies: An isotopic and REE study of Cambrian phosphorites. Chem. Geol. 2001, 175, 29–48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, B.; Jang, S.Y.; Yang, J.H.; Pi, D.H.; Ling, H.F.; Chen, Y.Q. Rare earth element and Sr-Nd isotope geochemistry of phosphate nodules from the lower Cambrian Niutitang Formation, NW Hunan Province, Shouth China. Palaeogeogr. Palaeoclimatol. Palaeoecol. 2014, 398, 132–143. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xin, H.; Jang, S.H.; Yang, J.H.; Wu, H.P.; Pi, D.H. Rare earth element and Sr-Nd isotope geochemistry of phosphatic rocks in Neoproterozoic Ediacaran Doushantuo Formation in Zhangcunping section from western Hubei Province, South China. Palaeogeogr. Palaeoclimatol. Palaeoecol. 2015, 440, 712–724. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wright, J.; Schrader, H.; Holser, W.T. Paleoredox variations in ancient oceans recorded by rare earth elements in fossil apatite. Geochim. Cosmochim. Acta 1987, 51, 631–644. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pourret, O.; Davranche, M.; Gruau, G.; Dia, A. New insights into cerium anomalies in organic-rich alkaline waters. Chem. Geol. 2008, 251, 120–127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Xiong, Z.; Li, T.; Algeo, T.; Chang, F.; Yin, X.; Xu, Z. Rare earth element geochemistry of laminated diatom mats from tropical West Pacific: Evidence for more reducing bottomwaters and higher primary productivity during the Last Glacial Maximum. Chem. Geol. 2012, 296, 103–118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Byrne, R.H.; Kim, K.-H. Rare earth element scavenging in seawater. Geochim. Cosmochim. Acta 1990, 54, 2645–2656. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ohta, A.; Kawabe, I. REE(III) adsorption onto Mn dioxide (δ-MnO2) and Fe oxyhydroxide: Ce(III) oxidation by δ-MnO2. Geochim. Cosmochim. Acta 2001, 65, 695–703. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Davranche, M.; Pourret, O.; Gruau, G.; Dia, A.; Jin, D.; Gaertner, D. Competitive binding of REE to humic acid and manganese oxide: Impact of reaction kinetics on development of cerium anomaly and REE adsorption. Chem. Geol. 2008, 247, 154–170. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pourret, O.; Davranche, M. Rare earth element sorption onto hydrous manganese oxide: A modeling study. J. Colloid Interface Sci. 2013, 395, 18–23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Bau, M.; Koschinsky, A. Oxidative scavenging of cerium on hydrous Fe oxide: Evidence from the distribution of rare earth elements and yttrium between Fe oxides and Mn oxides in hydrogenetic ferromanganese crusts. Geochem. J. 2009, 43, 37–47. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Bau, M.; Koschinsky, A.; Dulski, P.; Hein, J.R. Comparison of the partitioning behaviours of yttrium, rare earth elements, and titanium between hydrogenetic marine ferromanganese crusts and seawater. Geochim. Cosmochim. Acta 1996, 60, 1709–1725. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Holser, W.T. Evaluation of the application of rare-earth elements to paleoceanography. Palaeogeogr. Palaeoclimatol. Palaeoecol. 1997, 132, 309–323. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mills, R.A.; Wells, D.M.; Roberts, S. Genesis of ferromanganese crusts from the TAG hydrothermal field. Chem. Geol. 2001, 176, 283–293. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Murphy, E.; McMurtry, G.M.; Kim, K.H.; De Carlo, E.H. Geochemistry and geochronology of a hydrothermal ferromanganese deposit from the North Fiji Basin. Mar. Geol. 1991, 98, 297–312. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Surya Prakash, L.; Ray, D.; Paropkari, A.L.; Mudholkar, A.V.; Satyanarayanan, M.; Sreenivas, B.; Chandrasekharam, D.; Kota, D.; Kamesh Raju, K.A.; Kaisary, S.; et al. Distribution of REEs and yttrium among major geochemical phases of marine Fe–Mn-oxides: Comparative study between hydrogenous and hydrothermal deposits. Chem. Geol. 2012, 312–313, 127–137. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Beukes, N.J.; Swindell, E.P.W.; Wabo, H. Manganese deposits of Africa. Episodes 2016, 39, 285–317. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Viehmann, S.; Bau, M.; Smith, A.J.B.; Beukes, N.J.; Dantas, E.L.; Bühn, B. The reliability of ~2.9 Ga old Witwatersrand banded iron formations (South Africa) as archives for Mesoarchean seawater: Evidence from REE and Nd isotope systematics. J. Afr. Earth Sci. 2015, 111, 322–334. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Palmer, M.R.; Edmond, J.M. The strontium isotope budget of the modern ocean. Earth Planet. Sci. Lett. 1989, 92, 11–26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Taylor, A.S.; Lasaga, A.C. The role of basalt weathering in the Sr isotope budget of the oceans. Chem. Geol. 1999, 161, 199–214. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Elderfield, H. Strontium isotope stratigraphy. Palaeogeogr. Palaeoclimatol. Palaeoecol. 1986, 57, 71–90. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pearce, C.R.; Parkinson, I.J.; Gaillardet, J.; Charlier, B.L.A.; Mokadem, F.; Burton, K.W. Reassessing the stable (d88/86Sr) and radiogenic(87Sr/86Sr) strontium isotopic composition of marine inputs. Geochim. Cosmochim. Acta 2015, 157, 125–146. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brand, U.; Logan, A.; Hiller, N.; Richardson, J. Geochemistry of modern brachiopods: Applications and implications for oceanography and paleoceanography. Chem. Geol. 2003, 198, 305–334. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kani, T.; Fukui, M.; Isozaki, Y.; Nohda, S. The Paleozoic minimum of 87Sr/86Sr ratio in the Capitanian (Permian) mid-oceanic carbonates: A critical turning point in the Late Paleozoic. J. Asian Earth Sci. 2008, 32, 22–33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kani, T.; Hisanabe, C.; Isozaki, Y. The Capitanian (Permian) minimum of 87Sr/86Sr ratio in the midPanthalassan paleo-atoll carbonates and its demise by deglatiation and continental doming. Gondwana Res. 2013, 24, 212–221. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Korte, C.; Jasper, T.; Kozur, H.W.; Veizer, J. 87Sr/86Sr record of Permian seawater. Palaeogeogr. Palaeoclimatol. Palaeoecol. 2006, 240, 89–107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bau, M.; Dulski, P. Comparative study of yttrium and rare-earth element behaviours in fluorine-rich hydrothermal fluids. Contrib. Miner. Petrol. 1995, 119, 213–223. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Klein, C.; Beukes, N.J. Geochemistry and sedimentology of a facies transition from limestone to iron-formation deposition in the early Proterozoic Transvaal Supergroup, South Africa. Econ. Geol. 1989, 84, 1733–1774. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Goldstein, S.L.; Hemming, S.R. Long-lived isotopic tracers in oceanography, paleoceanography, and ice-sheet dynamics. In Treatise on Geochemistry; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2003; pp. 453–489. [Google Scholar]
- Frank, M. Radiogenic isotopes: Tracers of past ocean circulation and erosional input. Rev. Geophys. 2002, 40, 1. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Piepgras, D.J.; Wasserburg, G.J. Neodymium isotopic variations in seawater. Earth Planet. Sci. Lett. 1980, 50, 128–138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- German, C.R.; Von Damm, K.L. Hydrothermal processes. In Treatise on Geochemistry; Turekian, K.K., Holland, H.D., Eds.; Elsevier: Oxford, UK, 2014; Volume 8, pp. 191–233. [Google Scholar]
- Halliday, A.N.; Davidson, J.P.; Holden, P.; Owen, R.M.; Olivarez, A.M. Metalliferous sediments and the scavenging residence time of Nd near hydrothermal vents. Geophys. Res. Lett. 1992, 19, 761–764. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Jeandel, C. Concentration and isotopic composition of Nd in the South Atlantic Ocean. Earth Planet. Sci. Lett. 1993, 117, 581–591. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tachikawa, K.; Jeandel, C.; Roy-Barman, M. A new approach to the Nd residence time in the ocean: The role of atmospheric inputs. Earth Planet. Sci. Lett. 1999, 170, 433–446. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Keto, L.S.; Jacobsen, S.B. Nd isotopic variations of Phanerozoic paleoceans. Earth Planet. Sci. Lett. 1988, 90, 395–410. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ali, J.R.; Fitton, J.G.; Herzberg, C. Emeishan large igneous province (SW China)and the mantle-plume up-doming hypothesis. J. Geol. Soc. 2010, 167, 953–959. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]







Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Yan, H.; Pi, D.; Xu, L.; Sun, K. The Perturbation of the Guadalupian Marine Environment Triggered by Early-Stage Eruption of the Emeishan Large Igneous Province: Rare Earth Element and Sr-Nd Isotope Evidence from Zunyi Manganese Deposit, South China. Minerals 2023, 13, 965. https://doi.org/10.3390/min13070965
Yan H, Pi D, Xu L, Sun K. The Perturbation of the Guadalupian Marine Environment Triggered by Early-Stage Eruption of the Emeishan Large Igneous Province: Rare Earth Element and Sr-Nd Isotope Evidence from Zunyi Manganese Deposit, South China. Minerals. 2023; 13(7):965. https://doi.org/10.3390/min13070965
Chicago/Turabian StyleYan, Hao, Daohui Pi, Lingang Xu, and Kai Sun. 2023. "The Perturbation of the Guadalupian Marine Environment Triggered by Early-Stage Eruption of the Emeishan Large Igneous Province: Rare Earth Element and Sr-Nd Isotope Evidence from Zunyi Manganese Deposit, South China" Minerals 13, no. 7: 965. https://doi.org/10.3390/min13070965
APA StyleYan, H., Pi, D., Xu, L., & Sun, K. (2023). The Perturbation of the Guadalupian Marine Environment Triggered by Early-Stage Eruption of the Emeishan Large Igneous Province: Rare Earth Element and Sr-Nd Isotope Evidence from Zunyi Manganese Deposit, South China. Minerals, 13(7), 965. https://doi.org/10.3390/min13070965






