Abstract
Iron is one of the most stubborn impurities in quartz minerals, and the iron content partly determines the various applications of quartz. Iron can exist in quartz in the forms of iron minerals, fluid inclusions, and lattice impurities. The removal of iron and the consequent purification of quartz minerals are the key processes to obtaining high-quality quartz. Iron removal methods including conventional pre-treatment, magnetic separation, acid leaching, microbiological, roasting, and flotation, as well as combined iron removal methods in quartz ore, are herein summarized. The separation mechanism of quartz and iron impurities and the latest research progress were explained and summarized, and the development prospects of quartz purification in the future were proposed based on the current progress and limitations of quartz iron removal.
1. Introduction
Quartz is one of the most widely distributed minerals in the Earth’s crust and is widely distributed in the surface environment. Quartz is widely used due to its stable physical and chemical properties. High-purity quartz, given its excellent optical properties, extremely low impurity content, excellent thermal stability, and corrosion resistance, is the material foundation of strategic new silicon-based industries and is the basic raw material for high-tech industries such as the photovoltaic industry, semiconductor, optical communication, aerospace, etc. [1]. High-purity quartz is a highly sought-after mineral resource.
High-purity quartz is often purified from minerals with high SiO2 content. Quartz is widely distributed in nature, but unprocessed natural quartz does not easily meet the quality requirements of high-purity quartz, which is actually a quartz sand product with a high purity of SiO2 obtained through a relatively complex purification process using raw quartz ore [2]. Due to the scarcity of high-quality resources and expensive processing costs, it is particularly important to develop feasible and economical processing technology. Deep purification of quartz ore is the best way to obtain high-purity quartz products. However, there are certain impurities in most quartz mines, which seriously restrict the quality of high-purity quartz [3]. The total amount of impure elements is often used as a standard to determine the quality of high-purity quartz. High purity characteristics are only evident when the total impurity content in the quartz is less than 50 ppmw (parts per million weight) [4]. Currently, the internationally recognized standard for high-purity quartz is based on IoTA-CG from Unimin Corporation (now Sibico) in the United States, with twelve element impurities (Al, K, Na, Li, Ca, Mg, Fe, Mn, Cu, Cr, Ni, B) containing less than 20 ppm. High-tech products with alkali metals (K, Na, Li) must have less than 1 ppm.
In quartz lattice formed under different geological contexts, the types and contents of trace elements are very different. This diversity of trace elements can play a key role in indicating diagenesis. Due to metallogenic factors and other reasons, quartz ore is mainly composed of SiO2 and a small amount of aluminum, iron, magnesium, calcium, sodium, and potassium. The impure minerals containing aluminum in quartz ore are mainly clay minerals, such as feldspar, mica, kaolin, etc., while the impure minerals containing iron are mainly hematite and goethite [5]. A large number of impurities appear in the following ways: (1) loosely related minerals not chemically bound with silica; (2) fragments that bind to the silica surface through chemical and physical interactions; (3) those enveloped by silica particles or surrounded by silica aggregates that combine with each other; and (4) those acting as substitute atoms and interstitial ions within the silica lattice. The occurrence states and forms of various elements are summarized below in Table 1.

Table 1.
The occurrence states and existence forms of quartz impurity elements [4,6].
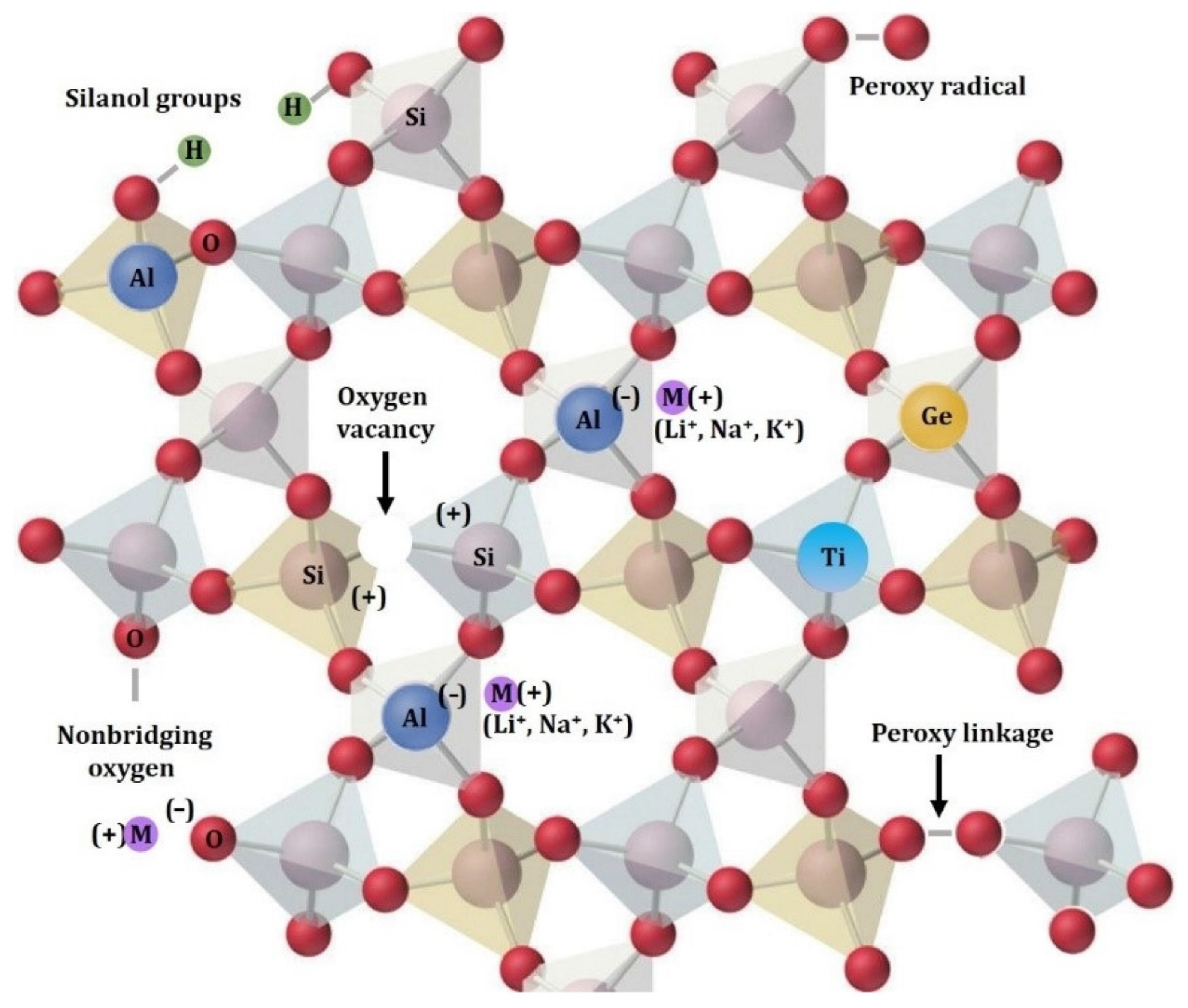
Impurity elements in quartz can exist in the form of minerals, fluid inclusions, lattice impurities, etc. Quartz belongs to the triclinic system, in which silicon atoms are tetracoordinated and the structural unit is a [SiO4] tetrahedron. Each [SiO4] tetrahedron is shared with the adjacent four [SiO4] tetrahedrons through its oxygen atoms at its four corner tips, thereby connecting them into an infinitely expanding frame-like structure in three-dimensional space. Because quartz crystal is a tetrahedral structure comprising extremely strong Si-O bonds, only a small amount of trace element impurities can enter the crystal structure of quartz through isomorphism. Al3+, Ga3+, Fe3+, Ge4+, Ti4+, and P5+ have been detected as substitutes [7], and various ions replace Si4+ in the three-dimensional lattice of SiO2. When nonequivalence class isomorphism occurs, it is usually accompanied by Li+, K+, Na+, or H+ ions, which help maintain the electrical neutrality of the SiO2 lattice. Additionally, oxygen vacancies and silicon vacancies may occur. More frequent O-vacancy is caused when one O atom is removed from the lattice, leaving a direct link between two Si atoms. The oxygen tetrahedra change into a planar arrangement of three oxygen ions as a result of losing an electron, creating the so-called E’ center. The Si-vacancy is less common because the Si ion is not replaced easily due to the small ion radius and high valence of Si4+. The crystal structure and common defects of quartz are depicted in Figure 1.

Figure 1.
The crystal structure and common defects of quartz [8].
The abovementioned reports detail the following: oxygen vacancy, silanol groups (possible substitution of Si4+ by four H+), non-bridging oxygen, peroxy linkage, and radicals, simple substitutions with Ti4+ and Ge4+, and Al3+ substitutions with interstitial cations (Li+, Na+, K+) [8,9,10,11]. It should be noted that some trace impure elements of quartz can form different types of color centers after irradiation, resulting in different colors [12]. For example, amethyst exists because its quartz lattice contains Fe [13]. Mineral luminescence is dependent on point defects, both inherent (lattice defects) and extrinsic (trace elements). The former is related to structural flaws in quartz such as Si- and O-vacancies that exist in every genuine crystal. Of the various impurities in high-purity quartz, iron is one of the most stubborn impurities in quartz sand, and iron oxide content is the main factor determining the application of quartz in different fields. Iron oxide causes the greatest damage to color and performance. Quartz used for semiconductors requires higher iron purity of <1.0 ppmw, and the high iron content in raw materials can damage the efficiency of solar silicon processing, the transmission of optical fibers, and the transparency of glass, and cause discoloration of ceramic products and reduce the melting point of refractory materials.
Iron-bearing impurity minerals in quartz minerals include goethite, hematite, limonite, ilmenite, magnetic pyrite, tourmaline, hornblende, biotite, etc. Iron impurities often occur in fine-grained states in clay or kaolinized feldspar: iron oxide film adheres to the surface of quartz and iron minerals or iron-containing minerals inherent within quartz particles in a diffuse state and exist in quartz as a solid solution. In addition, both Fe2+ and Fe3+ can replace Si in the quartz lattice in isomorphism, so Fe can widely distribute in quartz lattice [14]. High-purity quartz has extremely strict requirements for iron content, generally <10 ppmw. Iron removal is an essential process for processing high-grade quartz products, and various methods and processes have been devised for removing iron from quartz ore. The common methods are listed in Table 2. There exist strategies suitable for treating iron impurities in different occurrence states. Only by selecting appropriate treatment methods and processes based on the form of iron impurities in raw quartz minerals can good impurity removal results be accomplished.

Table 2.
Methods for removing iron from quartz.
2. Methods for Removing Iron Impurities from Quartz
2.1. Conventional Preprocessing Methods
Physical and chemical methods are employed to treat iron impurities in quartz. Most physical methods are pre-treatment-based, aimed to remove some iron impurities relatively easily, including the exposed iron film on the particle surface and impurity mineral phases, in preparation for further purification. Chemical methods such as acid leaching and complexation can further remove iron impurities that are difficult to eliminate. Physical and chemical methods play different roles in the impurity removal process of quartz minerals, so a combined physicochemical method will have a better likelihood of removing iron impurities.
Physical impurity removal methods include the scrubbing method, magnetic separation method, gravity separation method, etc. The commonly used methods for pre-beneficiation operations include crushing, grinding, grading, optical sorting, scrubbing, and acid washing. The crushing and grinding process requires crushing the material to the required particle size range, selectively releasing impurities and inclusions in quartz as much as possible, and minimizing quartz pollution caused by friction between the grinding medium and quartz during the crushing and grinding process. When using ceramic or alumina media for ball milling and stone milling, the amount of debris generated in the grinding medium is smaller than that of iron media, but the generated pollutants are more difficult to remove than iron pollutants. Optoelectronic color selection can be used to separate colored quartz. The different color changes in quartz often indicate a large number of certain impure elements. Due to the difficulty in removing impurities in quartz crystals, separating these particles through photoelectric color selection can improve the quality of high-purity quartz products. Optical sorting can also separate some colored impurity minerals such as rutile, biotite, etc. Presently, the particle size selection of quartz is limited to the 5–30 mm range. If fine-grained quartz can be sorted, it will be an economical and efficient new sorting technology.
Scrubbing is a mineral processing method that removes impurities attached to the mineral surface through mechanical force and the grinding force between mineral particles. Attrition scrubbing has been used as a physical decontamination treatment in many fields of mineral purification, especially in the removal of clay impurities from target mineral surfaces. It can crush mineral aggregates that have not yet formed into monomers and achieve further purification through grading operations. At present, the main methods are rod friction washing, mechanical scrubbing, and ultrasonic scrubbing. Quartz scrubbing removes the iron oxide film on the quartz particles’ surface and the iron-containing minerals attached to the quartz particles through the collision and friction between the equipment and mineral particles, as well as between mineral particles. The structural configuration of the scrubbing machine, the strength, scrubbing time, the concentration of slurry, and the added chemical medium all have some influence on the scrubbing effect. The slurry concentration can affect the dispersion and friction between particles, and it is necessary to determine the optimized final slurry concentration while only changing the slurry concentration. The added agent affects the scrubbing effect by changing the hydrophilicity of the particle surface and the repulsion between particles.
Scrubbing can cheaply remove these impurities and avoid affecting subsequent purification processes. During scrubbing, some diluted acids or alkalis, dispersants, and surfactants can be added to further promote the separation of pollutants from the quartz surface. When scrubbing, the slurry concentration is generally 50%. Coarse minerals should use a smaller slurry concentration, while fine-grained minerals should use a larger slurry concentration. Niu et al. [15] used rod grinding to treat particle size +30 μm quartz sand raw ore; good results were achieved, and the iron impurity percentage of impurities removed reached more than 47%. Niu and Ni [16] used an efficient and powerful scrubbing method that aimed to increase the electrical repulsion between impure minerals and quartz. The content of iron oxide in the product decreased from 0.25% in the raw ore to below 0.1%, and the content of silicon dioxide was also over 99%, achieving good washing and purification effects. Based on mechanical cleaning, Zhang et al. [17] used ultrasound to enhance the cleaning effect. After cleaning, the Fe2O3 content in quartz decreased from 0.3 wt% to 0.1 wt%, proving that ultrasound can significantly improve the cleaning effect. Li et al. [18] implemented HCl with a mass fraction concentration of 10% to conduct a two-stage scrubbing–two-stage washing operation for quartz sand after magnetic separation to further remove soluble iron impurities and clean the quartz surface. During scrubbing, the liquid–solid ratio was 1:1, the scrubbing stirring speed was 1600 r/min, each scrubbing time was 20 min, and the ultrapure water was used for scrubbing. After scrubbing, the SiO2 content in quartz sand was 98.728%, and the Fe2O3 content dropped to 698 ppmw, with 47.60% being removed. Wang [19] investigated a mixed sample of a certain powdered quartz. Under the conditions of a slurry concentration of 75%, a scrubbing machine speed of 1500 r/min, sodium hydroxide of 0.1%, sodium hexametaphosphate of 0.5%, and a scrubbing time of 15 min after adding reagent, it was found that the content of iron oxide decreased from 0.37% to 0.09%, with good impurity removal being reported [16].
The gravity separation method utilizes the density difference between iron impurities and quartz minerals to remove iron-containing heavy minerals and secondary iron impurities mixed in the crushing and grinding process. Gravitation separation includes desliming and hydraulic classification, and the commonly used gravitation separation equipment includes spiral concentrators, chutes, and shaking tables [2], among which the shaking table has a better sorting effect. Studies have shown that the grade of SiO2 decreases as the particle size becomes finer, while the grade of iron is the opposite. Consequently, sieving classification can achieve the function of desliming to reduce iron-containing impurities. Various types of hydrocyclones are widely used for classification treatment, and good results are achieved.
2.2. Magnetic Separation Method
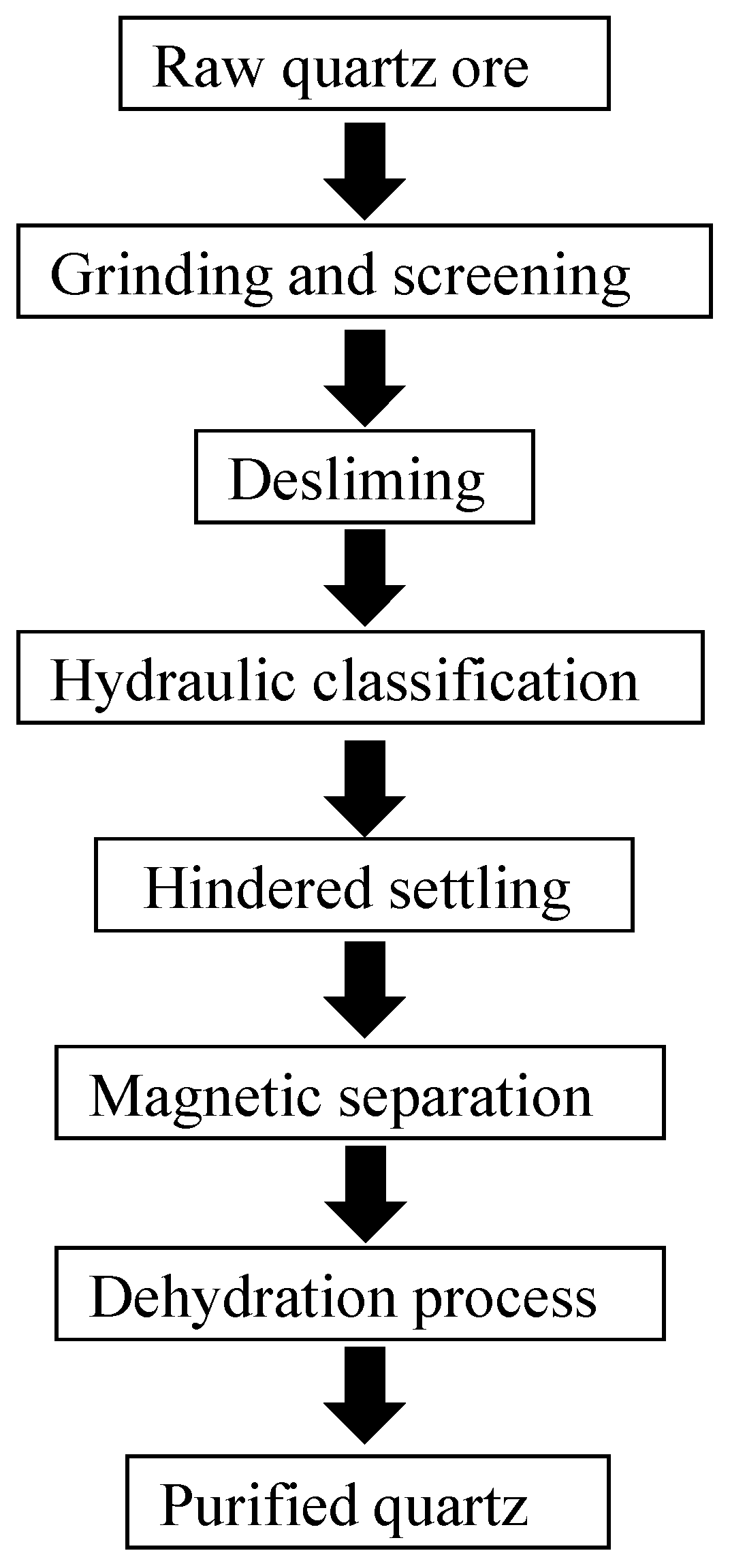
Magnetic separation impurity removal uses the magnetizable characteristics of impure iron minerals in quartz to separate such impurities in the quartz sand from the quartz minerals. This is achieved through a strong external magnetic field. A common magnetic separation process for purifying quartz is shown in Figure 2, where crushing and screening achieve ore crushing and preliminary screening, desliming treatment removes primary and secondary mud, hydraulic classification separates fine-grained quartz sand with particle sizes not meeting the standard, and hindered sedimentation is used to separate coarse-grained quartz sand with particle sizes not meeting the standard. Magnetic separation treatment mainly uses weak magnetic separation equipment to separate strong magnetic impurities. Subsequently, strong magnetic separation equipment is used to remove weak magnetic impurities from the minerals. Finally, after dehydration treatment, a purified quartz product is obtained.

Figure 2.
Schematic diagram of magnetic separation and purification process for quartz ore.
The magnetic susceptibility of iron-bearing quartz minerals increases when the iron content increases and the magnetic force acting on the sand particles rises with elevated magnetic susceptibility. When the magnetic force is greater than the combined force of all mechanical forces acting on the magnetic particles, the separation effect can be achieved. The number of operations and intensity of magnetic separation have a significant impact on the removal of iron impurities. The commonly used magnetic separation equipment includes wet high-gradient magnetic separators and dry high-gradient magnetic separators [20]. Ran and Zhang [21] utilized a two-stage dry high-intensity magnetic separation operation to reduce the Fe2O3 content of the product from 20 ppmw to 2 ppmw. Meanwhile, Liu et al. [22] used a two-stage wet high-gradient strong magnetic separation operation of 1.0 T and 1.2 T, and the purity of SiO2 in the obtained quartz ore increased from 99.05% to 99.82%, while the Fe2O3 content dropped from 530 ppmw to 150 ppmw. At present, wet high-strength magnetic separators serve to maximize the removal of magnetic impurities and minerals. The magnetic separation method cannot easily remove iron impurities with small particle sizes, low content, and weak magnetism [23].
The magnetic separation process can remove weakly magnetic impurities such as hematite and limonite, including intergrowth particles, to the maximum extent [24]. Cui et al. [25] conducted a magnetic separation purification experiment on a quartz sand ore sample. The crushed quartzite block ore was preconcentrated with a color separator, and some tailings were discarded. The obtained block concentrate was ground and graded, and then secondary purification was executed with a high-gradient strong magnetic separator. High-gradient high-intensity magnetic separation treatment helped to finally obtain super standard quartz sand concentrate with a yield of 67.00%, an iron content of 0.005%, and a silicon dioxide content of 99.90%. Miao et al. [26] selected a magnetic field intensity of 1.2 T for strong magnetic separation, and the results showed that the amount of iron oxide declined from 5.24% to 1.75%, while the content of silicon dioxide increased from 73.38% to 79.55%.
Under a 1.75 T field strength, Bao [27] achieved a removal efficiency of 72.46% for iron and 36.58% for aluminum. After the magnetic separation of quartz sand, most magnetic minerals with stronger magnetism and coarser particle size are separated, resulting in stronger magnetic separation particles, coarser magnetic particles, and higher iron content, while quartz sand has weaker magnetism and less iron. To further reduce the iron impurity content in quartz sand and improve its grade, it is necessary to remove all iron impurities adsorbed on the quartz sand surface and the iron impurities existing in quartz sand. This is difficult to achieve with only the magnetic separation process [28]. Studies have shown that high-intensity magnetic separation and scrubbing operations can improve the purity and whiteness of quartz. Zhang [29] conducted magnetic separation and scrubbing purification experiments on quartz using magnetic separators and scrubbing machines, showing that when the magnetic field intensity was 0.8 T, the iron removal efficiency in quartz could reach 70%, and when the magnetic field intensity increased to 2 T, the iron removal efficiency did not increase significantly. Scrubbing operations can effectively increase the whiteness of quartz. The combination of strong magnetic separation and scrubbing operations can improve quartz product quality.
2.3. Acid Leaching
Acid leaching is a strategy for removing iron impurities by understanding that quartz is not very soluble in acid (except hydrofluoric acid) and iron impurity minerals are soluble in acid, which is commonly used to remove iron thin films on the quartz surface and iron impurities inside quartz particles. Commonly used leaching reagents are sulfuric acid, hydrochloric acid, nitric acid, hydrofluoric acid, and oxalic acid. Usually, the addition of reducing agents such as alum (KAl(SO4)2·12H2O) and sulfite to the acid leaching process will greatly benefit the leaching of impure iron minerals [3]. Mixed acids are more effective at removing iron impurities, and the acid type and concentration, the time and temperature of leaching, the degree of slurry agitation, and the quartz particle size all influence the acid washing. Iron from discarded silica powder is removed by acid leaching using a reaction temperature of 60 °C, an acid concentration of 12%, a stirring speed of 200 rpm, and a liquid-to-solid ratio of 10 mL/g. The ideal leaching conditions resulted in 94.34% of the Fe being removed.
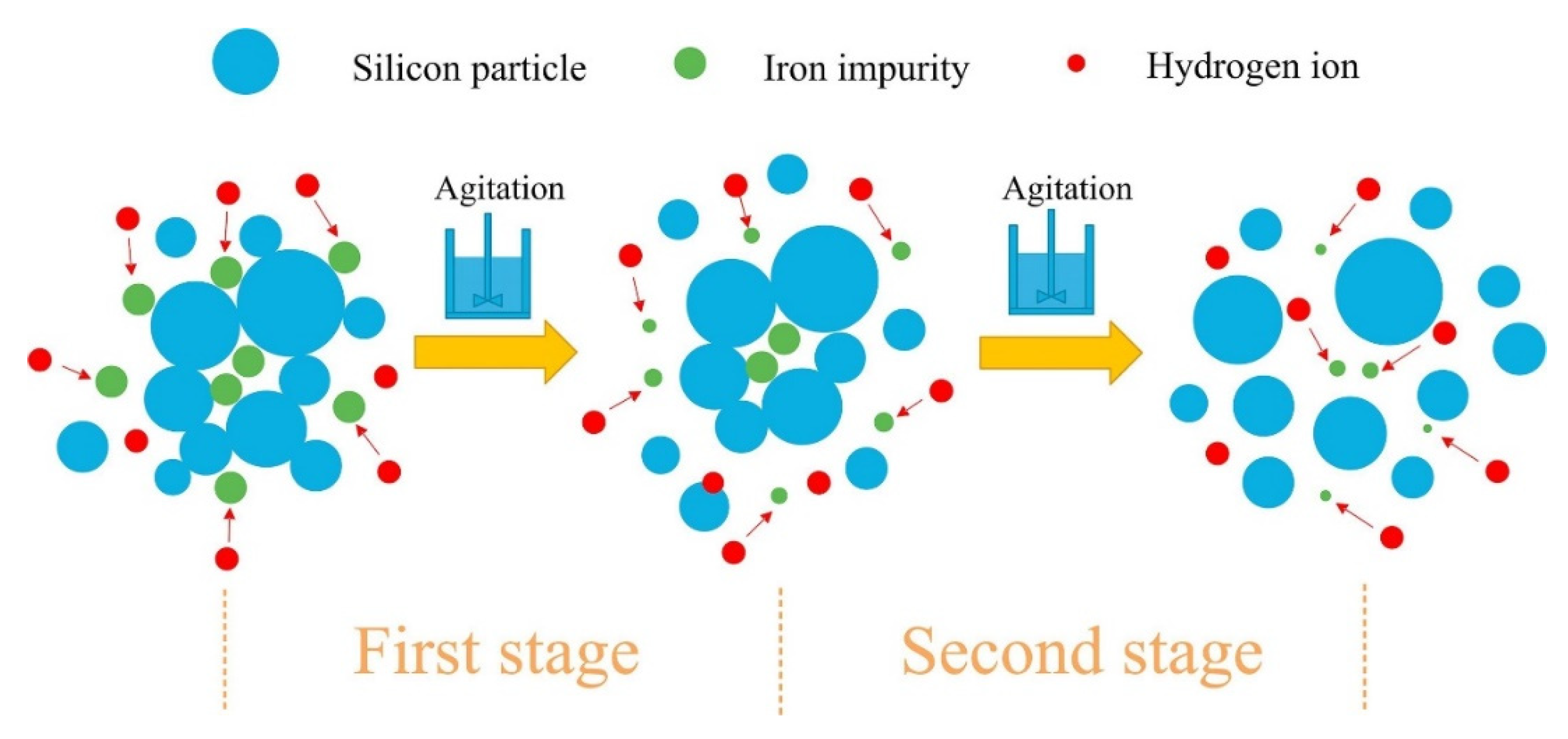
Kong J et al. [30] used the heterogeneous phase reaction method to study the kinetics of iron removal. The outcomes demonstrated that the iron removal process can be split into two phases (shown in Figure 3). The surface adhesive iron impurities on the silicon particles are dissolved in the first stage. The iron encapsulated in the aggregates is exposed to the acid solution and dissolved in the second stage, which involves the mechanical decomposition of the aggregates and subjection to mechanical stirring. According to the homogeneous phase reaction model, the activation energies for the second-order rate-controlled removal process were 10.78 kJ/mol and 35.97 kJ/mol, respectively.

Figure 3.
The leaching process of iron [30].
Mineral particle coarseness, acid selection, leaching temperature, and acid concentration all influence leaching and subsequent removal and purification. After studying different leaching combinations, Liu et al. discovered that mixed acid (nitric acid + hydrochloric acid + hydrofluoric acid) had the best effect on iron removal, as nitric acid oxidizes metal elements to produce soluble salts. Hydrochloric acid has good metal solubility and complexes iron ions while hydrofluoric acid has a solubilizing effect on quartz. Using mixed acid (Vacid:Vwater = 1:1) and a water bath reaction at 90 °C for 360 min, the removal of iron from quartz sand could reach 88.3%, which met the purity requirements of refined quartz sand [31]. Research has shown that iron oxide can be dissolved by oxalic acid and exists in the form of Fe(C2O4)33− and Fe(C2O4)22− in solution [32,33]. The chemical reactions can be summarized as follows:
Fe2O3 + 6H2C2O4 = 2Fe(C2O4)33− +6H+ + 3H2O;
2Fe(C2O4)33− + 6H+ + 4H2O = 2FeC2O4·2H2O + 3H2C2O4 + 2CO2;
Fe2O3 + 3H2C2O4 + 3H2O = 2FeC2O4·2H2O + 2CO2.
Optimizing process parameters and reaching a high degree of iron removal at minimum operating cost are important research goals. For example, the percentage of iron impurities leached from quartz sand by oxalic acid increases with rising leaching temperature, smaller particle size, and higher acid concentration [34,35,36,37] temperatures between 90 and 100 °C, and the maximum iron extraction that can be achieved is approximately 40%. Some other studies on acid leaching for iron removal are shown in Table 3.
However, some studies still reached inconsistent conclusions due to differences in systems, particle sizes, leaching temperatures, and oxalic acid concentrations. Taxiarchou et al. [38] concluded that oxalic acid concentration has almost no “effect” on the leaching efficiency of iron removal impurities. Similarly, Du et al. [39] revealed that the leaching percentage increased with increasing stirring speed and ultrasonic power, but it was also noted that the particle size of similar hard materials was independent of the input ultrasonic power, which was independent [40]. Veglio et al. [41] studied the oxalic acid–sulfuric acid Fe removal process under heated conditions. The sulfuric acid leaching of quartz sand for Fe removal produced a low removal efficiency, high acid consumption, and slow reaction rate. The iron removal effect improved, and the sulfuric acid dosage was reduced with the mixed addition of oxalic acid, when the addition of 3 kg/t oxalic acid, reacted at 90 °C for 4–5 h, the Fe removal efficiency increased significantly from 3%–9% to 35%–45%. Additionally, mineralogical studies of quartz ore showed that 52% of Fe was present in mica, which was the reason for limiting the Fe removal efficiency and this explains the further improvement.
Santos et al. [42] subjected a quartz concentrate after washing, grinding, and magnetic separation to acid washing with warm hydrochloric acid, and compared the metal content of the main impurities in the quartz after leaching with and without HF. It emerged that the combination of HCI and HF could convincingly remove feldspar, mica, and clay minerals from the quartz and further improve the quartz purity. Yan et al. [43] reduced the Fe concentration from 66.4 ppm to 0.8 ppm by mixing quartz feedstock with 2 wt% NaCl, calcining it at 820 °C for 2 h, and leaching it with 18% HCl and 2% HF at 50 °C for a period of time.

Table 3.
Iron removal from quartz using acid leaching method.
Table 3.
Iron removal from quartz using acid leaching method.
| Leaching Reagent | Fe2O3 Contents before Leaching (ppm) | Fe2O3 Contents after Leaching (ppm) | Fe2O3 Removal Yield (%) | References |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Oxalic acid | 290 | 174 | 40 | [38] |
| Oxalic acid | 600 | 147.6 | 75.4 | [39] |
| H2SO4, oxalic acid | 300 | 180 | 35–45 | [41] |
| Oxalic acid | 302 | 163 | 46.1 | [44] |
| Oxalic acid | 77 | <10 | 98–100 | [45] |
| H2SO4 | 420 | 84 | 80 | [46] |
| Oxalic acid | 3150 | 94 | 97.02 | [47] |
| Phosphoric acid | 481 | 110 | 77.1 | [48] |
It was verified by experiments that acid leaching alone cannot efficiently remove iron impurities’ internal occurrence of quartz particles. Various auxiliary means of acid leaching process were introduced into the quartz impurity removal process. For example, an ultrasonic cavitation effect occurred in the liquid, released a substantial amount of energy, and produced a local high temperature and powerful micro jet impact on quartz sand. With different ultrasonic input powers, the iron removal efficiency increased with an increase in ultrasonic input power. When the input power was 400 W, the Fe removal efficiency reached 51%. This is because the cavitation effect of ultrasonic waves occurs in the liquid, releasing a substantial amount of energy and producing a local high temperature and powerful micro jet impact on quartz sand. The “micro pit” produced by hydrochloric acid leaching of impurities on the quartz sand surface becomes larger and deeper under the strong effect of ultrasonic waves so that acid can penetrate the quartz sand and react with impurities.
Ultrasonic and acid repeated joint action will promote each other; quartz sand becomes more porous or even broken so the exposed internal iron impurities are dissolved by acid. Simultaneously, ultrasonic treatment can prevent the acid leaching of iron impurities attached to the quartz sand surface again, and this helps to improve the amount of iron that is removed [49]. Mixed acid leaching and external conditions in quartz impurity removal attempts are summarized in the following Table 4.

Table 4.
Removal efficiencies of different methods for various impurities.
2.4. Microbial Leaching Method
The microbial method utilizes microorganisms that adjust their own characteristics and mineral surface properties to function as mineral processing agents, which is more environmentally friendly. Thin film iron or disseminated iron on the quartz surface are often selected as research subjects. Zhao et al. [56] studied the leaching and purification experiments of Aspergillus niger on adaptation and showed that the iron impurity content dropped from 342.62 ppmw to 153.90 ppmw, with an iron removal efficiency of 55.08%. Aspergillus niger produces organic acids in suitable environments, which react with impurities in quartz to remove impurities. Mycobacterium phlei will produce extracellular polymers (EPS) and surfactants under specific conditions, which will lead to the flocculation of microorganisms or other solids and can be applied to the separation of hematite and quartz [7]. However, the iron removal efficiency of the microbial method is only related to the form of the iron elements present in quartz minerals, but not the amount of iron in the quartz minerals themselves. Only iron oxides or iron-containing minerals located on the quartz particle’s surface can be removed by this method [9]. The complexation law achieves the purification of quartz minerals by complexing various complexing solvents or other complexing reagents with impurities such as iron sulfate. Bahaj et al. [57] asserted that microbial metabolites can replace acidic leaching agents for purifying quartz. Organic acids produced by different bacteria and fungi can have a synergistic effect and be used to remove Fe impurities from quartz. Citric acid produced by Aspergillus niger metabolism has the most significant Fe removal outcome.
2.5. Flotation Removal of Iron
Flotation is mainly used for disseminated or lenticular iron in quartz particles, iron present in iron-containing minerals, and the removal of secondary iron impurities mixed in preparation processes such as crushing and grinding. The conventional flotation method involves using H2SO4 as a pH regulator and a mixed collection of anions and cations to remove iron, alternatively using HF as an activator and cationic amine collector in the hydrofluoric acid method, or an anionic collector to remove iron impurities under the action of an inhibitor [58]. Hong et al. [59] studied the reverse flotation effect of a dodecylamine kerosene-mixed collector on quartz in magnetite. Through single-factor test analysis, under certain conditions, the cumulative flotation recovery of quartz could reach 98.94%, and the separation effect of quartz and magnetite was good. In their experiment, Yin et al. [60] applied fine magnetite powder to the reverse flotation of hematite, and the selectivity of quartz separation by flotation was enhanced by the selective aggregation of magnetite and hematite through magnetic interaction. The method of neutral positive flotation functions suppressed iron-containing minerals with inhibitors, used collectors to float the decomposed quartz, and further reduced the amount of Fe2O3 in the quartz fine sand through rough selection and selection. The combined action of starch-based inhibitor CTSS, an amphoteric collector, and the foaming agent ZD-3 can reduce the disseminated iron oxide from 130–150 ppmw to 60–100 ppmw, among which the preferential adsorption of inhibitor CTSS with iron-containing minerals is one of the key factors for achieving neutral positive flotation purification of quartz [61].
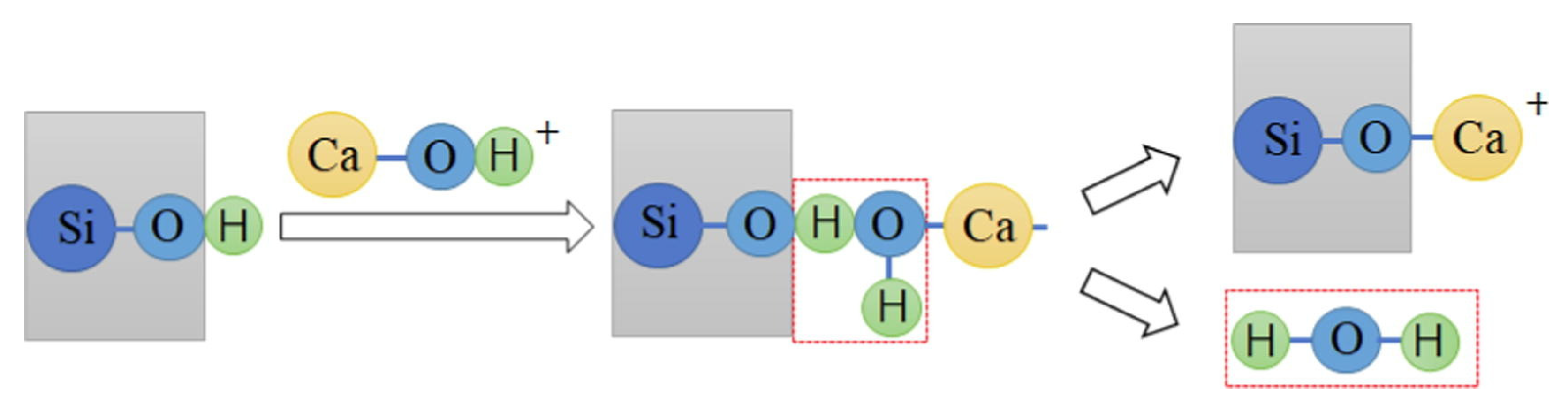
Ca2+ is widely used as an activator in quartz anionic flotation. It serves as a bridge for sodium oleate adsorption on the quartz surface, where Ca2+ first adsorbs onto the quartz surface and then chemically adsorbs with sodium oleate and Ca2+ on the quartz surface. Ca2+ undergoes hydration in alkaline environments and exists in the form of CaOH+. CaOH+ dehydrates with unsaturated O atoms on the quartz surface and forms a strong chemisorption. Subsequently, the unsaturated O on the quartz surface is the active site for Ca2+ adsorption. The adsorption mechanism of Ca2+ on the quartz surface is shown in Figure 4 [62].

Figure 4.
The mechanism of Ca2+ activation on the quartz surface [62].
Effects of α-Bromolauric acid (α-BLA) on the flotation behavior of iron minerals and quartz iron separation were investigated. The collector α-BLA was synthesized in the laboratory. The flotation behavior of quartz, hematite, and magnetite under the α-BLA reverse flotation system was investigated and the quartz–iron separation mechanism was assessed by contact angle, zeta-potential, and infrared spectroscopy analyses. The results showed that the optimum flotation pH was 11.5 for quartz, 6.45 for hematite, and 6.97 for magnetite. The optimum α-BLA concentrations were 75 mg/dm3 for quartz flotation and 125 mg/dm3 for hematite and magnetite flotation. The activator CaCl2 had little effect on the flotation of hematite and magnetite, but the minimum dosage of 50 mg/dm3 of activator CaCl2 was necessary for quartz flotation. Conversely, starch had no effect on the flotation of quartz, while the recoveries of magnetite and hematite tended to be 0% as starch concentration was more than 80 mg/dm3. The mechanism for separating quartz from iron minerals under the α-BLA reverse flotation system was that the starch could be selectively adsorbed on the surface of hematite and magnetite through the strong hydrogen bond adsorption. However, the same adsorption of starch did not occur on the quartz surface, so the α-BLA can be successfully adsorbed on the activated quartz surface, making the quartz strongly hydrophobic and then floating out [63].
Reverse froth flotation is used to separate quartz and iron ore. With sodium oleate as the collector and Ca2+ as the activator in an alkaline medium, the flotation effect of quartz is better, and starch can inhibit hematite [64]. Sodium oleate adsorbs on the mineral surface to form multiple layers of surfactants due to the lateral interaction between hydrocarbon chains. Quartz is attributed to the hydroxylation of the quartz surface at different pH values and collector concentrations, resulting in the quartz surface changes in zeta potential. Coated starch can transform the ζ potential of hematite particles transferred to a small positive value, and its potential difference with quartz is increased, thus supporting the separation of quartz hematite in the flotation process. Polyaspartic acid (PASP) proved to be an efficient and selective hematite depressant under alkaline conditions. PASP is selectively chemisorbed on the hematite surface mainly through the complex reaction between the -NH- and -COO- polar groups in its molecules and the types of iron ions on the hematite surface [65].
The effect of starch molecular structure on the inhibition of hematite is attributed to the difference in molecular reactivity and the number of adsorption sites exposed to the mineral surface. Under alkaline conditions, the chemical adsorption strength of starch and hematite is in the order of Waxy Starch > Normal Starch > Gelose 50, which is closely related to the proportion of amylose/amylopectin on the starch molecule. Stronger chemisorption occurs between high amylopectin and the hematite surface. However, no matter what the molecular structure of starch is, starch has virtually no inhibitory effect on quartz because there is only a slight hydrogen bond between starch and quartz [66].
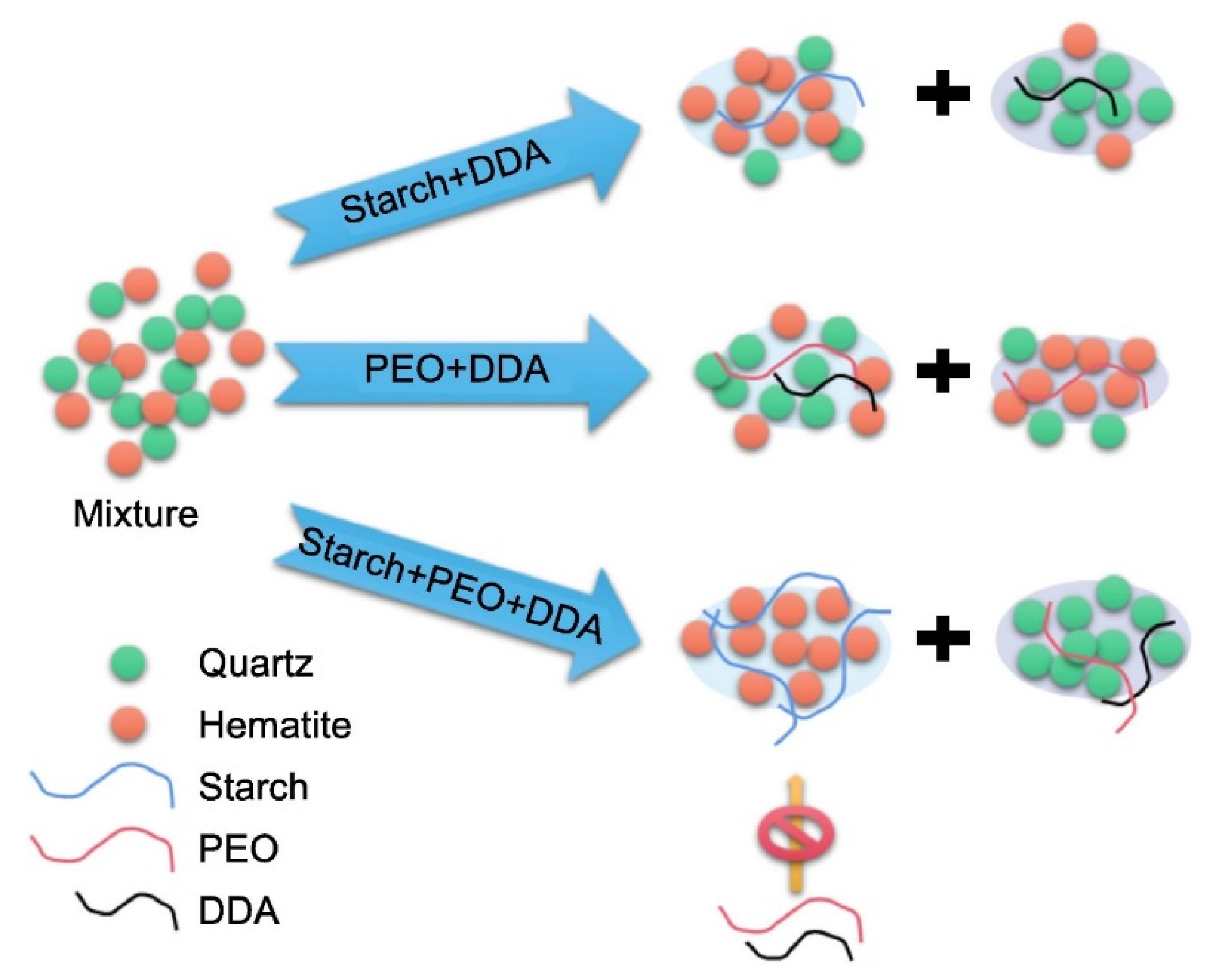
Asynchronous flocculation is introduced into the flotation separation of ultrafine hematite and quartz. For quartz gangue and hematite, respectively, starch and polyethylene oxide function as selective flocculants. The outcomes demonstrate that asynchronous flocculation flotation using dodecylamine (DDA) as the collector can enhance the separation of hematite from quartz. The entrainment of hematite concentrate (flotation tailings products) can be decreased by PEO through flocculating quartz and improving flotation recovery in foam products. The initial addition of starch preferentially flocculates ultra-fine hematite without impacting quartz with the addition of PEO, DDA, and starch. Hematite is unaffected by the subsequent addition of PEO because the starch on the flocculated hematite prevents PEO from adhering to it. The following addition of PEO causes the quartz to flocculate. Finally, the cationic collector DDA increases the hydrophobic flocculation of the hydrophobic PEO-coated quartz, making it hydrophobic and increasing the quartz flocculant’s size. The quartz flocculation of PEO significantly promotes the flotation of cation collectors [67]. The asynchronous flocculation flotation model of ultrafine quartz and hematite is shown in Figure 5.

Figure 5.
Schematic diagram of asynchronous flotation separation model of ultrafine quartz and ultrafine hematite [67].
Coarse particle flotation has the advantages of reducing grinding energy consumption, avoiding a series of problems during fine particle flotation, and facilitating the dehydration and comprehensive utilization of tailings. Zhao and Zhang [68] studied quartz, exploring the effects of variables such as reagent dosage, pulp concentration, impeller speed, inflation rate, particle size composition, etc., on the maximum floatable particle size. They found suitable conditions for coarse particle flotation, providing theoretical guidance for the coarse particle flotation process of quartz minerals.
2.6. Combined Treatment Method for Iron Removal
Iron impurities in quartz rocks have a complicated occurrence structure, making it challenging to remove them effectively using a single technique. As a result, operations to remove iron from quartz typically combine many processes. For example, magnetic separation leaching can effectively remove impurities in fused silica. The Fe impurity content is 797.98 ppmw in the SiO2 raw material. The screened raw materials with particle sizes in the 0.125 mm to 0.038 mm range were magnetically separated using the LGS-1500 high-gradient magnetic separator. When the magnetic induction intensity was 1.2 T and the slurry concentration was 15%, the Fe impurity content fell to 271.30 ppmw. Subsequently, after microbial leaching and magnetic separation with the Aspergillus niger culture solution, impurities were continually removed from the product.
When the slurry concentration was 5%, the leaching time lasted 12 h, the leaching temperature was 35 °C, and the pH of the Aspergillus niger culture solution amounted to 2.0. The Fe impurity content in quartz further decreased to 128.21 ppmw, the Fe impurity removal efficiency was 83.93%, and the SiO2 content increased to 99.96%. Additionally, mixed acid leaching was used to continue impurity removal for the products after magnetic separation. When the mixed acid conditions were 6.0 mol/L hydrochloric acid + 0.060 mol/L oxalic acid + 0.03 mol/L citric acid, the liquid–solid ratio was 5:1, the acid leaching temperature was 100 °C, and the acid leaching time lasted 9 h, the Fe impurity content diminished to 78.44 ppmw. Meanwhile, the Fe impurity removal efficiency was 90.17% and the SiO2 content increased to 99.99%.
To sum up, the impurities in fused silica can be effectively removed by two purification processes: magnetic separation microbial leaching and magnetic separation mixed acid leaching, with the impurity removal efficiency up to 79.35% [69]. The iron impurities in quartz sand are removed by roasting combined with acid leaching. After roasting at 600 °C, 900 °C, and 1200 °C for 4 h, the crystal structure of quartz is transformed (the phase transition of quartz with temperature is shown in Figure S1), and the target crystal structure is solidified by quenching to form a structure conducive to the removal of iron by acid leaching. The effect of crystal structure transformation on iron impurity removal in quartz sand was studied. Research showed that the transformation of crystal structure can effectively improve the efficiency of removing iron impurities. After roasting at 900 °C for 4 h, it was found that β-quartz content was as high as 94.7%. The formation of β-quartz improves the removal efficiency of iron impurities. The iron impurity removal efficiency was 75.5% when unburned quartz sand was leached by acid leaching of unburned samples and samples exhibited different calcination temperatures. At 900 °C, the removal efficiency of iron impurities reached as much as 98.7% [70].
Li et al. [71] employed a combination of microwave heating and ultrasound-assisted acid leaching treatment to remove the iron from quartz, and the iron content was reduced from 285 ppmw to less than 0.167 ppmw. The maximum removal rate of Fe reached 99.94%. Wang et al. [72] implemented the permanent magnetic high-intensity magnetic separation acid leaching process to purify quartz sand, and the SiO2 purity was 99.99%, and Fe content was 0.0004%, reaching the grade of ultra-high-purity quartz sand. Zang et al. [73] used the hot press mixing acid leaching method to treat quartz veins, achieving purity of 99.994% and opening a new technological path for the efficient utilization of plentiful supplies of quartz veins. Tan et al. [74] adopted the process of “grinding, classification, scrubbing, desliming, magnetic separation and acid treatment” for 93% grade quartz sandstone, and the purity of SiO2 in the high-purity quartz sand rose to over 99.9%, thus increasing the use value of the mine. Qiu et al. [75], in their research on a quartzite mine, showed that the purity of SiO2 in the product obtained through magnetic separation, scrubbing, and flotation combined with leaching calcination was as high as 99.94%. The purity of the product increased to 99.97% after secondary “acid washing calcination” treatment. The quartz vein was treated by a combination of pre-treatment with calcined water quenching, conventional purification methods, and subsequent unconventional purification processes such as ultrasound and chlorination roasting for degassing. The number of impurities in the produced ultrapure product and IOTA standard quartz sand was almost the same (there was still a certain gap between the gas–liquid inclusion characterized by hydroxyl [−OH] removal) [76].
A new purification process of “gravity separation, flotation, acid leaching” was proposed to remove Fe and Ti impurities in quartz sand. Quartz sand was pre-selected for impurity removal by gravity concentration and flotation and then cleaned and purified by two-stage acid leaching. The spiral chute was used for gravity separation to remove part of heavy minerals containing Fe and Ti by a roughing and a cleaning process, and the flotation used roughing and scavenging to remove rutile, the main mineral containing Ti. The final quartz sand concentrate was obtained by leaching quartz sand after beneficiation at 70 °C with 3 mol/L hydrochloric acid + 1 mol/L acetic acid + 0.5 mol/L hydrofluoric acid in the first stage and 3 mol/L hydrochloric acid + 1.5 mol/L sulfuric acid in the second stage for 2 h. The SiO2 content in the concentrate increased to 99.92%. The impurity Fe and Ti contents from 0.061% and 0.042% decreased to 0.005% and 0.012%, respectively, and the comprehensive removal efficiencies of Fe and Ti reached 91.80% and 71.43%, respectively [77].
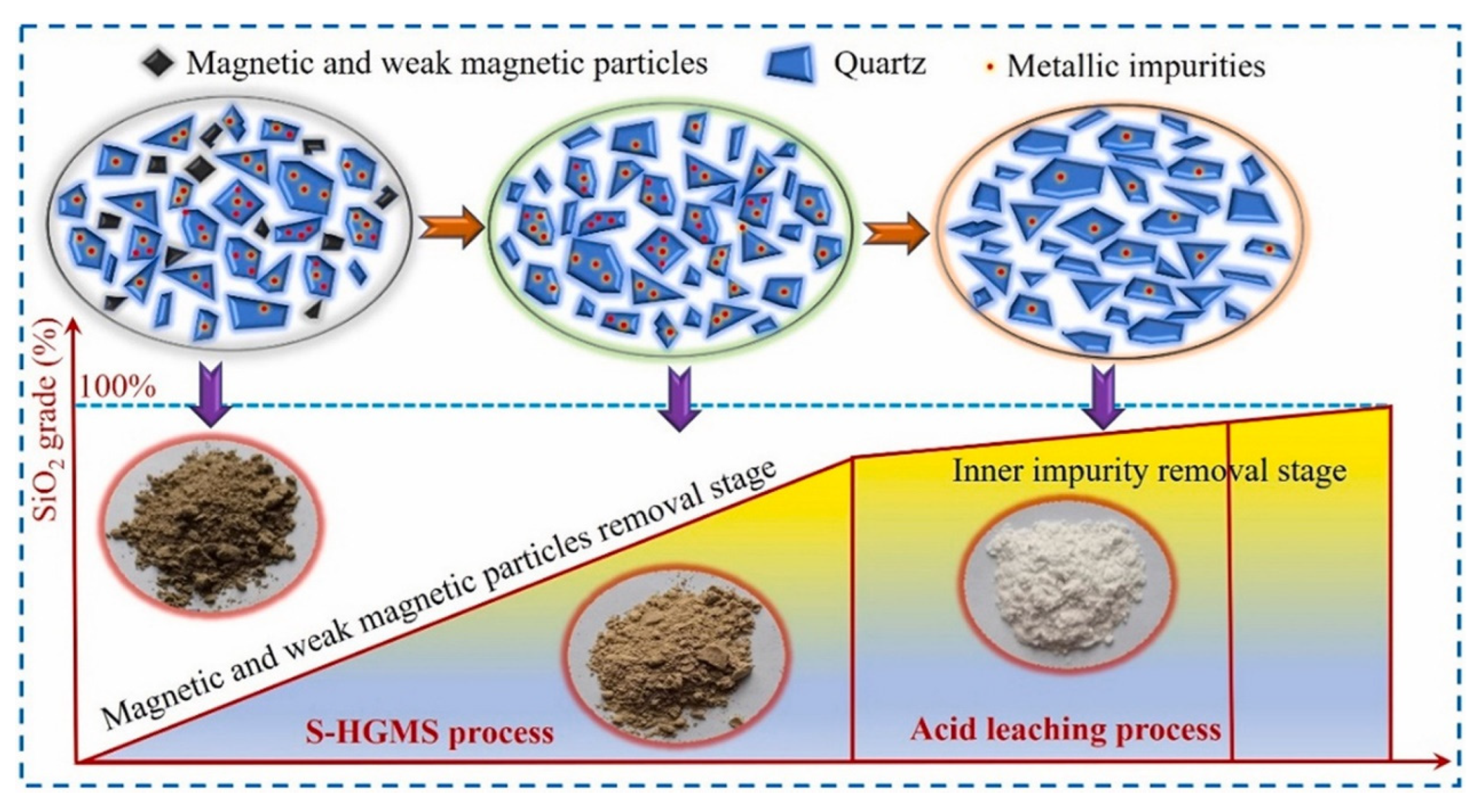
An eco-friendly technology was proposed for producing high-purity silica from high-silica IOTs by coupling superconducting high-gradient magnetic separation (S-HGMS) pre-concentration with leaching. This was followed using an ultrasound-assisted fluorine-free acid solution (shown in Figure 6).

Figure 6.
Schematic illustration of the preparation of high-purity silica from high-silica IOTs using S-HGMS coupling with ultrasound-assisted fluorine-free acid leaching technology [78].
The SiO2 grade increased from 69.32% in the raw sample to 93.12% in the quartz concentrate following the application of S-HGMS. Subsequently, employing the “ultrasound-assisted fluorine-free acid leaching process”, impure elements were removed and high-purity silica was produced. The SiO2 purity of silica sand increased to 97.42%. Following a three-stage acid leaching process with 4 mol/L HCl + 2 mol/L H2C2O4, the removal efficiency of Al, Ca, Fe, and Mg exceeded 97% for all cases, and the SiO2 purity in high-purity silica reached 99.93%.
The chlorination roasting process is one method for removing lattice impurities in quartz. It utilizes the gradient of chemical sites on the surface and inside of quartz minerals, promoting the diffusion of inclusions within quartz minerals. Chlorine gas (Cl2), as an example, has strong oxidizability at high temperatures. Due to the greater oxidizability of Cl2 compared with O2, metal impurities can be removed by chlorination reaction with metal oxides such as Fe2O3. Some of the reaction equations are as follows:
FeO + Cl2↑ → FeCl2↑ + O2↑
FeCl2 + Cl2↑ → FeCl3↑
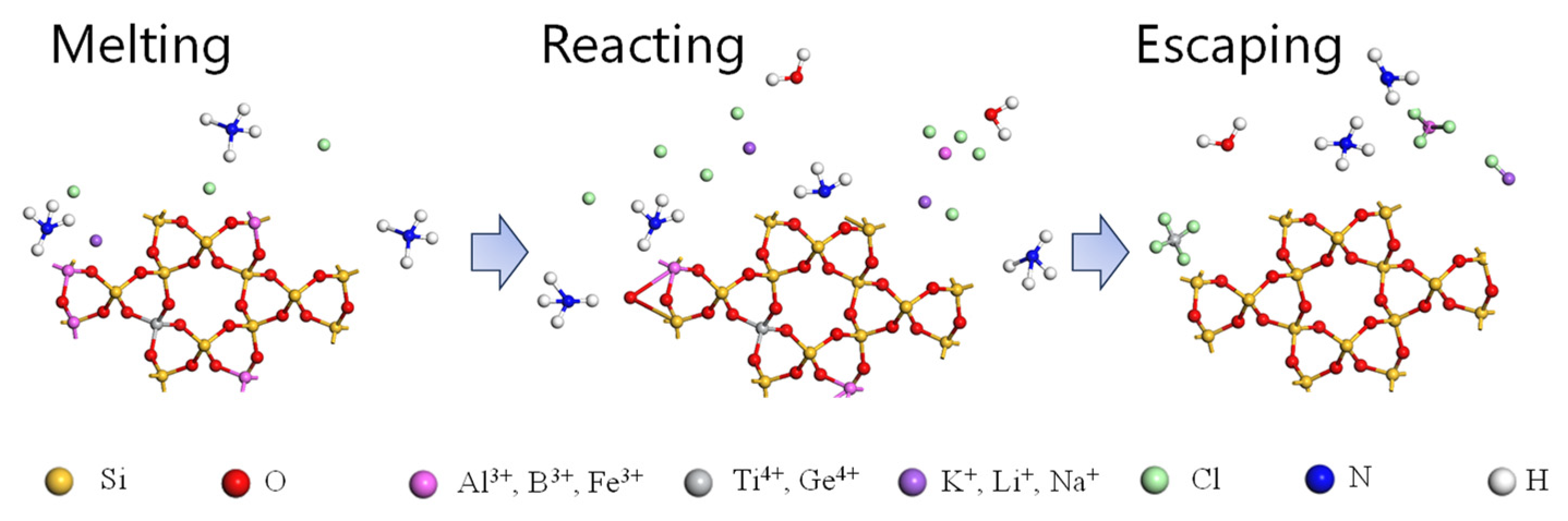
There are significant differences in the method and effect of different chlorinating agents on lattice impurities. Therefore, it is necessary to choose effective and reliable chlorinating agents. Chlorinating agents such as NH4Cl can react chemically with impurities in quartz, and the removal of lattice impurities in quartz is more obvious. The experimental research showed that the process of NH4Cl roasting to purify crystal lattice impurities may be divided into three stages: melting, reaction, and escape (shown in Figure 7).

Figure 7.
Schematic diagram of reaction mechanism for NH4Cl roasting lattice impurity in quartz [79].
After NH4+ ionized by NH4Cl melting captures active oxygen, metal ions combine with free Cl− or HCl to form chlorides and escape, which can remove impurities on or near the quartz sand surface. When the temperature was 600 °C, the optimum removal efficiency of iron was 70.46%. When the NH4Cl chlorination roasting temperature was 600 °C and the time was 180 min, the iron removal efficiency was 77.10%, and the content of other impurities was also significantly reduced [79]. Chlorination roasting not only is very convincing for removing lattice impurities but also is effective for other lattice impurities and the total amount of impurities compared with conventional methods with a total impurity content of 50.6% ppmw. NH4Cl solid chlorination roasting can reduce the total impurity content to 22.4 ppmw when combined with acid leaching and organic impurity removal can produce high-purity quartz that meets the 4N8 (ω(SiO2) ≥ 99.998%) standard [80].
3. Mechanism for Separating Iron Impurities from Quartz
Regarding the removal of iron impurities in quartz, most research has generally focused on the impurity removal process. Relatively little work has been carried out on theoretical explanations, and there has not been much research on the process mineralogy of quartz and the migration mechanism of iron impurities either. A few researchers have studied the mechanism of mineral roasting and magnetic separation. For example, Yuan et al. [81] used reverse flotation (RF) and suspension magnetization roasting–magnetic separation (SRM) to compare their effects on iron grade and iron recovery efficiency. The results showed that the second method could improve both the iron grade and the iron recovery, especially the iron recovery from 64.83% to 99.18%. The roasted products were analyzed by X-ray diffraction, Mossbauer spectrum, and X-ray photoelectron spectroscopy, and the results of the vibration sample magnetometry showed that most hematite in the roasted feed was reduced to magnetite, which significantly enhanced the saturation magnetization of the roasted product and effectively promoted the subsequent magnetic separation. It also applies to the removal of impurities from quartz.
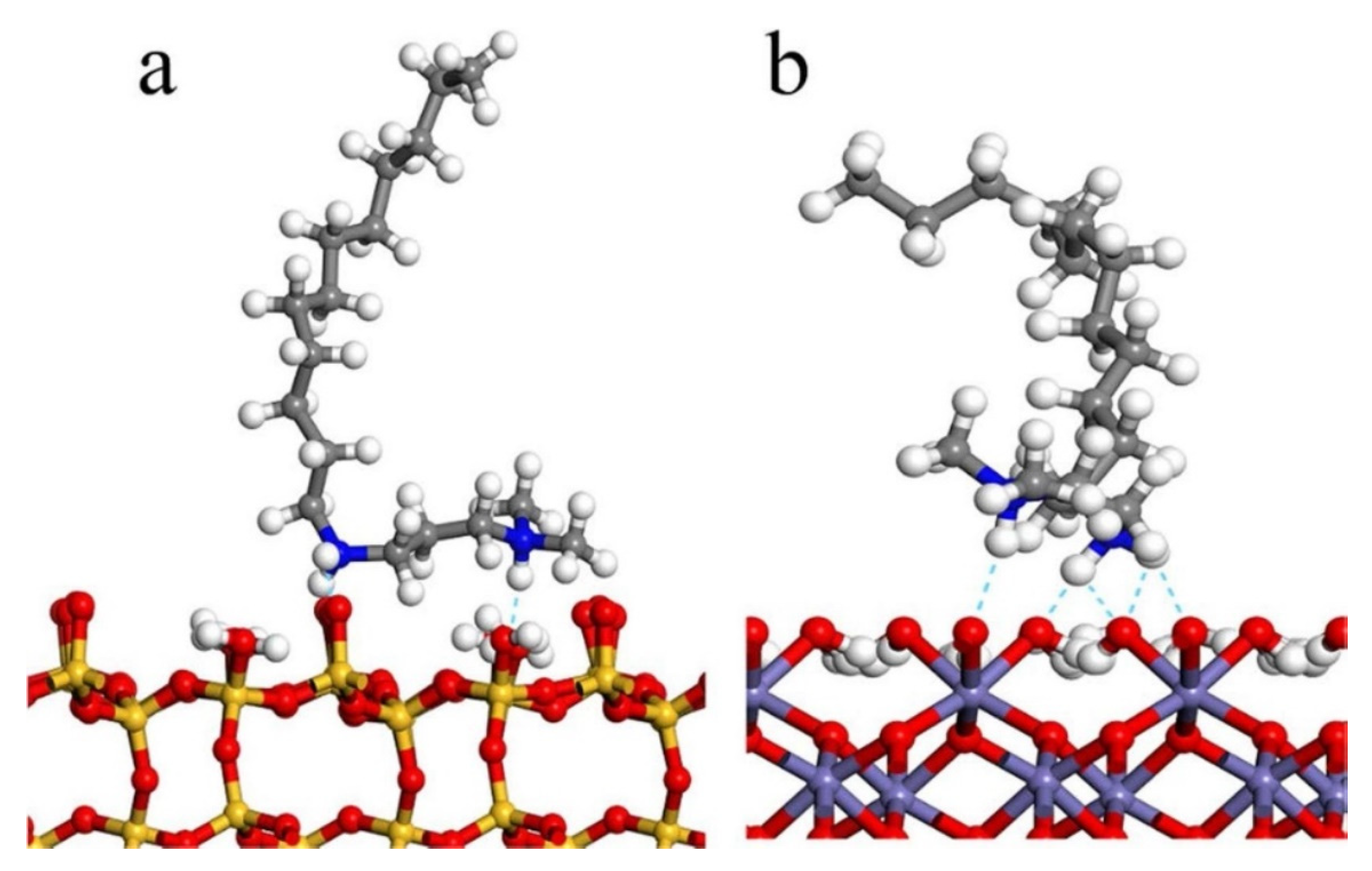
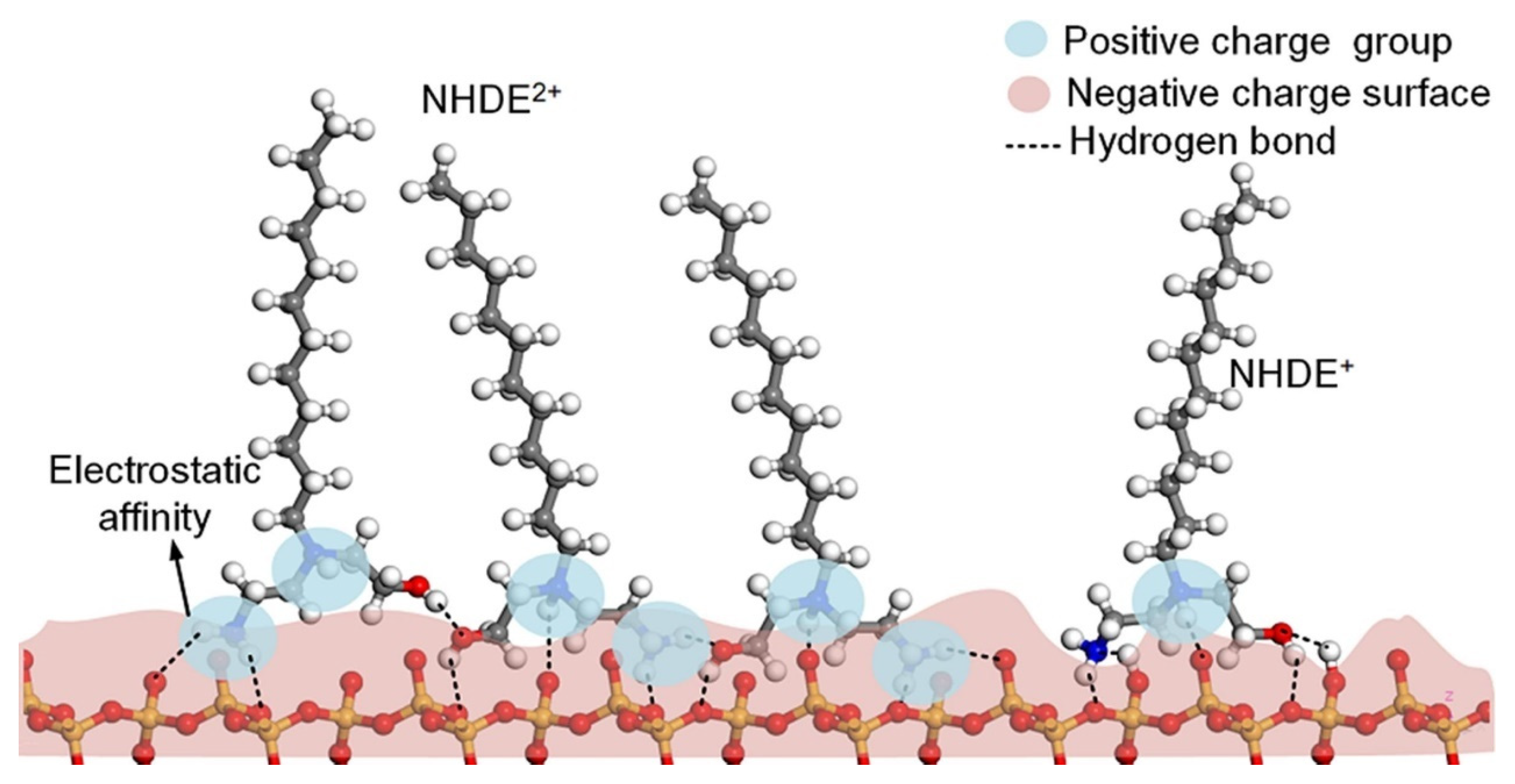
In iron removal by flotation from quartz, the design and synthesis of new reagents are widely studied at present, and their mechanism determines the separation effect. For example, Liu et al. [82] designed a new polyamine collector, N,N-dimethyl-N′-dodecyl-1,3-propanediamine (DPDA), by increasing the active center of reagent molecules and polar groups, which has a strong capture capacity and good selectivity and can achieve effective separation of quartz and hematite under neutral and weakly alkaline pulp conditions. DPDA2+ forms hydrogen bonds with O atoms exposed on the quartz and hematite surfaces (see Figure 8). The adsorption behavior can be attributed to electrostatic attraction and hydrogen bonding. Similarly, another reagent, NHDE, exhibited outstanding performance for collecting quartz, and the efficient flotation separation of quartz from its mixture with hematite could be conducted under pH 4.5–9.5 conditions. The adsorption of NHDE occurred on the quartz surface owing to the combination of electrostatic attractive force and the multiform hydrogen bonding (Figure 9). The multiform hydrogen bond not only enhanced the adsorption of NHDE on the quartz surface but also made NHDE form a stable packing layer on the quartz surface, which strengthened the hydrophobic nature of the surface [83].

Figure 8.
The adsorption stabilization model of quartz (a) and hematite (b) with DPDA2+. (The color representation is as follows: white—hydrogen atoms, gray—carbon atoms, red—oxygen atoms, blue—nitrogen atoms, yellow—silicon atoms, purple—iron atoms, sky blue—hydrogen bond).

Figure 9.
The adsorption model of NHDE on quartz surface based on pH.
Gungoren et al. [84] investigated the effect of ultrasound on the quartz amine flotation system. The results indicated that ultrasound had a certain impact on particle size, shape, and surface roughness to a certain extent. At the same time, it enhanced the contact angle of quartz and reduced the adhesion time of bubble particles. Ultrasound significantly improves the quartz flotation recovery rate, but when the power is high, it interrupts the physical adsorption between amine molecules and the surface, leading to a decline in the recovery rate of quartz flotation.
For disseminated iron oxide, which is difficult to remove when employing conventional scrubbing, strong magnetic separation, and acid reverse flotation, under neutral conditions, inhibitors serve to suppress iron-containing minerals, collectors are used to float the decomposed quartz, and the iron oxide residing in fine quartz sand is further reduced through rough selection and selection. The research shows that under natural pH, the amount of ferric oxide in this kind of quartz sand can be reduced efficiently through the combined action of a starch-based inhibitor, amphoteric collector CTSS, and foaming agent ZD-3. Meanwhile, thermodynamic calculation shows that when the standard free energy change (ΔG) in the chemical bond between the starch-based inhibitor CTSS and the iron ion on the iron oxide surface pH ≥ 5.5 is negative, the chemical bond exhibits a spontaneous trend, and the preferential adsorption of inhibitor CTSS and iron-bearing minerals is one of the keys to accomplish neutral positive flotation purification of quartz [61]. Decaethoxylated stearylamine (DEOSA, CH3(CH2)17N(CH2CH2O)10H2) was introduced as a high-performance collector in the flotation separation of hematite and quartz. The more DEOSA adsorbed onto quartz than hematite significantly enhanced the quartz surface hydrophobic whether with or without the depressant starch. The DEOSA adsorption onto the quartz mainly through the combination of hydrogen bonding and electrostatic attracting force. showing the efficient collection performance of DEOSA for quartz. Herein, DEOSA can be used as a strong-collection and high-performance quartz collector for separate hematite from quartz via reverse flotation [85]
N,N-Dimethyl aminopropyl dodecylamide oxide (LAO) is an eco-friendly amine oxide, and it was introduced as the collector in the flotation separation of hematite and quartz. Compared with the conventional amine collector DDA, LAO with low toxicity has better flotation performance and superior selectivity in the natural slurry. When the dosage of both LAO and DDA is 10 mg/L, the recoveries of quartz and hematite are 94.72% and 10.50%, respectively, but the recoveries of quartz and hematite under the action of DDA are only about 40% and 23%, respectively. In addition, the median effective inhibitory concentration (EC50) of LAO on Daphnia magna is 328.44 mg/L, meaning that LAO is a compound that is not toxic to aquatic organisms [86].
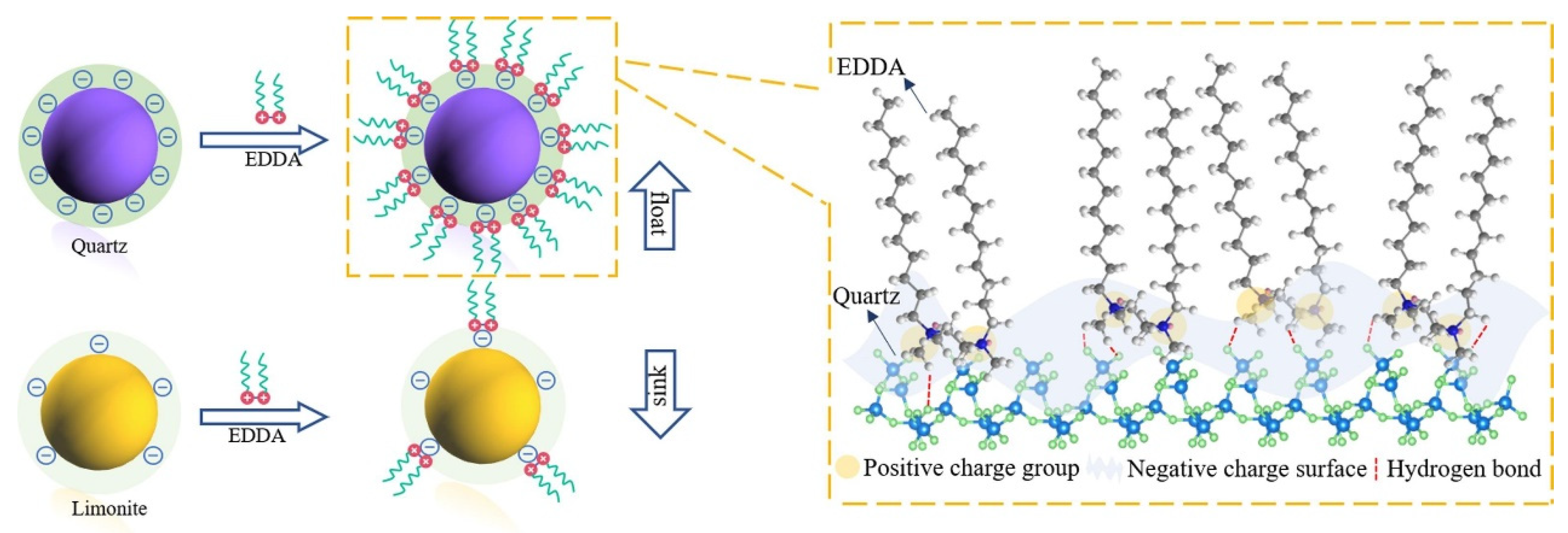
The synthesized ethane-1,2-dodecyldimethylammonium bromide (EDDA) was used as a novel collector for the separation of quartz and limonite. The separation model is shown below in Figure 10.

Figure 10.
Separation model of limonite and quartz in the presence of EDDA.
The two hydrophobic chains and two hydrophilic head groups of cationic gemini surfactants exerted a stronger effect on the collection and flotation of minerals. Additionally, EDDA used the difference of mineral surface potential to selectively adsorb more on the quartz surface to achieve efficient separation of limonite and quartz minerals [87].
4. Prospects for Purification of Quartz Minerals
With the rapid development of emerging industries such as new energy, semiconductors, aerospace, and other fields, the demand for high-purity quartz has also greatly increased. And different fields require quartz with different purity grades. The limitation of production cost and purification process leads to the insufficient supply of high-purity quartz.
The purity of high-purity quartz sand is not simply related to the content of impurity elements in the raw material but is closely related to the selectivity of impurities determined by the mineralogical characteristics of the raw material process. Therefore, basic research on quartz mineralogy should be strengthened to identify the content, occurrence state, and distribution characteristics of impurity elements within quartz crystals; And improve the separation of coexisting independent minerals, separation of inclusion impurities, and removal of lattice impurities to process high-purity quartz, thereby enhancing the purity and application of high-purity quartz sand.
A lot of research has been carried out on the raw material evaluation, purification processing, and detection technology of high-purity quartz. However, due to the disconnect between scientific research and production applications, there is a lack of intermediate experimental work between basic research and industrialization, and most of these technological achievements only remain in the laboratory stage. The failure to conduct a systematic and scientific evaluation of discovered quartz resources has resulted in a large number of high-quality vein quartz resources often being used to manufacture low-value-added products or potential high-purity quartz raw material resources. This issue needs to be rectified. As well, many studies have focused on copying mature conventional impurity removal techniques from quartz ore, but there is a relative lack of research on the theoretical mechanism of impurity removal. For example, there is less research on the bulk phase diffusion and grain boundary diffusion mechanisms of impurity elements.
Chemical synthesis to manufacture high-purity quartz is a future direction with significant development potential considering the depletion of high-quality but finite natural resources. In mineral flotation processes, the creation of environmentally friendly collectors is an important problem with great significance. Key theories and the refinement of high-purity quartz purification and preparation processes should both be highlighted. The preparation technology of high-purity quartz that combines theory and practice is currently a hot topic. It considers the origin of quartz, the quartz mineralogy, and the impurity element migration mechanism.
Supplementary Materials
The following supporting information can be downloaded at: https://www.mdpi.com/article/10.3390/min13091128/s1, Figure S1. The phase transition of quartz, [88].
Author Contributions
Conceptualization, C.L.; formal analysis, W.W. and C.Z.; data curation, H.W. and C.Z.; writing—original draft preparation, W.W. and H.W.; writing—review and editing, C.L. and B.R.; supervision, C.L. and B.R.; funding acquisition, C.L. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This research was funded by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (Nos.: 52104243 and 52274251), Natural Science Foundation of Anhui Province (2108085QE212), University-level key projects of Anhui University of science and technology (xjzd2020-21), Talent Introduction Fund of Anhui University of Science and Technology (13200007), Graduate Innovation Fund project of Anhui University of Science and Technology (2023cx2113).
Data Availability Statement
Not applicable.
Acknowledgments
This research was supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (52104243), Natural Science Foundation of Anhui Province (2108085QE212), University-level key projects of Anhui University of science and technology (xjzd2020-21), Talent Introduction Fund of Anhui University of Science and Technology (13200007), Graduate Innovation Fund project of Anhui University of Science and Technology (2023cx2113). The authors gratefully acknowledge financial support of the above-mentioned agencies.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
References
- Wang, L. Concept of high purity quartz and classification of its raw materials. Conserv. Util. Miner. Resour. 2022, 42, 55–63. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J. Global high purity quartz deposits: Resources distribution and exploitation status. Acta Mineral. Petrol. 2021, 40, 131–141. [Google Scholar]
- Guo, W.; Han, Y.; Zhu, Y.; Liu, Q.; Li, Y. Analysis of High-purity Quartz Sand Resources and It’s Processing Technologies. Met. Mine 2019, 2, 22–28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, H.; Müller, A.; Berndt, J. Quartz chemistry fingerprints melt evolution and metamorphic modifications in high-purity quartz deposits. Geochim. Cosmochim. Acta 2023, 356, 179–195. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abdellaoui, I.; Islam, M.M.; Sakurai, T.; Hamzaoui, S.; Akimoto, K. Impurities removal process for high-purity silica production from diatomite. Hydrometallurgy 2018, 179, 207–214. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Müller, A.; Wanvik, J.E.; Ihlen, P.M. Petrological and chemical characterisation of high-purity quartz deposits with examples from Norway. In Quartz: Deposits, Mineralogy and Analytics; Götze, J., Möckel, R., Eds.; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2012; pp. 71–118. [Google Scholar]
- Preusser, F.; Chithambo, M.L.; Götte, T.; Martini, M.; Ramseyer, K.; Sendezera, E.J.; Sunino, G.J.; Wintle, A.G. Quartz as a natural luminescence dosimeter. Earth-Sci. Rev. 2009, 97, 184–214. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ricci, G.; Monti, A.M.; Pagano, R.; Martini, M.; Caneve, L.; Artioli, G. Unusual Luminescence of Quartz from La Sassa, Tuscany: Insights on the Crystal and Defect Nanostructure of Quartz. Minerals 2021, 11, 1345. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Götze, J.; Plötze, M.; Habermann, D. Origin, spectral characteristics and practical applications of the cathodoluminescence (CL) of quartz—A review. Mineral. Petrol. 2001, 71, 225–250. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hashimoto, T. An Overview of Red-Thermoluminescence (RTL) Studies on Heated Quartz and RTL Application to Dosimetry and Dating. Geochronometria 2008, 30, 9–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.; Ma, Q.; Xia, Z.; Li, W.; Lei, S. Influences of Na2CO3 roasting and H3PO4 hot-pressure leaching on the purification of vein quartz to achieve high-purity quartz. Hydrometallurgy 2023, 218, 106065. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, R.; Lu, W.; Lu, J.; Pu, R.; Lin, J.; Yu, J. The color mechanism of iron on quartz by ion implantation. Phys. B Condens. Matter 2022, 627, 413550. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Perny, B.; Eberhardt, P.; Ramseyer, K.; Mullis, J.; Pankrath, R. Microdistribution of Al, Li, and Na in α quartz: Possible causes and correlation with short-lived cathodoluminescence. Am. Mineral. 1992, 77, 534–544. [Google Scholar]
- Chen, J.; Zhang, H. Trace elements in quartz lattice and their implications for petrogenesis and mineralization. Geol. J. China Univ. 2011, 17, 125–135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Niu, F.; Xu, X.; Gao, J.; Xu, J. Study on Purifying Quartzite by Mineral Processing. Yunnan Metall. 2001, 30, 18–21. [Google Scholar]
- Niu, F.; Ni, W. Study on High-Purity Quartzite by Mineral Processing. China Min. Mag. 2004, 6, 59–61. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, X.; Wang, X.; Deng, J.; Ma, Z.; Yang, J.; Cheng, N.; Chen, J. Study on Oxalic Acid Complexation Method of Removing Iron from Quartz. Bull. Chin. Ceram. Soc. 2012, 31, 852–855, 860. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.; Wei, Z.; Li, S.; Cao, S.; Song, Y. Experimental Study on the Purification of Quartz Sand from Hanzhong, Shaanxi Province. Conserv. Util. Miner. Resour. 2022, 42, 70–74. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, M. The Experiment of Scrubbing and Purifying a Quartz Mine. Hunan Nonferrous Met. 2020, 36, 20–23. [Google Scholar]
- Hu, Z.; Lu, D.; Zheng, X.; Wang, Y.; Xue, Z.; Xu, S. Development of a high-gradient magnetic separator for enhancing selective separation: A review. Powder Technol. 2023, 421, 118435. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ran, H.; Zhang, Z. Application of GCG-Type Dry Induced Roller High-Intensity Electromagnetic Separators in Production of High Grade Quartz Sand. Nonferrous Met. (Miner. Process. Sect.) 2007, 3, 43–46. [Google Scholar]
- Lui, S.; Gao, H.; Hu, T.; Guan, J.; Jing, J.; Reng, Z. Separation Experiment of Kaolin Tailing Quartz Sand in Guangxi Beihai. Met. Mine 2013, 444, 161–164, 167. [Google Scholar]
- Li, Y.; Zhang, M.; Zhang, X.; He, E. Influence of the Iron Impurity Absorbed by the Quartz Sand Surface on Iron-removing Efficiency. Bull. Chin. Ceram. Soc. 2013, 32, 2315–2318, 2324. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dai, P.; Yang, J.; Wei, Z.; Zeng, J.; Xue, Z.; Chen, L. Magnetic properties of chalcopyrite and arsenopyrite for high-gradient magnetic separation with Crystal-Field Theory. Miner. Eng. 2022, 189, 107893. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cui, Z.; Xie, Z.; Chen, L. Purification Experimental on a High Quality Quartz in Hebei. Mod. Min. 2019, 35, 119–120, 123. [Google Scholar]
- Miao, X.; Li, S.; Kong, j.; Yang, C.; Bao, S. Experiment Study on Extraction of SiO2 from Gold Tailings by High Magnetic Separation-Floatation Technology. Met. Mine 2018, 508, 184–188. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bao, S. Study on the Production of Ultra-Fine High Purify Quartz. Master’s Thesis, Wuhan University of Technology, Wuhan, China, 2004. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.; Feng, Y.; Hu, X.; Jiang, Y. Study on Rock Magnetic Properties of Fengyang Quartz Sand. Mineral. Petrol. 2022, 42, 1–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, F. DG type magnetic separator and SXG type scrubber for quartz purification application. Ind. Miner. Process. 1995, 26–27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kong, J.; Jin, X.; Liu, Y.; Wei, D.; Jiang, S.; Gao, S.; Feng, Z.; Xing, P.; Luo, X. Study on the kinetics of iron removal from silicon diamond-wire saw cutting waste: Comparison between heterogeneous and homogeneous reaction methods. Sep. Purif. Technol. 2019, 221, 261–268. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, J.; Li, J.; Bao, X.; Ban, B.; Sun, J.; Chen, J. Iron Removal Mechanism of Silica Sand Purification by Magnetic Separation and Acid Leaching. Nonferrous Met. (Miner. Process. Sect.) 2017, 4, 64–70. [Google Scholar]
- Hu, P.; Zhang, Y.; Liu, T.; Huang, J.; Yuan, Y.; Yang, Y. Separation and recovery of iron impurity from a vanadium-bearing stone coal via an oxalic acid leaching-reduction precipitation process. Sep. Purif. Technol. 2017, 180, 99–106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, Y.; Wang, X.; Wang, M.; Wang, H.; Xian, P. Recovery of iron from red mud by selective leach with oxalic acid. Hydrometallurgy 2015, 157, 239–245. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, S.O.; Tran, T.; Park, Y.Y.; Kim, S.J.; Kim, M.J. Study on the kinetics of iron oxide leaching by oxalic acid. Int. J. Miner. Process. 2006, 80, 144–152. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mandal, S.K.; Banerjee, P.C. Iron leaching from China clay with oxalic acid: Effect of different physico-chemical parameters. Int. J. Miner. Process. 2004, 74, 263–270. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martínez-Luévanos, A.; Rodríguez-Delgado, M.G.; Uribe-Salas, A.; Carrillo-Pedroza, F.R.; Osuna-Alarcón, J.G. Leaching kinetics of iron from low grade kaolin by oxalic acid solutions. Appl. Clay Sci. 2011, 51, 473–477. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, J.-S.; Li, X.-X.; Shen, Q.; Zhang, Z.-Z.; Du, F.-H. Further Purification of Industrial Quartz by Much Milder Conditions and a Harmless Method. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2010, 44, 7673–7677. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Taxiarchou, M.; Panias, D.; Douni, I.; Paspaliaris, I.; Kontopoulos, A. Removal of iron from silica sand by leaching with oxalic acid. Hydrometallurgy 1997, 46, 215–227. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Du, F.; Li, J.; Li, X.; Zhang, Z. Improvement of iron removal from silica sand using ultrasound-assisted oxalic acid. Ultrason. Sonochem. 2011, 18, 389–393. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Raman, V.; Abbas, A. Experimental investigations on ultrasound mediated particle breakage. Ultrason. Sonochem. 2008, 15, 55–64. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Veglió, F.; Passariello, B.; Barbaro, M.; Plescia, P.; Marabini, A.M. Drum leaching tests in iron removal from quartz using oxalic and sulphuric acids. Int. J. Miner. Process. 1998, 54, 183–200. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Santos, M.F.M.; Fujiwara, E.; Schenkel, E.A.; Enzweiler, J.; Suzuki, C.K. Processing of quartz lumps rejected by silicon industry to obtain a raw material for silica glass. Int. J. Miner. Process. 2015, 135, 65–70. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yan, Y.; Lu, Y.; Zheng, C.; Zhu, W. A new technology for Fe and Ti removal from quartz sand. Multipurp. Util. Miner. Resour. 2009, 16–19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ubaldini, S.; Piga, L.; Fornari, P.; Massidda, R. Removal of iron from quartz sands: A study by column leaching using a complete factorial design. Hydrometallurgy 1996, 40, 369–379. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vegliò, F.; Passariello, B.; Abbruzzese, C. Iron Removal Process for High-Purity Silica Sands Production by Oxalic Acid Leaching. Ind. Eng. Chem. Res. 1999, 38, 4443–4448. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Banza, A.N.; Quindt, J.; Gock, E. Improvement of the quartz sand processing at Hohenbocka. Int. J. Miner. Process. 2006, 79, 76–82. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arslan, V.; Bayat, O. Iron removal from Turkish quartz sand by chemical leaching and bioleaching. Min. Metall. Explor. 2009, 26, 35–40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Z.; Li, J.; Li, X.; Huang, H.; Zhou, L.; Xiong, T. High efficiency iron removal from quartz sand using phosphoric acid. Int. J. Miner. Process. 2012, 114–117, 30–34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bai, J.; Li, S.; Yang, C.; Kong, J. Study on the Influence of Ultrasound on Iron Removal by Acid Leaching for Quartz Sand. Non-Met. Mines 2016, 39, 69–71. [Google Scholar]
- Kong, J.; Xing, P.; Liu, Y.; Wang, J.; Jin, X.; Feng, Z.; Luo, X. An Economical Approach for the Recycling of High-Purity Silicon from Diamond-Wire Saw Kerf Slurry Waste. Silicon 2019, 11, 367–376. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, L.; Danaei, A.; Fang, M.; Thomas, S.; Luo, X.; Barati, M. A metallurgical route to upgrade silicon kerf derived from diamond-wire slicing process. Vacuum 2019, 163, 164–171. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, H.L.; Liu, I.T.; Liu, C.E.; Liu, H.P.; Hsu, C.W.L. Recycling and reuse of kerf-loss silicon from diamond wire sawing for photovoltaic industry. Waste Manag. 2019, 84, 204–210. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kong, J.; Xing, P.; Wei, D.; Jin, X.; Zhuang, Y. Ultrasound-Assisted Leaching of Iron from Silicon Diamond-Wire Saw Cutting Waste. JOM-US 2021, 73, 791–800. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hou, S.-Y.; Tie, S.-N.; Jiang, M.-Q.; Liu, Y.-J.; Li, H.-J. Microwave-Assisted Acid Leaching for Recovery of Silicon from Diamond-Wire Cutting Waste Slurry. JOM-US 2020, 72, 2656–2662. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, C.; Li, S.; Yang, R.; Bai, J.; Guo, Z. Recovery of silicon powder from kerf loss slurry waste using superconducting high gradient magnetic separation technology. J. Mater. Cycles Waste Manag. 2018, 20, 937–945. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, X.; Liu, X.; Wang, X.; Hong, Y.; Wang, D. Research on Purification of Quartz Sand by Organic Acid Leaching from Aspergillus Niger. Non-Met. Mines 2019, 42, 91–93. [Google Scholar]
- Bahaj, A.S.; James, P.A.B.; Kirby, C.E. Bioleaching of iron-stained sands. Trans. Inst. Min. Metall. Sect. C 1996, 105, C72–C74. [Google Scholar]
- Ding, Y. Investigation on the Preparation of High Purity Quartz from Low Grade Silica. Ph.D. Thesis, Northeastern University, Liaoning, China, 2010. [Google Scholar]
- Hong, Y.; Zhao, X.; Ren, R.; Liu, X.; Li, J.; Liu, G. Study on Flotation Separation of Magnetite and Quartz under the Action of Miscible Collector. Non-Met. Mines 2021, 44, 64–67. [Google Scholar]
- Yin, W.Z.; Wang, D.H.; Drelich, J.W.; Yang, B.; Li, D.; Zhu, Z.L.; Yao, J. Reverse flotation separation of hematite from quartz assisted with magnetic seeding aggregation. Miner. Eng. 2019, 139, 105873. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Q.; Shi, Q.; Wu, J.; Li, P.; Chang, Z. Preparation of low iron quartz by neutral direct flotation from iron oxide disseminated quartz. Chem. Ind. Eng. Prog. 2019, 38, 1218–1225. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, N.; Pang, T.; Han, R.; Zhu, Z.; Li, Z. Insight into anionic and cationic flotation discrepancy of quartz with altered surface roughness by acid etching. J. Mol. Liq. 2023, 381, 121816. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, Y.; Guo, W.; Zhu, Y.; Wei, Y.; Gu, X. Flotation behavior and separation mechanism of quartz and iron minerals in α-bromolauric acid reverse flotation system. Physicochem. Probl. Miner. Process. 2018, 54, 992–1003. [Google Scholar]
- Peçanhaa, E.R.; da Fonseca de Albuquerquea, M.D.; Simãob, R.A.; de Salles Leal Filhoc, L.; de Mello Monte, M.B. Interaction forces between colloidal starch and quartz and hematite particles in mineral flotation. Colloids Surf. A 2019, 562, 79–85. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, H.; Qiu, T.; Zhao, G.; Zhu, D.; Li, X.; Feng, B. Investigations on the reverse cationic flotation separation of quartz from hematite using polyaspartic acid as depressant. Appl. Surf. Sci. 2023, 614, 156143. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, S.; Xu, Y.; Kang, H.; Li, K.; Li, C. Investigation into starch adsorption on hematite and quartz in flotation: Role of starch molecular structure. Appl. Surf. Sci. 2023, 623, 157064. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, M.; Xiang, Y.; Chen, T.; Gao, X.; Liu, Q. Separation of ultra-fine hematite and quartz particles using asynchronous flocculation flotation. Miner. Eng. 2021, 164, 106817. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, Z.; Zhang, Z. Effect of Different Flotation Conditions on the Maximum Floatable Particle Size of Quartz. Met. Mine 2022, 8, 108–113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, X. Research on Iron Removal and Purification Process Technology of Fused Silica. Master’s Thesis, Liaoning Technical University, Liaoning, China, 2021. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, H.; Guo, S.; Wu, J.; Wu, D.; Wei, K.; Ma, W. Effect of quartz crystal structure transformations on the removal of iron impurities. Hydrometallurgy 2021, 204, 105715. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, F.F.; Jiang, X.S.; Zuo, Q.X.; Li, J.W.; Ban, B.Y.; Chen, J. Purification Mechanism of Quartz Sand by Combination of Microwave Heating and Ultrasound Assisted Acid Leaching Treatment. Silicon 2021, 13, 531–541. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.; Zhang, S.; Li, L. Experimental Research on Silica Sand Purification by Permanent Strong Magnetic Separation and Acid Leaching. Non-Met. Mines 2015, 38, 52–54. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, F.; Lei, S.; Zhong, L.; Pei, Z.; Yang, Y.; Xiong, K. Purification of vein quartz by mixed acid thermal pressure leaching and its mechanism. China Min. Mag. 2016, 25, 106–110. [Google Scholar]
- Jing, T.; Lei, W.; Lin, Y. Study of Quartz Sandstone Refinement in Muchuan, Sichuan Province. Guizhou Geol. 2010, 27, 312–316. [Google Scholar]
- Qiu, Q.; Zheng, S.; Xie, H. Experimental Study on Fine-Processing of Quartzite Ore. Non-Met. Mines 2008, 190, 22–24. [Google Scholar]
- Mao, L.; Gu, C.; Wu, J.; Yu, Y. Experimental Study on Replacing Crystal with Vein Quartz to Produce High Purity Quartz Sand. World Build. Mater. 2010, 31, 1–4. [Google Scholar]
- Mo, F.; Sun, S.; Zou, A.; Xu, K. Study on a New Purification Process of Quartz Sand in Sichuan Province by Removing Iron and Titanium. Conserv. Util. Miner. Resour. 2022, 139–143. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.; Li, S.; Pan, X.; Zhao, X.; Guo, P. Eco-friendly strategy for preparation of high-purity silica from high-silica IOTs using S-HGMS coupling with ultrasound-assisted fluorine-free acid leaching technology. J. Environ. Manag. 2023, 339, 117932. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, X. Selection and Evaluation of High Purity Quartz Materials and Purification Technology Research. Master’s Thesis, Southwest University of Science and Technology, Mianyang, China, 2016. [Google Scholar]
- Pan, J. Experimental Study of 4N8 Standard Grade High-Purity Quartz Prepared by Chlorination Roasting Method. Master’s Thesis, Chengdu University of Technology, Mianyang, China, 2015. [Google Scholar]
- Yuan, S.; Xiao, H.; Wang, R.; Li, Y.; Gao, P. Improved iron recovery from low-grade iron ore by efficient suspension magnetization roasting and magnetic separation. Miner. Eng. 2022, 186, 107761. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, W.; Liu, W.; Zhao, Q.; Peng, X.; Wang, B.; Zhou, S.; Zhao, L. Investigating the performance of a novel polyamine derivative for separation of quartz and hematite based on theoretical prediction and experiment. Sep. Purif. Technol. 2020, 237, 116370. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, W.; Liu, W.; Wang, B.; Duan, H.; Peng, X.; Chen, X.; Zhao, Q. Novel hydroxy polyamine surfactant N-(2-hydroxyethyl)-N-dodecyl-ethanediamine: Its synthesis and flotation performance study to quartz. Miner. Eng. 2019, 142, 105894. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gungoren, C.; Ozdemir, O.; Wang, X.; Ozkan, S.G.; Miller, J.D. Effect of ultrasound on bubble-particle interaction in quartz-amine flotation system. Ultrason. Sonochem. 2019, 52, 446–454. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, B.; Yin, W.-Z.; Yao, J.; Zhu, Z.-L.; Sun, H.-R.; Chen, K.-Q.; Wang, L.-Y. Differential adsorption of a high-performance collector at solid–liquid interface for the selective flotation of hematite from quartz. J. Mol. Liq. 2021, 339, 116828. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.; Liu, W.; Duan, H.; Liu, W.; Shen, Y.; Gu, X.; Qiu, J.; Jia, C. Potential application of an eco-friendly amine oxide collector in flotation separation of quartz from hematite. Sep. Purif. Technol. Sep. Purif. Technol. 2021, 278, 119668. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, C.; Deng, J.; Ni, C.; Wang, D.; Xue, K.; Xu, L.; Zhang, X. Reverse froth flotation separation of limonite and quartz with cationic gemini surfactant. Miner. Eng. 2022, 177, 107391. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pan, X.; Li, S.; Li, Y.; Guo, P.; Zhao, X.; Cai, Y. Resource, characteristic, purification and application of quartz: A review. Miner. Eng. 2022, 183, 107600. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).