Mild Conditions Method to Remediate Hazardous Jarosite and Its Application as Adsorbent of Arsenic(V) and Water
Abstract
:1. Introduction
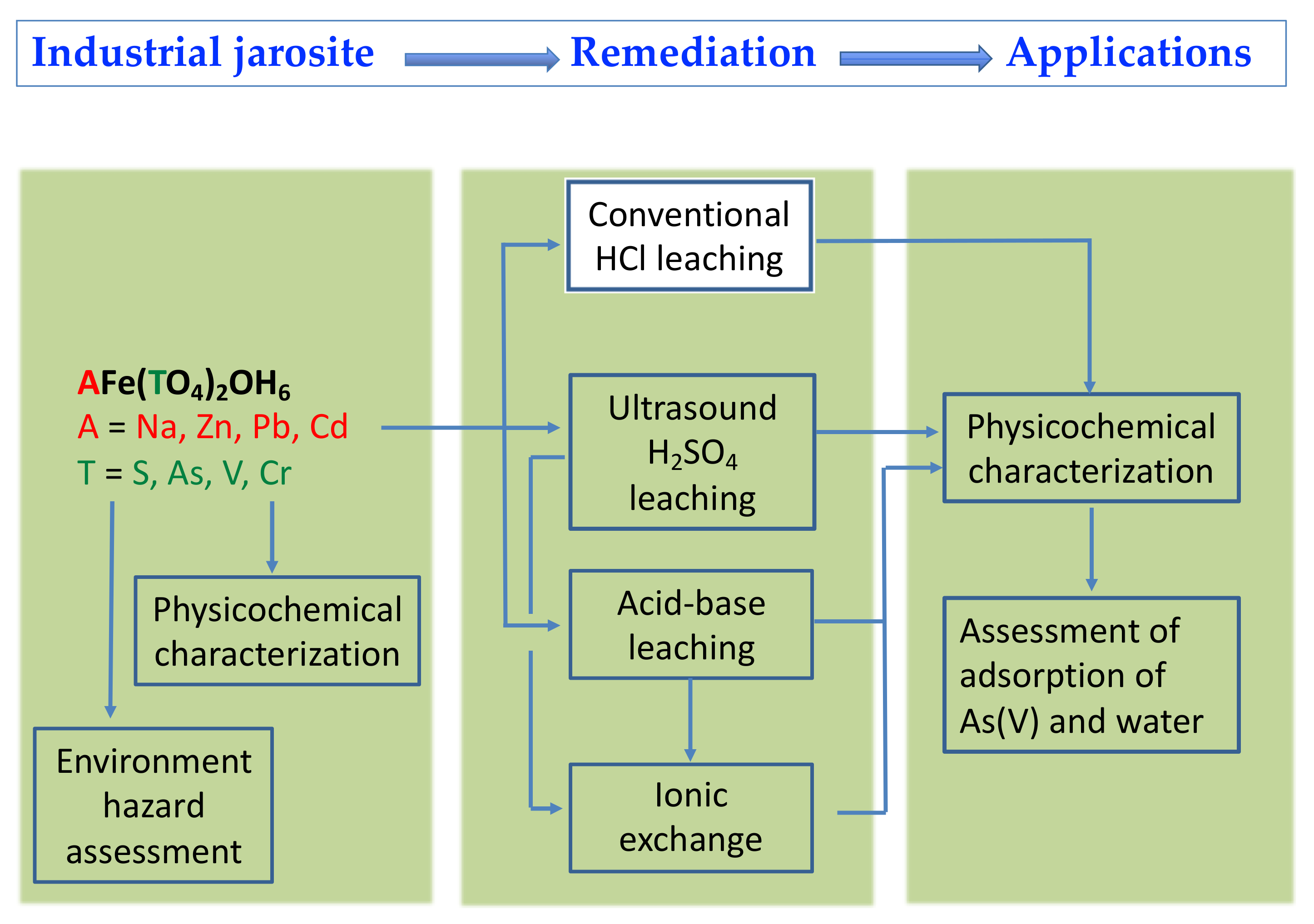
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Remediation of JAR by Removal of Regulated Heavy Metals
2.1.1. Jarosite Acid Leaching by Conventional Hydrothermal Treatment
2.1.2. Jarosite Ultrasound-Assisted Acid Leaching
2.1.3. Ion Exchange of Heavy Metals Contained in JAR
2.1.4. Extended Process for JAR Remediation
2.2. Environmental Risk Assessment of Jarosites
2.3. Evaluation of the Potential Use of Jarosites as Adsorbents
2.3.1. Arsenate Adsorption Study on Experimental Jarosites
2.3.2. The Water Adsorption Capacity of Jarosite
3. Results and Discussion
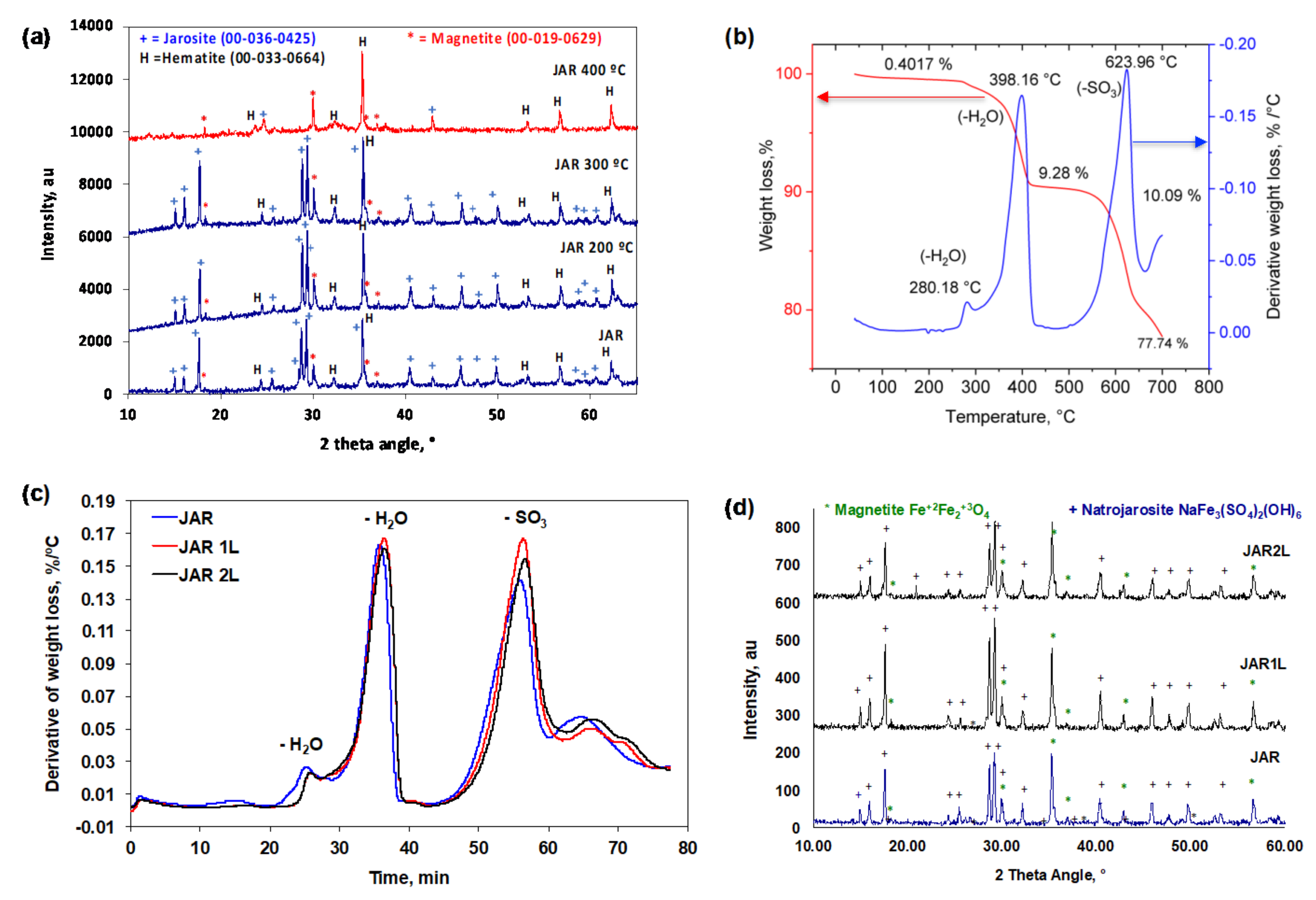
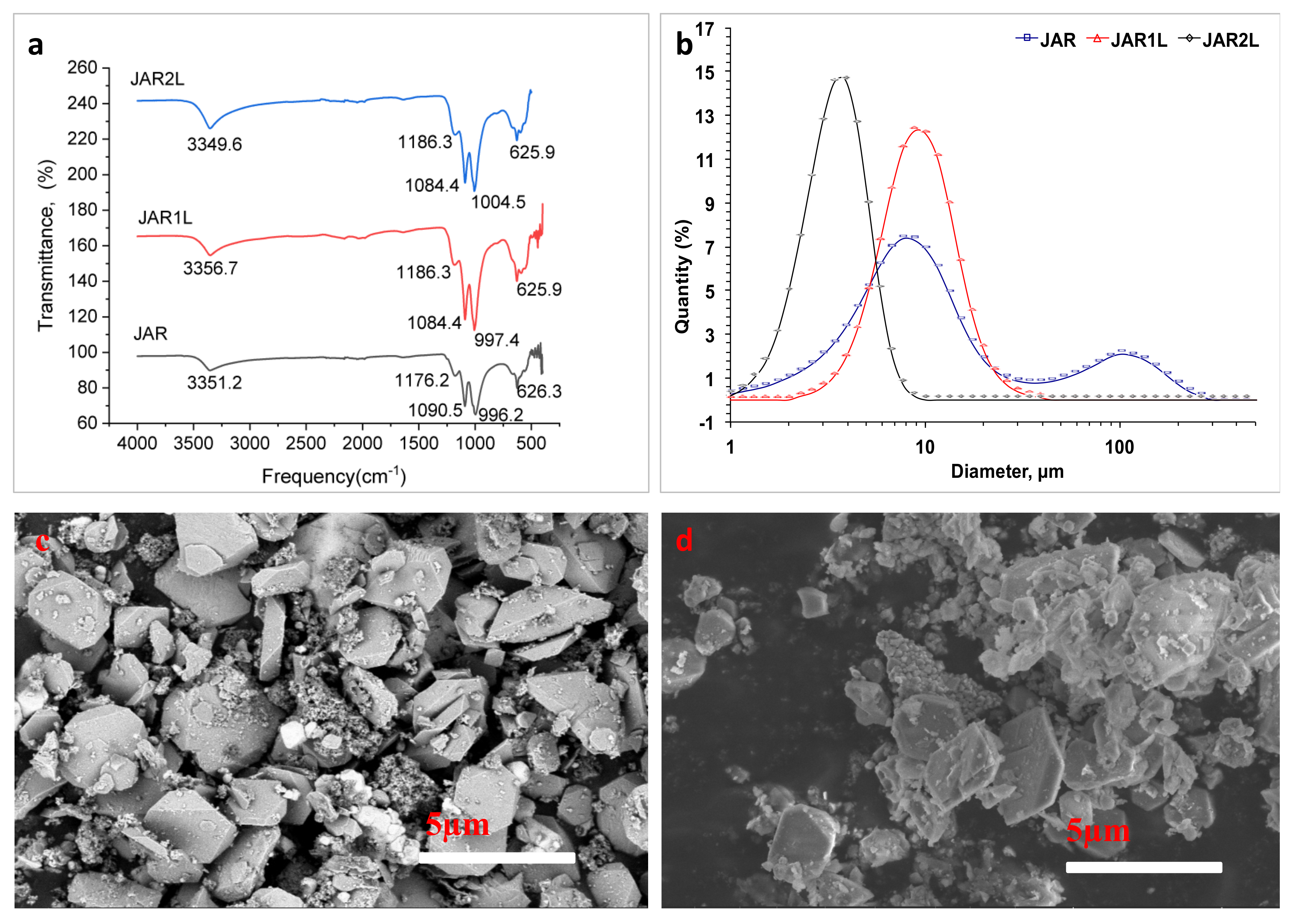
3.1. Characterization of Jarosites
3.2. Environmental Risk of Industrial and Remediated Jarosite
3.3. Remediation of JAR by Leaching and Ion Exchange
3.3.1. Remediation of JAR by Ultrasound-Assisted H2SO4 Leaching
3.3.2. Improving Remediation of JAR2L by Ion Exchange
3.3.3. Remediation of JAR by Conventional HCl Leaching
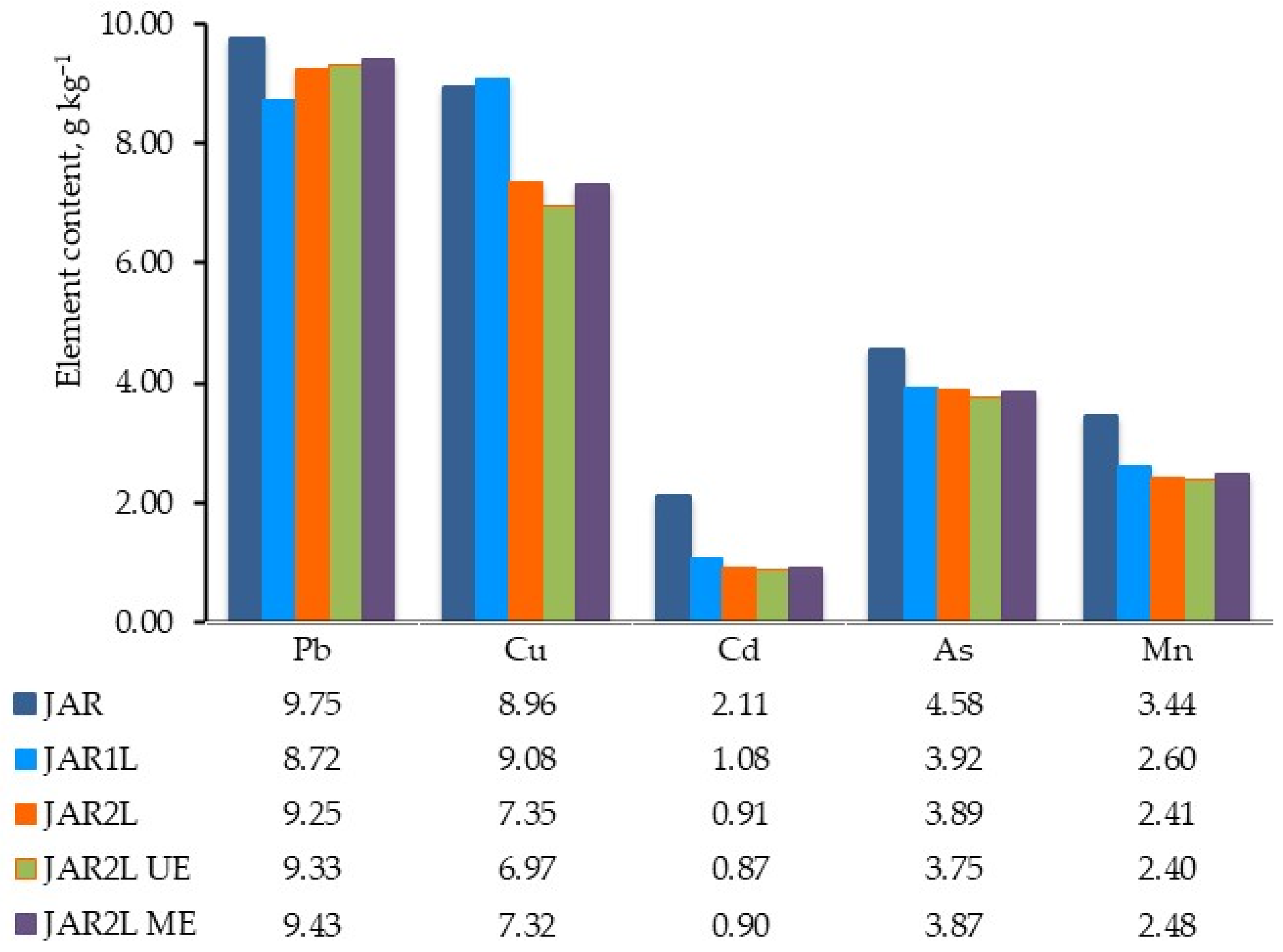
3.3.4. Metallic Contaminants in Jarosites Obtained by Extended Remediation
3.4. Potential Use of Jarosites as Adsorbents
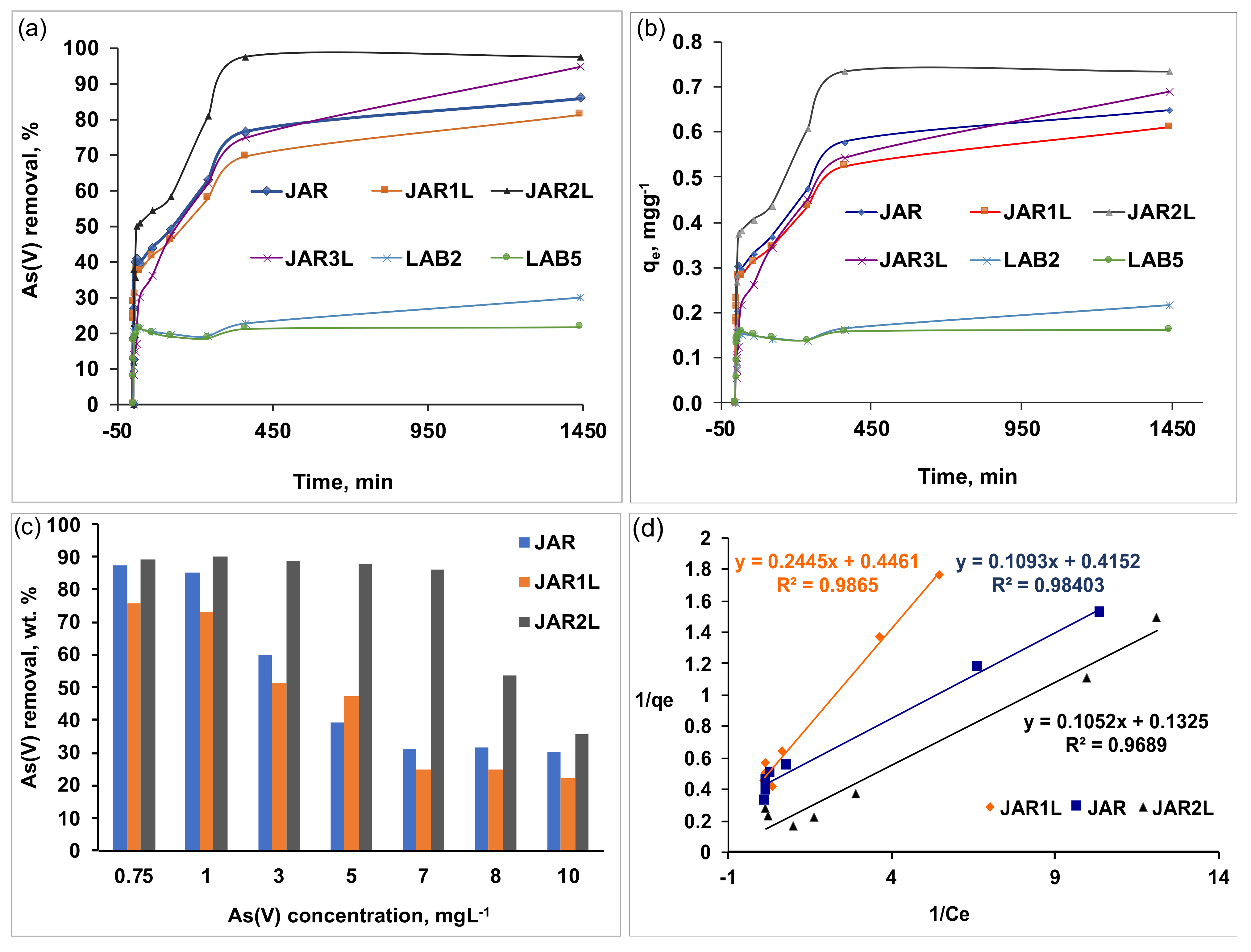
3.4.1. Removal of As(V) from an Aqueous Solution Using Jarosites
3.4.2. Water Adsorption Capacity of the Experimental Jarosites
4. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Shi, M.; Min, X.; Ke, Y.; Lin, Z.; Yang, Z.; Wang, S.; Peng, N.; Yan, X.; Luo, S.; Wu, J.; et al. Recent progress in understanding the mechanism of heavy metals retention by iron (oxyhydr)oxides. Sci. Total Environ. 2021, 752, 141930. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- López-Martínez, A.M.; Khamkure, S.; Gamero-Melo, P. Bifunctional Adsorbents Based on Jarosites for Removal of Inorganic Micropollutants from Water. Separations 2023, 10, 309. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cogram, P. Jarosite; Elsevier: London, UK, 2018. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Islas, H.; Patiño, F.; Reyes, M.; Flores, M.U.; Reyes, I.A.; Palacios, E.G.; Ordoñez, S.; Flores, V.H. Síntesis, caracterización y naturaleza de la reacción alcalina de jarosita de talio. Rev. Latinam. Metal. Mat. 2017, 37, 228–236. [Google Scholar]
- Calla-Choque, D.; Nava-Alonso, F.; Fuentes-Aceituno, J.C. Acid decomposition and thiourea leaching of silver from hazardous jarosite residues: Effect of some cations on the stability of the thiourea system. J. Hazard. Mater. 2016, 317, 440–448. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Islas, H.; Flores, M.U.; Reyes, I.A.; Juárez, J.C.; Reyes, M.; Teja, A.M.; Palacios, E.G.; Pandiyan, T.; Aguilar-Carrillo, J. Determination of the dissolution rate of hazardous jarosites in different conditions using the shrinking core kinetic model. J. Hazard. Mater. 2020, 386, 121664. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mombelli, D.; Mapelli, C.; Barella, S.; Gruttadauria, A.; Spada, E. Jarosite wastes reduction through blast furnace sludges for cast iron production. J. Environ. Chem. Eng. 2019, 7, 102966. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kerolli–Mustafa, M.; Fajković, H.; Rončević, S.; Ćurković, L. Assessment of metal risks from different depths of jarosite tailing waste of Trepça Zinc Industry, Kosovo based on BCR procedure. J. Geochem. Explor. 2015, 148, 161–168. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kaya, M.; Hussaini, S.; Kursunoglu, S. Critical review on secondary zinc resources and their recycling technologies. Hydrometallurgy 2020, 195, 105362. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- González-Ibarra, A.A.; Nava-Alonso, F.; Uribe-Salas, A.; Castillo-Ventureño, E.N. Decomposition kinetics of industrial jarosite in alkaline media for the recovery of precious metals by cyanidation. Can. Metall. Q. 2016, 55, 448–454. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Calla-Choque, D.; Lapidus, G.T. Acid decomposition and silver leaching with thiourea and oxalate from an industrial jarosite sample. Hydrometallurgy 2020, 192, 105289. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kasaini, H.; Kasongo, K.; Naude, N.; Katabua, J. Enhanced leachability of gold and silver in cyanide media: Effect of alkaline pre-treatment of jarosite minerals. Miner. Eng. 2008, 21, 1075–1082. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, J.; Chai, L.; Lin, Z.; Wei, Y.; Shi, M.; Peng, J.; Peng, N.; Yan, X. Fe(II)-induced transformation of Jarosite residues generated from zinc hydrometallurgy: Influence on metals behaviors during acid washing. Hydrometallurgy 2021, 200, 105523. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, X.; Tan, H.; Dong, F.; Li, B.; Wang, J.; He, X.; Liu, C. Influence of troilite on the decomposition of ammonium jarosite and estimated activation energy. J. Therm. Anal. Calorim. 2020, 139, 933–939. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, D.; Yang, C.; Pan, J.; Guo, Z.; Li, S. New pyrometallurgical route for separation and recovery of Fe, Zn, In, Ga and S from jarosite residues. J. Clean. Prod. 2018, 205, 781–788. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, H.; Sun, W.; Hu, Y.; Jia, B.; Tang, H. Anglesite and silver recovery from jarosite residues through roasting and sulfidization-flotation in zinc hydrometallurgy. J. Hazard. Mater. 2014, 278, 49–54. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Linsong, W.; Peng, Z.; Yu, F.; Sujun, L.; Yue, Y.; Li, W.; Wei, S. Recovery of metals from jarosite of hydrometallurgical nickel production by thermal treatment and leaching. Hydrometallurgy 2020, 198, 105493. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chanshetti, U. Concepts of Green Chemistry. Curr. Perspect. Chem. Sci. 2021, 7, 144–150. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grison, C.; Lock, Y.; Ki, T. Ecocatalysis, a new vision of Green and Sustainable Chemistry. Curr. Opin. Green Sustain. Chem. 2021, 29, 100461. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eftekhari, N.; Kargar, M.; Zamin, F.R.; Rastakhiz, N.; Manafi, Z. A Review on Various Aspects of Jarosite and Its Utilization Potentials. Ann. Chim.—Sci. Mat. 2020, 44, 43–52. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Patiño, F.; Reyes, I.A.; Flores, M.U.; Pandiyan, T.; Roca, A.; Reyes, M.; Hernández, J. Kinetic modeling and experimental design of the sodium arsenojarosite decomposition in alkaline media: Implications. Hydrometallurgy 2013, 137, 115–125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tang, X.; Liu, M.; Tang, Q.; Du, Z.; Bai, S.; Zhu, Y. Effect of ultrasound on the dissolution of magnesium hydroxide: pH-stat and nanoscale observation. Ultrason. Sonochem. 2019, 55, 223–231. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, H.; Zhang, L.; Xie, H.; Yin, S.; Peng, J.; Li, S.; Yang, K.; Zhu, F. Ultrasound-Assisted Silver Leaching Process for Cleaner Production. JOM 2020, 72, 766–773. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Larrabure, G.; Chero-Osorio, S.; Silva-Quiñones, D.; Benndorf, C.; Williams, M.; Gao, F.; Gamarra, C.; Alarcón, A.; Segura, C.; Teplyakov, A.; et al. Surface processes at a polymetallic (Mn-Fe-Pb) sulfide subject to cyanide leaching under sonication conditions and with an alkaline pretreatment: Understanding differences in silver extraction with X-ray photoelectron spectroscopy (XPS). Hydrometallurgy 2021, 200, 105544. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shunda, L.; Mamdouh, O.; Shenghui, G. Recovery of Metals and Rare Earth Elements by Microwave heating Technology—A Review. Curr. Microw. Chem. 2020, 7, 196–206. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sabzezari, B.; Koleini, S.M.J.; Ghassa, S.; Shahbazi, B.; Chelgani, S.C. Microwave-Leaching of Copper Smelting Dust for Cu and Zn. Extraction. Materials 2019, 12, 1822. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, S.; Zhang, Y.; Meng, Q.; Dong, P.; Fei, Z.; Li, Q. Recycling of LiCoO2 cathode material from spent lithium ion batteries by ultrasonic enhanced leaching and one-step regeneration. J. Environ. Manag. 2021, 277, 111426. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abdellaoui, Y.; Oualid, H.A.; Hsini, A.; Ibrahimi, B.E.; Laabd, M.; Ouardi, M.E.; Giácoman-Vallejos, G.; Gamero-Melo, P. Synthesis of zirconium-modified Merlinoite from fly ash for enhanced removal of phosphate in aqueous medium: Experimental studies supported by Monte Carlo/SA simulations. Chem. Eng. J. 2021, 404, 126600. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abdellaoui, Y.; Ibrahimi, B.E.; Oualid, H.A.; Kassab, Z.; Quintal-Franco, C.; Gíacoman-Vallejos, G.; Gamero-Melo, P. Iron-zirconium microwave-assisted modification of small-pore zeolite W and its alginate composites for enhanced aqueous removal of As(V) ions: Experimental and theoretical studies. Chem. Eng. J. 2021, 421, 129909. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- American Society for Testing and Materials Home Page. Available online: https://webstore.ansi.org/standards/astm/astmd4180132018 (accessed on 28 August 2023).
- Güngör, H.; Elik, A. Comparison of ultrasound-assisted leaching with conventional and acid bomb digestion for determination of metals in sediment samples. Microchem. J. 2007, 86, 65–70. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Official Mexican Standard Home Page. 2005. Available online: https://www.dof.gob.mx/normasOficiales/1055/SEMARNA/SEMARNA.htm (accessed on 28 August 2023).
- Official Mexican Standard Home Page. 1993. Available online: https://www.vertic.org/media/National%20Legislation/Mexico/MX_NOM-052-ECOL-1993.pdf (accessed on 28 August 2023).
- Desborough, G.A.; Smith, K.S.; Lowers, H.A.; Swayze, G.A.; Hammarstrom, J.M.; Diehl, S.F.; Leinz, R.W.; Driscoll, R.L. Mineralogical and chemical characteristics of some natural jarosites. Geochim. Cosmochim. Acta 2010, 74, 1041–1056. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, R.; Li, Y.; Chan, C.K. Synthesis of Jarosite and Vanadium Jarosite Analogues Using Microwave Hydrothermal Reaction and Evaluation of Composition-Dependent Electrochemical Properties. J. Phys. Chem. C 2016, 20, 9702–9712. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jaishankar, M.; Tseten, T.; Anbalagan, N.; Mathew, B.B.; Beeregowda, K.N. Toxicity, mechanism and health effects of some heavy metals. Interdiscip. Toxicol. 2014, 7, 60–72. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rathia, B.S.; Kumar, P.S. A review on sources, identification and treatment strategies for the removal of toxic Arsenic from water system. J. Hazard. Mater. 2021, 418, 126299. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hudson-Edwards, K.A.; Smith, A.M.L.; Dubbin, W.E.; Bennett, A.J.; Murphy, P.J.; Wright, K. Comparison of the structures of natural and synthetic Pb-Cu-jarosite-type compounds. Eur. J. Mineral. 2008, 20, 241–252. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meng, X.; Zhang, C.; Zhuang, J.; Zheng, G.; Zhou, L. Assessment of schwertmannite, jarosite and goethite as adsorbents for efficient adsorption of phenanthrene in water and the regeneration of spent adsorbents by heterogeneous fenton-like reaction. Chemosphere 2020, 244, 125523. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Picazo-Rodríguez, N.G.; Carrillo-Pedroza, F.R.; Soria-Aguilar, M.J.; Baltierra, G.; González, G.; Martinez-Luevanos, A.; Guzmán, I.A. Use of Thermally Modified Jarosite for the Removal of Hexavalent Chromium by Adsorption. Crystals 2022, 12, 80. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]


| Fe2O3 | SO3 | SiO2 | ZnO | Na2O | Al2O3 | CuO | As2O3 | MnO | CdO | K2O | CaO | PbO | LOI 1 | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Chemical composition on wet base, wt. % | ||||||||||||||
| RJAR | 30.07 | 18.97 | 4.57 | 7.25 | 2.65 | 1.20 | 0.89 | 0.33 | 0.00 | 0.22 | 0.12 | 0.00 | 0.67 | 31.90 |
| JAR | 33.75 | 18.13 | 4.06 | 6.67 | 2.23 | 1.13 | 0.95 | 0.49 | 0.40 | 0.23 | 0.30 | 1.09 | 0.94 | 29.50 |
| JAR Avg. | 31.91 | 18.55 | 4.32 | 6.96 | 2.44 | 1.17 | 0.92 | 0.41 | 0.20 | 0.23 | 0.21 | 0.55 | 0.81 | 30.70 |
| JAR1L | 30.80 | 20.50 | 4.86 | 6.34 | 3.41 | 0.67 | 0.84 | 0.41 | 0.40 | 0.20 | 0.37 | 1.29 | 0.80 | 28.90 |
| JAR2L | 35.18 | 18.41 | 4.98 | 6.02 | 3.31 | 0.73 | 0.96 | 0.41 | 0.40 | 0.12 | 0.40 | 0.06 | 0.94 | 27.90 |
| Chemical composition on dry base, wt. % | ||||||||||||||
| RJAR | 44.71 | 28.21 | 6.80 | 10.77 | 3.94 | 1.78 | 1.32 | 0.49 | 0.00 | 0.33 | 0.18 | 0.00 | 0.99 | - |
| JAR | 47.86 | 25.71 | 5.76 | 9.45 | 3.16 | 1.60 | 1.35 | 0.69 | 0.57 | 0.33 | 0.43 | 1.55 | 1.34 | - |
| JAR Avg. | 46.29 | 26.96 | 6.28 | 10.11 | 3.55 | 1.69 | 1.34 | 0.59 | 0.28 | 0.33 | 0.31 | 0.77 | 1.17 | - |
| JAR1L | 43.36 | 28.86 | 6.84 | 8.92 | 4.80 | 0.94 | 1.18 | 0.57 | 0.56 | 0.28 | 0.52 | 1.81 | 1.13 | - |
| JAR2L | 48.80 | 25.54 | 6.91 | 8.35 | 4.59 | 1.01 | 1.33 | 0.57 | 0.55 | 0.17 | 0.56 | 0.09 | 1.30 | - |
| Difference between JAR1L and JAR2L Vs. average JAR, wt. % | ||||||||||||||
| JAR1L | −2.93 | 1.90 | 0.56 | −1.19 | 1.25 | −0.75 | −0.15 | −0.02 | 0.28 | −0.04 | 0.22 | 1.04 | −0.03 | - |
| JAR2L | 2.52 | −1.42 | 0.63 | −1.76 | 1.04 | −0.69 | 0.00 | −0.02 | 0.27 | −0.16 | 0.25 | −0.69 | 0.13 | - |
| pH in Aqueous Suspension | Cd mg L−1 | Pb mg L−1 | As mg L−1 | Cyanides mg kg−1 | Sulfides mg kg−1 | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Permitted | 2–12.5 | 1 | 5 | 5 | 250 | 500 |
| JAR | 3.34 | 64.2 | 4.16 | 0.27 | <39.5 | <51.4 |
| JAR2L | 2.55 | 0.49 | 0.24 | <0.005 | <39.5 | <51.4 |
| Removal, wt. % | - | 94.23 | 99.23 | 98.15 | - | - |
| Element | Zn | Pb | Cu | Cd | As | Mn |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| RJAR | 91.90 | 9.20 | 10.00 | 3.00 | 4.50 | 4.80 |
| JAR average, g kg−1 | 69.59 | 9.75 | 8.96 | 2.11 | 4.58 | 3.44 |
| DESVEST | 9.49 | 1.77 | 0.08 | 0.69 | 0.88 | 0.79 |
| 1 kg of JAR; 5L of solution H2SO4 0.1 M; 5 L H2O; 2 washes with 5L of H2O | ||||||
| JAR2L average, g kg−1 | 54.54 | 9.25 | 7.27 | 0.91 | 3.89 | 2.41 |
| DESVEST | 0.80 | 0.14 | 0.11 | 0.05 | 0.17 | 0.02 |
| Extraction Efficiency, % | 21.62 | 5.16 | 18.78 | 56.71 | 14.97 | 30.04 |
| 1 kg of JAR; 5 L of solution H2SO4 0.1 M; 5 L H2O; 3 washes with 5 L of H2O | ||||||
| JAR3L average, g kg−1 | 41.13 | 8.73 | 8.63 | 1.53 | 4.17 | 2.43 |
| DESVEST | 0.32 | 0.21 | 0.21 | 0.15 | 0.06 | 0.06 |
| Extraction Efficiency, % | 40.89 | 10.43 | 3.59 | 27.33 | 8.93 | 29.26 |
| Extracted Elements | Zn | Pb | Cu | Cd | As | Mn |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Aqueous leaching: 1 kg of JAR; 5.25 L H2O; 3 washes with 3 L of H2O each, mg kg−1 | ||||||
| JAR1L F1 | 1227.92 | 7.93 | 288.49 | 198.08 | 3.62 | 513.77 |
| JAR1L W1 | 543.75 | 4.26 | 41.61 | 67.29 | 0.87 | 79.44 |
| JAR1L W2 | 72.75 | 3.93 | 6.66 | 83.85 | 0.60 | 5.01 |
| JAR1L W3 | 27.69 | 3.60 | 5.52 | 71.88 | 0.69 | 2.37 |
| Acid leaching: 1kg of JAR; 10 L HCl 0.015N; 3 washes with 3 L of H2O, mg kg−1 | ||||||
| JAR1L F2 | 12.00 | 582.10 | 27.60 | 13.00 | 4.00 | 0.00 |
| JAR1L W4 | 2.16 | 50.25 | 3.45 | 1.80 | 0.69 | 0.00 |
| JAR1L W5 | 0.66 | 3.39 | 0.66 | 0.36 | 0.57 | 0.00 |
| JAR1L W6 | 0.66 | 1.17 | 0.39 | 0.00 | 0.00 | 0.00 |
| Aqueous extraction | 1872.11 | 19.72 | 342.28 | 421.10 | 5.78 | 600.59 |
| Acid extraction | 15.48 | 636.91 | 32.10 | 15.16 | 5.26 | 0.00 |
| Total extraction | 1887.59 | 656.63 | 374.38 | 436.26 | 11.04 | 600.59 |
| Aqueous extraction, % | 99.18 | 3.00 | 91.43 | 96.53 | 52.37 | 100.00 |
| Acid extraction, % | 0.82 | 97.00 | 8.57 | 3.47 | 47.63 | 0.00 |
| Fraction of elements extracted with aqueous leaching, % | ||||||
| JAR1L F1 | 65.59 | 40.21 | 84.28 | 47.04 | 62.65 | 85.54 |
| JAR1L W1 | 29.04 | 21.61 | 12.16 | 15.98 | 15.05 | 13.23 |
| JAR1L W2 | 3.89 | 19.93 | 1.95 | 19.91 | 10.38 | 0.83 |
| JAR1L W3 | 1.48 | 18.26 | 1.61 | 17.07 | 11.93 | 0.39 |
| Fraction of elements extracted with acid leaching, % | ||||||
| JAR1L F2 | 77.52 | 91.39 | 85.98 | 85.75 | 76.05 | 0.00 |
| JAR1L W4 | 13.95 | 7.89 | 10.75 | 11.87 | 13.12 | 0.00 |
| JAR1L W5 | 4.26 | 0.53 | 2.06 | 2.37 | 10.84 | 0.00 |
| JAR1L W6 | 4.26 | 0.18 | 1.21 | 0.00 | 0.00 | 0.00 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
López-Martínez, A.M.; Gamero-Melo, P. Mild Conditions Method to Remediate Hazardous Jarosite and Its Application as Adsorbent of Arsenic(V) and Water. Minerals 2023, 13, 1148. https://doi.org/10.3390/min13091148
López-Martínez AM, Gamero-Melo P. Mild Conditions Method to Remediate Hazardous Jarosite and Its Application as Adsorbent of Arsenic(V) and Water. Minerals. 2023; 13(9):1148. https://doi.org/10.3390/min13091148
Chicago/Turabian StyleLópez-Martínez, Arely Monserrat, and Prócoro Gamero-Melo. 2023. "Mild Conditions Method to Remediate Hazardous Jarosite and Its Application as Adsorbent of Arsenic(V) and Water" Minerals 13, no. 9: 1148. https://doi.org/10.3390/min13091148
APA StyleLópez-Martínez, A. M., & Gamero-Melo, P. (2023). Mild Conditions Method to Remediate Hazardous Jarosite and Its Application as Adsorbent of Arsenic(V) and Water. Minerals, 13(9), 1148. https://doi.org/10.3390/min13091148






