Clinopyroxene Compositions of E-MORB-Type Gabbro from Bingdaban Ophiolites in Central Tianshan, NW China: Insights into the Evolution of the Magmatic System and Geodynamic Setting
Abstract
:1. Introduction
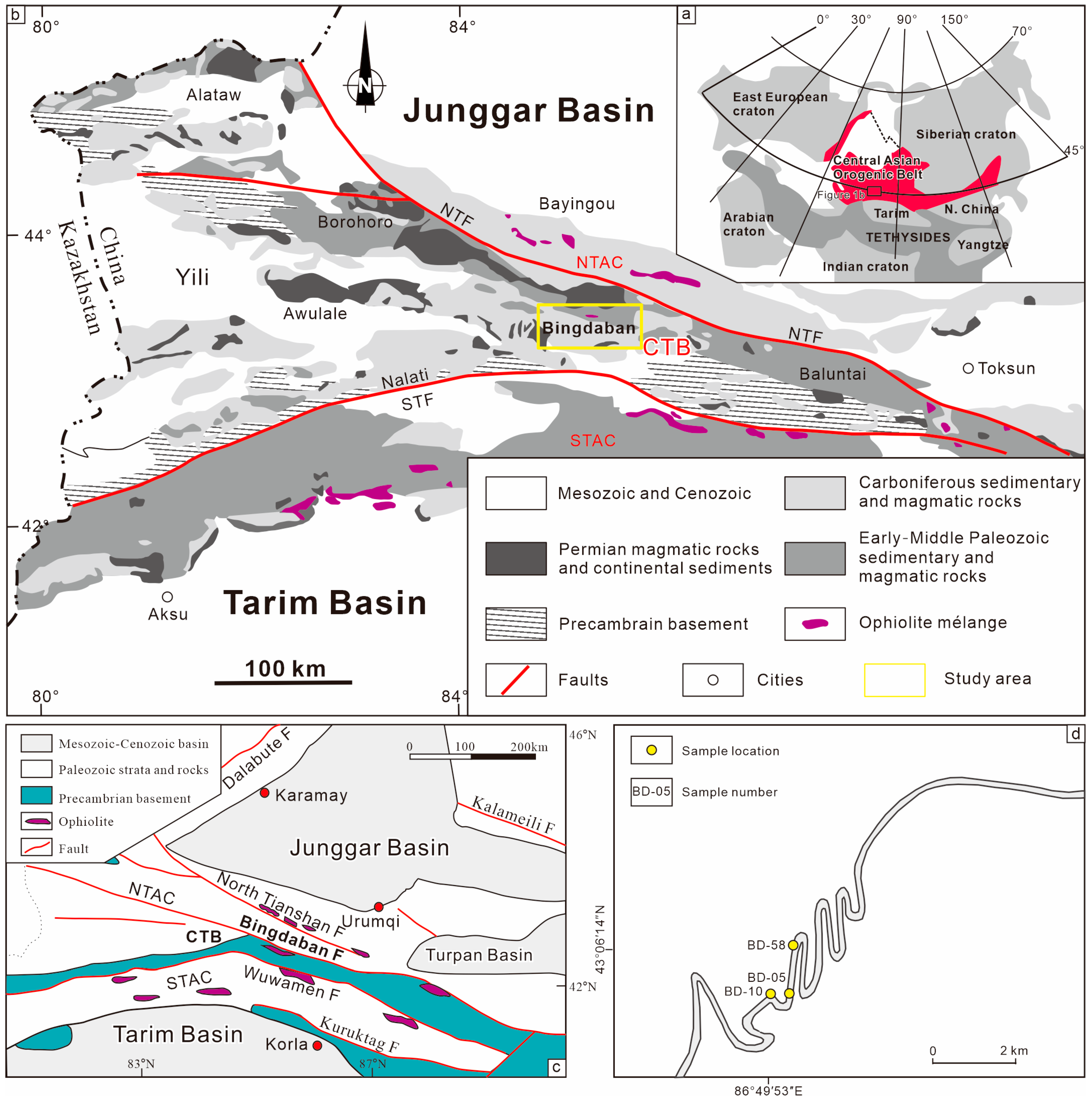
2. Geological Background and Sample Description
3. Analytical Methods
3.1. Zircon Geochronology
3.2. Whole-Rock Major and Trace Elements
3.3. Mineral Chemistry
4. Results
4.1. Zircon U–Pb Geochronology
4.2. Major and Trace Elements
4.3. Mineral Chemistry
5. Discussion
5.1. Magma Series
5.2. Temperatures and Pressures of Magma Formation
5.3. Equilibrium Parental Magma Compositions
5.4. Petrogenesis of E-MORB Gabbro
5.5. Geodynamic Evolution
6. Conclusions
- The crystallization age of zircon in the Bingdaban gabbro was 424.3 ± 5.9 Ma, representing the Late Silurian age of the Bingdaban ophiolite formation.
- The chemical composition of clinopyroxene in the Bingdaban gabbro indicates affinity for the subalkaline tholeiitic magma series. Along with magma evolution, clinopyroxene shows a decrease in Mg# and a slight increase in FeO, indicating an evolutionary trend from Mg- to Fe-rich compositions.
- Temperature and pressure estimations of the clinopyroxene indicate that the magmas were likely formed by high-temperature, low-pressure, shallow sources.
- The melting model calculated from the clinopyroxene showed similarities to the host rock, reflecting the genetic characteristics of an E-MORB setting. The origin of the magma can be attributed to a depleted mantle source with the involvement of minor enriched mantle material, likely forming an initial oceanic basin or immature back-arc basin tectonic setting.
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Burke, K.; Dewey, J.F.; Kidd, W.S.F. World distribution of sutures—The sites of former oceans. Tectonophysics 1977, 40, 69–99. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dewey, J.F. Suture zone complexities: A review. Tectonophysics 1977, 40, 53–67. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dilek, Y.; Furnes, H. Ophiolite genesis and global tectonics: Geochemical and tectonic fingerprinting of ancient oceanic lithosphere. Geol. Soc. Am. Bull. 2011, 123, 387–411. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saccani, E. A new method of discriminating different types of post-Archean ophiolitic basalts and their tectonic significance using Th-Nb and Ce-Dy-Yb systematics. Geosci. Front. 2015, 6, 481–501. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, B.; Faure, M.; Shu, L.S.; Cluzel, D.; Charvet, J.; De Jong, K.; Chen, Y. Paleozoic tectonic evolution of the Yili Block, western Chinese Tianshan. Bull. Soc. Geol. Fr. 2008, 179, 483–490. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Charvet, J.; Shu, L.S.; Laurent-Charvet, S. Paleozoic structural and geodynamic evolution of eastern Tianshan (NW China): Welding of the Tarim and Junggar Plates. Episodes 2007, 30, 162–186. [Google Scholar]
- Shu, L.S.; Charvet, J.; Guo, L.Z.; Lu, H.F.; Laurent-Charvet, S. A large-scale Palaeozoic dextral ductile strike-slip zone: The Aqqikkudug-Weiya zone along the northern margin of the central Tianshan belt, Xinjiang, NW China. Acta Geol. Sin. 1999, 2, 148–162. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, B.; Shu, L.S.; Faure, M.; Jahn, B.M.; Cluzel, D.; Charvet, J.; Chung, S.L.; Meffre, S. Paleozoic tectonics of the southern Chinese Tianshan: Insights from structural, chronological and geochemical studies of the Heiyingshan ophiolitic mélange (NW China). Tectonophysics 2011, 497, 85–104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Windley, B.F.; Allen, M.B.; Zhang, C.; Zhao, Z.Y.; Wang, G.R. Paleozoic accretion and Cenozoic redeformation of the Chinese Tien shan Range, central Asia. Geology 1990, 18, 128–131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, Z.P. Research on Ophiolites in Tianshan and Its Adjacent Areas and Evolution of Paleozoic Ocean Basins; Northwest University: Kirkland, DC, USA, 2007; (In Chinese with English Abstract). [Google Scholar]
- Dong, Y.P.; Zhang, G.W.; Zhou, B.W.; Luo, J.H.; Zhang, C.L.; Xia, L.Q.; Xu, X.Y.; Li, X.M. Determination and Tectonic Significance of Bingdaban Ophiolitic Mellitic Rocks in the Northern Margin of Central Tianshan; Science in China Press: Beijing, China, 2005; pp. 552–560, (In Chinese with English Abstract). [Google Scholar]
- Liu, X.J.; Zhang, Z.G.; Xu, J.F.; Xiao, W.; Shi, Y.; Gong, X.; Tan, Z.J.; Li, R. The youngest Permian Ocean in Central Asian Orogenic Belt: Evidence from Geochronology and Geochemistry of Bingdaban Ophiolitic Mélange in Central Tianshan, northwestern China. Geol. J. 2020, 55, 2062–2079. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nisbet, E.G.; Pearce, J.A. Clinopyroxene composition in mafic lavas from different tectonic settings. Contrib. Miner. Pet. 1977, 63, 149–160. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiao, X.C.; Tang, Y.Q.; Feng, Y.M. Tectonic Evolution of the Northern Xinjiang and Its Adjacent Regions; Geological Publishing House: Beijing, China, 1992; pp. 104–123. [Google Scholar]
- Gao, J.; Long, L.L.; Klemd, R.; Qian, Q.; Liu, D.Y.; Xiong, X.M.; Su, W.; Liu, W.; Wang, Y.T.; Yang, F.Q. Tectonic evolution of the South Tianshan orogen and adjacent regions, NW China: Geochemical and age constraints of granitoid rocks. Int. J. Earth Sci. 2009, 98, 1221–1238. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Long, L.L.; Gao, J.; Klemd, R.; Beier, C.; Qian, Q.; Zhang, X.; Wang, J.B.; Jiang, T. Geochemical and geochronological studies of granitoid rocks from the Western Tianshan Orogen: Implications for continental growth in the southwestern Central Asian Orogenic Belt. Lithos 2011, 126, 321–340. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qian, Q.; Gao, J.; Klemd, R.; He, G.Q.; Song, B.; Liu, D.Y.; Xu, R.H. Early Paleozoic tectonic evolution of the Chinese South Tianshan Orogen: Constraints from SHRIMP zircon U–Pb geochronology and geochemistry of basaltic and dioritic rocks from Xiate, NW China. Int. J. Earth Sci. 2009, 98, 551–569. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.S.; Gao, J.; Klemd, R.; Jiang, T.; Li, J.L.; Zhang, X.; Tan, Z.; Li, L.; Zhu, Z. Geochemistry and geochronology of the Precambrian high-grade metamorphic complex in the Southern Central Tianshan ophiolitic mélange, NW China. Precambrian Res. 2014, 254, 129–148. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alexeiev, D.V.; Biske, Y.S.; Wang, B.; Djenchuraeva, A.V.; Getman, O.F.; Aristov, V.A.; Kröner, A.; Liu, H.; Zhong, L. Tectono-stratigraphic framework and Palaeo-zoic evolution of the Chinese South Tianshan. Geotectonics 2015, 49, 93–122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Allen, M.B.; Windley, B.F.; Zhang, C. Paleozoic collisional tectonics and magmatism of the Chinese Tien shan, Central Asia. Tectonophysics 1993, 220, 89–115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, L.; Chen, H.Y.; Liu, C.F.; Zheng, Y. Ore genesis of the Saridala gold deposit, Western Tianshan, NW China: Constraints from fluid inclusion, S-Pb isotopes and 40Ar/39Ar dating. Ore. Geol. Rev. 2018, 100, 63–76. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Şengör, A.M.C.; Natal’in, B.A.; Burtman, V.S. Evolution of the Altaid tectonic collage and Palaeozoic crustal growth in Eurasia. Nature 1993, 364, 299–307. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, G.W.; Yang, J.X.; Liu, R.; Wang, L.X.; Wang, K. Geochemistry of mafic volcanics in the Bayingou ophiolitic mélange, Western Tianshan, NW China: Implications for magma genesis and tectonic setting. Lithos 2020, 352–353, 105292. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dong, Y.P.; Zhou, D.W.; Zhang, G.W.; Zhao, X.; Luo, J.H.; Xu, J.G. Geology and geochemistry of the Gangou ophiolitic melange at the northern margin of the Middle Tianshan Belt. Acta Pet. Sin. 2006, 22, 49–56, (In Chinese with English Abstract). [Google Scholar]
- Zhong, L.L.; Wang, B.; Shu, L.S.; Liu, H.S.; Mu, L.X.; Ma, Y.Z.; Zhai, Y.Z. Structural overprints of Early Paleozoic arc-related intrusive rocks in the Chinese Central Tianshan: Implications for Paleozoic accretionary tectonics in SW Central Asian Orogenic Belts. J. Asian Earth Sci. 2015, 113, 194–217. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- XBGMR. 1:200,000 Geological Map. Baluntai Sheet (K-45-10) 1977. Accessed on: 10 June 2021. 10 June.
- Chen, X.Y.; Wang, Y.J.; Sun, L.H.; Fan, W.M. Zircon SHRIMP U-Pb dating of the granitic gneisses from Bingdaban and Laserdundaban (Tianshan Orogen) and their geological significances. Geochimica 2009, 38, 424–431, (In Chinese with English Abstract). [Google Scholar]
- Xiao, W.J.; Windley, B.F.; Allen, M.B.; Han, C.M. Paleozoic multiple accretionary and collisional tectonics of the Chinese Tianshan orogenic collage. Gondwana Res. 2013, 23, 1316–1341. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, X.J.; Xu, J.F.; Castillo, P.R.; Xiao, W.J.; Shi, Y.; Zhang, Z.; Wang, X.-C.; Ao, S.; Wang, B.; Hu, R.; et al. Long-lived low Th/U Pacific-type isotopic mantle domain: Constraints from Nd and Pb isotopes of the Paleo-Asian Ocean mantle. Earth Planet Sci. Lett. 2021, 567, 117006. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, Y.J.; Liu, X.J.; Xiao, W.J.; Gong, X.H.; Liu, X.; Xiao, Y.; Zhang, Z.G.; Liu, P.D. Tectonic evolution of circum-Rodinia subduction: Evidence from Neoproterozoic A-type granitic magmatism in the Central Tianshan Block, northwest China. Precambrian Res. 2023, 387, 106976. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ludwig, K. User’s Manual for Isoplot 3.00: A Geochronological Toolkit for Microsoft Excel; Berkeley Geochronology Center: Berkeley, CA, USA, 2003; (Special Publications No. 4). [Google Scholar]
- Middlemost, E.A.K. Naming materials in the magma/igneous rock system. Earth-Sci. Rev. 1994, 37, 215–224. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miyashiro, A. Volcanic rock series in island arcs and active continental margins. Am. J. Sci. 1974, 274, 321–355. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, S.S.; McDonough, W.F. Chemical and isotopic systematics of oceanic basalts: Implications for mantle composition and processes. Geol. Soc. Spec. Publ. 1989, 42, 313–345. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Morimoto, N. Nomenclature of pyroxenes. Miner. Pet. 1988, 39, 55–76. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qiu, J.X.; Liao, Q.A. Petrogenesis and Cpx mineralchemistry of Cenozoic basalts from Zhejiang and Fujian of eastern China. Volcanol. Miner. Resour. 1996, 17, 16–25, (In Chinese with English Abstract). [Google Scholar]
- Kou, C.H.; Liu, Y.X.; Li, T.D.; Ding, X.Z.; Zhang, H.; Liu, Y. Petrogenesis and tectonic implications of the neoproterozoic mafic-ultramafic rocks in the western Jiangnan Orogen: Insights from in situ analysis of clinopyroxenes. Lithos 2021, 392–393, 106156. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zou, J.X.; Liu, X.F.; Deng, J.H.; Li, C.H.; Huang, Y.P.; Dong, Y.; Yi, L.W. Mineralogical composition characteristics and geological significance of the clinopyroxene from ultrabasic-basic rocks at Luoji Village, Shangri-la County, Yunnan Province. Acta Pet. Miner. 2012, 31, 701–711, (In Chinese with English Abstract). [Google Scholar]
- Le Bas, M.J. The role of aluminum in igneous clinopyroxenes with relation to their parentage. Am. J. Sci. 1962, 260, 267–288. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Putirka, K.D. Thermometers and barometers for volcanic systems. Rev. Miner. Geochem. 2008, 69, 61–120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Putirka, K.D.; Mikaelian, H.; Ryerson, F.; Shaw, H. New clinopyroxene-liquid thermobarometers for mafic, evolved, and volatile-bearing lava compositions, with applications to lavas from Tibet and the Snake River Plain, Idaho. Am. Miner. 2003, 88, 1542–1554. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Irving, A.J.; Frey, F.A. Trace element abundances in megacrysts and their host basalts: Constraints on partition coefficients and megacryst genesis. Geochim. Cosmochim. Acta 1984, 48, 1201–1221. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liotard, J.M.; Briot, D.; Boivin, P. Petrological and geochemical relationships between pyroxene megacrysts and associated alkali-basalts from Massif Central (France). Contrib. Miner. Pet. 1988, 98, 81–90. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wood, B.J.; Blundy, J.D. A predictive model for rare earth element partitioning between clinopyroxene and anhydrous silicate melt. Contrib. Miner. Pet. 1997, 129, 166–181. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Neave, D.A.; Putirka, K.D. A new clinopyroxene-liquid barometer, and implications for magma storage pressures under Icelandic rift zones. Am. Miner. 2017, 102, 777–794. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kinzler, R.J. Melting of mantle peridotite at pressures approaching the spinel to garnet transition: Application to Mid-Ocean Ridge basalt petrogenesis. J. Geophys. Res. 1997, 102, 853–874. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hart, S.R.; Dunn, T. Experimental cpx/melt partitioning of 24 trace elements. Contr. Mineral. Petrol. 1993, 113, 1–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arevalo, R.; McDonough, W.F. Chemical variations and regional diversity observed in MORB. Chem. Geol. 2010, 271, 70–85. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Z.X.; Li, C.L.; Nikolai, P.; Elena, I.; Yu, X.Q.; Zhou, G.; Xiao, W.F.; Han, S.Q.; Zailabidin, H.; Nurgazy, T.; et al. Tectonic division and Paleozoic ocean-continent transition in Western Tianshan Orogen. Geol. China 2017, 44, 623–641, (In Chinese with English Abstract). [Google Scholar]
- Liu, X.J.; Xu, J.F.; Wang, S.Q.; Hou, Q.Y.; Bai, Z.H.; Lei, M. Geochemistry and dating of E-MORB type mafic rocks from Dalabute ophiolite in West Junggar, Xinjiang and geological implications. Acta Petrol. Sin. 2009, 25, 1373–1389, (In Chinese with English Abstract). [Google Scholar]
- Guo, A.L.; Zhang, G.W.; Sun, Y.G.; Zheng, J.K.; Liu, Y.; Wang, J.Q. Geochemical and spatial distribution characteristics of OIB and MORB in the Animaqing ophiolitic belt: Evidence of hot spot tectonics in the ancient ocean ridge of Maji snow mountain. Sci. China 2006, 36, 618–629, (In Chinese with English Abstract). [Google Scholar]
- Donnelly, K.E.; Goldstein, S.L.; Langmuir, C.H.; Spiegelman, M. Origin of enriched ocean ridge basalts and implications for mantle dynamics. Earth Planet Sci. Lett. 2004, 226, 347–366. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schilling, J.-G. Iceland mantle plume: Geochemical study of Reykjanes Ridge. Nature 1973, 242, 565–571. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ulrich, M.; Hémond, C.; Nonnotte, P.; Jochum, K.P. OIB/seamount recycling as a possible process for E-MORB genesis. Geochem. Geophys. Geosyst. 2012, 13, 1–24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.; Su, Y.P.; Zheng, J.P.; Belousova, E.A.; Chen, M.; Dai, H.K.; Zhou, X. Petrogenesis of early Carboniferous bimodal-type volcanic rocks from the Junggar Basin (NW China) with implications for Phanerozoic crustal growth in Central Asian Orogenic Belt. Gondwana Res. 2021, 89, 220–237. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rudnick, R.; Gao, S. Composition of the continental crust. Treatise Geochem. 2003, 3, 1–64. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pearce, J.A. The role of sub-continental lithosphere in magma genesis at destructive plate margins. In Continental Basalts and Mantle Xenoliths; Hawkesworth, C.J., Norry, M.J., Eds.; Shiva: Nantwich, UK, 1983; pp. 230–249. [Google Scholar]
- Windley, B.F.; Alexeiev, D.; Xiao, W.J.; Kröner, A.; Badarch, G. Tectonic models for accretion of the Central Asian Orogenic Belt. J. Geol. Soc. 2007, 164, 31–47. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.R.; Chen, W.F.; Zhang, Q.; Jiao, S.T.; Yang, J.; Pan, Z.J.; Wang, S.H. Preliminary research on data mining of NMORBand E-MORB: Discussion on method of the basalt discrimination diagrams and the character of MORB’s mantle source. Acta Petrol. Sin. 2017, 33, 993–1005, (In Chinese with English Abstract). [Google Scholar]
- Charvet, J.; Shu, L.S.; Laurent-Charvet, S.; Wang, B.; Faure, M.; Cluzel, D.; Chen, Y.; De Jong, K.D. Palaeozoic tectonic evolution of the Tianshan belt, NW China. Sci. China Earth Sci. 2011, 54, 166–184. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]













Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Song, Y.; Liu, X.; Xiao, Y.; Liu, X.; Tian, H. Clinopyroxene Compositions of E-MORB-Type Gabbro from Bingdaban Ophiolites in Central Tianshan, NW China: Insights into the Evolution of the Magmatic System and Geodynamic Setting. Minerals 2023, 13, 1232. https://doi.org/10.3390/min13091232
Song Y, Liu X, Xiao Y, Liu X, Tian H. Clinopyroxene Compositions of E-MORB-Type Gabbro from Bingdaban Ophiolites in Central Tianshan, NW China: Insights into the Evolution of the Magmatic System and Geodynamic Setting. Minerals. 2023; 13(9):1232. https://doi.org/10.3390/min13091232
Chicago/Turabian StyleSong, Yujia, Xijun Liu, Yao Xiao, Xiao Liu, and Hao Tian. 2023. "Clinopyroxene Compositions of E-MORB-Type Gabbro from Bingdaban Ophiolites in Central Tianshan, NW China: Insights into the Evolution of the Magmatic System and Geodynamic Setting" Minerals 13, no. 9: 1232. https://doi.org/10.3390/min13091232
APA StyleSong, Y., Liu, X., Xiao, Y., Liu, X., & Tian, H. (2023). Clinopyroxene Compositions of E-MORB-Type Gabbro from Bingdaban Ophiolites in Central Tianshan, NW China: Insights into the Evolution of the Magmatic System and Geodynamic Setting. Minerals, 13(9), 1232. https://doi.org/10.3390/min13091232







