Characteristics and Influencing Factors of the Granite Weathering Profile: A Case Study of a High Latitude Area in Northeastern China
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
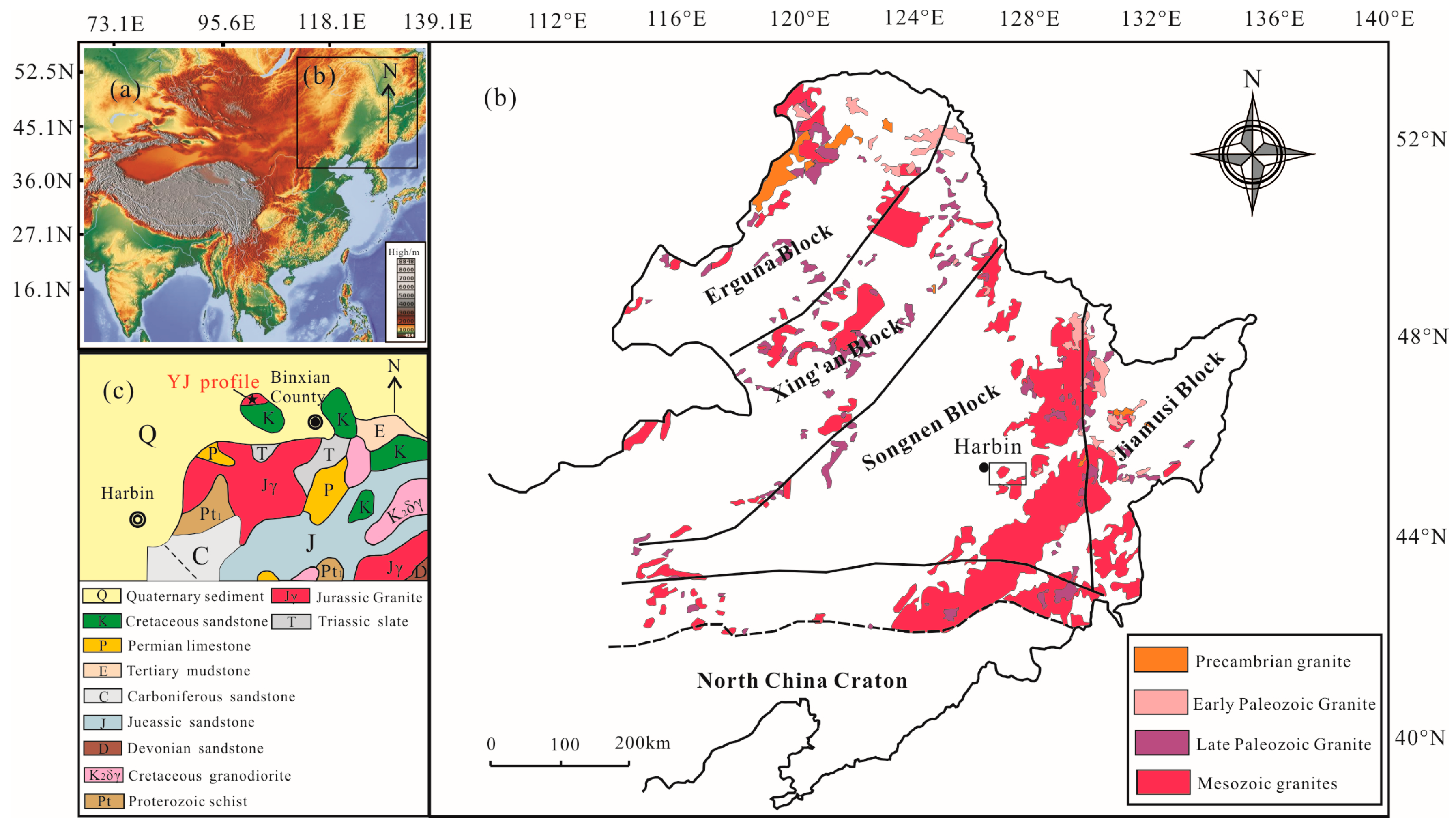
2.1. Regional Setting
2.2. Weathering Profile Description and Sampling
2.3. Laboratory Analysis
2.3.1. Element Geochemistry
2.3.2. Heavy Mineral Identification
2.3.3. Sr-Nd Isotope Analysis
2.3.4. Magnetic Susceptibility Test
2.3.5. Chromaticity Analysis
2.3.6. Loss on Ignition Test
2.4. Mathematical Calculation
2.4.1. Calculation of Chemical Weathering Index
2.4.2. Mass Transfer Calculations
2.4.3. Ce and Eu Anomaly Calculation
2.4.4. Calculation of Chromaticity and Frequency-Dependent Susceptibility
3. Results
3.1. Granite Parent Rock
3.2. Heavy Minerals and Geochemistry of Weathering Profile
3.2.1. Major Elements
3.2.2. Trace and Rare Earth Elements
3.2.3. Sr-Nd Isotopic Composition
3.2.4. Heavy Mineral Characteristics
3.3. Characteristics of Chromaticity and Magnetic Susceptibility
4. Discussion
4.1. Profile Weathering Characteristics
4.2. Effect of Chemical Weathering on the Weathering Granite
4.2.1. Property Determination of the Granite Weathering Products

4.2.2. Impact of Weathering on the Elemental and Mineral Composition of Granite
4.3. Influence of Foreign Substances
4.4. Effects of Biological Activities
4.5. Environmental Significance of the Granite Weathering Profile
5. Conclusions
- The granite has experienced a combination of physical and chemical weathering during the weathering process. The physical weathering is strong, resulting in a large number of cracks in the rock, while the chemical weathering process occurs mainly in the initial stage, as the highly-developed chemical weathering profile cannot develop because of the intervention of physical weathering before chemical weathering produces highly weathered minerals.
- The binary diagram (e.g., TiO2-Zr, and La/Sc-Co/Th) and geochemical genes (LG01 and LG03) reveal that the weathering products have a good inheritance from the parent rock. The influence of chemical weathering on the granite parent rock can be revealed through the characteristics of the elements and minerals in the weathering products.
- The Sr-Nd isotope, Th/Zr ratio, and CDF indicate an input of external materials during granite weathering. The ΔAl/Ti ratios and χfd% indicate the existence of biological activities during granite weathering. At the same time, the geochemical gene (LG03) also indicates the influence of the addition of external materials and biological activities on the weathering of granite.
- A comprehensive analysis shows that the Yingjie granite weathering profile belongs to the kinetic-limited weathering profile with a limited supply, and the weathering regime of the profile does not vary in geology time. The low temperature, low precipitation, and weak hydrological cycle in the study area inhibit the leaching of mobile cations from the regolith, resulting in rock weathering at the initial stage of chemical weathering.
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- West, A.; Galy, A.; Bickle, M. Tectonic and Climatic Controls on Silicate Weathering. Earth Planet. Sci. Lett. 2005, 235, 211–228. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bataille, C.P.; Willis, A.; Yang, X.; Liu, X.M. Continental Igneous Rock Composition: A Major Control of Past Global Chemical Weathering. Sci. Adv. 2017, 3, e1602183. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mao, H.; Zhao, Z.; Cui, L.; Liu, C. The Influence of Climate and Topography on Chemical Weathering of Granitic Regoliths in the Monsoon Region of China. Acta Geochim. 2018, 37, 758–768. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brantley, S.L.; Lebedeva, M. Learning to Read the Chemistry of Regolith to Understand the Critical Zone. Annu. Rev. Earth Planet. Sci. 2011, 39, 387–416. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Braga, M.A.S.; Prudêncio, M.I.; Gouveia, M.A. REE Mobilization, Fractionation and Precipitation during Weathering of Basalts. Chem. Geol. 1993, 107, 251–254. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rye, R. Geology and Geochemistry of Paleosols Developed on the Hekpoort Basalt, Pretoria Group, South Africa. Am. J. Sci. 2000, 300, 85–141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ma, J.L.; Wei, G.J.; Xu, Y.G.; Long, W.G.; Sun, W.D. Mobilization and Re-Distribution of Major and Trace Elements during Extreme Weathering of Basalt in Hainan Island, South China. Geochim. Cosmochim. Acta 2007, 71, 3223–3237. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, J.; Wei, G.; Xu, Y.; Long, W. Variations of Sr–Nd–Hf Isotopic Systematics in Basalt during Intensive Weathering. Chem. Geol. 2010, 269, 376–385. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Babechuk, M.G.; Widdowson, M.; Kamber, B.S. Quantifying Chemical Weathering Intensity and Trace Element Release from Two Contrasting Basalt Profiles, Deccan Traps, India. Chem. Geol. 2014, 363, 56–75. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Law, K.R.; Nesbitt, H.W.; Longstaffe, F.J. Weathering of Granitic Tills and the Genesis of a Podzol. Am. J. Sci. 1991, 291, 940–976. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mongelli, G. REE and Other Trace Elements in a Granitic Weathering Profile from “Serre”, Southern Italy. Chem. Geol. 1993, 103, 17–25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Minařík, L.; Žigová, A.; Bendl, J.; Skřivan, P.; Št’astný, M. The Behaviour of Rare-Earth Elements and Y during the Rock Weathering and Soil Formation in the Říčany Granite Massif, Central Bohemia. Sci. Total Environ. 1998, 215, 101–111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- White, A.F.; Bullen, T.D.; Schulz, M.S.; Blum, A.E.; Huntington, T.G.; Peters, N.E. Differential Rates of Feldspar Weathering in Granitic Regoliths. Geochim. Cosmochim. Acta 2001, 65, 847–869. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jeong, G.Y.; Kim, H.B. Mineralogy, Chemistry, and Formation of Oxidized Biotite in the Weathering Profile of Granitic Rocks. Am. Mineral. 2003, 88, 352–364. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kirschbaum, A.; Martínez, E.; Pettinari, G.; Herrero, S. Weathering Profiles in Granites, Sierra Norte (Córdoba, Argentina). J. South Am. Earth Sci. 2005, 19, 479–493. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Négrel, P. Water–Granite Interaction: Clues from Strontium, Neodymium and Rare Earth Elements in Soil and Waters. Appl. Geochem. 2006, 21, 1432–1454. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ceryan, S.; Zorlu, K.; Gokceoglu, C.; Temel, A. The Use of Cation Packing Index for Characterizing the Weathering Degree of Granitic Rocks. Eng. Geol. 2008, 98, 60–74. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Duzgoren-Aydin, N.S.; Aydin, A. Distribution of Rare Earth Elements and Oxyhydroxide Phases within a Weathered Felsic Igneous Profile in Hong Kong. J. Asian Earth Sci. 2009, 34, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Land, M.; Öhlander, B. Chemical weathering rates, erosion rates and mobility of major and trace elements in a boreal granitic till. Aquat. Geochem. 2000, 6, 435–460. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Blum, J.D.; Erel, Y. Rb-Sr Isotope Systematics of a Granitic Soil Chronosequence: The Importance of Biotite Weathering. Geochim. Cosmochim. Acta 1997, 61, 3193–3204. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pett-Ridge, J.C.; Derry, L.A.; Kurtz, A.C. Sr Isotopes as a Tracer of Weathering Processes and Dust Inputs in a Tropical Granitoid Watershed, Luquillo Mountains, Puerto Rico. Geochim. Cosmochim. Acta 2009, 73, 25–43. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shalkowski, A.; Kodama, Y.; Nakano, S. The Assessment of Weathering Stages in Granites Using an EC/pH Meter. Geomorphology 2009, 105, 253–260. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rasmussen, C.; Brantley, S.; Richter, D.D.; Blum, A.; Dixon, J.; White, A.F. Strong Climate and Tectonic Control on Plagioclase Weathering in Granitic Terrain. Earth Planet. Sci. Lett. 2011, 301, 521–530. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Riebe, C.S.; Kirchner, J.W.; Finkel, R.C. Erosional and Climatic Effects on Long-Term Chemical Weathering Rates in Granitic Landscapes Spanning Diverse Climate Regimes. Earth Planet. Sci. Lett. 2004, 224, 547–562. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- White, A.F.; Blum, A.E.; Bullen, T.D.; Vivit, D.V.; Schulz, M.; Fitzpatrick, J. The Effect of Temperature on Experimental and Natural Chemical Weathering Rates of Granitoid Rocks. Geochim. Cosmochim. Acta 1999, 63, 3277–3291. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Panahi, A.; Young, G.M.; Rainbird, R.H. Behavior of Major and Trace Elements (Including REE) during Paleoproterozoic Pedogenesis and Diagenetic Alteration of an Archean Granite near Ville Marie, Québec, Canada. Geochim. Cosmochim. Acta 2000, 64, 2199–2220. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Taunton, A.E.; Welch, S.A.; Banfield, J.F. Geomicrobiological Controls on Light Rare Earth Element, Y and Ba Distributions during Granite Weathering and Soil Formation. J. Alloys Compd. 2000, 303–304, 30–36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Taunton, A.E.; Welch, S.A.; Banfield, J.F. Microbial Controls on Phosphate and Lanthanide Distributions during Granite Weathering and Soil Formation. Chem. Geol. 2000, 169, 371–382. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bao, Z.; Zhao, Z. Geochemistry of Mineralization with Exchangeable REY in the Weathering Crusts of Granitic Rocks in South China. Ore Geol. Rev. 2008, 33, 519–535. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Babechuk, M.G.; Widdowson, M.; Murphy, M.; Kamber, B.S. A Combined Y/Ho, High Field Strength Element (HFSE) and Nd Isotope Perspective on Basalt Weathering, Deccan Traps, India. Chem. Geol. 2015, 396, 25–41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dixon, J.L.; Von Blanckenburg, F. Soils as Pacemakers and Limiters of Global Silicate Weathering. Comptes Rendus Geosci. 2012, 344, 597–609. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dere, A.L.; White, T.S.; April, R.H.; Reynolds, B.; Miller, T.E.; Knapp, E.P.; McKay, L.D.; Brantley, S.L. Climate Dependence of Feldspar Weathering in Shale Soils along a Latitudinal Gradient. Geochim. Cosmochim. Acta 2013, 122, 101–126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hahm, W.J.; Riebe, C.S.; Lukens, C.E.; Araki, S. Bedrock Composition Regulates Mountain Ecosystems and Landscape Evolution. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2014, 111, 3338–3343. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hayes, N.R.; Buss, H.L.; Moore, O.W.; Krám, P.; Pancost, R.D. Controls on Granitic Weathering Fronts in Contrasting Climates. Chem. Geol. 2020, 535, 119450. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maher, K. The Dependence of Chemical Weathering Rates on Fluid Residence Time. Earth Planet. Sci. Lett. 2010, 294, 101–110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Riebe, C.S.; Kirchner, J.W.; Granger, D.E.; Finkel, R.C. Strong Tectonic and Weak Climatic Control of Long-Term Chemical Weathering Rates. Geology 2001, 29, 511. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- St. Clair, J.; Moon, S.; Holbrook, W.S.; Perron, J.T.; Riebe, C.S.; Martel, S.J.; Carr, B.; Harman, C.; Singha, K.; Richter, D.D. Geophysical Imaging Reveals Topographic Stress Control of Bedrock Weathering. Science 2015, 350, 534–538. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- White, A.F.; Blum, A.E. Effects of Climate on Chemical Weathering in Watersheds. Geochim. Cosmochim. Acta 1995, 59, 1729–1747. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gabet, E.J.; Mudd, S.M. A Theoretical Model Coupling Chemical Weathering Rates with Denudation Rates. Geology 2009, 37, 151–154. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Riebe, C.S.; Hahm, W.J.; Brantley, S.L. Controls on Deep Critical Zone Architecture: A Historical Review and Four Testable Hypotheses. Earth Surf. Process. Landf. 2017, 42, 128–156. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ferrier, K.L.; Riebe, C.S.; Jesse Hahm, W. Testing for Supply-limited and Kinetic-limited Chemical Erosion in Field Measurements of Regolith Production and Chemical Depletion. Geochem. Geophys. Geosystems 2016, 17, 2270–2285. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Anderson, S.P. Breaking It Down: Mechanical Processes in the Weathering Engine. Elements 2019, 15, 247–252. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eppes, M.; Keanini, R. Mechanical Weathering and Rock Erosion by Climate-dependent Subcritical Cracking. Rev. Geophys. 2017, 55, 470–508. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eppes, M.C.; Magi, B.; Scheff, J.; Warren, K.; Ching, S.; Feng, T. Warmer, Wetter Climates Accelerate Mechanical Weathering in Field Data, Independent of Stress-Loading. Geophys. Res. Lett. 2020, 47, 2020GL089062. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Norton, K.P.; Von Blanckenburg, F. Silicate Weathering of Soil-Mantled Slopes in an Active Alpine Landscape. Geochim. Cosmochim. Acta 2010, 74, 5243–5258. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schoonejans, J.; Vanacker, V.; Opfergelt, S.; Ameijeiras-Mariño, Y.; Christl, M. Kinetically Limited Weathering at Low Denudation Rates in Semiarid Climatic Conditions. J. Geophys. Res. Earth Surf. 2016, 121, 336–350. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ferrier, K.L.; Kirchner, J.W. Effects of Physical Erosion on Chemical Denudation Rates: A Numerical Modeling Study of Soil-Mantled Hillslopes. Earth Planet. Sci. Lett. 2008, 272, 591–599. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ulusoy, M. Different Igneous Masonry Blocks and Salt Crystal Weathering Rates in the Architecture of Historical City of Konya. Build. Environ. 2007, 42, 3014–3024. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kalintsev, A.; Brugger, J.; Etschmann, B.; Ram, R. An in Situ, Micro-Scale Investigation of Inorganically and Organically Driven Rare-Earth Remobilisation during Weathering. Mineral. Mag. 2021, 85, 105–116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tang, J.; Johannesson, K.H. Rare Earth Elements Adsorption onto Carrizo Sand: Influence of Strong Solution Complexation. Chem. Geol. 2010, 279, 120–133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, M.; Liang, X.; Ma, L.; Huang, J.; He, H.; Zhu, J. Adsorption of REEs on Kaolinite and Halloysite: A Link to the REE Distribution on Clays in the Weathering Crust of Granite. Chem. Geol. 2019, 525, 210–217. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, M.Y.H.; Zhou, M.-F. The Role of Clay Minerals in Formation of the Regolith-Hosted Heavy Rare Earth Element Deposits. Am. Mineral. 2020, 105, 92–108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, Y.; Ma, L.; Li, X.; Wang, H.; Liang, X.; Zhu, J.; He, H. Mobilization and Fractionation of Rare Earth Elements during Experimental Bio-Weathering of Granites. Geochim. Cosmochim. Acta 2023, 343, 384–395. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Das, A.; Krishnaswami, S. Elemental Geochemistry of River Sediments from the Deccan Traps, India: Implications to Sources of Elements and Their Mobility during Basalt–Water Interaction. Chem. Geol. 2007, 242, 232–254. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wayne Nesbitt, H.; Markovics, G. Weathering of Granodioritic Crust, Long-Term Storage of Elements in Weathering Profiles, and Petrogenesis of Siliciclastic Sediments. Geochim. Cosmochim. Acta 1997, 61, 1653–1670. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Braun, J.-J.; Descloitres, M.; Riotte, J.; Fleury, S.; Barbiéro, L.; Boeglin, J.-L.; Violette, A.; Lacarce, E.; Ruiz, L.; Sekhar, M.; et al. Regolith Mass Balance Inferred from Combined Mineralogical, Geochemical and Geophysical Studies: Mule Hole Gneissic Watershed, South India. Geochim. Cosmochim. Acta 2009, 73, 935–961. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brimhall, G.H.; Dietrich, W.E. Constitutive Mass Balance Relations between Chemical Composition, Volume, Density, Porosity, and Strain in Metasomatic Hydrochemical Systems: Results on Weathering and Pedogenesis. Geochim. Cosmochim. Acta 1987, 51, 567–587. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Little, M.G.; Aeolus Lee, C.-T. On the Formation of an Inverted Weathering Profile on Mount Kilimanjaro, Tanzania: Buried Paleosol or Groundwater Weathering? Chem. Geol. 2006, 235, 205–221. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Riebe, C.S.; Kirchner, J.W.; Finkel, R.C. Long-Term Rates of Chemical Weathering and Physical Erosion from Cosmogenic Nuclides and Geochemical Mass Balance. Geochim. Cosmochim. Acta 2003, 67, 4411–4427. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Braun, J.J.; Viers, J.; Dupré, B.; Polve, M.; Ndam, J.; Muller, J.P. Solid/Liquid REE Fractionation in the Lateritic System of Goyoum, East Cameroon: The Implication for the Present Dynamics of the Soil Covers of the Humid Tropical Regions. Geochim. Cosmochim. Acta 1998, 62, 273–299. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shotyk, W.; Weiss, D.; Kramers, J.D.; Frei, R.; Cheburkin, A.K.; Gloor, M.; Reese, S. Geochemistry of the Peat Bog at Etang de La Gruère, Jura Mountains, Switzerland, and Its Record of Atmospheric Pb and Lithogenic Trace Metals (Sc, Ti, Y, Zr, and REE) since 12,370 14 C Yr BP. Geochim. Cosmochim. Acta 2001, 65, 2337–2360. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Millero, F.J. Stability Constants for the Formation of Rare Earth-Inorganic Complexes as a Function of Ionic Strength. Geochim. Cosmochim. Acta 1992, 56, 3123–3132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Johannesson, K.H.; Zhou, X. Origin of Middle Rare Earth Element Enrichments in Acid Waters of a Canadian High Arctic Lake. Geochim. Cosmochim. Acta 1999, 63, 153–165. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Möller, P.; Bau, M. Rare-Earth Patterns with Positive Cerium Anomaly in Alkaline Waters from Lake Van, Turkey. Earth Planet. Sci. Lett. 1993, 117, 671–676. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Johannesson, K.H.; Zhou, X.; Guo, C.; Stetzenbach, K.J.; Hodge, V.F. Origin of Rare Earth Element Signatures in Groundwaters of Circumneutral pH from Southern Nevada and Eastern California, USA. Chem. Geol. 2000, 164, 239–257. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Öhlander, B.; Land, M.; Ingri, J.; Widerlund, A. Mobility of Rare Earth Elements during Weathering of till in Northern Sweden. Appl. Geochem. 1996, 11, 93–99. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aubert, D.; Stille, P.; Probst, A. REE Fractionation during Granite Weathering and Removal by Waters and Suspended Loads: Sr and Nd Isotopic Evidence. Geochim. Cosmochim. Acta 2001, 65, 387–406. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Compton, J.S.; White, R.A.; Smith, M. Rare Earth Element Behavior in Soils and Salt Pan Sediments of a Semi-Arid Granitic Terrain in the Western Cape, South Africa. Chem. Geol. 2003, 201, 239–255. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Galán, E.; Fernández-Caliani, J.C.; Miras, A.; Aparicio, P.; Márquez, M.G. Residence and Fractionation of Rare Earth Elements during Kaolinization of Alkaline Peraluminous Granites in NW Spain. Clay Miner. 2007, 42, 341–352. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yusoff, Z.M.; Ngwenya, B.T.; Parsons, I. Mobility and Fractionation of REEs during Deep Weathering of Geochemically Contrasting Granites in a Tropical Setting, Malaysia. Chem. Geol. 2013, 349–350, 71–86. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vázquez-Ortega, A.; Perdrial, J.; Harpold, A.; Zapata-Ríos, X.; Rasmussen, C.; McIntosh, J.; Schaap, M.; Pelletier, J.D.; Brooks, P.D.; Amistadi, M.K.; et al. Rare Earth Elements as Reactive Tracers of Biogeochemical Weathering in Forested Rhyolitic Terrain. Chem. Geol. 2015, 391, 19–32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, C.Y.; Hseu, Z.Y. Pedochemical Behaviors of Rare Earth Elements in Soil Profiles along a Lithosequence in Eastern Taiwan. Catena 2023, 225, 107047. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Middelburg, J.J.; Van Der Weijden, C.H.; Woittiez, J.R.W. Chemical Processes Affecting the Mobility of Major, Minor and Trace Elements during Weathering of Granitic Rocks. Chem. Geol. 1988, 68, 253–273. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, C.; Song, L.K.; Liu, L.W. Research on the rare earth element existence in Guposhan main granite mass. Mineral. Petrol. 1992, 12, 38–45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kang, C.G.; Li, C.A.; Wang, J.T.; Shao, L. Heavy Minerals Characteristics of Sediments in Jianghan Plain and Its Indication to the Forming of the Three Gorges. Earth Sci.—J. China Univ. Geosci. 2009, 34, 419–427. [Google Scholar]
- Ma, Y.J.; Liu, C.Q. Geochemistry of strontium isotopes in the crust weathering system. Acta Mineral. Sin. 1998, 18, 350–358. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, Y.; Liu, C. Using strontium isotopes to trace nutrient element circulation and hydrochemical evolution within an ecosystem. Adv. Earth Sci. 1999, 14, 377. [Google Scholar]
- Nesbitt, H.W.; Markovics, G.; Price, R.C. Chemical Processes Affecting Alkalis and Alkaline Earths during Continental Weathering. Geochim. Cosmochim. Acta 1980, 44, 1659–1666. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fisher, C.M.; Paton, C.; Pearson, D.G.; Sarkar, C.; Luo, Y.; Tersmette, D.B.; Chacko, T. Data Reduction of Laser Ablation Split-Stream (LASS) Analyses Using Newly Developed Features Within Iolite: With Applications to Lu-Hf + U-Pb in Detrital Zircon and Sm-Nd + U-Pb in Igneous Monazite. Geochem. Geophys. Geosystems 2017, 18, 4604–4622. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, J.; Li, G.; Yang, J.; Rao, W.; Lu, H.; Balsam, W.; Sun, Y.; Ji, J. Nd and Sr Isotopic Characteristics of Chinese Deserts: Implications for the Provenances of Asian Dust. Geochim. Cosmochim. Acta 2007, 71, 3904–3914. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, Y.; Galy, A.; Fang, X.; Yang, R.; Zhang, W.; Song, B.; Liu, Y.; Han, W.; Zhang, W.; Yang, S. Neodymium Isotopic Constraints on Cenozoic Asian Dust Provenance Changes Linked to the Exhumation History of the Northern Tibetan Plateau and the Central Asian Orogenic Belt. Geochim. Cosmochim. Acta 2021, 296, 38–55. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yan, T.T.; Wu, X.; Quan, Y.K.; Gong, Q.J.; Li, X.L.; Wang, P.; Li, R.K. Heredity, Inheritance and Similarity of Element Behaviors Among Parent Rocks and Their Weathered Products: A Geochemical Lithogene. Geoscience 2018, 32, 453–467. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gong, Q.; Liu, N.; Wu, X.; Yan, T.; Fan, T.; Li, X.; Liu, M.; Li, R.; Albanese, S. Using Regional Geochemical Survey Data to Trace Anomalous Samples through Geochemical Genes: The Tieshanlong Tungsten Deposit Area (Southeastern China) Case Study. J. Geochem. Explor. 2020, 219, 106637. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gong, Q.J.; Wu, X.; Yan, T.T.; Liu, N.Q.; Li, X.L.; Li, R.K.; Liu, M.X. Construction and Test of Geochemical Genes: Case Studies in China. Geoscience 2020, 34, 865–882. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dolui, G.; Chatterjee, S.; Das Chatterjee, N. Geophysical and Geochemical Alteration of Rocks in Granitic Profiles during Intense Weathering in Southern Purulia District, West Bengal, India. Model. Earth Syst. Environ. 2016, 2, 132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fu, W.; Li, X.; Feng, Y.; Feng, M.; Peng, Z.; Yu, H.; Lin, H. Chemical Weathering of S-Type Granite and Formation of Rare Earth Element (REE)-Rich Regolith in South China: Critical Control of Lithology. Chem. Geol. 2019, 520, 33–51. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, W.; Liu, C.; Brantley, S.L.; Xu, Z.; Zhao, T.; Liu, T.; Yu, C.; Xue, D.; Zhao, Z.; Cui, L.; et al. Deep Weathering along a Granite Ridgeline in a Subtropical Climate. Chem. Geol. 2016, 427, 17–34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sequeira Braga, M.A.; Paquet, H.; Begonha, A. Weathering of Granites in a Temperate Climate (NW Portugal): Granitic Saprolites and Arenization. CATENA 2002, 49, 41–56. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Budihal, R.; Pujar, G. Redistribution and mass change geochemistry during weathering of laterites from the swarnagadde plateau, uttar kannada district, karnataka, India. Indian J. Appl. Res. 2018, 8, 53–56. [Google Scholar]
- Bolarinwa, A.T.; Adeola, A.J. Geochemistry of Weathered Profiles over Syenite and Younger Granite in Pankshin Area, North Central Nigeria. Earth Sci. Res. 2016, 6, 63. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kanamaru, T.; Suganuma, Y.; Oiwane, H.; Miura, H.; Miura, M.; Okuno, J.; Hayakawa, H. The Weathering of Granitic Rocks in a Hyper-Arid and Hypothermal Environment: A Case Study from the Sør-Rondane Mountains, East Antarctica. Geomorphology 2018, 317, 62–74. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, C.; Wu, X.W.; Liu, Z.H.; Zhang, Y.Y.; Guo, W. Precambrian geological events on the western margin of Songnen massif: Evidence from LA-ICP-MS-Pb geochronology of zircons from Paleoproterozoic granite in the Longjiang area. Acta Petrol. Sin. 2018, 34, 3137–3152. [Google Scholar]
- Wu, F.-Y.; Sun, D.-Y.; Ge, W.-C.; Zhang, Y.-B.; Grant, M.L.; Wilde, S.A.; Jahn, B.-M. Geochronology of the Phanerozoic Granitoids in Northeastern China. J. Asian Earth Sci. 2011, 41, 1–30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ye, X.; Sun, L.; Xu, Z.; Yan, D.; Yang, Q.; Zhu, D.; Feng, J.; Chen, L. Geochemistry and Zircon U–Pb Dating of Early Jurassic Syenogranite in the Kaoshan Area, Southern Part of the Zhangguangcai Range, NE China, and Tectonic Implications. Geol. J. 2022, 57, 440–461. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, H.J.; Fu, J.Y.; Qian, C.; Pang, X.J.; Zhong, H. Chronology and spatiotemporal distribution of Pre-Mesozoic granites in Northeast China. Geol. Bull. China 2021, 40, 827–844. [Google Scholar]
- Xu, W.L.; Wang, F.; Meng, E.; Gao, F.H.; Pei, F.P.; Yu, J.J.; Tang, J. Paleozoic-Early Mesozoic tectonic evolution in the eastern Heilongjiang Province, NE China: Evidence from igneous rock association and U-Pb geochronology of detrital zircons. J. Jilin Univ. 2012, 42, 1378–1389. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, F.; Xu, W.L.; Meng, E.; Cao, H.H.; Gao, F.H. Early Paleozoic Amalgamation of the Songnen–Zhangguangcai Range and Jiamusi Massifs in the Eastern Segment of the Central Asian Orogenic Belt: Geochronological and Geochemical Evidence from Granitoids and Rhyolites. J. Asian Earth Sci. 2012, 49, 234–248. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ge, M.H.; Zhang, J.J.; Li, L.; Liu, K.; Ling, Y.Y.; Wang, J.M.; Wang, M. Geochronology and Geochemistry of the Heilongjiang Complex and the Granitoids from the Lesser Xing’an-Zhangguangcai Range: Implications for the Late Paleozoic-Mesozoic Tectonics of Eastern NE China. Tectonophysics 2017, 717, 565–584. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, J.Y.; Liu, J.F.; Qu, J.F.; Zheng, R.G.; Zhao, S.; Zhang, J.; Sun, L.X.; Li, Y.F.; Yang, X.P.; Wang, L.J.; et al. Major Geological Features and Crustal Tectonic Framework of Northeast China. Acta Petrol. Sin. 2019, 35, 2989–3016. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ren, Y.J. Early-Middle Jurassic granitic magmatism and tectonic evolution in the southern part of Zhangguangcailing. Acta Geol. Sin. 2019, 93, 2813–2831. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Geng, W.; Qin, J.F.; Li, Y.F.; Lai, S.C. Geochemistry and LA-ICP-MS Zircon U-Pb Age of the Late Triassic Granite from Yimi-Anpo Area, Zhangguangcai Mountain, Heilongjiang Province. Geol. Bull. China 2014, 33, 1333–1341. [Google Scholar]
- Feng, G.Y.; Niu, X.L.; Liu, F.; Liu, S.; Yang, J.S. Petrogenesis of late Early Jurassic granodiorites and associated dioritic enclaves in the Zhangguangcai Range and its tectonic implications. Acta Geol. Sin. 2019, 93, 2598–2616. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiong, C.H.; Wang, X.L. Comparison of pretreatment methods for major elements such as potassium, calcium, etc., in determination of geological samples by inductively coupled plasma optical emission spectrometry. Anal. Test. Technol. Instrum. 2020, 26, 30–36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nesbitt, H.W.; Young, G.M. Early Proterozoic Climates and Plate Motions Inferred from Major Element Chemistry of Lutites. Nature 1982, 299, 715–717. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Harnois, L. The CIW Index: A New Chemical Index of Weathering. Sediment. Geol. 1988, 55, 319–322. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Colman, S.M. Chemical Weathering of Basalts and Andesites; Evidence from Weathering Rinds; U.S. Government Publishing Office: Washington, DC, USA, 1982.
- Gong, Q.; Deng, J.; Wang, C.; Wang, Z.; Zhou, L. Element Behaviors Due to Rock Weathering and Its Implication to Geochemical Anomaly Recognition: A Case Study on Linglong Biotite Granite in Jiaodong Peninsula, China. J. Geochem. Explor. 2013, 128, 14–24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fedo, C.M.; Wayne Nesbitt, H.; Young, G.M. Unraveling the Effects of Potassium Metasomatism in Sedimentary Rocks and Paleosols, with Implications for Paleoweathering Conditions and Provenance. Geology 1995, 23, 921. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hewawasam, T.; Von Blanckenburg, F.; Bouchez, J.; Dixon, J.L.; Schuessler, J.A.; Maekeler, R. Slow Advance of the Weathering Front during Deep, Supply-Limited Saprolite Formation in the Tropical Highlands of Sri Lanka. Geochim. Cosmochim. Acta 2013, 118, 202–230. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mao, H.; Cui, L.; Zhang, Z.; Xu, S.; Liu, C.; Zhao, Z. Influence of Monsoon Climate on Chemical Weathering of Granitic Regoliths. Glob. Biogeochem. Cycles 2022, 36, e2022GB007362. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Su, N.; Wu, Z.; Yang, S.; Xu, J. Re-Assessing the Effect of Differential Weathering of Minerals on Strontium Stable Isotope Behavior during Granodiorite Weathering. Chem. Geol. 2022, 613, 121160. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nesbitt, H.W. Mobility and Fractionation of Rare Earth Elements during Weathering of a Granodiorite. Nature 1979, 279, 206–210. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nesbitt, H.W.; Wilson, R.E. Recent Chemical Weathering of Basalts. Am. J. Sci. 1992, 292, 740–777. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Laveuf, C.; Cornu, S. A Review on the Potentiality of Rare Earth Elements to Trace Pedogenetic Processes. Geoderma 2009, 154, 1–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vermeire, M.L.; Cornu, S.; Fekiacova, Z.; Detienne, M.; Delvaux, B.; Cornélis, J.-T. Rare Earth Elements Dynamics along Pedogenesis in a Chronosequence of Podzolic Soils. Chem. Geol. 2016, 446, 163–174. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bau, M.; Dulski, P. Distribution of Yttrium and Rare-Earth Elements in the Penge and Kuruman Iron-Formations, Transvaal Supergroup, South Africa. Precambrian Res. 1996, 79, 37–55. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chapela Lara, M.; Buss, H.L.; Pett-Ridge, J.C. The Effects of Lithology on Trace Element and REE Behavior during Tropical Weathering. Chem. Geol. 2018, 500, 88–102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peccerillo, A.; Taylor, S.R. Geochemistry of Eocene Calc-Alkaline Volcanic Rocks from the Kastamonu Area, Northern Turkey. Contrib. Mineral. Petrol. 1976, 58, 63–81. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rickwood, P.C. Boundary Lines within Petrologic Diagrams Which Use Oxides of Major and Minor Elements. Lithos 1989, 22, 247–263. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jian, X.; Zhang, W.; Liang, H.; Guan, P.; Fu, L. Mineralogy, Petrography and Geochemistry of an Early Eocene Weathering Profile on Basement Granodiorite of Qaidam Basin, Northern Tibet: Tectonic and Paleoclimatic Implications. Catena 2019, 172, 54–64. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pyle, D.; MacKenzie, W.S.; Adams, A.E. A Colour Atlas of Rocks and Minerals in Thin Section. 192 Pp. London: Manson. Geol. Mag. 1994, 131, 576. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nesbitt, H.W.; Fedo, C.M.; Young, G.M. Quartz and Feldspar Stability, Steady and Non-Steady-State Weathering, and Petrogenesis of Siliciclastic Sands and Muds. J. Geol. 1997, 105, 173–192. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, T.; Wang, H.; Zhang, Z.Q.; Wang, H.J. Clay minerals as indicators of paleoclimate. Acta Petrol. Mineral. 2003, 22, 416–420. [Google Scholar]
- Ng, C.W.W.; Guan, P.; Shang, Y.J. Weathering Mechanisms and Indices of the Igneous Rocks of Hong Kong. Q. J. Eng. Geol. Hydrogeol. 2001, 34, 133–151. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mei, H.; Jian, X.; Zhang, W.; Fu, H.; Zhang, S. Behavioral Differences between Weathering and Pedogenesis in a Subtropical Humid Granitic Terrain: Implications for Chemical Weathering Intensity Evaluation. CATENA 2021, 203, 105368. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cullers, R.L.; Basu, A.; Suttner, L.J. Geochemical Signature of Provenance in Sand-Size Material in Soils and Stream Sediments near the Tobacco Root Batholith, Montana, U.S.A. Chem. Geol. 1988, 70, 335–348. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cullers, R.L. The Controls on the Major- and Trace-Element Evolution of Shales, Siltstones and Sandstones of Ordovician to Tertiary Age in the Wet Mountains Region, Colorado, U.S.A. Chem. Geol. 1995, 123, 107–131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wei, C.Y.; Xie, Y.Y.; Kang, C.G.; Chi, Y.P.; Sun, L.; Wu, P.; Wei, Z.Y.; Leng, Y.K. Sedimentological, mineralogical, and geochemical characteristics of the Luojiawopeng Fm. in Harbin: Implications for the sedimentary environment. Chin. J. Geol. 2022, 57, 172–189. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, J.H.; Xie, Y.Y.; Kang, C.G.; Chi, Y.P.; Wu, P.; Sun, L.; Wei, Z.Y.; Sun, Y. Stratigraphic properties of the Baitushan Formation in Ping’an Town, the eastern foot of the Great Hinggan Mountains—An indication of provenance and sedimentary environment. J. Stratigr. 2022, 46, 196–208. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dehghani, S.; Moore, F.; Vasiluk, L.; Hale, B.A. The Geochemical Fingerprinting of Geogenic Particles in Road Deposited Dust from Tehran Metropolis, Iran: Implications for Provenance Tracking. J. Geochem. Explor. 2018, 190, 411–423. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hayashi, K.I.; Fujisawa, H.; Holland, H.D.; Ohmoto, H. Geochemistry of ∼1.9 Ga Sedimentary Rocks from Northeastern Labrador, Canada. Geochim. Cosmochim. Acta 1997, 61, 4115–4137. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, J.; Liu, N.Q.; Gong, Q.J.; Wu, X.; Yan, T.T. Construction and Test of a Geochemical Lithogene Based on Trace Elements: Case Studies on Weathering Profiles in China. Geoscience 2021, 35, 1459–1470. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gong, Q.; Yan, T.; Wu, X.; Li, R.; Wang, X.; Liu, N.; Li, X.; Wu, Y.; Li, J. Geochemical Gene: A Promising Concept in Discrimination and Traceability of Geological Materials. Appl. Geochem. 2022, 136, 105133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Spalletti, L.A.; Queralt, I.; Matheos, S.D.; Colombo, F.; Maggi, J. Sedimentary Petrology and Geochemistry of Siliciclastic Rocks from the Upper Jurassic Tordillo Formation (Neuquén Basin, Western Argentina): Implications for Provenance and Tectonic Setting. J. S. Am. Earth Sci. 2008, 25, 440–463. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Uhlig, D.; Von Blanckenburg, F. How Slow Rock Weathering Balances Nutrient Loss During Fast Forest Floor Turnover in Montane, Temperate Forest Ecosystems. Front. Earth Sci. 2019, 7, 159. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oeser, R.A.; Von Blanckenburg, F. Do Degree and Rate of Silicate Weathering Depend on Plant Productivity? Biogeosciences 2020, 17, 4883–4917. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Von Blanckenburg, F.; Schuessler, J.A.; Bouchez, J.; Frings, P.J.; Uhlig, D.; Oelze, M.; Frick, D.A.; Hewawasam, T.; Dixon, J.; Norton, K. Rock Weathering and Nutrient Cycling along an Erodosequence. Am. J. Sci. 2021, 321, 1111–1163. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brantley, S.L.; White, A.F. Approaches to Modeling Weathered Regolith. Rev. Mineral. Geochem. 2009, 70, 435–484. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bonnet, M.; Caner, L.; Siitari-Kauppi, M.; Mazurier, A.; Mexias, A.S.; Dani, N.; Sardini, P. Weathering of Viamão Granodiorite, South Brazil: Part 1—Clay Minerals Formation and Increase in Total Porosity. Geoderma 2022, 424, 115968. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Buss, H.L.; Sak, P.B.; Webb, S.M.; Brantley, S.L. Weathering of the Rio Blanco Quartz Diorite, Luquillo Mountains, Puerto Rico: Coupling Oxidation, Dissolution, and Fracturing. Geochim. Cosmochim. Acta 2008, 72, 4488–4507. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, K.J.; Teng, F.Z.; Wei, G.J.; Ma, J.L.; Bao, Z.Y. Adsorption- and Desorption-Controlled Magnesium Isotope Fractionation during Extreme Weathering of Basalt in Hainan Island, China. Earth Planet. Sci. Lett. 2012, 359–360, 73–83. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brazier, J.M.; Schmitt, A.D.; Gangloff, S.; Pelt, E.; Chabaux, F.; Tertre, E. Calcium Isotopic Fractionation during Adsorption onto and Desorption from Soil Phyllosilicates (Kaolinite, Montmorillonite and Muscovite). Geochim. Cosmochim. Acta 2019, 250, 324–347. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nakano, T.; Yokoo, Y.; Nishikawa, M.; Koyanagi, H. Regional Sr–Nd Isotopic Ratios of Soil Minerals in Northern China as Asian Dust Fingerprints. Atmos. Environ. 2004, 38, 3061–3067. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- White, A.F.; Buss, H.L. Natural Weathering Rates of Silicate Minerals. In Treatise on Geochemistry; Drever, J.I., Ed.; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2014; pp. 115–155. ISBN 978-0-08-098300-4. [Google Scholar]
- Xie, J.; Ding, Z. Compositions of Heavy Minerals in Northeastern China Sandlands and Provenance Analysis. Sci. China Ser. Earth Sci. 2007, 50, 1715–1723. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Q.H.; Xie, Y.Y.; Kang, C.G.; Chi, Y.P.; Wu, P.; Sun, L.; Li, S.Q. Heavy mineral composition of the Songhua River system identified by manual and TIMA automatic methods and implications for provenance tracing. Mar. Geol. Quat. Geol. 2022, 42, 170–183. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, L.; Xie, Y.Y.; Kang, C.G.; Chi, Y.P.; Du, H.R.; Wang, J.X. Heavy minerals, Sr-Nd isotopic composition of sandy land in Hulun Buir, Inner Mongolia and their implications for Asian aeolian dust system. Geol. China 2021, 48, 1965–1974. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.Q.; Xie, Y.Y.; Kang, C.G.; Chi, Y.P.; Sun, L.; Wu, P.; Wei, Z.Y. Changing provenance of Harbin loess since the Middle Pleistocene: Evidence from TIMA automated quantification of minerals. J. Desert Res. 2022, 42, 25–35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wan, H.F. Characteristics of Heavy Mineral in Coarse Sediment and Its Indicative Significance in the Ningxia-Inner Mongolia Section of the Yellow River. J. Desert Res. 2013, 4, 1000–1008. [Google Scholar]
- Brantley, S.L.; Chesley, J.T.; Stillings, L.L. Isotopic Ratios and Release Rates of Strontium Measured from Weathering Feldspars. Geochim. Cosmochim. Acta 1998, 62, 1493–1500. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Blum, J.D.; Erel, Y. A Silicate Weathering Mechanism Linking Increases in Marine 87Sr/86Sr with Global Glaciation. Nature 1995, 373, 415–418. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Blum, J.D. The Effect of Late Cenozoic Glaciation and Tectonic Uplift on Silicate Weathering Rates and the Marine 87Sr/86Sr Record; Ruddiman, W.F., Ed.; Springer: Boston, MA, USA, 1997; pp. 259–288. [Google Scholar]
- Miller, E.K.; Blum, J.D.; Friedland, A.J. Determination of Soil Exchangeable-Cation Loss and Weathering Rates Using Sr Isotopes. Nature 1993, 362, 438–441. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bullen, T.D.; Krabbenhoft, D.P.; Kendall, C. Kinetic and Mineralogic Controls on the Evolution of Groundwater Chemistry and 87Sr/86Sr in a Sandy Silicate Aquifer, Northern Wisconsin, USA. Geochim. Cosmochim. Acta 1996, 60, 1807–1821. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bullen, T.; White, A.; Blum, A.; Harden, J.; Schulz, M. Chemical Weathering of a Soil Chronosequence on Granitoid Alluvium: II. Mineralogic and Isotopic Constraints on the Behavior of Strontium. Geochim. Cosmochim. Acta 1997, 61, 291–306. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, Y.J.; Liu, C.Q. Evolution of Sr isotope during chemical weathering of granite: Effects of relative weathering rates of minerals. Sci. China-Earth Sci. 2001, 44, 634–640. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xie, Y.Y.; Liu, L.; Kang, C.; Chi, Y. Sr-Nd Isotopic Characteristics of the Northeast Sandy Land, China and Their Implications for Tracing Sources of Regional Dust. Catena 2020, 184, 104303. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ling, Z.; Yang, S.; Xia, D.; Wang, X.; Chen, F. Source of the Aeolian Sediments in the Yarlung Tsangpo Valley and Its Potential Dust Contribution to Adjacent Oceans. Earth Surf. Process. Landf. 2022, 47, 1860–1871. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bayon, G.; Toucanne, S.; Skonieczny, C.; André, L.; Bermell, S.; Cheron, S.; Dennielou, B.; Etoubleau, J.; Freslon, N.; Gauchery, T.; et al. Rare Earth Elements and Neodymium Isotopes in World River Sediments Revisited. Geochim. Cosmochim. Acta 2015, 170, 17–38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Beaty, B.J.; Planavsky, N.J. A 3 b.y. Record of a Biotic Influence on Terrestrial Weathering. Geology 2021, 49, 407–411. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barker, W.W.; Welch, S.A.; Chu, S.; Banfield, J.F. Experimental Observations of the Effects of Bacteria on Aluminosilicate Weathering. Am. Mineral. 1998, 83, 1551–1563. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, L.; Jacobson, A.D.; Hausner, M. Characterization of Elemental Release during Microbe–Granite Interactions at T = 28 °C. Geochim. Cosmochim. Acta 2008, 72, 1076–1095. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ouyang, B.; Renock, D.; Akob, D.M. Effects of Organic Ligands and Background Electrolytes on Barite Dissolution. Geochim. Cosmochim. Acta 2019, 256, 6–19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, G.H.; Chi, Z.L.; Teng, H.H.; Dong, H.L.; Kappler, A.; Gillings, M.R.; Polizzotto, M.L.; Liu, C.Q.; Zhu, Y.G. Fungus-Initiated Catalytic Reactions at Hyphal-Mineral Interfaces Drive Iron Redox Cycling and Biomineralization. Geochim. Cosmochim. Acta 2019, 260, 192–203. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rogers, J.; Bennett, P. Mineral Stimulation of Subsurface Microorganisms: Release of Limiting Nutrients from Silicates. Chem. Geol. 2004, 203, 91–108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Valsami-Jones, E. An Experimental Study of Bacterially Induced Dissolution of K-Feldspar. Mineral. Mag. 1998, 62A, 1563–1564. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Delgado-Baquerizo, M.; Oliverio, A.M.; Brewer, T.E.; Benavent-González, A.; Eldridge, D.J.; Bardgett, R.D.; Maestre, F.T.; Singh, B.K.; Fierer, N. A Global Atlas of the Dominant Bacteria Found in Soil. Science 2018, 359, 320–325. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Neaman, A. Implications of the Evolution of Organic Acid Moieties for Basalt Weathering over Geological Time. Am. J. Sci. 2005, 305, 147–185. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Neaman, A.; Chorover, J.; Brantley, S.L. Element Mobility Patterns Record Organic Ligands in Soils on Early Earth. Geology 2005, 33, 117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hausrath, E.M.; Neaman, A.; Brantley, S.L. Elemental Release Rates from Dissolving Basalt and Granite with and without Organic Ligands. Am. J. Sci. 2009, 309, 633–660. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, X.; Cheng, T.; Wu, H. Do multiple cycles of aeolian deposit-pedogenesis exist in the reticulate red clay sections in southern China? Chin. Sci. Bull. 2003, 48, 1251–1258. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deng, C.; Vidic, N.J.; Verosub, K.L.; Singer, M.J.; Liu, Q.; Shaw, J.; Zhu, R. Mineral Magnetic Variation of the Jiaodao Chinese Loess/Paleosol Sequence and Its Bearing on Long-term Climatic Variability. J. Geophys. Res. Solid Earth 2005, 110, 2004JB003451. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fine, P.; Singer, M.J.; Verosub, K.L.; TenPas, J. New Evidence for the Origin of Ferrimagnetic Minerals in Loess from China. Soil Sci. Soc. Am. J. 1993, 57, 1537–1542. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fine, P.; Singer, M.J.; Verosub, K.L. Use of Magnetic-Susceptibility Measurements in Assessing Soil Uniformity in Chronosequence Studies. Soil Sci. Soc. Am. J. 1992, 56, 1195–1199. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hren, M.T.; Chamberlain, C.P.; Hilley, G.E.; Blisniuk, P.M.; Bookhagen, B. Major Ion Chemistry of the Yarlung Tsangpo–Brahmaputra River: Chemical Weathering, Erosion, and CO2 Consumption in the Southern Tibetan Plateau and Eastern Syntaxis of the Himalaya. Geochim. Cosmochim. Acta 2007, 71, 2907–2935. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stallard, R.F.; Edmond, J.M. Geochemistry of the Amazon: 2. The Influence of Geology and Weathering Environment on the Dissolved Load. J. Geophys. Res. Oceans 1983, 88, 9671–9688. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dixon, J.L.; Hartshorn, A.S.; Heimsath, A.M.; DiBiase, R.A.; Whipple, K.X. Chemical Weathering Response to Tectonic Forcing: A Soils Perspective from the San Gabriel Mountains, California. Earth Planet. Sci. Lett. 2012, 323–324, 40–49. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, L.; Wu, J.; Chen, Y.; Xiong, S.; Cui, J.; Ding, Z. Modern Silicate Weathering Regimes Across China Revealed by Geochemical Records From Surface Soils. J. Geophys. Res. Earth Surf. 2022, 127, e2022JF006728. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- White, P.D.; Schiebout, J. Paleogene Paleosols and Changes in Pedogenesis during the Initial Eocene Thermal Maximum: Big Bend National Park, Texas, USA. Geol. Soc. Am. Bull. 2008, 120, 1347–1361. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Z.; Ding, Z.; Yang, S.; Zhang, C.; Wang, X. Increased Precipitation and Weathering across the Paleocene-Eocene Thermal Maximum in Central China. Geochem. Geophys. Geosystems 2016, 17, 2286–2297. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Basak, C.; Martin, E.E. Antarctic Weathering and Carbonate Compensation at the Eocene–Oligocene Transition. Nat. Geosci. 2013, 6, 121–124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Goddéris, Y.; Donnadieu, Y.; Carretier, S.; Aretz, M.; Dera, G.; Macouin, M.; Regard, V. Onset and Ending of the Late Palaeozoic Ice Age Triggered by Tectonically Paced Rock Weathering. Nat. Geosci. 2017, 10, 382–386. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Donnadieu, Y.; Goddéris, Y.; Ramstein, G.; Nédélec, A.; Meert, J. A ‘Snowball Earth’ Climate Triggered by Continental Break-up through Changes in Runoff. Nature 2004, 428, 303–306. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maher, K.; Chamberlain, C.P. Hydrologic Regulation of Chemical Weathering and the Geologic Carbon Cycle. Science 2014, 343, 1502–1504. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hilley, G.; Chamberlain, C.; Moon, S.; Porder, S.; Willett, S. Competition between Erosion and Reaction Kinetics in Controlling Silicate-Weathering Rates. Earth Planet. Sci. Lett. 2010, 293, 191–199. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, H.Y.; Xie, Y.Y.; Chi, Y.P.; Kang, C.G.; Sun, L.; Wu, P.; Wei, Z.Y. Sedimentary composition and detrital zircon U-Pb dating of the sand-gravel profile in Binxian County, Harbin: Indications for sedimentary environment and regional tectonic evolution. Chin. J. Geol. 2023, 58, 1354–1372. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Leng, Y.K.; Xie, Y.Y.; Kang, C.G.; Chi, Y.P.; Sun, L.; Wu, P.; Wei, Z.Y.; Wei, C.Y. Sedimentary Characteristics and Environmental Significance of the Juren Sandy Gravel Profile in Harbin. Acta Sedimentol. Sin. 2023, 41, 472–484. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, M.; Xie, Y.Y.; Kang, C.G.; Chi, Y.P.; Wu, P.; Wei, Z.Y.; Zhang, Y.X.; Liu, L. Chemical Weathering Characteristics of the Loess-Paleosol Sequences in Harbin Huangshan Rock Core—Implication for Formation Environment of the Paleosol. Acta Pedol. Sin. 2021, 58, 673–684. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wilson, J. Weathering of the Primary Rock-Forming Minerals: Processes, Products and Rates. Clay Miner. 2004, 39, 233–266. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dong, Y.; Wang, S.M.; Yu, Q.; Chen, J.S.; Yang, H.; Ge, W.C.; Bi, J.H.; Jing, J.H. Late Paleozoic tectonic-magmatic evolution history of the northeastern China. Acta Petrol. Sin. 2022, 38, 2249–2276. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feng, J.L. Discussion on paleomagnetism dating to terra rossa profiles from yun-gui plateau, southwest China. Carsologica Sin. 2003, 22, 178–190. [Google Scholar]
- Chi, Q.H.; Yan, M.C. Applied Geochemical Element Abundance Data Book; Geology Press: Beijing, China, 2007; pp. 1–148. [Google Scholar]
- Sun, S.S.; McDonough, W.F. Chemical and isotopic systematics of oceanic basalts: Implications for mantle composition and processes. Geol. Soc. Lond. Spec. Publ. 1989, 42, 313–345. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]








| Samples | Zircon | Leucoxene | Rutile | Anatase | Epidote | Pyroxene | Hematite-Limonite | Magnetite | Others |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| YJ-2 | 0.68 | 0.00 | 0.00 | 0.03 | 0.56 | / | 81.82 | 14.28 | 2.63 |
| YJ-5 | 1.93 | 0.01 | / | 0.15 | △ | / | 91.76 | 0.60 | 5.55 |
| YJ-8 | 1.74 | 0.16 | / | 2.19 | △ | / | 88.50 | / | 7.42 |
| YJ-13 | 0.35 | 0.02 | / | 0.70 | / | △ | 90.60 | / | 8.33 |
| YJ-17 | 0.67 | 0.01 | / | 0.81 | / | △ | 89.63 | / | 8.87 |
| YJ-21 | 0.64 | 0.00 | / | 0.82 | △ | △ | 92.47 | / | 6.07 |
| YJ-26 | 3.16 | 0.01 | / | 0.64 | / | 0.15 | 89.51 | 0.59 | 5.94 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Liu, R.; Chi, Y.; Xie, Y.; Kang, C.; Sun, L.; Wu, P.; Wei, Z. Characteristics and Influencing Factors of the Granite Weathering Profile: A Case Study of a High Latitude Area in Northeastern China. Minerals 2024, 14, 17. https://doi.org/10.3390/min14010017
Liu R, Chi Y, Xie Y, Kang C, Sun L, Wu P, Wei Z. Characteristics and Influencing Factors of the Granite Weathering Profile: A Case Study of a High Latitude Area in Northeastern China. Minerals. 2024; 14(1):17. https://doi.org/10.3390/min14010017
Chicago/Turabian StyleLiu, Ruonan, Yunping Chi, Yuanyun Xie, Chunguo Kang, Lei Sun, Peng Wu, and Zhenyu Wei. 2024. "Characteristics and Influencing Factors of the Granite Weathering Profile: A Case Study of a High Latitude Area in Northeastern China" Minerals 14, no. 1: 17. https://doi.org/10.3390/min14010017
APA StyleLiu, R., Chi, Y., Xie, Y., Kang, C., Sun, L., Wu, P., & Wei, Z. (2024). Characteristics and Influencing Factors of the Granite Weathering Profile: A Case Study of a High Latitude Area in Northeastern China. Minerals, 14(1), 17. https://doi.org/10.3390/min14010017





